Surface-Modified Activated Carbon Fibers by a Facile Microwave Technique for Enhancing Hydrocarbon Adsorption
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Characterization
2.2.1. Surface Functional Group Analyses
2.2.2. Textural Properties
2.3. Evaluation of the Butane Working Capacity (BWC) of Activated Carbon Fibers
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. SEM-EDS
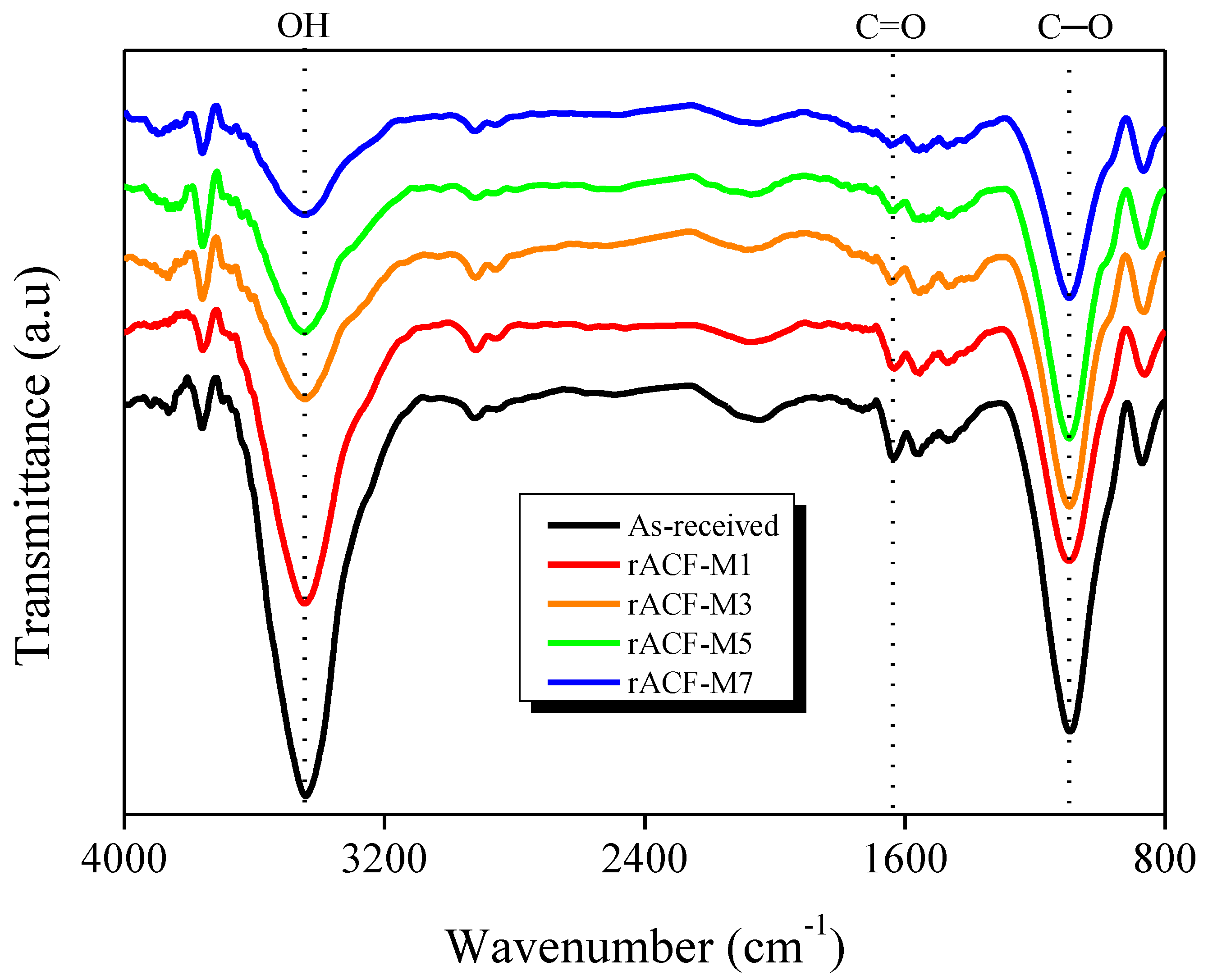
3.2. FT-IR
3.3. TGA-IR
3.4. XPS
3.5. N2/77K Adsorption–Desorption Isotherms
3.6. BWC
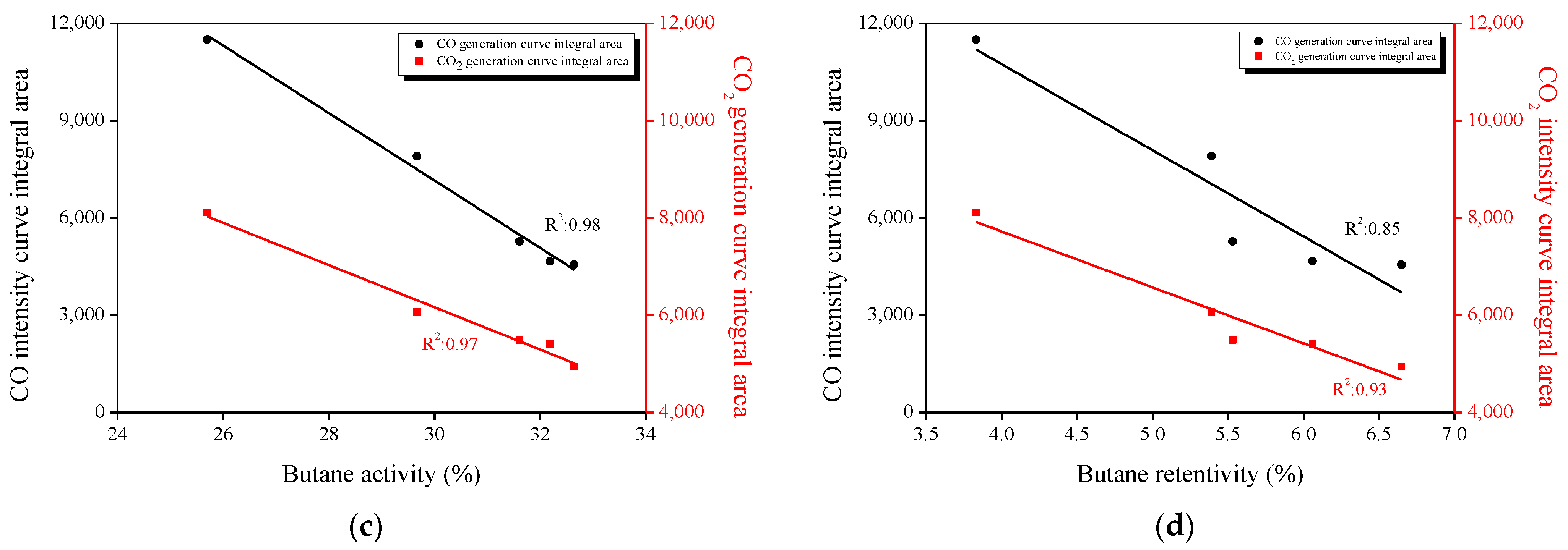
3.7. Correlation between the Textural Properties, Oxygen Functional Groups, and Butane Adsorption Behaviors
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miguet, M.; Goetz, V.; Plantard, G.; Jaeger, Y. Removal of a Chlorinated Volatile Organic Compound (Perchloroethylene) from the Aqueous Phase by Adsorption on Activated Carbon. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 9813–9823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jin, Y.; Chen, T.; Tang, F.; Cai, J.; Ma, J. Trimethylchlorosilane modified activated carbon for the adsorption of VOCs at high humidity. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 272, 118659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, R.; Mamaghani, A.H.; Boluk, Y.; Hashisho, Z. Synthesis and characterization of electrospun PAN-based activated carbon nanofibers reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals for adsorption of VOCs. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 410, 128412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Brook, R.; Crippa, M.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Schieberle, C.; Dore, C.; Guizzardi, D.; Muntean, M.; Schaaf, E.; Friedrich, R. Speciation of anthropogenic emissions of non-methane volatile organic compounds: A global gridded data set for 1970–2012. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 17, 7683–7701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hutchison, D.H.; Holden, F.R. An Inventory of Automobile Gases. J. Air Pollut. Control Assoc. 1955, 5, 71–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faith, W.L.; Goodwin, J.T., Jr.; Morriss, F.V.; Bolze, C. Automobile exhaust and smog formation. J. Air Pollut. Control Assoc. 1957, 7, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotin, P.; Falk, H.L. Atmospheric Factors in Pathogenesis of Lung Cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 1963, 7, 475–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnuolo, L.; Yang, R.; Frosina, E.; Rizzoni, G.; Andreozzi, A.; Senatore, A. Physical modeling of evaporative emission control system in gasoline fueled automobiles: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 116, 109462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H. Contribution of evaporative emissions from gasoline vehicles toward total VOC emissions in Japan. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 449, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, B.; Nelson, P.; Ye, Y.; Weeks, I. Speciated hydrocarbon profiles and calculated reactivities of exhaust and evaporative emissions from 82 in-use light-duty Australian vehicles. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S. Understanding and Designing Automotive Evaporative Emission Control Systems. SAE Tech. Pap. 2012, 1, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.Y.; Ngu, L.H.; Hashim, S.S.; Chew, J.J.; Sunarso, J. Review of oil palm-derived activated carbon for CO2 capture. Carbon Lett. 2021, 31, 201–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-M.; Lee, B.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; An, K.-H.; Park, S.-J.; Kim, B.-J. Determination of the optimum porosity for 2-CEES adsorption by activated carbon fiber from various precursors. Carbon Lett. 2019, 29, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alver, E.; Metin, A. Anionic dye removal from aqueous solutions using modified zeolite: Adsorption kinetics and isotherm studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 200–202, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.; Chua, H.; Chung, C.; Loke, C.; Kashiwagi, T.; Akisawa, A.; Saha, B. Experimental investigation of the silica gel–water adsorption isotherm characteristics. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2001, 21, 1631–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-F.; Wu, J.-K. Adsorption of Arsenite and Arsenate within Activated Alumina Grains: Equilibrium and Kinetics. Water Res. 2001, 35, 2049–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-M.; Lee, B.-H.; Park, S.-J.; An, K.-H.; Kim, B.-J. Pitch-Derived Activated Carbon Fibers for Emission Control of Low-Concentration Hydrocarbon. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.-H.; Lee, H.-M.; Jung, S.-C.; Chung, D.-C.; Kim, B.-J. Bamboo-Based Mesoporous Activated Carbon for High-Power-Density Electric Double-Layer Capacitors. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-M.; Kang, H.-R.; An, K.-H.; Kim, H.-G.; Kim, B.-J. Comparative studies of porous carbon nanofibers by various activation methods. Carbon Lett. 2013, 14, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.-M.; An, K.-H.; Kim, B.-J. Effects of carbonization temperature on pore development in polyacrylonitrile-based activated carbon nanofibers. Carbon Lett. 2014, 15, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiang, H.-L.; Chiang, P.; Huang, C. Ozonation of activated carbon and its effects on the adsorption of VOCs exemplified by methylethylketone and benzene. Chemosphere 2002, 47, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Song, M.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Y. The contribution of oxygen-containing functional groups to the gas-phase adsorption of volatile organic compounds with different polarities onto lignin-derived activated carbon fibers. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 7195–7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, B.-J.; Lee, H.-M. Effects of Oxygen-Containing Functional Groups on the Electrochemical Performance of Activated Carbon for EDLCs. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarifyanz, Y.; Kiselev, V.; Lezhnev, N.; Nikitina, O. Interaction of graphite fresh surface with different gases and vapours. Carbon 1967, 5, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez, J.A.; Radovic, L.R.; Xia, B.; Phillips, J. Low-Temperature Generation of Basic Carbon Surfaces by Hydrogen Spillover. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 17243–17248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.A.; Al-Raggad, M.; Shareef, N. Production of activated carbon derived from agricultural by-products via microwave-induced chemical activation: A review. Carbon Lett. 2021, 31, 957–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, Y.; Menéndez, J. Influence of feed characteristics on the microwave-assisted pyrolysis used to produce syngas from biomass wastes. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2011, 91, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Lei, H.; Wang, L.; Bu, Q.; Chen, S.; Wu, J.; Julson, J.; Ruan, R. Biofuel production and kinetics analysis for microwave pyrolysis of Douglas fir sawdust pellet. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2012, 94, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of Gases in Multimolecular Layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippens, B. Studies on pore systems in catalysts V. The t method. J. Catal. 1965, 4, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society for Testing and Materials. ASTM Standard D5228-16; Standard Test Method for Determination of Butane Working Capacity of Activated Carbon. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1992. Available online: https://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=ko&as_sdt=0%2C5&scioq=ASTM+D5228&q=D5228-16&btnG= (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Azhagapillai, P.; Al Shoaibi, A.; Chandrasekar, S. Surface functionalization methodologies on activated carbons and their benzene adsorption. Carbon Lett. 2020, 31, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.-J.; Jo, H.-K.; Jang, M.-H.; Han, G.-J.; Yoon, S.-J.; Oh, K.; Park, J.-I. Acid treatment enhances performance of beads activated carbon for formaldehyde removal. Carbon Lett. 2022, 33, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, B.K.; Sandle, N. Effect of different oxidizing agent treatments on the surface properties of activated carbons. Carbon 1999, 37, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.-W.; Park, S.-J.; Ryu, S.-K. Effect of modification with HNO3 and NaOH on metal adsorption by pitch-based activated carbon fibers. Carbon 2001, 39, 1635–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, P.S.D.V.; Hernández-Montoya, V.; Concheso, A.; Montes-Morán, M.A. Formation of cerussite and hydrocerussite during adsorption of lead from aqueous solution on oxidized carbons by cold oxygen plasma. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 386, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, J.L.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Freitas, M.M.A.; Órfão, J.J.M. Modification of the surface chemistry of activated carbons. Carbon 1999, 37, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otake, Y.; Jenkins, R.G. Characterization of oxygen-containing surface complexes created on a microporous carbon by air and nitric acid treatment. Carbon 1993, 31, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Puente, G.; Pis, J.; Menéndez, J.; Grange, P. Thermal stability of oxygenated functions in activated carbons. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 1997, 43, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puziy, A.; Poddubnaya, O.; Ziatdinov, A. On the chemical structure of phosphorus compounds in phosphoric acid-activated carbon. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005, 252, 8036–8038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.; Scudiero, L.; Espinal, J.; McEwen, J.-S.; Garcia-Perez, M. Improving the deconvolution and interpretation of XPS spectra from chars by ab initio calculations. Carbon 2016, 110, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sing, K.S.W. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (Recommendations 1984). Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-W.; Chu, H.-J. Toluene Desorption of Modified Activated Carbon for Microwave Irradiation. J. Environ. Sci. Int. 2011, 20, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Mi, M.; Li, B.; Dong, Y. Modification of Activated Carbon by Means of Microwave Heating and its Effects on the Pore Texture and Surface Chemistry. Res. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2013, 5, 1836–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cui, L.; Wang, Z.; Dong, Y. Modification of Activated Carbon Using Microwave Radiation and Its Effects on the Adsorption of SO2. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2016, 49, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

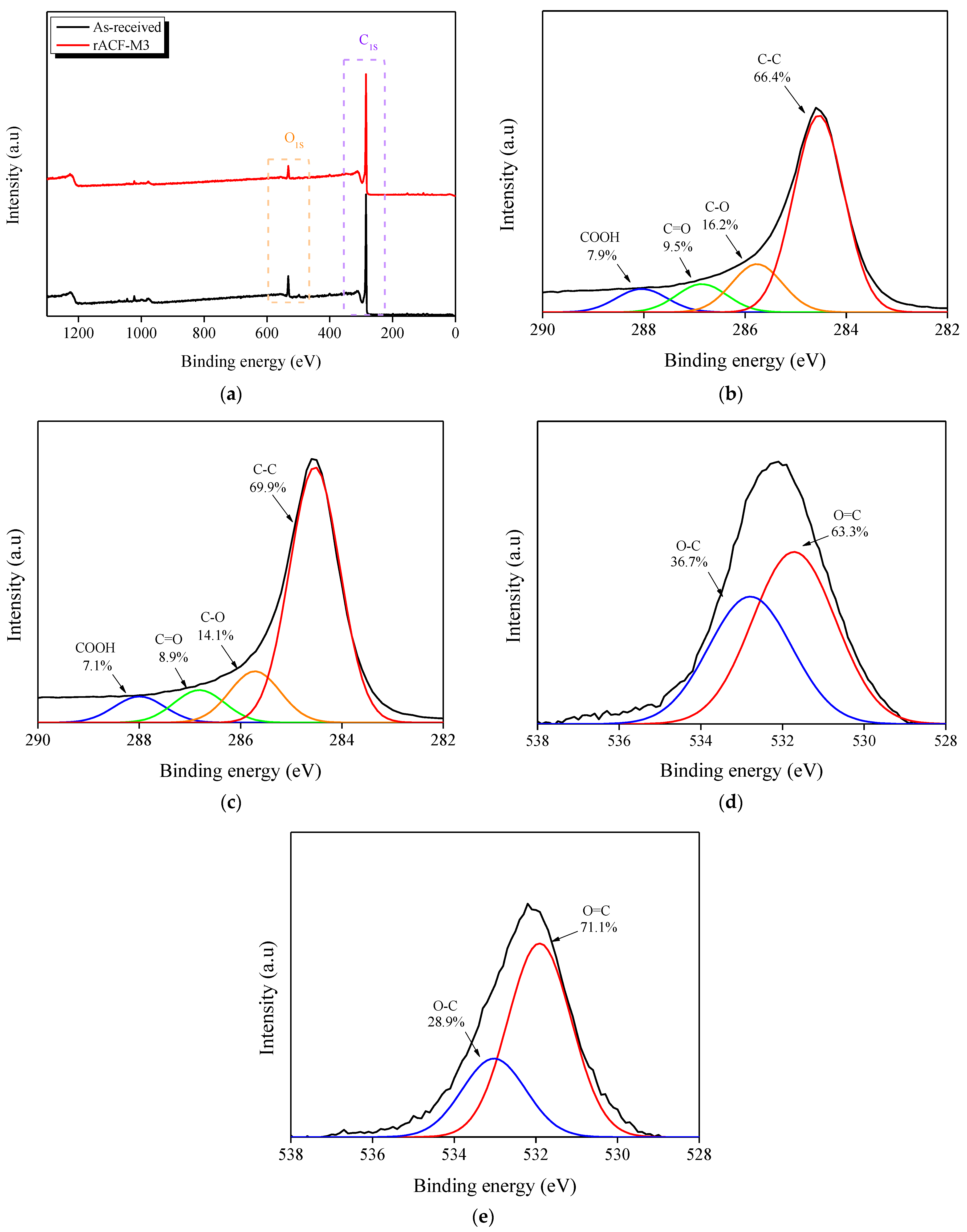



| Sample | C (at.%) | O (at.%) | O/C |
|---|---|---|---|
| As-received | 88.0 | 10.5 | 0.119 |
| rACF-M3 | 91.9 | 6.7 | 0.073 |
| rACF-M7 | 92.1 | 5.3 | 0.058 |
| Sample | SBET | VTotal | VMicro | VMeso | Micropore Ratio | Yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m2/g) | (cm3/g) | (cm3/g) | (cm3/g) | (%) | (%) | |
| As-received | 1090 | 0.48 | 0.46 | 0.02 | 95.8 | 100.0 |
| rACF-M1 | 1120 | 0.50 | 0.47 | 0.03 | 94.0 | 96.4 |
| rACF-M3 | 1110 | 0.49 | 0.46 | 0.03 | 93.9 | 94.7 |
| rACF-M5 | 1190 | 0.54 | 0.50 | 0.04 | 92.6 | 92.2 |
| rACF-M7 | 1170 | 0.52 | 0.48 | 0.04 | 92.3 | 91.4 |
| Sample | BWC 1 | BA 2 | BR 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (%) | (%) | |
| As-received | 21.84 | 25.67 | 3.83 |
| rACF-M1 | 24.17 | 29.55 | 5.39 |
| rACF-M3 | 26.09 | 31.62 | 5.53 |
| rACF-M5 | 26.17 | 32.23 | 6.06 |
| rACF-M7 | 25.98 | 32.63 | 6.65 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, B.-J. Surface-Modified Activated Carbon Fibers by a Facile Microwave Technique for Enhancing Hydrocarbon Adsorption. Environments 2023, 10, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10030052
Lee J-Y, Kim B-J. Surface-Modified Activated Carbon Fibers by a Facile Microwave Technique for Enhancing Hydrocarbon Adsorption. Environments. 2023; 10(3):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10030052
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jin-Young, and Byung-Joo Kim. 2023. "Surface-Modified Activated Carbon Fibers by a Facile Microwave Technique for Enhancing Hydrocarbon Adsorption" Environments 10, no. 3: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10030052
APA StyleLee, J.-Y., & Kim, B.-J. (2023). Surface-Modified Activated Carbon Fibers by a Facile Microwave Technique for Enhancing Hydrocarbon Adsorption. Environments, 10(3), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10030052








