Abstract
We identify the source of the Mw = 6.4 earthquake that rocked north-central Albania on November 26, 2019 02:54 UTC. We use synthetic aperture radar interferograms tied to the time series of coordinates of two permanent Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) stations (DUR2 and TIR2). We model the source by inverting the displacement data. Assuming in our model a half-space elastic medium and uniform slip along a rectangular fault surface, we invert the 104 picked measurements on a couple of ascending and descending interferograms to calculate the parameters of the fault. All inversions made with different input parameters converge towards a stable and robust solution with root mean square (r.m.s.) residual of 5.4 mm, thus ~1/5 of a fringe. They reveal that the earthquake occurred deep in the crust on a low-angle fault (23°) dipping towards east with a centroid at 16.5 km depth. The best-fitting length and width of the fault are 22 and 13 km, and the reverse slip, 0.55 m. The seismic moment deduced from our model agrees with those of the published seismic moment tensors. This geometry is compatible with a blind thrust fault that may root on the main basal thrust, i.e., along the thrust front that separates Adria–Apulia from Eurasia. It is notable that there is a 123 ns yr−1 active shortening of the crust between the GNSS stations DUR2-TIR2 (equivalent to a shortening rate of 3.6 mm yr−1), and roughly in the east–west direction. Given this amount of strain the recurrence time of M6+ earthquakes along this fault should be of the order of 150 years.
1. Introduction
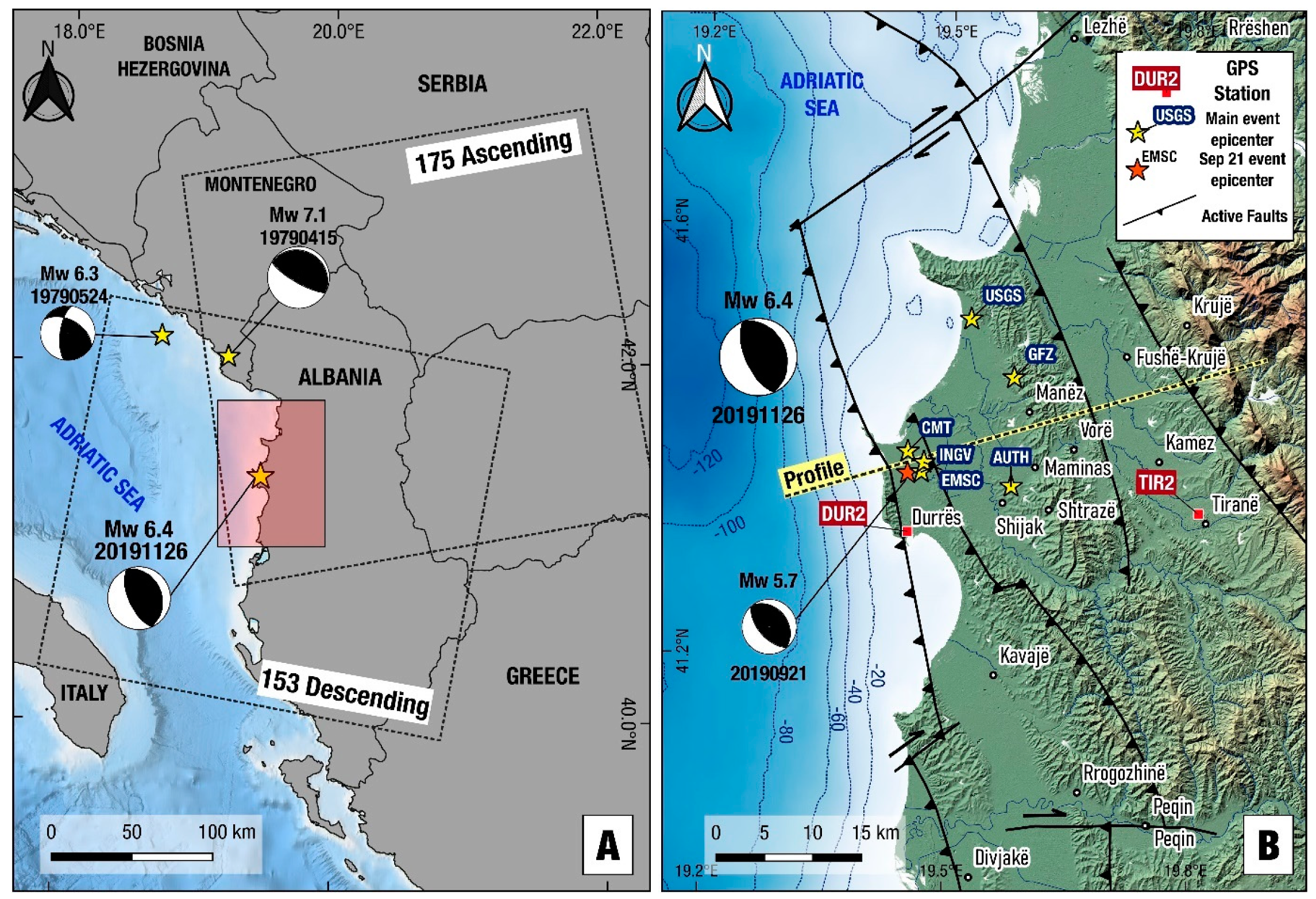
The tectonics of western and northern Albania are characterised by on-going compression due to collision between the Eurasian plate and the Adriatic block. Crustal deformation is characterised by shortening directed in a NNE–SSW to E–W orientation ([1,2,3,4,5,6]; Figure 1a). Geological data indicate that the region between Tirana and Durrës (Figure 1b) is the site of Neogene thrusting and folding [7,8,9]. The main thrusts are west-directed [10,11] while the thrust front is dextrally offset along two NE–SW transfer zones, the “Scutari-Pec” [11,12] ~60 km north of Tirana (near the town of Lezhe; Figure 1b) and the Elbasan-Vlora Transfer Zone [8] ~30 km south of Tirana. The inferred trace of the main basal thrust of Eurasia over Apulia (that is part of the Dinaric–Hellenic orogen) passes through Durrës with a general NNW–SSE orientation ([8]; their Figure 11b). Several west-verging reverse faults are reported [8] on an E–W geological cross-section to offset Pliocene–Miocene sediments near Tirana with significant cumulative displacements (1–2 km). The tectonic strain rate was estimated at 30–40 ns yr−1 of contraction [5,6] for north-central Albania which is comparable to other active areas of the peri-Adriatic, such as the south Apennines, as well as with areas in northern Greece such as Khalkidhiki [4].
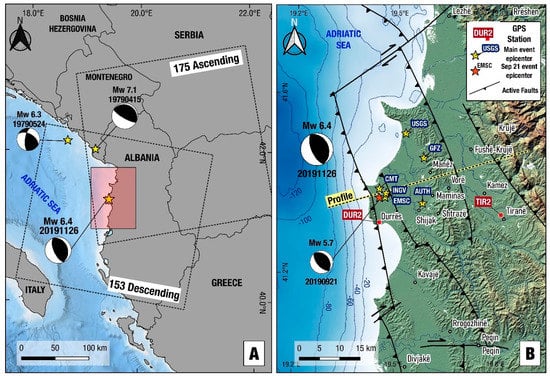
Figure 1.
(A) Map of the south Adriatic Sea—Albania showing extent of Sentinel-1 satellite frames. Adriatic Sea bathymetry data from https://www.emodnet-bathymetry.eu/. Beachballs indicate the focal mechanisms of recent strong, shallow earthquakes [14]; USGS, Table 2; compressional quadrants are shaded in black). Shaded rectangle indicates study area shown in 1b. (B) Relief map of the Durres–Tirana area in central-western Albania showing main geological structures (thrust faults; ticks on the upthrown side), epicentre (yellow stars) determined by various agencies and Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) stations that recorded the earthquake. Beachball indicates the United States Geological Survey (USGS) focal mechanism of the Nov. 26, 2019 earthquake. Red star indicates the European Mediterranean Seismological Centre (EMSC) epicentre of the September 21, 2019 Mw = 5.7 earthquake (Focal mechanism from USGS). Fault lines are from [22]. Yellow line indicates the profile in Figure 6.
The most significant earthquake of the recent history was the April 15, 1979 Mw = 6.9 “Montenegro” earthquake ([13]; Figure 1a) that occurred ~100 km towards the north of Durrës on a very low-angle (14°) thrust fault dipping towards the northeast [1,14]. On November 16, 1982, a Mw = 5.6 thrust faulting earthquake on a low angle fault (27°) event occurred to the SW of Tirana [1]. The Mw = 6.4 November 26, 2019 02:54 UTC earthquake ruptured another reverse fault near the city of Durrës [9,15,16,17,18]; see supplementary Figure S1 for a map with published moment tensors). Its centroid was determined in the range 6–26 km (Table 1; locations and magnitudes from the sources 1–7). The magnitude of the main aftershock (occurred on 06:08 UTC on the same day) was Mw = 5.4 according to the European Mediterranean Seismological Centre (EMSC). By November 30th, the death toll reached 51, while several thousands of residents were left homeless [16]. Many buildings in Durrës were levelled and many more were dangerously damaged [19]. A horizontal peak ground acceleration (PGA) of 192 cm s−2 was recorded by a strong motion station in Durrës [20].

Table 1.
Determination of the parametric data of the Nov. 26, 2019 02:54 UTC earthquake by various agencies.
The November 26 Mw = 6.4 event of Durrës was preceded by a Mw = 5.7 that occurred on September 21, 2019 14:04 UTC, with the same type of reverse-faulting kinematics ([21]; Figure 1b). This foreshock caused limited liquefaction effects near Durrës and damage to buildings of Durrës, Tirana and several settlements of the broader area [21]. The geometry and kinematics of both ruptures are similar. The Mw = 6.4 event moment tensor solution (USGS; Table 2) shows a NNW–SSE fault plane with strike, dip and rake angles 338°/27°/92°. The Mw = 5.7 event moment tensor solution (USGS) shows a NNW-SSE fault plane with angles 323°/32°/93°.

Table 2.
Focal mechanism data for the 26 November 2019 Mw = 6.4 earthquake.
Table 2.
Focal mechanism data for the 26 November 2019 Mw = 6.4 earthquake.
| Institute | Mw | Μ0 | Depth | Strike | Dip | Rake | Strike | Dip | Rake | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (N m−1) | (km) | (°) | (°) | (°) | (°) | (°) | (°) | |||
| GFZ | 6.4 | 5.20 × 1018 | 26 | 151 | 72 | 89 | 335 | 18 | 94 | 1 |
| GCMT | 6.4 | 5.65 × 1018 | 24.1 | 145 | 68 | 79 | 351 | 25 | 114 | 2 |
| USGS | 6.4 | 4.56 × 1018 | 19.5 | 156 | 63 | 89 | 338 | 27 | 92 | 3 |
| CPPT | 6.4 | 5.08 × 1018 | 15 | 168 | 69 | 104 | 312 | 25 | 57 | 4 |
| INGV | 6.2 | 2.38 × 1018 | 21 | 134 | 82 | 84 | 350 | 10 | 126 | 5 |
| AUTH | 6.1 | 1.34 × 1018 | 6 | 150 | 49 | 109 | 303 | 44 | 69 | 6 |
Sources: 1. https://geofon.gfz-potsdam.de/old/data/alerts/2019/gfz2019xdig/mt.txt, 2. https://www.globalcmt.org/CMTsearch.html, 3. https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/eventpage/us70006d0m/moment-tensor, 4. https://www.emsc-csem.org/Earthquake/mtfull.php?id=807751andyear=2019;INFO, 5. http://cnt.rm.ingv.it/en/event/23487611/?tab=MeccanismoFocale#TDMTinfo, 6. http://geophysics.geo.auth.gr/ss/.
Here we use Sentinel-1 synthetic aperture radar interferograms, tied at the offsets measured at two permanent Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) stations, to infer the parameters of the seismic fault. Our best-fitting model is a low-angle reverse fault dipping at 23° towards the northeast. The centroid of this fault is located at a depth of 16.5 km on a structure that could be a decollement at the base of the brittle crust. This finding contributes to the understanding of the present tectonic processes in the Apulia–Eurasia collision zone.
2. Data and Methods
2.1. InSAR Data Processing
We used synthetic aperture radar interferometry (InSAR) to capture the deformation produced by the Durrës earthquake (Figure 2). In the Mediterranean, InSAR is systematically used to map the ground deformation produced by large earthquakes after removing the signal from the topography (e.g., [23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31]) and minimising the tropospheric noise.
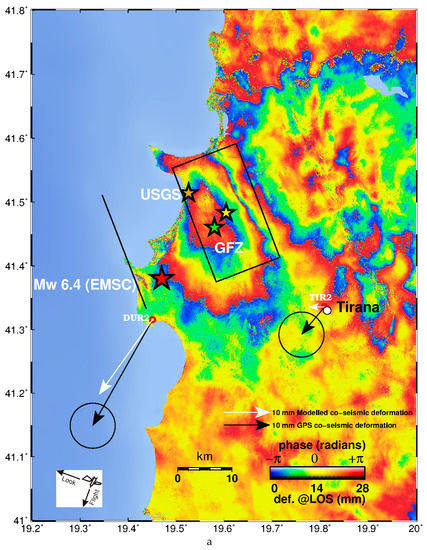
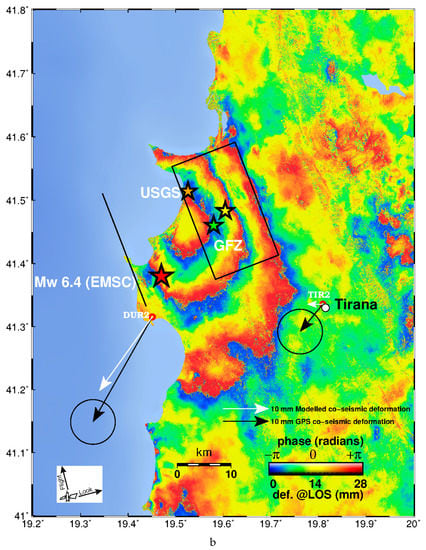
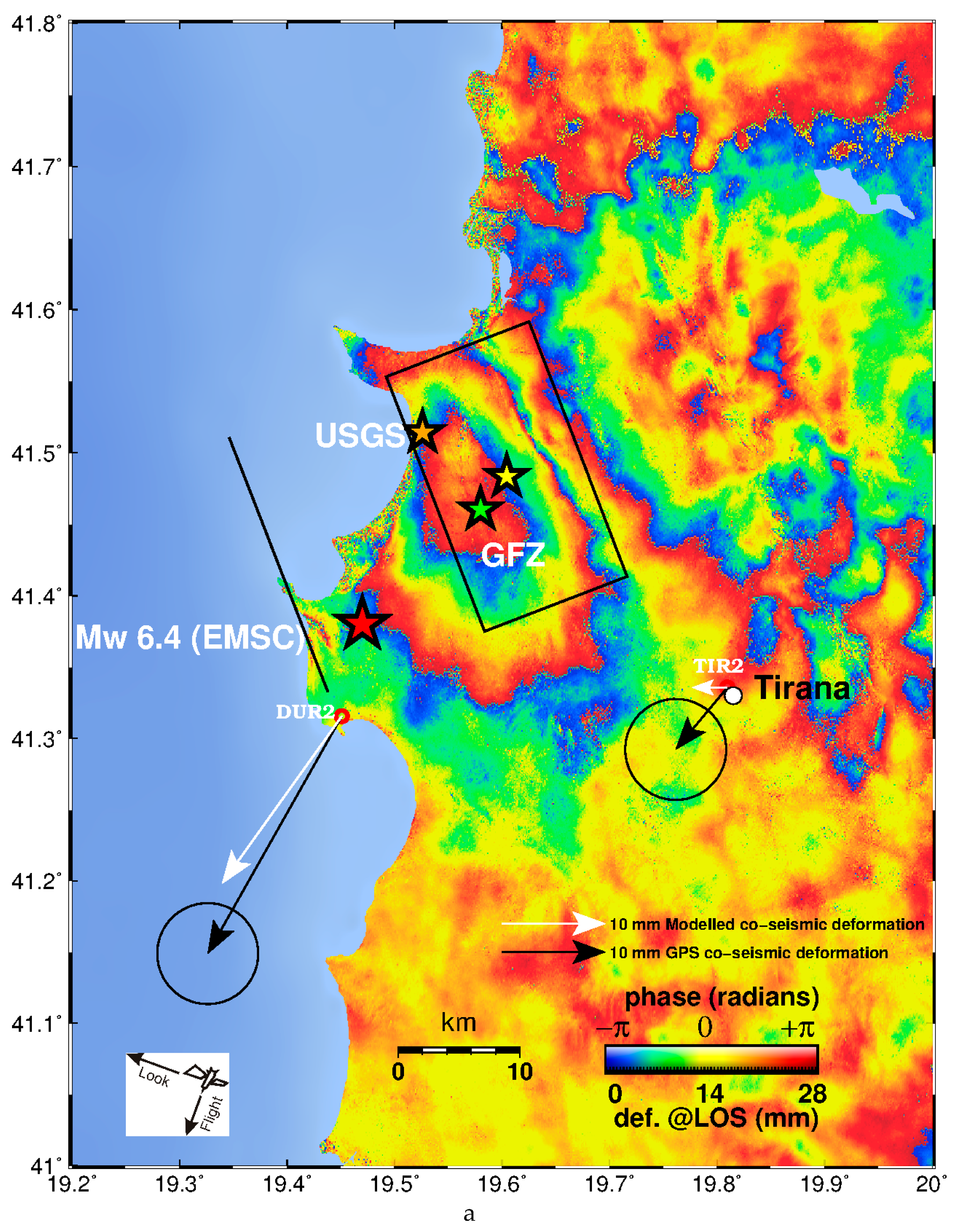
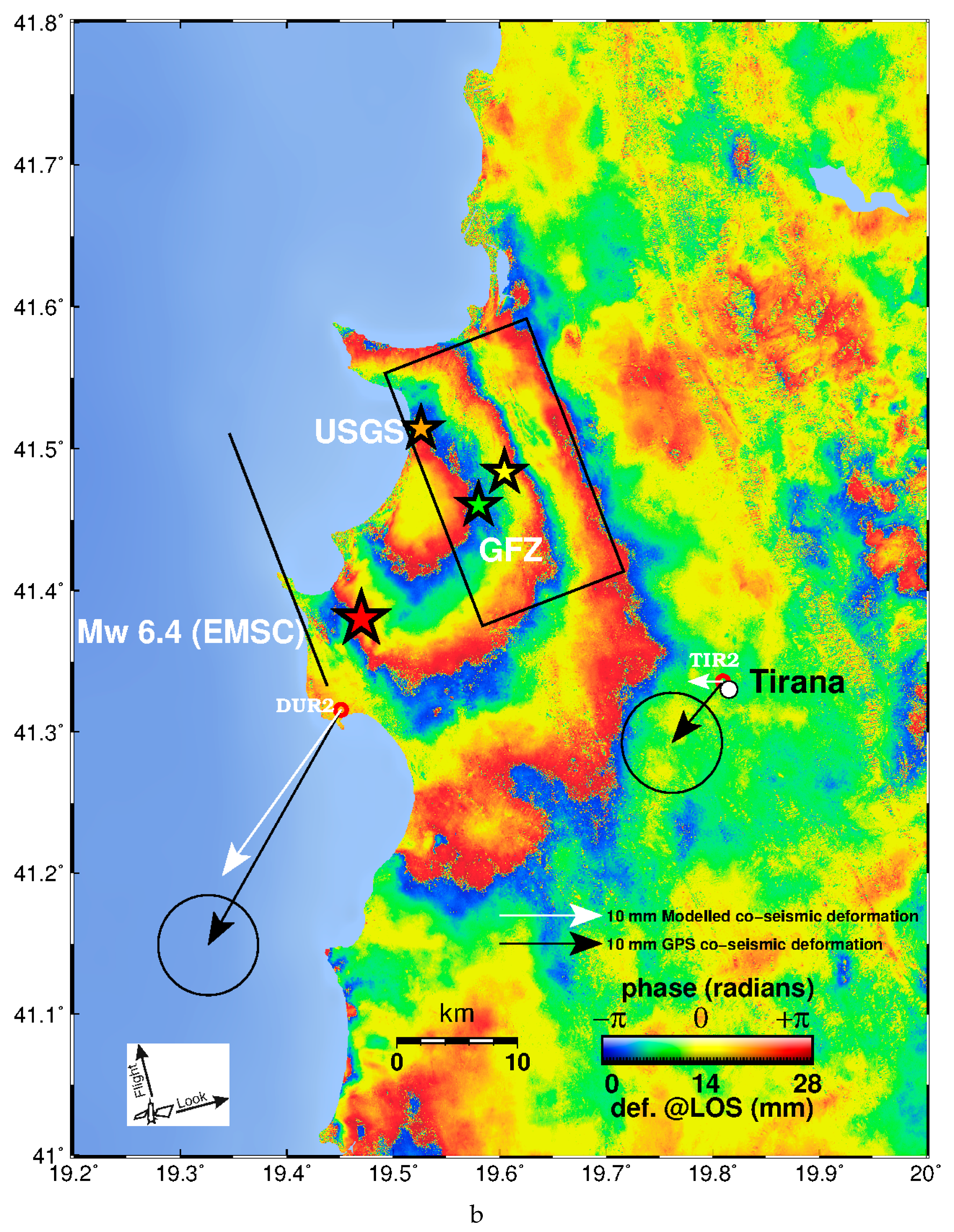
Figure 2.
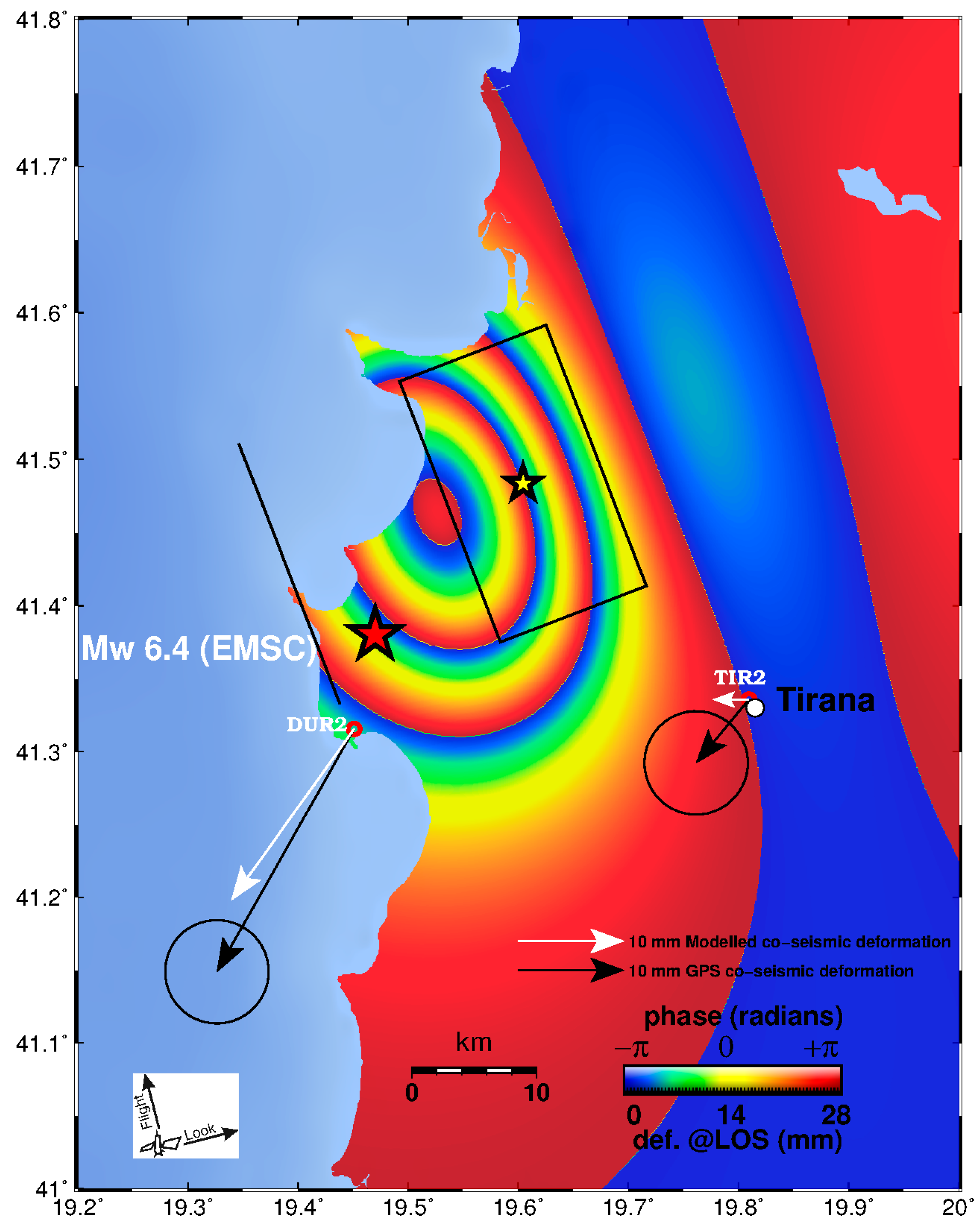
(a). Sentinel-1 wrapped interferogram descending track 153 (acquisition dates 20191125–20191201). Yellow star indicates the location of the geodetic centroid (this study). Black rectangle shows the surface projection of the seismic fault. Solid black line indicates fault plane intersection to the Earth’s surface. The red star indicates the earthquake epicentre (EMSC location), orange and green stars USGS and German Research Centre for Geosciences (GFZ) epicentres, respectively. The vector pairs represent the GPS measured (black) and modelled (white) co-seismic horizontal displacements at stations DUR2 and TIR2 respectively (see Table 3 for values). (b). Sentinel 1A wrapped interferogram ascending track 175 (acquisition dates 20,191,120 and 20,191,126 16:32 UTC). Yellow star indicates the location of the geodetic centroid (this study). Black rectangle shows the surface projection of the seismic fault. Solid black line indicates fault plane intersection to the Earth’s surface. The red star indicates the earthquake epicentre (EMSC location). The vector pairs represent the Global Positioning System (GPS) measured (black) and modelled (white) coseismic horizontal displacements at stations DUR2 and TIR2 respectively (see Table 3).
We processed Sentinel-1 Interferometric Wide (IW) acquisitions from ascending and descending orbits, tracks 175 and 153, respectively. We used the open-source SNAP v7.0 ESA software [32], implemented in an offline version of Automated Interferogram Processing Station (AIPS, http://aips.space.noa.gr) and the online facilities of the GEP-TEP (Geohazards Exploitation Platform -Thematic Exploitation Platform; http://geohazards-tep.eu). For the ascending track we use the data acquired on November 14 and 26 (16:32 UTC), and for the descending track those acquired on November 25 and December 1, 2019.
The two interferograms provided a measurement of the ground motion along two opposite line of sights (LOS; Figure 2a,b). The digital elevation model (DEM) used for the processing is the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) 1 Arc-Second Global ([33]; Digital Object Identifier number:/10.5066/F7PR7TFT). We enhanced the signal to noise ratio by applying the adaptive power spectrum filter of [34] with a window size of 3, Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) size of 64 and a coherence threshold of 0.2.
The existence and amplitude of tropospheric disturbances in InSAR can be partly assessed by looking at single interferograms. This is because the tropospheric effect (signal delay) can be separated in two components: one correlated with the topography and the other not correlated. In the case of our interferograms (Figure 2) we could find no correlation with topography. The estimated amplitude of the tropospheric noise at short spatial wavelengths (0.5–5 km) is low, below a quarter of a fringe. There are three fringes well visible in the ascending interferogram and two in the descending one, aligned in an area of ~40 km elongated NW–SE north of Durrës, mostly on-shore along the coastal plain (Figure 1 and Figure 2). The maximum ascending LOS change is ~8.4 cm towards the satellite.
Four moderate magnitude aftershocks (up to M = 5.4; EMSC magnitudes https://www.emsc-csem.org/Earthquake/europe/M5/) occurred in the 36-h period following the mainshock; they did not affect the deformation signal as all those events occurred relatively deep (the GFZ moment tensor solutions for two aftershocks indicate depths comparable to that of the mainshock; ~26 km) and with moderate magnitudes. We generated additional interferograms for the postseismic period (up to December 14, 2019), in order to clarify any possible impact on the estimated deformation. However, no postseismic deformation was detected (see supplementary Figure S2). We also processed Sentinel 1 interferometric pairs for the foreshock of September 21, 2019 (Mw = 5.7) to investigate the source geometry and depth, but no ground displacements were detected either (see supplementary Figure S3).
2.2. GNSS Data Processing
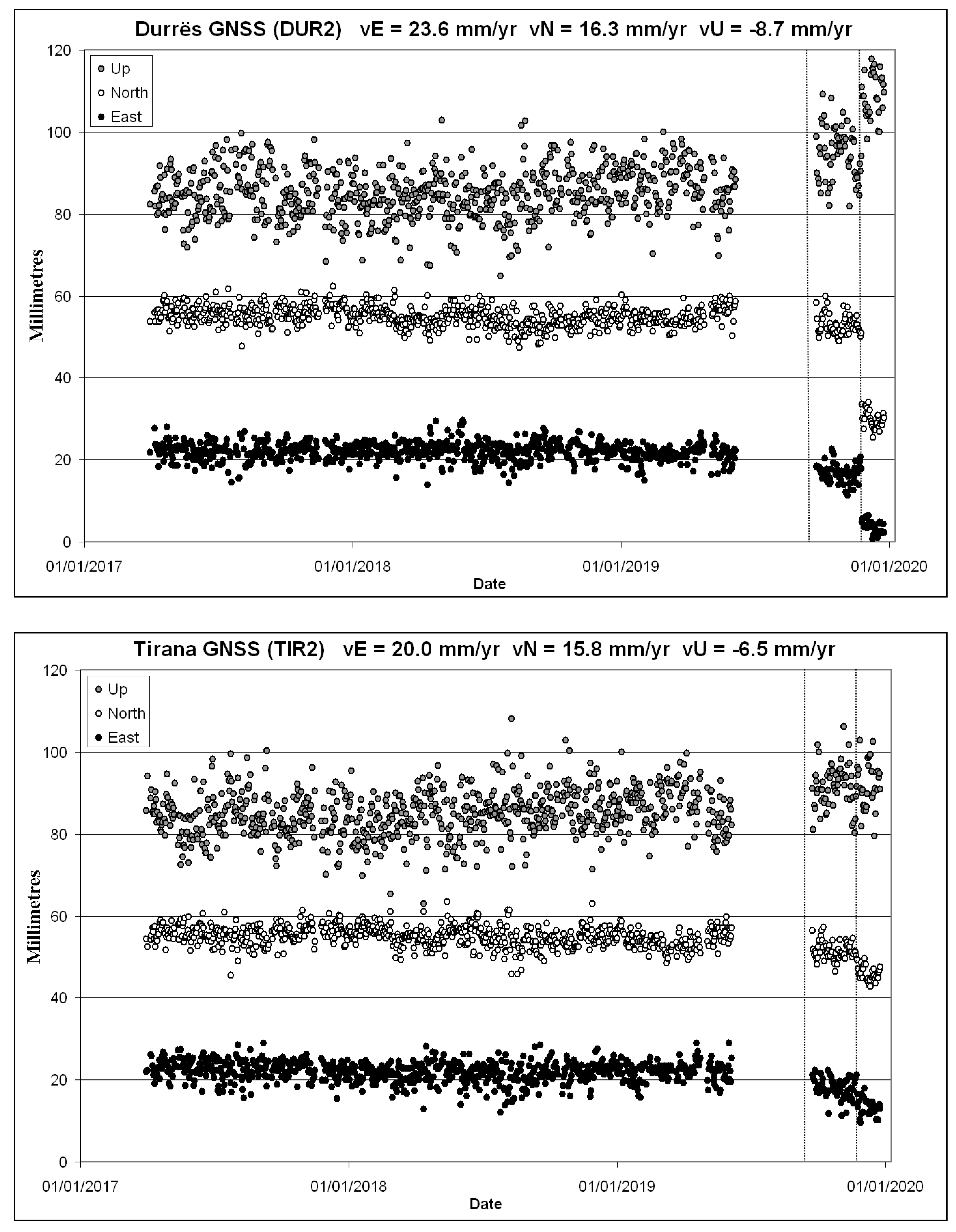
We analysed the GNSS data of the stations DUR2 (Durrës, 19.4510° E, 41.3156° N) and TIR2, (Tirana, 19.8095° E, 41.3357° N) both belonging to the Albanian Positioning Service (AlbPOS) geodetic network (http://www.geo/edu.al/gnss/albpos; see Figure 1b for locations). The processing was made with the Precise Point Positioning (PPP) strategy [35] by means of the GIPSY/OASIS II software (ver. 6.4) developed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL; http://gipsy-oasis.jpl.nasa.gov; [36]). We used the JPL final orbits (flinnR) and clocks, absolute antenna calibration, random walk troposphere estimation, and the FES2004 ocean loading model. We calculated the static offsets for both September 21, 2019 and November 26, 2019 events (Table 3; Figure 3, vertical lines indicate timing of earthquakes). The offsets indicate mm/cm size motion towards west, south and upwards (i.e., uplift), for both events. Regarding the large aftershock on Nov. 26, 2019 06:08:25 UTC (M = 5.4), we could not see any evidence of this aftershock in the GNSS time series. Furthermore, the GNSS time series show no evidence of fast postseismic motion in the days following the mainshock (Figure S4). This indicates that the interferograms (Figure 2) correspond to the coseismic displacements only and are not biased by postseismic motion signals.

Table 3.
Co-seismic displacements produced by the September 21, 2019 and November 26, 2019 earthquakes at the AlbPOS GNSS stations DUR2 and TIR2 (Figure 1b).
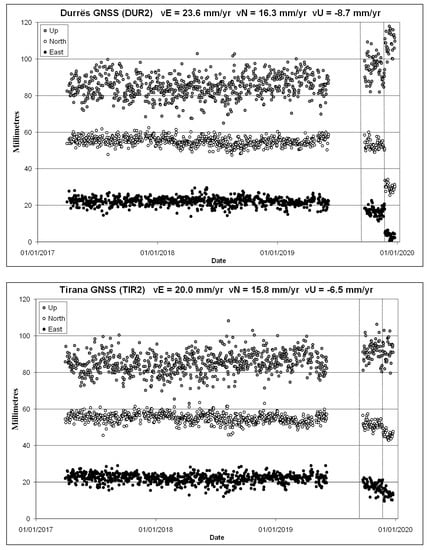
Figure 3.
GNSS time series (Up, North, East component from top to bottom series) at the permanent stations of Durrës (DUR2; top panel) and Tirana (TIR2; bottom panel). The figure shows the residuals after removing the tectonic velocities that are also estimated. The offsets produced by the two earthquakes of September 21, 2019 and November 26, 2019 are visible and can be measured (see Table 3). Vertical lines indicate timing of earthquakes.
The time series of coordinates are plotted in Figure 3 (a zoom on the week before and after the mainshock is presented in supplementary Figure S4). The long-term velocities, in the reference frame ITRF2014, are 23.6 ± 0.3 mm yr−1 in east and 16.3 ± 0.3 mm yr−1 in north at Durrës and 20.0 ± 0.3 mm yr−1 and 15.8 ± 0.3 mm yr−1 at Tirana. Therefore, the net motion of DUR2, assuming TIR2 fix, is 3.6 ± 0.5 mm yr−1 of shortening in the azimuth N80° E. It is notable that there is a 123 ns yr−1 active shortening of the crust between the two GNSS stations located at 30 km one to the other, and roughly in the east-west direction. This 1-D estimate of tectonic strain is about 2.4 larger than the 2-D estimates from regional studies (e.g., 30–40 ns yr−1, [5,6]). In addition, both GNSS stations exhibit long-term subsidence of −8.7 and −6.5 mm yr−1 respectively (Figure 3), presumably due mostly to anthropogenic reasons. The displacements and uncertainties retrieved from the analysis of the time series are reported in Table 3.
The LOS-projected (ascending and descending) motions measured at DUR2 for the November 26, 2019 event are used to give an absolute reference to the ascending and descending interferograms shown before (Figure 2). This absolute tie to GNSS is crucial for the inversion made in the next section. The LOS unit vector [East North Up] used is [−0.52 −0.12 0.84] and [0.63 −0.14 0.77], for the ascending and descending track, respectively.
3. Inversion of the Geodetic Data
Assuming a half-space elastic model with uniform slip along a rectangular fault surface, the source of the ground deformation was inverted using the InSAR data and the code inverse6 [37]. We fed the inversion with 104 LOS measurements that were picked manually on the interferograms (Figure 2), 52 points on the ascending and 32 for descending track.
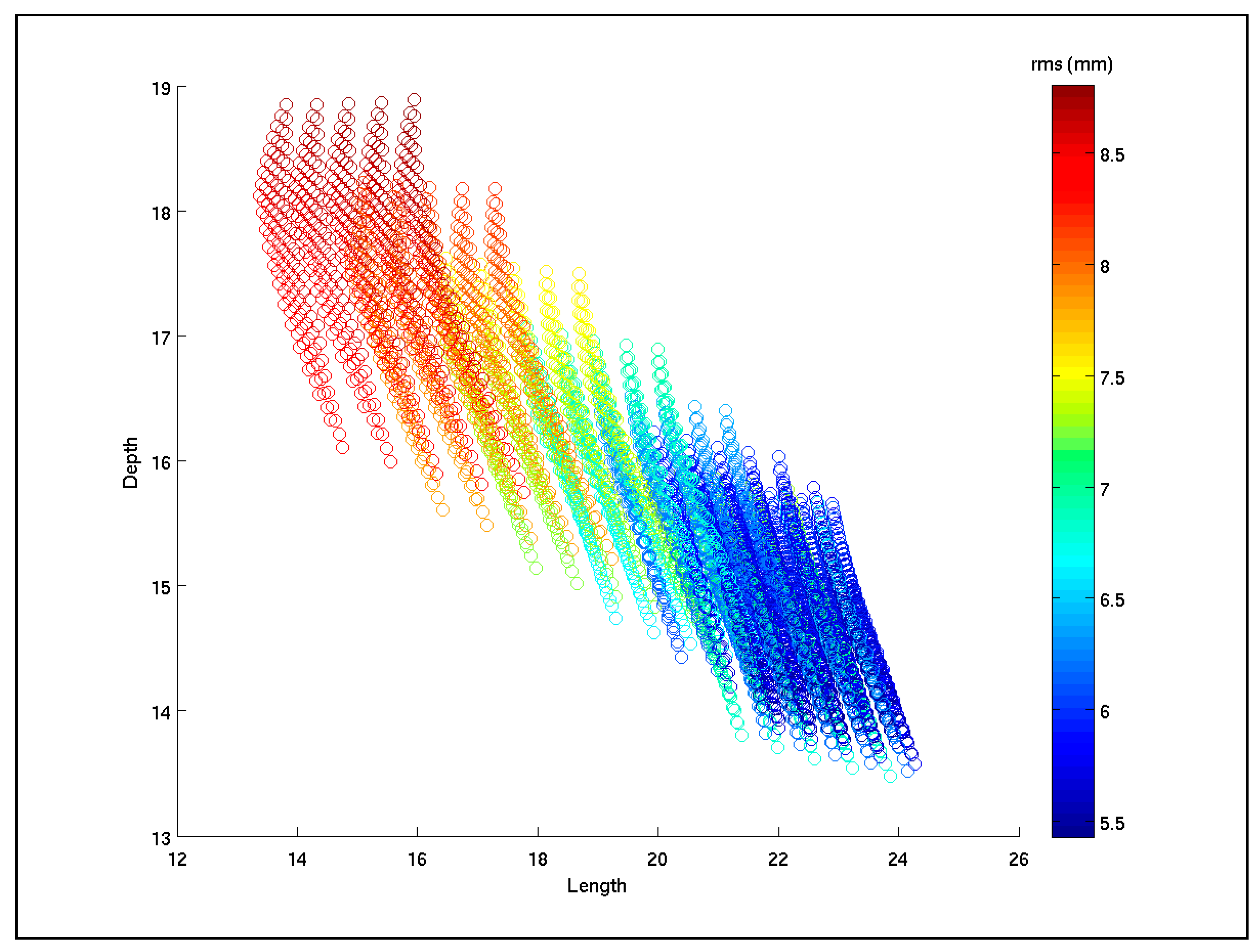
Taking various initial conditions compatible with the fault planes inferred from the seismological centres, we performed 6500 inversions. Those inversions define a stable and robust solution with root mean square (r.m.s.) residual of 5.4 mm thus ~1/5 of a fringe. The parameters of the best-fitting solution are in the Table 4. Table 4 also contains the uncertainties on the parameters of our final best-fitting fault model. The inversion result for depth to top-fault vs. fault length is shown in Figure 4 which is tailored to appreciate visually the range of values (and thus uncertainties) of the parameter couple: top-fault depth-fault length. All inversion results are included in supplementary Figure S5. In Figure S6 it is shown the fit only at the picked points of the modelled and measured displacements in the LOS, along with the r.m.s. misfit, which is 3.3 mm and 8.1 mm for the ascending and descending track respectively.

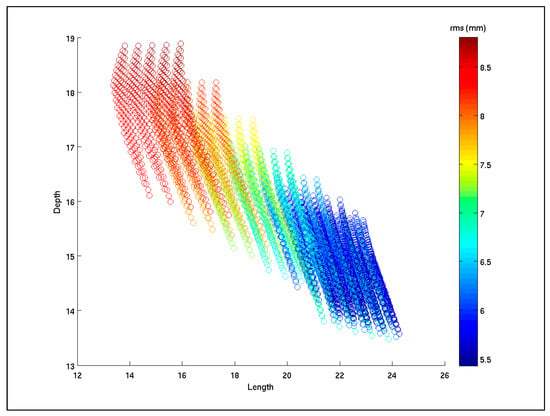
Figure 4.
Diagram of depth (of the top-edge of the fault; Y-axis) versus fault length (X-axis), with the values of root mean square (r.m.s.) error in colour of the inversions output (see vertical scale bar). The inversion series is converging to the lowest r.m.s. at a depth of 14 km and length of 22 km.
Our modelling demonstrates that the earthquake occurred deep in the crust on a low-angle reverse fault (23°) dipping towards east with centroid at 16.5 km depth. The best-fitting length and width of the fault are 22 and 13 km and the reverse slip 0.55 m (Figure 5). Assuming a medium rigidity of 3.3 × 1010 Pa, the seismic moment deduced from our model, 5.19 × 1018 N m−1, is closer to GFZ’s published seismic moment tensor (Table 2). The modelling also indicates that the top of the fault plane is buried at a depth of ~14 km, so there was no rupture in the shallow crust above that depth.
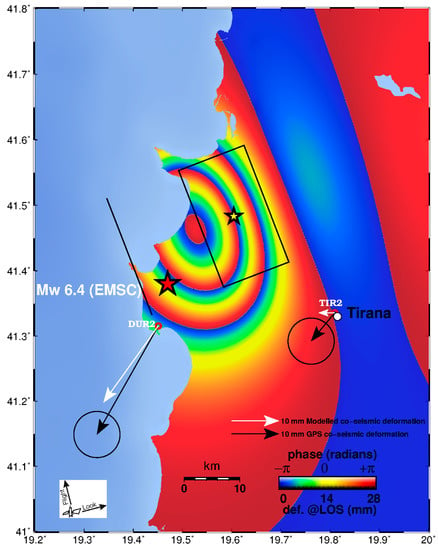
Figure 5.
Synthetic interferogram of the ascending track 175 using the fault parameters of Table 4. Yellow star indicates the geodetic centroid. Black rectangle shows the surface projection of the seismic fault. Solid black line indicates projected fault plane intersection (fault trace) at Earth’s surface. The red star indicates the earthquake epicentre (EMSC location). The vector pairs represent the GPS measured (black) and modelled (white) coseismic horizontal displacements at stations DUR2 and TIR2 respectively.
The geodetic fault-model is in agreement with published moment tensor solutions showing a NNW–SSE fault plane (see Table 2). The geodetic centroid is located ~15 km to the NE of the EMSC epicentre but a few km away from either the USGS or the GFZ epicentre (Figure 1b; Figure 2). The inferred fault geometry (see Figure 5 for a surface projection) is compatible with a blind thrust fault rooting on the main basal thrust front that separates Adria–Apulia from Eurasia.
4. Discussion
4.1. Geodetic Determination of Earthquake Parameters
Our modelling shows that the November 26, 2019 EMSC epicentre must be shifted by 15 km to match the geodetic data (see Figure 1b and Figure 5 for locations; the same distance holds for epicentres determined by CMT and INGV; see Figure 1b). On the other hand, the USGS epicentre is located about 7 km NW of the geodetic centroid and the GFZ epicentre about 3 km to the SW, respectively. We note that such shifts between the geodetic solution and the EMSC solution (among others) has been observed for several large earthquakes that occurred along the eastern Ionian coast in the recent years, i.e., the Cephalonia doublet 2014 [26], Lefkada 2015 [30] and Zakynthos 2018 [38]. This systematic shift might be primarily due to the velocity model used for the Ionian Sea and Adriatic area by some seismological agencies.
Like in all elastic models, we cannot solve independently all parameters of the modelled fault. In particular, there is a strong trade-off between fault width and amplitude of slip, and between fault azimuth and rake. In our case fixing the rake at 90° (based on the seismic moment tensors; Table 2) has a direct impact on the azimuth of the modelled fault. The fact that our modelled azimuth is consistent with the azimuth of the geological structures (Figure 1b; Figure 6) supports the reliability of our approach.
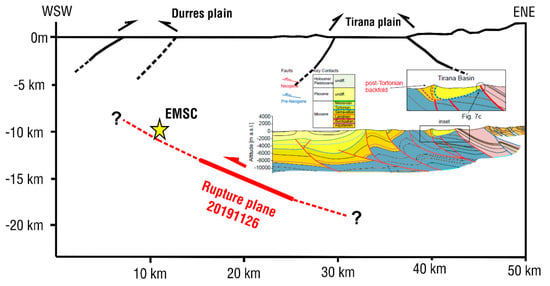
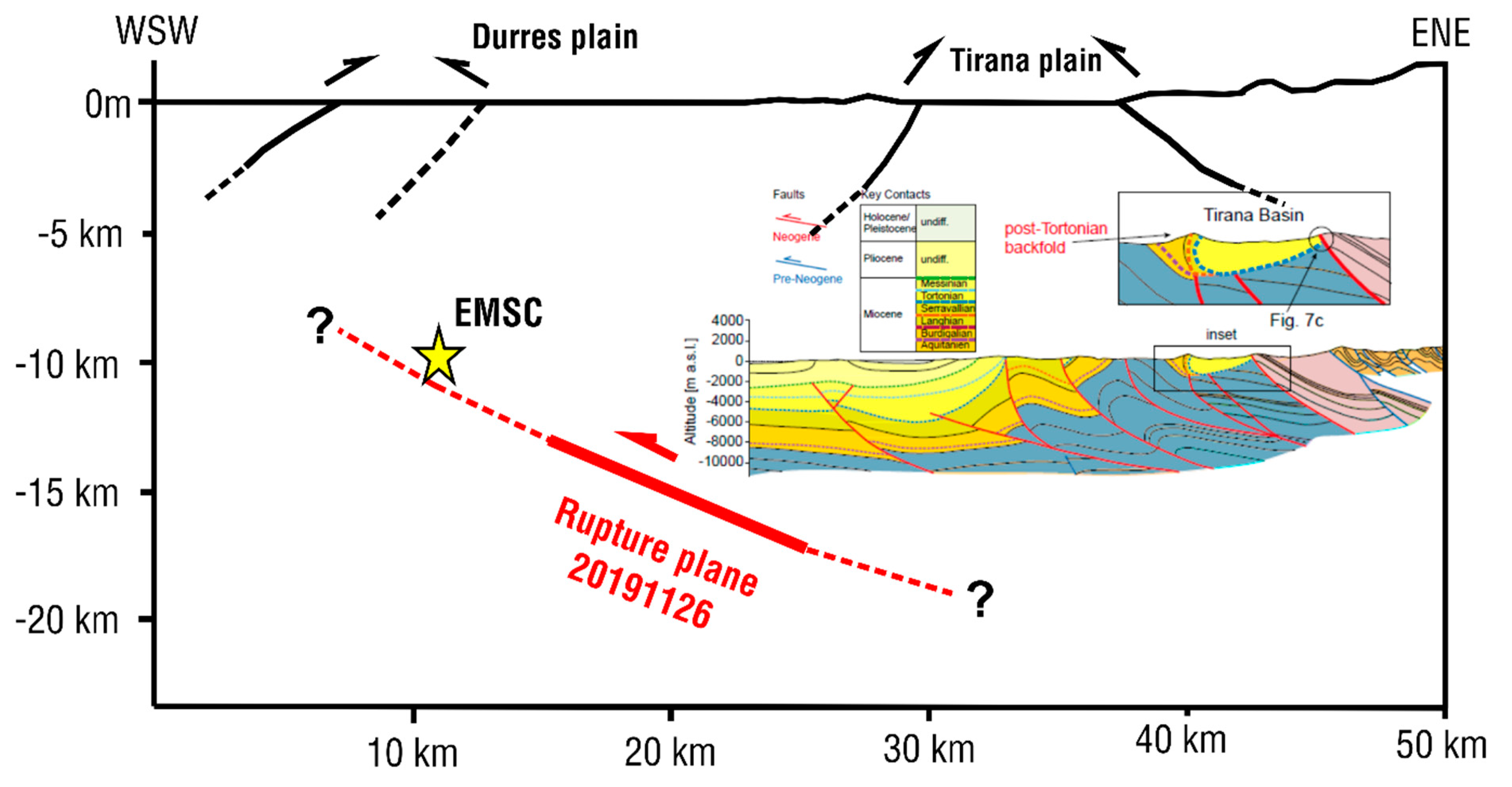
Figure 6.
Schematic cross section across the strike of the seismic fault of the November 26, 2019 earthquake. The inferred fault plane is indicated by the red line (half arrow denotes motion of the hanging wall of the fault). Inset profile shows geological structure [8]. No vertical exaggeration. The trace of the section is noted in Figure 1b.
Our fault model also indicates that the 8 ± 2 km depth proposed by [17] for the hypocentre is not supported by the geodetic data.
We emphasize the useful role of station DUR2 and, more generally, the importance of the presence of GNSS stations with a sufficient density to give control and absolute scale to InSAR data. In the case of the Durrës earthquake, one or two more permanent stations to the north and east of the geodetic centroid would have provided great added value for the near real-time determination of the fault location. GNSS and InSAR are valuable sources of displacement data. The real challenge now is to use them jointly more and more efficiently and quickly.
4.2. Tectonic Strain and Earthquake Recurrence
With GNSS data, we were able to estimate crustal shortening between Durrës and Tirana. This shortening amounts to 3.6 ± 0.5 mm yr−1 of 1-D strain in the azimuth N80° E. Such a large shortening rate in a small band of crust (about 30 km) and if the decollement at depth (active in that event) represents the main boundary of the blocks (i.e., the basal thrust), then we may be able to estimate earthquake recurrence along the seismic fault of November 26, 2019. Assuming a uniform slip of 0.55 ± 0.1 m that is released periodically (assuming full locking and uniform loading rates), then the recurrence time of M6+ earthquakes would be on the order of 152 ± 10 years (i.e., the amount of co-seismic slip of the event divided by the shortening rate). Further, assuming that shortening strain in the region between Durrës and Tirana is accommodated by two reverse faults (i.e., the 2019 seismic fault and its probable continuation toward south) then the mean recurrence time of a M6+ event would be in the range 70–80 years. We note that a strong M = 6.1 earthquake is reported on December 12, 1926 ([39]; 93 years ago) for the region of Durres with an elliptical isoseismal pattern (long-axis oriented NW–SE).
Using the fault model parameters (Table 4) we drew a cross section (1:1) along the direction ENE–WSW passing through Durrës and the surface projection of the east-dipping seismic fault. We then positioned the inferred seismic fault with its top near the depth of 14 km and its bottom near the depth of 18 km. We also projected the EMSC epicentre to show its position with respect to the inferred fault plane. The geometry of the inferred fault and its kinematics (reverse-slip) match the tectonic style for the region Durrës—Tirana ([8]; see inset geological profiles in Figure 6). The geological structure is interpreted as a result of Neogene thrusting and folding with west-directed shear indicators [8]. N-S to NW-SE oriented synclines, anticlines and thrust faults have been mapped in central Albania between Durrës and Tirana [7] and published cross sections (Figure 6 inset) depict series of E-dipping late Neogene thrusts at depths down to 10 km. It is therefore reasonable to suggest that the November 26, 2019 earthquake ruptured a basement reverse fault along the Neogene thrust front.
4.3. GNSS Magnitude of Durres Earthquake
A series of studies [40,41,42,43] produced GNSS peak-ground displacement (PGD) scaling laws and proposed algorithms for their real-time use as an unsaturated and reliable estimator of earthquake magnitude. One of them [42] modelled the magnitude scaling properties of peak ground horizontal displacements (PGD and PGD-S) for strong earthquake events using L1-norm minimisation regression. In this study we use only horizontal offsets at the two GNSS stations (DUR2 and TIR2; Figure 3, Figure S4) to calculate the GNSS magnitude of this earthquake. We used the coseismic offsets of Table 3 and the geodetic centroid location calculated by the inversion model (41.483° N, 19.604° E, 16.5 km depth; Table 4). The PGD formulas are defined as [42]:
PGD = (|AN-S| + |AE-W|)/2
PGD-S = (AN-S2 + AE-W2)1/2
Therefore, PGD is the mean value of the absolute horizontal displacement in two orthogonal directions (i.e., E-W, N-S; in cm), while PGD-S is the resultant horizontal displacement (in cm).
Plugging the relevant values to the PGD scaling laws (empirical Equations (3) and (4) below) that were proposed by [42] for the Aegean region, then we obtain a moment magnitude Mw(PGD) = 6.44 and Mw(PGD-S) = 6.42 assuming a hypocentral distance (R) of 27.957 km to the GNSS station DUR2 (Table 5).
MwPGD = [LOG(PGD) + 8.2849]/(1.6810 − 0.2453 × LOG(R))
MwPGD-S = [LOG(PGD-S) + 8.0839]/(1.6793 − 0.2447 × LOG(R))

Table 5.
Estimation of earthquake magnitude for the 2019 Durrës earthquake using the GNSS static offset data. PGD/PGD-S is in cm, R is in km. The magnitudes were calculated using the empirical relationships [42] of Equation (3) (PGD) and Equation (4) (PGD-S). R is the source (centroid) to station distance.
For station DUR2 the magnitude difference (ΔM) or Mw(seismology)—Mw(GNSS) is less than or equal to 0.04 units using the PGD/PGD-S approach [40,41,42,43]. There is a deviation observed in the case of station TIR2, where the estimated magnitude from GNSS is 6.07 (Table 5; PGD relationship) or 6.03 (PGD-S relationship), i.e., it is underestimated by 0.33–0.37 units of magnitude. The reason for this underestimation may be (a) the azimuthal distribution of the two GNSS stations with respect to the direction of seismic slip (assuming a rake of 90° the slip vector is directed towards N250° E, i.e., towards the west or the city of Durrës; Figure 5) and/or (b) the uneven distribution of the thick pile of sedimentary rocks in central Albania (including several km of Triassic evaporites) that may differently attenuate seismic energy at both stations.
5. Conclusions
- We identify the main source of the Mw = 6.4 earthquake that rocked north-central Albania on November 26, 2019 to be located within the frontal area of the basal thrust of the Dinaric–Hellenic orogen.
- We modelled the seismic fault by combining the ascending and descending Sentinel observations. Mixing ascending and descending orbits provides a more robust solution. We find that we can model the overall fringe pattern by reverse slip on an east-dipping fault. The fault plane is a low-angle thrust fault (22 by 13 km) that dips towards the east (23°).
- The inversion of geodetic data suggests that the upper edge of the fault is at a depth of 14 km, well constrained by the modelling of the interferograms.
- Geodetic data GNSS and InSAR (Figure 2) show ground motion to the southwest and surface uplift in agreement with moment tensor solutions from seismology.
- The epicentre published by EMSC is located 15 km southwest of the one deduced from geodesy, this might be due to insufficient inaccuracy of the velocity model of the crust beneath the Adriatic.
- It is notable that there is a 123 ns yr−1 active shortening of the crust between the GNSS stations DUR2-TIR2 (equivalent to a shortening rate of 3.6 mm yr−1), and roughly in the east-west direction.
- Given this amount of strain the recurrence time of M6+ earthquakes along this fault should be of the order of 150 years.
- The GNSS-derived magnitude in station DUR2 matches the moment magnitude from seismology to within 0.04 units.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3263/10/6/210/s1, Figure S1: EMSC map showing focal mechanisms published by various agencies (last accessed on May 11, 2020), Figure S2: Sentinel 1 wrapped interferogram tracks 153 (descending) and 175 (ascending) of the Durrës area showing no ground deformation during the postseismic period up to December 14, 2019, Figure S3: Sentinel 1 wrapped interferogram tracks 153 (descending) & 175 (ascending) of the Durrës area showing no ground deformation due to the Sept. 21, 2019 (Mw = 5.7) foreshock, Figure S4: Coseismic offsets at two GNSS stations (DUR2 & TIR2) at the East, North, Up components, respectively. Red dots represent the daily station position at each component. The station coordinates are approximately at: DUR2 (Lat. 41.3156°–Lon. 19.451°) and TIR2 (Lat. 41.3357°–Lon 19.8095°). Station locations are shown in Figure 1, Figure S5: Graphs showing inversion results for several fault parameters: (A) top-fault depth (km) (B) slip (m)—for reverse (C) length (km) and (D) width (km). Y-axis shows the r.m.s. misfit, Figure S6: Graphs showing fit of the modelling of the line-of-sight (LOS) displacements picked on the observed fringes, (a) for ascending track 175 and (b) for descending track 153.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: A.G. and P.B., Methodology: A.G., P.E. and P.B., Software: P.E., P.B., F.C. and V.T., Formal analysis: P.E. and P.B., Investigation: A.G. and S.V., Data curation: V.T. and E.I.P., Writing—original draft preparation: all authors, Writing—review and editing: A.G. and P.B., Visualization: S.V. and P.E., Supervision: A.G., Funding acquisition: A.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by “HELPOS-Hellenic Plate Observing System” (MIS 5002697) which is funded by the Operational Programme “Competitiveness, Entrepreneurship and Innovation” (NSRF 2014-2020) and co-financed by Greece and the European Union (European Regional Development Fund).
Acknowledgments
We thank two anonymous reviewers for constructive reviews and Efthimios Lekkas, Mark Handy, Christian Beck, Efthimios Sokos, and Nikos Theodoulidis for discussions. We thank ESA, Geohazards Lab and Terradue for providing access to Geohazards Exploitation Platform (GEP) for InSAR cloud processing. GNSS data were provided by ALBPOS and IGEWE https://www.geo.edu.al/gnss/ The ALOS global digital surface model-30 m used in Figure 1 is available from https://www.eorc.jaxa.jp/ALOS/en/aw3d30/index.htm We thank the QGIS Development Team—Open Source Geospatial Foundation Project http://qgis.osgeo.org.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Baker, C.; Hatzfeld, D.; Lyon-Caen, H.; Papadimitriou, E.; Rigo, A. Earthquake mechanisms of the Adriatic Sea and Western Greece: Implications for the oceanic subduction-continental collision transition. Geophys. J. Int. 1997, 131, 559–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louvari, E.; Kiratzi, A.; Papazachos, B.; Hatzidimitriou, P. Fault-plane Solutions Determined by Waveform Modeling Confirm Tectonic Collision in the Eastern Adriatic. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2001, 158, 1613–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouanne, F.; Mugnier, J.-L.; Koçi, R.; Bushati, S.; Matev, K.; Kuka, N.; Shinko, I.; Kociu, S.; Duni, L. GPS constraints on current tectonics of Albania. Tectonophysics 2012, 554, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérouse, E.; Chamot-Rooke, N.; Rabaute, A.; Briole, P.; Jouanne, F.; Georgiev, I.; Dimitrov, D. Bridging onshore and offshore present-day kinematics of central and eastern Mediterranean: Implications for crustal dynamics and mantle flow. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2012, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Métois, M.; D’Agostino, N.; Avallone, A.; Rabaute, A.; Duni, L.; Kuka, N.; Koçi, R.; Georgiev, I.; Chamot-Rooke, N. Insights on continental collisional processes from GPS data: Dynamics of the peri-Adriatic belts. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2015, 120, 8701–8719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, N.; Métois, M.; Koci, R.; Duni, L.; Kuka, N.; Ganas, A.; Georgiev, I.; Jouanne, F.; Kaludjerovic, N.; Kandić, R. Active crustal deformation and rotations in the southwestern Balkans from continuous GPS measurements. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2020, 539, 116246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xhomo, A.; Nazaj, S.; Nakuci, V.; Yzeiraj, D.; Lula, F.; Sadushi, P. Geological Map of Albania (1:200.000); Ministry of Industry and Energy, Ministry of Education and Science, Albanian Geological Survey, AlpPetrol, Polytechnical University of Tirana: Tirana, Albania, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Handy, M.R.; Giese, J.; Schmid, S.M.; Pleuger, J.; Spakman, W.; Onuzi, K.; Ustaszewski, K. Coupled Crust-Mantle Response to Slab Tearing, Bending, and Rollback Along the Dinaride-Hellenide Orogen. Tectonics 2019, 38, 2803–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handy, M.R.; Schmid, S.M.; Briole, P. The M 6.4 Albanian earthquake of Nov. 26, 2019 and its relation to structures at the Dinarides-Hellenides junctions. EGU Gen. Assem. 2020, 5409, 5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliaj, S.; Sulstarova, E.; Muço, B.; Koçiu, S. Seismotectonic Map of Albania, at Scale 1:500.000; Seismological Institute, Academy of Sciences: Tirana, Albania, 2000; p. 297. [Google Scholar]
- Basili, R.; Kastelic, V.; Demircioglu, M.B.; Garcia Moreno, D.; Nemser, E.S.; Petricca, P.; Sboras, S.P.; Besana-Ostman, G.M.; Cabral, J.; Camelbeeck, T.; et al. The European Database of Seismogenic Faults (EDSF) Compiled in the Framework of the Project SHARE. 2013. Available online: http://diss.rm.ingv.it/share-edsf/doi:10.6092/INGV.IT-SHARE-EDSF (accessed on 9 May 2020).
- Aubouin, J.; Dercourt, J. Les transversales dinariques dérivent-elles de paléofailles transformantes? Comptes Rendus Académie Sci. 1975, 281, 347–350. [Google Scholar]
- Ambraseys, N.N.; Ciborowski, A.; Despeyroux, J. The Earthquake of 15 April in Montenegro; The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization: Paris, France, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Benetatos, C.; Kiratzi, A. Finite-fault slip models for the 15 April 1979 (Mw 7.1) Montenegro earthquake and its strongest aftershock of 24 May 1979 (Mw 6.2). Tectonophysics 2006, 421, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, G.; Agalos, A.; Carydis, P.; Lekkas, E.; Mavroulis, S.; Triantafyllou, I. The Destructive Earthquake (Mw6.4) of 26 November 2019 in Albania: A First Report. EGU Gen. Assem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekkas, E.; Mavroulis, S.; Papa, D.; Carydis, P. The November 26, 2019 Mw 6.4 Durrës (Albania) Earthquake; Newsletter of Environmental, Disaster and Crises Management Strategies: Athens, Greece, 2019; p. 15. ISSN 2653-9454. [Google Scholar]
- Caporali, A.; Floris, M.; Chen, X.; Nurçe, B.; Bertocco, M.; Zurutuza, J. The November 2019 Seismic Sequence in Albania: Geodetic Constraints and Fault Interaction. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganas, A. Co-seismic deformation and preliminary fault model of the M6.4 Durres (Albania) Nov. 26, 2019 earthquake, based on space geodesy observations. EGU Gen. Assem. 2020. Available online: https://www.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=2ahUKEwivotmMg8_pAhUUhZQKHQIEA4kQFjAAegQIAhAB&url=https%3A%2F%2Fmeetingorganizer.copernicus.org%2FEGU2020%2FEGU2020-8478.html%3Fpdf&usg=AOvVaw0OfVQKceWMZpL3K9PRsJfT (accessed on 25 May 2020).
- Mavroulis, S.; Lekkas, E.; Carydis, P.; Papa, D. Factors controlling building damage distribution of the November 26 Mw 6.4 Albania earthquake. EGU Gen. Assem. 2020, 2020–18616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duni, L.; Theodoulidis, N. Short Note on the November 26, 2019, Durrës (Albania) M6.4 Earthquake: Strong Ground Motion with Emphasis in Durrës City. EMSC on Line Report. Available online: https://www.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwjP2v6Nhs_pAhXOGaYKHfTWChIQFjAAegQIAxAB&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.itsak.gr%2Fuploads%2Fnews%2Fearthquake_reports%2FEQ_Albania_2019-11-26_M6.4.pdf&usg=AOvVaw3sWTWRshmwbW_G2Uct-M4e (accessed on 9 May 2020).
- Lekkas, E.; Mavroulis, S.; Filis, C.; Carydis, P. The September 21, 2019 Mw 5.6 Albania Earthquake; Newsletter of Environmental, Disaster and Crises Management Strategies: Athens, Greece, 2019; p. 13. ISSN 2653-9454. [Google Scholar]
- Piccardi, L.; Toth, L.; Vittori, E.; Aliaj, S.; Cello, G.; Cunningham, D.W.; Drakatos, G.; Gosar, A.; Herak, D.; Herak, M.; et al. A First Attempt at Compiling a Map of Active Faults of the Adria Region; Geophysical Research Abstracts: Vienna, Austria, 2007; Volume 9, p. 09228. Available online: https://www.bib.irb.hr/297056 (accessed on 25 May 2020).
- Kontoes, C.; Elias, P.; Sykioti, O.; Briole, P.; Remy, D.; Sachpazi, M.; Veis, G.; Kotsis, I. Displacement field and fault model for the September 7, 1999 Athens Earthquake inferred from ERS2 Satellite radar interferometry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 3989–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzori, S.; Manunta, M.; Fornaro, G.; Ganas, A.; Salvi, S. Postseismic displacement of the 1999 Athens earthquake retrieved by the Differential Interferometry by Synthetic Aperture Radar time series. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2008, 113, 09309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzori, S.; Hunstad, I.; Chini, M.; Salvi, S.; Tolomei, C.; Bignami, C.; Stramondo, S.; Trasatti, E.; Antonioli, A.; Boschi, E. Finite fault inversion of DInSAR coseismic displacement of the 2009 L’Aquila earthquake (central Italy). Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briole, P.; Elias, P.; Parcharidis, I.; Bignami, C.; Benekos, G.; Samsonov, S.; Kyriakopoulos, C.; Stramondo, S.; Chamot-Rooke, N.; Drakatou, M.; et al. The seismic sequence of January–February 2014 at Cephalonia Island (Greece): Constraints from SAR interferometry and GPS. Geophys. J. Int. 2015, 203, 1528–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ilieva, M.; Briole, P.; Ganas, A.; Dimitrov, D.; Elias, P.; Mouratidis, A.; Charara, R. Fault plane modelling of the 2003 August 14 Lefkada Island (Greece) earthquake based on the analysis of ENVISAT SAR interferograms. Tectonophysics 2016, 693, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, G.A.; Ganas, A.; Agalos, A.; Papageorgiou, A.; Kontoes, C.; Diakogianni, G.; Papoutsis, I. Earthquake Triggering Inferred from Rupture Histories, DInSAR Ground Deformation and Stress-Transfer Modelling: The Case of Central Italy During August 2016–January 2017. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2017, 174, 3689–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgar, D.; Ganas, A.; Geng, J.; Liang, C.; Fielding, E.; Kassaras, I. Source characteristics of the 2015Mw6.5 Lefkada, Greece, strike-slip earthquake. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2017, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganas, A.; Elias, P.; Bozionelos, G.; Papathanassiou, G.; Avallone, A.; Papastergios, A.; Valkaniotis, S.; Parcharidis, I.; Briole, P. Coseismic deformation, field observations and seismic fault of the 17 November 2015 M = 6.5, Lefkada Island, Greece earthquake. Tectonophysics 2016, 687, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganas, A.; Elias, P.; Kapetanidis, V.; Valkaniotis, S.; Briole, P.; Kassaras, I.; Argyrakis, P.; Barberopoulou, A.; Moshou, A. The July 20, 2017 M6.6 Kos Earthquake: Seismic and Geodetic Evidence for an Active North-Dipping Normal Fault at the Western End of the Gulf of Gökova (SE Aegean Sea). Pure Appl. Geophys. 2019, 176, 4177–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veci, L.; Lu, J.; Prats-Iraola, P.; Scheiber, R.; Collard, F.; Fomferra, N.; Engdahl, M. The Sentinel-1 toolbox. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Quebec City, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Farr, T.; Rosen, P.A.; Caro, E.; Crippen, R.; Duren, R.; Hensley, S.; Kobrick, M.; Paller, M.; Rodríguez, E.; Roth, L.; et al. The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.M.; Werner, C.L. Radar interferogram filtering for geophysical applications. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 4035–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumberge, J.F.; Heflin, M.B.; Jefferson, D.C.; Watkins, M.M.; Webb, F.H. Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1997, 102, 5005–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertiger, W.; Desai, S.D.; Haines, B.; Harvey, N.; Moore, A.W.; Owen, S.; Weiss, J.P. Single receiver phase ambiguity resolution with GPS data. J. Geod. 2010, 84, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briole, P. Modelling of earthquake slip by inversion of GNSS and InSAR data assuming homogenous elastic medium. Zenodo 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganas, A.; Briole, P.; Bozionelos, G.; Barberopoulou, A.; Elias, P.; Tsironi, V.; Valkaniotis, S.; Moshou, A.; Mintourakis, I. The 25 October 2018 Mw = 6.7 Zakynthos earthquake (Ionian Sea, Greece): A low-angle fault model based on GNSS data, relocated seismicity, small tsunami and implications for the seismic hazard in the west Hellenic Arc. J. Geodyn. 2020, 101731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papazachos, B.C.; Comninakis, P.E.; Karakaisis, G.F.; Karakostas, B.G.; Papaioannou, C.A.; Papazachos, C.B.; Scordilis, E.M. A Catalogue of Earthquakes in Greece and Surrounding Area for the Period 550BC-1999; Publ. Geophys. Laboratory, University of Thessaloniki: Thessaloniki, Greece, 2000; Volume 1, p. 333. [Google Scholar]
- Crowell, B.W.; Melgar, D.; Bock, Y.; Haase, J.S.; Geng, J. Earthquake magnitude scaling using seismogeodetic data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 6089–6094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgar, D.; Crowell, B.W.; Geng, J.; Allen, R.M.; Bock, Y.; Riquelme, S.; Hill, E.M.; Protti, M.; Ganas, A. Earthquake magnitude calculation without saturation from the scaling of peak ground displacement. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 5197–5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganas, A.; Andritsou, N.; Kosma, C.; Argyrakis, P.; Tsironi, V.; Drakatos, G. A 20-yr database (1997–2017) of co-seismic displacements from GPS recordings in the Aegean area and their scaling with Mw and hypocentral distance. Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2018, 52, 98–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhl, C.J.; Melgar, D.; Geng, J.; Goldberg, D.E.; Crowell, B.W.; Allen, R.M.; Bock, Y.; Barrientos, S.; Muñoz, S.R.; Baez, J.C.; et al. A Global Database of Strong-Motion Displacement GNSS Recordings and an Example Application to PGD Scaling. Seism. Res. Lett. 2018, 90, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).