A Study of the Relationship between University Students’ Food Neophobia and Their Tendencies towards Orthorexia Nervosa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample of the Study
2.2. Collection of Data
2.3. Data Collection Tools
2.3.1. Sociodemographic Information Form
2.3.2. Food Neophobia Scale
2.3.3. Orthorexia Nervosa-11 (ORTO-11) Scale
2.4. Analyzing the Data
2.5. Ethical Dimension
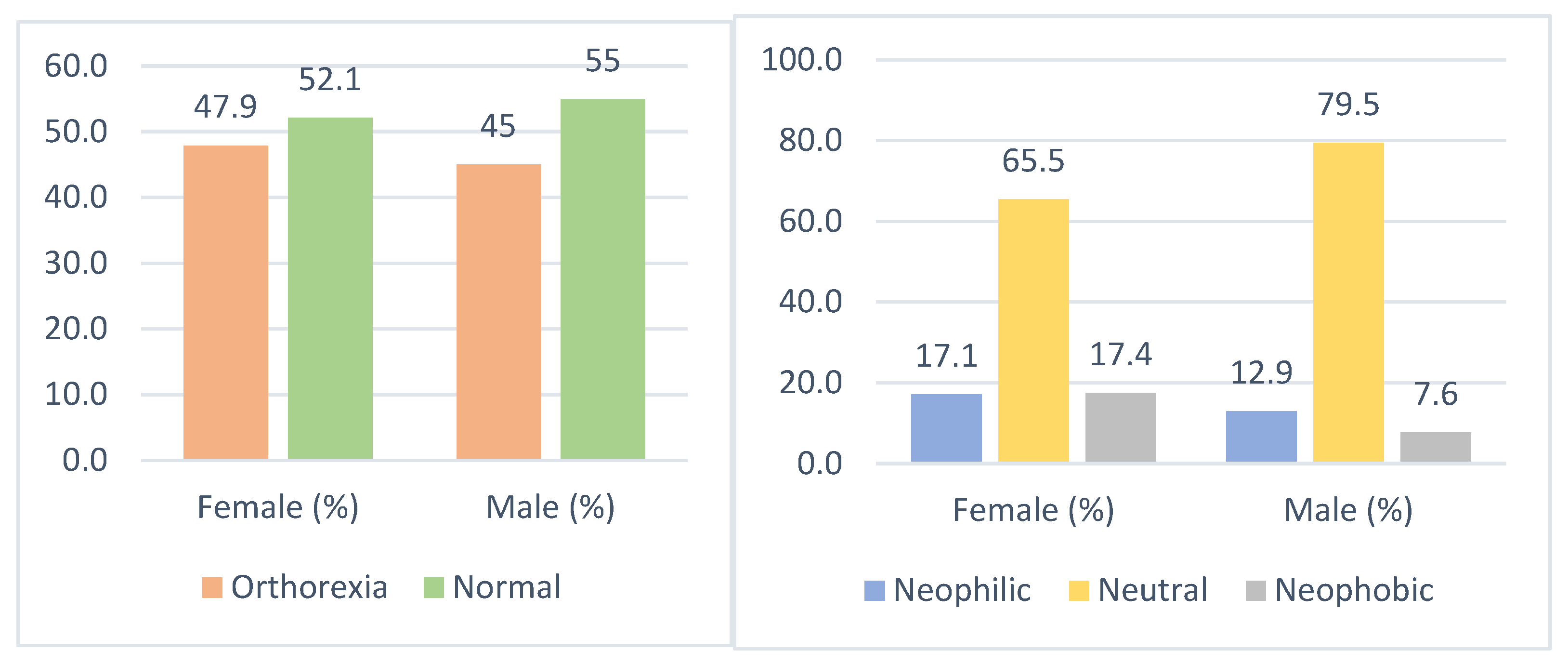
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Republic of Türkiye Ministry of Health. Turkey Nutrition Guide 2022; Pekcan, A.G., Şanlıer, N., Acar Tek, N., Gokmen Ozel, H., Eds.; Ministry of Health Publication No: 1031; Republic of Türkiye Ministry of Health: Ankara, Turkey, 2022; ISBN 2013206534.
- Aykut, M. The Importance of Community Nutrition. In Public Health; Erciyes University: Kayseri, Turkey, 2011; pp. 1247–1252. ISBN 978-605-125-274-2. [Google Scholar]
- Baysal, I.; Kızıltan, G. The Determination of the Relationship between Food Neophobia and Orthorexia Nervosa Tendencies and Nutritional Status of Individuals Who Engage in Sports. J. Nutr. Diet. 2020, 48, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabaran, S.; Mercanligil, S.M. Which Factors Affect Adolescent Food Preferences? Guncel Pediatr. 2014, 11, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumus, B.; Dedeoglu, B.B.; Shi, F. Gender and Generation as Antecedents of Food Neophobia and Food Neophilia. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2021, 37, 100773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.; Buhalis, D.; Beer, S. Dining Alone: Improving the Experience of Solo Restaurant Goers. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 32, 1347–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Yan, L. Selling Cute Destinations to East Asia. J. Hosp. Tour. Insights 2020, 4, 282–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdevelioglu, Y.; Yorusun, T.Ö. Investigation of Some Factors Related to Eating Attitudes and Behaviors of University Students. Gazi Sağlık Bilim. Derg. 2019, 4, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Sahrin, S.; Al Banna, M.H.; Rifat, M.A.; Tetteh, J.K.; Ara, T.; Hamiduzzaman, M.; Spence, C.; Kundu, S.; Abid, M.T.; Hasan, M.M.M. Food Neophobia and Its Association with Sociodemographic Factors and Food Preferences among Bangladeshi University Students: Evidence from a Cross-Sectional Study. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farchakh, Y.; Hallit, S.; Soufia, M. Association between Orthorexia Nervosa, Eating Attitudes and Anxiety among Medical Students in Lebanese Universities: Results of a Cross-Sectional Study. Eat. Weight Disord. 2019, 24, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dege, G.; Alphan, M.E. Determination of Orthorexia Nervosa in University. Sauhsd 2021, 4, 46–60. [Google Scholar]
- Schnettler, B.; Höger, Y.; Orellana, L.; Miranda, H.; Lobos, G.; Sepúlveda, J.; Sanchez, M.; Miranda-Zapata, E.; Denegri, M.; Grunert, K.G.; et al. Food Neophobia, Life Satisfaction and Family Eating Habits in University Students. Cad. Saude Publica 2017, 33, e00165615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olabi, A.; Najm, N.E.O.; Baghdadi, O.K.; Morton, J.M. Food Neophobia Levels of Lebanese and American College Students. Food Qual. Prefer. 2009, 20, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soucier, V.D.; Doma, K.M.; Farrell, E.L.; Leith-Bailey, E.R.; Duncan, A.M. An Examination of Food Neophobia in Older Adults. Food Qual. Prefer. 2019, 72, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roßbach, S.; Foterek, K.; Schmidt, I.; Hilbig, A.; Alexy, U. Food Neophobia in German Adolescents: Determinants and Association with Dietary Habits. Appetite 2016, 101, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal-Gil, N.Y.; Favila-Cisneros, H.J.; Zaragoza-Alonso, J.; Cuffia, F.; Rojas-Rivas, E. Using Projective Techniques and Food Neophobia Scale to Explore the Perception of Traditional Ethnic Foods in Central Mexico: A Preliminary Study on the Beverage Sende. J. Sens. Stud. 2020, 35, e12606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruth, B.R.; Ziegler, P.J.; Gordon, A.; Barr, S.I. Prevalence of Picky Eaters among Infants and Toddlers and Their Caregivers’ Decisions about Offering a New Food. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2004, 104, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proserpio, C.; Laureati, M.; Invitti, C.; Pagliarini, E. Reduced Taste Responsiveness and Increased Food Neophobia Characterize Obese Adults. Food Qual. Prefer. 2018, 63, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Predieri, S.; Sinesio, F.; Monteleone, E.; Spinelli, S.; Cianciabella, M.; Daniele, G.M.; Dinnella, C.; Gasperi, F.; Endrizzi, I.; Torri, L.; et al. Gender, Age, Geographical Area, Food Neophobia and Their Relationships with the Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet: New Insights from a Large Population Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidan, T.; Ertekin, V.; Isikay, S.; Kirpinar, I. Prevalence of Orthorexia among Medical Students in Erzurum, Turkey. Compr. Psychiatry 2010, 51, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.; Silva, C.; Oliveira, A. Food Neophobia and Its Association with Food Preferences and Dietary Intake of Adults. Nutr. Diet. 2020, 77, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basaran, A.G.; Ozbek, Y.D. An Evaluation of Nursing Students’ Food Neophobia and Diet Quality. Glob. J. Med. Res. L Nutr. Food Sci. 2022, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Sultana, M.S.; Islam, M.S.; Sayeed, A.; Koly, K.N.; Baker, K.; Hossain, R.; Ahmed, S.; Ferdous, M.Z.; Mubarak, M.; Potenza, M.N.; et al. Food Addiction, Orthorexia Nervosa and Dietary Diversity among Bangladeshi University Students: A Large Online Survey during the COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Eat. Disord. 2022, 10, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiello, P.; Peluso, I.; Villaño Valencia, D. Alcohol Consumption by Italian and Spanish University Students in Relation to Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and to the Food Neophobia: A Pilot Study. Healthcare 2022, 10, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Gao, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zou, L. The Food Neophobia Scale (FNS): Exploration and Confirmation of Factor Structure in a Healthy Chinese Sample. Food Qual. Prefer. 2020, 79, 103791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proserpio, C.; Almli, V.L.; Sandvik, P.; Sandell, M.; Methven, L.; Wallner, M.; Jilani, H.; Zeinstra, G.G.; Alfaro, B.; Laureati, M. Cross-National Differences in Child Food Neophobia: A Comparison of Five European Countries. Food Qual. Prefer. 2020, 81, 103861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zickgraf, H.F.; Ellis, J.M.; Essayli, J.H. Disentangling Orthorexia Nervosa from Healthy Eating and Other Eating Disorder Symptoms: Relationships with Clinical Impairment, Comorbidity, and Self-Reported Food Choices. Appetite 2019, 134, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şenol, B. A Type of Eating Disorder: Orthorexia Nervosa. Available online: https://www.yesilay.org.tr/tr/makaleler/bir-tur-yeme-bozuklugu-ortoreksiya-nervoza (accessed on 13 February 2023).
- Catalina Zamora, M.L.; Bote Bonaechea, B.; García Sánchez, F.; Ríos Rial, B. Orthorexia Nervosa. A New Eating Behavior Disorder? Actas Esp. Psiquiatr. 2005, 33, 66–68. [Google Scholar]
- Arusoglu, G.; Kabakci, E.; Koksal, G.; Merdol, T.K. Orthorexia Nervosa and Adapta on of ORTO-11 into Turkish. Türk Psikiyatr. Derg. Turkish J. Psychiatry 2008, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Koven, N.S.; Senbonmatsu, R. A Neuropsychological Evaluation of Orthorexia Nervosa. Open J. Psychiatry 2013, 03, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkiouleka, M.; Stavraki, C.; Sergentanis, T.N.; Vassilakou, T. Orthorexia Nervosa in Adolescents and Young Adults: A Literature Review. Children 2022, 9, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaki, B.; Pal, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Exploring Scientific Legitimacy of Orthorexia Nervosa: A Newly Emerging Eating Disorder. J. Hum. Sport Exerc. 2013, 8, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengul, R.; Hocaoglu, C. What Is Orthorexia Nervosa? Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches. KSU Med. J. 2019, 14, 101–104. [Google Scholar]
- Garipoglu, G.; Arslan, M.; Andac, S. Beslenme ve Diyetetik Bölümü’nde Okuyan Kız Öğrencilerin Ortoreksiya Nervoza Eğilimlerinin Belirlenmesi. J. Istanb. Sabahattin Zaim Univ. Inst. Sci. Technol. 2019, 1, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Pehlivan, E.; Mete, B.; Fırıncı, B.; Doğan, E. Prevalence of Orthorexia Nervosa and Relations with Health Literacy in University Students. Eskişehir Türk Dünyası Uygul. Ve Araştırma Merk. Halk Sağlığı Derg. 2019, 4, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammatikopoulou, M.G.; Gkiouras, K.; Markaki, A.; Theodoridis, X.; Tsakiri, V.; Mavridis, P.; Dardavessis, T.; Chourdakis, M. Food Addiction, Orthorexia, and Food-Related Stress among Dietetics Students. Eat. Weight Disord.-Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2018, 23, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Fernández, M.L.; Onieva-Zafra, M.D.; Fernández-Martínez, E.; Abreu-Sánchez, A.; Fernández-Muñoz, J.J. Assessing the Prevalence of Orthorexia Nervosa in a Sample of University Students Using Two Different Self-Report Measures. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busatta, D.; Cassioli, E.; Rossi, E.; Campanino, C.; Ricca, V.; Rotella, F. Orthorexia among Patients with Eating Disorders, Student Dietitians and General Population: A Pilot Study. Eat. Weight Disord.-Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2022, 27, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmetti, M.; Ferraro, O.E.; Gorrasi, I.S.R.; Carraro, E.; Bo, S.; Abbate-Daga, G.; Tagliabue, A.; Ferraris, C. Lifestyle-Related Risk Factors of Orthorexia Can Differ among the Students of Distinct University Courses. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogari, G.; Velez-Argumedo, C.; Gómez, M.; Mora, C. College Students and Eating Habits: A Study Using An Ecological Model for Healthy Behavior. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogur, S.; Aksoy, A. Determination of the Orthorexia Nervosa Tendency in University Students. BEU J. Sci. 2015, 4, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, E.; Ozkan, S. Investigation of Nutritional Habits in University Students. Fırat Sağlık Hizmetleri Derg. 2007, 2, 88–104. [Google Scholar]
- Palamutoglu, R.; Palamutoglu, I.; Kantar, A.G.; Corapcı, B.; Kazak, M.; Kasnak, C. Evaluation of University Students’ Meat Consumption and Food Neophobia. Kırşehir Ahi Evran Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilim. Derg. 2022, 6, 144–153. [Google Scholar]
- Duman, E.; Akcil Ok, M.; Keser, A. Adaptation of The Food Neophobia Scale Into Turkish: Validity and Reliability Study. Kocaeli Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilim. Derg. 2020, 6, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliner, P.; Hobden, K. Development of a Scale to Measure the Trait of Food Neophobia in Humans. Appetite 1992, 19, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ucar, E.M.; Sevim, S.; Kizil, M. Is There a Link to Food Neophobia and Orthorexia Nervosa? Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, S120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donini, L.M.; Marsili, D.; Graziani, M.P.; Imbriale, M.; Cannella, C. Orthorexia Nervosa: Validation of a Diagnosis Questionnaire. Eat. Weight Disord. 2005, 10, e28–e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazley, D.; McCarthy, S.N.; Stack, M.; Walton, J.; McNulty, B.A.; Flynn, A.; Kearney, J.M. Food Neophobia and Its Relationship with Dietary Variety and Quality in Irish Adults: Findings from a National Cross-Sectional Study. Appetite 2022, 169, 105859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jezewska-Zychowicz, M.; Plichta, M.; Drywień, M.E.; Hamulka, J. Food Neophobia among Adults: Differences in Dietary Patterns, Food Choice Motives, and Food Labels Reading in Poles. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, V.; Akar Sahingoz, S. Determination of Food Neophobia Level in Adult Individuals. J. Tour. Gastron. Stud. 2019, 7, 772–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, N.; Gul, F.H. Does Food Neophobia Affect Mediterranean Diet Adherence and Eating Disorders in University Students? Eur. BMC 2022, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuorila, H.; Lähteenmäki, L.; Pohjalainen, L.; Lotti, L. Food Neophobia among the Finns and Related Responses to Familiar and Unfamiliar Foods. Food Qual. Prefer. 2001, 12, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiselman, H.L.; King, S.C.; Gillette, M. The Demographics of Neophobia in a Large Commercial US Sample. Food Qual. Prefer. 2010, 21, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, S.R.; Rasmussen, M.A.; Prescott, J. Relationships between Food Neophobia and Food Intake and Preferences: Findings from a Sample of New Zealand Adults. Appetite 2017, 116, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahilli Bildir, S.; İflazoglu, N.; Birdir, K. The Fear of New Food (Neophobia) Experıment in Tour Guide Candidates. Gastroia J. Gastron. Travel Res. 2019, 3, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslantas, H.; Adana, F.; Öğüt, S.; Ayakdaş, D.; Korkmaz, A. Relationship Between Eating Behaviors of Nursing Students and Orthorexia Nervosa (Obsession with Healthy Eating): A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Psychiatr. Nurs. 2017, 8, 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Ozturk, M.E.; Ayhan, N.Y. Orthorexıa in Unıversıty Students and Determınıng Relatıonshıp with Healthy Lıfe Style Behavıo. J. Acad. Soc. Sci. 2017, 5, 455–465. [Google Scholar]
- Barthels, F.; Barrada, J.R.; Roncero, M. Orthorexia Nervosa and Healthy Orthorexia as New Eating Styles. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, P.G.; Lefevre, C.E. Instagram Use Is Linked to Increased Symptoms of Orthorexia Nervosa. Eat. Weight Disord. 2017, 22, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depa, J.; Barrada, J.; Roncero, M. Are the Motives for Food Choices Different in Orthorexia Nervosa and Healthy Orthorexia? Nutrients 2019, 11, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missbach, B.; Hinterbuchinger, B.; Dreiseitl, V.; Zellhofer, S.; Kurz, C.; König, J. When Eating Right, Is Measured Wrong! A Validation and Critical Examination of the ORTO-15 Questionnaire in German. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Independent Variables | N | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (SD) | 22.33 (SD = 4.94) | ||
| Sex | F | 438 | 71.9 |
| M | 171 | 28.1 | |
| Marital status | Single | 576 | 94.6 |
| Married | 33 | 5.4 | |
| Place of residence | Rural | 144 | 23.6 |
| Urban | 465 | 76.4 | |
| Smoking status | Smoker | 98 | 16.1 |
| Non-smoker | 472 | 77.5 | |
| Quit | 39 | 6.4 | |
| Alcohol consumption | Drinks | 43 | 7.1 |
| Does not drink | 566 | 92.9 | |
| Number of Main meals | 1 | 32 | 5.3 |
| 2 | 333 | 54.7 | |
| 3 | 227 | 37.3 | |
| 4 | 17 | 2.8 | |
| Number of Intermediate meals | 0 | 92 | 15.1 |
| 1 | 230 | 37.8 | |
| 2 | 200 | 32.8 | |
| 3 | 66 | 10.8 | |
| 4 | 21 | 3.4 | |
| Person/place providing new food recommendation | Family | 133 | 21.8 |
| Friend | 186 | 30.5 | |
| Social media | 87 | 14.3 | |
| Does not take suggestions | 203 | 33.3 | |
| Food Neophobia | Neophilic (≤30) | 97 | 15.9 |
| Neutral (31–48) | 423 | 69.5 | |
| Neophobic (≥49) | 89 | 14.6 | |
| ORTO-11 | Normal (>27) | 322 | 52.9 |
| Orthorexia risk (≤27) | 287 | 47.1 | |
| Scales | N | Min–Max | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food Neophobia | 609 | 10–67 | 39.41 | 9.23 |
| ORTO-11 | 609 | 14–41 | 27.43 | 5.35 |
| Independent Variables | N | Food Neophobia | p | ORTO-11 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Rank | Mean Rank | |||||
| Sex | Female | 438 | 306.85 | 0.678 | 303.64 | 0.760 |
| Male | 171 | 300.27 | 308.47 | |||
| U = 36640.5, Z = −0.415 | U = 36855.0, Z = −0.305 | |||||
| Marital Status | Single | 576 | 305.82 | 0.629 | 309.61 | 0.007 |
| Married | 33 | 290.61 | 224.6 | |||
| U = 9029.0, Z = −0.484 | U = 6851.0, Z= −2.704 | |||||
| Place of residence | Rural | 144 | 327.35 | 0.081 | 329.67 | 0.054 |
| Urban | 465 | 298.08 | 297.36 | |||
| U = 30261.0, Z= −0.747 | U = 29928.0, Z= −1.929 | |||||
| Alcohol Consumption | Drinks | 43 | 252.87 | 0.044 | 282.23 | 0.378 |
| Does not drink | 566 | 308.96 | 306.73 | |||
| U = 9927.5, Z= −2.017 | U = 11190.0, Z= −0.882 | |||||
| Smoking status | Smoker | 98 | 283.08 | 0.244 | 310.01 | 0.753 |
| Non-smoker | 472 | 311.44 | 305.57 | |||
| Quit | 39 | 282.10 | 285.4 | |||
| KW X2 = 2.821 | KW X2 = 0.566 | |||||
| Food allergy | Yes | 72 | 325.87 | 0.283 | 280.35 | 0.205 |
| No | 537 | 302.20 | 308.30 | |||
| U = 17829.5, Z = −1.073 | U = 11557.5, Z = −1.268 | |||||
| Number of Main meals | 1 | 32 | 312.42 | 0.461 | 334.30 | 0.695 |
| 2 | 333 | 311.74 | 307.78 | |||
| 3 | 227 | 298.21 | 297.64 | |||
| 4 | 17 | 249.53 | 293.56 | |||
| KW X2 = 2.579 | KW X2 = 1.444 | |||||
| Number of Intermediate meals | 0 | 92 | 319.03 | 0.214 | 281.33 | 0.034 |
| 1 | 230 | 313.47 | 306.77 | |||
| 2 | 200 | 305.43 | 296.58 | |||
| 3 | 66 | 258.77 | 323.94 | |||
| 4 | 21 | 292.00 | 410.07 | |||
| KW X2 = 5.801 | KW X2 = 10.437 | |||||
| Person/place providing new food recommendation | Family | 133 | 219.52 | 0.024 | 308.03 | 0.048 |
| Friend | 186 | 312.90 | 310.97 | |||
| Social media | 87 | 251.96 | 256.94 | |||
| Not taking suggestions | 203 | 311.03 | 318.15 | |||
| KWX2 = 9.475 | KWX2 = 7.907 | |||||
| Age | Food Neophobia | ORTO-11 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | r | 1 | 0.002 | −0.073 |
| p | 0.970 | 0.070 | ||
| Food neophobia | r | 1 | −0.016 | |
| p | 0.698 | |||
| ORTO-11 | r | 1 | ||
| p |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Basaran, A.G.; Ozbek, Y.D. A Study of the Relationship between University Students’ Food Neophobia and Their Tendencies towards Orthorexia Nervosa. Behav. Sci. 2023, 13, 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13120958
Basaran AG, Ozbek YD. A Study of the Relationship between University Students’ Food Neophobia and Their Tendencies towards Orthorexia Nervosa. Behavioral Sciences. 2023; 13(12):958. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13120958
Chicago/Turabian StyleBasaran, Ayse Gumusler, and Yagmur Demirel Ozbek. 2023. "A Study of the Relationship between University Students’ Food Neophobia and Their Tendencies towards Orthorexia Nervosa" Behavioral Sciences 13, no. 12: 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13120958
APA StyleBasaran, A. G., & Ozbek, Y. D. (2023). A Study of the Relationship between University Students’ Food Neophobia and Their Tendencies towards Orthorexia Nervosa. Behavioral Sciences, 13(12), 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13120958






