Sequential Semiology of Seizures and Brain Perfusion Patterns in Patients with Drug-Resistant Focal Epilepsies: A Perspective from Neural Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
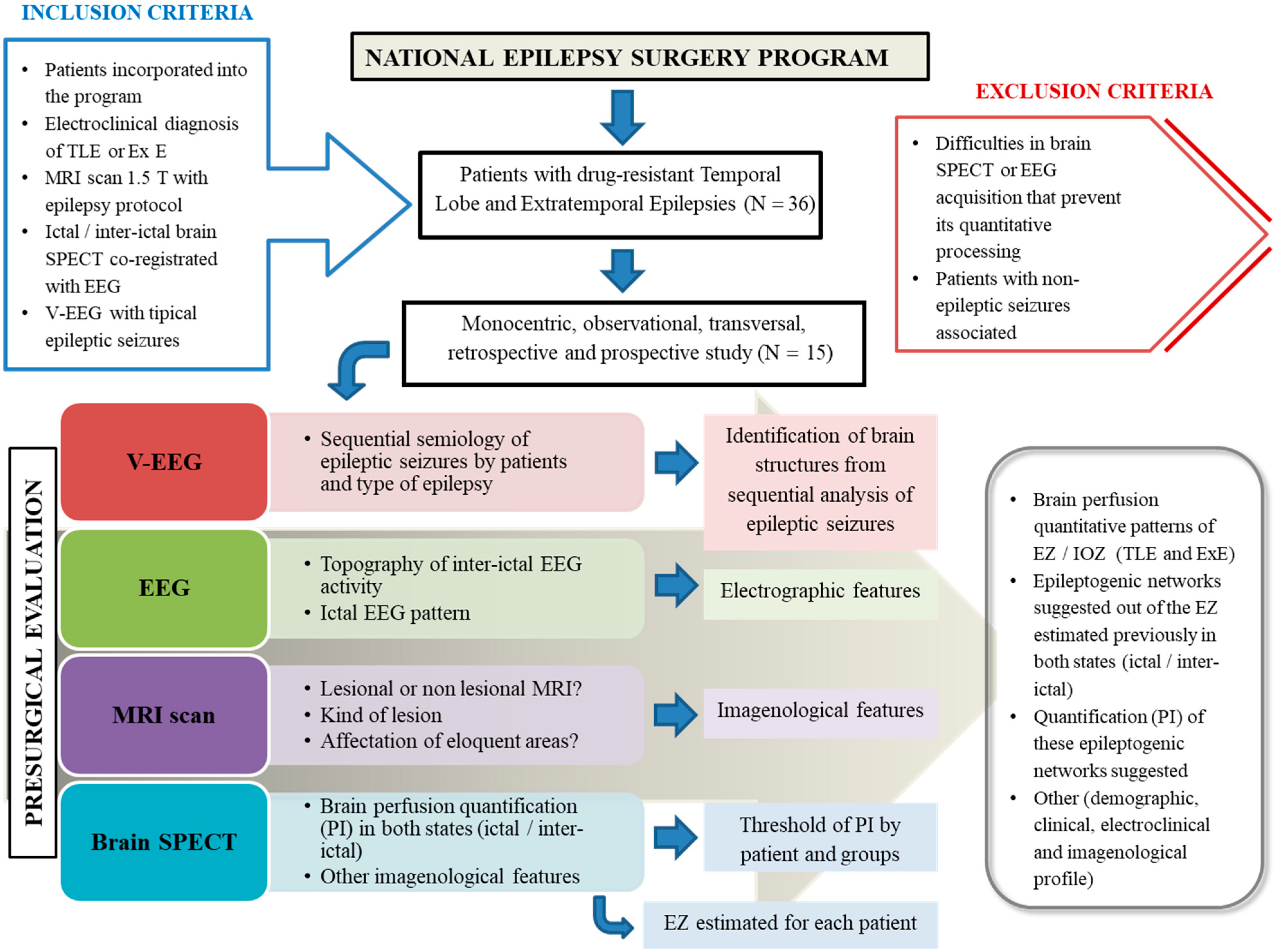
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Setting
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Methodology
- (a)
- Prolonged Video-Electroencephalography monitoring with scalp electrodes and additional electrodes considering the epileptogenic zone presumed;
- (b)
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging scans with a 1.5 T scanner (Siemens Magnetom Symphony) using an epilepsy protocol [10];
- (c)
- Interictal and ictal Electroencephalography (Micromed Software System plus Evolution and MEDICID V Amplifier System. Neuronic, Cuba) following the International System 10–20 with additional extracranial electrodes. The topography of interictal electroencephalography activity was determined, as well as the ictal electroencephalography pattern according to the different moments of the electrographic seizure;
- (d)
- SPECT: A brain perfusion SPECT was carried out in all subjects using a double-headed gamma camera (SMV DST-XLi, Buc Cedex, France) equipped with a fan-beam collimator. Ictal SPECT was performed on just 9 subjects (2 patients with temporal lobe epilepsy, 5 patients with frontal lobe epilepsy and 2 patients with posterior quadrant epilepsy). This occurred because the ictal SPECT could not be conducted, was useless for diagnosis, and it was impossible to achieve adequate quantitative processing. In the case of interictal SPECT, all patients were studied. In both studies, the subject remained monitored by electroencephalography during the intravenous radiopharmaceutical delivery (99 mTc-ethylene-cysteine dimer). For ictal SPECT, the radiopharmaceutical was injected when electroencephalographic seizure onset was identified. The authors took into account the fact that there is a pharmacokinetic arm-brain circulation time, estimated at approximately 15–30 s for extratemporal epilepsies and temporal lobe epilepsies, respectively, which is relevant, especially in ictal SPECT. For interictal SPECT, a radiopharmaceutical was delivered with the patient lying down in a seizure-free period more than 24 h and 35 min after the radiopharmaceutical administration.
2.3.1. Analysis and Processing of Information
Analysis of Ictal Semiology Sequences
Quantification of Cerebral Blood Flow by SPECT
2.3.2. Statistics Analysis
- To describe the individual behavior of the distribution by subject;
- To calculate the location and dispersion parameters;
- To compare the values obtained in ictal vs non-ictal through a t-Student’s test;
- To determine a threshold value for discriminating both behaviors (2 discrimination methods: traditional and classification trees Breimen et al., 1984).
2.3.3. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Demographic, Electroclinical and Imagenological Profile
3.2. Sequential Semiological Analysis of Behavioral Seizures and Brain Perfusion Quantitative Patterns of Epileptogenic Zone during Ictal State
3.3. Brain Perfusion Quantitative Patterns of Epileptogenic Zone during Interictal State
3.4. Analysis of Interictal and Ictal Epileptogenic Network from the Perfusion Index
3.4.1. Interictal Quantitative Perfusion
3.4.2. Ictal Quantitative Perfusion
3.4.3. Brain Structures Proposed as Part of the Epileptogenic Network Regardless of the Type of Focal Epilepsy
4. Discussion
4.1. Demographic, Clinical and Imagenological Data
4.2. Sequential Semiology of Seizures
4.3. Brain Perfusion Quantitative Patterns of the Epileptogenic Zone
4.4. Analysis of Interictal and Ictal Epileptogenic Network
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbott, D.F.; Archer, J.S.; Carney, P.W.; Vaughan, D.N.; Jackson, G.D. Functional Brain Mapping of Epilepsy Networks: Methods and Applications. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bender, J.E. Epilepsy, a burden health problem. Rev. Haban Cienc. Méd. 2018, 17, 1–3. Available online: http://www.revhabanera.sld.cu/index.php/rhab/article/view/2491 (accessed on 15 August 2020).
- Stamoulis, C.; Verma, N.; Kaulas, H.; Halford, J.; Duffy, F.H.; Pearl, P.L.; Treves, S.T. The promise of subtraction ictal SPECT co-registered to MRI for improved seizure localization in pediatric epilepsies: Affecting factors and relationship to the surgical outcome. Epilepsy Res. 2017, 129, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Begueria, R. Manual de Prácticas Médicas, 7th ed.; CEDISAP: Havana, Cuba, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, A.S.; Chacón, L.M.; Romanidy, M.U.; Hernández, L.P.; Vázquez, V.R.; García-Ramo, K.B. Epileptogenic zone surgery located in an eloquent area of the frontal lobe in an adolescent with epilepsy. Rev. Cubana Neurol. Neurocir. 2020, 10, e323. Available online: http://www.revneuro.sld.cu/index.php/neu/article/view/323/582 (accessed on 7 July 2020).
- Rings, T.; von Wrede, R.; Lehnertz, K. Precursors of seizures due to specific spatial-temporal modifications of evolving large-scale epileptic brain networks. Nature 2019, 9, 10623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toledano, R.; Martínez-Álvarez, R.; Jiménez-Huete, A.; García-Morales, I.; Aledo-Serrano, Á.; Cabrera, W.; Rey, G.; Campo, P.; Gómez-Angulo, J.; Blumcke, I.; et al. Estereoelectroencefalografía en la evaluación prequirúrgica de epilepsias focales refractarias: Experiencia de un centro de epilepsia. Neurología 2019, 95, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, L.M.; Báez, M.M.; Bender, J.E.; González, J.; García, M.E.; Lorigados, L.; González, M.E.; Díaz, M.L.; Estupiñán, B.O.; Pavón, N. Drug-resistant epilepsies. In Treatment in Cuba, 1st ed.; Medical Sciencies: Havana, Cuba, 2018; pp. 1–201. ISBN 978-959-313-301-2. [Google Scholar]
- Andalusian Epilepsy Society. Clinical Practice Guideline 2020. Diagnostic and Treatment of Epilepsy; 2020 ed.; Andalusian Epilepsy Society: Andalucia, Spain, 2020; pp. 1–514. ISBN 978-84-09-20877-7. [Google Scholar]
- Bernasconi, A.; Cendes, F.; Theodore, W.H.; Gill, R.S.; Koepp, M.J.; Hogan, R.E.; Jackson, G.; Federico, P.; Labate, A.; Vaudano, A.E.; et al. Recommendations for the use of structural magnetic resonance imaging in the care of patients with epilepsy: A consensus report from the International League against Epilepsy Neuroimaging Task Force. Epilepsia 2019, 60, 1054–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacón, L.M.M.; Catasus, C.A.S.; Martin, M.M.B.; Rojas, R.R.; Pedre, L.L.; Diaz, B.E. Multimodal imaging in nonlesional medically intractable focal epilepsy. Front. Biosci. 2015, 7, 42–57. [Google Scholar]
- Morales Chacón, L.M.; Garcia Maeso, I.; Baez Martin, M.M.; Bender del Busto, J.E.; García Navarro, M.E.; Quintanal Cordero, N.; Estupiñan Díaz, B.; Lorigados Pedre, L.; Valdés Yerena, R.; Gonzalez, J.; et al. Long-Term Electroclinical and Employment Follow up in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Surgery. A Cuban Comprehensive Epilepsy Surgery Program. Behav. Sci. 2018, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Englot, D.J.; Gonzalez, H.F.; Reynolds, B.B.; Konrad, P.E.; Jacobs, M.L.; Gore, J.C.; Landman, B.A.; Morgan, V.L. Relating structural and functional brainstem connectivity to disease measures in epilepsy. Neurology 2018, 91, e67–e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgana, V.L.; Changa, C.; Englot, D.J.; Rogers, B.P. Temporal lobe epilepsy alters spatio-temporal dynamics of the hippocampal functional network. NeuroImage Clin. 2020, 26, 102254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ren, J.; Wang, Q. Abnormal Brain Network in Epilepsy and Associated Comorbidites. Neuropsychiatry 2018, 8, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestú, F.; Pereda, E.; del Pozo, F. Conectividad funcional y anatómica en el cerebro humano. In Análisis de Señales y Aplicaciones en Ciencias de la Salud, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Barcelona, Spain, 2015; p. 295. ISBN 978-84-9022-819-7. [Google Scholar]
- Frings, L.; Schulze, A.; Spreer, J.; Wagner, K. Reduced interhemispheric hippocampal BOLD signal coupling related to early epilepsy onset. Seizure 2009, 18, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Lu, G.; Zhong, Y.; Tan, Q.; Liao, W.; Chen, Z.; Shi, J.; Liu, Y. Impaired perceptual networks in temporal lobe epilepsy revealed by resting fMRI. J. Neurol. 2009, 256, 1705–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertti, P.; Dal-Cól, M.L.C.; Wichert-Ana, L.; Kato, M.; Terra, V.C.; de Oliveira, J.A.C.; Velasco, T.R.; Sakamoto, A.C.; Garcia-Cairasco, N. The neurobiological substrates of behavioral manifestation during temporal lobe seizures: A neuroethological and ictal SPECT correlation study. Epilepsy Behav. 2010, 17, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertti, P.; Tejada, J.; Martins, A.P.P.; Dal-Cól, M.L.C.; Terra, V.; de Oliveira, J.A.C.; Velasco, T.R.; Sakamoto, A.C.; Garcia-Cairasco, N. Looking for complexity in quantitative semiology of frontal and temporal lobe seizures using neuroethology and graph theory. Epilepsy Behav. 2014, 38, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal-Cól, M.; Terra, V.; Velasco, T.; Oliveira, J.; Sakamoto, A.; Garcia-Cairasco, N. Neuroethology application for the study of human temporal lobe epilepsy: From basic to applied sciences. Epilepsy Behav. 2005, 8, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, M.; Beckmann, C.F.; Behrens, T.E.; Woolrich, M.W.; Smith, S.M. FSL. NeuroImage 2012, 62, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oishi, K.; Faria, A.; Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Akhter, K.; Zhang, J.; Hsu, J.T.; Miller, M.I.; van Zijl, P.C.; Albert, M.; et al. Atlas-Based Whole Brain White Matter Analysis Using Large Deformation Diffeomorphic Metric Mapping: Application to Normal Elderly and Alzheimer’s Disease Participants. NeuroImage 2009, 46, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlandsson, K.; Wong, A.T.; van Heertum, R.; Mann, J.J.; Parsey, R.V. An improved method for voxel-based partial volume correction in PET and SPECT. NeuroImage 2006, 31, 1–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacón, L.M.; González, J.G.; Batista, S.H.B.; García-Ramo, K.B.; Santos, A.; Ríos, M. Electroclinical Profile and Outcomes in Extratemporal Lobe Epilepsy Surgery Based on Intraoperative Electrocorticography. Neurol Disord. Epilepsy J. 2020, 3, 130. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/342800846_Electroclinical_Profile_and_Outcomes_in_Extratemporal_Lobe_Epilepsy_Surgery_Based_on_Intraoperative_Electrocorticography (accessed on 22 September 2020).
- Ortiz, B.; Naranjo, L.F.; Cornejo, J.W.; Solarte, R.A. Clinical, electroencephalographic e imagenological features in adults with temporal lobe epilepsy of Epilepsy program of Antioquia University: Descriptive-retrospective study in Medellin 2008–2012. Acta Neurol. Colomb. 2017, 33, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacón, L.M.; González, J.G.; Castillo, M.R.; Batista, S.B.; García-Ramo, K.B.; Santos, A.S.; Cordero, N.Q.; Bermúdez, M.Z.; Fernández, R.G.; Díaz, B.E.; et al. Surgical Outcome in Extratemporal Epilepsies Based on Multimodal Pre-Surgical Evaluation and Sequential Intraoperative Electrocorticography. Behav. Sci. 2021, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, C.S.; Clayden, J.D.; Cardoso, M.J.; Rodionov, R.; Duncan, J.S.; Scott, C.; Diehl, B.; Ourselin, S. Structural and effective connectivity in focal epilepsy. NeuroImage Clin. 2018, 17, 943–952. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5842760/ (accessed on 4 July 2019). [CrossRef]
- Dal-Cól, M.L.C.; Bertti, P.; Terra-Bustamante, V.C.; Velasco, T.R.; Rodrigues, M.C.A.; Wichert-Ana, L.; Sakamoto, A.C.; Garcia-Cairasco, N. Is dystonic posturing during temporal lobe epileptic seizures the expression of an endogenous anticonvulsant system? Epilepsy Behav. 2007, 1, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Mo, J.; Zheng, Z.; Ai, L.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, J.; Shao, X.-Q.; et al. Orbitofrontal epilepsy: Distinct neuronal networks underlying electroclinical subtypes and surgical outcomes. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleeren, E.; Premereur, E.; Casteels, C.; Goffin, K.; Janssen, P.; Van Paesschen, W. The effective connectivity of the seizure onset zone and ictal perfusion changes in amygala kindled rhesus monkeys. NeuroImage Clin. 2016, 12, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Theodore, W.H. Presurgical Focus Localization in Epilepsy: PET and SPECT. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2017, 47, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichert-Ana, L.; Velasco, T.R.; Terra, V.; Araújo, D.; Júnior, V.A.; Kato, M.; Leite, J.P.; Assirati, J.A.; Machado, H.; Bastos, A.C.; et al. Typical and atypical perfusion patterns in periictal SPECT of patients with unilateral temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 2001, 42, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanco, M. Alteraciones Neuropsicológicas en Epilepsia del Lóbulo Frontal en Niños; Universidad Complutense de Madrid: Madrid, Spain, 2020; Volume 1, pp. 1–192. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, L.A.; Harper, R.M.; Guye, M.; Kumar, R.; Ogren, J.A.; Vos, S.B.; Ourselin, S.; Scott, C.A.; Lhatoo, S.D.; Lemieux, L.; et al. Altered brain connectivity in sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP) revealed using resting-state fMRI. NeuroImage Clin. 2019, 24, 102060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, A.L.; Fernández, I.P.; Principe, A.; Ley, M.; Rocamora, R. SUDEP in Spain: First case series and epidemiological analysis. Seizure 2019, 69, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Peedicail, J.S.; Gaxiola-Valdez, I.; Li, E.; Mosher, V.; Wilson, W.; Perera, T.; Singh, S.; Teskey, G.C.; Federico, P. Postictal brainstem hypoperfusion and risk factors for sudden unexpected death in epilepsy. Neurology 2020, 12, e1694–e1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelan, C.D.; Altmann, A.; Botía, J.A.; Jahanshad, N.; Hibar, D.P.; Absil, J.; Alhusaini, S.; Alvim, M.K.M.; Auvinen, P.; Bartolini, E.; et al. Structural brain abnormalities in the common epilepsies assessed in a worldwide ENIGMA study. Brain 2018, 1, 391–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Hong, B.; Wang, H.; Lin, J.; Shi, J.; Zhao, T.; Bai, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, W. Electroclinical features of lateral and medial orbitofrontal epilepsy: A case series. Epileptic Disord. 2020, 1, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, M.R.; Berkovic, S.; Austin, M.C.; Rowe, C.C.; McKay, W.J.; Bladin, P.F. SPECT in the localisation of extratemporal and temporal seizure foci. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1995, 59, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Epilepsy Type | Subjects | Seizure Onset Y Mean/SD | Age at Evaluation Y Mean/SD | Sex | Past Medical History | Epilepsy Duration (Y) | Antiepileptic Drugs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TLE | Patient 1 | 34 | 12.2 ± 14.8 | 35 | 30.2 ± 6.29 | F | Migraine | 1 | LTG | |
| Patient 2 | 6 | 21 | F | No | 15 | CBZ | ||||
| Patient 3 | 8 | 32 | F | Depression | 24 | LTG | ||||
| Patient 4 | 0.8 | 33 | F | No | 33 | LTG, CBZ | ||||
| Ex E | FLE | Patient 1 | 6 | 7.37 ± 6.28 | 21 | 21.3 ± 5.85 | M | BA | 15 | CBZ |
| Patient 2 | 4 | 15 | M | No | 11 | VPA, LEV, LTG, Clobazam | ||||
| Patient 3 | 14 | 15 | F | No | 1 | TPM, Clobazam | ||||
| Patient 4 | 11 | 31 | M | PI | 20 | CBZ, VPA | ||||
| Patient 5 | 0 | 23 | M | PH | 23 | LTG, Clobazam | ||||
| Patient 6 | 18 | 21 | M | CF | 3 | CBZ, Clobazam | ||||
| Patient 7 | 3 | 17 | M | No | 14 | CBZ, Clobazam | ||||
| Patient 8 | 3 | 28 | M | AC | 25 | OXC, LTG, Clonazepam | ||||
| PQE | Patient 1 | 18 | 11.6 ± 5.51 | 29 | 24 ± 5.56 | F | No | 11 | LV, LTG | |
| Patient 2 | 9 | 25 | F | PH | 16 | CBZ, Clobazam | ||||
| Patient 3 | 8 | 18 | M | No | 10 | LTG | ||||
| TLE | Ex E | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FLE | PQE | |||||||||||||||
| Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | Patient 4 | Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | Patient 4 | Patient 5 | Patient 6 | Patient 7 | Patient 8 | Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | ||
| Number of epileptic seizures | Awake | 17 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 96 | 6 | 27 | 6 | 4 | 6 | 2 | 7 | 8 | 6 |
| Sleep | 3 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 10 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 0 | |
| Total | 20 | 7 | 7 | 9 | 5 | 101 | 16 | 29 | 7 | 5 | 8 | 5 | 12 | 11 | 6 | |
| Mean/SD | Awake (8 ± 5.9) Sleep (2.5 ± 1.9) Total (10.7 ± 6.2) | Awake (17.6 ± 30.3) Sleep (3.1 ± 2.9) Total (20.7 ± 31.1) | Awake (7 ± 1) Sleep (2.6 ± 2.5) Total (9.6 ± 3.2) | |||||||||||||
| Laterality of EZ | R | L | L | L | R | R | R | R | R | L | L | R | R | R | L | |
| Topography of interictal EEG activity | R | R | F | F | F | M | R | R | R | R | F | R | R | F | F | |
| EEG ictal pattern according to electrographic seizure time | <20 s | - | - | RS | RSSF | RS | RS | FRD | - | - | - | RSSF | RSSF | - | RS | RSSF |
| 20–59 s | - | - | RS | GLS | GLS | RS | GLS | - | - | - | NOR | GLS | - | GLS | GLS | |
| ≥1 min | - | - | RSSF | GLS | NOR | GLS | NOR | - | - | - | NOR | NOR | - | GLS | NOR | |
| Injection times (s) of radiopharmaceutical (ictal SPECT) | - | - | 7 | 17 | 2 | 8 | 4 | - | - | - | 10 | 5 | - | 3 | 6 | |
| Duration of de electrographic seizure (s) Mean/SD | Mean/SD | - | - | 97 | 72 | 95 | 45 | 16 | - | - | - | 14 | 20 | - | 34 | 8 |
| 71.3 ± 26 | 41 ± 31.5 | 29 ± 19 | ||||||||||||||
| 76.8 ± 118.4 * | ||||||||||||||||
| Time between behavioral pattern onset and electrographic seizure onset (s) | Mean/SD | - | - | 14 | 10 | 9 | 18 | 2 | - | - | - | 0 | 0 | - | 34 | 0 |
| 8 ± 7.21 | 9.28 ± 12.7 | 11.3 ± 19.6 | ||||||||||||||
| 8.7 ± 11 * | ||||||||||||||||
| Duration of epileptic seizures (minutes) Mean/SD | 0.57 | 1.05 | 1.49 | 1.02 | 3.06 | 1.06 | 0.19 | 1.02 | 1.55 | 1.24 | 0.35 | 1.12 | 1.38 | 1.13 | 0.56 | |
| 1.03 ± 0.37 | 1.19 ± 0.8 | 1.02 ± 0.42 | ||||||||||||||
| MRI evidence of lesion | L | NL | NL | L | NL | L | NL | NL | NL | L | NL | NL | L | L | NL | |
| Type of lesion | HS | - | - | CNST | - | CDD | - | - | - | CDD | - | - | CDD | CDD | ||
| Affectation of eloquent area | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | N | N | Y | N | N | |
| TLE | Ex E | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FLE | PQE | |||||||||||||||
| Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | Patient 4 | Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | Patient 4 | Patient 5 | Patient 6 | Patient 7 | Patient 8 | Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | ||
| Threshold of PI | 0.854 | 0.855 | 0.965 | 0.927 | 0.951 | 0.924 | 0.969 | 0.944 | 0.956 | 0.987 | 0.975 | 0.883 | 0.950 | 0.917 | 0.950 | |
| Brain structures | STG i | - | - | - | - | 0.942 | - | - | - | 0.941 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| STG c | - | - | - | - | 0.920 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.920 | |
| MTG i | - | - | - | - | 0.917 | 0.839 | - | - | - | 0.941 | 0.899 | - | - | 0.846 | - | |
| MTG c | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.911 | 0.931 | - | 0.911 | - | 0.915 | |
| ITG i | - | - | - | - | 0.940 | - | - | - | - | 0.890 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| ITG c | - | - | - | - | - | 0.906 | - | - | - | 0.902 | 0.917 | - | 0.887 | - | 0.880 | |
| A i | - | - | - | - | 0.934 | 0.864 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.772 | - | - | - | |
| A c | - | - | - | 0.864 | 0.916 | 0.507 | 0.888 | 0.943 | - | 0.869 | 0.892 | - | 0.840 | - | - | |
| H i | - | - | - | - | - | 0.856 | 0.626 | 0.873 | 0.888 | - | 0.934 | - | - | 0.904 | - | |
| H c | - | - | - | - | - | 0.878 | 0.936 | - | - | - | 0.833 | - | - | - | - | |
| PHG i | - | - | - | - | 0.932 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.817 | - | - | - | |
| PHG c | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| CingG i | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| CingG c | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| SFG i | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.954 | - | - | 0.942 | 0.807 | - | |
| SFG c | - | - | 0.885 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.856 | - | |
| MFG i | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.932 | |
| MFG c | - | - | 0.828 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| IFG i | - | - | 0.911 | - | 0.951 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.974 | - | - | - | 0.882 | |
| IFG c | - | - | 0.885 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| SPG i | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.845 | - | 0.884 | 0.956 | - | - | - | - | |
| SPG c | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| PrecG i | - | - | 0.854 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.959 | - | - | - | 0.919 | |
| PrecG c | - | - | 0.806 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| PostG i | - | - | - | 0.891 | - | - | - | 0.936 | 0.895 | 0.912 | 0.948 | 0.871 | - | - | 0.854 | |
| PostG c | - | - | - | - | - | 0.895 | - | - | 0.932 | 0.936 | 0.908 | - | - | - | 0.796 | |
| AG i | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.838 | 0.902 | 0.824 | 0.846 | - | - | - | - | |
| AG c | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.937 | - | 0.817 | 0.930 | - | - | - | - | |
| Supram i | - | - | - | 0.923 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.846 | 0.909 | - | - | - | - | |
| Supram c | - | - | 0.463 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.918 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Precuneus i | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Precuneus c | - | - | 0.946 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Cuneus i | - | - | - | 0.901 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Cuneus c | - | - | 0.895 | - | - | - | 0.934 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| LingG i | - | - | 0.945 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| LingG c | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| SOG i | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.904 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| SOG c | - | - | 0.934 | 0.904 | - | 0.866 | 0.881 | - | 0.845 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| FusifG i | - | - | - | - | 0.784 | - | 0.868 | - | 0.865 | 0.970 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| FusifG c | - | - | 0.963 | - | 0.833 | - | 0.908 | - | 0.854 | 0.929 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| IOG i | - | - | - | 0.856 | 0.801 | - | 0.858 | 0.881 | 0.886 | 0.704 | 0.807 | - | - | - | - | |
| IOG c | 0.835 | - | - | 0.867 | 0.865 | 0.903 | 0.947 | 0.687 | 0.808 | - | 0.856 | - | - | - | - | |
| MOG i | - | - | - | 0.827 | - | - | 0.944 | - | - | 0.878 | 0.903 | - | - | - | - | |
| MOG c | - | - | - | 0.679 | 0.869 | - | 0.829 | 0.860 | 0.929 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| MOFG i | - | 0.832 | - | 0.663 | 0.818 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.912 | - | 0.829 | |
| MOFG c | 0.804 | 0.851 | - | - | 0.943 | 0.886 | 0.890 | - | - | 0.932 | 0.893 | - | 0.800 | - | 0.287 | |
| LOFG i | - | - | - | 0.911 | 0.844 | - | - | - | - | 0.965 | 0.932 | - | - | - | 0.764 | |
| LOFG c | - | - | - | - | 0.819 | 0.896 | 0.952 | 0.906 | - | 0.977 | 0.927 | - | - | - | 0.641 | |
| STRAG c | - | - | 0.875 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Entor i | 0.791 | 0.741 | - | 0.623 | 0.751 | - | 0.855 | 0.909 | 0.877 | 0.756 | 0.856 | - | - | - | 0.924 | |
| Entor c | 0.727 | - | 0.949 | 0.850 | 0.924 | - | - | 0.904 | 0.899 | 0.929 | - | 0.801 | 0.785 | - | 0.741 | |
| Ínsul i | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Ínsul c | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.937 | - | - | |
| Cerebellum i | - | - | 0.562 | - | 0.900 | - | 0.931 | 0.909 | - | - | - | - | 0.916 | - | - | |
| Cerebellum c | - | - | - | - | 0.911 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.946 | |
| RedN i | 0.324 | 0.408 | - | 0.677 | 0.410 | 0.316 | 0.416 | 0.761 | 0.708 | 0.758 | 0.855 | 0.392 | 0.341 | 0.768 | 0.484 | |
| RedN c | 0.496 | 0.319 | - | 0.857 | 0.303 | 0.314 | 0.695 | 0.898 | 0.672 | 0.787 | 0.961 | 0.406 | 0.528 | 0.639 | 0.383 | |
| SNig i | 0.453 | 0.645 | - | 0.579 | 0.565 | 0.488 | 0.553 | - | - | 0.574 | 0.586 | 0.700 | 0.614 | - | 0.500 | |
| SNig c | 0.543 | 0.616 | - | 0.621 | 0.546 | 0.444 | 0.565 | 0.883 | - | 0.815 | 0.923 | 0.458 | 0.595 | - | 0.627 | |
| CN i | 0.824 | - | - | 0.679 | - | 0.815 | 0.852 | - | 0.807 | 0.973 | 0.929 | - | 0.887 | - | - | |
| CN c | 0.803 | 0.824 | - | - | 0.843 | 0.817 | 0.959 | - | 0.908 | 0.968 | 0.934 | 0.879 | - | 0.862 | - | |
| P c | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.946 | - | - | ||
| T i | 0.808 | 0.819 | - | 0.692 | 0.833 | 0.848 | 0.805 | - | 0.879 | - | - | 0.785 | 0.771 | - | 0.825 | |
| T c | 0.769 | - | 0.948 | 0.799 | 0.775 | 0.845 | 0.803 | - | - | - | - | 0.857 | 0.898 | - | 0.752 | |
| GP i | 0.649 | 0.618 | 0.955 | 0.683 | 0.767 | 0.700 | 0.930 | - | - | - | - | 0.613 | 0.870 | - | 0.817 | |
| GP c | 0.653 | 0.607 | - | 0.837 | 0.819 | 0.675 | 0.805 | - | - | - | - | 0.609 | 0.703 | - | 0.849 | |
| M i | 0.651 | 0.728 | 0.942 | 0.813 | 0.671 | 0.689 | 0.815 | 0.828 | 0.801 | 0.806 | 0.945 | 0.756 | 0.862 | 0.902 | - | |
| M c | 0.679 | 0.623 | - | 0.812 | 0.575 | 0.584 | 0.783 | 0.859 | 0.769 | 0.901 | - | 0.731 | 0.882 | 0.847 | 0.764 | |
| Pons i | - | - | 0.845 | 0.921 | 0.844 | - | 0.908 | - | - | 0.850 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Pons c | 0.809 | - | - | - | - | 0.665 | 0.922 | - | - | 0.945 | - | 0.869 | 0.893 | - | - | |
| MO i | 0.556 | 0.589 | - | 0.434 | 0.391 | 0.292 | 0.621 | 0.638 | 0.560 | 0.609 | 0.610 | 0.654 | 0.756 | 0.625 | - | |
| MO c | 0.523 | 0.478 | - | 0.538 | 0.358 | 0.461 | 0.562 | 0.753 | 0.718 | 0.413 | 0.622 | 0.648 | 0.624 | 0.474 | - | |
| TLE | Ex E | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FLE | PQE | |||||||||||||||
| Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | Patient 4 | Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | Patient 4 | Patient 5 | Patient 6 | Patient 7 | Patient 8 | Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | ||
| Threshold of PI | - | - | 1.171 | 1.148 | 1.118 | 1.114 | - | - | - | - | - | 1.142 | - | 1.155 | 1.154 | |
| Brain structures | STG i | - | - | - | 1.252 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| A i | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.493 | - | |
| A c | - | - | - | 1.222 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| PHG i | - | - | - | - | 1.143 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.378 | 1.409 | |
| PHG c | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| CingG i | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.227 | |
| CingG c | - | - | - | 1.154 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.205 | |
| IFG i | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.187 | - | |
| IFG c | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.240 | - | |
| SPG i | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| SPG c | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.222 | |
| PrecG i | - | - | - | - | 1.126 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| PostG i | - | - | 1.237 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Supram c | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Precuneus i | - | - | - | - | 1.247 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Precuneus c | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Cuneus i | - | - | 1.188 | 1.162 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.224 | - | - | - | |
| Cuneus c | - | - | - | 1.403 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| LingG i | - | - | - | 1.172 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| SOG i | - | - | 1.249 | - | 1.259 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.507 | - | |
| IOG c | - | - | - | - | 1.180 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| MOFG i | - | - | - | - | 1.180 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| MOFG c | - | - | - | - | 1.236 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.847 | - | |
| LOFG i | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| LOFG c | - | - | - | - | 1.121 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.346 | - | |
| STRAG i | - | - | - | - | 1.379 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.166 | - | - | 1.368 | |
| STRAG c | - | - | - | - | 1.206 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.530 | 1.579 | |
| Entor i | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.196 | - | 1.191 | - | |
| Entor c | - | - | - | 1.205 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.445 | - | |
| Ínsul i | - | - | - | - | 1.229 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.174 | - | - | 1.254 | |
| Ínsul c | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.259 | |
| Cerebellum c | - | - | 1.176 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| RedN c | - | - | 1.592 | 1.205 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| SNig c | - | - | 1.333 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| CN c | - | - | 1.446 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| P i | - | - | - | 1.409 | 1.236 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.382 | - | 1.277 | 1.179 | |
| P c | - | - | 1.386 | 1.387 | 1.120 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.515 | - | 1.236 | 1.244 | |
| T i | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.239 | - | - | - | |
| T c | - | - | - | 1.270 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.210 | - | - | - | |
| GP i | - | - | - | 1.364 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.346 | - | 1.356 | - | |
| GP c | - | - | 1.567 | 1.325 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.203 | - | - | - | |
| M c | - | - | - | 1.179 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Pons i | - | - | - | 1.204 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.174 | - | 1.240 | 1.262 | |
| Pons c | - | - | - | 1.262 | 1.132 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.533 | - | 1.193 | 1.254 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arocha Pérez, J.L.; Morales Chacón, L.M.; Batista García Ramo, K.; Galán García, L. Sequential Semiology of Seizures and Brain Perfusion Patterns in Patients with Drug-Resistant Focal Epilepsies: A Perspective from Neural Networks. Behav. Sci. 2022, 12, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs12040107
Arocha Pérez JL, Morales Chacón LM, Batista García Ramo K, Galán García L. Sequential Semiology of Seizures and Brain Perfusion Patterns in Patients with Drug-Resistant Focal Epilepsies: A Perspective from Neural Networks. Behavioral Sciences. 2022; 12(4):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs12040107
Chicago/Turabian StyleArocha Pérez, Jorge L., Lilia M. Morales Chacón, Karla Batista García Ramo, and Lídice Galán García. 2022. "Sequential Semiology of Seizures and Brain Perfusion Patterns in Patients with Drug-Resistant Focal Epilepsies: A Perspective from Neural Networks" Behavioral Sciences 12, no. 4: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs12040107
APA StyleArocha Pérez, J. L., Morales Chacón, L. M., Batista García Ramo, K., & Galán García, L. (2022). Sequential Semiology of Seizures and Brain Perfusion Patterns in Patients with Drug-Resistant Focal Epilepsies: A Perspective from Neural Networks. Behavioral Sciences, 12(4), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs12040107







