Comparison of the Anesthetic Effects of Alfaxalone Combined with Xylazine or Dexmedetomidine in Captive Formosa Serows (Capricornis swinhoei)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
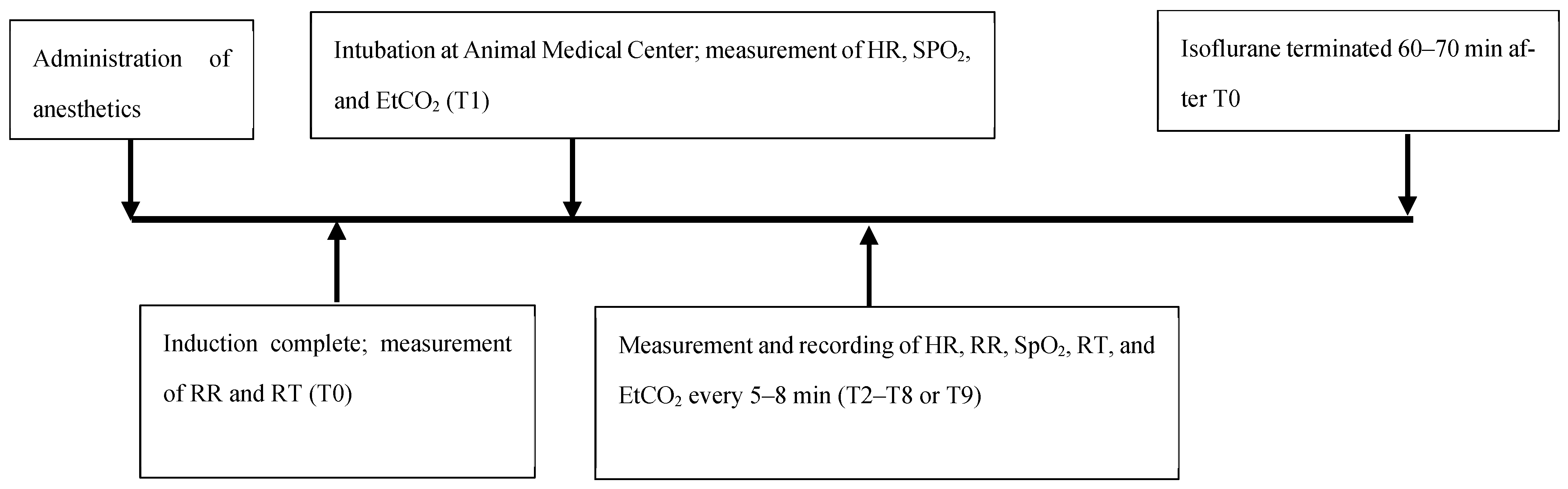
2.2. Anesthesia
2.3. Assessment of Physiological Parameters and Recovery
2.4. Statistical Analysis
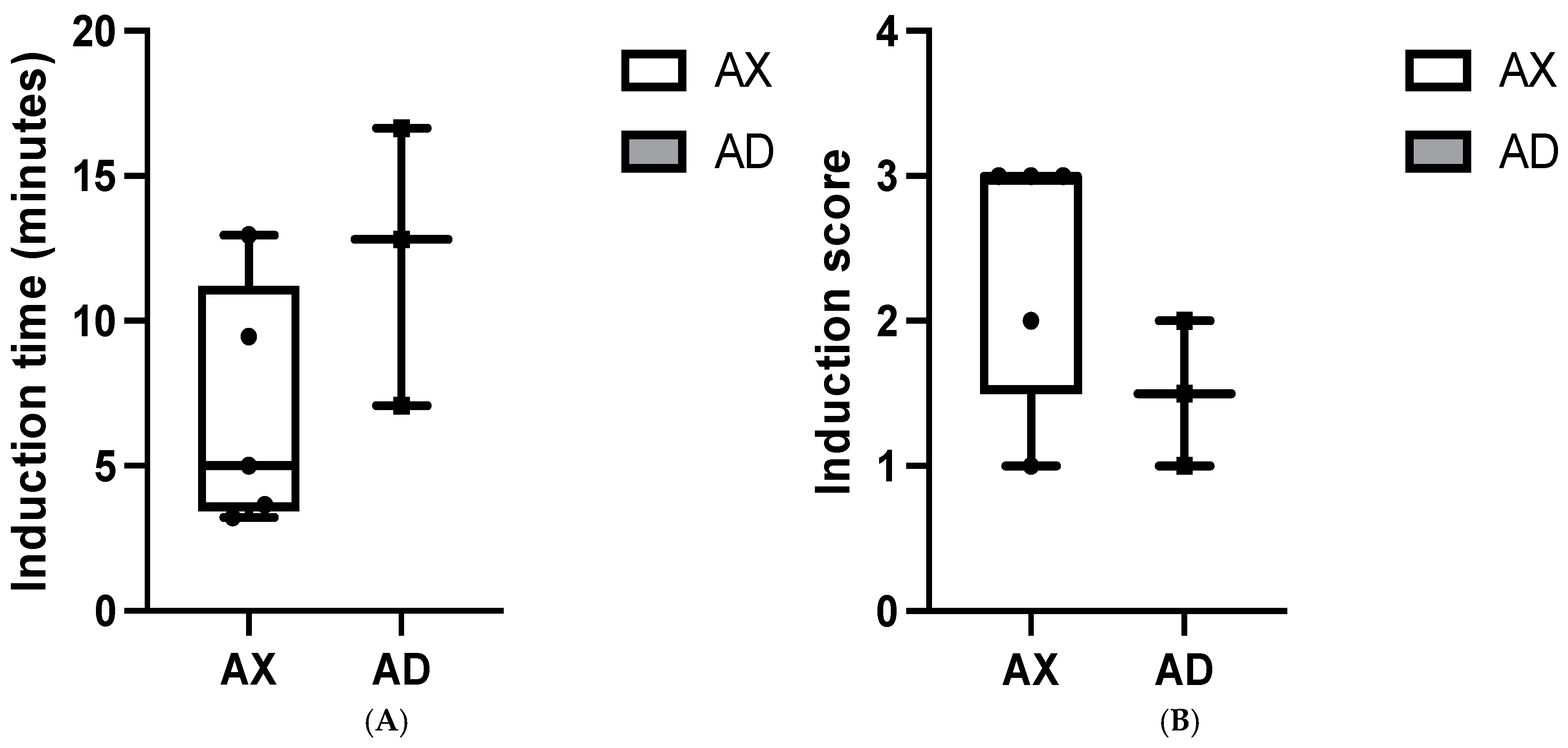
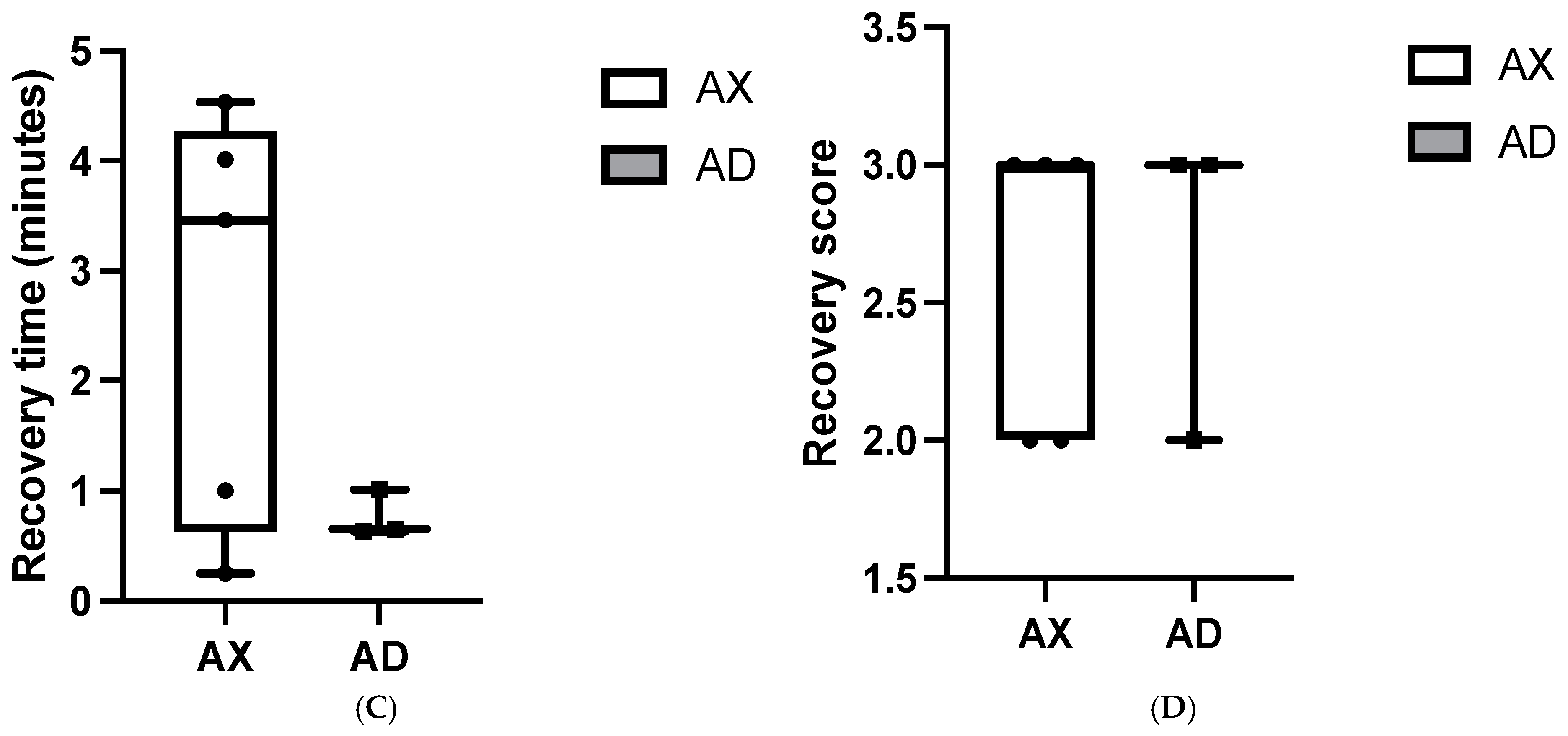
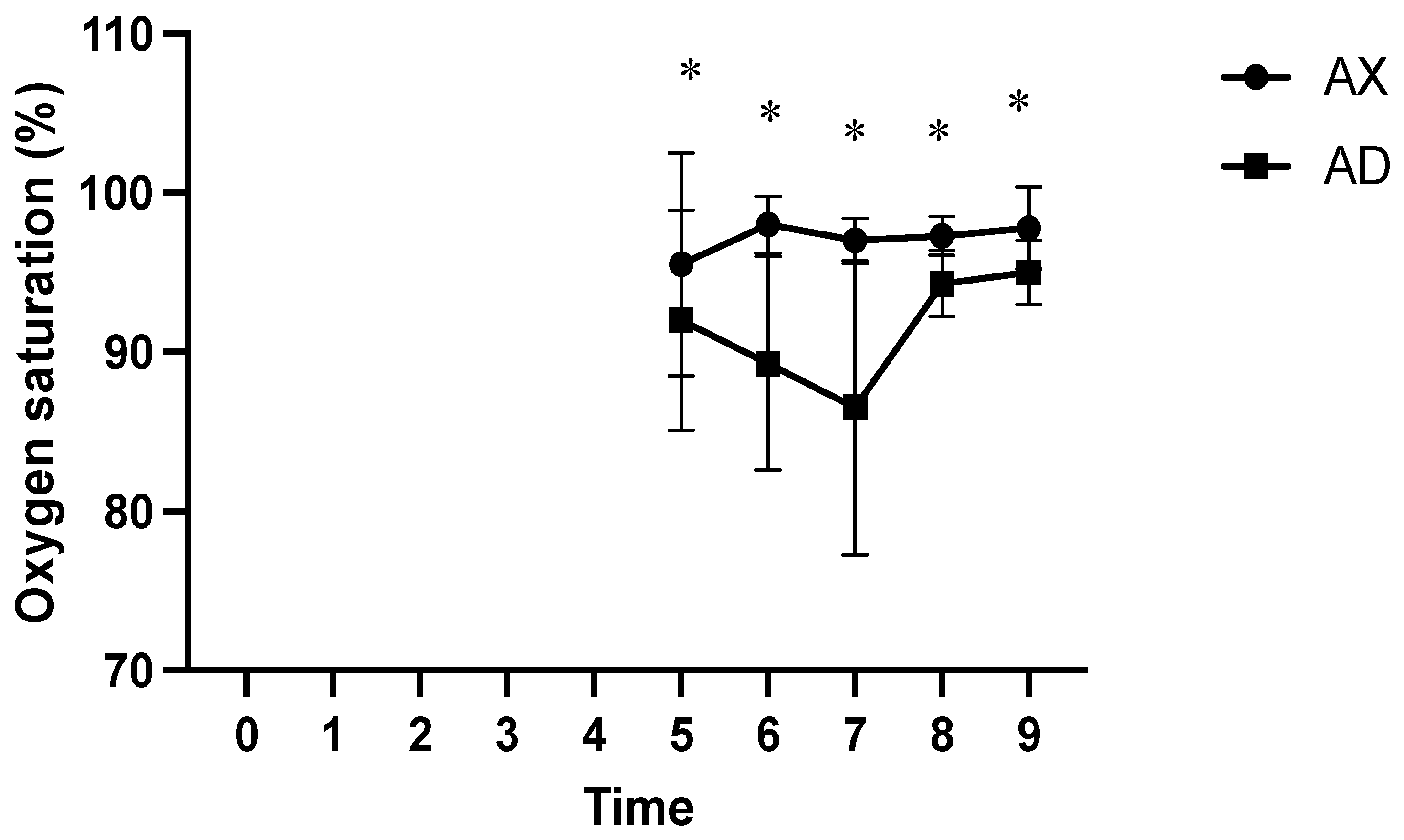
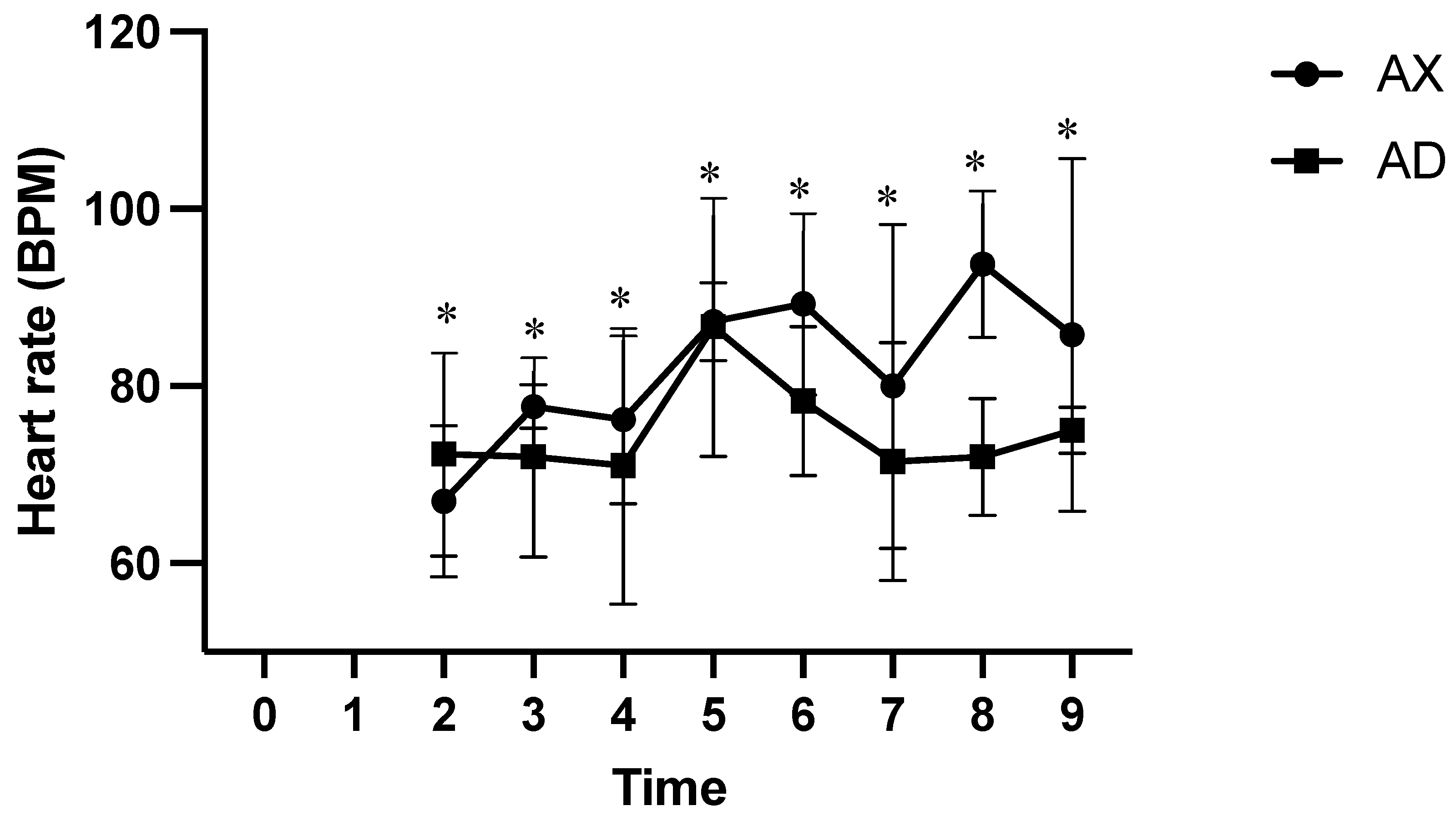
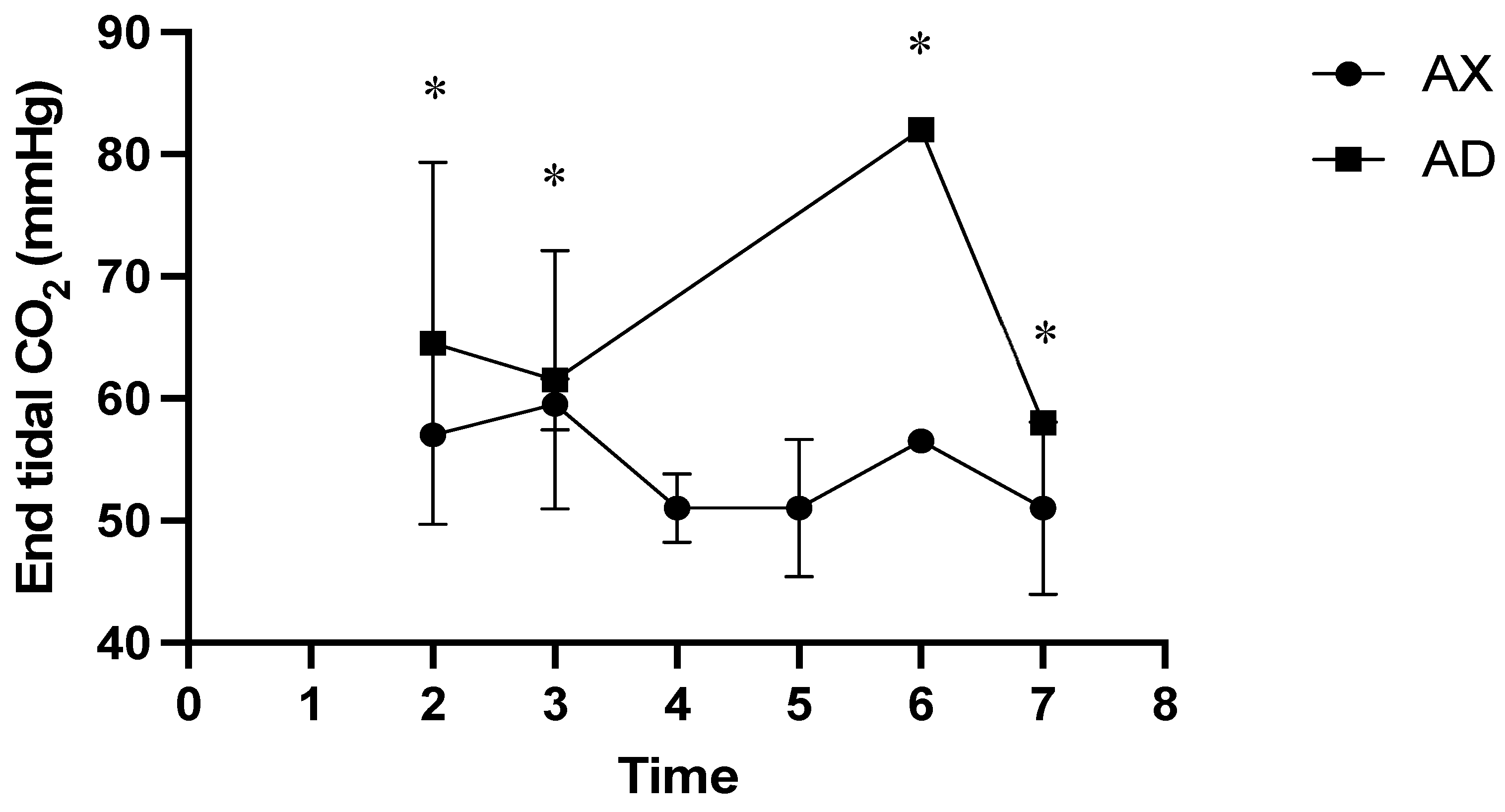
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HR | Heart rate |
| RR | Respiratory rate |
| EtCO2 | End-tidal CO2 |
| SpO2 | Peripheral saturation of oxygenation |
| RT | Rectal temperature |
| AX | Alfaxalone–xylazine |
| AD | Alfaxalone–dexmedetomidine |
References
- Lue, K.Y. A preliminary study on the ecology of Formosan serow Capricornis crispus swinhoei. In The Biology and Management of Capricornis and Related Mountain Antelopes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1987; pp. 125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Moberg, G.P. Biological response to stress: Implications for animal welfare. In The Biology of Animal Stress: Basic Principles and Implications for Animal Welfare; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2000; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ferré, P.J.; Pasloske, K.; Whittem, T.; Ranasinghe, M.G.; Li, Q.; Lefebvre, H.P. Plasma pharmacokinetics of alfaxalone in dogs after an intravenous bolus of Alfaxan-CD RTU. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2006, 33, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, L.W. Althesin in the larger animal. Postgrad. Med. J. 1972, 48 (Suppl. S2), 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Cottrell, G.A.; Lambert, J.J.; Peters, J.A. Modulation of GABAA receptor activity by alphaxalone. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1987, 90, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzikiti, B.T.; Ndawana, P.S.; Zeiler, G.; Ferreira, J.P.; Dzikiti, L.N. Determination of the minimum infusion rate of alfaxalone during its co-administration with fentanyl at three different doses by constant rate infusion intravenously in goats. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2016, 43, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzikiti, T.; Ndawana, P.; Zeiler, G.; Bester, L.; Dzikiti, L. Determination of the minimum infusion rate of alfaxalone during its co-administration with midazolam in goats. Vet. Rec. Open 2015, 2, e000065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzikiti, T.B.; Zeiler, G.E.; Dzikiti, L.N.; Garcia, E.R. The effects of midazolam and butorphanol, administered alone or combined, on the dose and quality of anaesthetic induction with alfaxalone in goats. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2014, 85, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremer, J.; Riccó, C.H. Cardiovascular, respiratory and sedative effects of intramuscular alfaxalone, butorphanol and dexmedetomidine compared with ketamine, butorphanol and dexmedetomidine in healthy cats. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2018, 20, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granfone, M.C.; Walker, J.M.; Smith, L.J. Evaluation of an intramuscular butorphanol and alfaxalone protocol for feline blood donation: A pilot study. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2018, 20, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankin, D.C. Sedatives and tranquilizers. Vet. Anesth. Analg. Fifth Ed. Lumb Jones 2015, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kästner, S.B. A2-agonists in sheep: A review. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2006, 33, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celly, C.S.; Atwal, O.S.; McDonell, W.N.; Black, W.D. Histopathologic alterations induced in the lungs of sheep by use of α2-adrenergic receptor agonists. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1999, 60, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, L.T.; Auckburally, A.; Santilli, J.; Vieira, B.H.; Garcia, D.O.; Honsho, C.S.; de Mattos-Junior, E. Effects of dexmedetomidine combined with commonly administered opioids on clinical variables in dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2018, 79, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grubb, T.; Sager, J.; Gaynor, J.S.; Montgomery, E.; Parker, J.A.; Shafford, H.; Tearney, C. 2020 AAHA anesthesia and monitoring guidelines for dogs and cats. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2020, 56, 59–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardinge, M.; Annandale, J.; Bourne, S.; Cooper, B.; Evans, A.; Freeman, D.; Green, A.; Hippolyte, S.; Knowles, V.; MacNee, W. British Thoracic Society guidelines for home oxygen use in adults: Accredited by NICE. Thorax 2015, 70 (Suppl. S1), i1–i43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, M.; de Lis, B.T.B.; Tendillo, F.J. Effects of intramuscular dexmedetomidine in combination with ketamine or alfaxalone in swine. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2016, 43, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattet, M.R.; Bourque, A.; Elkin, B.T.; Powley, K.D.; Dahlstrom, D.B.; Caulkett, N.A. Evaluation of the potential for injury with remote drug-delivery systems. Wildl. Soc. Bull. 2006, 34, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Suh, S.; Choi, R.; Hyun, C. Cardiorespiratory and anesthetic effects produced by the combination of butorphanol, medetomidine and alfaxalone administered intramuscularly in Beagle dogs. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2015, 77, 1677–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, J.; Ishizuka, T.; Fukui, S.; Oyama, N.; Kawase, K.; Itami, T.; Miyoshi, K.; Sano, T.; Pasloske, K.; Yamashita, K. Sedative effects of intramuscular alfaxalone administered to cats. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2015, 77, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, J.; Ishizuka, T.; Fukui, S.; Oyama, N.; Kawase, K.; Miyoshi, K.; Sano, T.; Pasloske, K.; Yamashita, K. The pharmacological effects of the anesthetic alfaxalone after intramuscular administration to dogs. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2015, 77, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.-F.; Lien, C.-Y.; Wang, L.-C. Comparison of xylazine–ketamine and dexmedetomidine–ketamine anesthesia in captive Formosan serows (Capriconis Swinhoei). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2014, 45, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.-J.; Weng, H.-Y.; Lien, C.-Y.; Chen, K.-S. Retrospective Comparison of the Anesthetic Effects of Tiletamine–Zolazepam with Dexmedetomidine and Ketamine with Dexmedetomidine in Captive Formosan Serow (Capricornis swinhoei). Animals 2024, 14, 1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muir, W.; Lerche, P.; Wiese, A.; Nelson, L.; Pasloske, K.; Whittem, T. The cardiorespiratory and anesthetic effects of clinical and supraclinical doses of alfaxalone in cats. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2009, 36, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiese, W.M.P.L.A.; Whittem, L.N.K.P.T. Cardiorespiratory and anesthetic effects of clinical and supraclinical doses of alfaxalone in dogs. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2008, 35, 451–462. [Google Scholar]
- Maney, J.K.; Shepard, M.K.; Braun, C.; Cremer, J.; Hofmeister, E.H. A comparison of cardiopulmonary and anesthetic effects of an induction dose of alfaxalone or propofol in dogs. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2013, 40, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurmon, J.C.; Ko, J.C.; Benson, G.J.; Tranquilli, W.J.; Olson, W.A. Hemodynamic and analgesic effects of propofol infusion in medetomidine-premedicated dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1994, 55, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouelfetouh, M.M.; Salah, E.; Ding, M.; Ding, Y. Application of α2-adrenergic agonists combined with anesthetics and their implication in pulmonary intravascular macrophages-insulted pulmonary edema and hypoxemia in ruminants. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 44, 478–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Short, C. Effects of anticholinergic treatment on the cardiac and respiratory systems in dogs sedated with medetomidine. Vet. Rec. 1991, 129, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okushima, S.; Vettorato, E.; Corletto, F. Chronotropic effect of propofol or alfaxalone following fentanyl administration in healthy dogs. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2015, 42, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maney, J.K. Sedative and physiologic effects of low-dose intramuscular alfaxalone in dogs. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2017, 44, 1184–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, E.; Scheinin, H.; Scheinin, M. Behavioural and neurochemical effects of medetomidine, a novel veterinary sedative. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1988, 158, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granholm, M.; McKusick, B.; Westerholm, F.; Aspegrén, J. Evaluation of the clinical efficacy and safety of intramuscular and intravenous doses of dexmedetomidine and medetomidine in dogs and their reversal with atipamezole. Vet. Rec. 2007, 160, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteith, K.L.; Monteith, K.B.; Delger, J.A.; Schmitz, L.E.; Brinkman, T.J.; Deperno, C.S.; Jenks, J.A. Immobilization of white-tailed deer with telazol, ketamine, and xylazine, and evaluation of antagonists. J. Wildl. Manag. 2012, 76, 1412–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caulkett, N.; Walzer, C. Wild sheep and goats. Zoo Anim. Wildl. Immobil. Anesth. 2014, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, M.; Caulkett, N.; Neuhaus, P.; Pasloske, K.; Ruckstuhl, K. The utility of a novel formulation of alfaxalone in a remote delivery system. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2021, 48, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, K.H.; Hull, R.; Morton, D.; Pfister, R.; Rabemampianina, Y.; Smith, D.; Vidal, J.M.; Vorstenbosch, C.V.D. A good practice guide to the administration of substances and removal of blood, including routes and volumes. J. Appl. Toxicol. Int. J. 2001, 21, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadola, F.; Costa, G.L.; Interlandi, C.; Musicò, M. Hyaluronidase, with xylazine and ketamine, reducing immobilization time in wild cattle (Bos taurus). Large Anim. Rev. 2019, 25, 159–161. [Google Scholar]



| Sex | Age (yrs) | Body Weight (kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| AX | F | 9 | 23.1 |
| F | 10 | 23.1 | |
| F | 6 | 16.3 | |
| MC | 11 | 23.4 | |
| MC | 15 | 21.8 | |
| AD | MC | 13 | 22.5 |
| F | 12 | 23.4 | |
| MC | 10 | 25.4 | |
| F | 14 | 23.1 |
| Score | Induction | Recovery |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | High excitement (vocalizes, jumps, or attempts to escape during physical restraint, unable to place the endotracheal tube) | Poor (several uncoordinated attempts to stand, ataxic) |
| 1 | Moderate excitement (some struggling, falling, or slipping after becoming recumbent; able to place the endotracheal tube) | Relatively Poor (several coordinated attempts to stand, ataxic) |
| 2 | Low excitement (some struggling, no falling or slipping; may or may not be intubated within 60 s) | Relatively calm (1–2 coordinated attempts to stand with minimal ataxia) |
| 3 | Excitement-free induction (no outward signs of excitement, tracheal intubation easy) | Excitement-free recovery (no outward signs of excitement, stood up smoothly and quickly) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, L.-J.; Ishihara, T.; Lien, C.-Y.; Chen, K.-S. Comparison of the Anesthetic Effects of Alfaxalone Combined with Xylazine or Dexmedetomidine in Captive Formosa Serows (Capricornis swinhoei). Animals 2025, 15, 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15030307
Chang L-J, Ishihara T, Lien C-Y, Chen K-S. Comparison of the Anesthetic Effects of Alfaxalone Combined with Xylazine or Dexmedetomidine in Captive Formosa Serows (Capricornis swinhoei). Animals. 2025; 15(3):307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15030307
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Li-Jen, Toshitsugu Ishihara, Chen-Yeh Lien, and Kuan-Sheng Chen. 2025. "Comparison of the Anesthetic Effects of Alfaxalone Combined with Xylazine or Dexmedetomidine in Captive Formosa Serows (Capricornis swinhoei)" Animals 15, no. 3: 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15030307
APA StyleChang, L.-J., Ishihara, T., Lien, C.-Y., & Chen, K.-S. (2025). Comparison of the Anesthetic Effects of Alfaxalone Combined with Xylazine or Dexmedetomidine in Captive Formosa Serows (Capricornis swinhoei). Animals, 15(3), 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15030307





