SNPs Analysis Indicates Non-Uniform Origins of Invasive Mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarck, 1819) on the Southern African Coast
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling, DNA Extraction and Genotyping
2.2. Bioinformatic Analyses
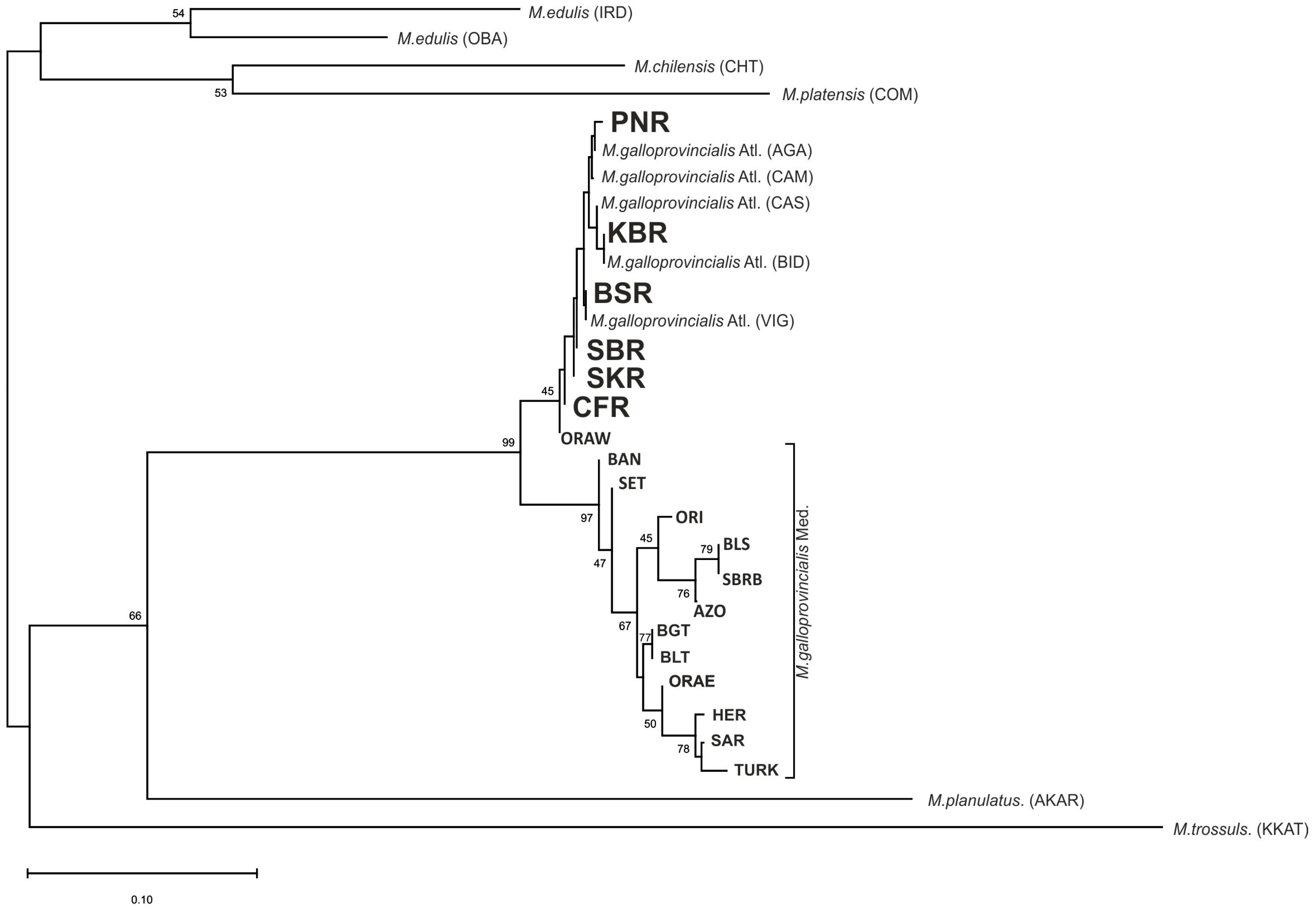
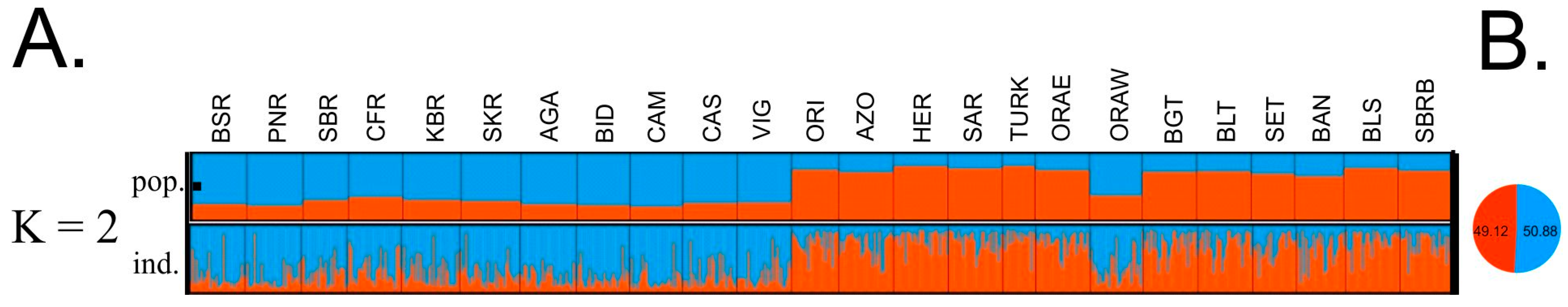
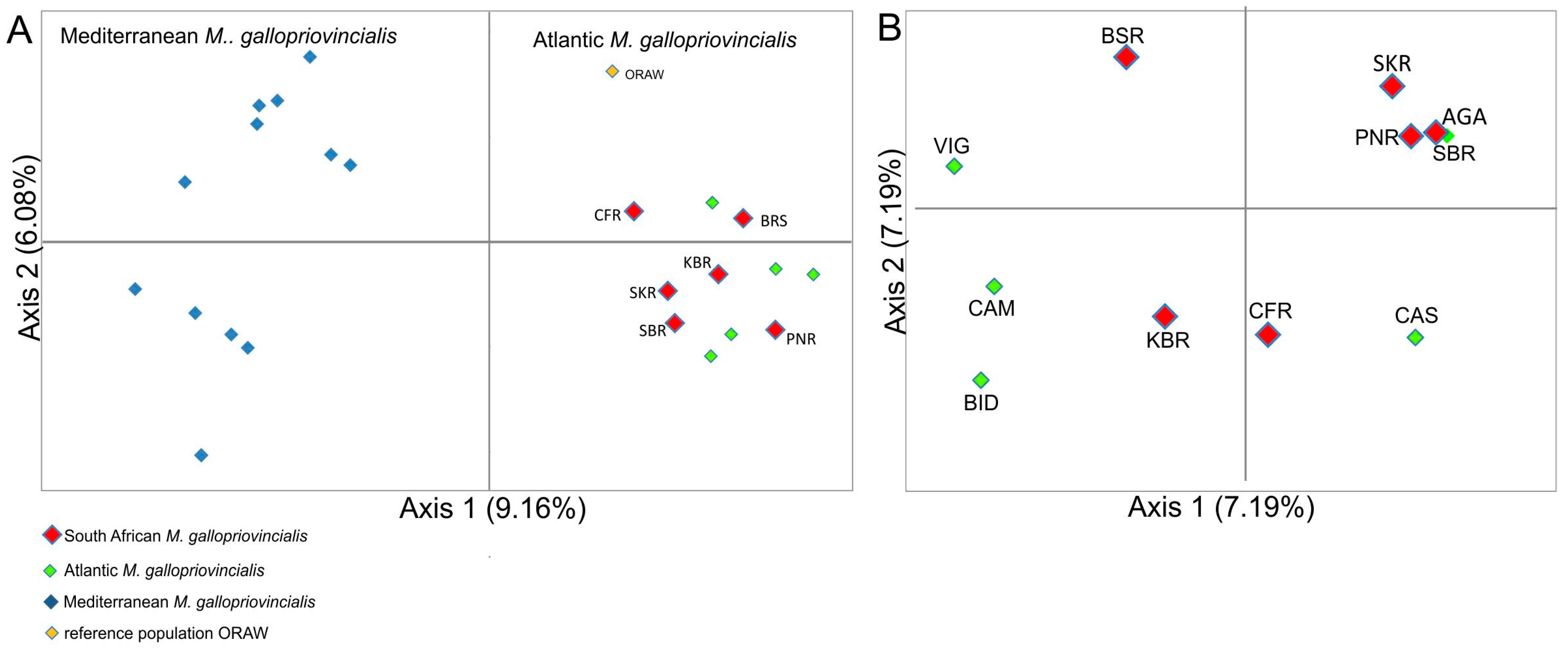
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of the Genetic Diversity of Mytilus Populations
3.2. Analysis of Genetic Structure and Genetic Relationships Among Populations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Greve, M.; Eric, C.; von der Meden, O.; Janion-Scheepers, C. Biological invasions in South Africa’s offshore sub-Antarctic territories. In Biological Invasions in South Africa; van Wilgen, B.W., Measey, J., Richardson, D.M., Wilson, J.R., Zengeya, T.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 205–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, K.T.; Burness, A.; Byrne, M.J.; Kumschick, S.; Peters, K.; Robertson, M.P.; Saccaggi, D.L.; Weyl, O.L.F.; Williams, V.L. South Africa’s pathways of introduction and dispersal and how they have changed over time. In Biological Invasions in South Africa; van Wilgen, B.W., Measey, J., Richardson, D.M., Wilson, J.R., Zengeya, T.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 311–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, J.H.; Seed, R.; Koehn, R.K. Allozymes and morphometric characters of three species of Mytilus in the northern and southern hemispheres. Mar. Biol. 1991, 111, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchanek, T.H.; Geller, J.B.; Kreiser, B.R.; Mitton, J.B. Zoogeographic distributions of the sibling species Mytilus galloprovincialis and M.trossulus (Bivalvia: Mytilidae) and their hybrids in the north Pacific. Biol. Bull. 1997, 193, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wonham, M.J. Mini-review: Distribution of the Mediterranean mussel, Mytilus galloprovincialis (Bivalvia: Mytilidae), and hybrids in the northeast Pacific. J. Shellfish. Res. 2004, 23, 535–543. [Google Scholar]
- Nascimento-Schulze, J.C.; Bean, T.P.; Penaloza, C.; Paris, J.R.; Whiting, J.R.; Simon, A.; Fraser, B.A.; Houston, R.D.; Bierne, N.; Ellis, R.P. SNP discovery and genetic structure in blue mussel species using low coverage sequencing and a medium density 60 K SNP-array. Evol. Appl. 2023, 16, 1044–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbawicka, M.; Trucco, M.I.; Wenne, R. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in native South American Atlantic coast populations of smooth shelled mussels: Hybridization with invasive European Mytilus galloprovincialis. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2018, 50, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birckolz, C.J.; Gernet, M.D.V.; Baggio, R.A.; Silveira, N.; Simone, L.; Belz, C.E. First record of the Mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis (Bivalvia, Mytilidae) in Brazil. Pap. Avulsos Zool. 2020, 60, e20206007. [Google Scholar]
- Lins, D.M.; Zbawicka, M.; Wenne, R.; Poćwierz-Kotus, A.; Molina, J.R.A.; Alves, L.P.; Rocha, R.M. Ecology and genetics of Mytilus galloprovincialis: A threat to bivalve aquaculture in southern Brazil. Aquaculture 2021, 540, 736753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daguin, C.; Borsa, P. Genetic relationships of Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarck populations worldwide: Evidence from nuclear-DNA markers. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2000, 177, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrain, M.A.; Diaz, N.F.; Lamas, C.; Vargas, C.; Araneda, C. Genetic composition of Mytilus species in mussel populations from southern Chile. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2012, 40, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larraín, M.A.; Zbawicka, M.; Araneda, C.; Gardner, J.P.A.; Wenne, R. Native and invasive taxa on the Pacific coast of South America: Impacts on aquaculture, traceability and biodiversity of blue mussels (Mytilus spp.). Evol. Appl. 2018, 11, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, C.W.; Guo, B.Y.; Chen, Y.J. Genetic diversity in ribosomal 18S rRNA and mitochondrial COIII genes in Chinese cultured populations of mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2015, 59, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.Q.; Mao, Y.L.; Shui, B.N.; Yanagimoto, T.; Gao, T.X. Genetic structure and unique origin of the introduced blue mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis in the north-western Pacific: Clues from mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase I (COI) sequences. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2017, 68, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartavtsev, Y.; Chichvarkhin, A.Y.; Kijima, A.; Hanzawa, N.; Park, I.S. Allozyme and morphometric analysis of two common mussel species of the genus Mytilus (Mollusca, Mytilidae) in Korean, Japanese and Russian waters. Korean J. Genet. 2005, 27, 289–306. [Google Scholar]
- Śmietanka, B.; Zbawicka, M.; Sańko, T.; Wenne, R.; Burzyński, A. Molecular population genetics of male and female mitochondrial genomes in subarctic Mytilus trossulus. Mar. Biol. 2013, 160, 1709–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skurikhina, L.A.; Kartavtsev, Y.F.; Chichvarkhin, A.Y.; Pan’kova, M.V. Study of two species of mussels, Mytilus trossulus and Mytilus galloprovincialis (Bivalvia, Mytilidae), and their hybrids in Peter the Great Bay of the Sea of Japan with the use of PCR markers. Russ. J. Genet. 2001, 37, 1448–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartavtsev, Y.P.; Katolikova, M.V.; Sharina, S.N.; Chichvarkhina, O.V.; Masalkova, N.A. A population genetic study of the hybrid zone of Mytilus trossulus Gould, 1850 and an introduced species, M. galloprovincialis Lamarck, 1819, (Bivalvia: Mytilidae) in peter the great bay in the Sea of Japan. Rus. J. Mar. Biol. 2014, 40, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, N.; Fujino, K.; Gosling, E. The Mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk in Japan. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2008, 20, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Waite, J.H.; Matsuoka, M.; Odo, S.; Harayama, S. Interspecific variations in adhesive protein sequences of Mytilus edulis, M. galloprovincialis, and M. trossulus. Biol. Bull. 1995, 189, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Odo, S.; Noda, T.; Nakao, S.; Takeyama, S.; Yamaha, E.; Yamazak, F.; Harayama, S. A possible hybrid zone in the Mytilus edulis complex in Japan revealed by PCR markers. Mar. Biol. 1997, 128, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brannock, P.M.; Wethey, D.S.; Hilbish, T.J. Extensive hybridization with minimal introgression in Mytilus galloprovincialis and M.trossulus in Hokkaido, Japan. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 383, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, J.P.A.; Zbawicka, M.; Westfall, K.M.; Wenne, R. Invasive blue mussels threaten regional scale genetic diversity in mainland and remote offshore locations: The need for baseline data and enhanced protection in the Southern Ocean. Glob. Change Biol. 2016, 22, 3182–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, J.P.A.; Oyarzún, P.A.; Toro, J.E.; Wenne, R.; Zbawicka, M. Phylogeography of Southern hemisphere blue mussels of the genus Mytilus: Evolution, biosecurity, aquaculture and food labelling. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. 2021, 59, 139–232. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, M.E.; Simon, C.A.; Griffiths, C.L.; Peters, K.; Sibanda, S.; Miza, S.; Groenewald, B.; Majiedt, P.; Sink, K.J.; Robinson, R.B. Back to the future: Reflections and directions of South African marine bio-invasion research. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2016, 38, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovic, I.; Matias, A.M.A.; Bierne, N.; Riginos, C. Twin introductions by independent invader mussel lineages are both associated with recent admixture with a native congener in Australia. Evol. Appl. 2020, 13, 515–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zbawicka, M.; Wenne, R.; Dias, P.J.; Gardner, J.P.A. Combined threats to native smooth-shelled mussels (genus Mytilus) in Australia: Bioinvasions and hybridization. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2022, 194, 1194–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.; Arbiol, C.; Nielsen, E.E.; Couteau, J.; Sussarellu, R.; Burgeot, T.; Bernard, I.; Coolen, J.W.P.; Lamy, J.-B.; Robert, S.; et al. Replicated anthropogenic hybridisations reveal parallel patterns of admixture in marine mussels. Evol. Appl. 2020, 13, 575–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlton, J.T.; Chapman, J.W.; Geller, J.B.; Miller, J.A.; Carlton, D.A.; McCuller, M.I.; Treneman, N.C.; Steves, B.P.; Ruiz, G.M. Tsunami-driven rafting: Transoceanic species dispersal and implications for marine biogeography. Science 2017, 357, 1402–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, W.S.; Cherry, M.I. Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk. In Southern Africa. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 1985, 90, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branch, G.M.; Steffani, C.N. Can we predict the effects of alien species? A case-history of the invasion of South Africa by Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lamarck). J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2004, 300, 189–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenton-Dozey, J.; Probyn, T.; Busby, A. Impact of mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) raft-culture on benthic macrofauna, in situ oxygen uptake, and nutrient fluxes in Saldanha Bay, South Africa. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2001, 58, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hockey, P.A.R.; Schurink, C.V.E. The invasive biology of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis on the southern African coast. Trans. R. Soc. S. Afr. 1992, 48, 123–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zardi, G.I.; McQuaid, C.D.; Teske, P.R.; Barker, N.P. Unexpected genetic structure of mussel populations in South Africa: Indigenous Perna perna and invasive Mytilus galloprovincialis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 337, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- McQuaid, C.D.; Phillips, T.E. Limited wind-driven dispersal of intertidal mussel larvae: In situ evidence from the plankton and the spread of the invasive species Mytilus galloprovincialis in South Africa. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 201, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assis, J.; Zupan, K.R.; Nicastro, G.I.; Zardi, C.D.; McQuaid, C.D.; Serrao, E.A. Oceanographic conditions limit the spread of a marine invader along southern African shores. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, T.B.; Peters, K.; Brooker, B. Coastal invasions: The south African context. In Biological Invasions in South Africa; Invading nature—springer series in invasion ecology; van Wilgen, B., Measey, J., Richardson, D., Wilson, J., Zengeya, T., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 14, pp. 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, T.B.; Branch, G.M.; Griffiths, C.L.; Govender, A.; Hockey, P.A.R. Changes in South African rocky intertidall invertebrate community structure associated with the invasion of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 340, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Alexander, M.E.; Adams, R.; Dick, J.T.A.; Robinson, T.B. Forecasting invasions: Resource use by mussels informs invasion patterns along the south African coast. Mar. Biol. 2015, 162, 2493–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathlean, J.; McQuaid, C.D. Biogeographic Variability in the Value of Mussel Beds as Ecosystem Engineers on South African Rocky Shores. Ecosystems 2017, 20, 568–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenton-Dozey, J.; Jackson, L.F.; Busby, A.J. Impact of Mussel Culture on Macrobenthic Community Structure in Saldanha Bay, South Africa. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1999, 39, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, D.; Heinecken, L.; Jackson, S. Mussel and oyster culture in Saldanha Bay, South Africa: Potential for sustainable growth, development and employment creation. Food Sec. 2013, 5, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, A.; Cherry, M.I.; Lombard, A.T. A cryptic species of Mytilus (Mollusca:Bivalvia) on the west coast of South Africa. S. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 1984, 2, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Harris, J.M.; Branch, G.M.; Elliott, B.L.; Currie, B.; Dye, A.H.; McQuaid, C.D.; Tomalin, B.J.; Velasquez, C. Spatial and temporal variability in recruitment of intertidal mussels around the coast of Southern Africa. S. Afr. J. Zool. 1998, 33, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Greef, K.; Griffiths, C.L.; Zeeman, Z. Deja vu? A second mytilid mussel, Semimytilus algosus, invades South Africa’s west coast. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2013, 35, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branch, G.M.; Steffani, N.; Pfaff, M.C.; Baliwe, N.G.; Zeeman, Z. Complex interplays between limpets and alien species in South Africa: Multispecies interactions, zonation and size effects. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1190456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zardi, G.I.; McQuaid, C.D.; Jacinto, R.; Laurenco, C.R.; Serrao, E.A.; Nicastro, K.R. Re-assessing the origins of the invasive mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis in southern Africa. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2018, 69, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenne, R.; Prądzińska, A.; Poćwierz-Kotus, A.; Larrain, M.A.; Arenada, C.; Zbawicka, M. Provenance of Mytilus food products in Europe using SNP genetic markers. Aquaculture 2022, 554, 738135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenne, R. Single nucleotide polymorphism markers with applications in conservation and exploitation of aquatic natural populations. Animals 2023, 13, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoarau, G.; Holla, S.; Lescasse, R.; Stam, W.T.; Olsen, J.L. Heteroplasmy and evidence for recombination in the mitochondrial control region of the flatfish Platichthys flesus. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 2261–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gabriel, S.; Ziaugra, L.; Tabbaa, D. SNP Genotyping Using the Sequenom MassARRAY iPLEX Platform. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2009, 60, 2.12.1–2.12.18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenne, R.; Zbawicka, M.; Bach, L.; Strelkov, P.; Gantsevich, M.; Kukliński, P.; Kijewski, T.; McDonald, J.H.; Sundsaasen, K.K.; Árnyasi, M.; et al. Trans-Atlantic distribution and introgression as inferred from single nucleotide polymorphism: Mussels Mytilus and environmental factors. Genes 2020, 11, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E.L. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GENALEX 6: Genetic Analysis in Excel. Population Genetic Software for Teaching and Research. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic Analysis in Excel. Population Genetic Software for Teaching and Research—An Update. Bioinf. Appl. Note 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earl, D.A.; von Holdt, B.M. STRUCTURE HARVESTER: A website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2012, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsson, M.; Rosenberg, N.A. CLUMPP: A cluster matching and permutation program for dealing with label switching and multimodality in analysis of population structure. Bioinforma. Oxf. Engl. 2007, 23, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, N.A. Distruct: A program for the graphical display of population structure: PROGRAM NOTE. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2003, 4, 137–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rannala, B.; Mountain, J.L. Detecting immigration by using multilocus genotypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 9197–9221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piry, S.; Alapetite, A.; Cornuet, J.M.; Paetkau, D.; Baudouin, L.; Estoup, A. GENECLASS2: A software for genetic assignment and first-generation migrant detection. J. Hered. 2004, 95, 536–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takezaki, N.; Nei, M.; Tamura, K. POPTREEW: Web version of POPTREE for constructing population trees from allele frequency data and computing some other quantities. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 1622–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Yekutieli, D. The control of the false discovery rate in multiple testing under dependency. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, S.J.; Aldridge, C.L.; Oyler-McCance, S.J. An empirical comparison of population genetic analyses using microsatellite and SNP data for a species of conservation concern. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouagajjou, Y.; Aghzar, A.; Presa, P. Population Genetic Divergence amongWorldwide Gene Pools of the Mediterranean Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Animals 2023, 13, 3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branch, G.M.; Griffiths, C.L. The Benguela ecosystem. Part V. Coast. Zone OMBAR 1988, 26, 295–486. [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel, B.P.; Bustamante, R.H.; Branch, G.M.; Eekhout, S.; Odendaal, F.J. A zoogeographic and functional approach to the selection of marine reserves on the west coast of South Africa. S. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 1992, 12, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutjeharms, J.R.S. Three decades of research on the greater Agulhas Current. Ocean Sci. 2007, 3, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zardi, G.I.; Nicastro, K.R.; McQuaid, C.D.; Hancke, L.; Helmuth, B. The combination of selection and dispersal helps explain genetic structure in intertidal mussels. Oecologia 2011, 165, 947–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.C.K.; Monsinjon, J.R.P.; Froneman, W.; McQuaid, C.D. Thermal stress gradient causes increasingly negative effects towards the range limit of an invasive mussel. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 865, 161184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeman, Z.; Branch, G.M.; Pillay, D.; von der Heyden, S. Origin and genetic diversity of the invasive mussel Semimytilus algosus in South Africa, relative to source populations in Chile and Namibia. Biol. Invasions 2020, 22, 2309–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobler, J.P.; Zhao, Z.; Jones, J.W.; Kotze, A. Magellan mussels Aulacomya atra from the South African coast show high diversity within populations but a lack of geographic differentiation. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2023, 45, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, C.R.; Nicastro, K.R.; McQuaid, C.D.; Chefaoui, R.M.; Assis, J.; Taleb, M.Z.; Zardi, G.I. Evidence for rangewide panmixia despite multiple barriers to dispersal in a marine mussel. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zardi, G.I.; Nicastro, K.R.; McQuaid, C.D.; Castilho, R.; Costa, J.; Serrão, E.A.; Pearson, G.A. Intraspecific genetic lineages of a marine mussel show behavioural divergence and spatial segregation over a tropical/subtropical biogeographic transition. BMC Evol. Biol. 2015, 15, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, R.L.; Nicastro, K.R.; Costa, J.; McQuaid, C.D.; Serrao, E.A.; Zardi, G.I. Wider sampling reveals a non-sister relationship for geographically contiguous lineages of a marine mussel. Ecol. Evol. 2014, 4, 2070–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicastro, K.R.; McQuaid, C.D.; Dievart, A.; Zardi, G.I. Intraspecific diversity in an ecological engineer functionally trumps interspecific diversity in shaping community structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | N | Location | Country | Water Area | Coordinates | Year | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BRS | 30 | Bloubergstrand | South Africa | Atlantic | 33°48′47.82″ S | 18°27′55.08″ E | 2012 |
| 2 | CFR | 30 | Cape St. Francis | South Africa | Indian Ocean | 34°12′11.43″ S | 24°50′21.15″ E | 2012 |
| 3 | KBR | 32 | Kaysers Beach | South Africa | Indian Ocean | 33°15′3.87″ S | 27°35′21.70″ E | 2012 |
| 4 | PNR | 31 | Port Nolloth | South Africa | Atlantic | 29°16′7.79″ S | 16°51′49.02″ E | 2012 |
| 5 | SBR | 25 | Saldanha Bay | South Africa | Atlantic | 33°1′37.64″ S | 18°1′27.32″ E | 2012 |
| 6 | SKR | 33 | Skoenmakerskop | South Africa | Indian Ocean | 34°2′50.62″ S | 5°32′42.28″ E | 2012 |
| 7 | AGA a | 31 | Agadir, Atlantic | Morocco | Atlantic | 30°18′3.36″ N | 9°48′56.60″ W | 2011 |
| 8 | BID a | 29 | Bidasoa | Spain | Atlantic | 43°21′38.71″ N | 1°51′11.15″ W | 2004 |
| 9 | CAM a | 29 | Camarinal | Spain | Atlantic | 36°4′48.01″ N | 5°47′58.00″ W | 2004 |
| 10 | CAS a | 30 | Cascais | Portugal | Atlantic | 38°34′14.89″ N | 9°19′8.95″ W | 2013 |
| 11 | VIG a | 30 | Vigo | Spain | Atlantic | 42°13′54.12″ N | 8°45′7.22″ W | 2004 |
| 12 | AZO b | 30 | Azov Sea | Ukraine | Azov Sea | 45°43′51.71″ N | 35°5′0.26″ E | 1997 |
| 13 | BAN b | 27 | Banyuls, Gulf of Lion | France | Mediterranean | 42°27′51.89″ N | 3°10′30.49″ E | 2004 |
| 14 | BGT b | 30 | Bizerta Bay, Gulf of Tunis | Tunisia | Mediterranean | 37°16′36.70″ N | 9°53′58.20″ E | 2013 |
| 15 | BLS b | 30 | Crimea | Ukraine | Mediterranean | 44°29′0.82″ N | 34°12′18.92″ E | 2007 |
| 16 | BLT b | 30 | Bizerta Lagoon | Tunisia | Mediterranean | 37°10′30.89″ N | 9°49′41.04″ E | 2013 |
| 17 | HER b | 30 | Heraklion, Crete, South Aegean S. | Greece | Mediterranean | 35°20′40.96″ N | 25° 8′56.50″ E | 2014 |
| 18 | ORAE b | 30 | Oran East, Alboran S. | Algeria | Mediterranean | 35°42′36.74″ N | 0°39′14.64″ W | 2016 |
| 19 | ORAW b | 29 | Oran West, Alboran S. | Algeria | Mediterranean | 35°10′44.16″ N | 1°38′57.67″ W | 2016 |
| 20 | ORI b | 29 | Oristano | Italy | Mediterranean | 39°47′59.88″ N | 8°31′9.72″ E | 2004 |
| 21 | SAR b | 30 | Saronikos Gulf, Aegean S. | Greece | Mediterranean | 37°35′39.64″ N | 23°16′58.52″ E | 2013 |
| 22 | SBRB b | 29 | Sunny Beach, South-East Black S. | Bulgaria | Black Sea | 42°41′58.74″ N | 27°43′3.38″ E | 2012 |
| 23 | SET b | 23 | Sete, Gulf of Lion | France | Mediterranean | 43°23′27.30″ N | 3°41′48.11″ E | 2013 |
| 24 | TURK b | 18 | Izmir, Aegean S. | Turkey | Mediterranean | 38° 4′26.33″ N | 27°1′19.61″ E | 2008 |
| 25 | IRD c | 25 | Indian River, Delaware | USA | Atlantic | 38°36′27.36″ N | 75°3′37.079″ W | 2012 |
| 26 | OBA c | 29 | Oban, Scottland | Great Britain | Atlantic | 6°24′49.40″ N | 5°28′23.00″ W | 2014 |
| 27 | KKAT d | 28 | Halifax | Canada | Atlantic | 44°30′33.79″ N | 63°29′24.91″ W | 1996 |
| 28 | AKAR e | 30 | Akaroa South Island | New Zealand | Pacific | 43°40′19″ S | 172°57′54″ E | 2008 |
| 29 | CHT f | 18 | Chiloe | Chile | Pacific | 42°24′0.54″ S | 74°10′48.49″ W | 2012 |
| 30 | COM g | 35 | Comodoro Rivadavia | Argentina | Atlantic | 45°56′00″ S | 67°32′0.00″ W | 2014 |
| GeneClass2, Assigned of Individuals to Origin Region | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exluding Self-Assignment | |||||||||
| M. galloprovincialis | |||||||||
| Atlantic | Mediterranean (Central) | Mediterranean (East) | Black Sea | ||||||
| Name | No ind | No ind | % | No ind | % | No ind | % | No ind | % |
| BSR | 30 | 25 | 83.333 | 2 | 6.667 | 3 | 10.000 | ||
| PNR | 31 | 29 | 93.548 | 1 | 3.226 | 1 | 3.226 | ||
| SBR | 25 | 22 | 88.000 | 3 | 12.000 | ||||
| CFR | 30 | 24 | 80.000 | 3 | 10.000 | 1 | 3.333 | 2 | 6.667 |
| KBR | 32 | 25 | 78.125 | 3 | 9.375 | 2 | 6.250 | 2 | 6.250 |
| SKR | 33 | 29 | 87.879 | 1 | 3.030 | 1 | 3.030 | 2 | 6.061 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poćwierz-Kotus, A.; McQuaid, C.D.; Lipinski, M.R.; Zbawicka, M.; Wenne, R. SNPs Analysis Indicates Non-Uniform Origins of Invasive Mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarck, 1819) on the Southern African Coast. Animals 2024, 14, 3080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14213080
Poćwierz-Kotus A, McQuaid CD, Lipinski MR, Zbawicka M, Wenne R. SNPs Analysis Indicates Non-Uniform Origins of Invasive Mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarck, 1819) on the Southern African Coast. Animals. 2024; 14(21):3080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14213080
Chicago/Turabian StylePoćwierz-Kotus, Anita, Christopher D. McQuaid, Marek R. Lipinski, Małgorzata Zbawicka, and Roman Wenne. 2024. "SNPs Analysis Indicates Non-Uniform Origins of Invasive Mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarck, 1819) on the Southern African Coast" Animals 14, no. 21: 3080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14213080
APA StylePoćwierz-Kotus, A., McQuaid, C. D., Lipinski, M. R., Zbawicka, M., & Wenne, R. (2024). SNPs Analysis Indicates Non-Uniform Origins of Invasive Mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarck, 1819) on the Southern African Coast. Animals, 14(21), 3080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14213080






