Effects of Ceftriaxone on Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in a Rat Model of Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Surgical Procedure
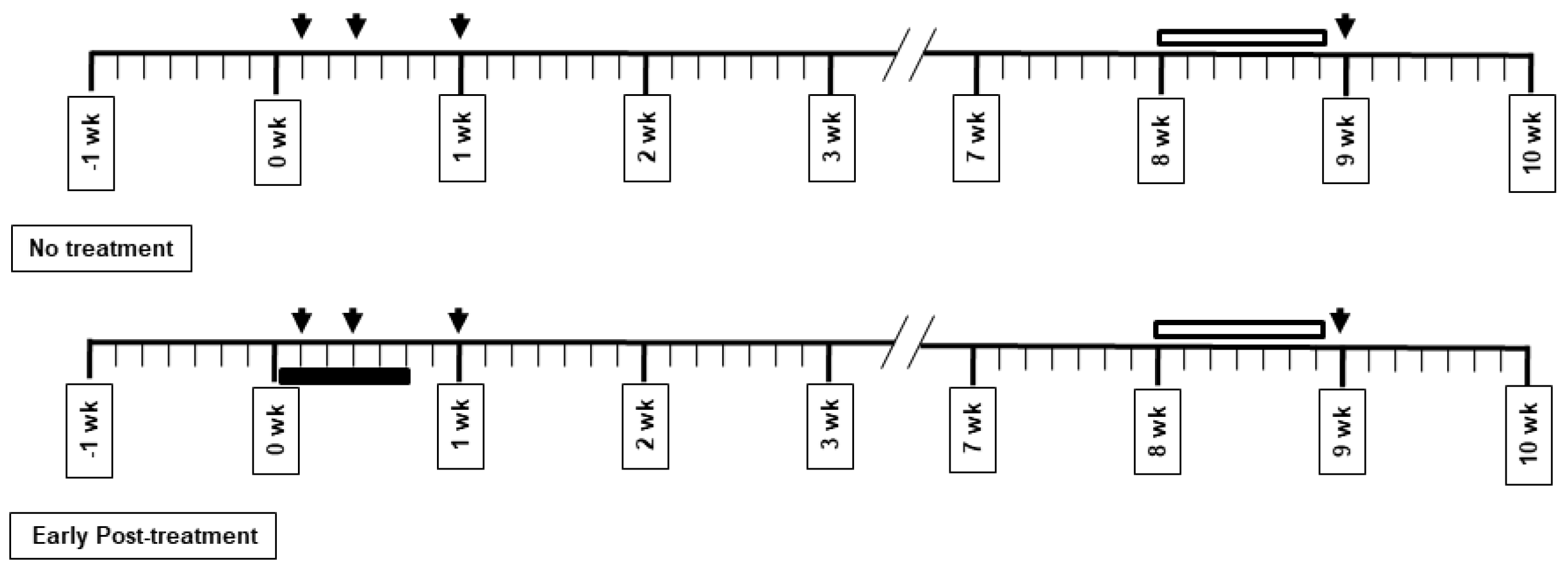
2.2. Drug Administration and Experimental Protocol
2.3. Morris Water Maze Test
2.4. Histological Assessment
2.5. Biochemical Measurement
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
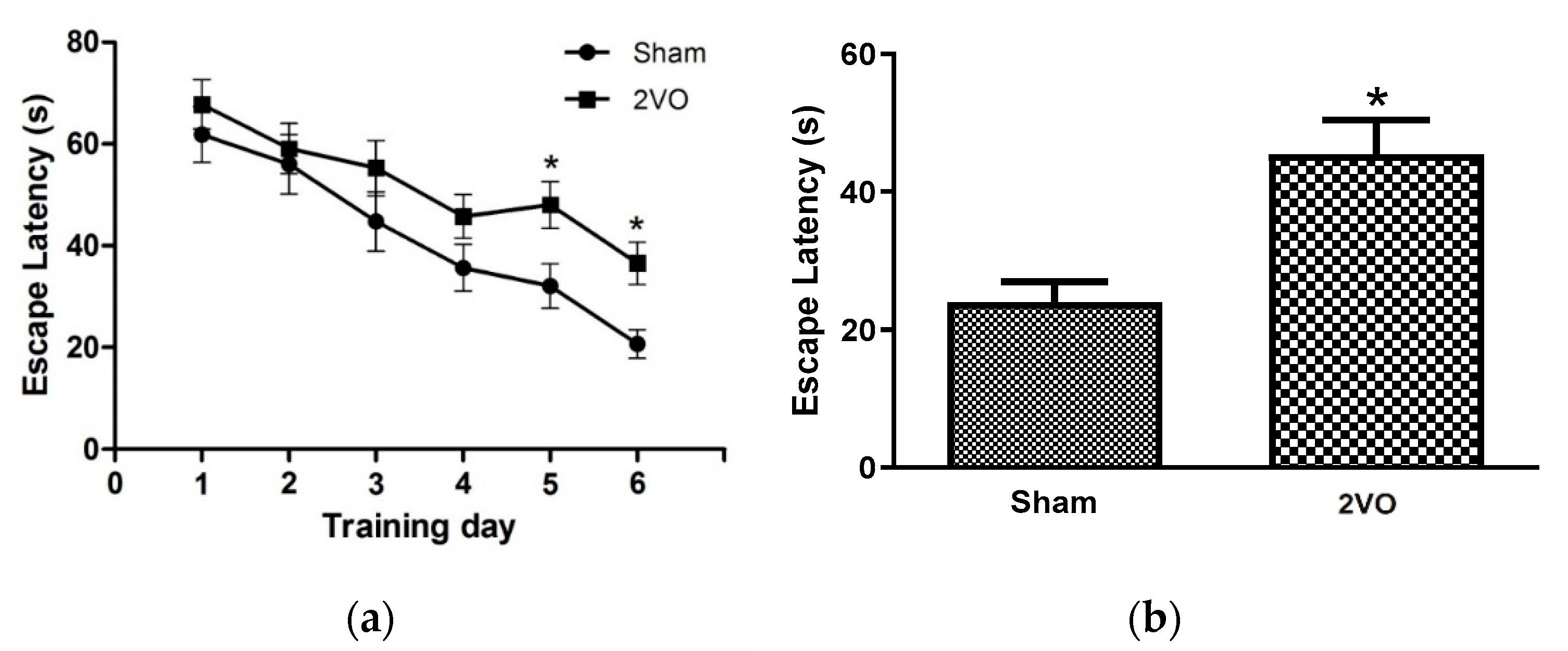
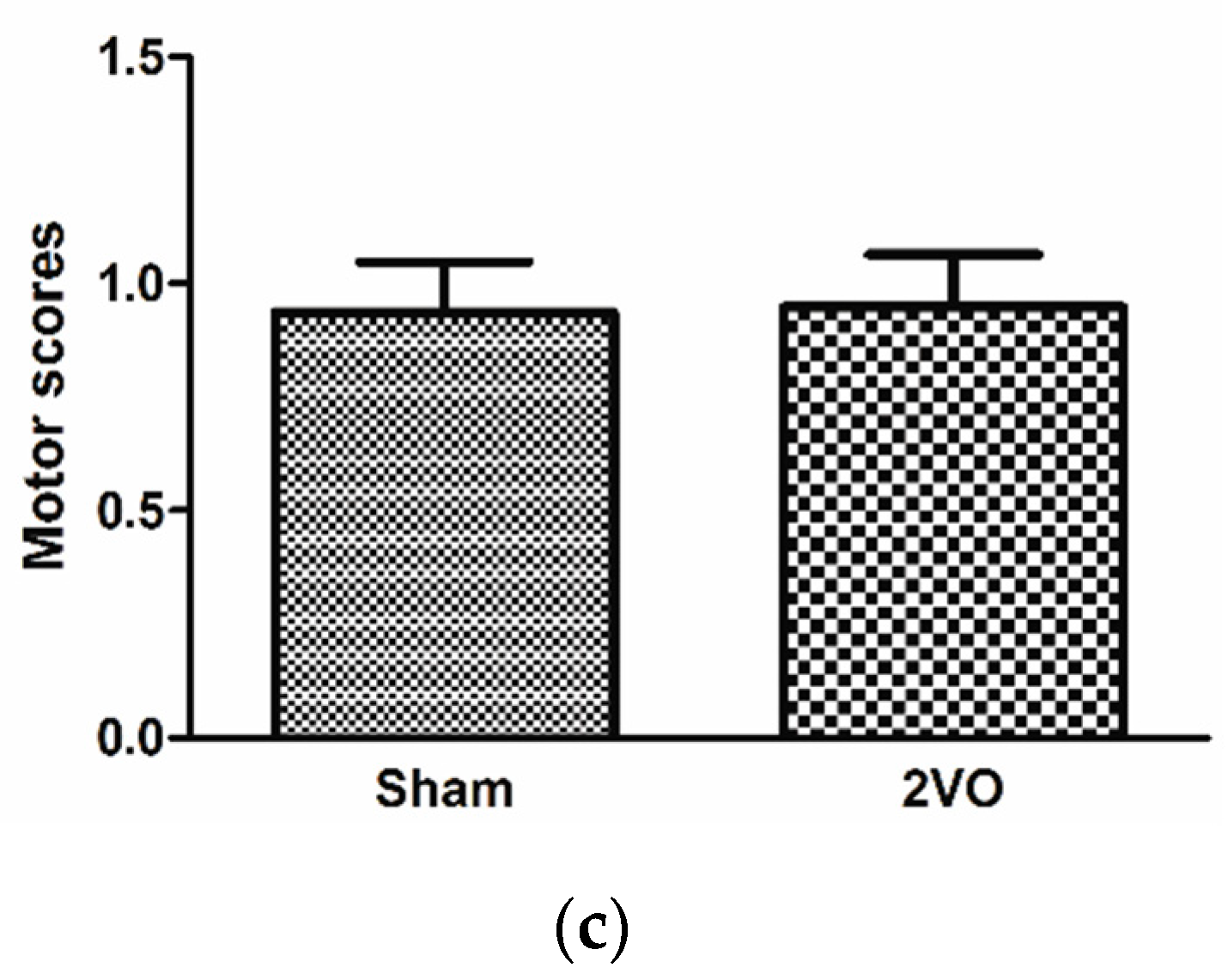
3.1. Effects of Bilateral Common Carotid Artery Occlusion on Learning and Memory Performance
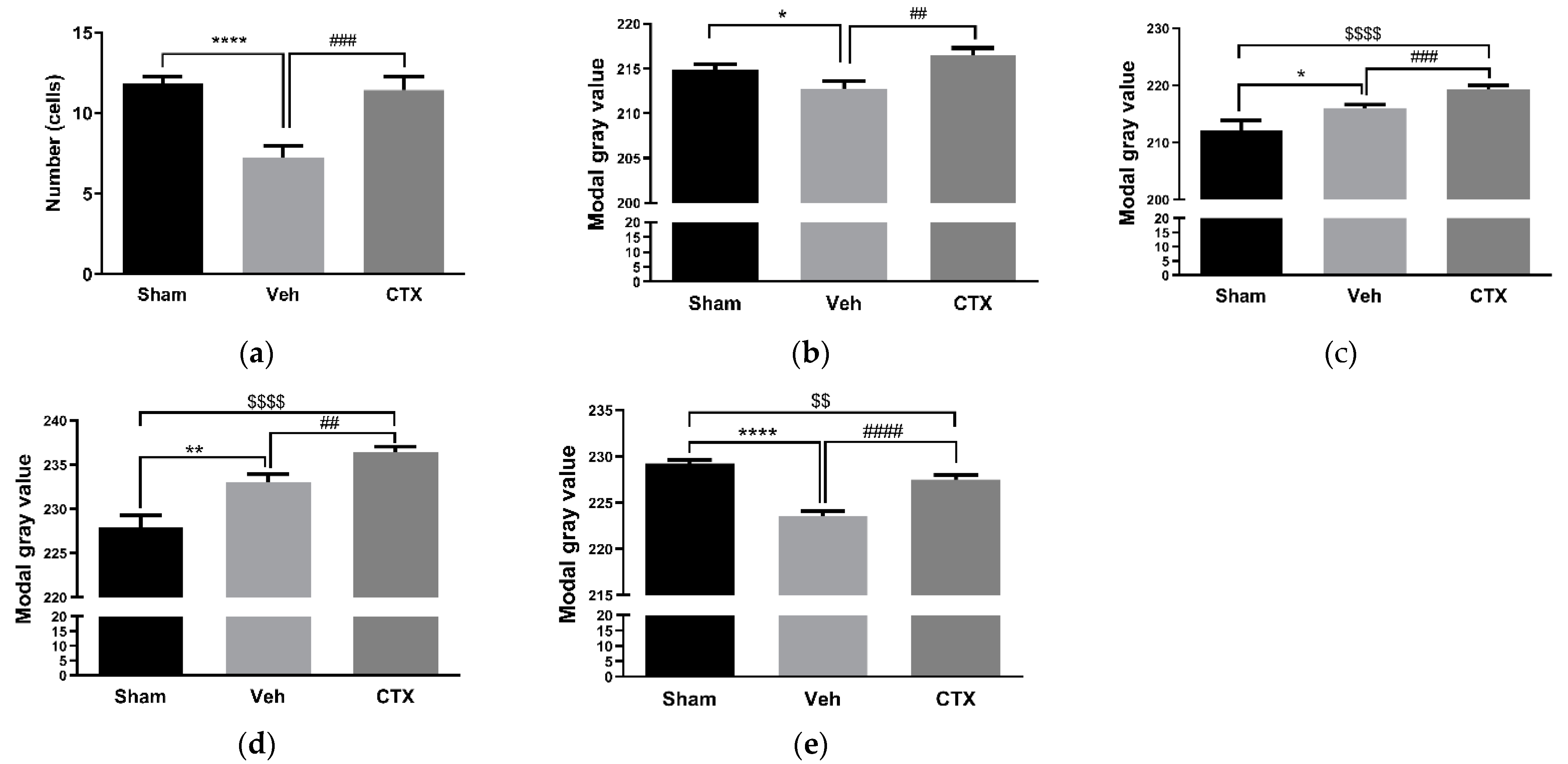
3.2. Effects of Ceftriaxone on White Matter Rarefaction
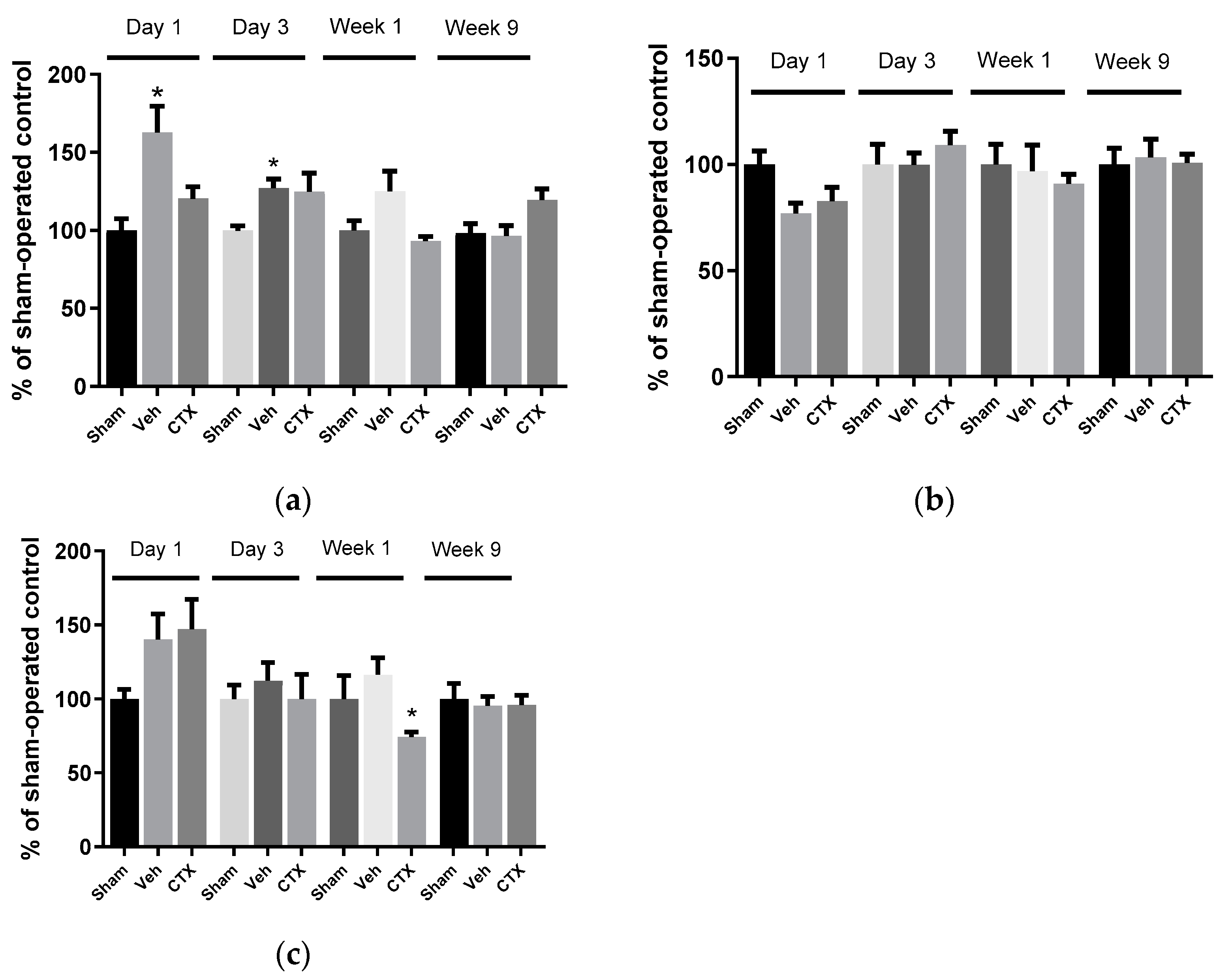
3.3. Effects of Ceftriaxone on Oxidative Stress
3.4. Effects of Ceftriaxone on Gliosis
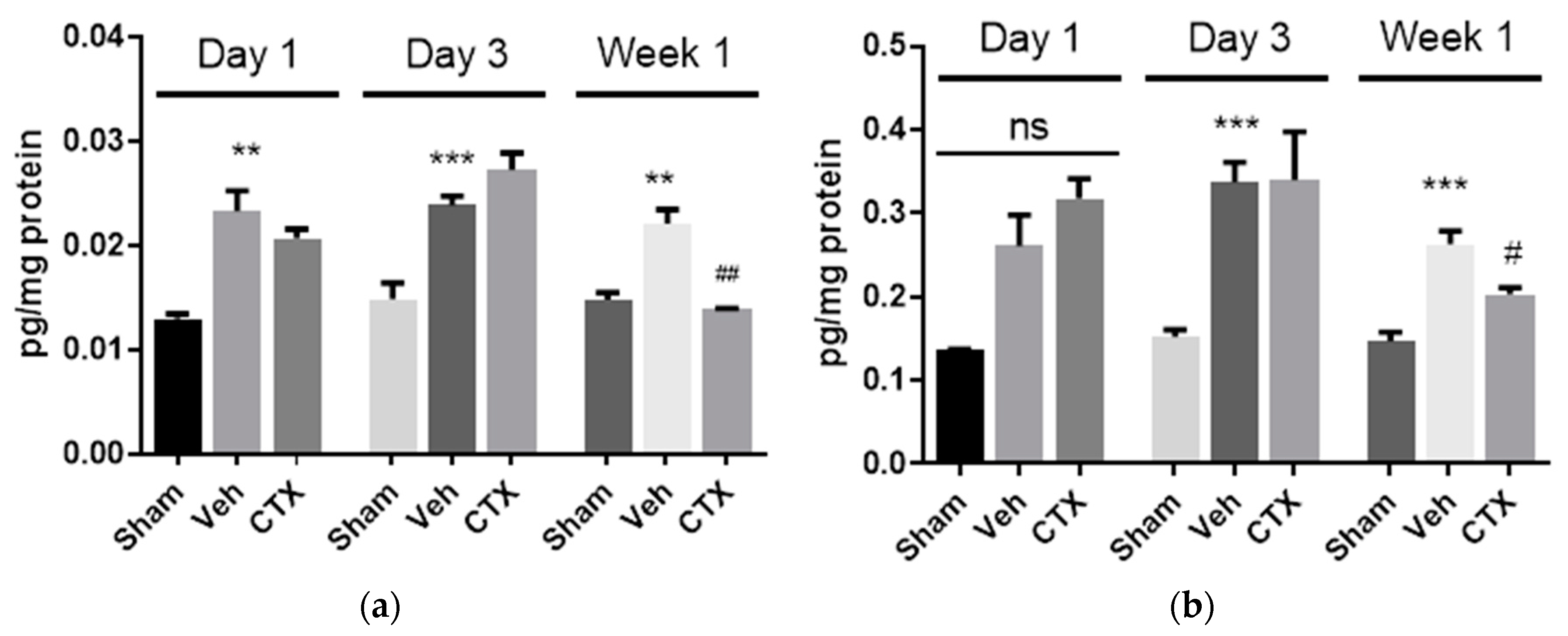
3.5. Effects of Ceftriaxone on Neuroinflammation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doyle, K.P.; Simon, R.P.; Stenzel-Poore, M.P. Mechanisms of ischemic brain damage. Neuropharmacology 2008, 55, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacigaluppi, M.; Comi, G.; Hermann, D.M. Animal models of ischemic stroke. Part two: Modeling cerebral ischemia. Open Neurol. J. 2010, 4, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiss, W.D. The ischemic penumbra: How does tissue injury evolve? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1268, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traystman, R.J. Animal models of focal and global cerebral ischemia. ILAR J. 2003, 44, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eltzschig, H.K.; Eckle, T. Ischemia and reperfusion—From mechanism to translation. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, T.W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.T. Excitotoxicity and stroke: Identifying novel targets for neuroprotection. Prog. Neurobiol. 2014, 115, 157–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmez, I.; Ozyurt, H. Reactive oxygen species and ischemic cerebrovascular disease. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 60, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.W. Excitotoxic cell death. J. Neurobiol. 1992, 23, 1261–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Foster, J.B.; Lin, C.-L.G. Glutamate transporter EAAT2: Regulation, function, and potential as a therapeutic target for neurological and psychiatric disease. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 3489–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothstein, J.D.; Patel, S.; Regan, M.R.; Haenggeli, C.; Huang, Y.H.; Bergles, D.E.; Jin, L.; Dykes Hoberg, M.; Vidensky, S.; Chung, D.S. β-Lactam antibiotics offer neuroprotection by increasing glutamate transporter expression. Nature 2005, 433, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, D.; Li, L.; Li, W.B. Ceftriaxone modulates uptake activity of glial glutamate transporter-1 against global brain ischemia in rats. J. Neurochem. 2015, 132, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hota, S.K.; Barhwal, K.; Ray, K.; Singh, S.B.; Ilavazhagan, G. Ceftriaxone rescues hippocampal neurons from excitotoxicity and enhances memory retrieval in chronic hypobaric hypoxia. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2008, 89, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thöne-Reineke, C.; Neumann, C.; Namsolleck, P.; Schmerbach, K.; Krikov, M.; Schefe, J.H.; Lucht, K.; Hörtnagl, H.; Godes, M.; Müller, S. The β-lactam antibiotic, ceftriaxone, dramatically improves survival, increases glutamate uptake and induces neurotrophins in stroke. J. Hypertens. 2008, 26, 2426–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koomhin, P.; Tilokskulchai, K.; Tapechum, S. Ceftriaxone improves spatial learning and memory in chronic cerebral hypoperfused rats. ScienceAsia 2012, 38, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Morris, R. Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J. Neurosci. Methods 1984, 11, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; He, Z.; Guo, L.; Wang, H. Improvement of cognitive deficit and neuronal damage in rats with chronic cerebral ischemia via relative long-term inhibition of rho-kinase. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2008, 28, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorhees, C.V.; Williams, M.T. Morris water maze: Procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of learning and memory. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, B.B. Functional outcome in rats transferred to an enriched environment 15 days after focal brain ischemia. Stroke 1996, 27, 324–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakita, H.; Tomimoto, H.; Akiguchi, I.; Matsuo, A.; Lin, J.-X.; Ihara, M.; McGeer, P.-L. Axonal damage and demyelination in the white matter after chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in the rat. Brain Res. 2002, 924, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu, M.; Yamashita, T.; Hirose, N.; Teramoto, S.; Kwak, S. The AMPA receptor antagonist perampanel robustly rescues amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) pathology in sporadic ALS model mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, K.; Lau, W.M.; Lau, H.T.; So, K.-F.; Chang, R.C.-C. Micro-dissection of rat brain for RNA or protein extraction from specific brain region. J. Vis. Exp. 2007, 7, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathyasaikumar, K.; Swapna, I.; Reddy, P.; Murthy, C.R.; Dutta Gupta, A.; Senthilkumaran, B.; Reddanna, P. Fulminant hepatic failure in rats induces oxidative stress differentially in cerebral cortex, cerebellum and pons medulla. Neurochem. Res. 2007, 32, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longstreth, W.; Manolio, T.A.; Arnold, A.; Burke, G.L.; Bryan, N.; Jungreis, C.A.; Enright, P.L.; O’Leary, D.; Fried, L. Clinical correlates of white matter findings on cranial magnetic resonance imaging of 3301 elderly people: The Cardiovascular Health Study. Stroke 1996, 27, 1274–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, H.Y.; Tang, X.C. Huperzine a improves chronic inflammation and cognitive decline in rats with cerebral hypoperfusion. J. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 88, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewar, D.; Underhill, S.M.; Goldberg, M.P. Oligodendrocytes and ischemic brain injury. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2003, 23, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, K.; Nakao, S.; Jomura, S.; Sakamoto, S.; Miyamoto, E.; Xu, Y.; Tomimoto, H.; Inada, T.; Shingu, K. Edaravone, a free radical scavenger, mitigates both gray and white matter damages after global cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res. 2009, 1279, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, E.; Luiten, P.G.; Bari, F. Permanent, bilateral common carotid artery occlusion in the rat: A model for chronic cerebral hypoperfusion-related neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res. Rev. 2007, 54, 162–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.-w.; Ohta, H.; Matsumoto, K.; Watanabe, H. Progressive cognitive impairment following chronic cerebral hypoperfusion induced by permanent occlusion of bilateral carotid arteries in rats. Brain Res. 1994, 653, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Kastner, R.; Aguirre-Chen, C.; Saul, I.; Yick, L.; Hamasaki, D.; Busto, R.; Ginsberg, M.D. Astrocytes react to oligemia in the forebrain induced by chronic bilateral common carotid artery occlusion in rats. Brain Res. 2005, 1052, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cechetti, F.; Pagnussat, A.S.; Worm, P.V.; Elsner, V.R.; Ben, J.; da Costa, M.S.; Mestriner, R.; Weis, S.N.; Netto, C.A. Chronic brain hypoperfusion causes early glial activation and neuronal death, and subsequent long-term memory impairment. Brain Res. Bull. 2012, 87, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomimoto, H.; Ihara, M.; Wakita, H.; Ohtani, R.; Lin, J.-X.; Akiguchi, I.; Kinoshita, M.; Shibasaki, H. Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion induces white matter lesions and loss of oligodendroglia with DNA fragmentation in the rat. Acta Neuropathol. 2003, 106, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matute, C. Glutamate and ATP signalling in white matter pathology. J. Anat. 2011, 219, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altaş, M.; Meydan, S.; Aras, M.; Yılmaz, N.; Ulutaş, K.; Okuyan, H.; Nacar, A. Effects of ceftriaxone on ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat brain. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 20, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballinger, E.C.; Ananth, M.; Talmage, D.A.; Role, L.W. Basal forebrain cholinergic circuits and signaling in cognition and cognitive decline. Neuron 2016, 91, 1199–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tikhonova, M.A.; Ho, S.-C.; Akopyan, A.A.; Kolosova, N.G.; Weng, J.-C.; Meng, W.-Y.; Lin, C.-L.; Amstislavskaya, T.G.; Ho, Y.-J. Neuroprotective effects of ceftriaxone treatment on cognitive and neuronal deficits in a rat model of accelerated senescence. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 330, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mracskó, É.; Hugyecz, M.; Institóris, Á.; Farkas, E.; Bari, F. Changes in pro-oxidant and antioxidant enzyme levels during cerebral hypoperfusion in rats. Brain Res. 2010, 1321, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodrich, G.S.; Kabakov, A.Y.; Hameed, M.Q.; Dhamne, S.C.; Rosenberg, P.A.; Rotenberg, A. Ceftriaxone treatment after traumatic brain injury restores expression of the glutamate transporter, GLT-1, reduces regional gliosis, and reduces post-traumatic seizures in the rat. J. Neurotrauma 2013, 30, 1434–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, A.Y.; Todd, K.G. Microglia in cerebral ischemia: Molecular actions and interactions. Can. J. Physiol. Pharm. 2006, 84, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomimoto, H.; Akiguchi, I.; Wakita, H.; Lin, J.-X.; Budka, H. Cyclooxygenase-2 is induced in microglia during chronic cerebral ischemia in humans. Acta Neuropathol. 2000, 99, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loddick, S.A.; Rothwell, N.J. Neuroprotective effects of human recombinant interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in focal cerebral ischaemia in the rat. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1996, 16, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulcahy, N.J.; Ross, J.; Rothwell, N.J.; Loddick, S.A. Delayed administration of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist protects against transient cerebral ischaemia in the rat. Br. J. Pharm. 2003, 140, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lujia, Y.; Xin, L.; Shiquan, W.; Yu, C.; Shuzhuo, Z.; Hong, Z. Ceftriaxone pretreatment protects rats against cerebral ischemic injury by attenuating microglial activation-induced IL-1β expression. Int. J. Neurosci. 2014, 124, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambertsen, K.L.; Meldgaard, M.; Ladeby, R.; Finsen, B. A quantitative study of microglial—Macrophage synthesis of tumor necrosis factor during acute and late focal cerebral ischemia in mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2005, 25, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sattayakhom, A.; Kalarat, K.; Rakmak, T.; Tapechum, S.; Monteil, A.; Punsawad, C.; Palipoch, S.; Koomhin, P. Effects of Ceftriaxone on Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in a Rat Model of Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion. Behav. Sci. 2022, 12, 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs12080287
Sattayakhom A, Kalarat K, Rakmak T, Tapechum S, Monteil A, Punsawad C, Palipoch S, Koomhin P. Effects of Ceftriaxone on Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in a Rat Model of Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion. Behavioral Sciences. 2022; 12(8):287. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs12080287
Chicago/Turabian StyleSattayakhom, Apsorn, Kosin Kalarat, Thatdao Rakmak, Sompol Tapechum, Arnaud Monteil, Chuchard Punsawad, Sarawoot Palipoch, and Phanit Koomhin. 2022. "Effects of Ceftriaxone on Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in a Rat Model of Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion" Behavioral Sciences 12, no. 8: 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs12080287
APA StyleSattayakhom, A., Kalarat, K., Rakmak, T., Tapechum, S., Monteil, A., Punsawad, C., Palipoch, S., & Koomhin, P. (2022). Effects of Ceftriaxone on Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in a Rat Model of Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion. Behavioral Sciences, 12(8), 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs12080287





