An Examination of the Performance of Blank Cartridges Used in Captive Bolt Devices for the Pre-Slaughter Stunning and Euthanasia of Animals
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
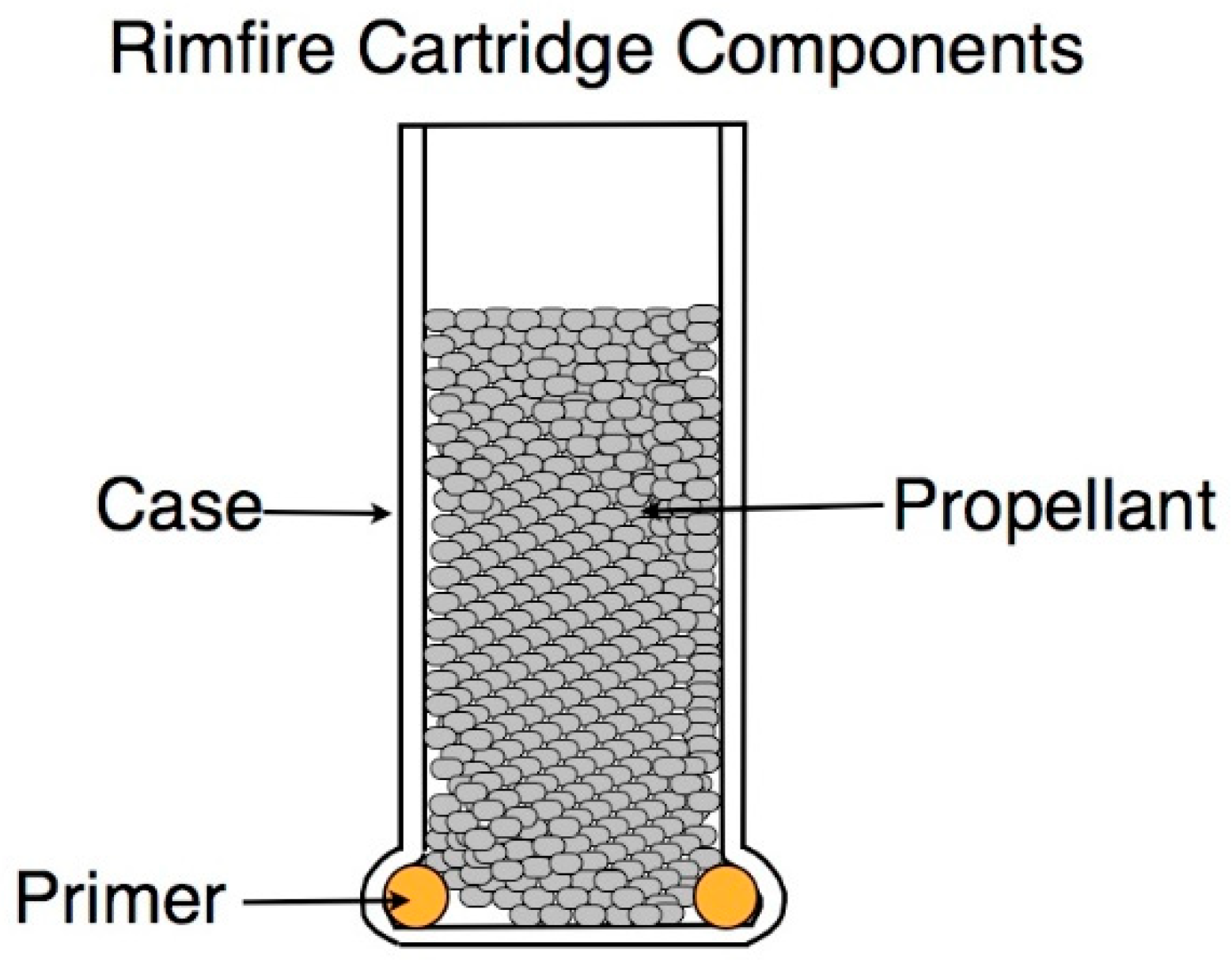
1.1. Cartridge Description
1.2. Case
1.3. Primer
1.4. Propellant
1.5. Rationale
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Trial One—Cartridge Weight
2.2. Trial Two—Cartridge Weight before and after Firing
2.3. Trial Three—Velocity Measurement (Velocimeter Method)
2.4. Trial Four—Velocity Measurement (Free Projectile Method)
2.5. Trial Five—In Vivo Velocity Measurement
2.6. Trial Six—Cartridge Fill Volume Assessment
2.7. Trial Seven—Case Deformity
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Trial One—Cartridge Weight (1-Grain—Brown Cap 0.22″ Calibre)
3.2. Trial Two—Cartridge Weight (3.00 Grain—Green Cap 0.22″ Calibre)
3.3. Trial Three—Velocity Measurement (Velocimeter Method)
3.4. Trial Four—Velocity Measurement Free Flight Method
- Study Gun 47 ± 6 J
- Gun 1 41 ± 7 J
- Gun 2 32 ± 10 J
3.5. Trial Five—In Vivo Velocity Measurement
3.6. Trial Six—Cartridge Fill Volume
3.7. Trial Seven—Case Deformity Due to Excessive Headspace
4. Discussions
4.1. Trial Two—Cartridge Weight before and after Firing (3.00 Grain Cartridges)
4.2. Trial Three—Velocity Measurement (Velocimeter Method)
4.3. Trial Four—(1 Grain Cartridges) Free Flight Method
4.4. Trial Five—In Vivo Velocity Measurement
4.5. Trial Six—Issues Arising from Cartridge Fill Volume
4.6. Trial Seven—Case Deformity
4.7. Case Splitting
4.8. Variation in Cartridge Performance
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Macnaughten, L. Pistol v Poleaxe. A Handbook on Humane Slaughter; Chapman and Hall Ltd.: London, UK, 1932; p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt, L. The development of a novel device for humanely dispatching casualty poultry. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Raj, A.B.M.; O’ Callaghan, M. Evaluation of a pneumatically operated captive bolt for stunning/killing broiler chickens. Br. Poult. Sci. 2001, 42, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grist, A.; Lines, J.; Knowles, T.; Mason, C.; Wotton, S. The Use of a Non-Penetrating Captive Bolt for the Euthanasia of Neonate Piglets. Animals 2018, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grist, A.; Lines, J.; Knowles, T.; Mason, C.; Wotton, S. Use of a Non-Penetrating Captive Bolt for Euthanasia of Neonate Goats. Animals 2018, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grist, A.; Lines, J.; Knowles, T.; Mason, C.; Wotton, S. The Use of a Mechanical Non-Penetrating Captive Bolt Device for the Euthanasia of Neonate Lambs. Animals 2018, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, M.; Franke, E.; Philipp, K.P.; Bockholdt, B.; Ekkernkamp, A. Ballistic parameters of cal. 9 mm x 17 mm industrial blank cartridges (cattle cartridges). Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2009, 192, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kneubuehl, B.P. Basics. In Wound Ballistics; Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 3–85. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, N.G.; Lee, C.J.; Widdicombe, J.P. Depth of concussion in cattle shot by penetrating captive bolt. Meat Sci. 2007, 77, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terlouw, E.M.C.; Bourguet, C.; Deiss, V. Consciousness, unconsciousness and death in the context of slaughter. Part, I. Neurobiological mechanisms underlying stunning and killing. Meat Sci. 2016, 118, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, C.C.; Gregory, N.G.; Wotton, S.B. Captive bolt stunning of cattle: Effects on brain function and role of bolt velocity. Brit. Vet. J. 1987, 143, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, N.; Shaw, F. Penetrating captive bolt stunning and exsanguination of cattle in abattoirs. J. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. 2000, 3, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Wenzlawowicz, M.; von Holleben, K.; Eser, E. Identifying reasons for stun failures in slaughterhouses for cattle and pigs: A field study. Anim. Welf. 2012, 21, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, S.; Velarde, A.; Algers, B. Assessment of stun quality at commercial slaughter in cattle shot with captive bolt. Anim. Welf. 2013, 22, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibson, T.J.; Mason, C.W.; Spence, J.Y.; Barker, H.; Gregory, N.G. Factors affecting penetrating captive bolt gun performance. J. Ann. Anim. Welf. Sci. 2015, 18, 222–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamenik, J.; Paral, V.; Pyszko, M.; Voslarova, E. Cattle stunning with a penetrative captive bolt device: A review. Anim. Sci. J. 2019, 90, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.A. National Forensic Science Technology Center (NFSTC), Firearm Examiner Training. Available online: https://projects.nfstc.org/firearms/module05/fir_m05_t06_01.htm (accessed on 16 May 2018).
- Heramb, R.M.; McCord, B.R. The manufacture of Smokeless Powders and their Forensic Analysis: A Brief Review. Forensic Sci. Communic. 2002, 4, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Folly, P.; Mäder, P. Propellant Chemistry. Chimia 2004, 58, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatcher, J.S. Hatcher’s Notebook – A Standard Reference Book for Shooters, Gunsmiths, Ballisticians, Historians, Hunters and Collectors; Martino Publishing: Eastford, CT, USA, 1948; ISBN 978-1-614-283-0. [Google Scholar]
- Von Holleben, K.; Schneider, Y.; von Wenzlawowicz, M. Study on the eligibility of a pneumatic captive bolt stunner for cattle stunning under routine conditions. FLEISCHWIRTSCHAFT 2018, 98, 94–98. [Google Scholar]
- Directive E, C. Council Regulation No 1099/2009 of 24 September 2009 on the protection of animals at the time of killing. Off. J. Eur. Union L 2009, 303, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Welfare of Animals at the Time of Slaughter Regulations (England). 2015. (SI No. 1782) HMSO. 2015. Available online: http://www.legislation.gov.uk/uksi/2015/1782/contents (accessed on 15 July 2018).
- Welfare of Animals at the Time of Slaughter Regulations (Scotland) 2012 (SI No.321) HMSO. Available online: http://www.legislation.gov.uk/ssi/2012/321/contents/ (accessed on 15 July 2018).
- Welfare of Animals at the Time of Slaughter Regulations (Wales) 2014 (SI No. 951 (W.92)) HMSO. Available online: http://www.legislation.gov.uk/wsi/2014/951/contents/ (accessed on 15 July 2018).




















© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grist, A.; Lines, J.A.; Bock, R.; Knowles, T.G.; Wotton, S.B. An Examination of the Performance of Blank Cartridges Used in Captive Bolt Devices for the Pre-Slaughter Stunning and Euthanasia of Animals. Animals 2019, 9, 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9080552
Grist A, Lines JA, Bock R, Knowles TG, Wotton SB. An Examination of the Performance of Blank Cartridges Used in Captive Bolt Devices for the Pre-Slaughter Stunning and Euthanasia of Animals. Animals. 2019; 9(8):552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9080552
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrist, Andrew, Jeff A. Lines, Randall Bock, Toby G. Knowles, and Stephen B. Wotton. 2019. "An Examination of the Performance of Blank Cartridges Used in Captive Bolt Devices for the Pre-Slaughter Stunning and Euthanasia of Animals" Animals 9, no. 8: 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9080552
APA StyleGrist, A., Lines, J. A., Bock, R., Knowles, T. G., & Wotton, S. B. (2019). An Examination of the Performance of Blank Cartridges Used in Captive Bolt Devices for the Pre-Slaughter Stunning and Euthanasia of Animals. Animals, 9(8), 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9080552




