Towards Non-Invasive Methods in Measuring Fish Welfare: The Measurement of Cortisol Concentrations in Fish Skin Mucus as a Biomarker of Habitat Quality
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Field Sampling
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Hematological Analysis
2.4. Cortisol Extraction and Biochemical Validation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Biochemical Validation of the EIA
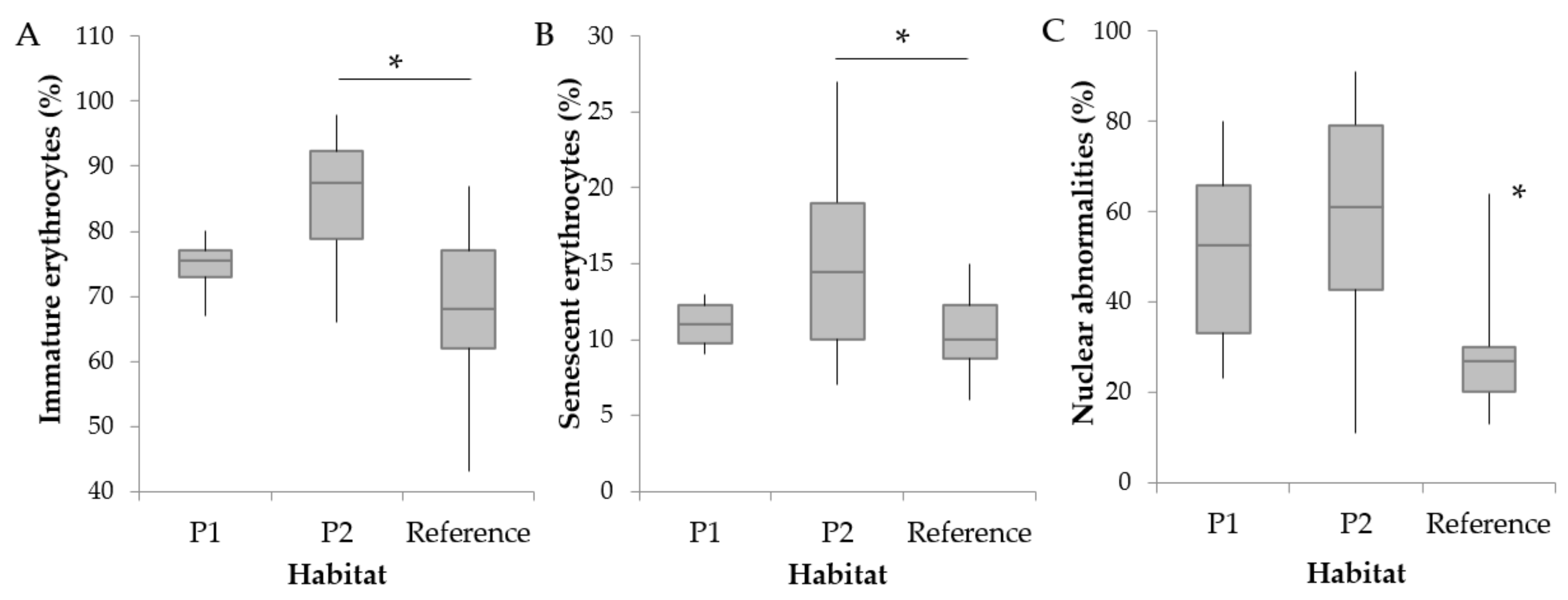
3.2. Hematological Parameters and Cortisol Levels
4. Discussion
4.1. Abnormal RBC Frequencies
4.2. Variations in WBC Counts
4.3. Changes in Cortisol Levels
4.4. Integrated Assessment
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pankhurst, N.W. The endocrinology of stress in fish: An environmental perspective. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2011, 170, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schreck, C.B.; Tort, L. Biology of Stress in Fish, 2016th ed.; Farrell, A.P., Brauner, C.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; ISBN 9780128027288. [Google Scholar]
- Sheriff, M.J.; Dantzer, B.; Delehanty, B.; Palme, R.; Boonstra, R. Measuring stress in wildlife: Techniques for quantifying glucocorticoids. Oecologia 2011, 166, 869–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingfield, J.C.; Kelley, J.P.; Angelier, F. What are extreme environmental conditions and how do organisms cope with them? Curr. Zool. 2011, 57, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, G.R.; Sloman, K.A. The effects of environmental pollutants on complex fish behaviour: Integrating behavioural and physiological indicators of toxicity. Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 68, 369–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantzer, B.; Fletcher, Q.E.; Boonstra, R.; Sheriff, M.J. Measures of physiological stress: A transparent or opaque window into the status, management and conservation of species? Conserv. Physiol. 2014, 2, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, D.U.; Adair, E.C.; Cardinale, B.J.; Byrnes, J.E.K.; Hungate, B.A.; Matulich, K.L.; Gonzalez, A.; Duffy, J.E.; Gamfeldt, L.; Connor, M.I. A global synthesis reveals biodiversity loss as a major driver of ecosystem change. Nature 2012, 486, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, J.D.; Hasler, C.T.; Chapman, J.M.; Cooke, S.J.; Suski, C.D. Linking landscape-scale disturbances to stress and condition of fish: Implications for restoration and conservation. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2015, 55, 618–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, C.P.; Reina, R.D.; Lill, A. Interpreting indices of physiological stress in free-living vertebrates. J. Comp. Physiol. B 2012, 182, 861–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maceda-Veiga, A.; Figuerola, J.; Martínez-Silvestre, A.; Viscor, G.; Ferrari, N.; Pacheco, M. Inside the Redbox: Applications of haematology in wildlife monitoring and ecosystem health assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 514, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colin, N.; Maceda-Veiga, A.; Monroy, M.; Ortega-Ribera, M.; Llorente, M.; de Sostoa, A. Trends in biomarkers, biotic indices, and fish population size revealed contrasting long-term effects of recycled water on the ecological status of a Mediterranean river. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 145, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, B.; Sultana, T.; Sultana, S.; Masoud, M.S.; Ahmed, Z.; Mahboob, S. Fish eco-genotoxicology: Comet and micronucleus assay in fish erythrocytes as in situ biomarker of freshwater pollution. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 25, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braham, R.P.; Blazer, V.S.; Shaw, C.H.; Mazik, P.M. Micronuclei and other erythrocyte nuclear abnormalities in fishes from the Great Lakes Basin, USA. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2017, 58, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castaño, A.; Sanchez, P.; Llorente, M.T.; Carballo, M.; De La Torre, A.; Muñoz, M.J. The use of alternative systems for the ecotoxicological screening of complex mixtures on fish populations. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 247, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, L.; Popovska-percinic, F.; Slavevska-stamenkovic, V.; Jordanova, M.; Rebok, K. Micronuclei and nuclear abnormalities in erythrocytes from barbel barbus peloponnesius revealing genotoxic pollution of the River Bregalnica. Maced. Vet. Rev. 2016, 39, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.K.; Maney, D.L.; Maerz, J.C. The use of leukocyte profiles to measure stress in vertebrates: A review for ecologists. Funct. Ecol. 2008, 22, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayati, A.; Jahanbakhshi, A. The effect of water-soluble fraction of diesel oil on some hematological indices in the great sturgeon Huso huso. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 38, 1753–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witeska, M. Stress in fish-hematological and immunological effects of heavy metals. Electron. J. Ichthyol. 2005, 1, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Busch, D.S.; Hayward, L.S. Stress in a conservation context: A discussion of glucocorticoid actions and how levels change with conservation-relevant variables. Biol. Conserv. 2009, 142, 2844–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homyack, J.A. Evaluating habitat quality of vertebrates using conservation physiology tools. Wildl. Res. 2010, 37, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mommsen, T.P.; Vijayan, M.M.; Moon, T.W. Cortisol in teleosts: Dynamics, mechanisms of action, and metabolic regulation. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 1999, 9, 211–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, G.D.; Chapman, J.M.; Cooke, S.J.; Suski, C.D. Stress in the neighborhood: Tissue glucocorticoids relative to stream quality for five species of fish. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 547, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Norris, D.O.; Donahue, S.; Dores, R.M.; Lee, J.K.; Tammy, A.; Ruth, T.; Woodling, J.D. Impaired Adrenocortical Response to Stress by Brown Trout, Salmo trutta, Living in Metal-Contaminated Waters of the Eagle River, Colorado. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1999, 113, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pottinger, T.G.; Williams, R.J.; Matthiessen, P. A comparison of two methods for the assessment of stress axis activity in wild fish in relation to wastewater effluent exposure. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2016, 230, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, J.; Metz, J.R.; Ampe, B.; Decostere, A.; Flik, G.; De Saeger, S. Scales Tell a Story on the Stress History of Fish. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 0123411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbajal, A.; Reyes-López, F.E.; Tallo-Parra, O.; Lopez-Bejar, M.; Tort, L. Comparative assessment of cortisol in plasma, skin mucus and scales as a measure of the hypothalamic-pituitary-interrenal axis activity in fish. Aquaculture 2019, 506, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbajal, A.; Tallo-Parra, O.; Monclús, L.; Vinyoles, D.; Solé, M.; Lacorte, S.; Lopez-Bejar, M. Variation in scale cortisol concentrations of a wild freshwater fish: Habitat quality or seasonal influences? Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2019, 275, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Mercado, E.; Larrán, A.M.; Pinedo, J.; Tomás-Almenar, C. Skin mucous: A new approach to assess stress in rainbow trout. Aquaculture 2018, 484, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardiola, F.A.; Cuesta, A.; Esteban, M.Á. Using skin mucus to evaluate stress in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 59, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simontacchi, C.; Poltronieri, C.; Carraro, C.; Bertotto, D.; Xiccato, G.; Trocino, A.; Radaelli, G. Alternative stress indicators in sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax, L. J. Fish Biol. 2008, 72, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertotto, D.; Poltronieri, C.; Negrato, E.; Majolini, D.; Radaelli, G.; Simontacchi, C. Alternative matrices for cortisol measurement in fish. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Alacid, L.; Sanahuja, I.; Ordóñez-Grande, B.; Sánchez-Nuño, S.; Herrera, M.; Ibarz, A. Skin mucus metabolites and cortisol in meagre fed acute stress-attenuating diets: Correlations between plasma and mucus. Aquaculture 2019, 499, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Martinez, L.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Martinez-Subiela, S.; Teles, M.; Tort, L. Chemiluminescent assay as an alternative to radioimmunoassay for the measurement of cortisol in plasma and skin mucus of Oncorhynchus mykiss. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 98, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doadrio, I.; Kottelat, M.; de Sostoa, A. Squalius laietanus, a new species of cyprinid fish from north-eastern Spain and southern France (Teleostei: Cyprinidae). Ichthyol. Explor. Freshw. 2007, 18, 247–256. [Google Scholar]
- Babatunde, A.O.; Zhao, Y.Q.; O’Neill, M.; O’Sullivan, B. Constructed wetlands for environmental pollution control: A review of developments, research and practice in Ireland. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brix, H.; Schierup, H.; Bourke, J.; Wroe, S.; Moreno, K.; McHenry, C.; Clausen, P.; Aller, L.; Lehr, J.; Petty, R.; et al. Use of Constructed Wetlands in Water Pollution Control: Historical Development, Present Status, and Future Perspectives. PLoS ONE 1994, 3, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J.; Březinová, T. The use of constructed wetlands for removal of pesticides from agricultural runoff and drainage: A review. Environ. Int. 2015, 75, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, J.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Hu, Z.; Liang, S.; Fan, J.; Liu, H. A review on the sustainability of constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: Design and operation. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 175, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guittonny-Philippe, A.; Masotti, V.; Höhener, P.; Boudenne, J.L.; Viglione, J.; Laffont-Schwob, I. Constructed wetlands to reduce metal pollution from industrial catchments in aquatic Mediterranean ecosystems: A review to overcome obstacles and suggest potential solutions. Environ. Int. 2014, 64, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatz, A.J.; Linder, R.S. Effects of Repeated Electroshocking on Condition, Growth, and Movement of Selected Warmwater Stream Fishes. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2008, 28, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagrodski, A.; Murchie, K.J.; Stamplecoskie, K.M.; Suski, C.D.; Cooke, S.J. Effects of an experimental short-term cortisol challenge on the behaviour of wild creek chub Semotilus atromaculatus in mesocosm and stream environments. J. Fish Biol. 2013, 82, 1138–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maceda-Veiga, A.; Monroy, M.; Navarro, E.; Viscor, G.; de Sostoa, A. Metal concentrations and pathological responses of wild native fish exposed to sewage discharge in a Mediterranean river. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 449, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stasinakis, A.S.; Mermigka, S.; Samaras, V.G.; Farmaki, E.; Thomaidis, N.S. Occurrence of endocrine disrupters and selected pharmaceuticals in Aisonas River (Greece) and environmental risk assessment using hazard indexes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 1574–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, L.M. Physiological stress in ecology: Lessons from biomedical research. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2004, 19, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, D.R.; Perez, N.; Tan, C.K.; Mendez, A.J.; Capo, T.R.; Snodgrass, D.; Prince, E.D.; Serafy, J.E. Concurrent levels of 11-ketotestosterone in fish surface mucus, muscle tissue and blood. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2005, 21, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodbred, S.L.; Patiño, R.; Torres, L.; Echols, K.R.; Jenkins, J.A.; Rosen, M.R.; Orsak, E. Are endocrine and reproductive biomarkers altered in contaminant-exposed wild male Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) of Lake Mead, Nevada/Arizona, USA? Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2015, 219, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, B.A.; Morgan, J.D.; Vljayan, M. Physiological and Condition-Related Indicators of Environmental Stress in Fish. Biol. Indic. Aquat. Ecosyst. Stress 1998, 111–148. [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco, M.; Santos, M.A. Induction of Micronuclei ad nuclear abnormalities in the erythrocytes of Anguilla angulila L. exposed either to cyclophosphamide or to bleached kraft pulp mill effluent. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 1996, 5, 746–751. [Google Scholar]
- Tavares-Dias, M. Cytochemical method for staining fish basophils. J. Fish Biol. 2006, 69, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbajal, A.; Monclús, L.; Tallo-Parra, O.; Sabes-Alsina, M.; Vinyoles, D.; Lopez-Bejar, M. Cortisol detection in fish scales by enzyme immunoassay: Biochemical and methodological validation. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2018, 34, 967–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maceda-Veiga, A.; Monroy, M.; Viscor, G.; De Sostoa, A. Changes in non-specific biomarkers in the Mediterranean barbel (Barbus meridionalis) exposed to sewage effluents in a Mediterranean stream (Catalonia, NE Spain). Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 100, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, N.; Porte, C.; Fernandes, D.; Barata, C.; Padrós, F.; Carrassón, M.; Monroy, M.; Cano-Rocabayera, O.; de Sostoa, A.; Piña, B.; et al. Ecological relevance of biomarkers in monitoring studies of macro-invertebrates and fish in Mediterranean rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 540, 307–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, M.; Santos, M.A. Biotransformation, genotoxic, and histopathological effects of environmental contaminants in European eel (Anguilla anguilla L.). Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2002, 53, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussali-Galante, P.; Tovar-Sánchez, E.; Valverde, M.; Rojas del Castillo, E. Biomarkers of Exposure for Assessing Environmental Metal Pollution: From Molecules To Ecosystems. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2013, 29, 117–140. [Google Scholar]
- Botelho, R.G.; Monteiro, S.H.; Christofoletti, C.A.; Moura-Andrade, G.C.R.; Tornisielo, V.L. Environmentally Relevant Concentrations of Atrazine and Ametrine Induce Micronuclei Formation and Nuclear Abnormalities in Erythrocytes of Fish. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 69, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Ahmad, M. FreshWater Fish, Channa Punctatus, as a Model for Pendimethalin Genotoxicity Testing: A New Approach toward Aquatic Environmental Contaminants. Environ. Toxicol. 2016, 31, 1520–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, H.B.; Hussein, W.R.; Tchounwou, P.B. Effects of tetrachloroethylene on the viability and development of embryos of the Japanese Medaka, Oryzias latipes. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2002, 42, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhou, Q.; Hu, X.; Hua, T.; Li, F. Single and joint toxicity of perchloroethylene and cadmium on Ctenopharyngodon idellus. J. Appl. Ecol. 2007, 18, 1120–1124. [Google Scholar]
- Augusto, L.G.D.S.; Lieber, S.R.; Ruiz, M.A.; De Souza, C.A. Micronucleus monitoring to assess human occupational exposure to organochlorides. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 1997, 29, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil Barcellos, L.J.; Kreutz, L.C.; de Souza, C.; Rodrigues, L.B.; Fioreze, I.; Quevedo, R.M.; Cericato, L.; Soso, A.B.; Fagundes, M.; Conrad, J.; et al. Hematological changes in jundiá (Rhamdia quelen Quoy and Gaimard Pimelodidae) after acute and chronic stress caused by usual aquacultural management, with emphasis on immunosuppressive effects. Aquaculture 2004, 237, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzelak, A.K.; Davis, D.J.; Caraker, S.M.; Crim, M.J.; Spitsbergen, J.M.; Wiedmeyer, C.E. Stress leukogram induced by acute and chronic stress in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Comp. Med. 2017, 67, 263–269. [Google Scholar]
- Wendelaar Bonga, S.E. The Stress Response in Fish. Physiol. Rev. 1997, 77, 591–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letcher, R.J.; Ove, J.; Dietz, R.; Jenssen, B.M.; Jørgensen, E.H.; Sonne, C.; Verreault, J.; Vijayan, M.M.; Gabrielsen, G.W. Exposure and effects assessment of persistent organohalogen contaminants in arctic wildlife and fish. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 2995–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares-Dias, M. A morphological and cytochemical study of erythrocytes, thrombocytes and leukocytes in four freshwater teleosts. J. Fish Biol. 2006, 68, 1822–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayati, A.; Hassan Nataj Niazie, E. Hematological changes of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) in response to Diazinon pesticide. J. Environ. Heal. Sci. Eng. 2015, 13, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, N.J. Review: Minimally invasive sampling media and the measurement of corticosteroids as biomarkers of stress in animals. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 92, 227–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knag, A.C.; Taugbøl, A. Acute exposure to offshore produced water has an effect on stress- and secondary stress responses in three-spined stickleback Gasterosteus aculeatus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 158, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottinger, T.G.; Matthiessen, P. Disruption of the stress response in wastewater treatment works effluent-exposed three-spined sticklebacks persists after translocation to an unpolluted environment. Ecotoxicology 2016, 25, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baos, R.; Blas, J.; Bortolotti, G.R.; Marchant, T.A.; Hiraldo, F. Adrenocortical response to stress and thyroid hormone status in free-living nestling white storks (Ciconia ciconia) exposed to heavy metal and arsenic contamination. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 1497–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, R.J.; Pereira, M.G.; Shore, R.F.; Henrys, P.A.; Pottinger, T.G. Feather corticosterone content in predatory birds in relation to body condition and hepatic metal concentration. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2015, 214, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wikelski, M.; Wong, V.; Chevalier, B.; Rattenborg, N.; Snell, H.L. Marine iguanas die from trace oil pollution. Nature 2002, 417, 607–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blevins, Z.W.; Wahl, D.H.; Suski, C.D. Reach-Scale Land Use Drives the Stress Responses of a Resident Stream Fish. Physiol. Biochem. Zool. 2013, 87, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gesto, M.; Soengas, J.L.; Míguez, J.M. Acute and prolonged stress responses of brain monoaminergic activity and plasma cortisol levels in rainbow trout are modified by PAHs (naphthalene, β-naphthoflavone and benzo(a)pyrene) treatment. Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 86, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, M.; Pacheco, M.; Santos, M.A. Fish thyroidal and stress responses in contamination monitoring-An integrated biomarker approach. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pottinger, T.G.; Henrys, P.A.; Williams, R.J.; Matthiessen, P. The stress response of three-spined sticklebacks is modified in proportion to effluent exposure downstream of wastewater treatment works. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 126, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonstra, R. The ecology of stress: A marriage of disciplines. Funct. Ecol. 2013, 27, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.R.; Gobush, K.S.; Vynne, C.H. Review of factors influencing stress hormones in fish and wildlife. J. Nat. Conserv. 2013, 21, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, A.H. Review: Are the Classical Hematological Variables Acceptable Indicators of Fish Health? Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1997, 126, 879–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, M.R.; Alagawany, M. Erythrocytes as a biological model for screening of xenobiotics toxicity. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 279, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikinmaa, M. How does environmental pollution affect red cell function in fish? Aquat. Toxicol. 1992, 22, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickens, M.J.; Romero, L.M. A consensus endocrine profile for chronically stressed wild animals does not exist. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2013, 191, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Compound | Sites | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | P2 | Reference | |
| CEC (µg/L) | |||
| Volatile organic compounds | |||
| Tetrachloroethene | <LOD | 0.6 | <LOD |
| Pesticides | |||
| Simazine | 0.13 | 0.13 | <LOD |
| Diuron | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| Isoproturon | 0.04 | 0.04 | <LOD |
| Pharmaceutical products | |||
| Diclofenac | 1.61 | 0.29 | <LOD |
| Alkylphenols | |||
| 4-tert-octylphenol | 0.025 | <LOD | <LOD |
| Nonylphenol | 0.14 | <LOD | <LOD |
| Physico-Chemical Data (mg/L) | |||
| NH4+ | 12.6 | 10.6 | 0.07 |
| NO3− | 3.31 | 2.83 | 0.18 |
| PO4− | 0.8 | 1 | 0.4 |
| TOC 1 | 9.25 | 6.39 | 2.16 |
| COD 2 | 29.9 | 30.5 | 5.88 |
| SS 3 | 7 | 9.5 | 0.5 |
| Turbidity (NTU 4) | 4.47 | 3.01 | 0.66 |
| White Blood Cell Type | Sites | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | P2 | Reference | |
| N:L ratio | 10.54 ± 4.49 a | 8.00 ± 3.46 a | 4.79 ± 2.91 b |
| Monocytes | 4.50 ± 3.67 | 7.47 ± 3.83 | 6.05 ± 2.82 |
| Eosinophils | 0.67 ± 0.82 | 1.35 ± 1.17 | 1.18 ± 1.30 |
| Basophils | 0.33 ± 0.52 ab | 1.24 ± 1.20 a | 0.36 ± 0.58 b |
| Variable | MCC (r) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Cortisol | ||
| Plasma cortisol concentration | 0.55 | <0.01 |
| Red blood cells | ||
| Immature erythrocytes | 0.40 | 0.03 |
| Senescent erythrocytes | 0.23 | 0.24 |
| Erythrocytic nuclear abnormalities | 0.41 | 0.02 |
| Micronucleus | −0.001 | 0.99 |
| White blood cells | ||
| N:L ratio | 0.34 | 0.05 |
| Monocytes | −0.01 | 0.97 |
| Eosinophils | −0.21 | 0.20 |
| Basophils | 0.24 | 0.17 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carbajal, A.; Soler, P.; Tallo-Parra, O.; Isasa, M.; Echevarria, C.; Lopez-Bejar, M.; Vinyoles, D. Towards Non-Invasive Methods in Measuring Fish Welfare: The Measurement of Cortisol Concentrations in Fish Skin Mucus as a Biomarker of Habitat Quality. Animals 2019, 9, 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9110939
Carbajal A, Soler P, Tallo-Parra O, Isasa M, Echevarria C, Lopez-Bejar M, Vinyoles D. Towards Non-Invasive Methods in Measuring Fish Welfare: The Measurement of Cortisol Concentrations in Fish Skin Mucus as a Biomarker of Habitat Quality. Animals. 2019; 9(11):939. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9110939
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarbajal, Annaïs, Patricia Soler, Oriol Tallo-Parra, Marina Isasa, Carlos Echevarria, Manel Lopez-Bejar, and Dolors Vinyoles. 2019. "Towards Non-Invasive Methods in Measuring Fish Welfare: The Measurement of Cortisol Concentrations in Fish Skin Mucus as a Biomarker of Habitat Quality" Animals 9, no. 11: 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9110939
APA StyleCarbajal, A., Soler, P., Tallo-Parra, O., Isasa, M., Echevarria, C., Lopez-Bejar, M., & Vinyoles, D. (2019). Towards Non-Invasive Methods in Measuring Fish Welfare: The Measurement of Cortisol Concentrations in Fish Skin Mucus as a Biomarker of Habitat Quality. Animals, 9(11), 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9110939






