The Relationship between Uterine, Fecal, Bedding, and Airborne Dust Microbiota from Dairy Cows and Their Environment: A Pilot Study
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Blood Analyses
2.3. DNA Extraction
2.4. Illumina MiSeq Sequencing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
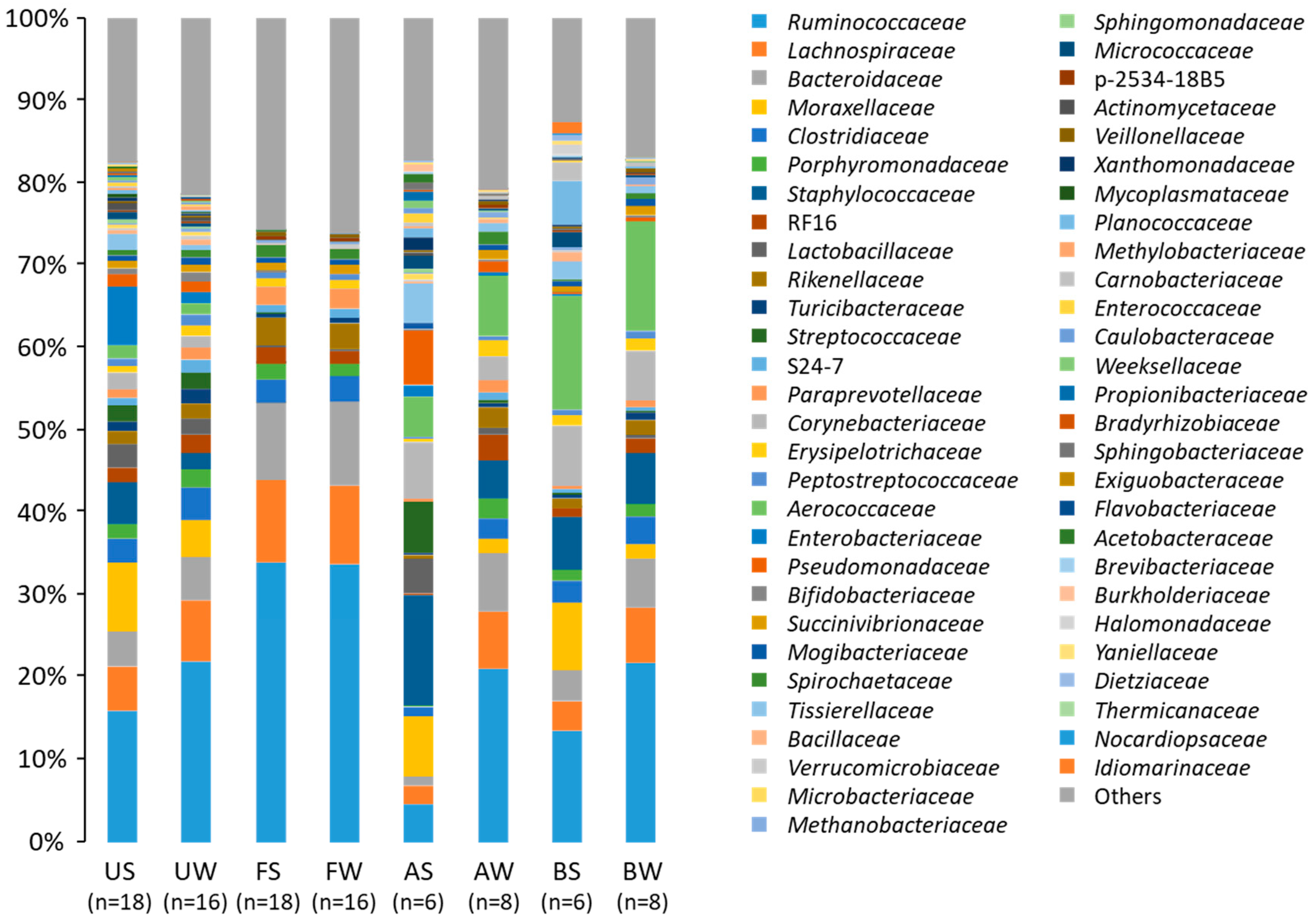
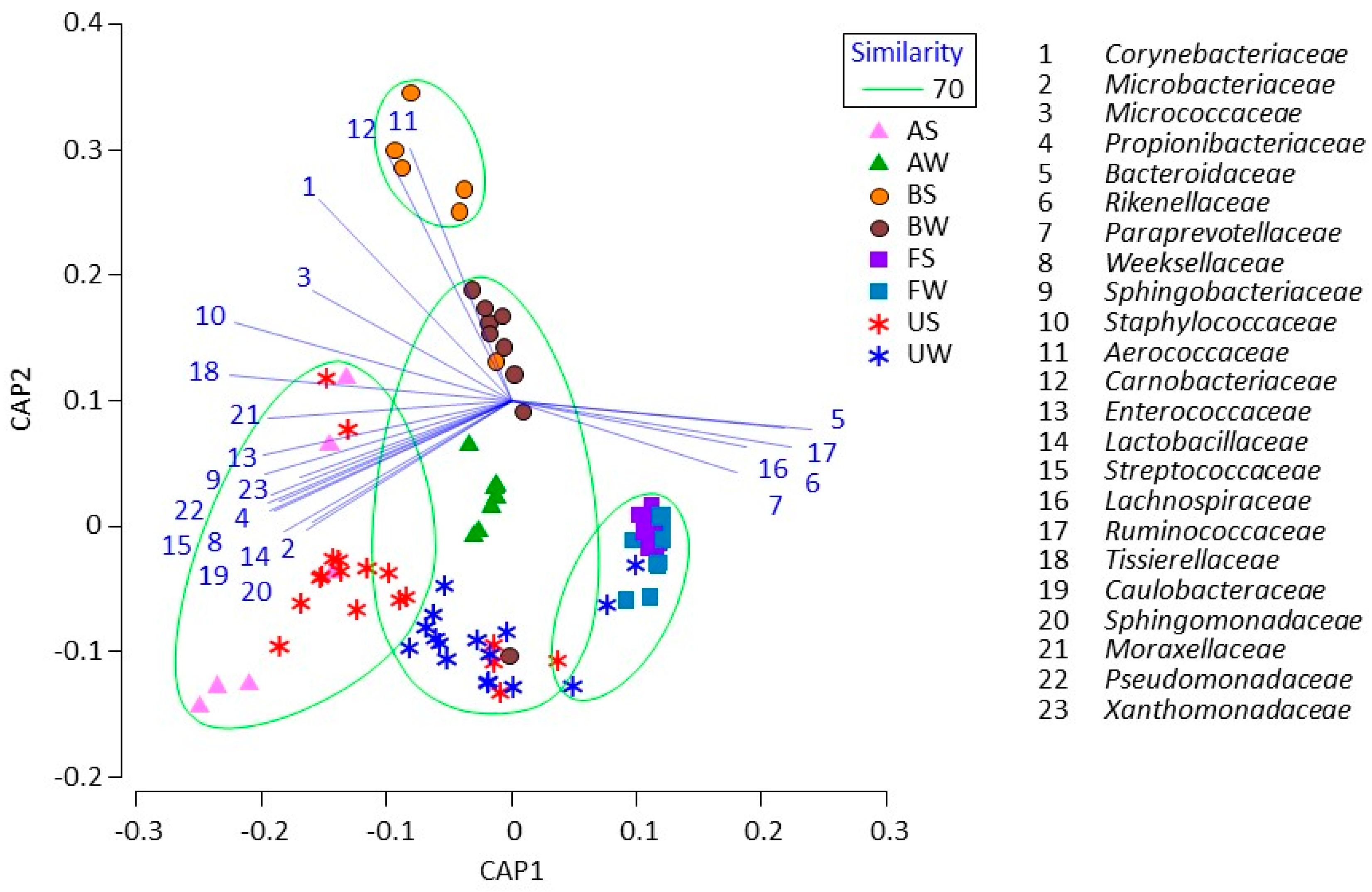
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sheldon, I.M.; Lewis, G.; LeBlanc, S.; Gilbert, R. Defining postpartum uterine disease in dairy cattle. Theriogenology 2006, 65, 1516–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanem, M.E.; Tezuka, E.; Devkota, B.; Izaike, Y.; Osawa, T. Persistence of uterine bacterial infection, and its associations with endometritis and ovarian function in postpartum dairy cows. J. Reprod. Dev. 2015, 61, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, G.S. Uterine health and disorders. J. Dairy Sci. 1997, 80, 984–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, S.J.; Duffield, T.F.; Leslie, K.E.; Bateman, K.G.; Keefe, G.P.; Walton, J.S.; Johnson, W.H. Defining and diagnosing postpartum clinical endometritis and its impact on reproductive performance in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2002, 85, 2223–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.M.; Gilbert, R.O.; Bicalho, R.C. Metagenomic analysis of the uterine bacterial microbiota in healthy and metritic postpartum dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, V.S.; Oikonomou, G.; Bicalho, M.L.; Knauer, W.A.; Gilbert, R.; Bicalho, R.C. Investigation of postpartum dairy cows’ uterine microbial diversity using metagenomic pyrosequencing of the 16S rRNA gene. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 159, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, L.R.; Karstrup, C.C.; Pedersen, H.G.; Angen, Ø.; Agerholm, J.S.; Rasmussen, E.L.; Jensen, T.K.; Klitgaard, K. An investigation of the microbiota in uterine flush samples and endometrial biopsies from dairy cows during the first 7 weeks postpartum. Theriogenology 2016, 86, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, I.M.; Williams, E.J.; Miller, A.N.A.; Nash, D.M.; Herath, S. Uterine diseases in cattle after parturition. Vet. J. 2008, 176, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, G.; Nakao, T.; Yusuf, M.; Koike, K. Prevalence of endometritis during the postpartum period and its impact on subsequent reproductive performance in two Japanese dairy herds. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2009, 116, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.G.; Ericsson, A.C.; Poock, S.E.; Melendez, P.; Lucy, M.C. 16S rRNA gene sequencing reveals the microbiome of the virgin and pregnant bovine uterus. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 4953–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karstrup, C.C.; Klitgaard, K.; Jensen, T.K.; Agerholm, J.S.; Pedersen, H.G. Presence of bacteria in the endometrium and placentomes of pregnant cows. Theriogenology 2017, 99, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.J.; Vieira-Neto, A.; Gobikrushanth, M.; Daetz, R.; Mingoti, R.D.; Parize, A.C.; de Freitas, S.L.; da Costa, A.N.; Bicalho, R.C.; Lima, S.; et al. Uterine microbiota progression from calving until establishment of metritis in dairy cows. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 6324–6332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Morrison, M. Improved extraction of PCR-quality community DNA from digesta and fecal samples. Biotechniques 2004, 36, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.T.; Han, H.; Yu, Z.; Tsuruta, T.; Nishino, N. Variability, stability, and resilience of fecal microbiota in dairy cows fed whole crop corn silage. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 6355–6364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, S.J.; Osawa, T.; Dubuc, J. Reproductive tract defense and disease in postpartum dairy cows. Theriogenology 2011, 76, 1610–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.H.; Jeong, J.K.; Choi, I.S.; Moon, S.H.; Lee, S.C.; Kang, H.G.; Park, S.B.; Kim, I.H. Associations between serum haptoglobin concentration and peri- and postpartum disorders, milk yield, and reproductive performance in dairy cows. Livest. Sci. 2018, 213, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, C.; Suwanai, M.; Honda, T.; Teramura, M.; Kida, K.; Hanada, M.; Miyamoto, A.; Matsui, M. Relationship of vaginal discharge characteristics evaluated by Metricheck device to metabolic status in postpartum dairy cows. Reprod. Dom. Anim. 2018, 53, 1396–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.P.W.; Chang, C.C.; Hsu, W.H.; Liu, W.B.; Chen, T.H. Association of increased serum acute-phase protein concentrations with reproductive performance in dairy cows with postpartum metritis. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2010, 39, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nightingale, C.R.; Sellers, M.D.; Ballou, M.A. Elevated plasma haptoglobin concentrations following parturition are associated with elevated leukocyte responses and decreased subsequent reproductive efficiency in multiparous Holstein dairy cows. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2015, 164, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, A.; Burfeind, O.; Heuwieser, W. The associations between postpartum serum haptoglobin concentration and metabolic status, calving difficulties, retained fetal membranes, and metritis. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 4544–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.L.; Liu, M.C.; Xu, J.; An, L.G.; Wang, J.F.; Zhu, Y.H. Uterine microbiota of dairy cows with clinical and subclinical. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bicalho, M.L.S.; Lima, S.; Higgins, C.H.; Machado, V.S.; Lima, F.S.; Bicalho, R.C. Genetic and functional analysis of the bovine uterine microbiota. Part I: Metritis versus healthy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 3850–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pothmann, H.; Prunner, I.; Wagener, K.; Jaureguiberry, M.; de la Sota, R.L.; Erber, R.; Aurich, C.; Ehling-Schulz, M.; Drillich, M. The prevalence of subclinical endometritis and intrauterine infections in repeat breeder cows. Theriogenology 2015, 83, 1249–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagener, K.; Prunner, I.; Pothmann, H.; Drillich, M.; Ehling-Schulz, M. Diversity and health status specific fluctuations of intrauterine microbial communities in postpartum dairy cows. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 175, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutkiewicz, J.; Pomorski, Z.J.H.; Sitkowska, J.; Krysinska-Traczyk, E.; Skorska, C.; Prazmo, Z.; Cholewa, G.; Wojtowicz, H. Airborne microorganisms and endotoxicin in animal houses. Grana 1994, 33, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsapko, V.G.; Chudnovets, A.J.; Sterenbogen, M.J.; Papach, V.V.; Dutkiewicz, J.; Skorska, C.; Krysinska-Traczyk, E.; Golec, M. Exposure to bioaerosols in the selected agricultural facilities of the Ukraine and Poland–A review. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2011, 18, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Item | Summer | Winter | Mann-Whitney U Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1M (n = 9) | 2M (n = 9) | 1M (n = 8) | 2M (n = 8) | Season | Month | |
| Milk yield (kg/day) | 39.0 ± 5.98 | 39.2 ± 6.93 | 34.6 ± 11.4 | 38.2 ± 9.95 | NS | NS |
| Blood metabolites | ||||||
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.57 ± 0.22 | 3.56 ± 0.28 | 3.29 ± 0.32 | 3.11 ± 0.28 | ** | NS |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 13.4 ± 2.16 | 12.6 ± 2.82 | 11.9 ± 3.64 | 11.5 ± 2.30 | NS | NS |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 151 ± 23.3 | 197 ± 25.1 | 148 ± 26.9 | 175 ± 32.5 | NS | ** |
| NEFA (μEq/L) | 0.37 ± 0.37 | 0.20 ± 0.19 | 0.14 ± 0.74 | 0.13 ± 0.59 | NS | NS |
| Calcium (mg/dL) | 8.92 ± 0.36 | 9.06 ± 0.67 | 9.13 ± 1.44 | 8.74 ± 1.57 | NS | NS |
| Phosphorus (mg/dL) | 6.72 ± 0.75 | 5.69 ± 1.14 | 5.84 ± 0.86 | 5.84 ± 0.93 | NS | NS |
| AST (U/L) | 45.1 ± 3.82 | 52.5 ± 6.60 | 55.2 ± 11.8 | 52.2 ± 4.78 | NS | NS |
| ALT (U/L) | 11.1 ± 2.55 | 12.5 ± 1.90 | 12.7 ± 2.21 | 13.9 ± 1.22 | NS | NS |
| Haptoglobin (μg/L) | 19.4 ± 4.62 | 101 ± 168 | 151 ± 276 | 42.3 ± 65.4 | NS | NS |
| Phylum/Family | Summer | Winter | Mann-Whitney U Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1M (n = 9) | 2M (n = 9) | 1M (n = 8) | 2M (n = 8) | Season | Month | |
| Actinobacteria | 7.31 ± 6.78 | 7.27 ± 6.20 | 5.04 ± 2.66 | 3.50 ± 2.92 | NS | NS |
| Actinomycetaceae | 0.53 ± 0.96 | 2.34 ± 6.32 | 0.37 ± 0.22 | 0.23 ± 0.23 | NS | NS |
| Bifidobacteriaceae | 0.14 ± 0.16 | 0.17 ± 0.16 | 1.30 ± 0.60 | 1.06 ± 0.79 | ** | NS |
| Corynebacteriaceae | 2.75 ± 2.49 | 2.03 ± 0.91 | 1.76 ± 0.97 | 1.15 ± 1.03 | NS | NS |
| Micrococcaceae | 1.67 ± 2.09 | 1.17 ± 0.46 | 0.38 ± 0.29 | 0.25 ± 0.24 | ** | NS |
| Bacteroidetes | 14.5 ± 12.9 | 12.2 ± 8.61 | 19.1 ± 4.74 | 22.1 ± 5.28 | ** | NS |
| Bacteroidaceae | 3.57 ± 3.63 | 3.09 ± 2.14 | 4.77 ± 1.29 | 6.18 ± 1.96 | ** | NS |
| Paraprevotellaceae | 0.73 ± 0.77 | 0.78 ± 0.82 | 1.40 ± 0.95 | 1.62 ± 0.78 | ** | NS |
| Porphyromonadaceae | 2.38 ± 3.43 | 1.16 ± 0.89 | 2.06 ± 0.51 | 2.23 ± 0.65 | ** | NS |
| RF16 | 1.23 ± 1.42 | 1.31 ± 1.44 | 1.91 ± 1.69 | 2.19 ± 1.00 | * | NS |
| Rikenellaceae | 1.36 ± 1.38 | 1.07 ± 0.87 | 1.65 ± 0.88 | 2.08 ± 0.70 | * | NS |
| S24-7 | 0.35 ± 0.35 | 0.28 ± 0.13 | 2.10 ± 1.83 | 1.11 ± 0.71 | ** | NS |
| Firmicutes | 44.2 ± 7.65 | 42.1 ± 4.43 | 55.8 ± 5.71 | 59.7 ± 4.70 | ** | NS |
| Aerococcaceae | 2.30 ± 3.26 | 1.01 ± 0.35 | 1.22 ± 0.67 | 1.42 ± 1.31 | NS | NS |
| Bacillaceae | 0.50 ± 0.60 | 0.27 ± 0.12 | 1.28 ± 3.06 | 0.11 ± 0.12 | NS | NS |
| Clostridiaceae | 1.78 ± 0.94 | 1.46 ± 0.54 | 3.88 ± 2.13 | 4.01 ± 0.62 | ** | NS |
| Erysipelotrichaceae | 0.50 ± 0.42 | 0.46 ± 0.19 | 1.40 ± 0.64 | 1.29 ± 0.48 | ** | NS |
| Exiguobacteraceae | 0.09 ± 0.10 | 1.01 ± 1.96 | 0.14 ± 0.22 | 0.04 ± 0.05 | NS | NS |
| Lachnospiraceae | 3.57 ± 2.69 | 3.12 ± 1.42 | 6.63 ± 2.06 | 7.97 ± 1.79 | ** | NS |
| Lactobacillaceae | 3.05 ± 1.98 | 4.67 ± 1.22 | 2.82 ± 1.91 | 1.28 ± 0.85 | ** | NS |
| Peptostreptococcaceae | 0.38 ± 0.22 | 0.45 ± 0.16 | 1.26 ± 0.59 | 1.38 ± 0.89 | ** | NS |
| Ruminococcaceae | 11.8 ± 10.9 | 10.1 ± 5.84 | 19.6 ± 6.76 | 24.9 ± 5.56 | ** | NS |
| Staphylococcaceae | 8.14 ± 5.85 | 7.12 ± 2.88 | 2.45 ± 1.17 | 1.75 ± 1.57 | ** | NS |
| Streptococcaceae | 2.03 ± 1.18 | 2.44 ± 0.92 | 1.96 ± 1.42 | 1.69 ± 1.48 | NS | NS |
| Tissierellaceae | 2.80 ± 1.73 | 3.02 ± 1.33 | 0.83 ± 0.48 | 0.60 ± 0.62 | ** | NS |
| Turicibacteraceae | 0.33 ± 0.19 | 0.33 ± 0.13 | 2.10 ± 1.19 | 1.56 ± 0.99 | ** | NS |
| Proteobacteria | 29.0 ± 16.0 | 35.0 ± 10.5 | 13.5 ± 6.72 | 8.40 ± 4.42 | ** | NS |
| Enterobacteriaceae | 11.9 ± 9.19 | 12.8 ± 4.80 | 1.41 ± 0.84 | 1.12 ± 1.04 | ** | NS |
| Moraxellaceae | 9.94 ± 6.15 | 14.2 ± 4.94 | 5.87 ± 6.14 | 2.99 ± 2.82 | ** | NS |
| Pseudomonadaceae | 1.51 ± 0.97 | 2.32 ± 1.06 | 1.63 ± 0.88 | 0.83 ± 0.64 | * | NS |
| Succinivibrionaceae | 1.28 ± 2.33 | 0.97 ± 0.79 | 0.71 ± 0.48 | 1.10 ± 0.89 | NS | NS |
| Tenericutes | 2.54 ± 3.69 | 1.13 ± 0.63 | 2.33 ± 1.64 | 2.62 ± 0.48 | ** | NS |
| Mycoplasmataceae | 1.32 ± 3.87 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 0.41 ± 1.07 | 0.10 ± 0.09 | * | NS |
| Phylum/Family | Summer | Winter | Mann-Whitney U Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1M (n = 9) | 2M (n = 9) | 1M (n = 8) | 2M (n = 8) | Season | Month | |
| Bacteroidetes | 32.2 ± 4.55 | 31.6 ± 2.90 | 28.6 ± 2.27 | 30.8 ± 5.06 | NS | NS |
| Bacteroidaceae | 10.3 ± 2.78 | 12.3 ± 2.92 | 9.68 ± 2.10 | 8.65 ± 1.76 | NS | NS |
| Paraprevotellaceae | 2.55 ± 1.10 | 2.27 ± 0.88 | 1.61 ± 1.15 | 2.70 ± 0.63 | NS | NS |
| Porphyromonadaceae | 1.47 ± 2.00 | 1.26 ± 0.69 | 2.13 ± 0.99 | 1.85 ± 1.15 | * | NS |
| RF16 | 1.01 ± 0.57 | 1.33 ± 0.91 | 1.51 ± 0.49 | 2.48 ± 1.55 | * | NS |
| Rikenellaceae | 3.13 ± 0.61 | 3.20 ± 0.80 | 3.42 ± 0.40 | 3.37 ± 0.78 | NS | NS |
| S24-7 | 1.39 ± 0.58 | 1.46 ± 0.41 | 0.79 ± 0.52 | 1.27 ± 0.54 | * | NS |
| Firmicutes | 60.2 ± 4.38 | 60.1 ± 2.92 | 63.1 ± 3.48 | 60.8 ± 5.42 | NS | NS |
| Clostridiaceae | 2.89 ± 1.05 | 2.89 ± 0.68 | 3.04 ± 0.94 | 2.87 ± 0.63 | NS | NS |
| Erysipelotrichaceae | 1.22 ± 0.51 | 1.44 ± 0.39 | 0.94 ± 0.20 | 1.26 ± 0.56 | NS | * |
| Lachnospiraceae | 9.32 ± 4.64 | 9.06 ± 2.30 | 9.38 ± 1.67 | 10.7 ± 4.56 | NS | NS |
| Ruminococcaceae | 33.8 ± 5.05 | 33.9 ± 1.87 | 37.2 ± 2.46 | 31.7 ± 3.28 | NS | * |
| Proteobacteria | 1.35 ± 0.87 | 1.72 ± 0.85 | 2.15 ± 1.39 | 1.32 ± 0.61 | NS | NS |
| Succinivibrionaceae | 1.11 ± 0.93 | 1.15 ± 0.84 | 1.16 ± 1.09 | 0.72 ± 0.65 | NS | NS |
| Spirochaetes | 0.94 ± 0.72 | 1.18 ± 0.60 | 1.93 ± 1.02 | 1.72 ± 1.16 | * | NS |
| Spirochaetaceae | 0.92 ± 0.71 | 1.12 ± 0.60 | 1.72 ± 1.01 | 1.67 ± 1.17 | * | NS |
| Phylum/Family | Summer (n = 6) | Winter (n = 9) | Mann-Whitney U Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| Actinobacteria | 11.4 ± 3.90 | 6.97 ± 3.60 | * |
| Corynebacteriaceae | 7.28 ± 2.89 | 6.01 ± 3.48 | NS |
| Micrococcaceae | 1.78 ± 0.92 | 0.27 ± 0.19 | ** |
| Bacteroidetes | 11.4 ± 5.24 | 16.8 ± 3.80 | * |
| Bacteroidaceae | 3.75 ± 2.08 | 5.95 ± 1.61 | NS |
| Porphyromonadaceae | 1.28 ± 0.40 | 1.71 ± 0.67 | NS |
| RF16 | 0.93 ± 0.59 | 1.65 ± 0.67 | * |
| Rikenellaceae | 1.04 ± 0.55 | 1.74 ± 0.36 | * |
| Firmicutes | 60.2 ± 2.48 | 66.7 ± 3.49 | ** |
| Aerococcaceae | 13.8 ± 2.66 | 13.3 ± 6.92 | NS |
| Carnobacteriaceae | 2.21 ± 0.48 | 0.63 ± 0.31 | ** |
| Clostridiaceae | 2.11 ± 0.25 | 2.45 ± 0.30 | NS |
| Erysipelotrichaceae | 1.32 ± 0.31 | 1.56 ± 0.33 | NS |
| Lachnospiraceae | 3.40 ± 1.22 | 6.59 ± 1.76 | ** |
| Mogibacteriaceae | 0.70 ± 0.24 | 1.01 ± 0.17 | * |
| Peptostreptococcaceae | 1.18 ± 0.36 | 1.75 ± 0.45 | * |
| Planococcaceae | 5.65 ± 4.32 | 0.09 ± 0.20 | ** |
| Ruminococcaceae | 10.8 ± 5.35 | 17.0 ± 2.31 | * |
| Staphylococcaceae | 6.62 ± 2.32 | 6.27 ± 2.82 | NS |
| Tissierellaceae | 2.32 ± 1.30 | 1.11 ± 0.53 | * |
| Proteobacteria | 13.8 ± 5.22 | 4.37 ± 1.90 | ** |
| Halomonadaceae | 1.33 ± 0.93 | 0.12 ± 0.09 | ** |
| Idiomarinaceae | 1.46 ± 2.12 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | ** |
| Moraxellaceae | 8.32 ± 3.72 | 1.80 ± 1.15 | ** |
| Succinivibrionaceae | 0.55 ± 0.36 | 1.01 ± 0.71 | NS |
| Phylum/Family | Summer (n = 6) | Winter (n = 9) | Mann-Whitney U Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| Actinobacteria | 12.4 ± 4.64 | 4.31 ± 0.81 | ** |
| Corynebacteriaceae | 6.95 ± 3.52 | 2.97 ± 0.36 | ** |
| Micrococcaceae | 1.52 ± 0.84 | 0.35 ± 0.40 | ** |
| Propionibacteriaceae | 1.13 ± 0.50 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | ** |
| Bacteroidetes | 5.33 ± 1.68 | 23.1 ± 1.35 | ** |
| Bacteroidaceae | 1.13 ± 0.85 | 7.05 ± 0.65 | ** |
| Paraprevotellaceae | 0.35 ± 0.17 | 1.52 ± 0.11 | ** |
| Porphyromonadaceae | 0.35 ± 0.23 | 2.41 ± 0.15 | ** |
| RF16 | 0.21 ± 0.22 | 3.01 ± 0.33 | ** |
| Rikenellaceae | 0.44 ± 0.25 | 2.28 ± 0.26 | ** |
| Firmicutes | 56.9 ± 2.17 | 58.1 ± 1.44 | NS |
| Aerococcaceae | 4.75 ± 4.34 | 7.28 ± 0.95 | NS |
| Clostridiaceae | 0.80 ± 0.51 | 2.12 ± 0.14 | ** |
| Erysipelotrichaceae | 0.31 ± 0.25 | 1.94 ± 0.17 | ** |
| Lachnospiraceae | 2.22 ± 1.48 | 6.79 ± 0.44 | ** |
| Lactobacillaceae | 4.10 ± 4.44 | 0.97 ± 0.91 | * |
| Peptostreptococcaceae | 0.69 ± 0.56 | 1.00 ± 0.15 | NS |
| Planococcaceae | 1.12 ± 1.05 | 0.05 ± 0.04 | ** |
| Ruminococcaceae | 3.73 ± 3.02 | 17.4 ± 1.13 | ** |
| Staphylococcaceae | 13.4 ± 2.05 | 4.72 ± 1.26 | ** |
| Streptococcaceae | 6.10 ± 2.50 | 0.31 ± 1.94 | ** |
| Tissierellaceae | 4.98 ± 0.84 | 1.09 ± 0.14 | ** |
| Proteobacteria | 22.6 ± 7.21 | 6.75 ± 1.12 | ** |
| Enterobacteriaceae | 1.32 ± 0.66 | 0.35 ± 0.35 | * |
| Moraxellaceae | 7.19 ± 1.94 | 1.78 ± 0.55 | ** |
| Pseudomonadaceae | 6.72 ± 2.68 | 1.34 ± 0.31 | ** |
| Xanthomonadaceae | 1.57 ± 0.61 | 0.07 ± 0.03 | ** |
| Spirochaetes | 0.11 ± 0.11 | 1.57 ± 0.24 | ** |
| Spirochaetaceae | 0.07 ± 0.08 | 1.49 ± 0.26 | ** |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, T.T.; Miyake, A.; Tran, T.T.M.; Tsuruta, T.; Nishino, N. The Relationship between Uterine, Fecal, Bedding, and Airborne Dust Microbiota from Dairy Cows and Their Environment: A Pilot Study. Animals 2019, 9, 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9121007
Nguyen TT, Miyake A, Tran TTM, Tsuruta T, Nishino N. The Relationship between Uterine, Fecal, Bedding, and Airborne Dust Microbiota from Dairy Cows and Their Environment: A Pilot Study. Animals. 2019; 9(12):1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9121007
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Thuong T., Ayumi Miyake, Tu T.M. Tran, Takeshi Tsuruta, and Naoki Nishino. 2019. "The Relationship between Uterine, Fecal, Bedding, and Airborne Dust Microbiota from Dairy Cows and Their Environment: A Pilot Study" Animals 9, no. 12: 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9121007
APA StyleNguyen, T. T., Miyake, A., Tran, T. T. M., Tsuruta, T., & Nishino, N. (2019). The Relationship between Uterine, Fecal, Bedding, and Airborne Dust Microbiota from Dairy Cows and Their Environment: A Pilot Study. Animals, 9(12), 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9121007





