Whole-Genome Sequencing for Identifying Candidate Genes Related to the Special Phenotypes of the Taihu Dianzi Pigeon
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Animals and Whole Genome Sequencing
2.3. Variants Identification and Annotation
2.4. Population Genetics Analysis
2.5. Selective Sweep Analysis
2.6. Genome-Wide Association Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genome Resequencing of Five Pigeon Groups
3.2. Identification and Annotation of Variants
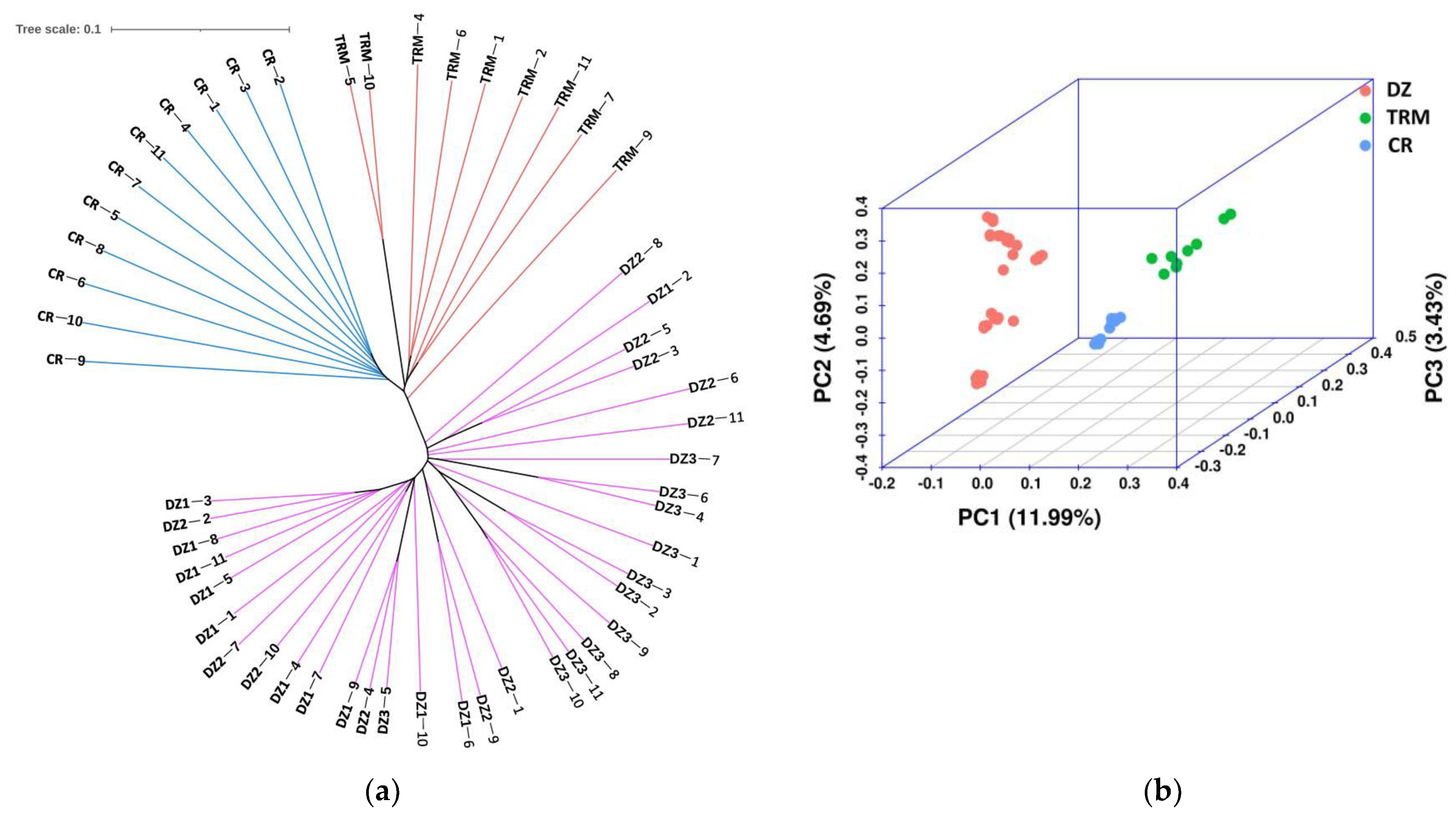
3.3. Population Genetics
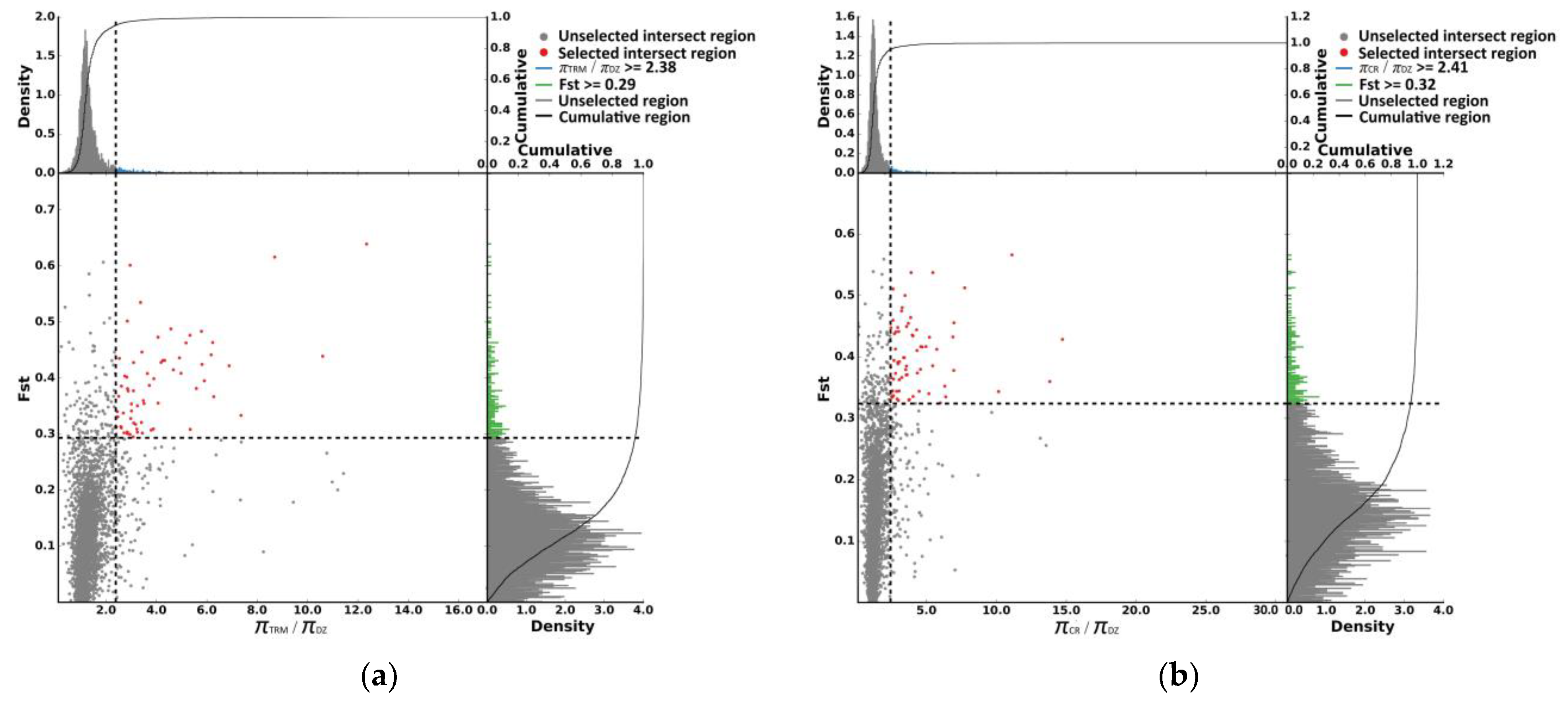
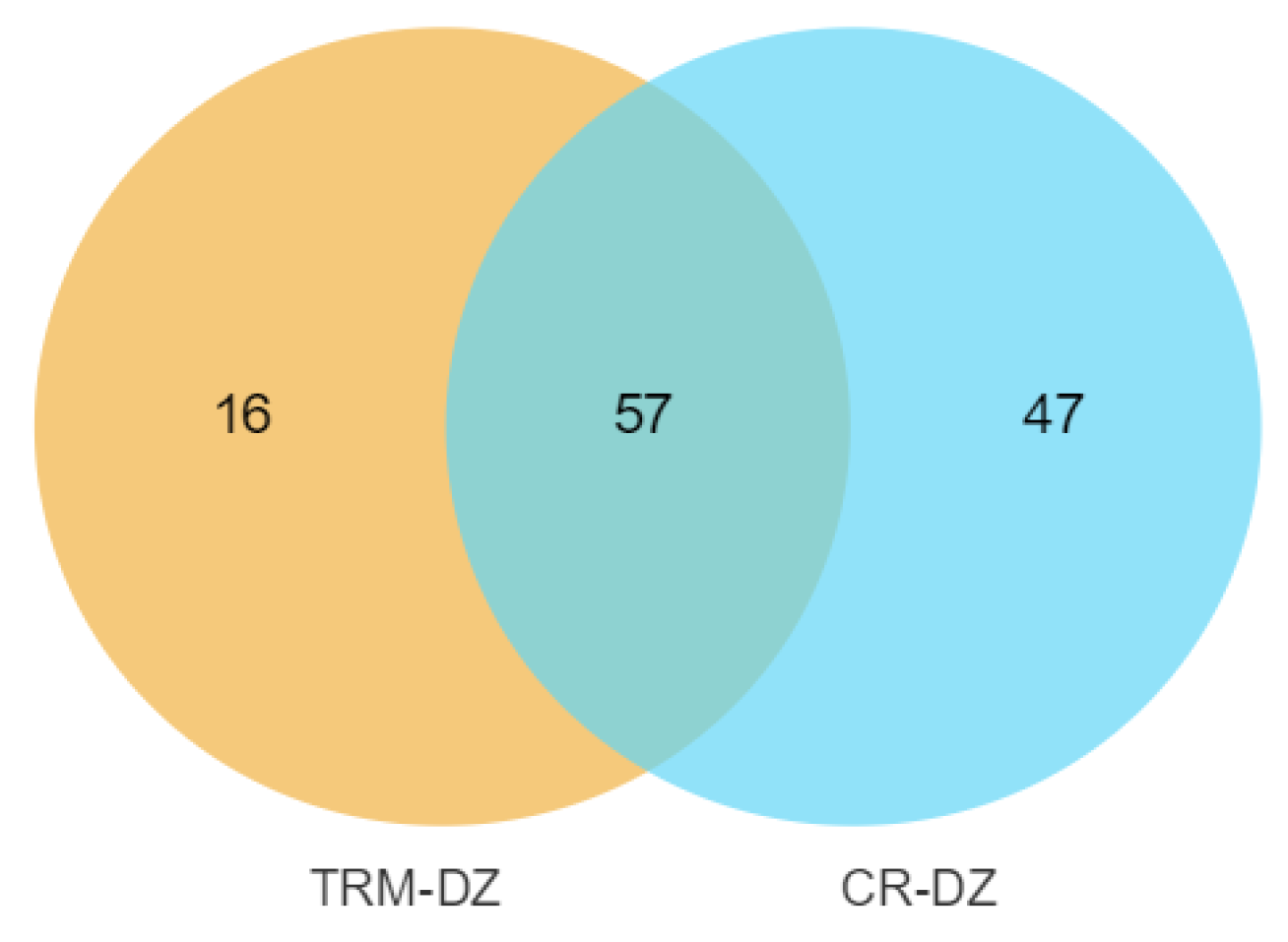
3.4. Selective Sweep Signals for the Taihu Dianzi Pigeon Special Piebalding
3.5. Selective-Sweep Signals in Crested Pigeons
3.6. Selective-Sweep Signals in Polydactyl Pigeons
3.7. Genome-Wide Association Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stringham, S.A.; Mulroy, E.E.; Xing, J.; Record, D.; Guernsey, M.W.; Aldenhoven, J.T.; Osborne, E.J.; Shapiro, M.D. Divergence, convergence, and the ancestry of feral populations in the domestic rock pigeon. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, C.; Campbell, M.; Keays, D.A.; Edelman, N.; Kapusta, A.; Maclary, E.; Domyan, E.; Suh, A.; Warren, W.C.; Yandell, M.; et al. Improved genome assembly and annotation for the rock pigeon (Columba livia). G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2018, 8, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmailizadeh, A.; Kharrati-Koopaee, H.; Nanaei, H.A. Whole genome resequencing data for rock pigeon (Columba livia). BMC Res. Notes 2021, 14, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerolmack, C. Animal archeology: Domestic pigeons and the nature-culture dialectic. Qual. Sociol. Rev. 2007, 3, 74–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, M.D.; Domyan, E.T. Domestic pigeons. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, R302–R303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maclary, E.T.; Wauer, R.; Phillips, B.; Brown, A.; Boer, E.F.; Samani, A.M.; Shapiro, M.D. An allelic series at the EDNRB2 locus controls diverse piebalding patterns in the domestic pigeon. PLoS Genet. 2023, 19, e1010880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joller, S.; Ammann, P.; Flury, C.; Drögemüller, C. Evaluation of HOXC 8 in crested Swiss chicken. Anim. Genet. 2018, 49, 334–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Lee, M.O.; Davis, B.W.; Wu, P.; Hsieh Li, S.M.; Chuong, C.M.; Andersson, L. The crest phenotype in domestic chicken is caused by a 195 bp duplication in the intron of HOXC10. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2021, 11, jkaa048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, L.C.; Jull, M.A. On the inheritance of some characters op the silky fowl. J. Genet. 1927, 19, 27–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, G.; Yuan, X.; Guo, Q.; Bai, H.; Cao, X.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, B.; Wang, S.; Jiang, Y.; et al. The first crested duck genome reveals clues to genetic compensation and crest cushion formation. Genom. Proteom. Bioinf. 2023, 21, 483–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, M.D.; Kronenberg, Z.; Li, C.; Domyan, E.T.; Pan, H.; Campbell, M.; Tan, H.; Huff, C.D.; Hu, H.; Vickrey, A.I.; et al. Genomic diversity and evolution of the head crest in the rock pigeon. Science 2013, 339, 1063–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, D.C. Inheritance of polydactylism in the fowl. Genetics 1944, 29, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Nie, C.; Jia, Y.; Jiang, R.; Xia, H.; Lv, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Ning, Z.; et al. Parallel evolution of polydactyly traits in Chinese and European chickens. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: Functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Lee, S.H.; Goddard, M.E.; Visscher, P.M. GCTA: A tool for genome-wide complex trait analysis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 88, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nei, M.; Li, W.H. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 5269–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Yu, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Lun, Y.; Li, S.; et al. Genomic analyses provide insights into the history of tomato breeding. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, R.R.; Slatkin, M.; Maddison, W.P. Estimation of levels of gene flow from DNA sequence data. Genetics 1992, 132, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, B.; Wittelsbürger, U.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Lercher, M.J. PopGenome: An efficient Swiss army knife for population genomic analyses in R. Molecular biology and evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 1929–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbury, P.J.; Zhang, Z.; Kroon, D.E.; Casstevens, T.M.; Ramdoss, Y.; Buckler, E.S. TASSEL: Software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2633–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Alonso, G.; Ramos-Madrigal, J.; van Grouw, H.; Ciucani, M.M.; Cavill, E.L.; Sinding, M.H.S.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Pacheco, G.; Gilbert, M.T.P. Redefining the evolutionary history of the rock dove, Columba livia, using whole genome sequences. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2023, 40, msad243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Stidham, T.A.; Li, Z.H. Reexamination of the oldest pigeon (Aves: Columbidae) from Asia: Columba congi from the Early Pleistocene of Zhoukoudian, Beijing, China. Vertebr. Palasiat. 2021, 59, 245–256. [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco, G.; Van Grouw, H.; Shapiro, M.D.; Gilbert, M.T.P.; Vieira, F.G. Darwin’s fancy revised: An updated understanding of the genomic constitution of pigeon breeds. Genome Biol. Evol. 2020, 12, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Shen, J.; Hanif, Q.; Chen, N.; Huang, Y.; Dang, R.; Lan, X.; Chen, H.; Lei, C. Whole genome analyses revealed genomic difference between European taurine and East Asian taurine. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2021, 138, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, X.; Zhao, S.; Xiang, W.; Jin, H.; Chen, N.; Lei, C.; Jia, Y.; Xu, L. Genetic diversity and selective signature in Dabieshan cattle revealed by whole-genome resequencing. Biology 2022, 11, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, S.F.; Lawal, R.A.; Adeola, A.C.; Nie, Q. The study of selection signature and its applications on identification of candidate genes using whole genome sequencing data in chicken-a review. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Shan, Y.; Ji, G.; Ju, X.; Zou, J.; Shu, J. Identifying signatures of selection related to comb development. Poult. Sci. 2021, 58, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Tan, X.; Wang, J.; Jin, Q.; Meng, X.; Cai, Z.; Cai, Z.; Cui, X.; Wang, K. Whole genome sequencing of Luxi Black Head sheep for screening selection signatures associated with important traits. Anim. Biosci. 2022, 35, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, W. Genetic hitchhiking versus background selection: The controversy and its implications. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, H.; Wang, X.; Ding, W.; Xiao, C.; Cai, X.; Lv, W.; Tu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Yao, J.; Yang, C. Whole-genome sequencing reveals the artificial selection and local environmental adaptability of pigeons (Columba livia). Evol. Appl. 2022, 15, 603–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Bi, Y.; Chen, G.; Bai, H.; Chang, G. Genome-wide analysis identifies candidate genes encoding feather color in ducks. Genes 2018, 13, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, R.L.; Tao, Y.X. Melanocortin-1 receptor mutations and pigmentation: Insights from large animals. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2022, 189, 179–213. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Xiong, S.Y.; Xiao, S.J.; Zhang, Z.K.; Tu, J.M.; Cui, D.S.; Yu, N.B.; Huang, Z.Y.; Li, L.Y.; Guo, Y.M. Association between MC1R gene and coat color segregation in Shanxia long black pig and Lulai black pig. BMC Genom. Data 2023, 24, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Cao, C.; Zhang, H.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Kang, Y.; Fang, W.; Lan, X.; Li, R.; Pan, C. Convergent changes in melanocortin receptor 1 gene are associated with black-headed coat color in sheep. J. Anim. Sci. 2023, 101, skad084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.L.; Li, X.L.; Li, Y.; Gu, Z.L.; Zheng, C.S.; Wei, Z.H.; Wang, J.S.; Zhou, R.Y.; Zheng, H.Q. Genetic variation of chicken MC1R gene in different plumage colour populations. Br. Poult. Sci. 2010, 51, 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.X.; Adeola, A.C.; Sola-Ojo, F.E.; Abubakar, I.A.; Fatima, I.H.; Olaoluwa, O.J.; Abodurin, A.B.; Olasunkanmi, O.A.; Abisola, O.H.; Uthman, O.; et al. Association of MC1R variation and plumage color diversity of Nigerian domestic pigeon (Columba livia domestica). J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2022, 9, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Tang, Q.P.; Mu, C.Y.; Yang, M.J.; Xia, A.P.; Fu, S.Y.; Chang, L.L.; Bu, Z. The amplification and sequence analysis of MC1R gene of different plumage color pigeons. Chin. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 57, 96–100+105. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, D.Y.; Chen, J.J.; Su, P.C.; Liu, I.M.; Yeh, S.H.H.; Chen, C.K.; Cheng, H.C.; Chen, C.F.; Li, W.H.; Ng, C.S. Chicken HOXC8 and HOXC10 genes may play a role in the altered skull morphology associated with the Crest phenotype. J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2023, 340, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Imsland, F.; Gu, X.; Feng, C.; Liu, R.; Song, C.; Tixier-Boichard, M.; Gourichon, D.; Li, Q.; et al. The crest phenotype in chicken is associated with ectopic expression of HOXC8 in cranial skin. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yao, W.; Wang, B.; Lu, L.; Xu, Q.; Chang, G.; Chen, G. Expression analysis of crest phenotype related genes from crested white duck. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis 2018, 30, 707–710. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, Q.; Bian, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Q.; Chang, G.; Chen, G. Whole genome re-sequencing of crested traits and expression analysis of key candidate genes in duck. Gene 2018, 729, 144282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaib, T.; Ji, W.; Saleem, K.; Nie, G.; Li, C.; Xu, B.; Dong, K.; Yu, H.; Hao, X.; Xue, Y.; et al. A heterozygous duplication variant of the HOXDl3 gene caused synpolydactyly type 1 with variable expressivity in a Chinese family. BMC Med. Genet. 2019, 20, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, R.M.; Marker, P.C.; Kingsley, D.M. A novel candidate gene for mouse and human preaxial polydactyly with altered expression in limbs of Hemimelic extra-toes mutant mice. Genomics 2000, 67, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriazis, Z.; Kollia, P.; Grivea, I.; Stefanou, N.; Sotiriou, S.; Dailiana, Z.H. Polydactyly: Clinical and molecular manifestations. World. J. Orthop. 2023, 14, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, R.; Zhao, G.; Zheng, M.; Sun, Y.; Yu, X.; Li, P.; Wen, J. Genome-wide linkage analysis and association study identifies loci for polydactyly in chickens. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2014, 4, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Chen, Y.; Yang, K.; Zhai, Z.; Zhao, W.; Liu, S.; Ding, J.; Dai, R.; Yang, L.; Xu, K.; et al. Genetic pattern and gene localization of polydactyly in Beijing fatty chicken. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesecker, L.G. Polydactyly: How many disorders and how many genes? 2010 update. Dev. Dyn. 2011, 240, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pál, M.; Vetró, É.; Nagy, N.; Nagy, D.; Horváth, E.; Bokor, B.A.; Varga, A.; Seres, L.; Oláh, J.; Piffkó, J.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing identified two novel pathogenic mutations in the PTCH1 gene in BCNS. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 5293–5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
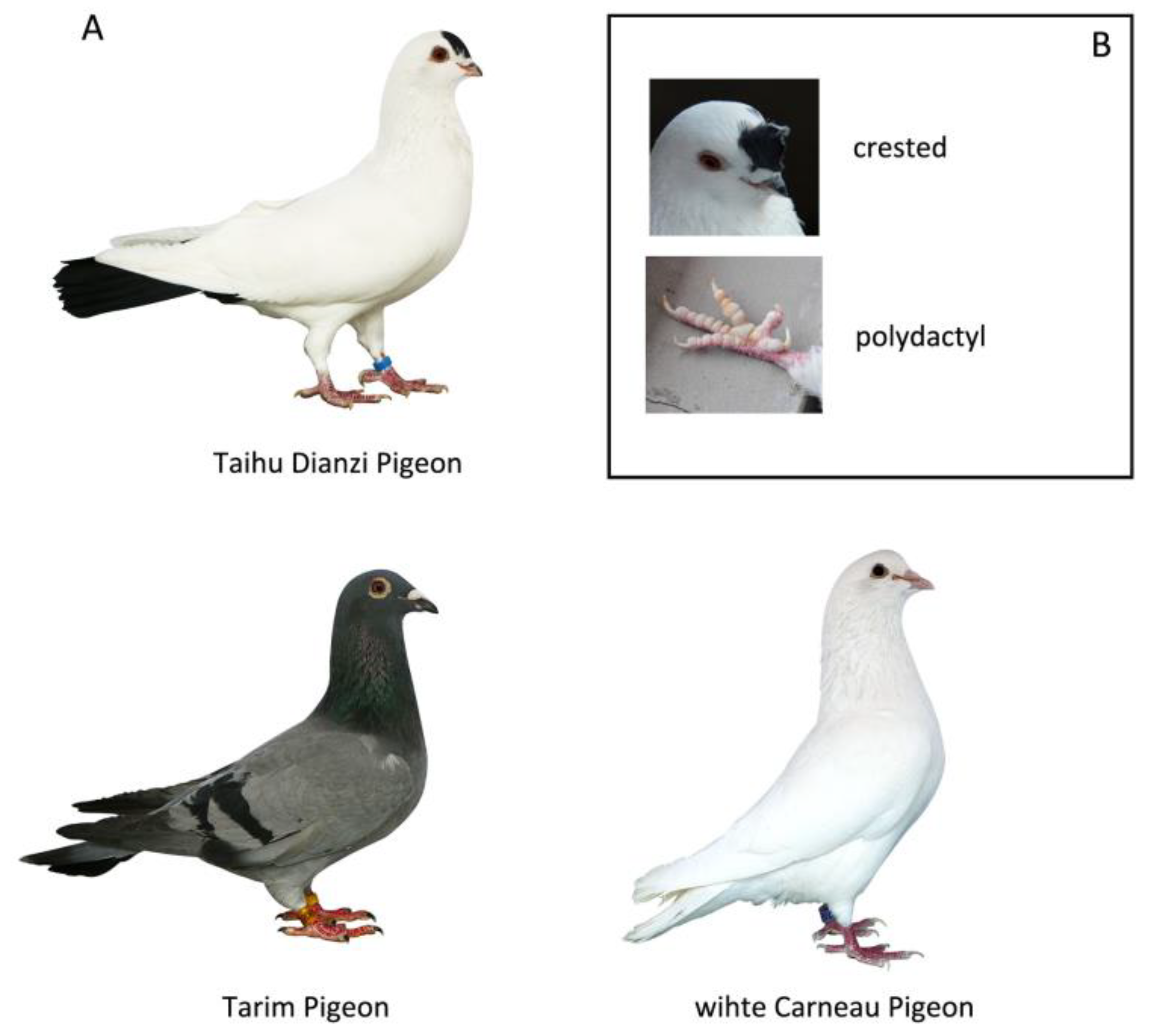



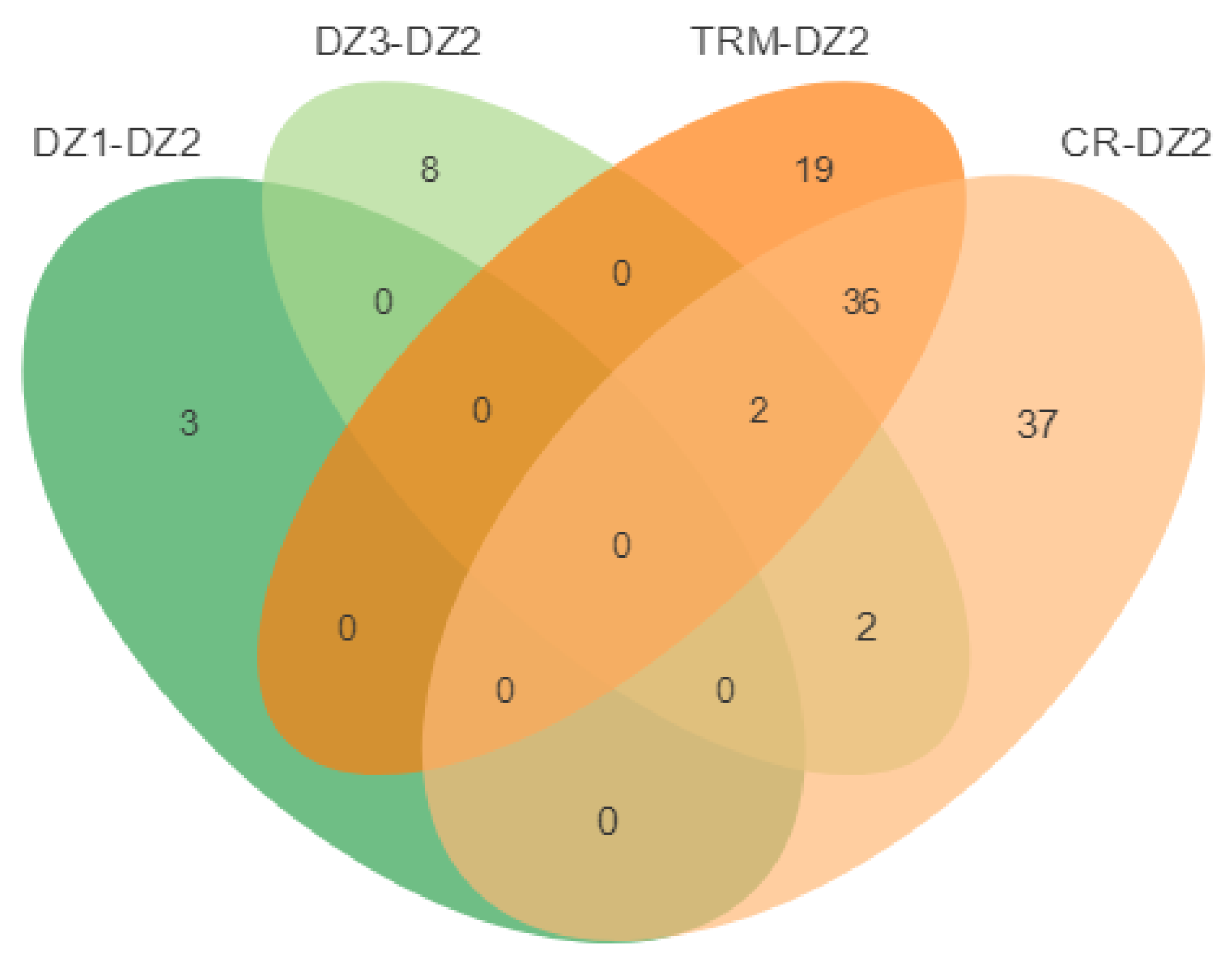

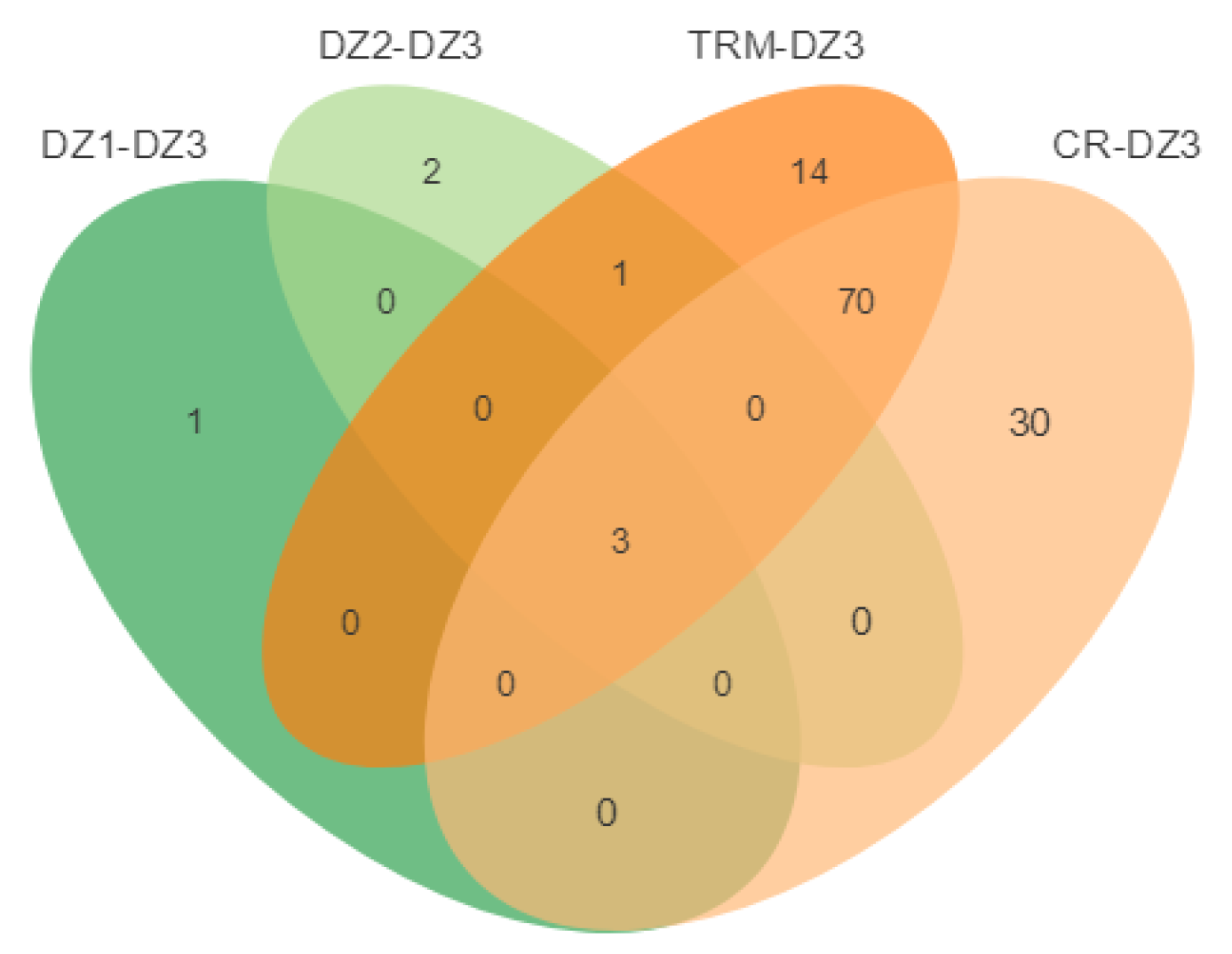


| Sample | N | Raw Data (G) | Clean Data (G) | Mapping Rate (%) | Sequence Depth (x) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DZ | 33 | 18.26 | 17.71 | 97.60 | 17.16 |
| TRM | 9 | 17.74 | 17.18 | 97.77 | 16.64 |
| CR | 11 | 16.27 | 15.80 | 97.63 | 15.30 |
| DZ | TRM | CR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNP | Total number of SNPs | 11,578,452 | 11,866,346 | 12,516,118 |
| Intergenic | 6,424,331 | 6,593,463 | 6,939,604 | |
| Intronic | 4,591,330 | 4,697,697 | 4,966,006 | |
| Exonic | 24,179 | 24,456 | 26,186 | |
| Non-synonymous | 42,855 | 42,599 | 46,243 | |
| Stop gain | 385 | 332 | 386 | |
| Stop loss | 46 | 49 | 58 | |
| Synonymous | 91,583 | 93,845 | 99,427 | |
| Upstream | 135,942 | 139,623 | 147,456 | |
| Downstream | 134,886 | 137,653 | 145,885 | |
| UTR | 84,396 | 86,490 | 92,215 | |
| Splicing | 491 | 434 | 469 | |
| ncRNA | 48,028 | 49,705 | 52,183 | |
| InDel | Total number of InDels | 835,848 | 846,354 | 879,372 |
| Intergenic | 456,527 | 462,451 | 478,820 | |
| Intronic | 344,699 | 349,138 | 364,232 | |
| Exonic | 348 | 347 | 348 | |
| Non-synonymous | 626 | 640 | 665 | |
| Stop gain | 12 | 12 | 13 | |
| Stop loss | 2 | 1 | 2 | |
| Synonymous | 545 | 556 | 577 | |
| Upstream | 10,641 | 10,676 | 11,073 | |
| Downstream | 12,134 | 12,173 | 12,694 | |
| UTR | 6528 | 6581 | 6971 | |
| Splicing | 171 | 178 | 187 | |
| ncRNA | 3615 | 3601 | 3790 |
| SNP | Chr | Location | Mutation | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNP1 | AKCR02000002.1 | 505029 | T>G | 4.7727 × 10−11 |
| SNP2 | AKCR02000006.1 | 33844338 | G>A | 1.1403 × 10−10 |
| SNP3 | AKCR02000006.1 | 33896741 | C>T | 1.0102 × 10−10 |
| SNP4 | AKCR02000006.1 | 33898464 | G>A | 9.6488 × 10−14 |
| SNP5 | AKCR02000006.1 | 33898620 | C>T | 9.6488 × 10−14 |
| SNP6 | AKCR02000006.1 | 33901426 | C>A | 2.6008 × 10−14 |
| Gene | SNP | p | Genotype | Phenotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLC52A3 | exon1:c.222G>A | 1.2529 × 10−13 | GG | non-polydactyly |
| GA | non-polydactyly | |||
| AA | polydactyly | |||
| ANGPT4 | 5’UTR:c.-169G>A | 1.2529 × 10−13 | GG | non-polydactyly |
| GA | non-polydactyly | |||
| AA | polydactyly | |||
| exon5:c.786G>A | 1.2529 × 10−13 | GG | non-polydactyly | |
| GA | non-polydactyly | |||
| AA | polydactyly | |||
| exon8:c.1172T>C | 1.2529 × 10−13 | TT | non-polydactyly | |
| TC | non-polydactyly | |||
| CC | polydactyly |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R.; Mu, C.; Chang, L.; Shen, X.; Bu, Z.; Yang, M.; Fu, S.; Tang, Q.; Liu, P.; Yang, X. Whole-Genome Sequencing for Identifying Candidate Genes Related to the Special Phenotypes of the Taihu Dianzi Pigeon. Animals 2024, 14, 1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14071047
Zhang R, Mu C, Chang L, Shen X, Bu Z, Yang M, Fu S, Tang Q, Liu P, Yang X. Whole-Genome Sequencing for Identifying Candidate Genes Related to the Special Phenotypes of the Taihu Dianzi Pigeon. Animals. 2024; 14(7):1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14071047
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Rui, Chunyu Mu, Lingling Chang, Xinyue Shen, Zhu Bu, Mingjun Yang, Shengyong Fu, Qingping Tang, Peiyao Liu, and Xiaoming Yang. 2024. "Whole-Genome Sequencing for Identifying Candidate Genes Related to the Special Phenotypes of the Taihu Dianzi Pigeon" Animals 14, no. 7: 1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14071047
APA StyleZhang, R., Mu, C., Chang, L., Shen, X., Bu, Z., Yang, M., Fu, S., Tang, Q., Liu, P., & Yang, X. (2024). Whole-Genome Sequencing for Identifying Candidate Genes Related to the Special Phenotypes of the Taihu Dianzi Pigeon. Animals, 14(7), 1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14071047





