Habits and Persistent Food Restriction in Patients with Anorexia Nervosa: A Scoping Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (RQ1) What evidence is available on how habits contribute to food restriction in AN?
- (RQ2) What methods are used to evaluate habits related to food restriction in AN?
- (RQ3) What are the mechanisms of habit learning in food restriction in AN?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Sources of Information and Search Strategy
2.4. Selection of Sources of Evidence
2.5. Data Extraction and Items
2.6. Summary of Results
3. Results
3.1. Selection of Sources of Evidence
3.2. Characteristics of Evidence Sources
3.3. Characteristics of the Participants
3.4. Results of Sources of Evidence
3.4.1. Methods for Evaluating Habits
Scale
Neuroimaging
Experimental and Behavioural Tasks
3.5. Habit Mechanism in AN Food Restriction
3.5.1. Behavioural Mechanisms
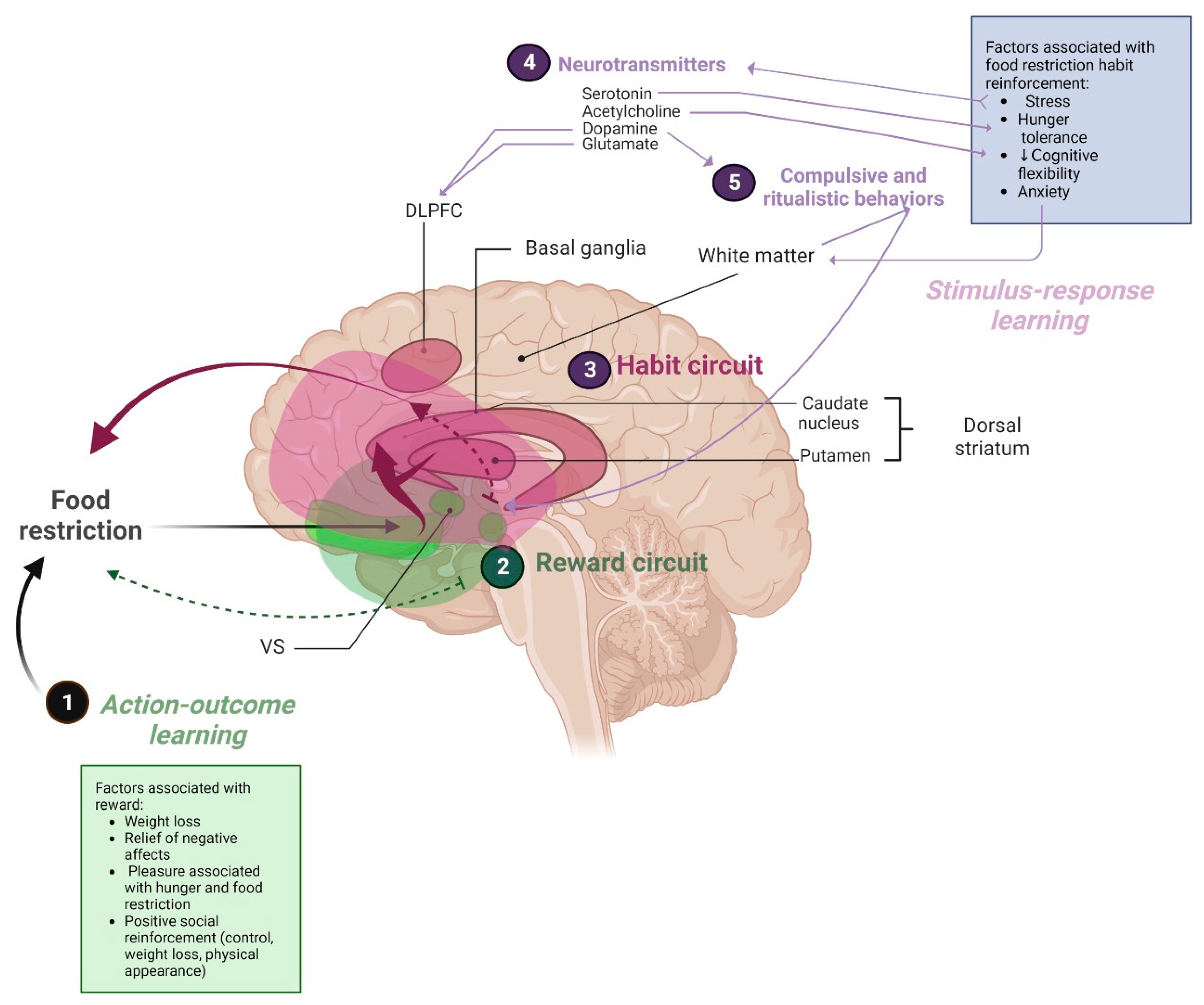
3.5.2. Neural Mechanisms
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Evidence
4.1.1. (RQ1) Evidence Available
4.1.2. (RQ2) Habit-Related Measures of Food Restriction in AN
4.1.3. (RQ3) Mechanisms of Habit-Learning in AN Persistence
4.1.4. Behavioural Mechanisms Involving Habits
4.1.5. Neural Mechanisms Involving Habits
4.2. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Psychiatric Association, Diagnostic, and American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Treasure, J.; Duarte, T.A.; Schmidt, U. Eating Disorders. Lancet 2020, 395, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Eeden, A.E.; Van Hoeken, D.; Hoek, H.W. Incidence, prevalence and mortality of anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2021, 34, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrescu, S.R.; Dinkler, L.; Gillberg, C.; Råstam, M.; Gillberg, C.; Wentz, E. Anorexia nervosa: 30-year outcome. Br. J. Psychiatry 2020, 216, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcelus, J.; Mitchell, A.J.; Wales, J.; Nielsen, S. Mortality Rates in Patients with Anorexia Nervosa and Other Eating Disorders: A Meta-Analysis of 36 Studies. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2011, 68, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinhut, M.; Godart, N.; Benadjaoud, M.A.; Melchior, J.C.; Hanachi, M. Five-year mortality of severely malnourished patients with chronic anorexia nervosa admitted to a medical unit. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2021, 143, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Lancet. Eating Disorders: Innovation and Progress Urgently Needed. Lancet 2020, 395, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Burgos, D.; Wilhelm, P.; Vögele, C.; Munsch, S. Food Restriction in Anorexia Nervosa in the Light of Modern Learning Theory: A Narrative Review. Behav. Sci. 2023, 13, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, L.; Walsh, B.T.; Schebendach, J.; Glasofer, D.R.; Steinglass, J.E. Habits are stronger with longer duration of illness and greater severity in anorexia nervosa. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2020, 53, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mysliwiec, R. Neuroscience of Adolescent Anorexia Nervosa: Implications for Family-Based Treatment (FBT). Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufin, T.; Steinglass, J.E. How Anxiety and Habits Contribute to Anorexia Nervosa. Psichiatr. Times 2019, 36, 30–31. [Google Scholar]
- Frank, G.K.W.; Shott, M.E.; DeGuzman, M.C. Recent advances in understanding anorexia nervosa. F1000Research 2019, 8, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasneem, A. Neurobiological Underpinnings of Anorexia Nervosa. Univ. Tor. Med. J. 2018, 95, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Steinglass, J.E.; Walsh, B.T. Neurobiological Model of the Persistence of Anorexia Nervosa. J. Eat. Disord. 2016, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godier, L.R.; de Wit, S.; Pinto, A.; Steinglass, J.E.; Greene, A.L.; Scaife, J.; Gillan, C.M.; Walsh, B.T.; Simpson, H.B.; Park, R.J. An Investigation of Habit Learning in Anorexia Nervosa. Psychiatry Res. 2016, 244, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hara, C.B.; Campbell, I.C.; Schmidt, U. A Reward-Centred Model of Anorexia Nervosa: A Focussed Narrative Review of the Neurological and Psychophysiological Literature. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 52, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compan, V.; Walsh, B.T.; Kaye, W.; Geliebter, A. How Does the Brain Implement Adaptive Decision-Making to Eat? J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 13868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, B.T. The Enigmatic Persistence of Anorexia Nervosa. Am. J. Psychiatry 2013, 170, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinglass, J.; Walsh, B.T. Habit Learning and Anorexia Nervosa: A Cognitive Neuroscience Hypothesis. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2006, 39, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uniacke, B.; Walsh, B.T.; Foerde, K.; Steinglass, J. The role of habits in anorexia nervosa: Where we are and where to go from here? Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2018, 20, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, W.; Rünger, D. Psychology of Habit. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2016, 67, 289–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMAScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 Statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- P Peters, M.D.J.; Godfrey, C.; McInerney, P.; Munn, Z.; Tricco, A.C.; Khalil, H. Chapter 11: Scoping Reviews (2020 version). In JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis; Aromataris, E., Munn, Z., Eds.; 2020; pp. 406–451. Available online: https://synthesismanual.jbi.global (accessed on 5 September 2023).
- Greenhalgh, T.; Peacock, R. Effectiveness and Efficiency of Search Methods in Systematic Reviews of Complex Evidence: Audit of Primary Sources. BMJ 2005, 331, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, S.B.; Cabeen, R.P.; Jann, K.; Tadayonnejad, R.; Strober, M.; Feusner, J.D. White Matter Microstructure in Habit and Reward Circuits in Anorexia Nervosa: Insights from a Neurite Orientation Dispersion and Density Imaging Study. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2023, 147, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidel, M.; Joseph, A.K.; Fürtjes, S.; Labitzke, N.; Wronski, M.L.; Boehm, I.; Hennig, J.; Gramatke, K.; Roessner, V.; Ehrlich, S. Increased Habit Frequency in the Daily Lives of Patients with Acute Anorexia Nervosa. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muratore, A.F.; Bershad, M.; Steinglass, J.E.; Foerde, K.E.; Gianini, L.; Broft, A.; Attia, E. Use of High-Frequency Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation to Probe the Neural Circuitry of Food Choice in Anorexia Nervosa: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2021, 54, 2031–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinglass, J.; Lloyd, C.; Foerde, K.; Jablonski, M.; Hong, S.; Posner, J. Behavioral and neural mechanisms of food choice among adolescents with anorexia nervosa. In Neuropsychopharmacology; Springer Nature Campus: London, UK, 2021; Volume 46, p. 174. [Google Scholar]
- Tadayonnejad, R.; Pizzagalli, F.; Murray, S.B.; Pauli, W.M.; Conde, G.; Bari, A.A.; Strober, M.; O’Doherty, J.P.; Feusner, J.D. White Matter Tracts Characteristics in Habitual Decision-Making Circuit Underlie Ritual Behaviors in Anorexia Nervosa. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foerde, K.; Walsh, B.T.; Dalack, M.; Daw, N.; Shohamy, D.; Steinglass, J.E. Changes in brain and behavior during food-based decision-making following treatment of anorexia nervosa. J. Eat. Disord. 2021, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favier, M.; Janickova, H.; Justo, D.; Kljakic, O.; Runtz, L.; Natsheh, J.Y.; Pascoal, T.A.; Germann, J.; Gallino, D.; Kang, J.I.; et al. Cholinergic dysfunction in the dorsal striatum promotes habit formation and maladaptive eating. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 6616–6630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, B.; Foerde, K.; Bartholdy, S.; McClelland, J.; Kekic, M.; Grycuk, L.; Campbell, I.C.; Schmidt, U.; Steinglass, J.E. The effect of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on food choice-related self-control in patients with severe, enduring anorexia nervosa. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2020, 53, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, V.; Dittrich, M.; Horndasch, S.; Kratz, O.; Moll, G.H.; Erim, Y.; Paslakis, G.; Rauh, E.; Sabine, S.L. Pavlovian-to-instrumental Transfer in Anorexia Nervosa: A pilot study on conditioned learning and instrumental responding to low-and high-calorie food stimuli. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2020, 51, 1794–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leppanen, J.; Cardi, V.; Sedgewick, F.; Treasure, J.; Tchanturia, K. Basal Ganglia Volume and Shape in Anorexia Nervosa. Appetite 2020, 144, 104480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinglass, J. Computational and Neural Systems underpinning maladaptive behavior in anorexia nervosa. In Neuropsychopharmacology; Nature Publishing Group Macmillan Building: London, UK, 2019; Volume 44, pp. 33–34. [Google Scholar]
- Steding, J.; Boehm, I.; King, J.A.; Geisler, D.; Ritschel, F.; Seidel, M.; Doose, A.; Jaite, C.; Roessner, V.; Smolka, M.N.; et al. Goal-Directed vs. Habitual Instrumental Behavior during Reward Processing in Anorexia Nervosa: An FMRI Study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynos, A.F.; Hall, L.M.J.; Lavender, J.M.; Peterson, C.B.; Crow, S.J.; Klimes-Dougan, B.; Cullen, K.R.; Lim, K.O.; Camchong, J. Resting-state functional connectivity of networks associated with reward and habit in anorexia nervosa. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2019, 40, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinglass, J.E.; Glasofer, D.R.; Walsh, E.; Guzman, G.; Peterson, C.B.; Walsh, B.T.; Attia, E.; Wonderlich, S.A. Targeting Habits in Anorexia Nervosa: A Proof-of-Concept Randomized Trial. Psychol. Med. 2018, 48, 2584–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coniglio, K.A.; Becker, K.R.; Franko, D.L.; Zayas, L.V.; Plessow, F.; Eddy, K.T.; Thomas, J.J. Won’t Stop or Can’t Stop? Food Restriction as a Habitual Behavior among Individuals with Anorexia Nervosa or Atypical Anorexia Nervosa. Eat. Behav. 2017, 26, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, E.C.; Frampton, I.; Verplanken, B.; Haase, A.M. How extreme dieting becomes compulsive: A novel hypothesis for the role of anxiety in the development and maintenance of anorexia nervosa. Med. Hypotheses 2017, 108, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.A.; Geisler, D.; Bernardoni, F.; Ritschel, F.; Böhm, I.; Seidel, M.; Mennigen, E.; Ripke, S.; Smolka, M.N.; Roessner, V.; et al. Altered neural efficiency of decision making during temporal reward discounting in anorexia nervosa. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2016, 55, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foerde, K.; Steinglass, J.E.; Shohamy, D.; Walsh, B.T. Neural Mechanisms Supporting Maladaptive Food Choices in Anorexia Nervosa. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 1571–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothemund, Y.; Buchwald, C.; Georgiewa, P.; Bohner, G.; Bauknecht, H.C.; Ballmaier, M.; Klapp, B.F.; Klingebiel, R. Compulsivity Predicts Fronto Striatal Activation in Severely Anorectic Individuals. Neuroscience 2011, 197, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarda, A.S.; Schreyer, C.C.; Boersma, G.J.; Tamashiro, K.L.; Moran, T.H. Anorexia nervosa as a motivated behavior: Relevance of anxiety, stress, fear and learning. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 152, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godier, L.R.; Park, R.J. Compulsivity in Anorexia Nervosa: A Transdiagnostic Concept. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, R.J.; Godier, L.R.; Cowdrey, F.A. Hungry for Reward: How Can Neuroscience Inform the Development of Treatment for Anorexia Nervosa? Behav. Res. Ther. 2014, 62, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, R.; Steinglass, J.E.; Graziano, K.; Peterson, B.S.; Walsh, B.T. Self-regulatory control and habit learning in the development of eating disorders. Curr. Psychiatry Rev. 2007, 3, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadayonnejad, R.; Pauli, W.M.; O’Doherty, J.P.; Feusner, J.D. Structural Hyperconnectivity of a corticostriatal circuit involved in habitual decision-making in anorexia nervosa and its associations with compulsive behaviors. In Neuropsychopharmacology; Nature Publishing Group Macmillan Building: London, UK, 2019; Volume 44, p. 237. [Google Scholar]
- El Mestikawy, S.; Favier, M. Dysregulation of habit formation and vulnerability to eating disorders: Role of Striatal cholinergic interneurons. Med. Sci. 2021, 37, 719–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foerde, K.; Schebendach, J.E.; Davis, L.; Daw, N.; Walsh, B.T.; Shohamy, D.; Steinglass, J.E. Restrictive Eating across a Spectrum from Healthy to Unhealthy: Behavioral and Neural Mechanisms. Psychol. Med. 2022, 52, 1755–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foerde, K.; Schebendach, J.; Daw, N.; Walsh, T.; Shohamy, D.; Steinglass, J.E. Neural and behavioral mechanisms of food decision making across a spectrum of restrictive eating. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 87, S20–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinglass, J.; Foerde, K.; Shohamy, D.; Walsh, B.T. Restrictive Food Choice Shows Neurological Signature of Habit. Appetite 2016, 100, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinglass, J.E. 43.1 Linking brain and behavior: Neural mechanisms of persistent illness in anorexia nervosa. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2016, 10, S326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arksey, H.; O’Malley, L. Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework. Int. J. Soc. Res. Method 2005, 8, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tappe, K.; Tarves, E.; Oltarzewski, J.; Frum, D. Habit formation among regular exercisers at fitness centres: An exploratory study. J. Phys. Act. Health 2013, 10, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGowan, L.; Cooke, L.J.; Gardner, B.; Beeken, R.J.; Croker, H.; Wardle, J. Healthy feeding habits: Efficacy results from a cluster-randomised, controlled exploratory trial of a novel, habit-based intervention with parents. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 98, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verplanken, B.; Orbell, S. Reflections on past behavior: A self-report index of habit strength. J. Appl. Soc. Psychol. 2003, 33, 1313–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddy, K.T.; Plessow, F.; Breithaupt, L.; Becker, K.R.; Slattery, M.; Mancuso, C.J.; Izquierdo, A.M.; Van De Water, A.L.; Kahn, D.L.; Dreier, M.J.; et al. Neural activation of regions involved in food reward and cognitive control in young females with anorexia nervosa and atypical anorexia nervosa versus healthy controls. Transl. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajebrahimi, F.; Velioglu, H.A.; Bayraktaroglu, Z.; Yilmaz, N.H.; Hanoglu, L. Clinical evaluation and resting state fMRI analysis of virtual reality based training in Parkinson’s disease through a randomised controlled trial. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, W.; Huang, L.; Tian, Y.; Luo, H.; Chen, S.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Fu, J.; Yu, Q.; Xu, L. Effect and mechanism of mirror therapy on lower limb rehabilitation after ischemic stroke: A fMRI study. NeuroRehabilitation 2022, 51, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steward, T.; Menchon, J.M.; Jiménez-Murcia, S.; Soriano-Mas, C.; Fernandez-Aranda, F. Neural Network Alterations Across Eating Disorders: A Narrative Review of fMRI Studies. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 1150–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, M.S.M.; Wu, S.L.; Webb, S.E.; Gluskin, K.; Yew, D.T. Functional magnetic resonance imaging and the brain: A brief review. World J. Radiol. 2017, 9, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugurbil, K. What is feasible with imaging human brain function and connectivity using functional magnetic resonance imaging? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 371, 20150361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, C.; Salvador, A.; Valabrègue, R.; Roze, E.; Palminteri, S.; Vidailhet, M.; de Wit, S.; Robbins, T.; Hartmann, A.; Worbe, Y. Enhanced habit formation in Gilles de la Tourette syndrome. Brain 2016, 139, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjoerds, Z.; Dietrich, A.; Deserno, L.; de Wit, S.; Villringer, A.; Heinze, H.J.; Schlagenhauf, F.; Horstmann, A. Slips of Action and Sequential Decisions: A Cross-Validation Study of Tasks Assessing Habitual and Goal-Directed Action Control. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Wit, S.; Watson, P.; Harsay, H.A.; Cohen, M.X.; Van de Vijver, I.; Ridderinkhof, K.R. Corticostriatal connectivity underlies individual differences in the balance between habitual and goal-directed action control. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 12066–12075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbit, L.H.; Balleine, B.W. Double dissociation of basolateral and central amygdala lesions on the general and outcome-specific forms of pavlovian-instrumental transfer. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartoni, E.; Puglisi-Allegra, S.; Baldassarre, G. The three principles of action: A Pavlovian-instrumental transfer hypothesis. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, R.Q.M.; Furukawa, E.; Hoefle, S.; Moll, J.; Tripp, G.; Mattos, P. An Adaptation of Pavlovian-to-Instrumental Transfer (PIT) Methodology to Examine the Energising Effects of Reward-Predicting Cues on Behavior in Young Adults. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbusow, M.; Ebrahimi, C.; Riemerschmid, C.; Daldrup, L.; Rothkirch, M.; Chen, K.; Chen, H.; Belanger, M.J.; Hentschel, A.; Smolka, M.N.; et al. Pavlovian-to-Instrumental Transfer across Mental Disorders: A Review. Neuropsychobiology 2022, 81, 418–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danner, U.N.; Aarts, H.; de Vries, N.K. Habit vs. intention in the prediction of future behaviour: The role of frequency, context stability and mental accessibility of past behaviour. Br. J. Soc. Psychol. 2008, 47, 245–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wit, S.; Dickinson, A. Associative theories of goal-directed behaviour: A case for animal–human translational models. Psychol. Res. 2009, 73, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friederich, H.C.; Herzog, W. Cognitive-behavioral flexibility in anorexia nervosa. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2011, 6, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternheim, L.C.; van Passel, B.; Dingemans, A.; Cath, D.; Danner, U.N. Cognitive and Experienced Flexibility in Patients with Anorexia Nervosa and Obsessive Compulsive Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 868921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, W.; Mazar, A.; Neal, D.T. Habits and Goals in Human Behavior: Separate but Interacting Systems. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2022, 17, 590–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meneguzzo, P.; Collantoni, E.; Solmi, M.; Tenconi, E.; Favaro, A. Anorexia nervosa and diffusion weighted imaging: An open methodological question raised by a systematic review and a fractional anisotropy anatomical likelihood estimation meta-analysis. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2019, 52, 1237–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balleine, B.W.; O’Doherty, J.P. Human and rodent homologies in action control: Corticostriatal determinants of goal-directed and habitual action. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 48–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luque, D.; Beesley, T.; Morris, R.W.; Jack, B.N.; Griffiths, O.; Whitford, T.J.; Le Pelley, M.E. Goal-Directed and Habit-Like Modulations of Stimulus Processing during Reinforcement Learning. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 3009–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tik, M.; Hoffmann, A.; Sladky, R.; Tomova, L.; Hummer, A.; Navarro de Lara, L.; Bukowski, H.; Pripfl, J.; Biswal, B.; Lamm, C.; et al. Towards understanding rTMS mechanism of action: Stimulation of the DLPFC causes network-specific increase in functional connectivity. Neuroimage 2017, 162, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Burgos, D. Associative learning and high-level cognitive processes in the control of food-related behaviors. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2022, 47, 101207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.D.; Godfrey, C.M.; Khalil, H.; McInerney, P.; Parker, D.; Soares, C.B. Guidance for conducting systematic scoping reviews. JBI Evid. Implement. 2015, 13, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Criterion | Participants | Concept | Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inclusion | 1. Human sample with AN: a. Structured interviews (e.g., EDE, SCID). b. Accepted classification system (e.g., DSM, ICD). c. No age, gender, or race restrictions. 2. Animal model sample with AN. | Habits: A habit is a frequently repeated behaviour elicited by a stimulus that leads to a fixed action, resulting from a learned stimulus–response association. Habit assessment in the context of AN: 1. Neuroimaging (e.g., dorsolateral striatum/putamen). 2. Scales (e.g., self-report habit index adapted for food restriction). 3. Experimental behavioural techniques (e.g., outcome/reinforcer devaluation). Food restriction in AN: Conceptualised as successful food avoidance or reducing caloric intake. Measures determined by authors of primary studies will be considered. | 1. Primary care, hospital services, community, and remote access. 2. Any country. 3. Duration of disease and resistance to treatment. 4. Race, gender, and socioeconomic status. |
| Exclusion | 1. Risk behaviours for eating disorders. 2. Overweight/obesity 3. Other eating disorders (e.g., bulimia nervosa, binge eating disorder). 4. Pregnant women and nursing mothers. | Habits: 1. Outside the context of AN. 2. Usual physical activity. 3. Habitual meal and food intake with no focus on food restriction. Food restriction: 1. Outside the context of AN. 2. Professional-oriented diet for specific diseases (e.g., obesity, diabetes). 3. Dietary intakes in AN assessed by daily energy/nutrients or dietary patterns. | None. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Conceição, I.S.R.; Garcia-Burgos, D.; de Macêdo, P.F.C.; Nepomuceno, C.M.M.; Pereira, E.M.; Cunha, C.d.M.; Ribeiro, C.D.F.; de Santana, M.L.P. Habits and Persistent Food Restriction in Patients with Anorexia Nervosa: A Scoping Review. Behav. Sci. 2023, 13, 883. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13110883
Conceição ISR, Garcia-Burgos D, de Macêdo PFC, Nepomuceno CMM, Pereira EM, Cunha CdM, Ribeiro CDF, de Santana MLP. Habits and Persistent Food Restriction in Patients with Anorexia Nervosa: A Scoping Review. Behavioral Sciences. 2023; 13(11):883. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13110883
Chicago/Turabian StyleConceição, Ismara Santos Rocha, David Garcia-Burgos, Patrícia Fortes Cavalcanti de Macêdo, Carina Marcia Magalhães Nepomuceno, Emile Miranda Pereira, Carla de Magalhães Cunha, Camila Duarte Ferreira Ribeiro, and Mônica Leila Portela de Santana. 2023. "Habits and Persistent Food Restriction in Patients with Anorexia Nervosa: A Scoping Review" Behavioral Sciences 13, no. 11: 883. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13110883
APA StyleConceição, I. S. R., Garcia-Burgos, D., de Macêdo, P. F. C., Nepomuceno, C. M. M., Pereira, E. M., Cunha, C. d. M., Ribeiro, C. D. F., & de Santana, M. L. P. (2023). Habits and Persistent Food Restriction in Patients with Anorexia Nervosa: A Scoping Review. Behavioral Sciences, 13(11), 883. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13110883





