1. Introduction
Gossip has received more attention as of late as an inevitable fact and phenomenon within organisational communication networks [
1,
2,
3]. Gossip is often used by employees in the workplace, either as a strategic and political tool or as a means of seeking relief and responding to social injustice [
4]. Gossip can affect policies with contradictory roles at the organisational level. In particular, employees gossip during their official duties due to the instrumental ties between them that arise [
5] and within private relationships when they are with friends or giving advice to one another [
6]. Regarding its negative role, gossip is associated with organisational issues, such as lost reputations, social undermining, decreased productivity, and wasted time [
7,
8,
9].
On the other hand, gossip has positive roles in the organisation, such as information acquisition, relationship building, social enjoyment and group protection, and organisational citizenship behaviours [
10,
11,
12]. Organisations are affected by the positive and negative aspects of gossip, and this effect can play a significant role in determining organisational development and human resource policies. The underlying motives for gossiping behaviour involve many different motives, such as information gathering, relationship building, social enjoyment, and having a negative influence on others [
13]. This study focuses on three types of gossip: information gathering, relationship building, and negative influence. Information gathering gossip exchanges are evaluative (positive or negative) information about third parties [
12]. Relationship building gossip builds relationships or strengthen relationships between gossipers via the subject of the person who is gossiped about [
14]. Negative influence gossip is the influence of others and manipulation of their opinions, typically negatively [
15].
Gossip in an organisational setting is determined and sustained by organisational possibilities that regulate and govern the survival of the individual and the group [
16]. While most of the current studies in the literature have focused on determining the managerial-level consequences of gossip in organisations [
17,
18,
19], there are few studies on how gossip starts [
2]. Most studies that explain the structural antecedents of gossip in organisations and determine the reasons for participating in gossip at the individual level point to the organisational context [
7,
20]. Thus, the contextual nature of gossip [
9] makes it an intriguing phenomenon worth investigating in live situational settings [
2]. In particular, an organisational context involving abusive supervision as a stressor [
21] provides an opportunity for an in-depth examination of behaviours.
Abusive supervision refers to a perceptual representation of the psychological state induced by a manager in his or her subordinates [
22]. Previous research has reported differing views on the effects of abusive supervision on employees’ well-being, attitudes, and behaviour. Some have expressed the adverse effects of abusive supervision on subordinates and the negative reactions of subordinates [
23,
24,
25], while others believe that subordinates are not always negatively affected and will not react negatively [
26,
27,
28]. For this reason, a call for a more balanced perspective through studies examining the differing effects of abusive supervision on subordinates is expressed in the literature [
28]. Despite opposing views, studies confirm that subordinates’ reactions to deliberately unexpected behaviour by a supervisor will vary depending on individual and situational characteristics [
23,
25].
The connection between contextual factors and individual traits is debated through the trait activation theory (TAT). The choice of this theory as the framework for this study stems from its potential to enhance our understanding of how internal psychological mechanisms are triggered when an abusive supervisor creates a hostile environment and puts subordinates in a vulnerable position [
29,
30]. Tett and Burnett [
31] argue that personality traits are only behaviourally active once contextual factors activate them. These factors include daily tasks, social demands from working with supervisors, and organisational culture [
32].
Trait activation may occur due to social demands from peers, subordinates, customers, and supervisors [
31]. TAT is broad enough to be applied to various personalities, which could fuel more systematic research on person–situation interactionism in predicting behaviours such as organisational gossip [
30]. Considering the current debates, personality is seen as a phenomenon that interacts with many other factors that affect human behaviour [
33]. Considering that gossip is, to some extent, personality dependent [
9,
13], personality may explain the psychological mechanism of the relationship between abusive supervision and these types of gossip. Various models for understanding personalities include HEXACO, the Myers–Briggs Type Indicator, the 16 personality factors, and the Big Five personality traits [
34]. Moreover, there are three personality traits, Machiavellianism, narcissism, and psychopathy, on the dark side of relating, which is an inevitable part of interacting with others [
35]. It is reported that individuals with a dark triad are more ready to gossip for their own good, engage in selfish actions, and ignore norms [
13]. Furthermore, dark triads (narcissism, Machiavellianism, and psychopathy) may be activated due to subordinates’ negative emotions. They may seek supportive activities (such as information gathering and relationship building) under the direction of these traits, and gossip can help this process.
Researchers distinguish between intense situations with normative expectations and clear roles that limit behaviour and relaxed situations that allow for more freedom. It has been argued that one’s behaviour in intense situations is based on situational conditions rather than individual personality [
13,
36]. Therefore, this study included two educational institutions, a public high school and a public university, to explore the relationships between the variables for a deeper understanding. Educators working in public high schools, where quite intense situations are assumed to occur, must adjust their behaviour to comply with the rules and achieve organisational goals. On the other hand, educators at public universities are subject to fewer regulations and guidelines and regulate their conduct based on their own internalized standards [
37].
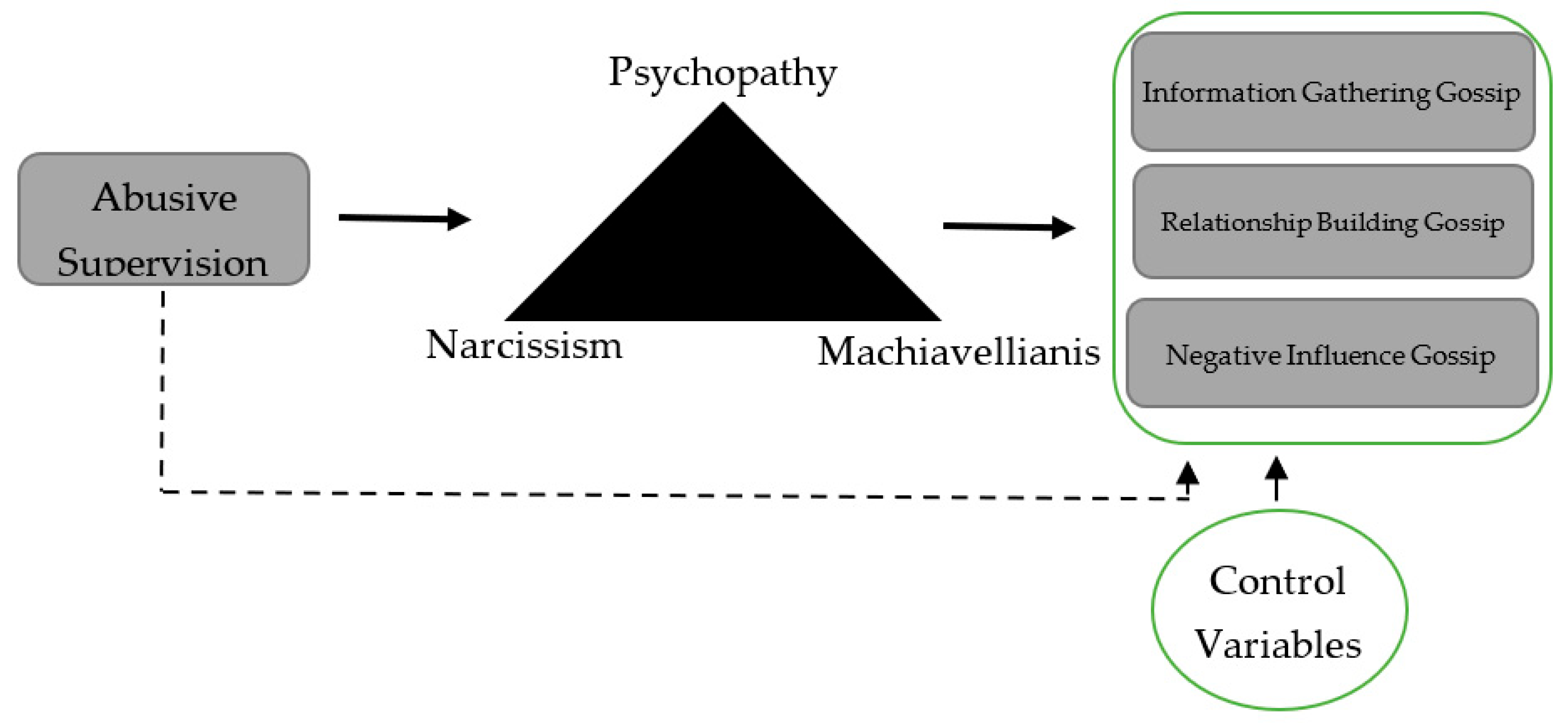
Based on these explanations and to the best of our knowledge, this study investigates the influence of abusive supervision on organisational gossip for the first time and examines the potential mediating role of the dark triad from the perspective of TAT for educational organisations. This study addresses the existing research gap by examining three different types of organisational gossip and making several contributions to the literature. First, this study re-examines the internal mechanism that leads subordinates to gossip when faced with abusive supervision and offers a new perspective for understanding the relationship between the two. Second, this paper employs Machiavellianism, narcissism, and psychopathy as mediator variables. When integrated into the model separately, the dark triad supports a deeper understanding of the internal mechanism by mediating the relationship between abusive supervision and organisational gossip. Thirdly, based on trait activation theory, this study provides an in-depth understanding of how subordinates, who use personality traits triggered by negative situations as a tool, resort to organisational gossip to cope with abusive supervision. Thus, it helps to understand how the dark triad of employees acts as a buffer when facing negative situations. Consequently, this research has contributed significantly to the existing literature by thoroughly examining examples in educational organisations.
This paper is structured as follows:
Section 2 provides an overview of the conceptual framework and hypothesis relationships. The modelling, data sources, and methods are explained in
Section 3. In
Section 4, the empirical outcomes and discussion are indicated. The last section evaluates the empirical results and proposes organisational policies for educational organisations.
4. Results
The descriptive analysis results and correlations of abusive supervision, narcissism, Machiavellianism, psychopathy, information gathering gossip, relationship building gossip, and negative influence gossip are presented in
Table 1 and
Table 2. Abusive supervision was found to be significantly positively related to narcissism, Machiavellianism, psychopathy, information gathering gossip, and relationship building gossip but was significantly negatively related to negative influence gossip. Meanwhile, narcissism was positively and significantly related to Machiavellianism, psychopathy, information gathering gossip, relationship building gossip, and negative influence gossip. Machiavellianism was significantly and positively related to psychopathy, information gathering gossip, and relationship building gossip but negatively related to negative influence gossip. Psychopathy was positively related to information gathering gossip and relationship building gossip but negatively related to negative influence gossip.
The complete structural model shown in
Figure 1 was evaluated separately for both samples. A mediation analysis explored how abusive supervision is related to information gathering, relationship building, and negative influence gossip. The bootstrapping method was used to test the existence of mediating effects, as recommended by Hayes [
98]. Bootstrapping is used in mediational analyses to generate an empirically derived representation of the sampling distribution of the indirect effect and then bootstrapped confidence intervals. The results of the 5000-bootstrap sample at the 95% confidence interval are shown in
Table 5,
Table 6 and
Table 7. If the 95% confidence limits include zero, the indirect effect test is insignificant at the 95% confidence interval.
Table 5,
Table 6 and
Table 7 present the results of the mediation models used to test the hypotheses. These three tables examine the direct and indirect effects of information gathering, relationship building, and negative influence gossip, which are the types of organisational gossip. As they represent different types of gossip, the hypothesis tests for each type of organisational gossip were analysed separately. Using the obtained effect size estimate and the standard error for all hypothesis relationships, we calculate the Type-S and Type-M errors with the help of Rstudio (alpha = 0.05 is the default significance level, and n.sims = 10,000 is the default number of simulations). As Gelman and Carlin [
86] point out, we ensured the Type-S (size) error rate was less than 0.5, and the Type-M (magnitude) error rate was greater than 1 in each of our analyses.
4.1. Mediated Regression Results for Information Gathering Gossip
A mediation analysis explored how abusive supervision is related to information gathering gossip. First, the results showed that the model adequately fit the data for both samples (S1: χ
2/df = 2.16 GFI = 0.880; NFI = 0.940; CFI = 0.950; RMSEA = 0.50)–(S2: χ
2/df = 3.38; GFI = 0.885; NFI = 0.901; CFI = 0.951 RMSEA = 0.049). Second, this study employed
p-values, beta values, confidence intervals, and Type-S and Type-M errors to confirm the statistical significance and the direction were positive, and the results for the structural model assessment are illustrated in
Table 5. H1a was tested and confirmed as there was a positive and significant association between abusive supervision and information gathering gossip. As shown in
Table 5, the direct effect of abusive supervision on information gathering gossip was not statistically significant for sample 1 (β = 0.085,
p = 0.086, 95% CI [−0.013, 0.187] S/M = 0.144/6.264) and there was a significant effect for sample 2 (β = 0.111,
p= 0.001, 95% CI [0.041, 0.180]; S/M = 0.042/3.625).
Three indirect effects (mediating variables) were introduced and are proposed in
Table 5. All of these three mediating roles were accepted for both samples. Hypotheses H2a, H3a, and H4a confirmed that narcissism, Machiavellianism, and psychopathy positively mediated the relationship between abusive supervision and information gathering gossip. Narcissism significantly and positively mediated the relationship between abusive supervision and information gathering gossip for both samples (S1: β = 0.076,
p = 0.014, 95% CI [0.014, 0.180] S/M = 0.102/5.192; S2: β = 0.047,
p = 0.001, 95% CI [0.021, 0.082] S/M = 0.001/1.919). Machiavellianism significantly and positively mediated the relationship between abusive supervision and information gathering gossip for both samples (S1: β = 0.074,
p = 0.050, 95% CI [0.002, 0.204] S/M = 0.048/3.783; S2: β = 0.036,
p = 0.001, 95% CI [0.014, 0.071] S/M = 0.006/2.348) Psychopathy significantly and positively mediated the relationship between abusive supervision and information gathering gossip for both samples (S1: β = 0.186,
p < 0.001, 95% CI [0.070, 0.300] S/M = 0.139/6.077; S2: β = 0.052,
p < 0.001, 95% CI [0.019, 0.110] S/M = 0.299/12.899). As a result, the higher the level of abusive supervision, the higher the level of narcissism, Machiavellianism, and psychopathy, leading to better information gathering gossip. Therefore, an indirect effect test indicated that narcissism, Machiavellianism, and psychopathy (fully mediated in sample 1 and partially mediated in sample 2) mediated the relationship between abusive supervision and information gathering gossip. The effects of the control variables are shown in
Table 5. The direct effect of the gender and age of the subordinates on information gathering gossip was not statistically significant for both samples. Furthermore, the Type-S rates, which indicate that, based on our sample size, the risk that the sign indicates the effect we observe is incorrect, is low, and the Type-M rates, which indicate that, based on our sample size, there is not any risk that we are overestimating the magnitude of the significant effect uncovered for all significant hypotheses.
4.2. Mediated Regression Results for Relationship Building Gossip
The model fit values showed an acceptable fit in
Table 6, which showed the situation in which relationship building gossip is the dependent variable (S1: χ
2/df = 2.18; GFI = 0.858; NFI= 0.941; CFI = 0.953 RMSEA = 0.050), (S2: χ
2/df = 3.41; GFI = 0.887; NFI= 0.912; CFI = 0.967 RMSEA = 0.049). The H1b is tested and confirmed that a positive and significant association between abusive supervision and relationship building gossip exists. The results are presented in
Table 6. The direct effect of abusive supervision on relationship building gossip was not statistically significant for both samples (S1:β = 0.055,
p = 0.255, 95% CI [−0.050, 0.167] S/M = 0.186/7.418; S2:β = 0.039,
p = 0.241, 95% CI [−0.031, 0.112] S/M = 0.039/3.567).
Hypotheses H2b, H3b, and H4b confirmed that narcissism, Machiavellianism, and psychopathy positively mediated the relationship between abusive supervision and relationship building gossip. Narcissism significantly and positively mediated the relationship between abusive supervision and relationship building gossip for both samples (S1: β = 0.069,
p = 0.011, 95% CI [0.015, 0.161] S/M = 0.069/4.341; S2: β = 0.027,
p = 0.001, 95% CI [0.011, 0.051] S/M = 0.003/1.969). Machiavellianism significantly and positively mediated the relationship between abusive supervision and relationship building gossip for both samples (S1: β = 0.101,
p = 0.012, 95% CI [0.012, 0.249] S/M = 0.034/3.416; S2: β = 0.065,
p < 0.001, 95% CI [0.036, 0.108] S/M = 0.001/1.068). Psychopathy significantly and positively mediated the relationship between abusive supervision and relationship building gossip for both samples (S1: β = 0.149,
p = 0.001, 95% CI [0.052, 0.313] S/M = 0.151/6.440; S2: β = 0.088,
p < 0.001, 95% CI [0.044, 0.154] S/M = 0.010/1.797). The higher the level of abusive supervision, the higher the level of the dark triad, leading to better relationship building gossip. Therefore, an indirect effect test indicated that narcissism, Machiavellianism, and psychopathy fully mediated the relationship between abusive supervision and relationship building gossip for both samples. The effects of the control variables are shown in
Table 6. The direct effect of the gender and age of the subordinates on relationship building gossip was not statistically significant for both samples. The Type-S rates are low, indicating there is a low risk that the sign of the effect we observed is incorrect, and the Type-M rates indicate that there is no risk that we are overestimating the magnitude of the significant effect uncovered for all significant hypotheses.
4.3. Mediated Regression Model for Negative Influence Gossip
A mediation analysis was conducted to explore how abusive supervision is related to negative influence gossip. First, the results showed that the model adequately fit the data for both samples (S1: χ
2/df = 2.06; GFI = 0.857; NFI= 0.942; CFI = 0.952 RMSEA = 0.048)–(S2: χ
2/df = 3.14; GFI = 0.887; NFI= 0.890; CFI = 0.922 RMSEA = 0.047). Our second hypothesis, Hypothesis 1c, predicted that abusive supervision is negatively related to negative influence gossip. An examination of
Table 7 reveals that we did not find statistically significant support for Hypothesis 1c; abusive supervision was not positively related to negative influence gossip in either of the samples (S1: β = −0.051,
p = 0.339, 95% CI [−0.150, 0.055] S/M = 0.474/109.339; S2: β = 0.001,
p= 0.985, 95% CI [−0.073, 0.072] S/M= 0.373/21.564).
Hypotheses H2c, H3c, and H4c confirmed that narcissism, Machiavellianism, and psychopathy negatively mediated the relationship between abusive supervision and negative influence gossip. Contrary to our expectations, narcissism significantly and positively mediated the relationship between abusive supervision and negative influence gossip for sample 1 (S1: β = 0.053,
p = 0.011, 95% CI [0.009, 0.146] S/M = 0.004/2.157). However, there was no significant indirect effect for sample 2 (S2: β = 0.009,
p = 0.230, 95% CI [−0.006, 0.031] S/M = 0.015/2.764). Machiavellianism significantly and negatively mediated the relationship between abusive supervision and negative influence gossip for both samples (S1: β = −0.106,
p = 0.016, 95% CI [−0.018, −0.261] S/M = 0.479/132.381; S2: β = −0.036,
p = 0.003, 95% CI [−0.072, −0.011] S/M = 0.281/11.756). The higher the level of abusive supervision, the higher the level of Machiavellianism, leading to more negative influence gossip. Psychopathy significantly and negatively mediated the relationship between abusive supervision and negative influence gossip for sample 2 (β = −0.035,
p = 0.003, 95% CI [−0.081, −0.011] S/M = 0.328/15.352). However, there was no significant indirect effect for sample 1 (β = −0.054,
p = 0.263, 95% CI [−0.233, 0.045] S/M = 0.328/15.352). Therefore, an indirect effect test indicated that the dark triad fully mediated the relationship between abusive supervision and negative influence gossip for sample 1. The effects of the control variables are shown in
Table 7. The direct effect of the gender of the subordinates on the negative influence of gossip was not statistically significant for either of the samples. The direct effect of age on the negative influence of gossip was statistically significant for sample 2 but not for sample 1. Furthermore, the risk that the sign of the effect we observed is incorrect is low, and there is not any risk that we are overestimating the magnitude of the significant effect uncovered for all significant hypotheses.
5. Discussion
Based on trait activation theory, the current study deepened our understanding of the role of trait factors (i.e., the dark triad) in organisational gossip by clarifying how abusive supervision is associated with information gathering, developing relations, and negative influence gossip. While many studies have investigated the effect of gossip on abusive supervision [
17,
18,
28,
56], the current study is the first to examine whether abusive supervision affects organisational gossip types and the mediating effect of dark triad characteristics on this relationship. A total of 470 participants from sample 1 and 990 from sample 2 within educational organisations were investigated for our empirical analysis of the proposed hypotheses, and our results demonstrate the following. (1a) Abusive supervision favourably influences information gathering gossip for both studies. (2a, 3a, 4a) Narcissism, Machiavellianism, and psychopathy play a mediating role in the relationship between abusive supervision and information gathering gossip for both studies. (1b) The direct effect of abusive supervision on relationship building gossip is not statistically significant for both studies. (2b, 3b, 4b) Narcissism, Machiavellianism, and psychopathy play a mediating role in the relationship between abusive supervision and relationship building gossip. (3a) The direct effect of abusive supervision on negative influence gossip is not statistically significant for either of the studies. (2c) Narcissism is a mediating factor in the relationship between abusive supervision and negative influence gossip for sample 1. However, it is not significant for sample 2. (3c) Machiavellianism is a mediating factor in the relationship between abusive supervision and negative influence gossip for both studies. (4c) Psychopathy plays a mediating role in the relationship between abusive supervision and negative influence gossip for sample 2 but is not significant for sample 1.
To begin with, the findings of this study indicated a low occurrence of abusive supervision in both samples. One potential explanation for this trend is the study’s location in Turkey, a country with a high power distance score (66). In such an environment, hierarchical superiors, often perceived as paternal figures, tend to be distant and inaccessible [
99]. High power distance, one of the distinctive cultural values in Turkey, indicates that employees there might respond differently to malicious supervision compared to those in countries with low power distance. Thus, the present study allowed for a richer assessment of abusive supervision that takes cultural contexts into account [
28].
The results indicate that abusive supervision has a significant positive effect on information gathering gossip. This finding contradicts the assumption that “reactions to interpersonal threats are always negative” [
100]. Given that gossip often serves as an information gathering tool, subordinates may engage in gossip to gain insight into navigating and mitigating exposure to a supervisor’s abusive behaviour or how to respond to such attitudes [
50]. Similarly, studies that posit employees who encounter abusive supervision will gossip to seek information [
55,
101] align with this finding. However, it is worth noting that the direct effects of abusive supervision on relationship building gossip and negative influence gossip are not statistically significant. These findings contrast with those of previous studies [
17,
18,
26].
Our study contributes to the development of trait activation theory (TAT). TAT posits that specific work-related factors influence an individual’s psychological tendencies and that the influence of personality traits may vary depending on the context [
57]. These factors include aspects such as the task itself (e.g., daily tasks, responsibilities, and procedures), social dynamics (e.g., social demands arising from interactions with peers, supervisors, subordinates, and customers) and organisational factors (e.g., organisational culture, climate, and structure) [
32]. This theory furthers our knowledge of how abusive supervision affects the types of organisational gossip and the conditions that activate employees’ dark triad features. This study also demonstrates the significance of the dark triad in the relationship between supervisors and employees. The results indicate that abusive supervision influences the tendencies of organisational gossip, mediated by the presence of narcissism, Machiavellianism, and psychopathy. This result is consistent with Chaby, Sheriff, Hirrlinger, and Braithwaite [
49]’s findings and the Yerkes–Dodson law. Chaby et al. [
49] highlight the importance of context in behaviour and performance, stating that in the case of fear conditioning, behaviour changes according to the Yerkes–Dodson law. Considering that an abusive supervisor creates a threatening environment and risky situation for subordinates [
25], there are social conditions (such as abusive supervision) in which the dark triad can be activated. Exposure to workplace mismanagement predisposes subordinates to seek solutions to get them out of the situation and to develop complicated and hostile personalities that reflect a faster coping strategy (such as gossip). The study also examines the factors that activate employees’ personality traits, starting with the conditions created by abusive management, and makes a significant contribution to research on employees’ gossiping behaviour.
Michelson and Mouly [
9] claim that few published studies reveal personality-related factors that affect the frequency or nature of gossip. There are different reasons why people may be motivated to engage in information gathering, relationship building, and negative influence gossip [
12,
17,
69,
102]. Firstly, narcissists, who often have an extreme love of self, a grandiose sense of self-importance, and a powerful sense of entitlement, are motivated to maintain their identity and legitimacy [
103]. Consistent with Pertuz-Peralta et al. [
104]’s findings, this study is quite interesting as it shows that narcissistic subordinates activated by abusive supervision, characterized by a sense of greatness and need for admiration, tend to gossip, which will increase information sharing with other subordinates. Characterized by amoral manipulation, a distrust of others, the desire for control, and the desire for status, Machiavellians may perceive they are threatened by others in their pursuit of maximizing their interests. A strong position would be a good option [
105]. Our findings suggest that, unlike the findings of Liu [
106], Machiavellians turn to gossip to gather information when faced with abusive supervision. Although there is a consensus that psychopathy is an underlying factor in deviant interpersonal behaviours that cause distress for co-workers [
107], results show that psychopathy explains the relationship between abusive supervision and information gathering gossip. People high in psychopathy generally resist stress, including interpersonal abuse, and seem to need fewer positive relationships than others [
108].
Our findings suggest that subordinates tend to be more impulsive, callous, and manipulative when exposed to a supervisor’s behaviour. Therefore, our findings are consistent with those of Jones and Paulhus [
109], who stated that narcissism, Machiavellianism, and psychopathy traits are associated with exploitative interpersonal behaviour. Insensitive to the concerns and social restrictions of others, narcissists carry out most of their identity-targeting efforts in the social sphere [
61]. Our mediation analysis supports those with the narcissistic personality trait facing abusive supervision will strive to maintain a positive self-image at all costs. The findings of Smalley and Stake [
110] show that they suppress hostility by showing positive gossip tendencies (relationship building), as opposed to the finding that narcissism is associated with hostility versus humiliation and hostility. Consequently, our study demonstrates that narcissists can utilize the impact of abusive control to legitimize organisational gossip mechanisms.
Inconsistent previous studies [
30,
32] showed that Machiavellians are more willing to behave socially when they experience abusive supervisor behaviour. Machiavellians, who are more manipulative towards others, may view stressful situations as potentially harmful, believing they can exploit them if they cannot manipulate others [
111]. Our study shows that abusive supervision can easily provoke Machiavellianism. This finding may be associated with Machiavellians being more willing to provide support and learn. As a result, when faced with a difficult situation, Machiavellians are willing to gather information to manipulate others or provide social support to meet their interests. The finding that psychopathy mediates the relationship between abusive supervision and developing relations gossip confirms that people with psychopathic tendencies can better cope with stressful situations [
112]. Moreover, findings suggest that individuals with high levels of psychopathy remain unaffected by abusive behaviours.
We should note the unexpected results produced for narcissism and psychopathy’s mediating role. Interestingly, our results showed a significant difference in the mediated role of narcissism and psychopathy between abusive supervision and negative influence gossip for both studies. Narcissism was an intermediary between abusive supervision and negative influence gossip for sample 1, but not for sample 2. Psychopathy was an intermediary between abusive supervision and negative influence for sample 2, not for sample 1. The differences in our findings across sample 1 and sample 2 may be due to differences in organisational cultures and differences in the operationalization of gossip behaviours. This finding supported that the logic that aversive behaviour, narcissism, Machiavellianism, and psychopathy are related to bad things. The finding that Machiavellianism has a negative mediating effect for negative influence gossip supports the explanation that Machiavellians exhibit corporate citizenship behaviours that can lead to positive social impressions [
113]. Another possible reason is that as they identify with their organisation; employees with a stronger sense of harmony with their workgroup buffer their tendency to gossip about their leaders negatively to protect the organisation’s image [
26]. That is, even though employees who value their organisation may be inclined to participate in gossip for negative influence when confronted with an abusive supervisor, they will be less inclined to gossip to protect the organisation’s image from potentially harmful consequences. These findings support studies claiming that employees who identify with their organisations experience more favourable outcomes regarding well-being and behaviour, even in challenging and persistent personal contexts [
114,
115].
Furthermore, it was found that gender was not associated with information gathering, developing relations, and negative influence gossip. The analysis yielded consistent results for both samples. The high school teachers in sample 1 were not accessible during their school hours. However, they were free before or after their teaching hours, whereas the academics in sample 2 were more independent than the teachers [
116]. The nature of these occupations meant that these two samples were not biased in their gender composition. These unique sample characteristics may explain why, for example, gender was not a significant control variable in this study. Finally, the results indicated that age did not associate with developing relationships. However, our results indicated a significant difference in the association between age and information gathering and the negative influence of gossip for both samples. The probable reason for this result is the difference in the average age of the samples (Sample 1 had an average age of 34.9 and Sample 2 had an average of 43.2). Those in Sample 2 were almost a decade older with lots more experience than those in Sample 1. Despite the limited literature, our findings differ from Massar, Buunk, and Rempt [
80]’s study. Massar et al. [
80] found a significant negative effect between a participant’s age and their tendency to gossip. The difference in experience between the two samples may be a possible reason for this result.
7. Conclusions and Policy Implications
The dark side of management and unregulated organisational communication systems endangers the sustainability of organisations and the peace climate within organisations. This research examines the types of organisational gossip from the perspective of trait activation theory in educational organisations by applying structural equation modelling. In this context, the current research sheds light on the literature on organisational behaviour by integrating the effects of abusive supervision on organisational gossip, considering the mediating role of the dark triad. The results show that abusive supervision affects information gathering gossip but not relationship building gossip or negatively influence gossip. Moreover, the empirical evidence further confirms the mediating role of narcissism, Machiavellianism, and psychopathy on the relationship between abusive supervision and the three categories of organisational gossip. Furthermore, the results of this study indicate that abusive supervision may serve as a situational factor that activates narcissism, Machiavellianism, and psychopathy and predicts information.
Based on these findings, this study offers policy suggestions for educational organisations in particular and for all organisations in general. Even if educators have some autonomy in their school/faculty, their share of participatory activities in management should be improved. Last, the findings demonstrated that despite the ramifications of abusive supervision, a sense of trust, organisational identification, and perceptions of organisational justice can significantly affect organisational gossip. Consequently, human resource policies that enhance employees’ personal characteristics and organisational identity should be adopted, management–employee relationships strengthened, and perceptions of organisational justice increased.