An Evaluation of the Genetic Structure of Geese Maintained in Poland on the Basis of Microsatellite Markers
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Animals and DNA Isolation
2.2. Microsatellite DNA Amplification
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Notter, D.R. The importance of genetic diversity in livestock populations of the future. J. Anim. Sci. 1999, 77, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, J.; Düttmann, H.; Wink, M. Phylogenetic relationships based on two mitochondrial genes and hybridization patterns in Anatidae. J. Zool. 2009, 279, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donne-Goussé, C.; Laudet, V.; Hänni, C. A molecular phylogeny of anseriformes based on mitochondrial DNA analysis. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2002, 23, 339–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badowski, J. 50 lat hodowli gęsi w Instytucie Zootechniki. Wiad. Zootech. 2006, 4, 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- Parada, R.; Książkiewicz, J.; Kawka, M.; Jaszczak, K. Studies on resources of genetic diversity in conservative flocks of geese using microsatellite DNA polymorphic markers. Mol. Boil. Rep. 2012, 39, 5291–5297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodzime rasy i odmiany gęsi. Available online: www.bioroznorodnosc.izoo.krakow.pl/drob/gesi (accessed on 21 March 2019).
- Andres, K.; Kapkowska, E. Applicability of anatid and galliform microsatellite markers to the genetic diversity studies of domestic geese (Anser anser domesticus) through the genotyping of the endangered zatorska breed. BMC Res. Notes 2011, 4, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiß, B.M.; Poggemann, K.; Olek, K.; Foerster, K.; Hirschenhauser, K. Isolation and characterization of microsatellite marker loci in the greylag goose (Anser anser). Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2008, 8, 1411–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cathey, J.C.; DeWoody, J.A.; Smith, L.M. Brief communication. Microsatellite markers in Canada geese (Branta canadensis). J. Hered. 1998, 89, 173–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.J.; Chen, K.W.; Zhang, S.J.; Tang, Q.P.; Gao, Y.S.; Yang, N. Genetic diversity of 14 indigenous grey goose breeds in China based on microsatellite markers. Asian-Aust. J. Anim. Sci. 2005, 19, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, R.L.; Scribner, K.T. Isolation and characterization of novel waterfowl microsatellite loci: Cross-species comparisons and research applications. Mol. Ecol. 1997, 6, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noreikiene, K.; Teacher, A.G.; Madsen, J.; Gienapp, P. Isolation and characterization of 55 novel microsatellite markers for the pink-footed goose (Anser brachyrhynchus). Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2012, 4, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Guo, J.; Chen, K.; Lu, H.; Su, J. Microsatellite DNA typing for assessment of genetic variability in Taihu goose: A major breed of China. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2009, 8, 2153–2157. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.F.; Chen, K.W.; Yang, N.; Song, W.T.; Tang, Q.P. Evaluation of genetic diversity of Chinese native geese revealed by microsatellite markers. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2007, 63, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, F.Y.; Tu, P.A.; Ding, S.T.; Lin, M.J.; Chang, S.C.; Lin, E.C.; Lo, L.L.; Wang, P.H. Survey of genetic structure of geese using novel microsatellite markers. Asian-Austr. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 31, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veillet, A.; Shrestha, R.; Price, D.K. Polymorphic microsatellites in nēnē, the endangered Hawaiian goose (Branta sandvicensis). Mol. Ecol. Res. 2008, 8, 1158–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mindek, S.; Mindeková, S.; Hrnčár, C.; Weis, J.; Gašparík, J. Genetic diversity and structure of Slovak domestic goose breeds. Vet. ir Zootech. 2014, 67, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Nei, M.; Takezaki, N. Estimation of genetic distances and phylogenetic trees from DNA analysis. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 1983, 21, 405–412. [Google Scholar]
- Simianer, H. Use of molecular markers and other information for sampling germplasm to create an animal gene bank. In The Role of Biotechnology in Exploring and Protecting Agricultural Genetic Resources; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2006; pp. 81–96. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.H.; Crittenden, L.B. Microsatellite markers for genetic mapping in the chicken. Poult. Sci. 1994, 73, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamara, D.; Gyenai, K.B.; Geng, T.; Hammade, H.; Smith, E.J. Microsatellite marker-based genetic analysis of relatedness between commercial and heritage turkeys (Meleagris gallopavo). Poult. Sci. 2007, 86, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botstein, D.; White, R.L.; Skolnick, M.; Davis, R.W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am. J. Hum. Gene. 1980, 32, 314. [Google Scholar]
- Earl, D.A. STRUCTURE HARVESTER: A website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv. Gene. Res. 2012, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, I.; Cucco, M.; Follestad, A.; Boos, M. Lack of genetic structure in greylag goose (Anser anser) populations along the European Atlantic flyway. Peer J. 2015, 3, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleven, O.; Kroglund, R.T.; Østnes, J.E. Isolation, characterization and multiplex PCR development of Bean Goose (Anser fabalis) microsatellite loci. J. Ornithol. 2016, 157, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, J.S.F. Animal breeding and conservation genetics. In Conservation Genetics; Loeschcke, V., Tomiuk, J., Jain, S.K., Eds.; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 1994; pp. 381–395. [Google Scholar]
- Książkiewicz, J. Rys historyczny tworzenia stad zachowawczych gesi znajdujacych sie w posiadaniu Instytutu Zootechniki-PIB. Wiadomości Zootech. 2007, 3, 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Książkiewicz, J. Rola i znaczenie rodzimych odmian gęsi objętych programem ochrony zasobów genetycznych. Wiadomości Zootech. 2006, 4, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Wrzaszcz, Ł. Ocena genetycznego zróżnicowania populacji gęsi na podstawie polimorfizmu DNA. Ph.D. Thesis, Uniwersytet Przyrodniczo—Humanistyczny w Siedlcach, Siedlce, Poland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Herbut, E. Puch od gęsi Białej Kołudzkiej. Wiadomości Zootech. 2018, 1, 178–183. [Google Scholar]
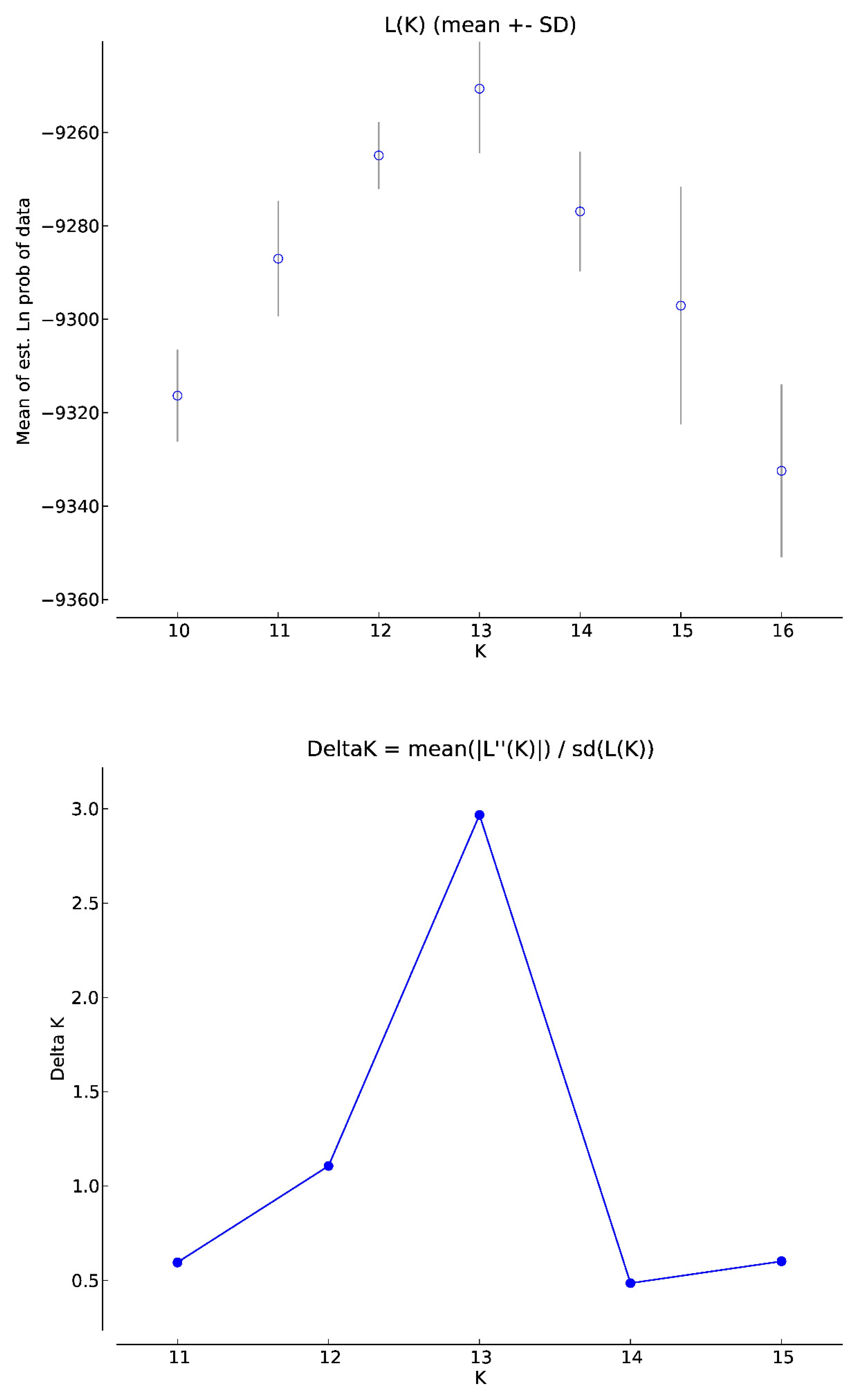
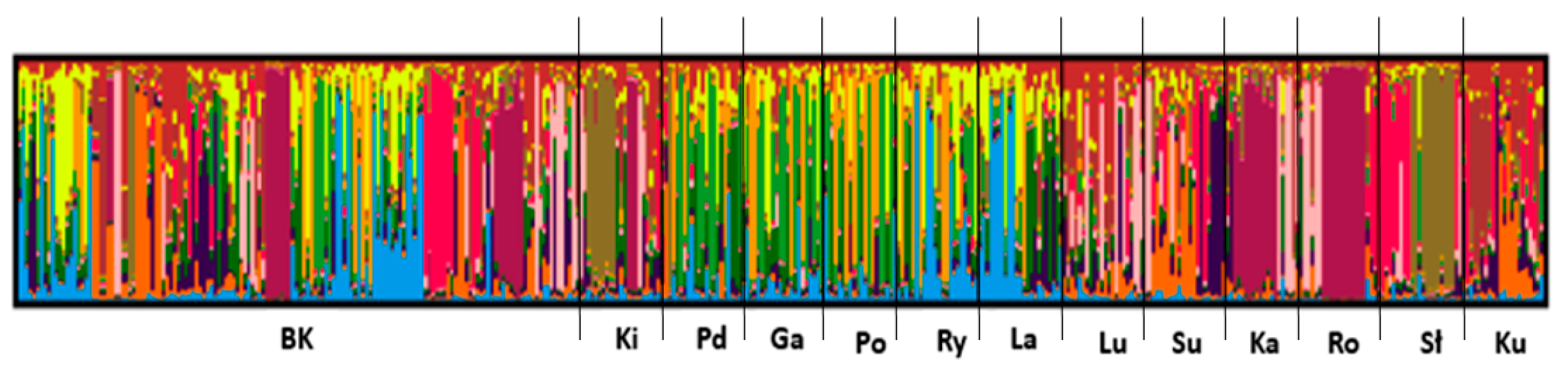



| Locus | GeneBank Accesion No. | Source Species | Repeat Motif of Sequenced Clone | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) | Temp. of Amplification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bca µ1 | AF025889 | Branta canadensis | (TA)15 (CA)10 | F: TGCTTTTTACCCCCAGTGTTCT R: AGAATCTGCTATATTATTTCCAGCTC | 61 |
| TTUCG5 | U66093 | Branta canadensis | TCTAT | F: GGGTGTTTTCCAACTCAG R: CACTTTCCTTACCTCATCTT | 61 |
| CKW21 | - | Anser cygnoides | (TTA)10 | F: CAAGGTAGTCATAAACCCAGAACA R: ACAAAACTAATGGCAGGAAAC | 62 |
| Bca µ9 | AF025897 | Branta canadensis | (CA)9 | F: CCCAGTTCCTCTCATTCTCCTT R: AAACAGGGAGGTGAAAGT | 61 |
| Bca µ8 | AF025896 | Branta canadensis | (CA)8 | F: CCCAAGACTCACAAAACCAGAAAT R: ATGAAAGAAGAGTTAAACGTGTGCAA | 58 |
| Ans02 | EU833383 | Anser anser | (AG)17 | F: TTCTGTGCAGGGGCGAGTT R: AGGGAACCGATCACGACATG | 58 |
| Ans18 | EU833373 | Anser anser | (AC)12 AT(AC)6 | F: GTGTTCTCTGTTTATGATATTAC R: AACAGAATTTGCTTGAAACTGC | 58 |
| Ans25 | EU833378 | Anser anser | (GT)18 | F: CACTTATTAATGGCACTTGAAA R: GTTCTCTTGTCACAACTGGA | 58 |
| CAUD-G013 | AY493258 | Anas platyrhynchos domesticus | (AC)9 | F: ACAATAGATTCCAGATGCTGAA R: ATGTCTGAGTCCTCGGAGC | 61 |
| CAUD-G007 | AY493252 | Anas platyrhynchos domesticus | (CAG)5 (GCA)5 | F: ACTTCTCTTGTAGGCATGTCA R: CACCTGTTGCTCCTGCTGT | 61 |
| Aal µ1 | U63689 | Anser albifrons | TG | F: CATGCGTGTTTAAGGGGTAT R: TAAGACTTGCGTGAGGAATA | 55 |
| Afa35 | KT698203 | Anser fabalis | (AGAC)10 (AGAA)7 | F: ACCCTGCCAGATCTCTTGTC R: GCCCATTTTTCTAAAGAAGATGCC | 60 |
| CAUD-G012 | AY493257 | Anas platyrhynchos domesticus | (AC)10 | F: ATTGCCTTTCAGTGGAGTTTC R: CGGCTCTAAACACATGAATG | 57 |
| CKW47 | AY790335 | Anser cygnoides | (T)8(TG)7 | F: AACTTCTGCACCTAAAAACTGTCA R:TGCTGAGGTAACAGGAATTAAAA | 62 |
| Ans07 | EU833363 | Anser anser | (CA)11 | F: GACTGAGGAACTACAATTGACT R: ACAAAGACTACTACTGCCAAG | 58 |
| Population | BK | Ki | Pd | Ga | Po | Ry | La | Lu | Su | Ka | Ro | Sł | Ku | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 152 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 20 | 22 | 23 | 22 | 22 | 20 | 21 | 23 | 22 | - |
| Na | 6929 | 4,857 | 3214 | 2714 | 2786 | 2714 | 2929 | 3714 | 4000 | 4714 | 5000 | 3929 | 3857 | 3951 |
| Ne | 2348 | 2446 | 1870 | 1805 | 1928 | 1800 | 1746 | 2147 | 2191 | 2822 | 3041 | 2420 | 2056 | 2202 |
| Ho | 0.362 | 0.308 | 0.334 | 0.328 | 0.329 | 0.295 | 0.280 | 0.396 | 0.409 | 0.479 | 0.415 | 0.401 | 0.354 | 0.361 |
| He | 0.490 | 0.479 | 0.384 | 0.365 | 0.369 | 0.340 | 0.305 | 0.423 | 0.479 | 0.620 | 0.638 | 0.478 | 0.442 | 0.447 |
| FST | 0.073 | 0.074 | 0.077 | 0.078 | 0.077 | 0.078 | 0.080 | 0.076 | 0.074 | 0.069 | 0.068 | 0.074 | 0.075 | 0.075 |
| Populations | Bca µ1 | TTUCG5 | CKW21 | Bca µ9 | Bca µ8 | Ans02 | Ans18 | Ans25 | CAUD-G013 | CAUD-G007 | Aal µ1 | Afa35 | CAUD-G012 | Ans07 | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fst | 0.077 | 0.095 | 0.068 | 0.106 | 0.117 | 0.140 | 0.300 | 0.084 | 0.089 | 0.151 | 0.061 | 0.156 | 0.139 | 0.127 | 0.122 |
| PIC | 0.381 | 0.813 | 0.686 | 0.447 | 0.561 | 0.299 | 0.331 | 0.633 | 0.444 | 0.165 | 0.551 | 0.191 | 0.546 | 0.433 | 0.463 |
| Ho | 0.366 | 0.721 | 0.620 | 0.358 | 0.400 | 0.235 | 0.045 | 0.600 | 0.430 | 0.122 | 0.519 | 0.119 | 0.437 | 0.075 | 0.361 |
| He | 0.386 | 0.754 | 0.664 | 0.446 | 0.557 | 0.283 | 0.252 | 0.623 | 0.506 | 0.138 | 0.560 | 0.017 | 0.507 | 0.415 | 0.447 |
| Population | Inferred Clusters | Number of Individuals | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | ||
| BK | 0.057 | 0.09 | 0.066 | 0.087 | 0.035 | 0.077 | 0.068 | 0.077 | 0.07 | 0.119 | 0.076 | 0.097 | 0.08 | 132 |
| Ki | 0.017 | 0.051 | 0.022 | 0.053 | 0.31 | 0.109 | 0.087 | 0.066 | 0.078 | 0.022 | 0.024 | 0.123 | 0.038 | 22 |
| Pd | 0.128 | 0.131 | 0.277 | 0.155 | 0.049 | 0.014 | 0.051 | 0.042 | 0.017 | 0.071 | 0.04 | 0.003 | 0.021 | 22 |
| Ga | 0.178 | 0.13 | 0.335 | 0.131 | 0.014 | 0.018 | 0.036 | 0.031 | 0.025 | 0.078 | 0.013 | 0.002 | 0.009 | 22 |
| Po | 0.259 | 0.112 | 0.317 | 0.127 | 0.008 | 0.01 | 0.016 | 0.039 | 0.01 | 0.078 | 0.011 | 0.002 | 0.01 | 20 |
| Ry | 0.212 | 0.17 | 0.097 | 0.159 | 0.027 | 0.008 | 0.022 | 0.031 | 0.015 | 0.222 | 0.022 | 0.002 | 0.013 | 22 |
| La | 0.059 | 0.178 | 0.056 | 0.181 | 0.051 | 0.015 | 0.034 | 0.089 | 0.033 | 0.278 | 0.012 | 0.003 | 0.011 | 23 |
| Lu | 0.017 | 0.043 | 0.023 | 0.044 | 0.025 | 0.264 | 0.279 | 0.077 | 0.118 | 0.022 | 0.046 | 0.003 | 0.039 | 22 |
| Su | 0.015 | 0.038 | 0.016 | 0.039 | 0.04 | 0.135 | 0.033 | 0.223 | 0.074 | 0.019 | 0.216 | 0.007 | 0.146 | 22 |
| Ka | 0.009 | 0.031 | 0.017 | 0.033 | 0.047 | 0.173 | 0.033 | 0.049 | 0.062 | 0.016 | 0.029 | 0.487 | 0.015 | 20 |
| Ro | 0.007 | 0.024 | 0.013 | 0.027 | 0.009 | 0.176 | 0.024 | 0.017 | 0.031 | 0.011 | 0.025 | 0.559 | 0.076 | 21 |
| Sł | 0.009 | 0.025 | 0.031 | 0.021 | 0.43 | 0.071 | 0.017 | 0.025 | 0.02 | 0.018 | 0.016 | 0.003 | 0.316 | 23 |
| Ku | 0.017 | 0.027 | 0.031 | 0.023 | 0.043 | 0.026 | 0.152 | 0.118 | 0.261 | 0.024 | 0.136 | 0.007 | 0.137 | 22 |
| BK | Ki | Pd | Ga | Po | Ry | La | Lu | Su | Ka | Ro | Sł | Ku | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BK | 0.000 | ||||||||||||
| Ki | 0.008 | 0.000 | |||||||||||
| Pd | 0.022 | 0.058 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| Ga | 0.019 | 0.055 | 0.009 | 0.000 | |||||||||
| Po | 0.026 | 0.067 | 0.019 | 0.005 | 0.000 | ||||||||
| Ry | 0.020 | 0.068 | 0.033 | 0.010 | 0.003 | 0.000 | |||||||
| La | 0.023 | 0.047 | 0.064 | 0.032 | 0.052 | 0.009 | 0.000 | ||||||
| Lu | 0.030 | 0.017 | 0.067 | 0.090 | 0.095 | 0.099 | 0.091 | 0.000 | |||||
| Su | 0.033 | 0.037 | 0.088 | 0.094 | 0.104 | 0.090 | 0.104 | 0.058 | 0.000 | ||||
| Ka | 0.106 | 0.098 | 0.155 | 0.161 | 0.166 | 0.190 | 0.204 | 0.152 | 0.130 | 0.000 | |||
| Ro | 0.163 | 0.148 | 0.208 | 0.220 | 0.208 | 0.233 | 0.261 | 0.208 | 0.183 | 0.051 | 0.000 | ||
| Sł | 0.036 | 0.019 | 0.088 | 0.088 | 0.109 | 0.099 | 0.083 | 0.049 | 0.043 | 0.120 | 0.187 | 0.000 | |
| Ku | 0.017 | 0.014 | 0.058 | 0.064 | 0.089 | 0.084 | 0.080 | 0.027 | 0.025 | 0.118 | 0.191 | 0.024 | 0.000 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Warzecha, J.; Oczkowicz, M.; Rubis, D.; Fornal, A.; Szmatoła, T.; Bugno-Poniewierska, M. An Evaluation of the Genetic Structure of Geese Maintained in Poland on the Basis of Microsatellite Markers. Animals 2019, 9, 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9100737
Warzecha J, Oczkowicz M, Rubis D, Fornal A, Szmatoła T, Bugno-Poniewierska M. An Evaluation of the Genetic Structure of Geese Maintained in Poland on the Basis of Microsatellite Markers. Animals. 2019; 9(10):737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9100737
Chicago/Turabian StyleWarzecha, Joanna, Maria Oczkowicz, Dominika Rubis, Agnieszka Fornal, Tomasz Szmatoła, and Monika Bugno-Poniewierska. 2019. "An Evaluation of the Genetic Structure of Geese Maintained in Poland on the Basis of Microsatellite Markers" Animals 9, no. 10: 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9100737
APA StyleWarzecha, J., Oczkowicz, M., Rubis, D., Fornal, A., Szmatoła, T., & Bugno-Poniewierska, M. (2019). An Evaluation of the Genetic Structure of Geese Maintained in Poland on the Basis of Microsatellite Markers. Animals, 9(10), 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9100737





