Abstract
The strain of red microalgae Galdieria sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 was evaluated in a controlled laboratory environment for its ability to tolerate and remove two heavy metal (HM) ions: cadmium [Cd(II)] and lead [Pb(II)] in aqueous solutions as a single metal species. Various concentrations (0 mg L−1 to 5 mg L−1) of Cd and Pb ions were added to the Cyanidium medium in which the chosen microalgae strain G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 was grown at an acidic pH of 2.5. The effectiveness of G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 in tolerating and removing these two metal ions was measured by analyzing its growth profile, growth rate, nutrient removal, and metal ion removal efficiency. The growth of G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 was inhibited during the initial days of incubation, and the growth rate decreased when the HM concentration in the media was increased. Nutrient removal in the HM-containing media is comparable to that in the control media at low metal concentrations but decreases as the metal concentration rises. G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 has the highest removal efficiency for Cd and Pb in a medium containing 2.5 mg L−1 of metal ions, which is 49.80% and 25.10%, and the corresponding sorption capacity is 1.45 mg g−1 and 0.53 mg g−1 of dry biomass, respectively. These findings suggest that G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 holds potential as a viable bioremediation solution for extracting Cd and Pb from wastewater, alongside its capacity to remove nutrients concurrently. The study underscores the dual advantage of G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1, making it a promising candidate for addressing heavy metal pollution in wastewater treatment processes.
1. Introduction
The surge in industrialization and urbanization has given rise to a significant influx of wastewater into the natural water ecosystem. The widespread utilization of metals in industrial processes has resulted in the release of substantial quantities of metal-laden waste into the environment. Industries spanning oils, textiles, fossil fuels, metallurgy, electroplating, galvanization, and others contribute to the discharge of harmful HM ions into the surroundings [1,2]. Given the non-biodegradable nature of HMs and their propensity to accumulate within the food chain, their introduction into the environment carries detrimental implications [3]. The presence of HM pollution bears unfavorable consequences for human health and exerts adverse impacts on ecosystems and aquatic biodiversity. Recognizing the potential severity of the issue, environmental regulations have been instated to safeguard natural water sources against HM contamination. This is especially vital as the pollution of natural water bodies by HMs has emerged as a pressing concern in recent times [4].
Cd and Pb stand as examples of toxic inorganic metals inherent to the Earth’s crust. Their exceptionally low tolerance thresholds for toxicity classify both Cd and Pb as non-threshold toxins. Pb, recognized as a hazardous HM, finds its way into wastewater through human-induced activities, such as mining and the combustion of fossil fuels [5]. Similarly, Cd is a very poisonous, invasive HM released into the environment due to mining, battery disposal, and other human activities [6]. Remarkably, these HMs have detrimental implications for the environment and human well-being, even in minuscule quantities. Depending on the extent of exposure, these HMs can elicit both moderate and severe effects on human health. Consequences encompass a spectrum of ailments including, but not limited to, elevated blood pressure, damage to vital organs, such as the kidneys, liver, and lungs, gastrointestinal disorders, cancer, and even fatality [1,7,8]. The pervasiveness of these potential effects emphasizes the urgency of addressing Cd and Pb contamination due to their far-reaching consequences.
An array of physical, chemical, and biological processes, encompassing adsorption, chemical precipitation, ion exchange, and electrochemical treatment, have demonstrated the ability to eliminate metal ions from aqueous solutions [9,10]. However, these technologies often encounter limitations, including heightened energy demands, incomplete removal of HMs, generation of secondary contamination, and the imposition of substantial operation and maintenance costs [11,12]. Furthermore, many of these methods prove ineffective and unsuitable for addressing HM concentrations below 100 mg L−1 [8]. In light of these challenges, a pressing necessity arises to establish environmentally sound approaches for extracting HMs from wastewater. This urgency is driven by the need to surmount the shortcomings of existing techniques and develop efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable solutions that tackle varying concentrations of HMs, particularly those at lower levels.
The phycoremediation approach of removing HMs is based on interactions between HMs and microalgae. Microalgae play a vital role in establishing and maintaining healthy ecological relationships and interactions in aquatic environments [13]. The ecological role of microalgae is being investigated for its potential to purify water and wastewater that contains HMs [14]. Microalgae are increasingly recognized for their ability to eliminate both nutrients and HMs from wastewater due to their exceptional photosynthetic efficiency, pronounced binding affinity, abundant binding sites, and expansive surface area [8]. Despite the potential for elevated metal concentrations to induce toxic effects and hinder growth, numerous microalgae have evolved adaptive mechanisms for counteracting excessive metals. These mechanisms include secretion, compartmentalization, and chelation with metal ligands, enabling microalgae to detoxify surplus metals [15]. This dual capability of nutrient removal and HM detoxification underscores the value of microalgae-based strategies in environmental remediation.
G. sulphuraria, CCMEE 5587.1, a unicellular red alga, demonstrates remarkable resilience in challenging environments, such as high temperatures (37–55 °C) and extremely low pH levels (0.0–4.0) [16]. Moreover, its resistance to HMs commonly found in sulfur springs has been documented [17]. Given its affiliation with such demanding conditions, G. sulphuraria stands out as a promising subject for investigating its tolerance to HMs and its potential in phycoremediation practices [18]. The versatility of G. sulphuraria’s metabolism is notable; it can thrive using over 50 distinct carbon sources, adeptly switching between autotrophic, heterotrophic, and mixotrophic growth modes. This adaptability positions it as a prospective asset in biotechnology applications [19]. Notably, G. sulphuraria has showcased its capability to effectively eliminate carbon and nutrients, such as ammoniacal nitrogen (NH4-N) and phosphate-P (PO4-P) from various sources, including municipal wastewater, landfill leachate, and produced water [16,20,21,22,23]. Research findings reveal that G. sulphuraria harnesses these nutrients for its growth, leading to a reduction of these elements within the wastewater effluent. This ability to utilize and mitigate nutrients underscores its potential as a valuable component in wastewater treatment strategies.
Domestic wastewater and landfill leachate are typically characterized by their richness in nutrients and containing trace amounts of HMs. Landfill leachate, for instance, showcases a Pb concentration spanning 2–5 mg L−1 [24], whereas Cd content remains below 1 mg L−1 [25]. Given the relatively low metal concentrations observed in municipal wastewater and landfill leachate, the implementation of distinct chemical and physical recovery techniques often proves unfeasible or cost-prohibitive. Furthermore, some industries and mining operations, such as acid mine drainage (AMD), release extremely acidic wastewater that includes HM [26,27]. This effluent can then find its way into municipal wastewater treatment systems. Treatment of this kind of effluent may be best accomplished by the use of acid-resistant microalgae, such as G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1.
This study embarks on assessing the effectiveness of G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 in the removal of Cd and Pb at low concentrations (<5 mg L−1), simultaneously engaging in nutrient removal at acidic pH. Moreover, the study endeavors to quantitatively gauge the inhibitory impact of Cd and Pb ions on the growth and biomass production of G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1. By delving into these aspects, the research aims to ascertain the viability of G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 as a potential solution for mitigating Cd and Pb contamination while also addressing the interplay between metal toxicity and microalgae growth.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Algal Strain
This study assessed the feasibility of G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 isolates sourced from the Culture Collection of Microorganisms from Extreme Environments at the University of Oregon. The chosen strain was cultivated within an incubator (Percival, IA, USA) at a temperature of 40 °C, with constant illumination maintained at 4000 lux for a duration of 24 h [23,28]. The cultivation process began with axenic cultures achieved through streaking cultures onto agar plates. Subsequently, single colonies were selected for transfer to progressively larger flasks, ultimately culminating in 4 L Erlenmeyer flasks.
2.2. Cultural Media
In the research, G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 was grown in Cyanidium medium (CM). The following macro and micro level ingredients were utilized in the preparation of CM: (NH4)2SO4: 1.32 g L−1; KH2PO4: 0.27 g L−1; NaCl: 0.12 g L−1; MgSO4⋅7H2O: 0.25 g L−1; CaCl2⋅2H2O: 0.07 g L−1; Nitch’s Trace Element Solution: 0.5 mL L−1; FeCl3 (solution = 0.29 g L−1): 1.0 mL L−1 [16]. The media’s pH was maintained at 2.5 using 10 N H2SO4. To ensure the complete sterility of the medium, it underwent autoclaving at 121 °C for a duration of 50 min prior to utilization.
2.3. Synthetic Wastewater Solution Preparation
To simulate actual wastewater concentrations, a solution containing Cd and Pb below 5 mg L−1 was prepared by diluting PbCl2 and CdCl2 with CM media that contains the nutrients for algal growth. All the chemicals used were analytical-grade, and all the glassware was autoclaved prior to use. The Cd and Pb stock solution of 5 mg L−1 was made first, and then the solutions were diluted to the desired concentrations.
2.4. Exposure of G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 to Cd and Pb Added Media
G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 was harvested during the exponential growth phase and centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 10 min at 4 °C using Centrifuge 5920R (Eppendorf AG 22331 Hamberg, Germany). After the centrifugation, the supernatant was discarded, and the biomass was re-suspended in Cd and Pb-added media.
2.5. Metal and Nutrient Removal Experiment
The experiments were carried out in 125 mL Erlenmeyer flasks holding 50 mL of the experimental sample. The experiment contained three metal concentrations of 5 mg L−1, 2.5 mg L−1, and 1.25 mg L−1. For each concentration, two controls (one without G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 and one with G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 with no HM ions) were included to verify the presence of metal contamination and the impact of environmental circumstances and factors on the removal process. All flasks were placed on a New Brunswick Innova 2050 platform shaker (Eppendorf, Edison, NJ, USA) and rotated at 120 rpm for 7 days.
2.6. Measurement of Biomass Density
The biomass density was determined by measuring the optical density (OD) at 750 nm with a HACH DR 3900 spectrophotometer (HACH, Loveland, CO, USA). Daily measurements of OD were taken to determine the maximum possible growth rate. Ash-free dry weight (g AFDW L−1) was used to quantify biomass density, and this value was shown to be proportional to OD at 750 nm using the formula [22]:
Y = Ash-free dry wt. (AFDW)
X = OD value at 750 nm
2.7. Measurements of Nutrients
Nutrient (ammoniacal nitrogen and phosphorus) measurements were carried out at the start and end of each experiment. The measurements were performed with a HACH DR 3900 (HACH, Loveland, CO, USA) spectrophotometer, and the related methods were Salicylate TNT Method 10,031 and Phosver 3Method 8048 [22].
2.8. Measurement of Cd and Pb Concentration
After seven days of incubation, samples were collected and centrifuged at 6000 rpm for 10 min with a AccuSpin 400 centrifuge, (Fisher Scientific, D-77520 Osterode, Germany) to separate the supernatant fraction from the cell fraction. The concentration of Cd and Pb in the supernatant was measured by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES) (SHIMADZU ICPE 9820 simultaneous ICP atomic emission spectroscopy). The Cd and Pb ion removal efficiency was calculated by using the following equation:
ci and cf represent the metal ion concentrations in the supernatant on Day 7 in the media without algal cells and with algal cells, respectively.
2.9. Statistical Analysis and Graph Plotting
All experimental results were gathered from three independent biological replications and provided as a mean of replicates ± standard deviation. Microsoft Excel was used to determine the mean and standard deviation of the sample. ORIGINPRO 2023 was used to generate all the featured graphs.
3. Results
3.1. Growth of G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 in Different Concentrations of Cd and Pb
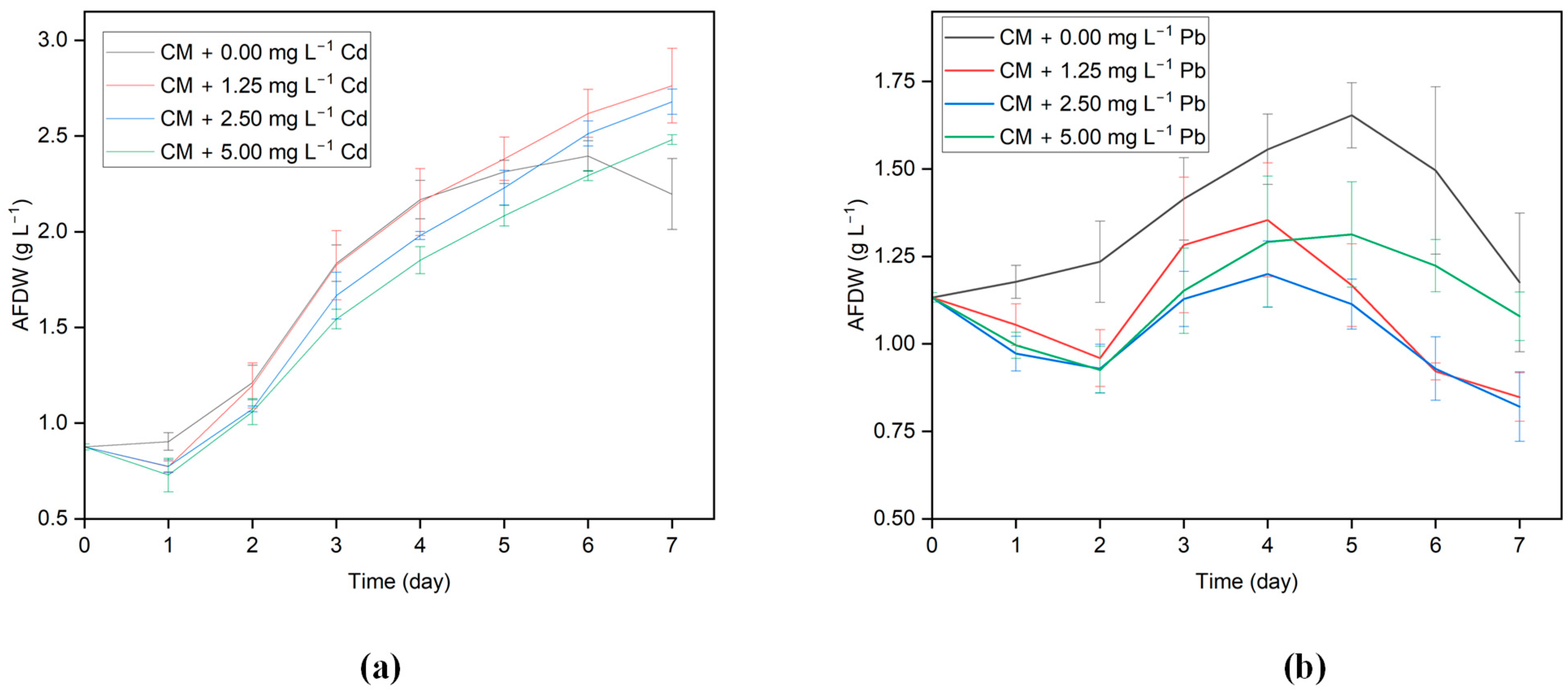
Exposure of algal cells to HMs is known to induce notable morphological and metabolic transformations, consequently impacting growth. To investigate the effects of Cd and Pb ions on growth, G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 was cultivated both in the absence and presence of Cd and Pb across concentrations spanning from 0 to 5 mg L−1. Results from the growth profiles demonstrate that when G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 was exposed to varied concentrations of the tested metal ions, there were clear changes in the biomass density of algal cells between the control and treated groups. The growth curves for G. Sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 subjected to various concentrations of Cd and Pb are shown in Figure 1a,b. G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 went through a lag, exponential, and stationary growth phase during the seven-day incubation period. For Days 1 and 2, after being exposed to Cd and Pb added media, G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1’s growth was inhibited and decreased. In the Pb-added media, there was a more significant inhibition in the growth of G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 on the initial day, and the exponential growth phase was delayed.
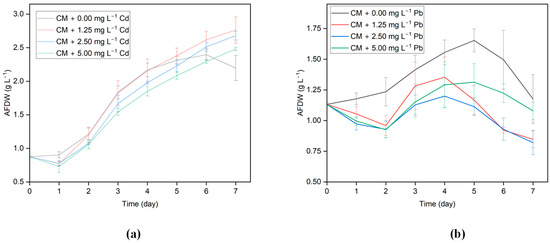
Figure 1.
Growth profile of G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 in the media with different concentrations of (a) Cd and (b) Pb.
3.2. Growth Rate
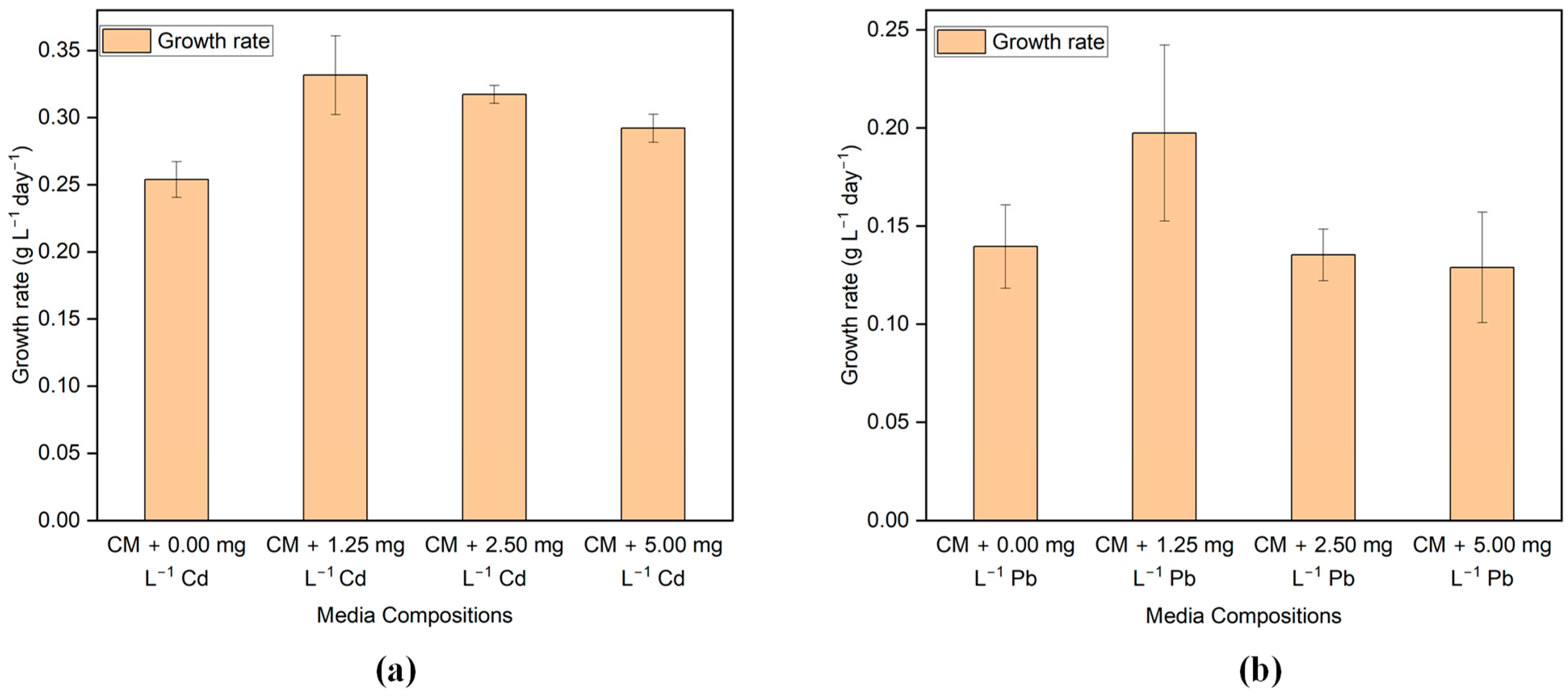
The growth rate was estimated based on the growth in the exponential phase. Figure 2a,b illustrates the effects of varying concentrations of Cd and Pb on the growth rate of G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1. The first two days after being exposed to Cd and Pb, G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 grew slower than the control group, but after two days, it grew faster than the control group. This could be attributed to the fact that G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 requires a period to acclimate to environments contaminated with HMs, which has not been previously exposed.
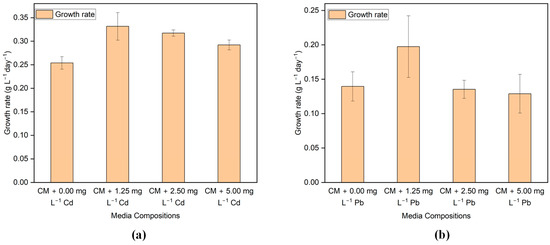
Figure 2.
The growth rate of G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 in the media with different concentrations of (a) Cd and (b) Pb.
The growth rate of G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 exposed to Cd-added media was greater than that of the control media for every Cd concentration despite a brief initial lag phase on the first day. Exposed to 1.25, 2.5, and 5 mg L−1 of Cd, the growth rates were 0.331 ± 0.029, 0.317 ± 0.006, and 0.292 ± 0.010 g L−1 day−1, correspondingly, whereas the growth rate was 0.253 ± 0.013 g L−1 day−1 in the control media. In the case of Pb-added media, the growth rate of G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 is higher than the control media in the media having a Pb concentration of 1.25 mg L−1. However, the growth rate is less than the control media in the media having a Pb concentration of 2.5 and 5 mg L−1. In detail, the growth rate was 0.197 ± 0.044, 0.135 ± 0.013, 0.128 ± 0.028 g L−1 day−1 when exposed to 1.25, 2.5, and 5 mg L−1 of Pb added media, respectively, whereas the growth rate is 0.139 ± 0.021 g L−1 day−1 in the control media.
3.3. Bioremoval of Cd and Pb
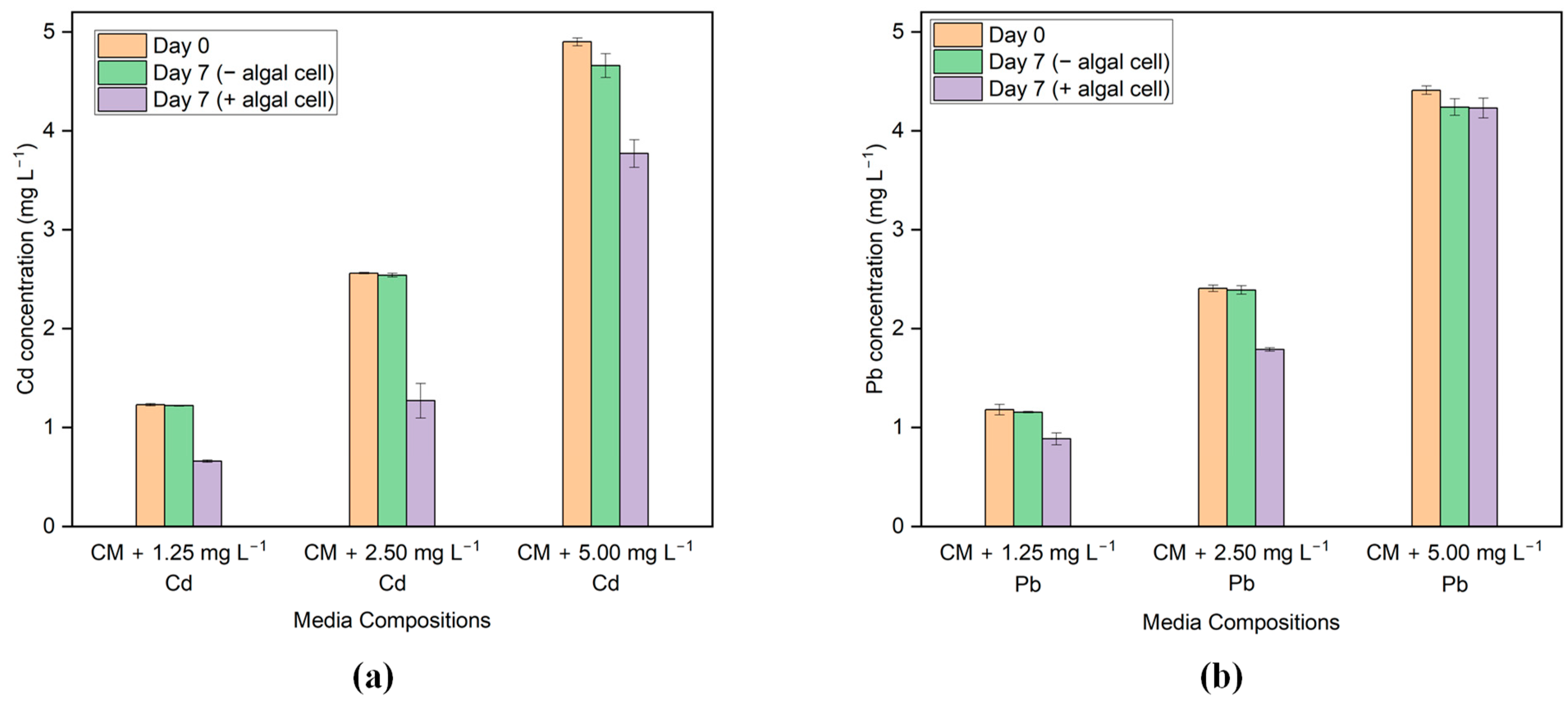
G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 was able to remove Cd and Pb from the media after seven days of treatment with living cells. The results of the ICP_AES analysis performed on the initial and final samples are shown in Figure 3a,b. Based on the results, G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 exhibits varying levels of effectiveness in the removal of Cd and Pb.
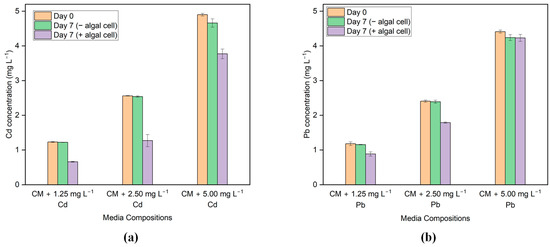
Figure 3.
HM concentration before and after the treatment in the media with different concentrations of (a) Cd and (b) Pb.
In the case of Cd, the highest Cd removal efficiency by G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 occurs in the media containing 2.5 mg L−1 Cd, which is 49.80%. However, the removal efficiency was only 19.09% in the media that included a Cd concentration of 5 mg L−1. In addition, the removal effectiveness was 45.90% in the media when the Cd content was 1.25 mg L−1. Moreover, the sorption capacity is highest in the media containing 2.5 mg L−1 Cd, which is 1.45 mg g−1 of dry biomass, and the lowest value is 0.64 mg g−1 of dry biomass in the media containing 1.25 mg L−1 Cd.
In the case of Pb, the highest Pb removal by G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 occurs in the media containing 2.5 mg L−1 of Pb, which is 25.10%. In addition, the removal efficiency was only 23.47% in the media, which included a Pb concentration of 1.25 mg L−1. However, no removal was observed in the media with a Pb concentration of 5 mg L−1. Moreover, the sorption capacity is highest in the media containing 2.5 mg L−1 Pb, which is 0.53 mg g−1 of dry biomass, and the lowest value is 0.23 mg g−1 of dry mass in the media containing 1.25 mg L−1 Pb.
3.4. Nutrient Removal
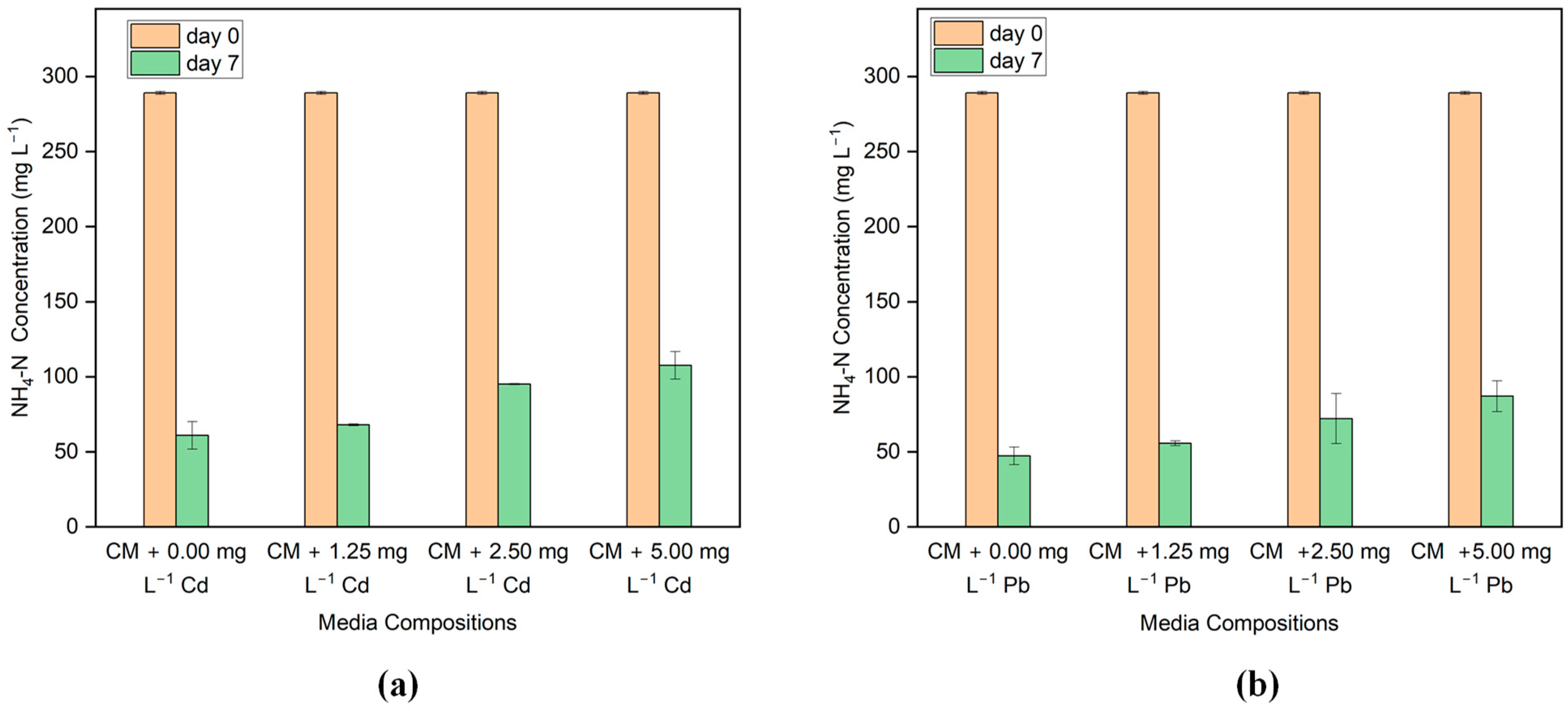
In addition to Cd and Pb concentrations, nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations in the media were monitored to infer the efficacy of G. Sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 for the removal of nutrients in the presence of these toxic HM. The nitrogen content is measured as ammoniacal nitrogen (NH4-N) in the media. Figure 4a,b shows the NH4-N concentration present in Cd and Pb-added media before and after the incubation. On Day 0, the medium contains around 290 mg L−1 NH4-N. On Day 7, media with 0, 1.25, 2.5, and 5 mg L−1 Cd show NH4-N removal of 78.9%, 76.47%, 67.11%, and 62.10%, respectively. Similarly, on Day 7, NH4-N removal is 83.6% in media with no Pb, 80.74% in media with 1.25 mg L−1 Pb, 75.05% in media with 2.5 mg L−1 Pb, and 69.89% in media with 5 mg L−1 Pb. The removal of NH4-N is nearly comparable to the control media when adding lower metal ion concentrations in the media. However, as the metal ion concentration rises, the efficiency of removal decreases.
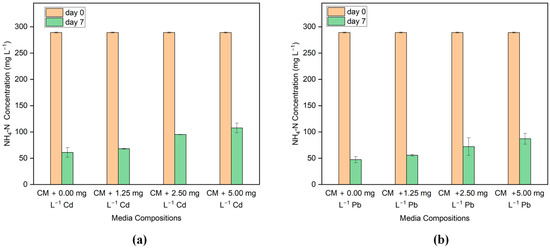
Figure 4.
Ammoniacal nitrogen concentration before and after the treatment in the media with different concentrations of (a) Cd and (b) Pb.
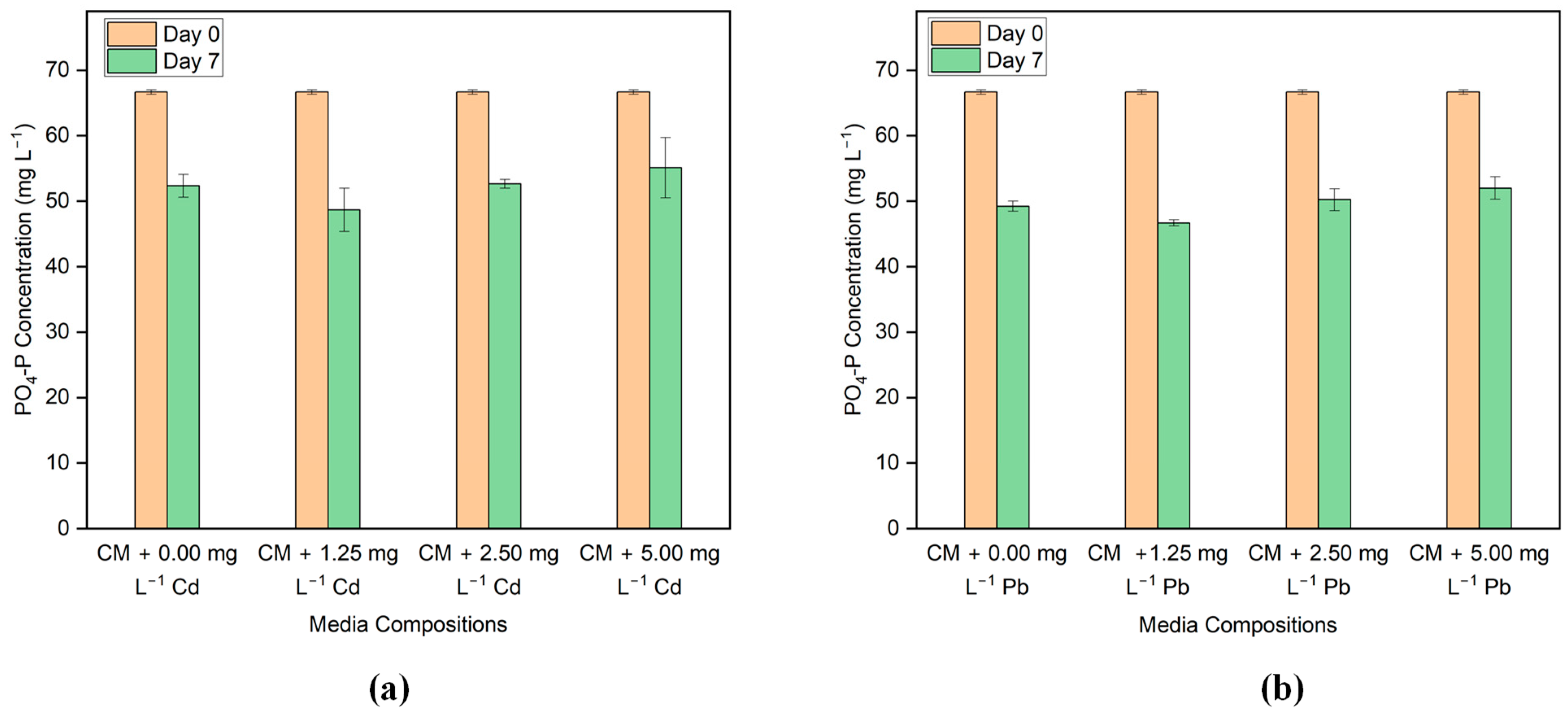
Phosphorus content is measured as phosphate-P (PO4-P) in the media. Figure 5a,b shows comparisons of the PO4-P content in Cd and Pb-added media before and after incubation. The initial concentration of PO4-P in the medium is about 67 mg L−1. Graphs show that on Day 7, PO4-P removal is nearly the same as the control media in the media having Cd and Pb concentrations. From the nutrient removal results, it can be said that there is no significant effect on PO4-P removal in the presence of low concentrations of Cd and Pb.
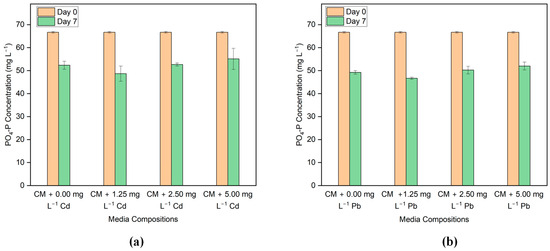
Figure 5.
Phosphorus concentration before and after the treatment in the media with different concentrations of (a) Cd and (b) Pb.
4. Discussions
Phycoremediation represents an innovative strategy for water and wastewater treatment, leveraging the inherent biological capabilities of microalgae to facilitate the removal of contaminants. Current research extensively explores the bioremoval of Cd and Pb from wastewater using diverse green and red algae strains. The primary aim of this study was to evaluate G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1’s removal potential for Cd and Pb within a seven-day incubation period. It was found that G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 can remove Cd and Pb from the contaminated media with varied effectiveness.
The highest Cd removal efficiency and sorption capacity for G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 for the given concentrations were 49.80% and 1.45 mg g−1, respectively. Previous investigations have explored Cd bioremoval with red algal strains. Isachsen et al. [29] investigated Cyanidioschyzon merolae strains MS1 and 10D, finding that strain 10D achieved a 31.55% removal efficiency after a seven-day treatment, while strain MS1 achieved 1.16%. Another study by Ostroumov et al. [30] employed the G. sulphuraria IPPAS P-513 strain, effectively removing Cd, Cu, Pb, and Ni over 30 days of incubation, resulting in a 24% reduction in average Cd content. The literature indicates that most of the research for Cd bioremoval has been conducted with green algae strains. According to the research conducted by Abinandan et al. [6], acid-tolerant microalgae Heterochlorella sp. MAS3 and Desmodesmus sp. MAS1 were used to remove 2 mg L−1 Cd from the solution and achieved the results with approximately 80% and 60% removal efficiency and 0.36 and 0.77 mg g−1 sorption capacity, respectively. Plohn et al. [3] investigated Cd-tolerant microalgal strains in Nordic environments where Chlorella vulgaris and Coelastrella sp. demonstrated substantial removal abilities, eliminating 72% and 82% of Cd, respectively, with maximum sorption capacities of 49 mg g-1 and 65 mg g−1. Under heterotrophic conditions, Chlorella minutissima UTEX2341 exhibited impressive Cd removal efficacy, achieving a 74.34% removal efficiency and a maximum sorption capacity of 35.65 mg g−1 [31]. Additional successes include the use of living seaweed Ulva lactuca [32], achieving 56% Cd removal efficiency, Pseudochlorococcum typicum [33] achieving 86%, Chlorella vulgaris [4] reaching 95.20%, and Oedogonium westti [34] with a range of 55–95% Cd removal efficiencies. Table 1 demonstrates the comparisons between the results of this study and other literature studies on the removal of Cd from wastewater using various algal species at different concentrations of Cd and pH conditions.

Table 1.
Removal efficiency of Cd using live algae from this study vs. the literature review.
In this research, G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 exhibited a maximum Pb removal efficiency of 25.10% and a sorption capacity of 0.53 mg g−1 across the tested concentrations. Studies have primarily focused on green algal strains for Pb bioremoval, with fewer investigations on red algal strains. Cho et al. [17] explored Pb biosorption in three red algal strains: Cyanidium caldarium NIES 551, Cyanidioschyzon merolae NIES 3377, and Galdieria maximum, at a pH of 5.0. Among these, Cyanidium caldarium demonstrated the highest maximum Pb sorption capacity of 298.4 mg g−1, while Galdieria maxima showed the lowest at 38.2 mg g−1. Similarly, Cyanidioschyzon merolae displayed a maximum sorption capacity of 214.0 mg g−1. In the study conducted by Ostroumov et al. [30], after 30 days of incubation, the average Pb concentration was reduced by 84% using G. sulphuraria IPPAS P-513. However, in a separate study by Ostroumov et al. [35], both stripping voltammetry and vitrified mortmass techniques failed to detect Pb in the biomass. Investigation into Pb removal efficiency using the green microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii was conducted by Flouty et al. [36], yielding an 8% removal efficiency. Additionally, living seaweed Ulva lactuca [32] achieved 87% Pb removal efficiency, Pseudochlorococcum typicum [33] achieved 70%, Chlorella vulgaris [37] reached 98.70%, and Oedogonium westti [34] exhibited a range of 61–96% removal efficiencies. In the context of literature studies, most investigations involving green algal strains were conducted around neutral pH conditions, simplifying the underlying chemistry. It is worth noting that our investigation employed initial metal concentrations of up to 5 mg L−1, whereas many Pb removal studies used concentrations of 1 mg L−1 or lower. For a comprehensive overview, refer to Table 2, which presents comparisons between the outcomes of this study and other literature investigations focusing on Pb removal from wastewater, highlighting different algal species, Pb concentrations, and pH conditions.
The maximum allowable levels of Cd and Pb in drinking water are 0.005 and 0.015 mg L−1, respectively, as set by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) [38]. However, the regulation limit of Cd and Pb in wastewater effluent is determined by several variables, including the nature and purpose of the industry, the state of the art in terms of feasible control technology, and the method of discharge (direct or indirect). For instance, Cd and Pb levels in centralized waste treatment effluent cannot exceed 0.163 and 0.283 mg L−1, respectively, as stated by the US EPA in 40 CFR part 437 [39]. Under the conditions of this investigation, the final concentration of Cd and Pb is greater than the EPA’s allowable concentration in drinking water and wastewater effluent. Future studies will focus on optimizing this system and figuring out how to combine this technology with others to obtain the targeted final concentration.

Table 2.
Removal efficiency of Pb using live algae from this study vs. the literature review.
Table 2.
Removal efficiency of Pb using live algae from this study vs. the literature review.
| Algal Strain | Initial Pb Concentration (mg L−1) | pH | Sorption Capacity (mg g−1) | Removal Efficiency (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green Algae | |||||
| Chlamydomonas reinhardtii | 0.10 | 6.0 | 0.042 | 8.00 | [36] |
| Chlorella vulgaris | 1.95–4.83 | 6.2 | - | 71.81–98.70 | [37] |
| Oedogonium westii | 0.10–0.80 | 5.0 | 0.261 | 61.00–96.00 | [34] |
| Ulva lactuca | 1.00 | 7.8 | 0.145 | 87.00 | [32] |
| Dunaliella salina AL-1 | 5.00–10.00 | - | - | 95.00 | [40] |
| Scenedesmus sp. | 0.05–10.00 | - | 13.60 | 70.00 | [41] |
| Pseudochlorococcum typicum | 10.00 | 7.0 | 5.11 | 70.06 | [33] |
| Red Algae | |||||
| Galdieria sulphuraria | 0.10 | 2.4 | - | 0.00 | [35] |
| Galdieria sulphuraria IPPAS P-513 | 5.00 | 2.7 | - | 84.00 | [30] |
| Galdieria maxima | 0.00–500.00 | 5.0 | 38.20 | - | [17] |
| Cyanidioschyzon merolae NIES 3377 | 0.00–500.00 | 5.0 | 214.00 | - | [17] |
| Cyanidium caldariumNIES 551 | 0.00–500.00 | 5.0 | 298.80 | - | [17] |
| Galdieria sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 | 5.00 | 2.5 | 0.00 | 0.00 | Existing Study |
| 2.50 | 0.5 | 25.10 | |||
| 1.25 | 0.225 | 23.47 | |||
Our study’s findings highlight the efficacy of G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 in removing Cd and Pb, particularly at lower metal concentrations. However, as the metal concentration increases, the removal efficiency diminishes, aligning with conclusions from other published studies. Pham et al. [41] employed the green algal strain Scenedesmus sp. to address various Pb concentrations spanning 0.05–10 mg g−1. Their results revealed the highest removal efficiency at an initial Pb concentration of 2 mg L−1, while the lowest was observed at 10 mg L−1, indicating a decline in efficiency as Pb concentration rises. Similarly, Regaldo et al. [37] employed Chlorella vulgaris cells to tackle different Pb concentrations within the range of 1.95–4.83 mg g−1. Their outcomes demonstrated that removal efficiency decreases with higher Pb concentrations but increases with extended exposure time. The observed removal efficiencies ranged from 71.81% to 98.70%. Furthermore, the green macroalgae Oedogonium westti exhibited Cd removal efficiencies ranging from 55% to 95% and Pb removal efficiencies ranging from 61% to 96% within a different initial metal concentration [34]. Notably, the highest removal efficiency was achieved at lower initial metal concentrations. This trend can be attributed to the phenomenon where, at lower concentrations, all metal ions in the solution interact with binding sites, optimizing adsorption. Conversely, higher concentrations can saturate these binding sites, resulting in unabsorbed ions [42].
Another noteworthy finding from our study is the initial inhibition and subsequent reduction in the growth of G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 during the experiment’s early stages. These findings resonate with the research of Bajguz et al. [43], who worked with Chlorella vulgaris and observed a decrease in growth and chemical composition (chlorophyll, monosaccharides, and protein content) during the initial 48 h of cultivation under HM ion stress. Furthermore, the current study found a direct correlation between growth inhibition and the amount of metal concentration at which microalgae were exposed, and similar conclusions were drawn by Monteiro et al. [44] and Yang et al. [31]. Interestingly, our study also underscores that Pb ions have more pronounced inhibitory effects on growth compared to Cd ions. This observation aligns with the results presented by Alharbi et al. [45], wherein Pb ion demonstrated greater inhibiting effects among Pb, Cd, and Zn ion on Chroococcus minutus and Chlorococcum aegyptiacum. The findings collectively suggest that initial growth inhibition is a common response to HM exposure in various microalgae species, and the extent of inhibition correlates with the concentration of the metal. Furthermore, the differential inhibitory effects of various HMs, such as Pb and Cd, on microalgal growth are consistent with prior research.
Although this study did not investigate the actual mechanisms involved in the removal of Cd and Pb by using G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1, an attempt has been made to discuss the possible defense mechanisms involved in microalgae in order to mitigate the toxic effects of HM on microalgal cells. The biosorption process of HMs by microalgal cells involves two distinct stages. Initially, metal ions are adsorbed onto the cell surface. This step may or may not involve metabolic activities. In the subsequent phase, metal ions traverse through the internal pathways of living cells and accumulate within the cytoplasm. This process occurs at a relatively gradual pace and necessitates metabolic processes, as described by Flouty et al. [36] and Priyadarshini et al. [2]. Active uptake of metal ions is a common occurrence in living cells, often driven by the need for microbial growth or intracellular accumulation. However, the reactivity of many HMs makes them hazardous to living cells. The toxicity of HMs primarily stems from their oxidative effects on the components within cells. Within the algal cell, antioxidants, such as glutathione, play a crucial role in safeguarding against oxidative stress induced by metals and other contaminants, as noted by Pinto et al. [46]. When intracellular HM levels rise, they can hinder the effectiveness of antioxidant defenses. This interference can lead to damage in the chloroplast, subsequently slowing down photosynthesis and overall biomass production. Moreover, the presence of HMs can also disrupt essential cellular functions. For instance, the competition between HMs and crucial ions, such as calcium and sodium, at binding sites has been shown to inhibit growth, a phenomenon highlighted by Yang et al. [31]. Additionally, the functional groups of biologically essential molecules, such as enzymes and transport mechanisms for vital nutrients, can be obstructed by HMs, resulting in toxicity within the organism, an observation also made by Napan et al. [47].
The toxicity of HMs is counteracted by a diverse array of extracellular and intracellular removal mechanisms present in various organisms. In the case of living microalgae, a range of defense strategies is employed to counteract HM toxicity. These mechanisms include the biosorption of HMs on the cell wall and extracellular polymeric substances, bioaccumulation of HMs within intracellular compartments, and the transformation of HMs by algal cells, as highlighted in research by Danouche et al. [14]. A prevalent detoxification strategy involves sequestering HMs within internal organelles such as vacuoles, chloroplasts, and mitochondria. Shanab et al. [33] conducted research using Pseudochlorococcum typicum and observed an electron-dense layer on the surfaces of cells treated with both Cd and Pb. Additionally, Pb-treated cells exhibited spherical electron-dense bodies within the cell. These observations might be attributed to metal ions bonding with various functional groups on the cell surface, while the presence of spherical electron-dense bodies in Pb treated cells suggests the bioaccumulation of metal ions within the cell. Elleuch et al. [40] investigated metal removal mechanisms using marine microalgae Dunaliella salina and found that both intracellular and extracellular removal mechanisms contribute to the removal process. Yang et al. [31] conducted research on Chlorella minutissima UTEX2341 and found that Cd removal primarily occurs through intracellular accumulation supplemented by extracellular immobilization. The carboxylic moieties present in the cell walls were identified as responsible for Cd removal in Chlorella vulgaris and Coelastrella sp., as observed in the study by Plohn et al. [3]. Notably, Euglena gracilis responds to Cd exposure by forming Cd complexes within the chloroplast as a removal mechanism, as indicated by research conducted by Mendoza et al. [48]. These diverse mechanisms collectively underscore the adaptability of microalgae in countering HM toxicity.
5. Conclusions
This research examines the various studies of G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1, including daily biomass density, growth rate, nutrient removal, and metal ion removal, to determine its biosorption efficiency for the removal of Cd and Pb from wastewater. The study’s findings unveil that both Cd and Pb ions manifest inhibitory effects on the initial growth of G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1, contingent on the prevailing concentrations. Nevertheless, by the conclusion of the culture period, effective elimination of Cd and Pb from the aqueous solution is attained, accompanied by notable nutrient removal. While this study contributes valuable insights, there remain unexplored avenues that warrant further investigation. Among these are the intricate mechanisms underpinning the removal of Cd and Pb, the feasibility of scaling up these processes for large-scale applications, and the system’s performance when confronted with real wastewater effluents. Notably, G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1’s ability to thrive within an environment containing toxic HMs, such as Cd and Pb, coupled with its capacity to extract substantial quantities of metal ions from the system, presents an exciting prospect. This discovery might pave the way for the incorporation of G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1 into phycoremediation strategies. As the research continues to evolve, it holds the potential to not only enhance our comprehension of microalgal interactions with HMs but also to offer practical solutions for wastewater treatment through the utilization of G. sulphuraria CCMEE 5587.1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.S. and H.L.K.; methodology, T.S., H.L.K. and I.S.; software, T.S. and H.L.K.; validation, T.S.; formal analysis, T.S. and H.L.K.; investigation, T.S., H.L.K., M.T. and I.S.; resources, T.S.; data curation, T.S. and H.L.K.; writing—original draft preparation, T..S., H.L.K. and I.S; writing—review and editing, T.S., H.L.K., M.T. and I.S.; visualization, T.S. and H.L.K.; supervision, T.S.; project administration, T.S.; funding acquisition, T.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported with funds from the State of Texas as part of a program of the Texas Hazardous Waste Research Center (THWRC). The contents do not necessarily reflect the views and policies of the sponsor, nor does the mention of trade names or commercial products constitute endorsement or recommendation for use.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding authors. The data are not publicly available due to the continuation of a follow-up study by the authors.
Acknowledgments
The support provided by the Center for Advances in Water and Air Quality (CAWAQ) at Lamar University and The Office of Undergraduate Research at Lamar University in the undergraduate author’s SURF fellowship are acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Abdi, O.; Kazemi, M. A review study of biosorption of heavy metals and comparison between different biosorbents. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2015, 6, 1386–1399. [Google Scholar]
- Priyadarshini, E.; Priyadarshini, S.S.; Pradhan, N. Heavy metal resistance in algae and its application for metal nanoparticle synthesis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 3297–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plöhn, M.; Escudero-Oñate, C.; Funk, C. Biosorption of Cd(II) by Nordic microalgae: Tolerance, kinetics and equilibrium studies. Algal Res. 2021, 59, 102471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Yin, W.; Chang, Z.; Lundholm, N.; Jiang, Z. Biosorption capacity and kinetics of cadmium(II) on live and dead Chlorella vulgaris. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 29, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purushanahalli Shivagangaiah, C.; Sanyal, D.; Dasgupta, S.; Banik, A. Phycoremediation and photosynthetic toxicity assessment of lead by two freshwater microalgae Scenedesmus acutus and Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 173, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abinandan, S.; Subashchandrabose, S.R.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Perera, I.A.; Megharaj, M. Acid-tolerant microalgae can withstand higher concentrations of invasive cadmium and produce sustainable biomass and biodiesel at pH 3.5. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 281, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Qu, Z.; Wang, J.; Cao, L.; Han, Q. Microalgal bioremediation of heavy metal pollution in water: Recent advances, challenges, and prospects. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, Y.K.; Chang, J.-S. Bioremediation of heavy metals using microalgae: Recent advances and mechanisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 303, 122886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, C. Biosorbents for heavy metals removal and their future. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 195–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, S.; Gaur, J. Use of algae for removing heavy metal ions from wastewater: Progress and prospects. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2005, 25, 113–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, R.; Agrawal, K.; Shah, M.; Verma, P. Bioremediation of heavy metals from wastewater: A current perspective on microalgae-based future. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 75, 701–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, R.; Ban, S.; Devkota, S.; Sharma, S.; Joshi, R.; Tiwari, A.P.; Kim, H.Y.; Joshi, M.K. Technological trends in heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afkar, E.; Ababna, H.; Fathi, A. Toxicological response of the green alga Chlorella vulgaris, to some heavy metals. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 6, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danouche, M.; El Ghachtouli, N.; El Arroussi, H. Phycoremediation mechanisms of heavy metals using living green microalgae: Physicochemical and molecular approaches for enhancing selectivity and removal capacity. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.L. Cellular mechanisms for heavy metal detoxification and tolerance. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaratnam, T.; Pan, S.; Rahman, A.; Tan, M.; Kharel, H.L.; Agrawal, S.; Nawaz, T. Bioremediation of Raw Landfill Leachate Using Galdieria sulphuraria: An Algal-Based System for Landfill Leachate Treatment. Water 2022, 14, 2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.-L.; Lee, Y.-C.; Hsu, L.-C.; Wang, C.-C.; Chen, P.-C.; Liu, S.-L.; Teah, H.-Y.; Liu, Y.-T.; Tzou, Y.-M. Molecular mechanisms for Pb removal by Cyanidiales: A potential biomaterial applied in thermo-acidic conditions. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 401, 125828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharel, H.L.; Shrestha, I.; Tan, M.; Nikookar, M.; Saraei, N.; Selvaratnam, T. Cyanidiales-Based Bioremediation of Heavy Metals. BioTech 2023, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oesterhelt, C.; Schmälzlin, E.; Schmitt, J.M.; Lokstein, H. Regulation of photosynthesis in the unicellular acidophilic red alga Galdieria sulphuraria. Plant J. 2007, 51, 500–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaratnam, T.; Pegallapati, A.; Montelya, F.; Rodriguez, G.; Nirmalakhandan, N.; Van Voorhies, W.; Lammers, P. Evaluation of a thermo-tolerant acidophilic alga, Galdieria sulphuraria, for nutrient removal from urban wastewaters. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 156, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaratnam, T.; Pegallapati, A.; Reddy, H.; Kanapathipillai, N.; Nirmalakhandan, N.; Deng, S.; Lammers, P. Algal biofuels from urban wastewaters: Maximizing biomass yield using nutrients recycled from hydrothermal processing of biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 182, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, S.; Dixon, K.L.; Nawaz, T.; Rahman, A.; Selvaratnam, T. Evaluation of Galdieria sulphuraria for nitrogen removal and biomass production from raw landfill leachate. Algal Res. 2021, 54, 102183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Pan, S.; Houston, C.; Selvaratnam, T. Evaluation of Galdieria sulphuraria and Chlorella vulgaris for the Bioremediation of Produced Water. Water 2021, 13, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherasim, C.-V.; Křivčík, J.; Mikulášek, P. Investigation of batch electrodialysis process for removal of lead ions from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 256, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Kushwaha, A.; Goswami, L.; Singh, A.K.; Sikandar, M. A review on advances and mechanism for the phycoremediation of cadmium contaminated wastewater. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2021, 5, 100288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Jang, M.; Cho, S.-H.; Khim, J.; Cannon, F.S. A continuous pilot-scale system using coal-mine drainage sludge to treat acid mine drainage contaminated with high concentrations of Pb, Zn, and other heavy metals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 215, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, H.; Killoran, E.; Sheehan, M.; Berner, F.; Heimann, K. Assessment of microalga biofilms for simultaneous remediation and biofuel generation in mine tailings water. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 234, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toplin, J.A.; Norris, T.B.; Lehr, C.R.; McDermott, T.R.; Castenholz, R.W. Biogeographic and phylogenetic diversity of thermoacidophilic cyanidiales in Yellowstone National Park, Japan, and New Zealand. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2822–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isachsen, I. Cadmium Tolerance in the Thermo-Acidophilic Red Alga C. merolae, Possible Mechanisms and Implications for Bioremediation; Arizona State University: Tempe, AZ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ostroumov, S.; Tropin, I.; Kiryushin, A. Removal of cadmium and other toxic metals from water: Thermophiles and new biotechnologies. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2018, 88, 2962–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Cao, J.; Xing, G.; Yuan, H. Lipid production combined with biosorption and bioaccumulation of cadmium, copper, manganese and zinc by oleaginous microalgae Chlorella minutissima UTEX2341. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 175, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, B.; Teixeira, A.; Figueira, P.; Reis, A.T.; Almeida, J.; Vale, C.; Pereira, E. Simultaneous removal of trace elements from contaminated waters by living Ulva lactuca. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanab, S.; Essa, A.; Shalaby, E. Bioremoval capacity of three heavy metals by some microalgae species (Egyptian Isolates). Plant Signal. Behav. 2012, 7, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamshad, I.; Khan, S.; Waqas, M.; Asma, M.; Nawab, J.; Gul, N.; Raiz, A.; Li, G. Heavy metal uptake capacity of fresh water algae (Oedogonium westti) from aqueous solution: A mesocosm research. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2016, 18, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostroumov, S.; Shestakova, T.; Tropin, I. Biosorption of copper by biomass of extremophilic algae. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2015, 85, 2961–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flouty, R.; Estephane, G. Bioaccumulation and biosorption of copper and lead by a unicellular algae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii in single and binary metal systems: A comparative study. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 111, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regaldo, L.M.; Gervasio, S.G.; Troiani, H.E.; Gagneten, A.M. Bioaccumulation and Toxicity of Copper and Lead in Chlorella vulgaris. J. Algal Biomass Utln. 2013, 4, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Kinuthia, G.K.; Ngure, V.; Beti, D.; Lugalia, R.; Wangila, A.; Kamau, L. Levels of heavy metals in wastewater and soil samples from open drainage channels in Nairobi, Kenya: Community health implication. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA, Effluent Guidelines Database. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/eg/effluent-guidelines-database (accessed on 20 September 2023).
- Elleuch, J.; Hmani, R.; Drira, M.; Michaud, P.; Fendri, I.; Abdelkafi, S. Potential of three local marine microalgae from Tunisian coasts for cadmium, lead and chromium removals. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.-L.; Dao, T.-S.; Bui, H.N.; Pham, T.K.N.; Ngo, T.T.H.; Bui, H.M. Lipid production combined with removal and bioaccumulation of Pb by Scenedesmus sp. Green Alga. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 1785–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.N.; Oommen, C. Removal of heavy metals by biosorption using freshwater alga Spirogyra hyalina. J. Environ. Biol. 2012, 33, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Bajguz, A. Suppression of Chlorella vulgaris growth by cadmium, lead, and copper stress and its restoration by endogenous brassinolide. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 60, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, C.M.; Fonseca, S.C.; Castro, P.M.; Malcata, F.X. Toxicity of cadmium and zinc on two microalgae, Scenedesmus obliquus and Desmodesmus pleiomorphus, from Northern Portugal. J. Appl. Phycol. 2011, 23, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, R.M. Toxicity and bioaccumulation of lead, cadmium and zinc in Chroococcus minutus and Chlorococcum aegyptiacum. Int. J. Pharm. Res. Allied Sci. 2017, 6, 290–300. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, E.; Sigaud-kutner, T.C.; Leitao, M.A.; Okamoto, O.K.; Morse, D.; Colepicolo, P. Heavy metal–induced oxidative stress in algae 1. J. Phycol. 2003, 39, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napan, K.; Teng, L.; Quinn, J.C.; Wood, B.D. Impact of heavy metals from flue gas integration with microalgae production. Algal Res. 2015, 8, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Cózatl, D.G.; Moreno-Sánchez, R. Cd2+ transport and storage in the chloroplast of Euglena gracilis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Bioenerg. 2005, 1706, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).