The Efficacy of a Ferric Sillen Core-Linked Polymer in Suppressing the Pathogenicity of Campylobacter jejuni
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Culture Conditions
2.2. Production of a Ferric Sillen Core-Linked Polymer (FSCLP)
2.3. Evaluation of the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Against C. jejuni
2.4. Reverse Transcription Real-Time Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.5. Cell Culture Conditions
2.6. Infection Assay
2.7. Invasion Assay
2.8. Adhesion Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
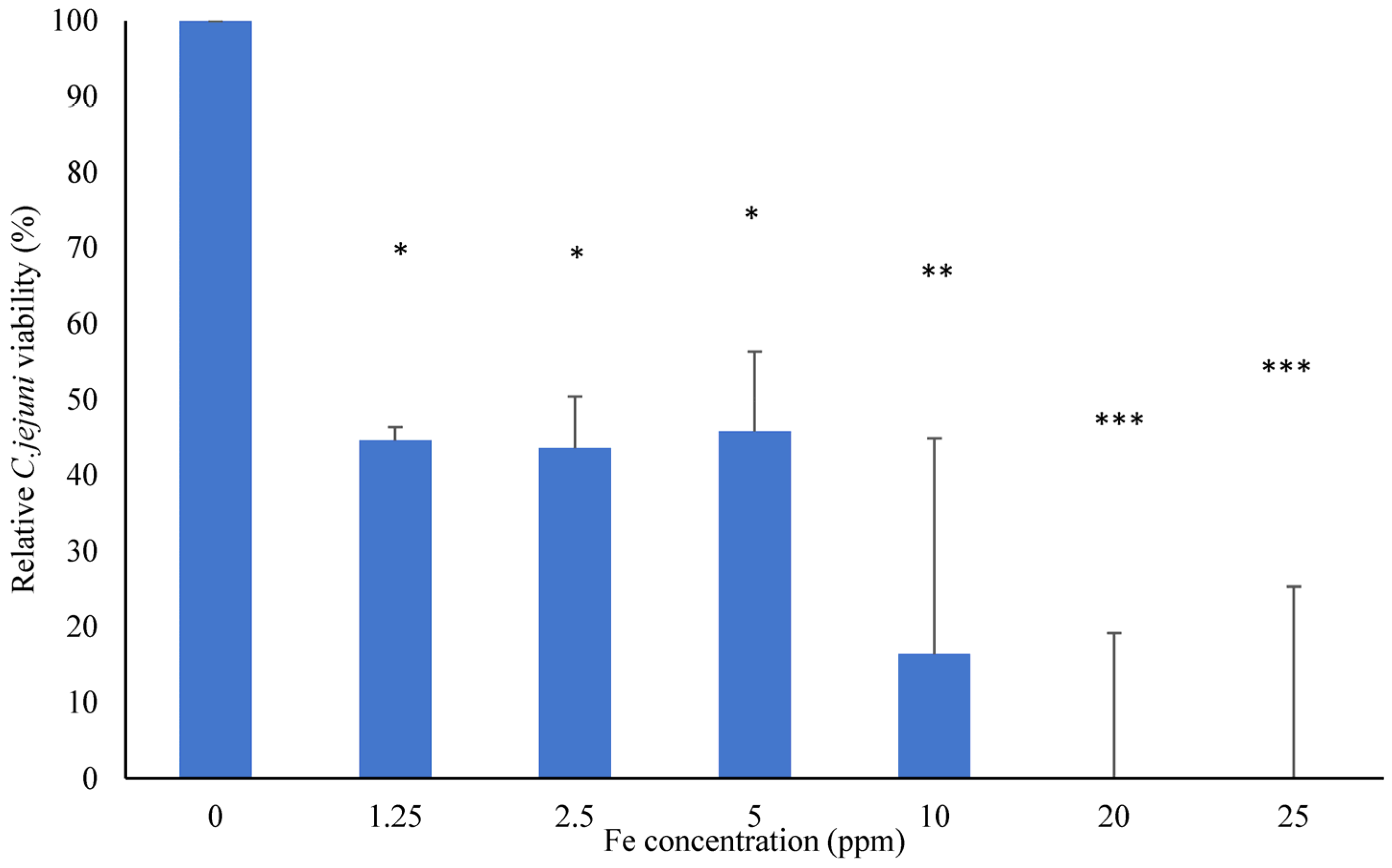
3.1. Evaluation of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) of FSCLP Against C. jejuni Using Alamar Blue®
3.2. FSCLP’s Impact on the Expression Levels of C. jejuni Virulence Genes
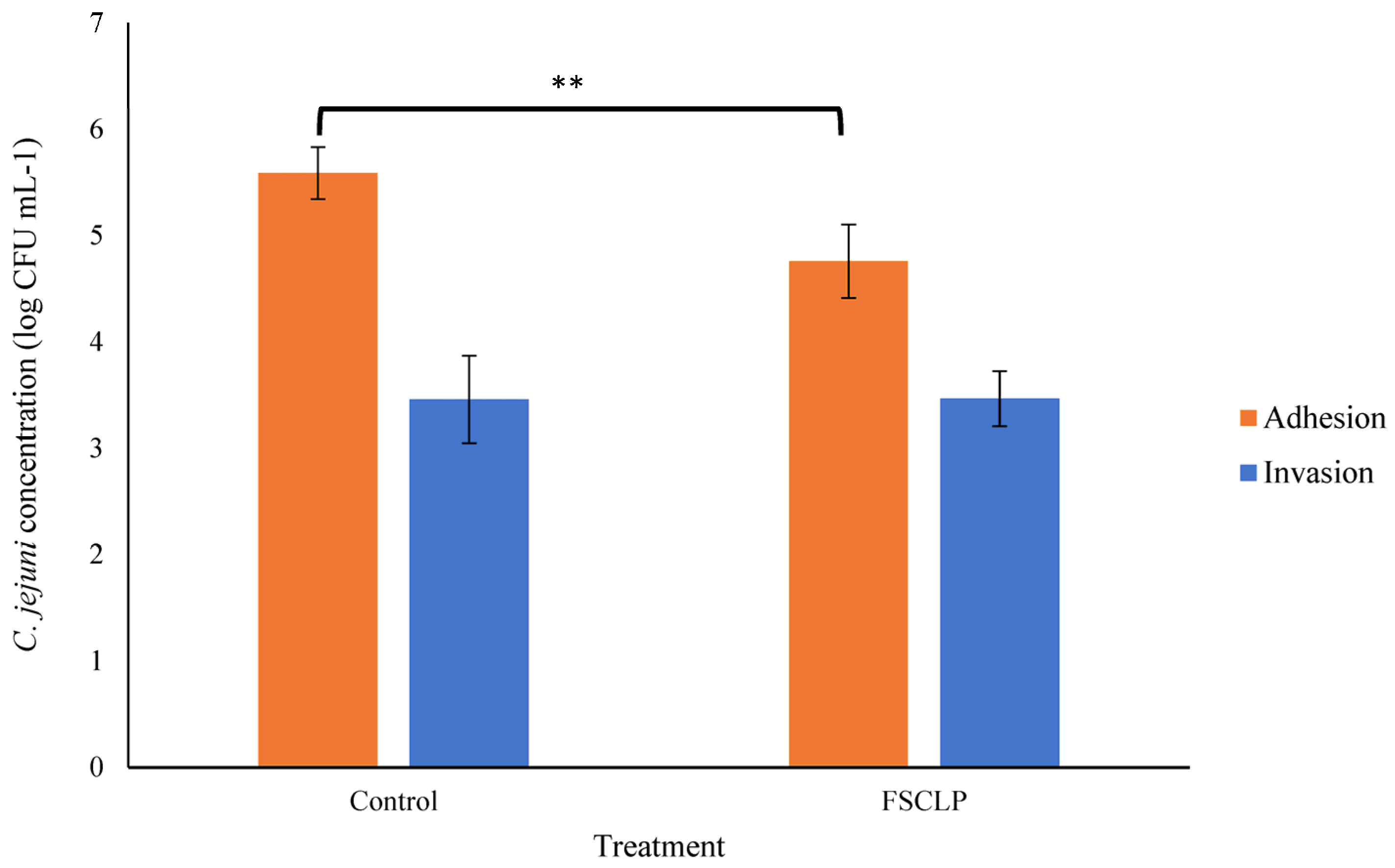
3.3. The Impact of the FSCLP on the Ability of C. jejuni to Attach to or Invade Porcine Intestinal Cells (IPEC-J2)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuhn, K.G.; Nielsen, E.M.; Mølbak, K.; Ethelberg, S. Epidemiology of Campylobacteriosis in Denmark 2000–2015. Zoonoses Public Health 2018, 65, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirk, M.D.; Pires, S.M.; Black, R.E.; Caipo, M.; Crump, J.A.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Döpfer, D.; Fazil, A.; Fischer-Walker, C.L.; Hald, T.; et al. World Health Organization Estimates of the Global and Regional Disease Burden of 22 Foodborne Bacterial, Protozoal, and Viral Diseases, 2010: A Data Synthesis. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Lee, S.A.; Xue, J.; Riordan, S.M.; Zhang, L. Global Epidemiology of Campylobacteriosis and the Impact of COVID-19. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 979055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awada, R.; Ghssein, G.; Roz, A.E.; Farhat, M.; Nehme, N.; Hassan, H.F. Prevalence of Campylobacter Spp. in Broilers in North Lebanon. Vet. World 2023, 16, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, J.N.; Eghnatios, E.; El Roz, A.; Fardoun, T.; Ghssein, G. Prevalence, Antimicrobial Resistance and Risk Factors for Campylobacteriosis in Lebanon. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2019, 13, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaakoush, N.O.; Castaño-Rodríguez, N.; Mitchell, H.M.; Man, S.M. Global Epidemiology of Campylobacter Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 687–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klancnik, A.; Guzej, B.; Jamnik, P.; Vucković, D.; Abram, M.; Mozina, S.S. Stress Response and Pathogenic Potential of Campylobacter jejuni Cells Exposed to Starvation. Res. Microbiol. 2009, 160, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreling, V.; Falcone, F.H.; Kehrenberg, C.; Hensel, A. Campylobacter Sp.: Pathogenicity Factors and Prevention Methods—New Molecular Targets for Innovative Antivirulence Drugs? Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 10409–10436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Othman, S.; Jõudu, I.; Bhat, R. Bioactives from Agri-Food Wastes: Present Insights and Future Challenges. Molecules 2020, 25, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-García, M.; Sol, C.; de Nova, P.J.G.; Puyalto, M.; Mesas, L.; Puente, H.; Mencía-Ares, Ó.; Miranda, R.; Argüello, H.; Rubio, P.; et al. Antimicrobial Activity of a Selection of Organic Acids, Their Salts and Essential Oils against Swine Enteropathogenic Bacteria. Porc. Health Manag. 2019, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittoe, D.K.; Ricke, S.C.; Kiess, A.S. Organic Acids and Potential for Modifying the Avian Gastrointestinal Tract and Reducing Pathogens and Disease. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, S.M.; Al-Rasheed, H.H.; Albering, J.H.; El-Faham, A. Fe(III) Complexes Based on Mono- and Bis-Pyrazolyl-s-Triazine Ligands: Synthesis, Molecular Structure, Hirshfeld, and Antimicrobial Evaluations. Molecules 2020, 25, 5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandio, A.A.; Ali Memon, A.; Memon, S.; Memon, F.N.; Panhwar, Q.K.; Durmaz, F.; Nizamani, S.M.; Brohi, N.A. Synthesis and Antimicrobial Assessment of Fe3+ Inclusion Complex of P-Tert-Butylcalix[4]Arene Diamide Derivative. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, e2534072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, L.; DiRita, V. Growth and Laboratory Maintenance of Campylobacter jejuni. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 8A.1.1–8A.1.7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Miao, M.; Cao, X.; An, Z. One-Pot RAFT Synthesis of Core Cross-Linked Star Polymers of polyPEGMA in Water by Sequential Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Polymerizations. Polym. Chem. 2012, 3, 2656–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christanseen, S. Targeted Campylobacter Control: The Development and Analysis of Novel Feed Additives on Campylobacter Growth. Ph.D. Thesis, Dublin City University, Dublin, Ireland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, L.L.; Feero, S.E. The Campylobacter Fetus S Layer Provides Resistance to Photoactivated Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Can. J. Microbiol. 2019, 65, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing Real-Time PCR Data by the Comparative CT Method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−∆∆CT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schierack, P.; Nordhoff, M.; Pollmann, M.; Weyrauch, K.D.; Amasheh, S.; Lodemann, U.; Jores, J.; Tachu, B.; Kleta, S.; Blikslager, A.; et al. Characterization of a Porcine Intestinal Epithelial Cell Line for in Vitro Studies of Microbial Pathogenesis in Swine. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 125, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, M.; Krause-Gruszczynska, M.; Rohde, M.; Tegtmeyer, N.; Takahashi, S.; Oyarzabal, O.A.; Backert, S. Major Host Factors Involved in Epithelial Cell Invasion of Campylobacter jejuni: Role of Fibronectin, Integrin Beta1, FAK, Tiam-1, and DOCK180 in Activating Rho GTPase Rac1. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2011, 1, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stintzi, A. Gene Expression Profile of Campylobacter jejuni in Response to Growth Temperature Variation. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 2009–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, M.; Butcher, J.; Stintzi, A. Nutrient Acquisition and Metabolism by Campylobacter jejuni. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askoura, M.; Youns, M.; Halim Hegazy, W.A. Investigating the Influence of Iron on Campylobacter jejuni Transcriptome in Response to Acid Stress. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 138, 103777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birk, T.; Wik, M.T.; Lametsch, R.; Knøchel, S. Acid Stress Response and Protein Induction in Campylobacter jejuni Isolates with Different Acid Tolerance. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra-Arguello, Y.M.; Perdoncini, G.; Rodrigues, L.B.; Ruschel dos Santos, L.; Apellanis Borges, K.; Quedi Furian, T.; Pippi Salle, C.T.; de Souza Moraes, H.L.; Pereira Gomes, M.J.; Pinheiro do Nascimento, V. Identification of Pathogenic Genes in Campylobacter jejuni Isolated from Broiler Carcasses and Broiler Slaughterhouses. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Hanning, I.; Slavik, M. Stress-Induced Adaptive Tolerance Response and Virulence Gene Expression in Campylobacter jejuni. J. Food Saf. 2009, 29, 126–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konkel, M.E.; Kim, B.J.; Rivera-Amill, V.; Garvis, S.G. Bacterial Secreted Proteins Are Required for the Internalization of Campylobacter jejuni into Cultured Mammalian Cells. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 32, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, K.; Mulholland, F.; Pearson, B.M.; Pin, C.; McNicholl-Kennedy, J.; Ketley, J.M.; Wells, J.M.Y. Campylobacter jejuni Gene Expression in Response to Iron Limitation and the Role of Fur. Microbiology 2005, 151, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.-K.; Chen, Y.-A.; Lin, C.-J.; Lin, H.-J.; Kao, M.-C.; Huang, M.-Z.; Lin, Y.-H.; Chiang-Ni, C.; Chen, C.-J.; Lo, U.-G.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms and Potential Clinical Applications of Campylobacter jejuni Cytolethal Distending Toxin. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, C.; Nilsson, A.; Kaden, R.; Rautelin, H. Differences in Virulence Gene Expression between Human Blood and Stool Campylobacter Coli Clade 1 ST828CC Isolates. Gut Pathog. 2019, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinadasa, R.N.; Bloom, S.E.; Weiss, R.S.; Duhamel, G.E. Cytolethal Distending Toxin: A Conserved Bacterial Genotoxin That Blocks Cell Cycle Progression, Leading to Apoptosis of a Broad Range of Mammalian Cell Lineages. Microbiology 2011, 157, 1851–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apel, D.; Ellermeier, J.; Pryjma, M.; DiRita, V.J.; Gaynor, E.C. Characterization of Campylobacter jejuni RacRS Reveals Roles in the Heat Shock Response, Motility, and Maintenance of Cell Length Homogeneity. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 2342–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konkel, M.E.; Kim, B.J.; Klena, J.D.; Young, C.R.; Ziprin, R. Characterization of the Thermal Stress Response of Campylobacter jejuni. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 3666–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Yan, G.; Chang, J.; Wang, P.; Yin, Q.; Liu, C.; Liu, S.; Zhu, Q.; Lu, F. Astilbin Ameliorates Deoxynivalenol-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in Intestinal Porcine Epithelial Cells (IPEC-J2). J. Appl. Toxicol. JAT 2020, 40, 1362–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šikić Pogačar, M.; Langerholc, T.; Mičetić-Turk, D.; Možina, S.S.; Klančnik, A. Effect of Lactobacillus Spp. on Adhesion, Invasion, and Translocation of Campylobacter jejuni in Chicken and Pig Small-Intestinal Epithelial Cell Lines. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | Direction | Accession No. | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| aspA | F | KC405084 | TGAAAGGTTCAAAATGGGAACAAGA |
| R | AACCTCATCAGAGATTTCCAATTCC | ||
| cfrA | F | CP001876 | CCAGGCGTTGATTTATATGC |
| R | CCCATCAATCAAAACCAAAG | ||
| p19 | F | CP001876 | CAATCCAAATGGTTTTCCAG |
| R | ATTGCACCTGTGTCGGTATT | ||
| ciaB | F | CP054847 | AAAAGCTTGGCAAGAAGCTG |
| R | ATGCCACCGCATGAGTATAA | ||
| cfbpA | F | CP001876 | TAGCTTCGCCTGCAAATACT |
| R | GGCTAAAGGTGTGCTTGAAA | ||
| cadF | F | KJ875965 | TTCTATGGTTTAGCAGGTGGAGG |
| R | CCGCGCCATAATGTCCAAA | ||
| cdtB | F | KX495592 | CGCAGCCACAGAAAGCAAAT |
| R | AGCTCCTACATCAACGCGAG | ||
| racR | F | KJ477104 | TGTGGGGCTTCAAATCGGT |
| R | CAACTCTTTTTGTGCGACGA | ||
| dnaJ | F | KY792734 | AGTGTCGAGCTTAATATCCC |
| R | GGCGATGATCTTAACATACA |
| log10 Fold Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | 4 h | 8 h | 24 h | Gene Function |
| cfrA | 0.03 | −0.10 | −0.38 | Ferric enterobactin receptor |
| p19 | 0.19 | −0.18 | −0.18 | Ferric acquisition |
| ciaB | 0.23 | −0.16 | −0.23 | Invasion |
| cfbpA | 0.06 | −0.26 | −0.42 | Ferric acquisition |
| cadF | 0.07 | −0.17 | −0.17 | Adhesion |
| cdtB | 0.01 | −0.30 | −0.46 | Toxin production |
| racR | 0.20 | −0.20 | −0.26 | Response to heat shock |
| dnaJ | 0.17 | −0.22 | −0.23 | Response to hyperosmotic and heat shock |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Christanseen, S.; Walls, D.; White, B.; Murphy, R.; Horgan, K. The Efficacy of a Ferric Sillen Core-Linked Polymer in Suppressing the Pathogenicity of Campylobacter jejuni. Animals 2024, 14, 3150. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14213150
Christanseen S, Walls D, White B, Murphy R, Horgan K. The Efficacy of a Ferric Sillen Core-Linked Polymer in Suppressing the Pathogenicity of Campylobacter jejuni. Animals. 2024; 14(21):3150. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14213150
Chicago/Turabian StyleChristanseen, Seán, Dermot Walls, Blánaid White, Richard Murphy, and Karina Horgan. 2024. "The Efficacy of a Ferric Sillen Core-Linked Polymer in Suppressing the Pathogenicity of Campylobacter jejuni" Animals 14, no. 21: 3150. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14213150
APA StyleChristanseen, S., Walls, D., White, B., Murphy, R., & Horgan, K. (2024). The Efficacy of a Ferric Sillen Core-Linked Polymer in Suppressing the Pathogenicity of Campylobacter jejuni. Animals, 14(21), 3150. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14213150






