Magnetic Anomaly and Model of the Lonar Meteorite Impact Crater in Maharashtra, India
Abstract
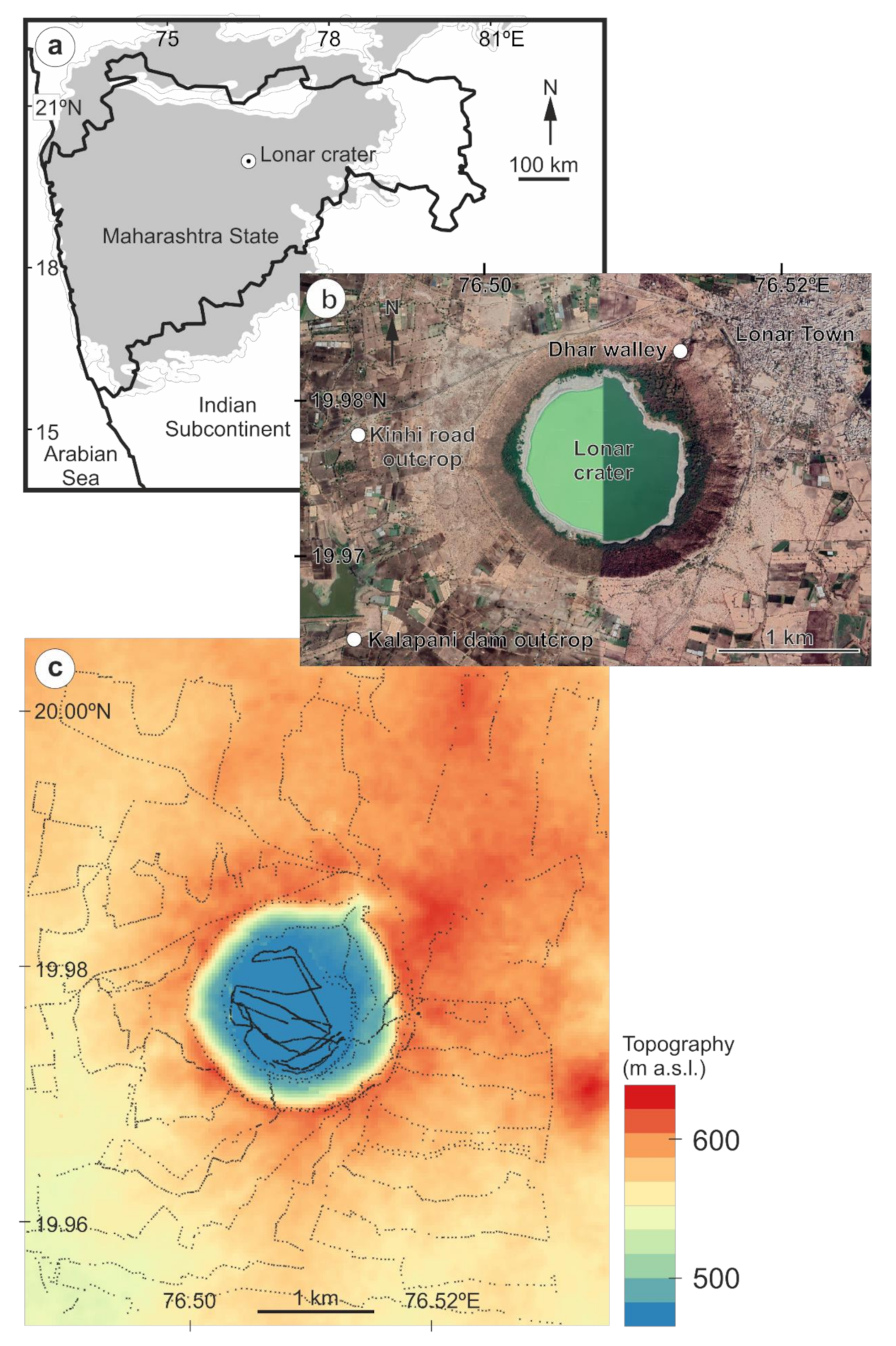
:1. Introduction
2. Previous Geophysical Research at the Lonar Crater
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
4.1. Magnetic Field
4.2. Magnetic Properties
4.3. Model
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sengupta, D.; Bhandari, N. Formation age of the Lonar Crater. Abstr. Pap. Submitt. Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. 1988, 19, 1059–1060. [Google Scholar]
- Maloof, A.C.; Stewart, S.T.; Weiss, B.P.; Soule, S.A.; Swanson-Hysell, N.L.; Louzada, K.L.; Garrick-Bethell, I.; Poussart, P.M. Geology of Lonar Crater, India. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2010, 122, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdan, F.; Moynier, F.; Koeberl, C.; Eroglu, S. 40Ar/39Ar age of the Lonar crater and consequence for the geochronology of planetary impacts. Geology 2011, 39, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredriksson, K.; Dube, A.; Milton, D.J.; Balasundaram, M.S. Lonar Lake, India: An Impact Crater in Basalt. Science 1973, 180, 862–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, G.K. The origin of hypotheses illustrated by the discussion of a topographic problem. Science 1896, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cotton, C.A. Volcanoes: As Landscape Forms; Whitcombe and Tombs Ltd.: Christchurch, New Zealand, 1952. [Google Scholar]
- Nandy, N.; Deo, V. Origin of the Lonar Lake and its alkalinity. TISCO 1961, 8, 144–155. [Google Scholar]
- Lafond, E.C.; Dietz, R.S. Lonar Crater, India, a Meteorite Crater? Meteoritics 1964, 2, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaitis, V.L. Impact structures of northeastern Eurasia: The territories of Russia and adjacent countries. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 1999, 34, 691–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosta, A.P.; Kazzuo-Vieira, C.; Pitarello, L.; Koeberl, C.; Kenkmann, T. Geology and impact features of Vargeão Dome, southern Brazil. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 2012, 47, 51–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crosta, A.P.; Vasconcelos, M.A.R. Update on the current knowledge of the Brazilian impact craters. Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. 2013, 44, 4–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chenet, A.; Quidelleur, X.; Fluteau, F.; Courtillot, V.; Bajpai, S. 40K–40Ar dating of the Main Deccan large igneous province: Further evidence of KTB age and short duration. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2007, 263, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, K. Age and duration of the Deccan Traps, India: A review of radiometric and paleomagnetic constraints. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2002, 111, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidhyanathan, R.; Ramakrishnan, M. Geology of India; Geological Society of India: Bangalore, India, 2008; Volume 2, pp. 733–784. [Google Scholar]
- Philpotts, A.; Ague, J. Principles of Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jay, A.E.; Widdowson, M. Stratigraphy, structure and volcanology of the SE Deccan continental flood basalt province: Implications for eruptive extent and volumes. J. Geol. Soc. 2008, 165, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenet, A.L.; Courtillot, V.; Fluteau, F.; Gérard, M.; Quidelleur, X.; Khadri, S.F.R.; Subbarao, K.V.; Thordarson, T. Determination of rapid Deccan eruptions across the Cretaceous-Tertiary boundary using paleomagnetic secular variation: 2. Constraints from analysis of eight new sections and synthesis for a 3500-m-thick composite section. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, 6103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harinarayana, T.; Patro, B.P.K.; Veeraswamy, K.; Manoj, C.; Naganjaneyulu, K.; Murthy, D.N.; Virupakshi, G. Regional geoelectric structure beneath Deccan Volcanic Province of the Indian subcontinent using magnetotellurics. Tectonophysics 2007, 445, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fudali, R.F.; Milton, D.J.; Fredriksson, K.; Dube, A. Morphology of Lonar Crater, India: Comparisons and implications. Moon Planets 1980, 23, 493–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbarao, K.V.; Chandrasekharam, D.; Navaneethakrishnan, P.; Hooper, P.R. Stratigraphy and Structure of Parts of the Central Deccan Basalt Province: Eruptive Models; Volcanism, Wiley Eastern Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 1994; pp. 321–332. [Google Scholar]
- Subbarao, K.V. Deccan Volcanic Province: Memoir 43 (1 and 2); Geological Society of India: Bangalore, India, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, A.; Yokoyama, Y.; Sekine, Y.; Goto, K.; Komatsu, G.; Kumar, P.S.; Matsuzaki, H.; Kaneoka, I.; Matsui, T. Formation and geomorphologic history of the Lonar impact crater deduced from in situ cosmogenic 10 Be and 26 Al. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2014, 15, 3190–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, D.V.; Madhav, T.; Chandrakala, P.; Nagabhushanam, P. A perspective of alkaline Lonar Lake, Maharashtra, India with reference to its hydrochemistry. Curr. Sci. 2015, 109, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, A.; Gupta, S. Detailed Investigation of Lonar Crater Buldana District, Maharashtra; Geological Survey of India: Bangalore, India, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Rajasekhar, R.P.; Mishra, D. Analysis of gravity and magnetic anomalies over Lonar lake, India: An impact crater in a basalt province. Curr. Sci. 2005, 88, 1836–1840. [Google Scholar]
- Grieve, R.A.F.; Garvin, J.B.; Coderre, J.M.; Rupert, J. Test of a geometric model for the modification stage of simple impact crater development. Meteoritics 1989, 24, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, J.; Bleil, U.; Hornemann, U. Shock magnetization and demagnetization of basalt by transient stress up to 10kbar. J. Geophys. 1975, 41, 23–41. [Google Scholar]
- Gilder, S.A.; Pohl, J.; Eitel, M. Magnetic fields in the Solar System; Lühr, H., Wicht, J., Gilder, S., Holschneider, M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2018; Chapter 13; pp. 357–382. [Google Scholar]
- Hargraves, R.B.; Perkins, W.E. Investigations of the effect of shock on natural remanent magnetism. J. Geophys. Res. 1969, 74, 2576–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reznik, B.; Kontny, A.; Fritz, J. Effect of moderate shock waves on magnetic susceptibility and microstructure of a magnetite-bearing ore. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 2017, 52, 1495–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, E.C.T. Pressure and Temperature Histories of Impact Metamorphosed Rocks—Based on Petrographic Observations; Mono Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1968; pp. 135–158. [Google Scholar]
- Louzada, K.L.; Weiss, B.P.; Maloof, A.C.; Stewart, S.T.; Swanson-Hysell, N.L.; Soule, S.A. Paleomagnetism of Lonar impact crater, India. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2008, 275, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilkington, M.; Grieve, R.A.F. The geophysical signature of terrestrial impact craters. Rev. Geophys. 1992, 30, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kailasam, L.N.; Gupta Sarma, D.; Bhanumurth, Y.R.; Das, P.C. Research Report; Geological Survey of India: Kolkata, India, 1964; Unpublished. [Google Scholar]
- Subrahmanyam, B. Lonar Crater, India: A Crypto-Volcanic Origin. Geol. Soc. India 1985, 26, 326–335. [Google Scholar]
- Fudali, R.F.; Subrahmanyam, B. Gravity reconnaissance at Lonar Crater, Maharastra. Spec. Publ. Ser. Geol. Surv. India 1983, 2, 83–87. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, A.; Kontny, A.; Srivastava, D.C.; Greiling, R.O. Shock pressure estimates in target basalts of a pristine crater: A case study in the Lonar crater, India. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2015, 128, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.; Basavaiah, N.; Misra, S.; Deenadayalan, K. Variations in magnetic properties of target basalts with the direction of asteroid impact: Example from Lonar crater, India. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 2012, 47, 1305–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, G.V.S.P.; Bhalla, M.S. Lonar Lake: Palaeomagnetic evidence of shock origin. Geophys. J. Int. 1984, 77, 847–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sangode, S.J.; Sharma, R.; Mahajan, R.; Basavaiah, N.; Srivastava, P.; Gudadhe, S.S.; Meshram, D.C.; Venkateshwarulu, M. Anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility and rock magnetic applications in the Deccan volcanic province based on some case studies. J. Geol. Soc. India 2017, 89, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.; Arif, M.; Basavaiah, N.; Srivastava, P.K.; Dube, A. Structural and anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility (AMS) evidence for oblique impact on terrestrial basalt flows: Lonar crater, India. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2010, 122, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisowski, S.M.; Fuller, M. The effect of shock on the magnetism of terrestrial rocks. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1978, 83, 3441–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poornachandra Rao, G.V.S.; Bhalla, M.S. Palaeomagnetism of Dhar traps and drift of the subcontinent during the Deccan volcanism. Geophys. J. Int. 1981, 65, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandrasekhar, D.V.; Mishra, D.C.; Poornachandra Rao, G.V.S.; Mallikharjuna Rao, J. Gravity and magnetic signatures of volcanic plugs related to Deccan volcanism in Saurashtra, India and their physical and geochemical properties. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2002, 201, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandamme, D.; Courtillot, V.; Besse, J.; Montigny, R. Paleomagnetism and age determinations of the Deccan Traps (India): Results of a Nagpur-Bombay Traverse and review of earlier work. Rev. Geophys. 1991, 29, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athavale, R.N.; Anjaneyulu, G.R. Palaeomagnetic results on the Deccan trap lavas of the Aurangabad region and their tectonic significance. Tectonophysics 1972, 14, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, R.L.; Huestis, S.P. The inversion of magnetic anomalies in the presence of topography. J. Geophys. Res. 1974, 79, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugalde, H.; Morris, B. An assessment of topographic effects on airborne and ground magnetic data. Lead. Edge 2008, 27, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smekalova, T.N.; Bevan, B.W. The Magnetic Anomaly of a Mound; 2002. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/272489033_The_Magnetic_Anomaly_of_a_Mound (accessed on 20 October 2020).
- Melosh, H.J. Impact Cratering. A Geologic Process; Oxford Monographs on Geology and Geophysics Series; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1989; ISBN 0 19 504284 0. [Google Scholar]
- Das Gupta, R.; Banerjee, A.; Goderis, S.; Claeys, P.; Vanhaecke, F.; Chakrabarti, R. Evidence for a chondritic impactor, evaporation-condensation effects and melting of the Precambrian basement beneath the ‘target’ Deccan basalts at Lonar crater, India. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2017, 215, 51–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.; Newsom, H.E.; Prasad, M.S.; Geissman, J.W.; Dube, A.; Sengupta, D. Geochemical identification of impactor for Lonar crater, India. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 2009, 44, 1001–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkel, H.; Ekneligoda, T.C.; Aaro, S. The extent of impact induced fracturing from gravity modeling of the Granby and Tvären simple craters. Tectonophysics 2010, 485, 290–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plado, J.; Pesonen, L.J.; Puura, V. Effect of erosion on gravity and magnetic signatures of complex impact structures: Geophysical modeling and applications. In Large Meteorite Impacts and Planetary Evolution II; Dressler, B.O., Sharpton, V.L., Eds.; Geological Society of America Special Papers; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1999; Volume 339, pp. 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Magnetic Susceptibility (10−6 SI) | Q-Ratio (-) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | Min. | Max. | St.dev. | ||
| Deccan Traps | |||||
| Lonar lake [39] | 26,000 | 17,000 | 40,200 | 7200 | 2.5–10.1 Average 5.93 |
| Saurashtra [44] | 55,000 | 1 | |||
| Dhar region [43] | 43,800 | 15,700 | 72,000 | 2.35–9.81 | |
| Lonar lake [37] | 39,500 | 26,000 | 55,800 | 15,200 | |
| Present study | |||||
| Lonar basalts (n = 89) | 24,000 | 11,200 | 65,500 | 9532 | |
| Lonar lake silt sediments (n = 46) | 3100 | 700 | 7900 | 2100 | |
| Lonar lake basalt sand (n = 5) | 13,580 | 10,900 | 21,400 | 3900 | |
| Lonar paleosols (n = 5) | 6100 | 4930 | 9330 | 2470 | |
| Road to Kinhi outcrop ejecta (n = 16) basalt boulders (n = 1) | 7900 | 3560 | 11,400 24,400 | 2141 | |
| Kalapani dam outcrop ejecta (n = 27) basalt boulders (n = 14) | 7000 19,400 | 2390 12,400 | 8820 30,500 | 1425 4970 | |
| Body | Magnetic Susceptibility (10−6 SI) | Natural Remanent Magnetization | Q-Ratio (-) | Side Length (m) | Density (g/cm3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intensity (A/m) | Declination (°) | Inclination (°) | |||||
| Post-impact sediments | 6000 | 0.21 | 0 | 10 | 1.0 | 1100 | 2.07 |
| Breccia lens | 24,000 | 0.0 | n.a. | n.a. | 1.0 | 1850 | 2.60 |
| Deccan Trap | 40,000 | 4.2 | 150 | 48 | 3.0 | 100,000; ∞ | 2.72 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kiik, K.; Plado, J.; Lingadevaru, M.; Jeelani, S.H.; Szyszka, M. Magnetic Anomaly and Model of the Lonar Meteorite Impact Crater in Maharashtra, India. Geosciences 2020, 10, 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10100417
Kiik K, Plado J, Lingadevaru M, Jeelani SH, Szyszka M. Magnetic Anomaly and Model of the Lonar Meteorite Impact Crater in Maharashtra, India. Geosciences. 2020; 10(10):417. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10100417
Chicago/Turabian StyleKiik, Kalle, Jüri Plado, Muddaramaiah Lingadevaru, Syed Hamim Jeelani, and Mateusz Szyszka. 2020. "Magnetic Anomaly and Model of the Lonar Meteorite Impact Crater in Maharashtra, India" Geosciences 10, no. 10: 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10100417
APA StyleKiik, K., Plado, J., Lingadevaru, M., Jeelani, S. H., & Szyszka, M. (2020). Magnetic Anomaly and Model of the Lonar Meteorite Impact Crater in Maharashtra, India. Geosciences, 10(10), 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10100417






