Intervention Effect of Group Sensory Integration Training on Social Responsiveness and N170 Event-Related Potential of Children with Autism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Group Sensory Integration Training
2.3. Social Responsiveness Scale
2.4. Event-Related Potentials
2.5. Experiment Design and Procedure
3. Results
3.1. SRS Scores Exhibit Alterations Pre and Post Intervention
3.2. EEG Processing and Statistical Analysis
3.2.1. Latency of the N170
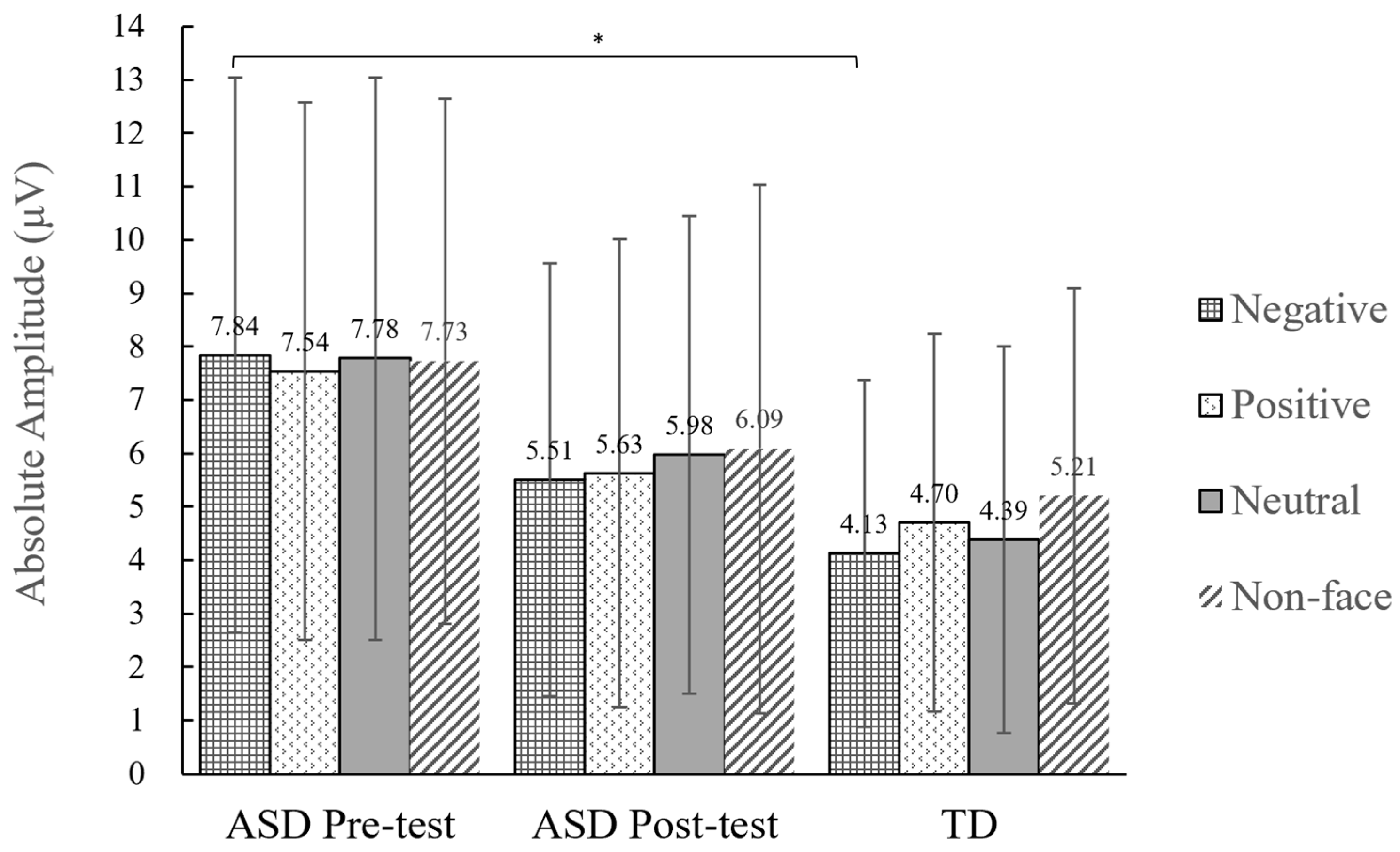
3.2.2. Peak Amplitude of the N170
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of the Group Sensory Integration Training
4.2. N170 and Face Processing in Children with ASD
4.2.1. Changes in N170 Latency Pre and Post Intervention
4.2.2. Pre-Test N170 Amplitude Is Significantly Larger among Children with ASD Than in TD Children
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Almuqhim, F.; Saeed, F. ASD-SAENet: A sparse autoencoder, and Deep-Neural Network Model for detecting autism spectrum disorder (ASD) using fMRI data. Front. Comput. Neurosc. 2021, 15, 654315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, H.; Fealko, C.; Soares, N. Autism spectrum disorder: Definition, epidemiology, causes, and clinical evaluation. Transl. Pediatr. 2020, 9, S55–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlier, S.; Van der Paelt, S.; Ongenae, F.; De Backere, F.; De Turck, F. Empowering children with ASD and their parents: Design of a serious game for anxiety and stress reduction. Sensors 2020, 20, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrachko, A.A.; Kaczmarek, L.A. Examining paraprofessional interventions to increase social communication for young children with ASD. Top Early Child Spec. 2017, 37, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, G.; Webb, S.J.; Wijsman, E.; Schellenberg, G.; Estes, A.; Munson, J.; Faja, S. Neurocognitive and electrophysiological evidence of altered face processing in parents of children with autism: Implications for a model of abnormal development of social brain circuitry in autism. Dev. Psychopathol. 2005, 17, 679–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, R.T. Developmental deficits in social perception in autism: The role of the amygdala and fusiform face area. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2005, 23, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, S.; Sohn, I.; Kim, N.; Sim, H.J.; Cheon, K. Characteristics of brains in autism spectrum disorder: Structure, function and connectivity across the lifespan. Exp. Neurobiol. 2015, 24, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Tachibana, M.; Rahman, S.; Kagitani Shimono, K. Atypical structural connectivity of language networks in autism spectrum disorder: A meta-analysis of diffusion tensor imaging studies. Autism Res. 2022, 15, 1585–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safar, K.; Vandewouw, M.M.; Taylor, M.J. Atypical development of emotional face processing networks in autism spectrum disorder from childhood through to adulthood. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2021, 51, 101003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Styliadis, C.; Leung, R.; Özcan, S.; Moulton, E.A.; Pang, E.; Taylor, M.J.; Papadelis, C. Atypical spatiotemporal activation of cerebellar lobules during emotional face processing in adolescents with autism. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2021, 42, 2099–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, Ü.; Cañigueral, R.; Tye, C.; McLoughlin, G. Face processing in young adults with autism and ADHD: An event related potentials study. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1080681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Ma, X.; Qi, C. N170 adaptation effect for repeated faces and words. Neuroscience 2015, 294, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinojosa, J.A.; Mercado, F.; Carretie, L. N170 sensitivity to facial expression: A meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. R. 2015, 55, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPartland, J.C.; Crowley, M.J.; Perszyk, D.R.; Naples, A.J.; Mukerji, C.E.; Wu, J.; Molfese, P.; Bolling, D.Z.; Pelphrey, K.A.; Mayes, L.C. Temporal dynamics reveal atypical brain response to social exclusion in autism. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2011, 1, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPartland, J.C.; Wu, J.; Bailey, C.A.; Mayes, L.C.; Schultz, R.T.; Klin, A. Atypical neural specialization for social percepts in autism spectrum disorder. Soc. Neurosci. 2011, 6, 436–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, T.C.; Crowley, M.J.; Naples, A.J.; Rolison, M.J.; Wu, J.; Trapani, J.A.; McPartland, J.C. The N170 event-related potential reflects delayed neural response to faces when visual attention is directed to the eyes in youths with ASD. Autism Res. 2021, 14, 1347–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidet-Caulet, A.; Latinus, M.; Roux, S.; Malvy, J.; Bonnet-Brilhault, F.; Bruneau, N. Atypical sound discrimination in children with ASD as indicated by cortical ERPs. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2017, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klin, A.; Jones, W.; Schultz, R.; Volkmar, F.; Cohen, D. Visual fixation patterns during viewing of naturalistic social situations as predictors of social competence in individuals with autism. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2002, 59, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundy, P. A review of joint attention and social-cognitive brain systems in typical development and autism spectrum disorder. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2018, 47, 497–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tager-Flusberg, H. Understanding the language and communicative impairments in autism. In International Review of Research in Mental Retardation; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000; Volume 23, pp. 185–205. [Google Scholar]
- McPartland, J.C. Considerations in biomarker development for neurodevelopmental disorders. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2016, 29, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwaigenbaum, L.; Bauman, M.L.; Choueiri, R.; Kasari, C.; Carter, A.; Granpeesheh, D.; Mailloux, Z.; Smith Roley, S.; Wagner, S.; Fein, D.; et al. Early intervention for children with autism spectrum disorder under 3 years of age: Recommendations for practice and research. Pediatrics 2015, 136, S60–S81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashefimehr, B.; Kayihan, H.; Huri, M. The effect of sensory integration therapy on occupational performance in children with autism. OTJR 2018, 38, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5™, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bölte, S. Brief Report: The Social Responsiveness Scale for Adults (SRS-A): Initial results in a German cohort. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2012, 42, 1998–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, Y.-J. Standardization and assessment of college students’ facial expression of emotion. Chin. J. Clin. Psychol. 2005, 13, 396–398. [Google Scholar]
- Aguado, L.; Dieguez-Risco, T.; Villalba-García, C.; Hinojosa, J.A. Double-checking emotions: Valence and emotion category in contextual integration of facial expressions of emotion. Biol. Psychol. 2019, 146, 107723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lissa, P.; Sorensen, S.; Badcock, N.; Thie, J.; McArthur, G. Measuring the face-sensitive N170 with a gaming EEG system: A validation study. J. Neurosci. Meth. 2015, 253, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuhaus, E.; Kresse, A.; Faja, S.; Bernier, R.A.; Webb, S.J. Face processing among twins with and without autism: Social correlates and twin concordance. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neur. 2016, 11, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, P.P.; Mouga, S.S.; Oliveira, G.G.; Castelo-Branco, M. Preserved face inversion effects in adults with autism spectrum disorder: An event-related potential study. Neuroreport 2016, 27, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yizengaw, S.S. Effect of social skills training on interpersonal interactions of children with autism: An interventional research. Int. J. Dev. Disabil. 2022, 68, 858–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roley, S.S.; Mailloux, Z.; Parham, L.D.; Schaaf, R.C.; Lane, C.J.; Cermak, S. Sensory integration and praxis patterns in children with autism. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2015, 69, 1688714582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranek, G.T.; David, F.J.; Poe, M.D.; Stone, W.L.; Watson, L.R. Sensory Experiences Questionnaire: Discriminating sensory features in young children with autism, developmental delays, and typical development. J. Child Psychol. Psyc. 2006, 47, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavassoli, T.; Miller, L.J.; Schoen, S.A.; Jo Brout, J.; Sullivan, J.; Baron-Cohen, S. Sensory reactivity, empathizing and systemizing in autism spectrum conditions and sensory processing disorder. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2018, 29, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, R.; Reilly, M.O.; Healy, O.; Rispoli, M.; Lydon, H.; Streusand, W.; Davis, T.; Kang, S.; Sigafoos, J.; Lancioni, G.; et al. Sensory integration therapy for autism spectrum disorders: A systematic review. Res. Autism Spect. Dis. 2012, 6, 1004–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.; Keifer, C.M.; Levy, E.J.; Foss-Feig, J.H.; McPartland, J.C.; Lerner, M.D. Atypicality of the N170 Event-Related Potential in autism spectrum disorder: A meta-analysis. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2018, 3, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsabbagh, M.; Fernandes, J.; Jane Webb, S.; Dawson, G.; Charman, T.; Johnson, M.H. Disengagement of visual attention in infancy is associated with emerging autism in toddlerhood. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 74, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kala, S.; Rolison, M.J.; Trevisan, D.A.; Naples, A.J.; Pelphrey, K.; Ventola, P.; McPartland, J.C. Brief report: Preliminary evidence of the N170 as a biomarker of response to treatment in autism spectrum disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 709382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, E.J.; Isenstein, E.L.; Foss-Feig, J.; Srihari, V.; Anticevic, A.; Naples, A.J.; McPartland, J.C. Electrophysiological studies of reception of facial communication in autism spectrum disorder and schizophrenia. Rev. J. Autism Dev. Dis. 2022, 9, 521–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, G.; Webb, S.J.; McPartland, J. Understanding the nature of face processing impairment in autism: Insights from behavioral and electrophysiological studies. Dev. Neuropsychol. 2005, 27, 403–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPartland, J.; Dawson, G.; Webb, S.J.; Panagiotides, H.; Carver, L.J. Event-related brain potentials reveal anomalies in temporal processing of faces in autism spectrum disorder. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2004, 45, 1235–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feuerriegel, D.; Churches, O.; Hofmann, J.; Keage, H.A.D. The N170 and face perception in psychiatric and neurological disorders: A systematic review. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 1141–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Pre-Test | Post-Test | T | d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M (SD) | M (SD) | |||
| SRS Total | 94.25 (14.49) | 86.83 (12.64) | 2.55 * | 0.73 |
| AWR | 13.08 (2.61) | 11.67 (2.74) | 3.40 ** | 0.99 |
| COG | 20.25 (3.22) | 18.33 (3.11) | 1.65 | 0.48 |
| COMM | 30.83 (5.59) | 28.75 (4.69) | 2.21 * | 0.63 |
| MOT | 13.5 (4.62) | 13.67 (3.50) | −0.19 | 0.06 |
| RRB | 16.58 (4.08) | 14.42 (3.75) | 2.90 * | 0.84 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shu, D.; Zhang, G.; Xue, C.; Lai, Q.; He, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jia, F.; Liu, D. Intervention Effect of Group Sensory Integration Training on Social Responsiveness and N170 Event-Related Potential of Children with Autism. Behav. Sci. 2024, 14, 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14030202
Shu D, Zhang G, Xue C, Lai Q, He Y, Feng Y, Zhang J, Jia F, Liu D. Intervention Effect of Group Sensory Integration Training on Social Responsiveness and N170 Event-Related Potential of Children with Autism. Behavioral Sciences. 2024; 14(3):202. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14030202
Chicago/Turabian StyleShu, Deming, Gongliang Zhang, Chang Xue, Qiqi Lai, Yueyao He, Yifei Feng, Jianxin Zhang, Fengqin Jia, and Dianzhi Liu. 2024. "Intervention Effect of Group Sensory Integration Training on Social Responsiveness and N170 Event-Related Potential of Children with Autism" Behavioral Sciences 14, no. 3: 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14030202
APA StyleShu, D., Zhang, G., Xue, C., Lai, Q., He, Y., Feng, Y., Zhang, J., Jia, F., & Liu, D. (2024). Intervention Effect of Group Sensory Integration Training on Social Responsiveness and N170 Event-Related Potential of Children with Autism. Behavioral Sciences, 14(3), 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14030202






