Antinociceptive and Cardiorespiratory Effects of a Single Dose of Dexmedetomidine in Laboratory Mice Subjected to Craniotomy under General Anaesthesia with Isoflurane and Carprofen or Meloxicam
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Animals
2.3. Housing
2.4. Anaesthesia Induction and Treatments
2.5. Anaesthesia Monitoring
2.6. Surgical Procedures
2.7. Postoperative Management and Observation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
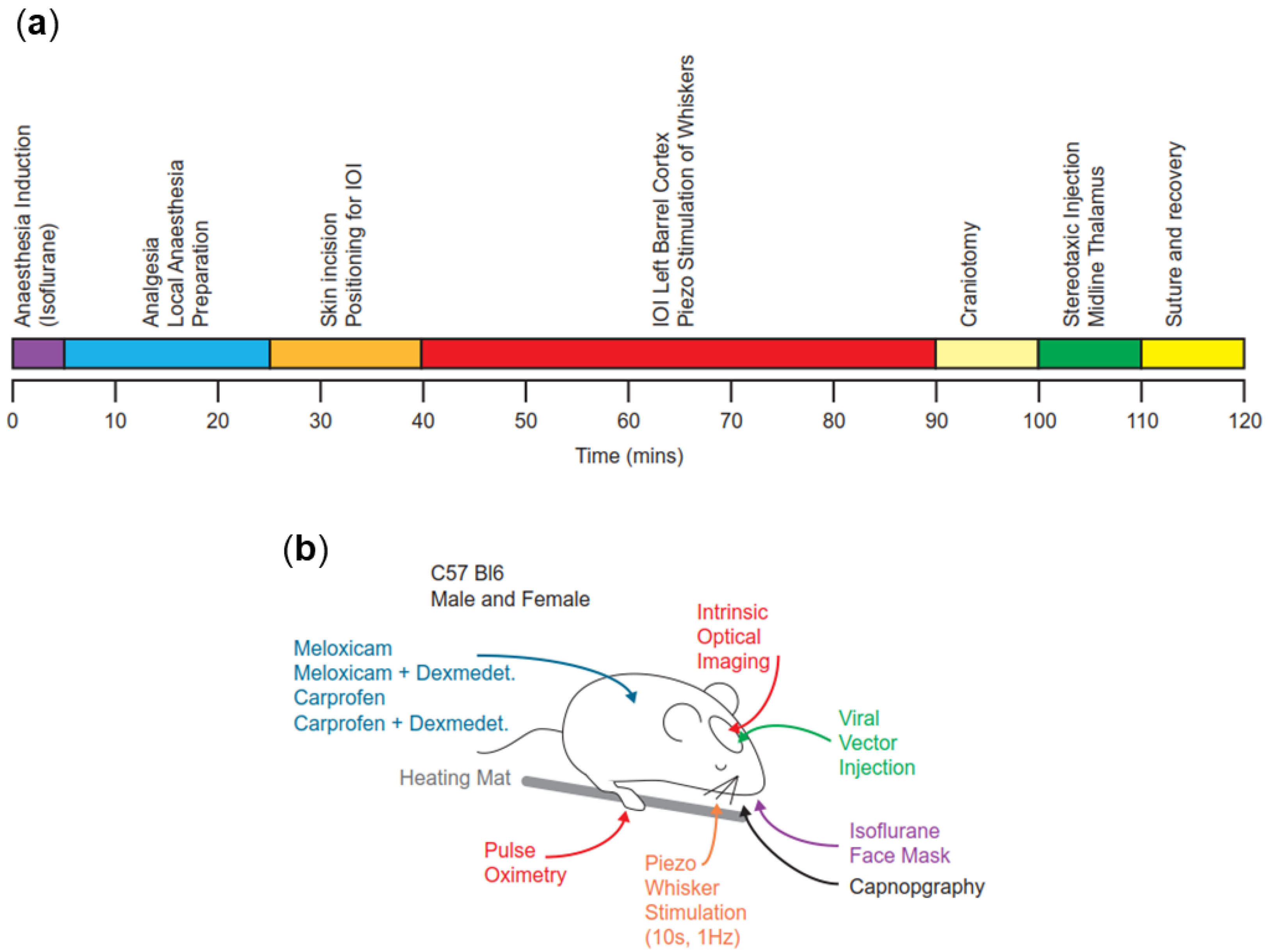
3.1. Relevant Timing
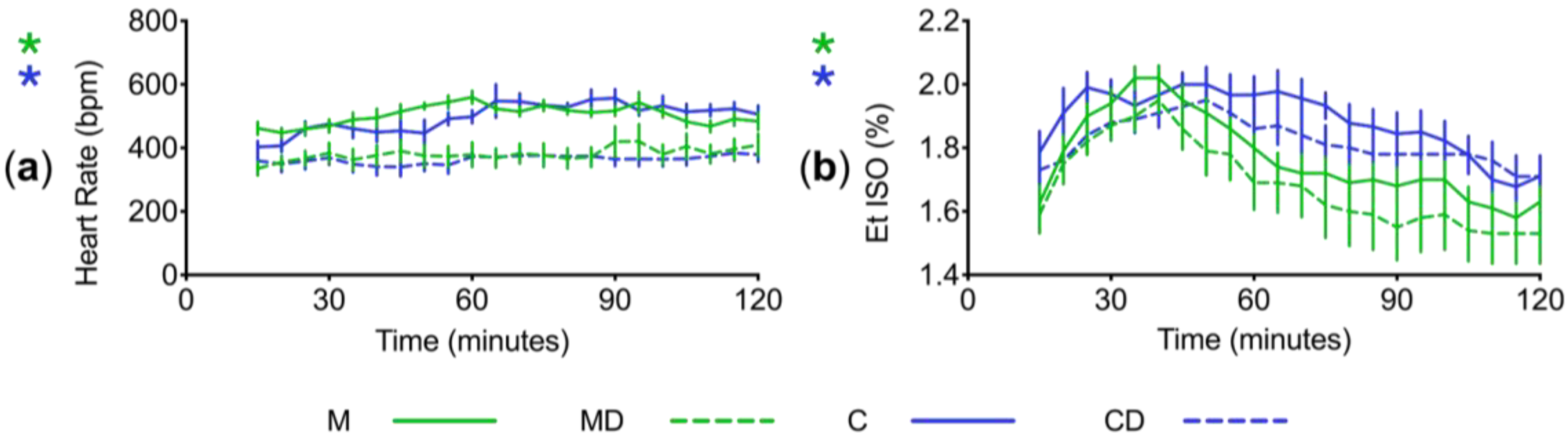
3.2. Variables throughout Anaesthesia
3.3. Variables before and after Defined Stimuli
3.4. Postoperative Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cetin, A.; Komai, S.; Eliava, M.; Seeburg, P.H.; Osten, P. Stereotaxic gene delivery in the rodent brain. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 3166–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, P.A.; Matias, S.; Mainen, Z.F. Stereotaxic adeno-associated virus injection and cannula implantation in the dorsal raphe nucleus of mice. Bio-Protocol 2017, 7, e2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, A.L.; Hauglund, N.L.; von Holstein-Rathlou, S.; Li, Q.; Sanggaard, S.; Lou, N.; Lundgaard, I.; Nedergaard, M. Cannula implantation into the cisterna magna of rodents. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 135, 57378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadarlat, M.C.; Sun, Y.; Stryker, M.P. Widespread activation of awake mouse cortex by electrical stimulation. In Proceedings of the 2019 9th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering (NER), San Francisco, CA, USA, 20–23 March 2019; pp. 1113–1117. [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann, K.; Flecknell, P. Retrospective review of anesthetic and analgesic regimens used in animal research proposals. Altex 2019, 36, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.S.; Brennum, J.; Moltke, F.B.; Dahl, J.B. Suboptimal pain treatment after craniotomy. Dan. Med. J. 2013, 60, A4569. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Cardona, J.; Bendo, A.A. Perioperative pain management in the neurosurgical patient. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2007, 25, 655–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirkof, P. Side effects of pain and analgesia in animal experimentation. Lab. Anim. 2017, 46, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, L.; Austin, J. Pain and laboratory animals: Publication practices for better data reproducibility and better animal welfare. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, K.; Jin, X.-H.; Liu, S.-L.; Ji, F.-H. Effect of intraoperative dexmedetomidine on post-craniotomy pain. Clin. Ther. 2015, 37, 1114–1121.e1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Shen, J.; Ge, L.; Arango, M.F.; Tang, X.; Moodie, J.; McConnell, B.; Cheng, D.; Martin, J. Dexmedetomidine for craniotomy under general anesthesia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J. Clin. Anesth. 2019, 54, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobar, A.; Pypendop, B.H.; Siao, K.; Stanley, S.D.; Ilkiw, J. Effect of dexmedetomidine on the minimum alveolar concentration of isoflurane in cats. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 35, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascoe, P.J.; Raekallio, M.; Kuusela, E.; McKusick, B.; Granholm, M. Changes in the minimum alveolar concentration of isoflurane and some cardiopulmonary measurements during three continuous infusion rates of dexmedetomidine in dogs. VAA 2006, 33, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rioja, E.; Santos, M.; Martinez Taboada, F.; Ibancovichi, J.; Tendillo, F. Cardiorespiratory and minimum alveolar concentration sparing effects of a continuous intravenous infusion of dexmedetomidine in halothane or isoflurane-anaesthetized rats. Lab. Anim. 2006, 40, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.K.; Seddighi, R.; Cox, S.K.; Sun, X.; Knych, H.K.; Doherty, T.J. Effect of dexmedetomidine on the minimum infusion rate of propofol preventing movement in dogs. VAA 2017, 44, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, S.; Hutcherson, M.T.; Sessler, D.I.; Kurz, A.; Yang, D.; Ghobrial, M.; Liu, J.; Avitsian, R. The effects of dexmedetomidine and remifentanil on hemodynamic stability and analgesic requirement after craniotomy: A randomized controlled trial. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 2016, 28, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, A.; Nossaman, B.; Carollo, D.; Ramadhyani, U. Dexmedetomidine for neurosurgical procedures. Curr. Anesthesiol. Rep. 2013, 3, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Shen, Z.; Hu, C.; Zhang, K.; Guo, M.; Wang, F.; Qin, K. Dexmedetomidine ameliorates postoperative cognitive dysfunction in aged mice. Neurochem. Res. 2021, 46, 2415–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Fan, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhang, J. Dexmedetomidine attenuates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis and improves neuronal function after traumatic brain injury in mice. Brain Res. 2020, 1732, 146682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.-L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, M.-Z.; Zhou, Y.-B.; Zhang, J.-M.; Han, L.; Peng, Y.-M.; Jiang, J.-h.; Wang, Q.-D. Dexmedetomidine improves early postoperative cognitive dysfunction in aged mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 746, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, R.A.; Marinho, B.G.; Fernandes, P.D.; de Moura, R.S.; Lessa, M.A. Pharmacological mechanisms involved in the antinociceptive effects of dexmedetomidine in mice. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 28, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.; Yeom, M.-Y.; Kang, E.-S.; Kang, J.-W.; Song, H.-K. The antinociceptive effect of dexmedetomidine modulates spleen cell immunity in mice. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 11, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-c.; Meng, Q.-t.; Pan, X.; Xia, Z.-y.; Chen, X.-d. Dexmedetomidine produced analgesic effect via inhibition of HCN currents. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maze, M.; Tranquilli, W. Alpha-2 adrenoceptor agonists: Defining the role in clinical anesthesia. Anesthesiology 1991, 74, 581–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, K.A.; Lamont, L.A.; Tranquilli, W.J.; Greene, S.A.; Robertson, S.A. Sedatives and Tranquillizers. In Veterinary Anesthesia and Analgesia, 5th ed.; Rankin, D.C., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 196–206. [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson, B.R.; Forsman, M.; Roald, O.K.; Heier, M.S.; Steen, P.A. Effect of dexmedetomidine, a selective and potent alpha 2-agonist, on cerebral blood flow and oxygen consumption during halothane anesthesia in dogs. Anesth. Analg. 1990, 71, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Singh, P. Current role of dexmedetomidine in clinical anesthesia and intensive care. Anesth. Essays Res. 2011, 5, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekker, A.; Sturaitis, M.K. Dexmedetomidine for neurological surgery. Oper. Neurosurg. 2005, 57, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-F.; Chen, M.Y.-C.; Chen, T.-I.; Cheng, C.-F. Dose-dependent effects of isoflurane on cardiovascular function in rats. Tzu Chi Med. J. 2014, 26, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Zuo, Z. Isoflurane induces hippocampal cell injury and cognitive impairments in adult rats. Neuropharmacology 2011, 61, 1354–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culley, D.J.; Baxter, M.; Yukhananov, R.; Crosby, G. The memory effects of general anesthesia persist for weeks in young and aged rats. Anesth. Analg. 2003, 96, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinides, C.; Mean, R.; Janssen, B.J. Effects of isoflurane anesthesia on the cardiovascular function of the C57BL/6 mouse. ILAR J. 2011, 52, e21. [Google Scholar]
- Arras, M.; Rettich, A.; Cinelli, P.; Kasermann, H.P.; Burki, K. Assessment of post-laparotomy pain in laboratory mice by telemetric recording of heart rate and heart rate variability. BMC Vet. Res. 2007, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cividjian, A.; Petitjeans, F.; Liu, N.; Ghignone, M.; de Kock, M.; Quintin, L. Do we feel pain during anesthesia? A critical review on surgery-evoked circulatory changes and pain perception. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2017, 31, 445–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prescott, T.J.; Mitchinson, B.; Grant, R.A. Vibrissal behavior and function. In Scholarpedia of Touch; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Brennan, T.J. Comparison of skin incision vs. skin plus deep tissue incision on ongoing pain and spontaneous activity in dorsal horn neurons. Pain 2009, 144, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duke-Novakovski, T.; de Vries, M.; Seymour, C. Pain management II: Local and regional anaesthetic techniques. In BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Anaesthesia and Analgesia, 3rd ed.; Duke-Novakovski, T., Ed.; BSAVA Library: Gloucester, UK, 2016; pp. 143–158. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.H.; Boyd, K.L.; Fickle, E.K.; Locuson, C.W. Subcutaneous meloxicam suspension pharmacokinetics in mice and dose considerations for postoperative analgesia. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 39, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendall, L.V.; Hansen, R.J.; Dorsey, K.; Kang, S.; Lunghofer, P.J.; Gustafson, D.L. Pharmacokinetics of sustained-release analgesics in mice. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2014, 53, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Foley, P.L.; Kendall, L.V.; Turner, P.V. Clinical management of pain in rodents. Comp. Med. 2019, 69, 468–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lees, P.; Landoni, M.F.; Giraudel, J.; Toutain, P.-L. Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in species of veterinary interest. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 27, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraudel, J.M.; Diquelou, A.; Laroute, V.; Lees, P.; Toutain, P.L. Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modelling of NSAIDs in a model of reversible inflammation in the cat. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 146, 642–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeunesse, E.C.; Bargues, I.A.; Toutain, C.E.; Lacroix, M.Z.; Letellier, I.M.; Giraudel, J.M.; Toutain, P.-L. Paw inflammation model in dogs for preclinical pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic investigations of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 338, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lees, P.; Giraudel, J.; Landoni, M.; Toutain, P.-L. PK–PD integration and PK–PD modelling of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Principles and applications in veterinary pharmacology. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 27, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flecknell, P. Laboratory Animal Anaesthesia, 4th ed.; Academic press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 170–178. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, S.; Pacharinsak, C. Mouse anesthesia and analgesia. Curr. Protoc. Mouse Biol. 2015, 5, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright-Williams, S.L.; Courade, J.-P.; Richardson, C.A.; Roughan, J.V.; Flecknell, P.A. Effects of vasectomy surgery and meloxicam treatment on faecal corticosterone levels and behaviour in two strains of laboratory mouse. Pain 2007, 130, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumiya, L.C.; Sorge, R.E.; Sotocinal, S.G.; Tabaka, J.M.; Wieskopf, J.S.; Zaloum, A.; King, O.D.; Mogil, J.S. Using the Mouse Grimace Scale to reevaluate the efficacy of postoperative analgesics in laboratory mice. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2012, 51, 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- Kommula, L.K.; Bansal, S.; Umamaheswara Rao, G.S. Analgesia nociception index monitoring during supratentorial craniotomy. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 2019, 31, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Roberts, M.S. Dermal and underlying tissue pharmacokinetics of lidocaine after topical application. J. Pharm. Sci. 1994, 83, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bol, C.J.; Danhof, M.; Stanski, D.R.; Mandema, J.W. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic characterization of the cardiovascular, hypnotic, EEG and ventilatory responses to dexmedetomidine in the rat. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997, 283, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, D.; Abdul-Rasool, I.; Ward, D.; Hsieh, J.; Kobayashi, D.; Hadlock, S.; Singer, F.; Bloor, B. Ventilatory effects of dexmedetomidine, atipamezole, and isoflurane in dogs. Anesthesiology 1992, 76, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, K.A.; Lamont, L.A.; Tranquilli, W.J.; Greene, S.A.; Robertson, S.A. Monitoring Anesthetized Patients. In Veterinary Anesthesia and Analgesia, 5th ed.; Haskins, S.C., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 86–113. [Google Scholar]
- Duke-Novakovski, T.; de Vries, M.; Seymour, C. Patient monitoring and monitoring equipment. In BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Anaesthesia and Analgesia, 3rd ed.; Schauvliege, S., Ed.; BSAVA Library: Gloucester, UK, 2016; pp. 77–96. [Google Scholar]
- Auckburally, A. Pulse oximetry and oxygenation assessment in small animal practice. In Pract. 2016, 38, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Woodske, M.E.; Zou, B.; O’Donnell, C.P. Dynamic arterial blood gas analysis in conscious, unrestrained C57BL/6J mice during exposure to intermittent hypoxia. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 107, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendall, L.V.; Wegenast, D.J.; Smith, B.J.; Dorsey, K.M.; Kang, S.; Lee, N.Y.; Hess, A.M. Efficacy of sustained-release buprenorphine in an experimental laparotomy model in female mice. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2016, 55, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jirkof, P.; Tourvieille, A.; Cinelli, P.; Arras, M. Buprenorphine for pain relief in mice: Repeated injections vs sustained-release depot formulation. Lab. Anim. 2015, 49, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Avalos, I.; Flores-Gasca, E.; Mota-Rojas, D.; Casas-Alvarado, A.; Miranda-Cortés, A.; Domínguez-Oliva, A. Neurobiology of anesthetic-surgical stress and induced behavioral changes in dogs and cats: A review. Vet. World 2021, 14, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, K.A.; Lamont, L.A.; Tranquilli, W.J.; Greene, S.A.; Robertson, S.A. Opioids. In Veterinary Anesthesia and Analgesia, 5th ed.; KuKanich, B., Wiese, A.J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 207–226. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schiele, A.R.; Henze, I.S.; Bettschart-Wolfensberger, R.; Gent, T.C. Antinociceptive and Cardiorespiratory Effects of a Single Dose of Dexmedetomidine in Laboratory Mice Subjected to Craniotomy under General Anaesthesia with Isoflurane and Carprofen or Meloxicam. Animals 2024, 14, 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14060913
Schiele AR, Henze IS, Bettschart-Wolfensberger R, Gent TC. Antinociceptive and Cardiorespiratory Effects of a Single Dose of Dexmedetomidine in Laboratory Mice Subjected to Craniotomy under General Anaesthesia with Isoflurane and Carprofen or Meloxicam. Animals. 2024; 14(6):913. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14060913
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchiele, Anika R., Inken S. Henze, Regula Bettschart-Wolfensberger, and Thomas C. Gent. 2024. "Antinociceptive and Cardiorespiratory Effects of a Single Dose of Dexmedetomidine in Laboratory Mice Subjected to Craniotomy under General Anaesthesia with Isoflurane and Carprofen or Meloxicam" Animals 14, no. 6: 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14060913
APA StyleSchiele, A. R., Henze, I. S., Bettschart-Wolfensberger, R., & Gent, T. C. (2024). Antinociceptive and Cardiorespiratory Effects of a Single Dose of Dexmedetomidine in Laboratory Mice Subjected to Craniotomy under General Anaesthesia with Isoflurane and Carprofen or Meloxicam. Animals, 14(6), 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14060913




