A Study of Genomic Prediction of 12 Important Traits in the Domesticated Yak (Bos grunniens)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Population Selection
2.2. Phenotype Data Acquisition and Processing
2.3. SNP Chip Genotyping and Quality Control
2.4. Method of Calculation of GP
2.5. Evaluation of Genetic Parameters in Yak Population
2.6. Assessment of Accuracy of Various Models
3. Results
3.1. Quality Control Results for Genotype Data
3.2. Basic Statistics of Phenotype Data
3.3. Estimation of Genetic Parameters
3.4. GP Results Using the Three Methods
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chu, M.; Wu, X.; Liang, C.; Pei, J.; Ding, X.; Guo, X.; Bao, P.J.; Yan, P. The complete sequence of mitochondrial genome of polled yak (Bos grunniens). Mitochondrial DNA 2014, 27, 2032–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wu, X.; Guo, X.; Bao, P.J.; Ding, X.; Chu, M.; Liang, C.; Yan, P. Comparative iTRAQ proteomics revealed proteins associated with horn development in yak. Proteome Sci. 2018, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, J.; Bao, P.J.; Chu, M.; Liang, C.; Ding, X.; Wang, H.; Wu, X.; Guo, X.; Yan, P. Evaluation of 17 microsatellite markers for parentage testing and individual identification of domestic yak (Bos grunniens). PeerJ 2018, 6, e5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heino, M. Stock Identification Methods, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Chapter 4; pp. 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Collado, D.; Byrne, T.; Díaz, C.; Amer, P.R. Complexity of animal breeding choice making. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2018, 135, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadar, M.; Vâtcă, A.; Corniou, I.; Rotaru, A.; Toader, I. Students Involved in Animal Breeding. Bull. UASVM Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 73, 341–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nayak, S.; Singh, V.K.; Varshney, R.K. Encyclopedia of Applied Plant Sciences. Encycl. Appl. Plant Sci. 2016, 2, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuwissen, T.H.E.; Hayes, B.J.B.; Goddard, M.E.M. Prediction of Total Genetic Value Using Genome-Wide Dense Marker Maps. Genetics 2001, 157, 1819–1829. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.; Mal, G.; Gautam, S.; Mukesh, M. Whole-Genome Selection in Livestock. Adv. Anim. Biotechnol. 2019, 134, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.; Taylor, K.; Decker, J. Holsteins are the genomic selection poster cows. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 201608144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoré, A.; Fontanesi, L. Genomic selection in pigs: State of the art and perspectives. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 15, 211–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L. Applications of genome selection in sheep breeding. Hereditas (Beijing) 2019, 41, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.F.; McKay, S.D.; Rolf, M.M.; Ramey, H.R.; Decker, J.E.; Schnabel, R.D. Bovine Genomics; Womack, J.E., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, E.; Fikse, F.; Rönnegård, L.; Mouresan, E.F. Genomic Selection. Popul. Genom. 2018, 186, 427–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaoming, M.; Jia, C.; Fu, D.; Chu, M.; Ding, X.; Wu, X.; Guo, X.; Pei, J.; Bao, P.J.; Liang, C.; et al. Analysis of Hematological Traits in Polled Yak by Genome-Wide Association Studies Using Individual SNPs and Haplotypes. Genes 2019, 10, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A. Breeding for Genetic Resistance to Diseases in Poultry and Farm Animals; CABI: Delémont, Switzerland, 2019; Available online: https://www.cabi.org/bookshop/book/9781845935559/ (accessed on 6 November 2019). [CrossRef]
- Littell, P.R.; Henry, C.B. Ammerman, Statistical analysis of repeated measures data using SAS procedures. J. Anim. Sci. 1998, 76, 1216–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, C.; Wang, H.; Li, C.; Wu, X.; Zan, L.; Ding, X.; Guo, X.; Bao, P.J.; Pei, J.; Chu, M.; et al. Genome-wide detection of copy number variations in polled yak using the Illumina BovineHD BeadChip. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slifer, S.H. PLINK: Key Functions for Data Analysis. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2018, 97, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanRaden, P.M. Efficient Methods to Compute Genomic Predictions. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 4414–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dworsky, L.N. Bayesian Statistics. In Probably Not; Dworsky, L.N., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: London, UK, 2019; pp. 199–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isik, F.; Holland, J.; Maltecca, C. Genetic Data Analysis for Plant and Animal Breeding; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 311–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinecen, M. Comparison of Genomic Best Linear Unbiased Prediction and Bayesian Regularization Neural Networks for Genomic Selection. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 79199–79210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Wang, Q.; Tian, F.; Su, Z.; Pan, Y.; Liu, D.; Lipka, A.E.; et al. GAPIT Version 2: An Enhanced Integrated Tool for Genomic Association and Prediction. Plant Genome 2016, 9, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessau, R.; Pipper, C. “R” project for statistical computing. Ugeskr. Laeger 2008, 170, 328–330. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Mao, S. Bayesian B-spline estimation of the generalized varying-coefficient models. J. Syst. Sci. Math. Sci. 2006, 26, 655–662. [Google Scholar]
- Alkema, L.; New, J.R. Global estimation of child mortality using a Bayesian B-spline Bias-reduction model. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2013, 8, 2122–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, P. Bayesian Methods. In Analysis of Incidence Rates; Taylor & Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chihara, L.M.; Hesterberg, T.C. Bayesian Methods. In Mathematical Statistics with Resampling and R; John Wiley & Sons: London, UK, 2019; pp. 5207–5215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal-Vasquez, A.-M.; Möhring, J.; Schmidt, M.; Schönleben, M.; Schön, C.-C.; Piepho, H.-P. The importance of phenotypic data analysis for genomic prediction—A case study comparing different spatial models in rye. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, B.; Martin, M.; Ben, B.; Steve, W. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, P.; de Los Campos, G. Genome-Wide Regression & Prediction with the BGLR Statistical Package. Genetics. 2014, 198, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-M.; Tamba, C.A. fast mrMLM algorithm for multi-locus genome-wide association studies. Biorxiv 2018, 175, 145–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdemir, D.; Isidro-Sánchez, J. Design of training populations for selective phenotyping in genomic prediction. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouresan, E.F.; Selle, M.; Rönnegård, L. Genomic Prediction Including SNP-Specific Variance Predictors. Genes Genomes Genet. 2019, 9, 3333–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höt, S. Probability Theory. In Information and Communication Theory; Höt, S., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: London, UK, 2019; pp. 5–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard, M.E.; Hayes, B.J. Mapping genes for complex traits in domestic animals and their use in breeding programmes. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habier, D.; Tetens, J.; Seefried, F.; Lichtner, P.; Thaller, G. The impact of genetic relationship on genomic breeding values in German Holstein cattle. Genet. Sel. Evol. GSE 2010, 42, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calus, M. Genomic breeding value prediction: Methods and procedures. Anim. Int. J. Anim. Biosci. 2010, 4, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Druet, T. Marker imputation with low-density marker panels in Dutch Holstein cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 5487–5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Habier, D.; Fernando, R.; Garrick, D.; Dekkers, J. Genomic breeding value prediction and QTL mapping of QTLMAS2010 data using Bayesian Methods. BMC Proc. 2011, 5, S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szydlowski, M.; Paczyńska, P. QTLMAS 2010: Simulated dataset. BMC Proc. 2011, 5, S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edriss, V.; Fernando, R.; Su, G.; Lund, M.; Guldbrandtsen, B. The effect of using genealogy-based haplotypes for genomic prediction. Genet. Sel. Evol. GSE 2013, 45, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, H. Preliminary Study on Genome Selection by Using Haplotype in Chinese Simmental. Chin. Acad. Agric. Sci. 2016, 147, 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, P. Comparison of selection efficiency in several genomicevaluating methods. Sichuan Agric. Univ. 2013, 156, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
| Description | Count |
|---|---|
| Original SNPs | 777,962 |
| Original Individuals | 354 |
| SNPs left after QC | 96,087 |
| Individuals after QC | 354 |
| Traits | Abbreviation | Values 1 | Counts 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Body length (cm) | BL | 101.613 ± 5.683± | 320 |
| Body weight (kg) | BW | 122.39 ± 12.397 | 259 |
| Chest girth (cm) | CG | 137.803 ± 8.784 | 315 |
| Withers height (cm) | WH | 101.765 ± 5.816 | 319 |
| Red blood cell count (1012/L) | RBC | 10.124 ± 1.083 | 308 |
| Hemoglobin (g/L) | HGB | 137.136 ± 16.794 | 310 |
| Hematocrit (%) | HCT | 0.430 ± 0.052 | 306 |
| Platelet count (109/L) | PLT | 326.193 ± 169.875 | 311 |
| Lymphocyte count (109/L) | LYM | 4.475 ± 1.5478 | 273 |
| Medium white blood cell count (109/L) | OTHR | 4.550 ± 1.426 | 267 |
| Platelet distribution width (%) | PDW | 8.776 ± 1.310 | 169 |
| Mean platelet volume (fl) | MPV | 7.146 ± 0.624 | 171 |
| Trait | F + E 1 | Phenotype 2 | Additive 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL | 21.002 | 33.141 | 12.140 | 0.366 |
| BW | 83.011 | 168.709 | 85.698 | 0.508 |
| WH | 15.434 | 37.590 | 22.156 | 0.589 |
| CG | 66.251 | 101.141 | 34.890 | 0.345 |
| RBC | 0.909 | 1.182 | 0.273 | 0.231 |
| HGB | 175.259 | 279.663 | 104.404 | 0.373 |
| HCT | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.444 |
| PLT | 15,282.669 | 28,121.015 | 12,838.346 | 0.457 |
| LYM | 1.147 | 2.140 | 0.993 | 0.464 |
| OTHR | 1.099 | 2.038 | 0.939 | 0.461 |
| PDW | 0.737 | 1.576 | 0.839 | 0.533 |
| MPV | 0.149 | 0.383 | 0.233 | 0.610 |
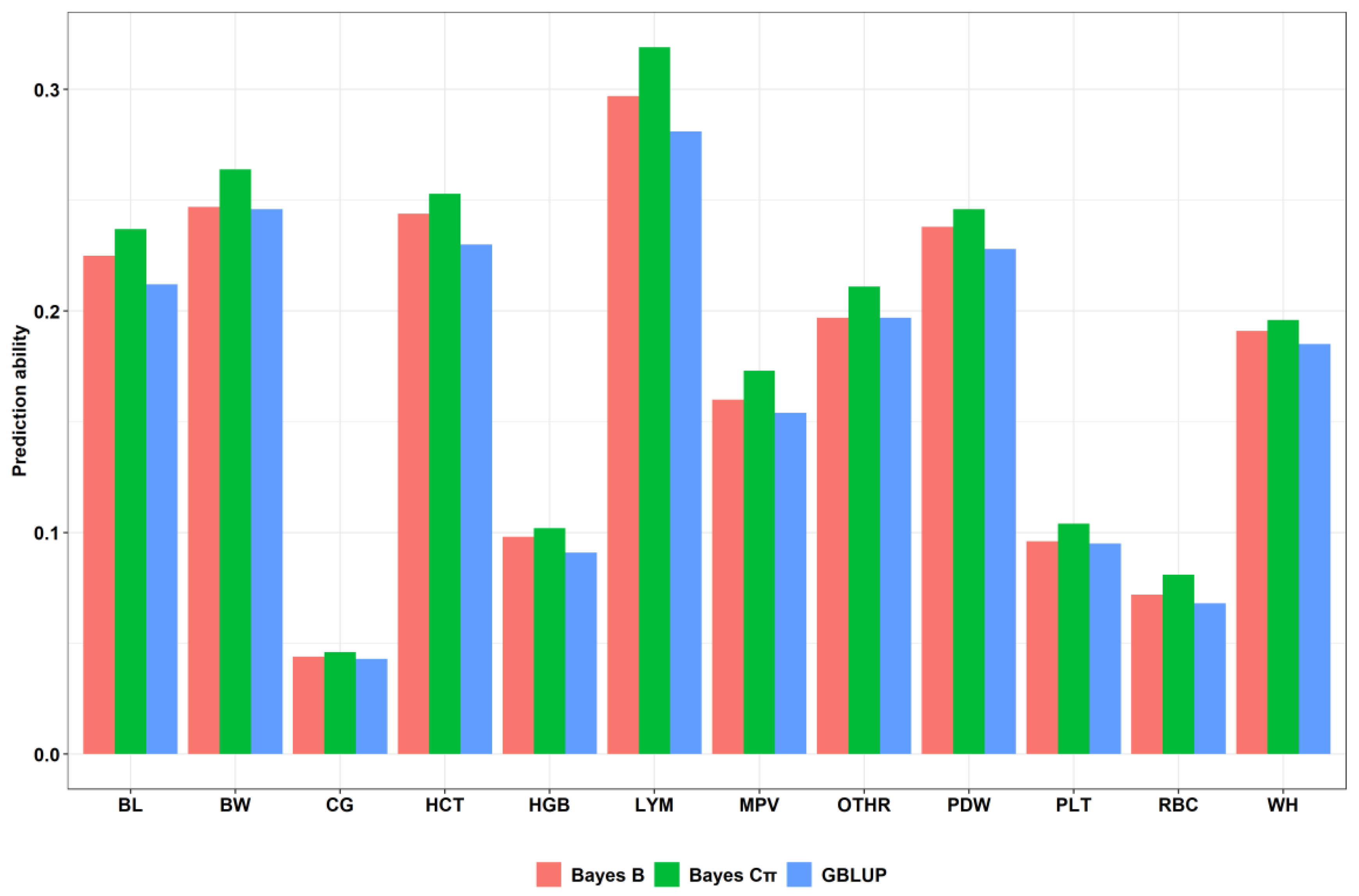
| Trait | Prediction Accuracy Using Individual SNPs | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| GBLUP 1 | Bayes B 2 | Bayes Cπ 3 | |
| BL | 0.212 | 0.225 | 0.237 |
| BW | 0.246 | 0.247 | 0.264 |
| WH | 0.185 | 0.191 | 0.196 |
| CG | 0.043 | 0.044 | 0.046 |
| RBC | 0.068 | 0.072 | 0.081 |
| HGB | 0.091 | 0.098 | 0.102 |
| HCT | 0.23 | 0.244 | 0.253 |
| PLT | 0.095 | 0.096 | 0.104 |
| LYM | 0.281 | 0.297 | 0.319 |
| OTHR | 0.197 | 0.197 | 0.205 |
| PDW | 0.228 | 0.238 | 0.246 |
| MPV | 0.154 | 0.16 | 0.173 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, D.; Ma, X.; Jia, C.; Chu, M.; Lei, Q.; Wen, Z.; Wu, X.; Pei, J.; Bao, P.; Ding, X.; et al. A Study of Genomic Prediction of 12 Important Traits in the Domesticated Yak (Bos grunniens). Animals 2019, 9, 927. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9110927
Fu D, Ma X, Jia C, Chu M, Lei Q, Wen Z, Wu X, Pei J, Bao P, Ding X, et al. A Study of Genomic Prediction of 12 Important Traits in the Domesticated Yak (Bos grunniens). Animals. 2019; 9(11):927. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9110927
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Donghai, Xiaoming Ma, Congjun Jia, Min Chu, Qinhui Lei, Zhiping Wen, Xiaoyun Wu, Jie Pei, Pengjia Bao, Xuezhi Ding, and et al. 2019. "A Study of Genomic Prediction of 12 Important Traits in the Domesticated Yak (Bos grunniens)" Animals 9, no. 11: 927. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9110927
APA StyleFu, D., Ma, X., Jia, C., Chu, M., Lei, Q., Wen, Z., Wu, X., Pei, J., Bao, P., Ding, X., Guo, X., Yan, P., & Liang, C. (2019). A Study of Genomic Prediction of 12 Important Traits in the Domesticated Yak (Bos grunniens). Animals, 9(11), 927. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9110927





