Seawater Intrusion on the Arctic Coast (Svalbard): The Concept of Onshore-Permafrost Wedge
Abstract
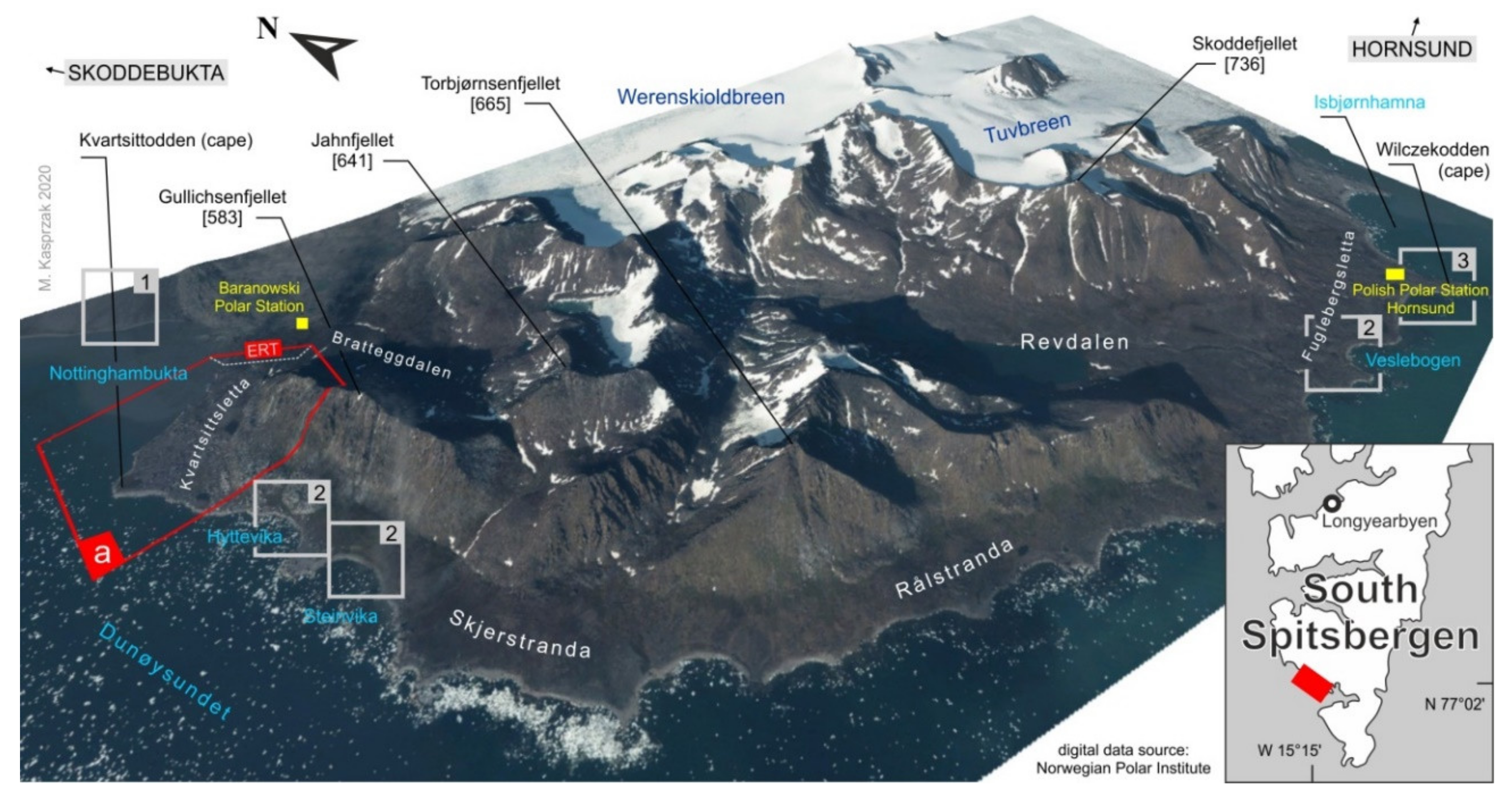
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
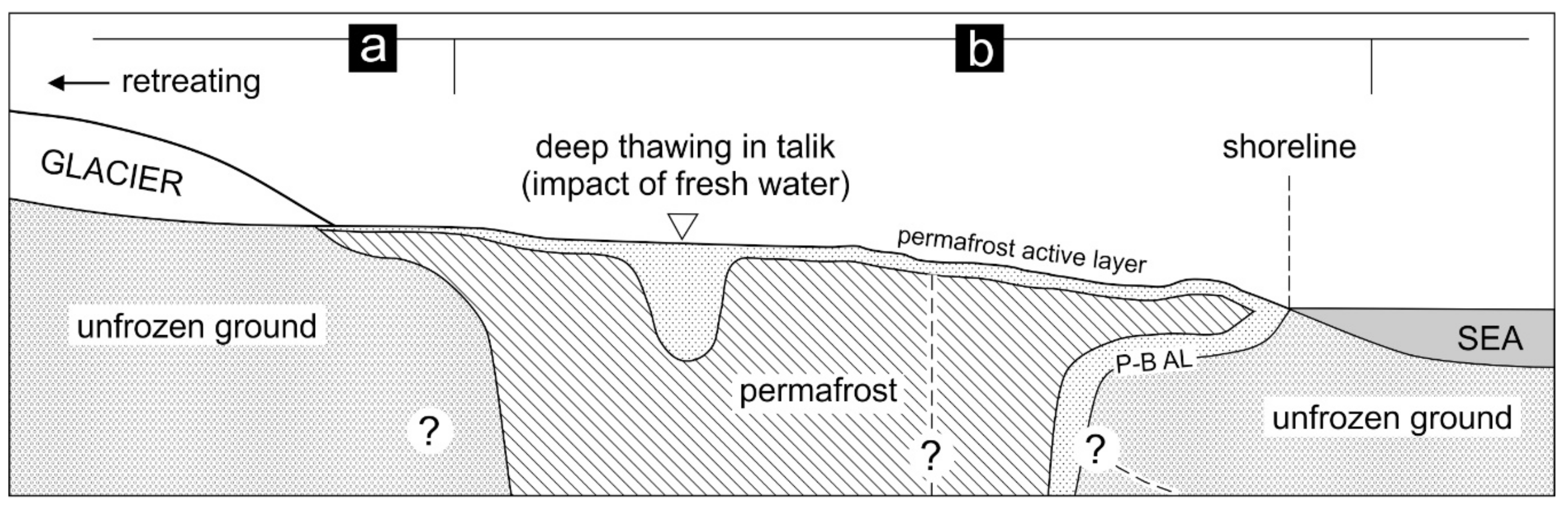
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cooper, H.H., Jr.; Kohout, F.A.; Henry, H.R.; Glover, R.E. Sea Water in Coastal Aquifers; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1964; pp. C1–C84.
- Oude Essink, G.H.P. Density Dependent Groundwater Flow Salt Water Intrusion and Heat Transport. KHTP/GWM II Hydrological Transport Processes/Groundwater Modelling II; Utrecht University: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- López-Geta, J.A.; de Dios Gómez, J.; Orden, J.A.d.l.; Ramos, G.; Rodríguez, L. (Eds.) Coastal Aquifers Intrusion Technology: Mediterranean Countries. The state of sea Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers of the Mediterranean and Assessment Techniques; Publicaciones del Instituto Geológico y Minero de España: Madrid, Spain, 2003; p. 330. [Google Scholar]
- Kirch, R. Groundwater quality—Saltwater intrusions. In Groundwater Geophysics. A tool for Hydrogeology, 2nd ed.; Kirch, R., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 475–490. [Google Scholar]
- Kuria, Z.N.; Woldai, T.; Opiyo-Akech, N. Imaging saltwater intrusion into coastal aquifers with electrical resistivity tomography at Lamu Island, south coast Kenya. AJST Sci. Eng. Ser. 2010, 11, 57–72. [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen, F.; Scheer, W.; Thomsen, S.; Sonnenborg, T.O.; Hinsby, K.; Wiederhold, H.; Schamper, C.; Burschil, T.; Roth, B.; Kirsch, R.; et al. Transboundary geophysical mapping of geological elements and salinity distribution critical for the assessment of future sea water intrusion in response to sea level rise. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 1845–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Werner, A.D.; Ward, J.D.; Morgan, L.K.; Simmons, C.T.; Robinson, N.I.; Teubner, M.D. Vulnerability Indicators of Sea Water Intrusion. Ground Water 2012, 50, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asfahani, J.; Abou Zakhem, B. Geoelectrical and Hydrochemical Investigations for Characterizing the Salt Water Intrusion in the Khanasser Valley, Northern Syria. Acta Geophys. 2013, 61, 422–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofi, J.; Pezard, P.; Bouchette, F.; Raynal, O.; Sabatier, P.; Denchik, N.; Levannier, A.; Dezileau, L.; Certain, R. Integrated Onshore-Offshore Investigation of a Mediterranean Layered Coastal Aquifer. Groundwater 2013, 51, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, A.S.; Oliver, D.H.; Srinivas, Y. Forecasting groundwater vulnerability in the coastal region of southern Tamil Nadu, India—A fuzzy-based approach. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylroie, J.E.; Carew, J.L. Speleogenesis in coastal and oceanic settings. In Speleogenesis. Evolution of Karst Aquifers; Klimchouk, A.B., Ford, D.C., Palmer, A.N., Dreybrodt, W., Eds.; National Speleological Society: Huntsville, AL, USA, 2000; pp. 226–233. [Google Scholar]
- Mylroie, J.E.; Carew, J.L. Karst development on carbonate islands. Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. 2003, 1, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Comte, J.-C.; Banton, O. Cross-validation of geo-electrical and hydrogeological models to evaluate seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L10402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Franco, R.; Biella, G.; Tosi, L.; Teatini, P.; Lozej, A.; Chiozzotto, B.; Giada, M.; Rizzetto, F.; Claude, C.; Mayer, A.; et al. Monitoring the saltwater intrusion by time lapse electrical resistivity tomography: The Chioggia test site (Venice Lagoon, Italy). J. App. Geophys. 2009, 69, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.; Benavente, J.; García-Aróstegui, J.L.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Reyd, J. Contribution of electrical resistivity tomography to the study of detrital aquifers affected by seawater intrusion–extrusion effects: The river Vélez delta (Vélez-Málaga, Southern Spain). Eng. Geol. 2009, 108, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, F.J.; Ingham, M.R.; McConchie, J.A. Monitoring of tidal influences on the saline interface using resistivity traversing and cross-borehole resistivity tomography. J. Hydrol. 2010, 389, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabelsi, F.; Mammou, A.B.; Tarhouni, J.; Piga, C.; Ranieri, G. Delineation of saltwater intrusion zones using the time domain electromagnetic method: The Nabeul-Hammamet coastal aquifer case study (NE Tunisia). Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 2004–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaujean, J.; Nguyen, F.; Kemna, A.; Antonsson, A.; Engesgaard, P. Calibration of seawater intrusion models: Inverse parameterestimation using surface electrical resistivity tomography and borehole data. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 6828–6849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martorana, R.; Lombardo, L.; Messina, N.; Luzio, D. Integrated geophysical survey for 3D modelling of a coastal aquifer polluted by seawater. Near Surf. Geophys. 2014, 12, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pidlisecky, A.; Moran, T.; Hansen, B.; Knight, R. Electrical Resistivity Imaging of Seawater Intrusion into the Monterey Bay Aquifer System. Groundwater 2016, 54, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaksen, K.; Holmlund, P.; Sollid, J.L.; Harris, C. Three Deep Alpine-Permafrost Boreholes in Svalbard and Scandinavia. Permafr. Periglac. Process 2001, 12, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, H.H.; Etzelmüller, B.; Isaksen, K.; Juliussen, H.; Farbrot, H.; Humlum, O.; Johansson, M.; Ingeman-Nielsen, T.; Kristensen, L.; Hjort, J.; et al. The thermal state of permafrost in the Nordic Area during the International Polar Year 2007–2009. Permafr. Periglac. Process 2010, 21, 156–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liestøl, O. Pingos, springs, and permafrost in Spitsbergen. Nor. Polarinst. Årb. 1975, 7–29. [Google Scholar]
- Haldorsen, S.; Heim, M.; Dale, B.; Landvik, J.Y.; van der Ploeg, M.; Leijnse, A.; Salvigsen, O.; Hagen, J.O.; Banks, D. Sensitivity to long-term climate change of subpermafrost groundwater systems in Svalbard. Quat. Res. 2010, 73, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploeg, M.J.; van der Haldorsen, S.; Leijnse, A.; Heom, M. Subpermafrost groundwater systems: Dealing with virtual reality while having virtually no data. J. Hydrol. 2012, 475, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzak, M.; Strzelecki, M.C.; Traczyk, A.; Kondracka, M.; Lim, M.; Migała, K. On the potential for a bottom active layer below coastal permafrost: The impact of seawater on permafrost degradation imaged by electrical resistivity tomography (Hornsund, SW Spitsbergen). Geomorphology 2017, 293, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strzelecki, M.C.; Kasprzak, M.; Lim, M.; Świrad, Z.M.; Jaskólski, M.; Pawłowski, Ł.; Modzel, P. Cryo-conditioned rocky coast systems: A case study from Wilczekodden, Svalbard. STOTEN 2017, 607–608, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kasprzak, M.; Łopuch, M.; Głowacki, T.; Milczarek, W. Evolution of Near-Shore Outwash Fans and Permafrost Spreading Under Their Surface: A Case Study from Svalbard. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keating, K.; Binley, A.; Bense, V.; Van Dam, R.; Christiansen, H.H. Combined geophysical measurements provide evidence for unfrozen water in permafrost in the Adventdalen Valley in Svalbard. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 7606–7614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glazer, M.; Dobiński, W.; Marciniak, A.; Majdański, M.; Błaszczyk, M. Spatial distribution and controls of permafrost development in non-glacial Arctic catchment over the Holocene, Fuglebekken, SW Spitsbergen. Geomorphology 2020, 358, 107128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingeman-Nielsen, T.; Tomaškovičová, S. Multidisciplinary site investigations for improved infrastructure design in Qaanaaq, North Greenland. In Proceedings of the 5th European Conference on Permafrost, Chamonix, France, 23 June–1 July 2018; pp. 156–157. [Google Scholar]
- Oldenborger, G.A.; LeBlanc, A.-M. Geophysical characterization of permafrost terrain at Iqaluit International Airport, Nunavut. J. Appl. Geophys. 2015, 123, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterkamp, T.E. Sub-sea permafrost. In Encyclopedia of Ocean Sciences; Cochran, J.K., Bokuniewicz, H.J., Yager, P.L., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001; pp. 2902–2912. [Google Scholar]
- Rachold, V.; Bolshiyanov, D.Y.; Grigoriev, M.N.; Hubberten, H.-W.; Junker, R.; Kunitsky, V.V.; Overduin, P.; Schneider, W. Nearshore Arctic Subsea Permafrost in Transition. EOS Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2007, 88, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Overduin, P.P.; Wetterich, S.; Günther, F.; Grigoriev, M.N.; Grosse, G.; Schirrmester, L.; Hubberten, H.-W.; Makarov, A.S. Coastal dynamics and submarine permafrost in shallow water of the central Laptev Sea, East Siberia. Cryosphere 2016, 10, 1449–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, F. On the thermal regime of a high Arctic valley glacier. J. Glaciol. 1976, 16, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobiński, W. Permafrost active layer. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 208, 103301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerny, J.; Kieres, A.; Manecki, M.; Rajchel, J. Geological Map of the SW Part of Wedel Jarlsberg Land, Spitsbergen 1:25,000 (with Explanations); Manecki, A., Ed.; Institute of Geology and Mineral Deposits, University of Mining and Metallurgy: Cracow, Poland, 1993; pp. 1–61. [Google Scholar]
- Kasprzak, M.; Szymanowski, M. Terrain determinants of permafrost active layer thermal conditions: A case study from Arctic deglaciated catchment (Bratteggdalen, SW Spitsbergen). PeerJ Prepr. 2018, 6, e27119v2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKay, D.K. Electrical resistivity measurements in frozen ground, Mackenzie Delta area, Northwest Territories. In Association Internationale d’Hydrologie Scientifique, Actes du Colloque de Becarest, Reprint Ser; Inland Waters Branch, Department of Energy, Mines and Resources: Ceuterick, Belgium, 1969; Volume 82, pp. 363–375. [Google Scholar]
- King, L.; Seppälä,M. Permafrost thickness and distribution in Finnish Lapland—Results of geoelectrical soundings. Polarforschung 1987, 57, 127–147. [Google Scholar]
- Hauck, C. Frozen ground monitoring using DC resistivity tomography. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 12-1–12-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, M. Application of DC resistivity imaging to frozen ground investigations. J. Jpn. Soc. Snow Ice 2004, 66, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneisel, C.; Hauck, C. Electrical methods. In Applied Geophysics in Periglacial Environments; Hauck, C., Kneisel, C., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008; pp. 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Hilbich, C.; Marescot, L.; Hauck, C.; Loke, M.H.; Mäusbacher, R. Applicability of electrical resistivity tomography monitoring to coarse blocky and ice-rich permafrost landforms. Permaf. Periglac. Process 2009, 20, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewkowicz, A.G.; Etzelmüller, B.; Smith, S.L. Characteristics of discontinuous permafrost based on ground temperature measurements and electrical resistivity tomography, Southern Yukon, Canada. Permaf. Periglac. Process 2011, 22, 320–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Yu, Q.; Pan, X.; Wang, X.; Guo, L. Application of electrical resistivity tomography in investigating depth of permafrost base and permafrost structure in Tibetan Plateau. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2013, 87, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, M.H. Electrical Imaging Syrveys for Environmental and Engineering Studies. 2000. Available online: https://pages.mtu.edu/~ctyoung/LOKENOTE.PDF (accessed on 11 February 2020).
- Milsom, J. Resistivity methods. In Field Geophysics, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2003; pp. 97–116. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, J.M. Electrical resistivity methods. In An Introduction to Applied and Environmental Geophysics, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2011; pp. 289–372. [Google Scholar]
- Loke, M.H. Manual for RES3DINV. Rapid 3-D Resistivity & IP Inversion Using the Least-Squares Method (for 3-D Surveys Using the Pole–Pole, Pole–Dipole, Dipole–Dipole, Rectangular, Wenner, Wenner-Schlumberger and Non-Conventional Arrays). On Land, Aquatic and Cross-Borehole Surveys, Geoelectrical Imaging 2-D & 3-D; Geotomo Software SDN BHD: Penang, Malaysia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle, J.A.; Brevik, E.C. The use of electromagnetic induction techniques in soils studies. Geoderma 2014, 223–225, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balkov, E.V.; Fadeev, D.I.; Karin, Y.G.; Manshtein, A.K.; Manshtein, Y.A.; Panin, G.L. A new approach to shallow-depth electromagnetic sounding. Russ. Geol. Geophys. 2017, 58, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafflon, B.; Hubbard, S.S.; Ulrich, C.; Peterson, J.E. Electrical Conductivity Imaging of Active Layer and Permafrost in an Arctic Ecosystem, through Advanced Inversion of Electromagnetic Induction Data. Vadose Zone J. 2013, 12, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayley, K.; Bentley, L.R.; Gharibi, M.; Nightingale, M. Low temperature dependence of electrical resistivity: Implications for near surface geophysical monitoring. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L18402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telford, W.M.; Geldart, L.P.; Sheriff, R.E. Applied Geophysics, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Kearey, P.; Brooks, M.; Hill, I. Electrical surveying. In An Introduction to Geophysical Exploration, 3rd ed.; Blackwell Science: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 183–207. [Google Scholar]
- Ruppel, C.D.; Herman, B.M.; Brothers, L.L.; Hart, P. ESubsea ice-bearing permafrost on the U.S. Beaufort Margin: 2. Borehole constraints. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2016, 17, 4333–4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sherman, D.; Constable, S. Permafrost extent on the Alaskan Beaufort shelf from surface-towed controlled-source electromagnetic surveys. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 7253–7265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregersen, O.; Eidsmoen, T. Permafrost conditions in the shore area at Svalbard. In Proceedings of the Permafrost Fifth International Conference, Trondheim, Norway, 2–5 August 1988; Senneset, K., Ed.; Tapir Publishers: Trondheim, Norway, 1988; Volume 2, pp. 933–936. [Google Scholar]
- Gregersen, O.; Phukan, A.; Johansen, T. Engineering properties and foundation design alternatives in marine Svea clay, Svalbard. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Permafrost 4, Fairbanks, AK, USA, 17–22 July 1983; National Academy of Sciences: Washington, DC, USA, 1983; pp. 384–388. [Google Scholar]
- Tsytovich, N.A.; Kronik, Y.A.; Markin, K.F.; Aksenov, V.I.; Samuel’son, M.V. Physical and mechanical properties of saline soils. In Proceedings of the Permafrost Second International Conference, Yakutsk, Russia, 13–28 July 1973; Sanger, F.J., Hyde, P.J., Eds.; National Academy of Sciences: Washington, DC, USA, 1978; pp. 238–247. [Google Scholar]
- Zajączkowski, M.; Szczuciński, W.; Plessen, B.; Jernas, P. Benthic foraminifera in Hornsund, Svalbard: Implications for paleoenvironmental reconstructions. Pol. Polar Res. 2010, 31, 349–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promińska, A.; Falck, E.; Walczowski, W. Interannual variability in hydrography and water mass distribution in Hornsund, an Arctic fjord in Svalbard. Polar Res. 2018, 37, 1495546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lech, J.; Walczowski, W. Data Report on Hydrological Measurements: Norwegian Sea, Fjords, Polar Front, 13.06–09.08.1994, Cruise AREX-94; Institute of Oceanology PAS: Sopot, Poland, 1994. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Włodarska-Kowalczuk, M.; Węsławski, J.M.; Kotwicki, L. Spitsbergen glacial bays macrobenthos–A comperative study. Polar Biol. 1998, 20, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olichwer, T.; Tarka, T.; Modelska, M. Chemical composition of groundwaters in the Hornsund region, southern Spitsbergen. Hydrol. Res. 2013, 44, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachnik, Ł.; Majchrowska, E.; Yde, J.C.; Nawrot, A.; Cichała-Kamrowska, K.; Ignatiuk, D.; Piechota, A. Chemical denudation and the role of sulfide oxidation at Werenskioldbreen, Svalbard. J. Hydrol. 2016, 538, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oberman, N.G.; Kakunov, B.B. Determination of the thickness of permafrost on the Arctic coast. In Proceedings of the Permafrost Second International Conference, Yakutsk, Russia, 13–28 July 1973; Sanger, F.J., Hyde, P.J., Eds.; National Academy of Sciences: Washington, DC, USA, 1978; pp. 143–147. [Google Scholar]
- Osterkamp, T.E.; Baker, G.C.; Harrison, W.D.; Matava, T. Characteristics of the Active Layer and Shallow Subsea Permafrost. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 16227–16236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kasprzak, M. Seawater Intrusion on the Arctic Coast (Svalbard): The Concept of Onshore-Permafrost Wedge. Geosciences 2020, 10, 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10090349
Kasprzak M. Seawater Intrusion on the Arctic Coast (Svalbard): The Concept of Onshore-Permafrost Wedge. Geosciences. 2020; 10(9):349. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10090349
Chicago/Turabian StyleKasprzak, Marek. 2020. "Seawater Intrusion on the Arctic Coast (Svalbard): The Concept of Onshore-Permafrost Wedge" Geosciences 10, no. 9: 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10090349
APA StyleKasprzak, M. (2020). Seawater Intrusion on the Arctic Coast (Svalbard): The Concept of Onshore-Permafrost Wedge. Geosciences, 10(9), 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10090349





