Linking Context to Language Switching: Effects of Background Noise on Bilingual Language Comprehension
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment 1
2.1. Participants
2.2. Materials
2.3. Task and Procedure
2.4. Data Analyses
2.5. Results
2.5.1. Frequentist Analyses on Experiment 1
2.5.2. Bayesian Analyses on Experiment 1
2.6. Discussion of Experiment 1
3. Experiment 2
3.1. Participants
3.2. Material and Task
3.3. Data Analyses
3.4. Results
3.4.1. Frequentist Analyses of Experiment 2
3.4.2. Bayesian Analyses of Experiment 2
3.5. Discussion of Experiment 2
4. General Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B

References
- Aparicio, X., & Lavaur, J.-M. (2014). Recognising words in three languages: Effects of language dominance and language switching. International Journal of Multilingualism, 11(2), 164–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D., Mächler, M., Bolker, B., & Walker, S. (2015). Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bsharat-Maalouf, D., & Karawani, H. (2022). Bilinguals’ speech perception in noise: Perceptual and neural associations. PLOS ONE, 17(2), e0264282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bürkner, P.-C. (2017). Advanced Bayesian multilevel modeling with the R package brms. The R Journal, 10, 395–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, R. K., Lindén, H., Nakamura, M., & Barkat, T. R. (2019). White noise background improves tone discrimination by suppressing cortical tuning curves. Cell Reports, 29(7), 2041–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, A., Santesteban, M., & Ivanova, I. (2006). How do highly proficient bilinguals control their lexicalization process? Inhibitory and language-specific selection mechanisms are both functional. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 32(5), 1057–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coumel, M., Liu, C., Trenkic, D., & De Bruin, A. (2024). Do accent and input modality modulate processing of language switches in bilingual language comprehension? Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 50(4), 395–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Declerck, M., & Grainger, J. (2017). Inducing asymmetrical switch costs in bilingual language comprehension by language practice. Acta Psychologica, 178, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Declerck, M., & Philipp, A. M. (2015). A review of control processes and their locus in language switching. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 22(6), 1630–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Declerck, M., Koch, I., Duñabeitia, J. A., Grainger, J., & Stephan, D. N. (2019). What absent switch costs and mixing costs during bilingual language comprehension can tell us about language control. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 45(6), 771–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Declerck, M., Lemhöfer, K., & Grainger, J. (2017). Bilingual language interference initiates error detection: Evidence from language intrusions. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition, 20(5), 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, T., & Van Heuven, W. J. B. (1998). The BIA model and bilingual word recognition. In Localist connectionist approaches to human cognition (pp. 189–225). Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers. [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra, T., & Van Heuven, W. J. B. (2002). The architecture of the bilingual word recognition system: From identification to decision. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition, 5(3), 175–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudero, P., Jones Diaz, C., Hajek, J., Wigglesworth, G., & Smit, E. A. (2020). Probability of heritage language use at a supportive early childhood setting in Australia. Frontiers in Education, 5, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, P. B., Leibold, L., Buss, E., Calandruccio, L., & Rodriguez, B. (2018). Code-switching in highly proficient Spanish/English bilingual adults: Impact on masked word recognition. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 61(9), 2353–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelman, A. (2020). Prior choice recommendations. Available online: https://github.com/stan-dev/stan/wiki/Prior-Choice-Recommendations (accessed on 17 October 2024).
- Grainger, J., & Dijkstra, T. (1992). On the representation and use of language information in bilinguals. In Advances in psychology (Vol. 83, pp. 207–220). Elsevier. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grainger, J., Midgley, K., & Holcomb, P. J. (2010). Chapter 14. Re-thinking the bilingual interactive-activation model from a developmental perspective (BIA-d). In M. Kail, & M. Hickmann (Eds.), Language acquisition and language disorders (Vol. 52, pp. 267–283). John Benjamins Publishing Company. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D. W., & Abutalebi, J. (2013). Language control in bilinguals: The adaptive control hypothesis. Journal of Cognitive Psychology, 25(5), 515–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, M. C., Patel, H., & Kaushanskaya, M. (2021). Processing of code-switched sentences in noise by bilingual children. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 64(4), 1283–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S., Meng, Y., & Chen, B. (2024). The impact of emotional states on bilingual language control in cued and voluntary switching contexts. Journal of Memory and Language, 137, 104527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lago, S., Stone, K., Oltrogge, E., & Veríssimo, J. (2023). Possessive processing in bilingual comprehension. Language Learning, 73(3), 904–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C., Jiao, L., Wang, Z., Wang, M., Wang, R., & Wu, Y. J. (2019). Symmetries of bilingual language switch costs in conflicting versus non-conflicting contexts. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition, 22(3), 624–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C., Timmer, K., Jiao, L., & Wang, R. (2020). Symmetries of comprehension-based language switch costs in conflicting versus non-conflicting contexts. International Journal of Bilingualism, 24(4), 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macizo, P., Bajo, T., & Paolieri, D. (2012). Language switching and language competition. Second Language Research, 28(2), 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuter, R. F. I., & Allport, A. (1999). Bilingual language switching in naming: Asymmetrical costs of language selection. Journal of Memory and Language, 40(1), 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, A. J., & Herff, S. A. (2020). The perceptual relevance of balance, evenness, and entropy in musical rhythms. Cognition, 203, 104233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosca, M., & De Bot, K. (2017). Bilingual language switching: Production vs. recognition. Frontiers in Psychology, 8, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, F. (2004). Stochastic resonance and sensory information processing: A tutorial and review of application. Clinical Neurophysiology, 115(2), 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, D. J. (2017). Bilingual language switching costs in auditory comprehension. Language, Cognition and Neuroscience, 32(4), 494–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipp, A. M., & Huestegge, L. (2015). Language switching between sentences in reading: Exogenous and endogenous effects on eye movements and comprehension. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition, 18(4), 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccinini, P. E., & Garellek, M. (2014). Cross language speech-in-noise perception by early Spanish-English bilinguals and English monolinguals. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 135(4), 2352–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch, V. H., Bauch, E. M., & Bunzeck, N. (2014). White noise improves learning by modulating activity in dopaminergic midbrain regions and right superior temporal sulcus. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 26(7), 1469–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharenborg, O., & Van Os, M. (2019). Why listening in background noise is harder in a non-native language than in a native language: A review. Speech Communication, 108, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snodgrass, J. G., & Vanderwart, M. (1980). A standardized set of 260 pictures: Norms for name agreement, image agreement, familiarity, and visual complexity. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Learning and Memory, 6(2), 174–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thierry, G., & Wu, Y. J. (2007). Brain potentials reveal unconscious translation during foreign-language comprehension. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 104(30), 12530–12535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmer, K., Christoffels, I. K., & Costa, A. (2019). On the flexibility of bilingual language control: The effect of language context. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition, 22(3), 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, P. C. M., Uppunda, A. K., Parrish, T. B., & Dhar, S. (2008). Cortical mechanisms of speech perception in noise. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 51(4), 1026–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| L1 | L2 | |
|---|---|---|
| AoA (years) | - | 8.23 (3.18) |
| Self-reported proficiency (1–7) | ||
| Listening | 6.48 (0.89) | 3.55 (0.99) |
| Speaking | 6.45 (0.92) | 3.35 (0.66) |
| Reading | 6.45 (0.81) | 4.13 (0.92) |
| Writing | 6.23 (0.88) | 3.58 (0.76) |
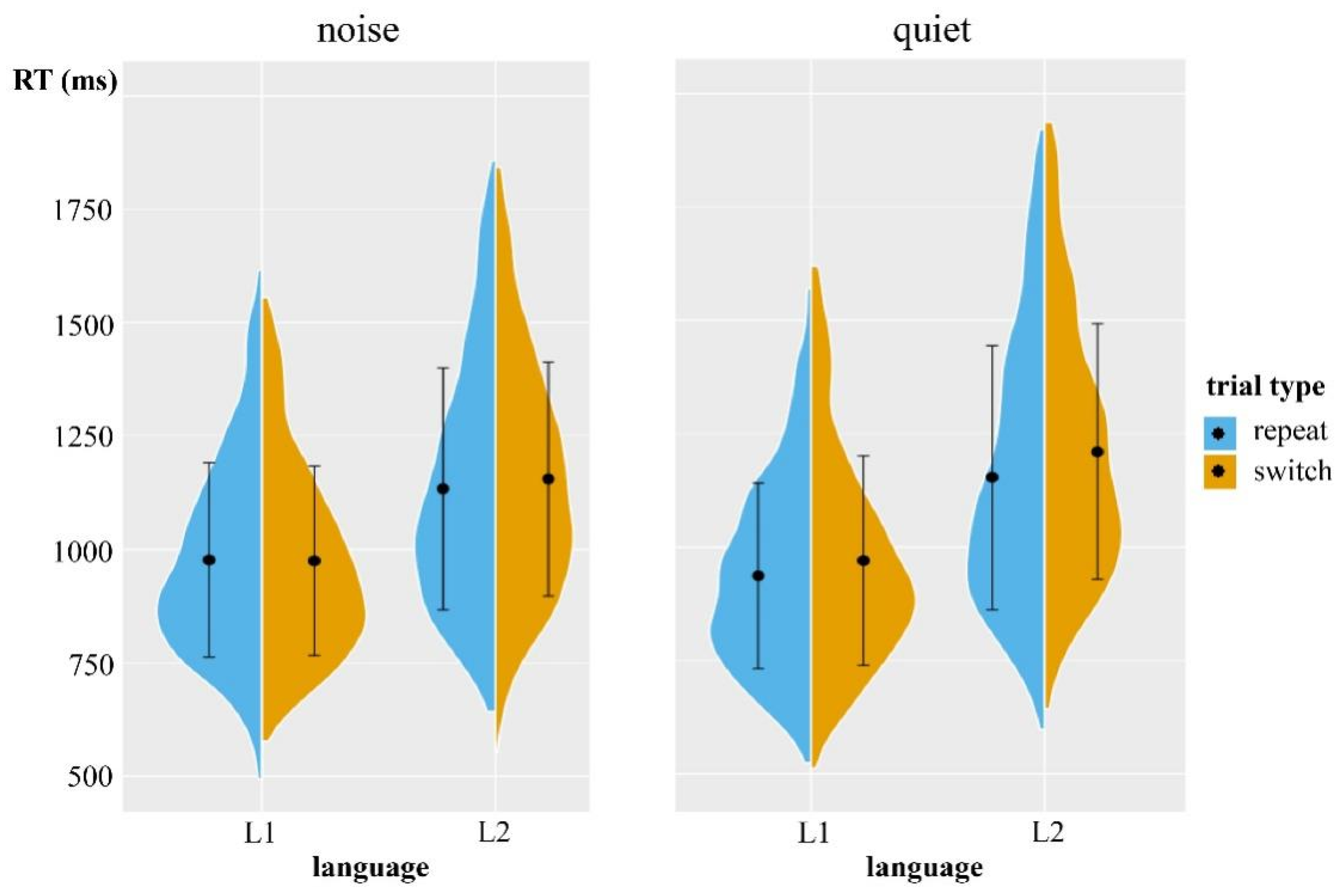
| L1 | L2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Repeat | Switch | Switch Costs | Repeat | Switch | Switch Costs | |
| quiet | 910.94 (87.54) | 941.46 (92.20) | 30.53 (44.63) | 1092.98 (91.96) | 1144.65 (108.59) | 51.68 (47.72) |
| noise | 1004.98 (100.86) | 1017.53 (103.70) | 12.55 (49.64) | 1109.96 (122.54) | 1123.87 (122.89) | 13.91 (41.95) |
| Fixed Effects | Estimated | SE | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (intercept) | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.93 | 0.35 |
| condition | 0.19 | 0.07 | 2.75 | <0.01 |
| language | 0.63 | 0.08 | 7.85 | <0.01 |
| type | 0.16 | 0.03 | 4.93 | <0.01 |
| condition × language | −0.34 | 0.10 | −3.52 | <0.01 |
| condition × type | −0.23 | 0.06 | −3.48 | <0.01 |
| language × type | 0.08 | 0.06 | 1.23 | 0.22 |
| condition × language × type | −0.28 | 0.13 | −2.17 | 0.03 |
| Family: Gaussian Links: mu = identity Formula: RT ~ condition × type × language + (condition × type × language|participant) + (condition × type × language|item) Data: Experiment 1 data Samples: 4 chains, each with iter = 10,000; warmup = 1000; thin = 1; total post-warmup samples = 36,000 | |||||||
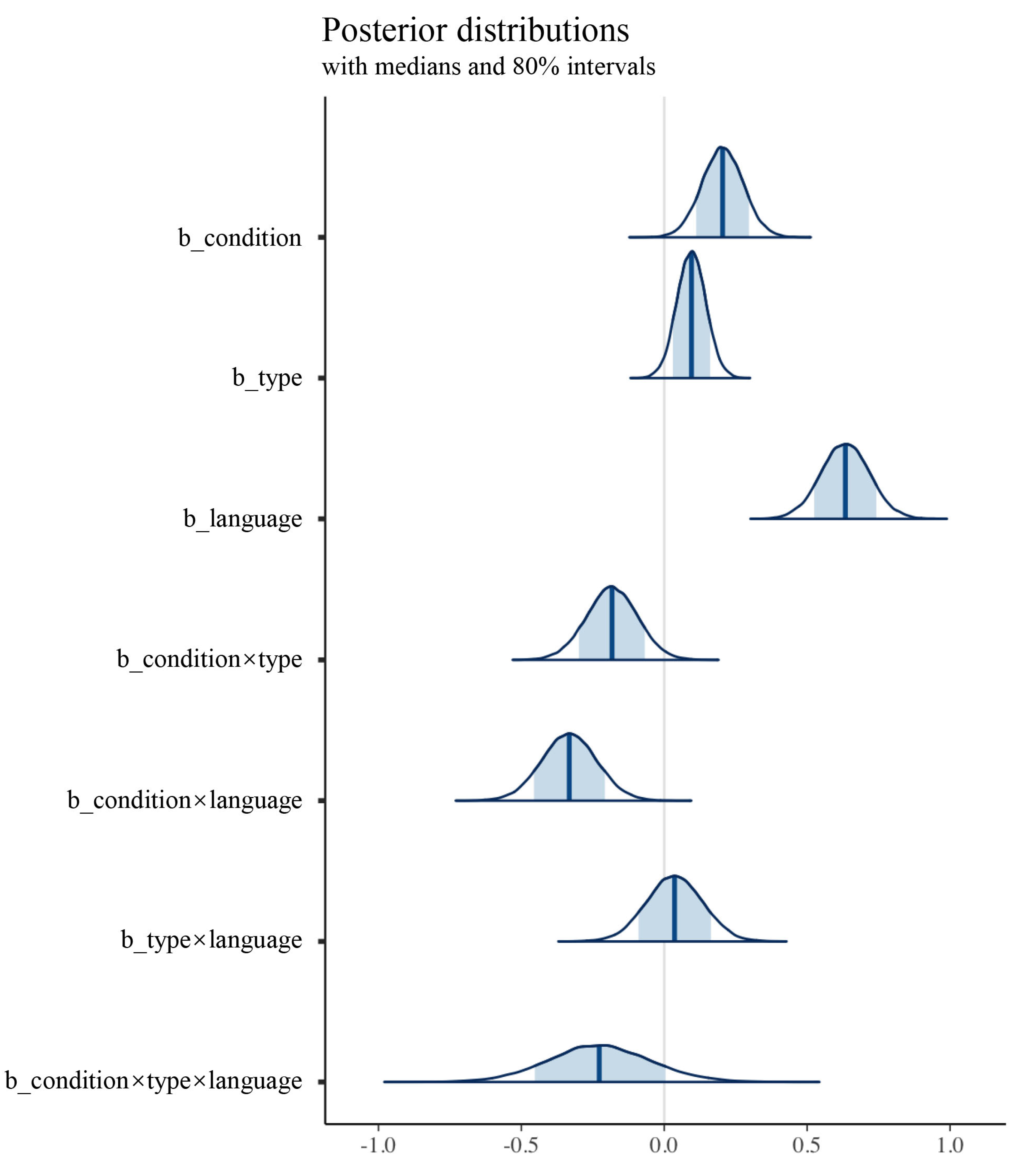
| Hypothesis | Estimated | SE | 95% CI | Evid. Ratio | Post. Prob | Star | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| condition > 0 | 0.20 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.32 | 366.35 | 1.00 | * |
| language > 0 | 0.63 | 0.09 | 0.49 | 0.77 | >9999 | 1.00 | * |
| type > 0 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.18 | 30.80 | 0.97 | * |
| condition × language < 0 | −0.33 | 0.10 | −0.49 | −0.17 | 2768.23 | 1.00 | * |
| condition × type < 0 | −0.18 | 0.09 | −0.33 | −0.03 | 44.63 | 0.98 | * |
| language × type < 0 | 0.04 | 0.10 | −0.12 | 0.20 | 0.56 | 0.36 | |
| condition × language × type < 0 | −0.23 | 0.18 | −0.52 | 0.07 | 8.62 | 0.90 | |
| Experiment 2 | Independent-Samples t-Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | L2 | L1 | L2 | |
| AoA(years) | - | 7.76 (1.88) | - | 0.69 |
| Self-reported proficiency (1–7) | ||||
| Listening | 6.48 (0.73) | 3.96 (1.08) | 0.05 | −1.55 |
| Speaking | 6.31 (0.85) | 3.55 (0.83) | 0.61 | −1.50 |
| Reading | 6.45 (0.78) | 4.28 (1.03) | 0.02 | −0.58 |
| Writing | 6.07 (0.99) | 3.72 (0.96) | 0.65 | −0.64 |
| L1 | L2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Repeat | Switch | Switch Costs | Repeat | Switch | Switch Costs | |
| quiet | 939.14 (91.80) | 972.80 (101.40) | 33.67 (45.03) | 1159.66 (117.21) | 1216.62 (131.74) | 56.96 (61.94) |
| noise | 979.75 (102.31) | 977.48 (101.41) | −2.28 (43.77) | 1136.38 (135.25) | 1160.99 (126.28) | 24.62 (47.91) |
| Fixed Effects | Estimated | SE | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (intercept) | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.80 | 0.43 |
| condition | −0.01 | 0.06 | −0.05 | 0.96 |
| language | 0.79 | 0.09 | 8.92 | <0.01 |
| type | 0.15 | 0.04 | 3.40 | <0.01 |
| condition × language | −0.22 | 0.07 | −3.13 | <0.01 |
| condition × type | −0.21 | 0.07 | −3.05 | <0.01 |
| language × type | 0.10 | 0.09 | 1.18 | 0.24 |
| condition × language × type | −0.02 | 0.14 | −0.13 | 0.90 |
| Family: Gaussian Links: mu = identity Formula: RT ~ condition × type × language + (condition × type × language|participant) + (condition × type × language|item) Data: Experiment 2 data Samples: 4 chains, each with iter = 10,000; warmup = 1000; thin = 1; total post-warmup samples = 36,000 | |||||||
| Hypothesis | Estimated | SE | 95% CI | Evid. Ratio | Post. Prob | Star | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| condition > 0 | −0.01 | 0.07 | −0.12 | 0.10 | 0.74 | 0.43 | |
| language > 0 | 0.78 | 0.09 | 0.63 | 0.94 | >9999 | 1.00 | * |
| type > 0 | 0.13 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.21 | 492.15 | 1.00 | * |
| condition × language < 0 | −0.19 | 0.08 | −0.33 | −0.06 | 115.88 | 0.99 | * |
| condition × type < 0 | −0.20 | 0.08 | −0.34 | −0.06 | 100.98 | 0.99 | * |
| language × type < 0 | 0.09 | 0.09 | −0.06 | 0.23 | 0.19 | 0.16 | |
| condition × language × type < 0 | −0.04 | 0.17 | −0.31 | 0.24 | 1.44 | 0.59 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiao, L.; Wang, Z.; Duan, X.; Yu, Y.; Liu, C. Linking Context to Language Switching: Effects of Background Noise on Bilingual Language Comprehension. Behav. Sci. 2025, 15, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15010060
Jiao L, Wang Z, Duan X, Yu Y, Liu C. Linking Context to Language Switching: Effects of Background Noise on Bilingual Language Comprehension. Behavioral Sciences. 2025; 15(1):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15010060
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiao, Lu, Zejun Wang, Xiaoting Duan, Yingying Yu, and Cong Liu. 2025. "Linking Context to Language Switching: Effects of Background Noise on Bilingual Language Comprehension" Behavioral Sciences 15, no. 1: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15010060
APA StyleJiao, L., Wang, Z., Duan, X., Yu, Y., & Liu, C. (2025). Linking Context to Language Switching: Effects of Background Noise on Bilingual Language Comprehension. Behavioral Sciences, 15(1), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15010060






