Ten Years of Mediterranean Monk Seal Stranding Records in Greece under the Microscope: What Do the Data Suggest?
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
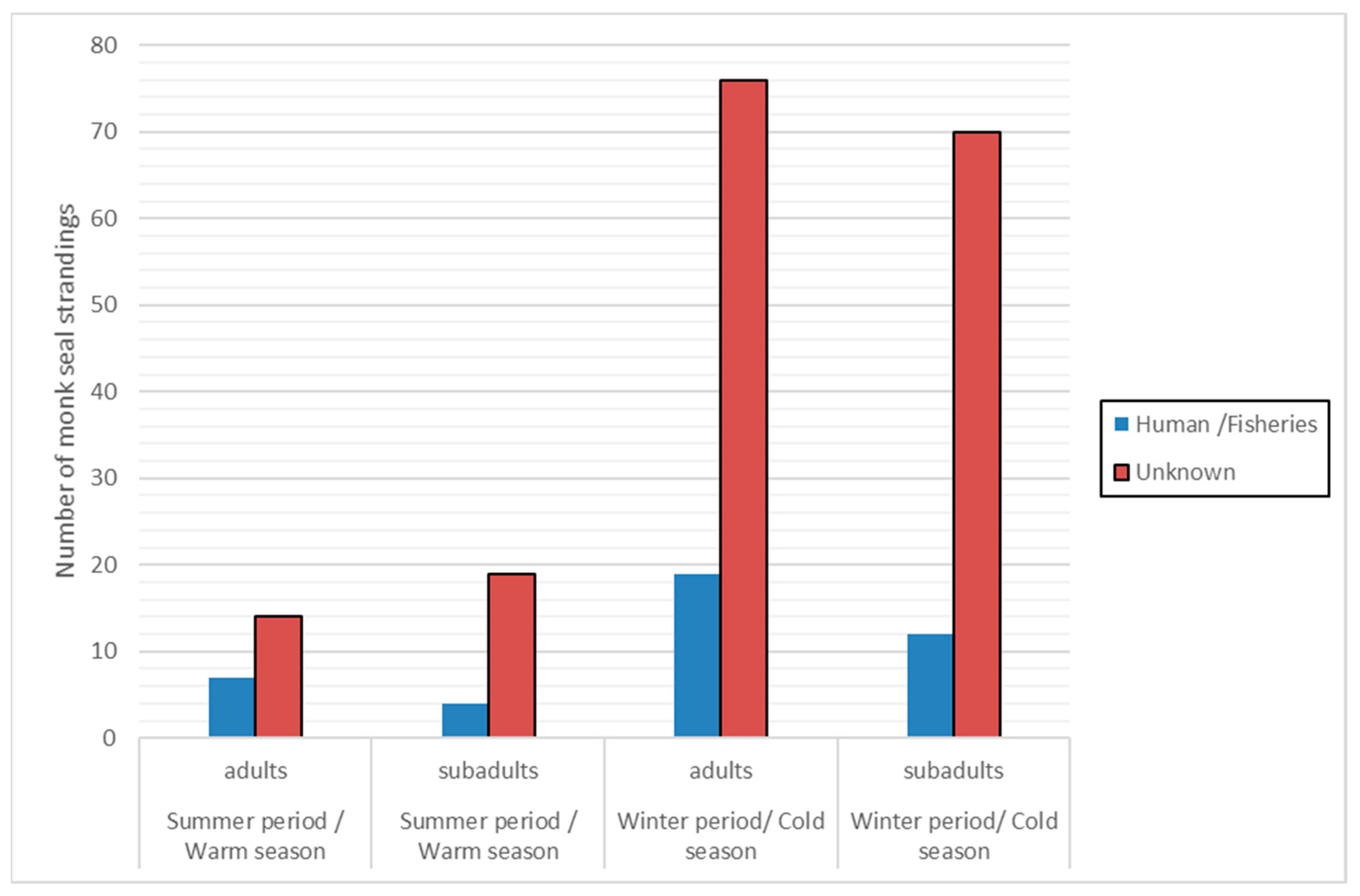
2.1. Data Mining: Cause of Death
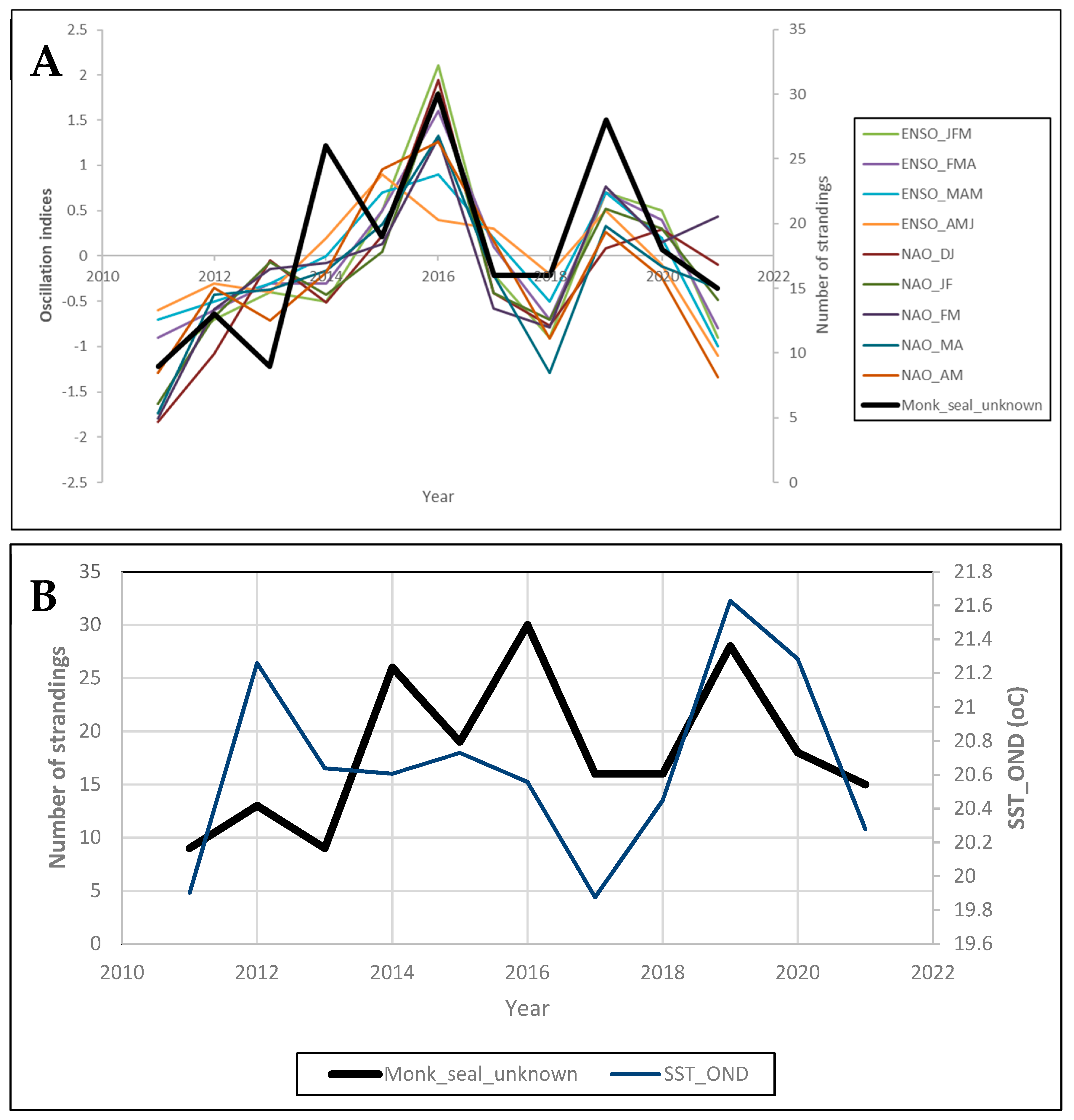
2.2. Temporal Trends in Stranding Events Related to Environmental Variability
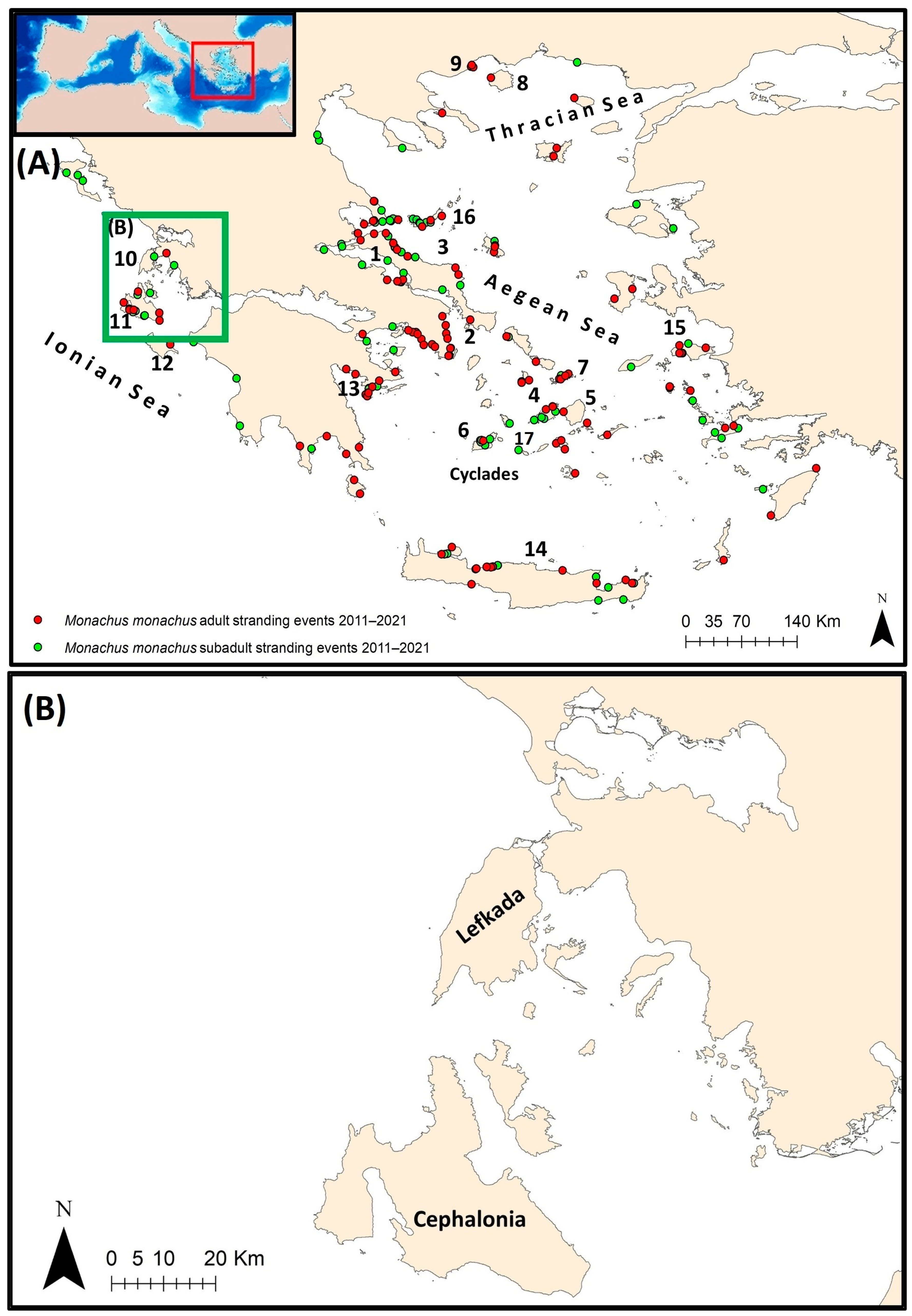
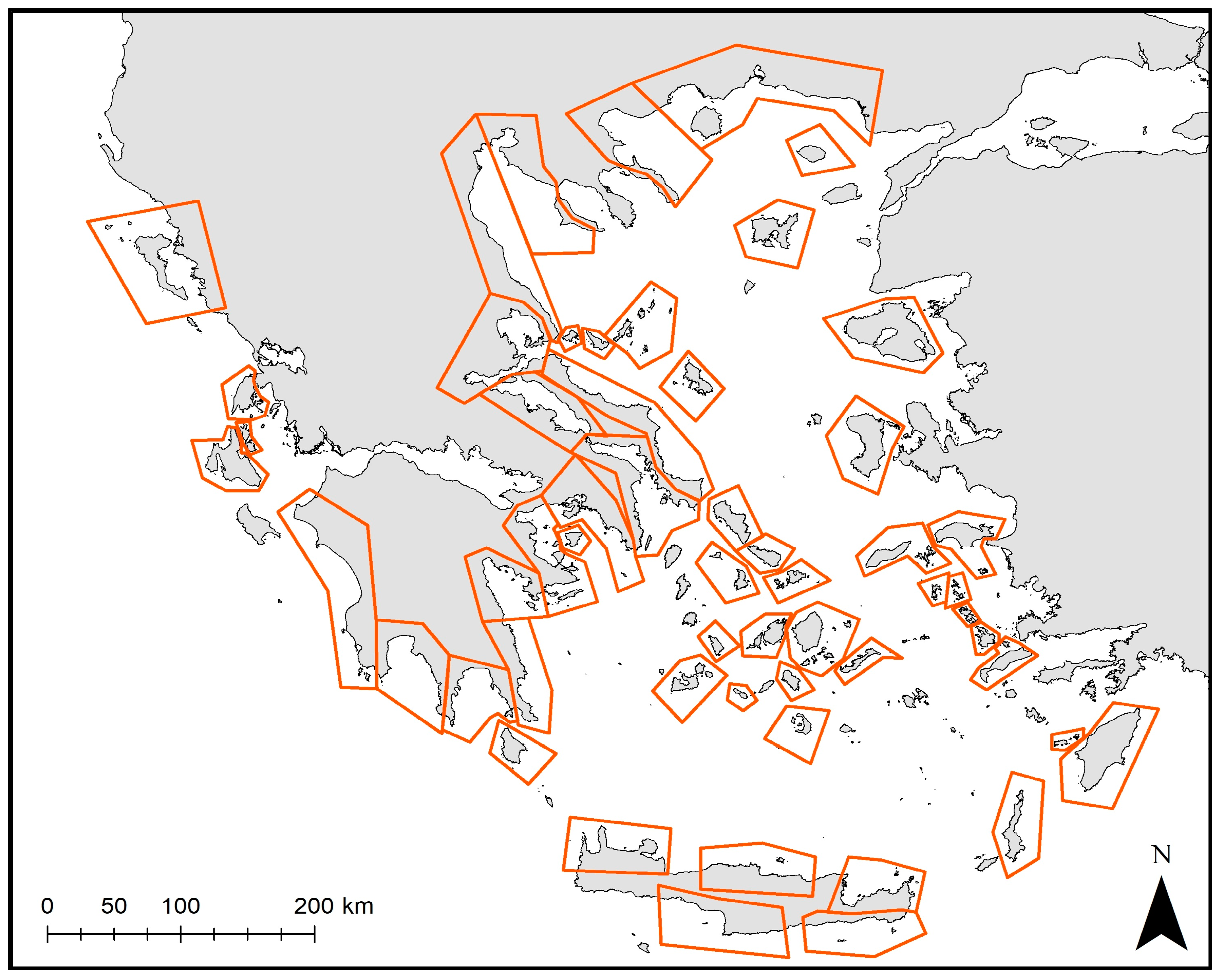
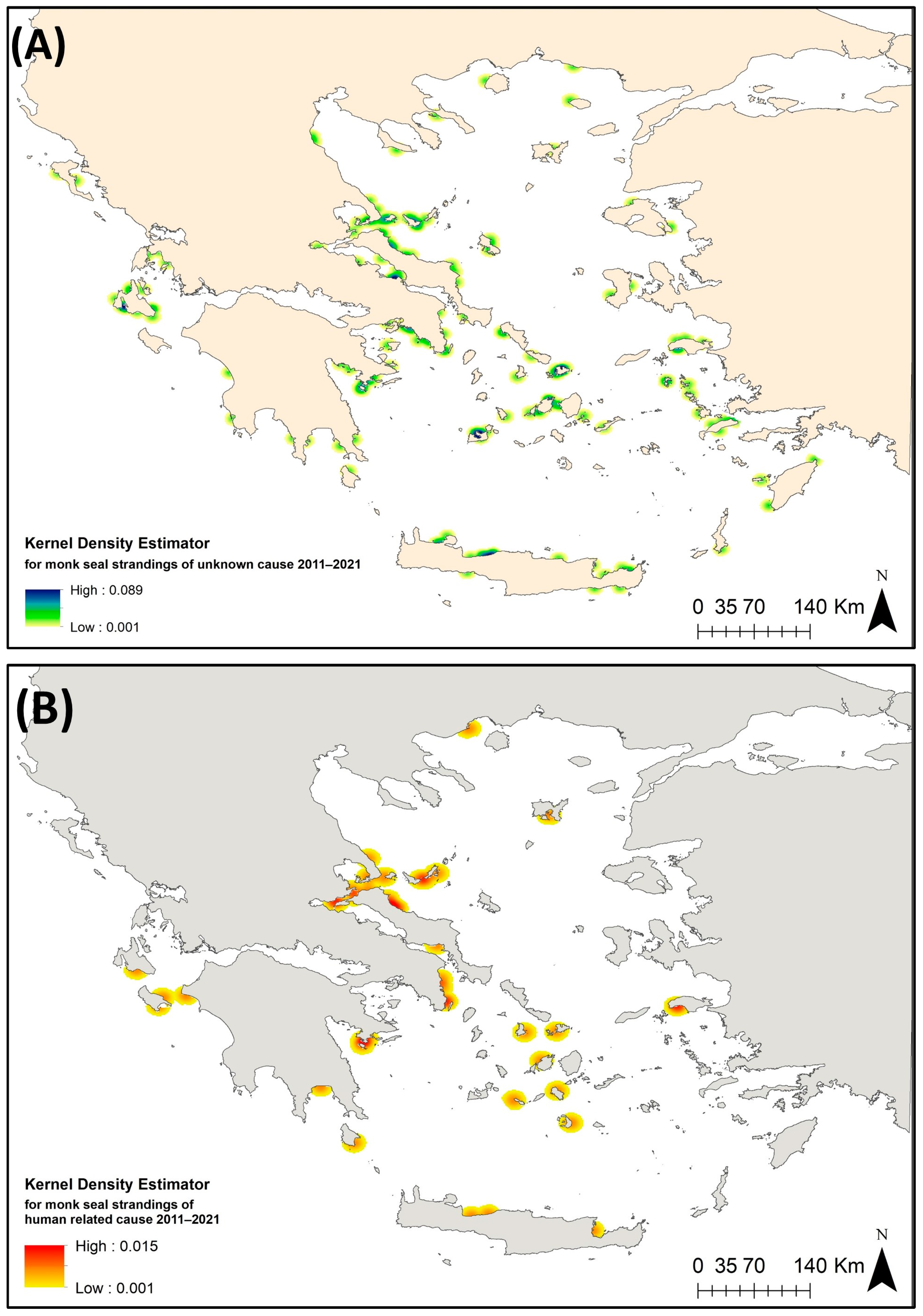
2.3. Spatial Analysis: Identifying Hotspot Stranding Areas
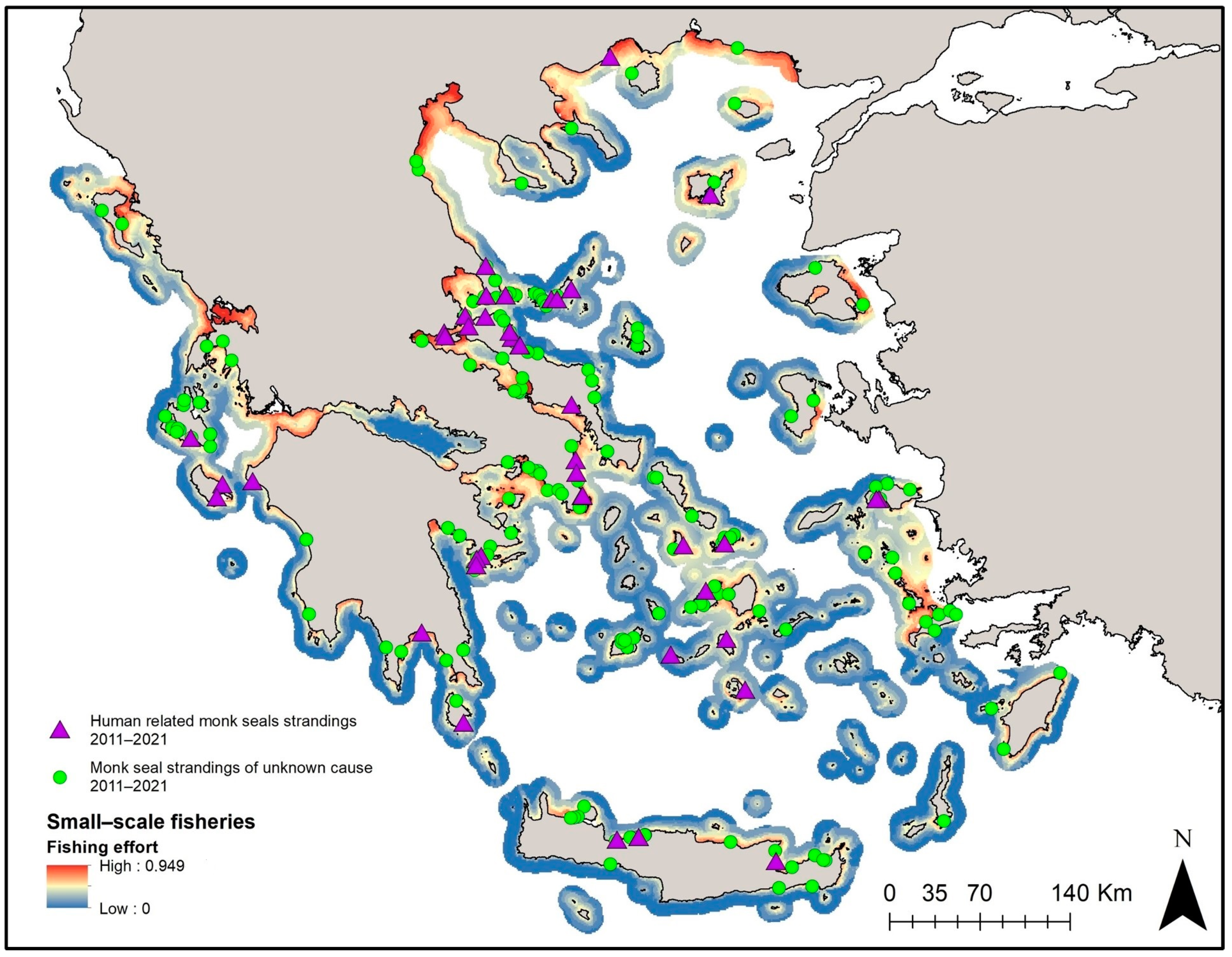
2.4. Identifying Factors Related to the Spatial Pattern of Monk Seal Strandings
- The size of fishing grounds of the small-scale fishery (SSF): the fishing area that corresponds to the upper 50% of the accounted small-scale fishing density estimated as the average for the 2011–2021 period (based on [17]).
- The size of potential feeding grounds: the estimation was based on the catch of undersized discarded fish from commercial bottom trawls (modeled based [25,26]). Based on these data, the feeding area that corresponds to the upper 25% of the accounted coastal bony fish biomass was estimated and assigned per subarea.
- Monk seal sightings: Sightings might be considered as a rough proxy of the distribution or as an indicator of the activity of the monk seal population in the Greek Seas. Based on Dendrinos et al. [27], a tentative number of sightings was assigned per subarea, ranging from 10 to 150 sightings.
- Breeding sites (including potential and confirmed ones) and resting sites. The level of density of existing caves (based on [27]) was assigned per subarea. We acknowledge the fact that available information can be less accurate for certain areas; however, it is the best information currently available.
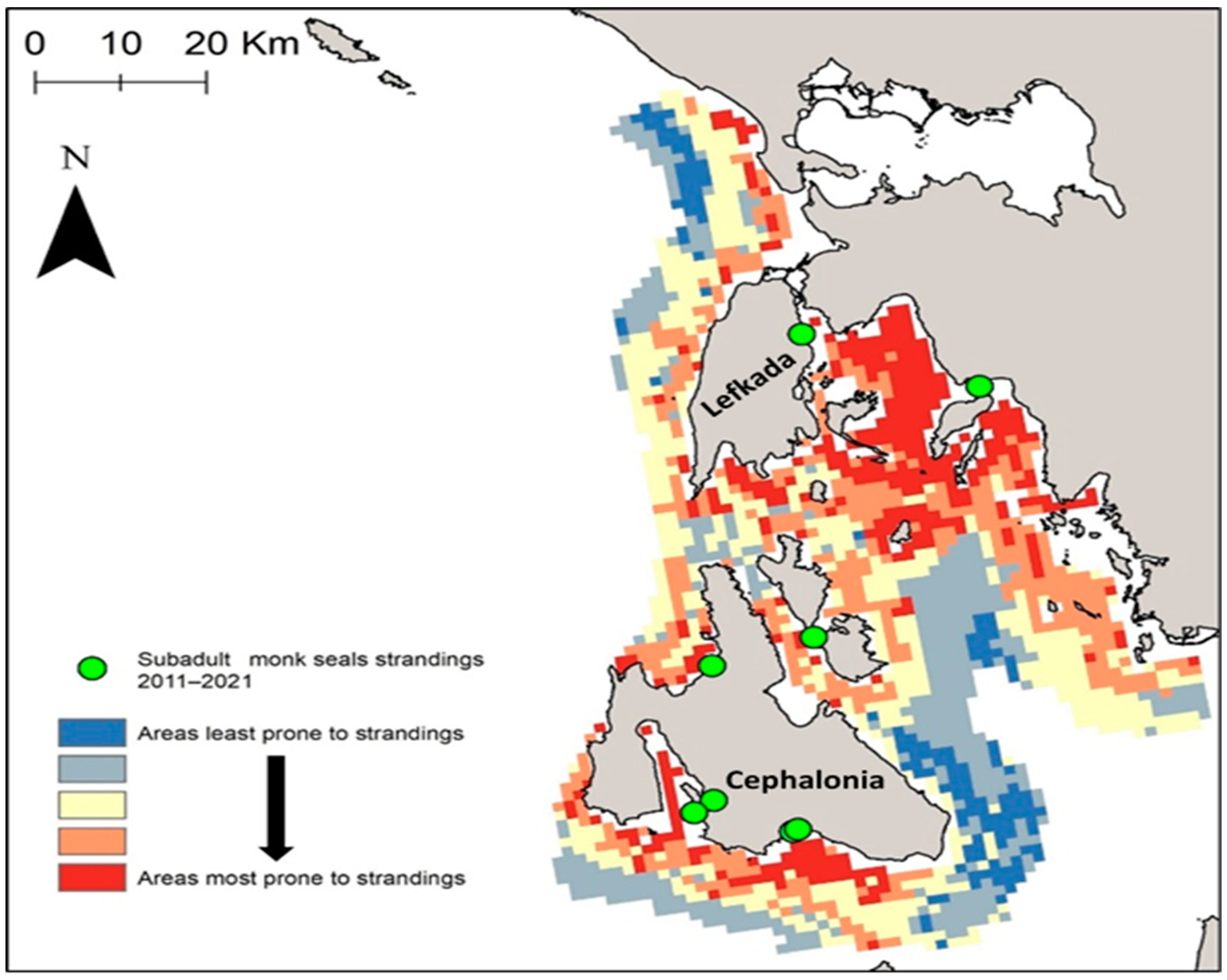
2.5. Identifying Areas with High Susceptibility to Subadult Strandings at Small-Scale Basis: Focusing on the Central Part of the Ionian Sea
3. Results
3.1. Data Mining: Cause of Death
3.2. Temporal Trends in Stranding Events Related to Environmental Variability
3.3. Spatial Analysis: Identifying Hotspot Stranding Areas
3.4. Identifying Factors Related to the Spatial Pattern of Monk Seal Strandings
3.5. Identifying Important Areas at Small-Scale Basis: Focusing on the Ionian Sea
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karamanlidis, A.A.; Dendrinos, P.; Fernandez de Larrinoa, P.; Kıraç, C.O.; Nicolaou, H.; Pires, R. Monachus Monachus. In The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2023; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2023; p. E.T13653A238637039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamanlidis, A.A.; Dendrinos, P.; de Larrinoa, P.F.; Gücü, A.C.; Johnson, W.M.; Kiraç, C.O.; Pires, R. The Mediterranean Monk Seal Monachus Monachus: Status, Biology, Threats, and Conservation Priorities. Mammal Rev. 2016, 46, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsakis, J. Etat de la Population du Phoque Moine; Université d’Athènes: Athens, Greece, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Panou, A.; Jacobs, J.; Panos, D. The Endangered Mediterranean Monk Seal Monachus Monachus in the Ionian Sea, Greece. Biol. Conserv. 1993, 64, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archipelagos. Technical-Economical Investigation of the Effects of the Mediterranean Monk Seal on Coastal Fisheries on the Western Coasts of Zakynthos Island. Final Report, Sub-Project WWF Greece, EU Programme LIFE96NAT/GR/3225, Contract B4-3200/96/500 “The Mediterranean Monk Seal in Greece: Conservation in Action”, Co-Ordinated by the Hellenic Society for the Study and Protection of the Monk Seal HSSPMS-MOm); Archipelagos—Environment and Development: Argostoli, Greece, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Karamanlidis, A.A.; Jeff Curtis, P.; Hirons, A.C.; Psaradellis, M.; Dendrinos, P.; Hopkins III, J.B. Isotopes in Environmental and Health Studies Stable Isotopes Confirm a Coastal Diet for Critically Endangered Mediterranean Monk Seals Stable Isotopes Confirm a Coastal Diet for Critically Endangered Mediterranean Monk Seals. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2014, 50, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dendrinos, P.; Karamanlidis, A.A.; Androukaki, E.; McConnell, B.J. Diving Development and Behavior of a Rehabilitated Mediterranean Monk Seal (Monachus Monachus). Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2007, 23, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamantopoulou, S.; Androukaki, E.; Dendrinos, P.; Kotomatas, S.; Paravas, V.; Psaradellis, M.; Tounta, E.; Karamanlidis, A.A. Movements of Mediterranean Monk Seals (Monachus Monachus) in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Aquat. Mamm. 2011, 37, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dendrinos, P.; Adamantopoulou, S.; Koemtzopoulos, K.; Mpatzios, P.; Paxinos, O.; Tounta, E.; Tsiakalos, D.; Karamanlidis, A.A. Anecdotal Observations of Open Beach Use by Female Mediterranean Monk Seals (Monachus Monachus) and Their Pups in Greece: Implications for Conservation. Aquat. Mamm. 2022, 48, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeney, R.H.; Amies, R.; Broderick, A.C.; Witt, M.J.; Loveridge, J.; Doyle, J.; Godley, B.J.; Leeney, R.H.; Amies, R.; Broderick, A.C.; et al. Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Cetacean Strandings and Bycatch in a UK Fisheries Hotspot. Biodivers. Conserv. 2008, 17, 2323–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltier, H.; Baagøe, H.J.; Camphuysen, K.C.J.; Czeck, R.; Dabin, W.; Daniel, P.; Deaville, R.; Haelters, J.; Jauniaux, T.; Jensen, L.F.; et al. The Stranding Anomaly as Population Indicator: The Case of Harbour Porpoise Phocoena Phocoena in North-Western Europe. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panou, A.; Giannoulaki, M.; Varda, D.; Lazaj, L.; Pojana, G.; Bundone, L. Towards a Strategy for the Recovering of the Mediterranean Monk Seal in the Adriatic-Ionian Basin. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1034124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harwood, J.; Anderson, S.S.; Prime, J.H. Special Measures for the Conservation of Monk Seals in the European Community; Commission of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Belton, V.; Stewart, T.J. Multiple Criteria Decision Analysis; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tercan, E.; Tapkın, S.; Latinopoulos, D.; Dereli, M.A.; Tsiropoulos, A.; Ak, M.F. A GIS-Based Multi-Criteria Model for Offshore Wind Energy Power Plants Site Selection in Both Sides of the Aegean Sea. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullick, M.R.A.; Tanim, A.H.; Islam, S.M.S. Coastal Vulnerability Analysis of Bangladesh Coast Using Fuzzy Logic Based Geospatial Techniques. Ocean Coast Manag. 2019, 174, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavadas, S.; Maina, I.; Damalas, D.; Dokos, I.; Pantazi, M.; Vassilopoulou, V. Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2015, 16, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESRI. ArcGIS Desktop: Release 10.4; Environmental Systems Research Institute: Redlands, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Solow, A.R. Detecting Change in the Composition of a Multispecies Community. Biometrics 1994, 50, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuur, A.F. Analysing Biological and Environmental Field Data; Highland Statistics Ltd.: Aberdeen, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, K.F.; Frid, C.L.J. Coincident Changes in Four Components of the North Sea Ecosystem. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 1999, 79, 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Guzmán, J.A.; Dimitrakopoulos, R. Computational Properties of Min/Max Autocorrelation Factors. Comput. Geosci. 2003, 29, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erzini, K.; Inejih, C.A.O.; Stobberup, K.A. An Application of Two Techniques for the Analysis of Short, Multivariate Non-Stationary Time-Series of Mauritanian Trawl Survey Data. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2005, 62, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, B.W. Density Estimation for Statistics and Data Analysis; Chapman & Hall: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Despoti, S.; Stergiou, K.I.; Vassilopoulou, V.; Machias, A.; Kallianiotis, A.; Valavanis, V.D.; Giannoulaki, M. Suitability Maps to Show Potential Areas of High Concentrations of Unwanted Catch. Can They Be a New Tool to Aid Fisheries Management? In Proceedings of the ICES Annual Science Conference 2016, Riga, Latvia, 19–23 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Despoti, S.; Ligas, A.; Sbrana, M.; Tserpes, G.; Tsagkarakis, K.; Pyrounaki, M.-M.; Papadopoulou, N.; Machias, A.; Stergiou, K.I.; Giannoulaki, M. Where Is the Discarded Catch of Species with Minimum Conservation Reference Size? In Proceedings of the 12th Panhellenic Symposium of Oceanography & Fisheries, Kerkyra, Greece, 30 May–3 June 2018; p. 117. [Google Scholar]
- Dendrinos, P.; Karamanlidis, A.A.; Adamantopoulou, S.; Koemtzopoulos, K.; Komninou, A.; Tounta, E. LIFE-IP 4 NATURA: Integrated Actions for the Conservation and Management of Natura 2000 Sites, Species, Habitats and Ecosystems in Greece; Deliverable Action A.1: Action Plan for the Mediterranean Monk Seal (Monachus Monachus); Ministry of Environment and Energy: Athens, Greece, 2020.
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Exploring the Nature of Covariate Effects in the Proportional Hazards Model. Biometrics 1990, 46, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S. Generalized Additive Models: An Introduction with R, 2nd ed.; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 7 January 2024).
- Marra, G.; Wood, S.N. Practical Variable Selection for Generalized Additive Models. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2011, 55, 2372–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDaniels, T.L. Using Judgment in Resource Management: A Multiple Objective Analysis of a Fisheries Management Decision. Oper Res 1995, 43, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malczewski, J. GIS and Multicriteria Decision Analysis; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, T.L. Analytic Hierarchy Process Planning, Priority Setting, Resource Allocation. In Advanced Optimization and Decision-Making Techniques in Textile Manufacturing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1980; 287p. [Google Scholar]
- Boroushaki, S.; Malczewski, J. Implementing an Extension of the Analytical Hierarchy Process Using Ordered Weighted Averaging Operators with Fuzzy Quantifiers in ArcGIS. Comput. Geosci. 2008, 34, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ye, G.; Zeng, J.; Hu, W. Siting MPAs for Multiple Protecting Purposes by Co-Consideration of Ecological Importance and Anthropogenic Impacts. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 337, 117718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamanlidis, A.A.; Androukaki, E.; Adamantopoulou, S.; Chatzispyrou, A.; Johnson, W.M.; Kotomatas, S.; Papadopoulos, A.; Paravas, V.; Paximadis, G.; Pires, R.; et al. Assessing Accidental Entanglement as a Threat to the Mediterranean Monk Seal Monachus Monachus. Endanger. Species Res. 2008, 5, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossi, M.C.; Pedà, C.; Compa, M.; Tsangaris, C.; Alomar, C.; Claro, F.; Ioakeimidis, C.; Galgani, F.; Hema, T.; Deudero, S.; et al. Bioindicators for Monitoring Marine Litter Ingestion and Its Impacts on Mediterranean Biodiversity. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 1023–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Song, B.; Liang, J.; Niu, Q.; Zeng, G.; Shen, M.; Deng, J.; Luo, Y.; Wen, X.; Zhang, Y. Microplastics and Associated Contaminants in the Aquatic Environment: A Review on Their Ecotoxicological Effects, Trophic Transfer, and Potential Impacts to Human Health. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Milian, G.; Tsangaris, C.; Anestis, A.; Fossi, M.C.; Baini, M.; Caliani, I.; Panti, C.; Bundone, L.; Panou, A. Monk Seal Faeces as a Non-Invasive Technique to Monitor the Incidence of Ingested Microplastics and Potential Presence of Plastic Additives. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 193, 115227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trillmich, F.; Ono, K.A. (Eds.) Pinnipeds and El Niño; Ecological Studies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1991; Volume 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmona, J.; Dayon, J.; Lecompte, E.; Karamanlidis, A.A.; Aguilar, A.; Fernandez De Larrinoa, P.; Pires, R.; Mo, G.; Panou, A.; Agnesi, S.; et al. The Antique Genetic Plight of the Mediterranean Monk Seal (Monachus Monachus). Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2022, 289, 20220846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronis, T.; Raitsos, D.E.; Kassis, D.; Sarantopoulos, A. The Summer North Atlantic Oscillation Influence on the Eastern Mediterranean. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 5584–5596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelis, G.A.; Baker, J.D.; Polovina, J.J. Improved Body Condition of Weaned Hawaiian Monk Seal Pups Associated with El Niño Events: Potential Benefits to an Endangered Species. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2003, 19, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katara, I.; Pierce, G.J.; Illian, J.; Scott, B.E. Environmental Drivers of the Anchovy/Sardine Complex in the Eastern Mediterranean. Hydrobiologia 2011, 670, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albouy, C.; Delattre, V.; Donati, G.; Frölicher, T.L.; Albouy-Boyer, S.; Rufino, M.; Pellissier, L.; Mouillot, D.; Leprieur, F. Global Vulnerability of Marine Mammals to Global Warming. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poloczanska, E.S.; Burrows, M.T.; Brown, C.J.; Molinos, J.G.; Halpern, B.S.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Kappel, C.V.; Moore, P.J.; Richardson, A.J.; Schoeman, D.S.; et al. Responses of Marine Organisms to Climate Change across Oceans. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, M.P.; Ragen, T.J. Body Size, Survival, and Decline of Juvenile Hawaiian Monk Seals, Monachus Schauinslandi. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 1999, 15, 786–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.D.; Polovina, J.J.; Howell, E.A. Effect of Variable Oceanic Productivity on the Survival of an Upper Trophic Predator, the Hawaiian Monk Seal Monachus Schauinslandi. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 346, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrish, F.A.; Marshall, G.J.; Buhleier, B.; Antonelis, G.A. Foraging Interaction between Monk Seals and Large Predatory Fish in the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands. Endanger. Species Res. 2008, 4, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltier, H.; Authier, M.; Dabin, W.; Dars, C.; Demaret, F.; Doremus, G.; Van Canneyt, O.; Laran, S.; Mendez-Fernandez, P.; Spitz, J.; et al. Can Modelling the Drift of Bycaught Dolphin Stranded Carcasses Help Identify Involved Fisheries? An Exploratory Study. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 21, e00843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltier, H.; Authier, M.; Caurant, F.; Dabin, W.; Daniel, P.; Dars, C.; Demaret, F.; Meheust, E.; Van Canneyt, O.; Spitz, J.; et al. In the Wrong Place at the Wrong Time: Identifying Spatiotemporal Co-Occurrence of Bycaught Common Dolphins and Fisheries in the Bay of Biscay (NE Atlantic) From 2010 to 2019. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 617342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Factor | Correlation | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Feeding grounds | Negative (−) | 21.13% |
| (Distance from) breeding and disturbed caves | Negative (−) | 21.13% |
| (Distance from) aquaculture | Negative (−) | 4.94% |
| (Distance from) NATURA 2000 sites | Positive (+) | 4.94% |
| SSF fishing grounds | Positive (+) | 47.9% |
| Cause of Death | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|
| Gunshot | 20.9 |
| Internal bleeding (Dynamite) | 7.2 |
| Net or fish hook entanglement | 25.4 |
| Serious one or multiple wounds (head, abdominal, pelvic, tail) | 46.5 |
| Feeding Grounds | (Distance From) Breeding and Disturbed Caves | (Distance From) Aquaculture | (Distance From) NATURA 2000Sites | SSF Fishing Grounds | Weight | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feeding grounds | 1 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 1/3 | 21.1% |
| (Distance from) breeding and disturbed caves | 1 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 1/3 | 21.1% |
| (Distance from) aquaculture | 1/5 | 1/5 | 1 | 1 | 1/7 | 4.9% |
| (Distance from) NATURA 2000 sites | 1/5 | 1/5 | 1 | 1 | 1/7 | 4.9% |
| SSF fishing grounds | 3 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 1 | 47.9% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Solanou, M.; Panou, A.; Maina, I.; Kavadas, S.; Giannoulaki, M. Ten Years of Mediterranean Monk Seal Stranding Records in Greece under the Microscope: What Do the Data Suggest? Animals 2024, 14, 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14091309
Solanou M, Panou A, Maina I, Kavadas S, Giannoulaki M. Ten Years of Mediterranean Monk Seal Stranding Records in Greece under the Microscope: What Do the Data Suggest? Animals. 2024; 14(9):1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14091309
Chicago/Turabian StyleSolanou, Maria, Aliki Panou, Irida Maina, Stefanos Kavadas, and Marianna Giannoulaki. 2024. "Ten Years of Mediterranean Monk Seal Stranding Records in Greece under the Microscope: What Do the Data Suggest?" Animals 14, no. 9: 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14091309
APA StyleSolanou, M., Panou, A., Maina, I., Kavadas, S., & Giannoulaki, M. (2024). Ten Years of Mediterranean Monk Seal Stranding Records in Greece under the Microscope: What Do the Data Suggest? Animals, 14(9), 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14091309





