Associations Between Landfill Proximity and Water Quality Analytes from Private Domestic Wells in Rural Virginia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
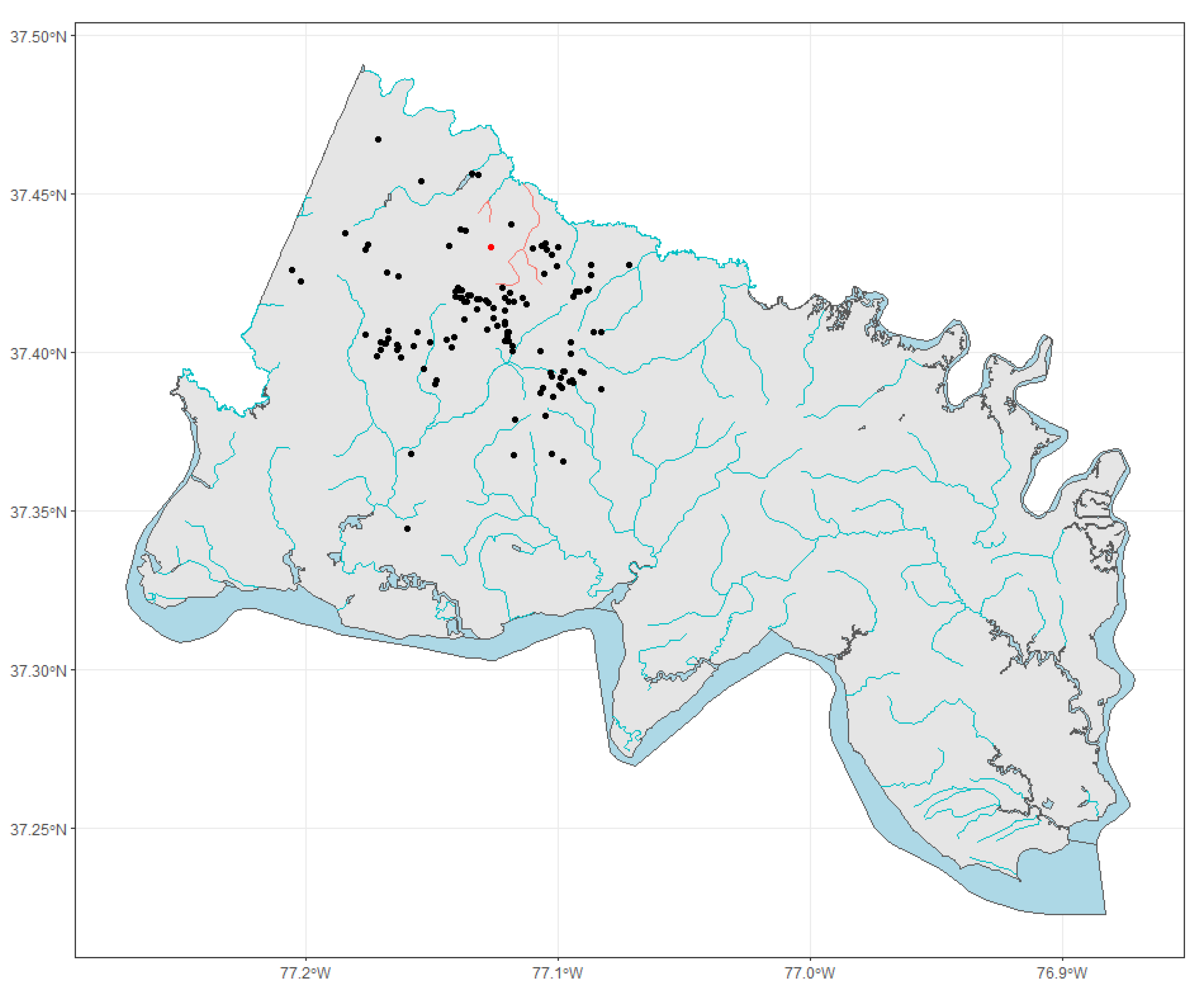
2.1. Study Sample and Design
2.2. Description of the Landfill, Proximate Streams, and Underlying Geology
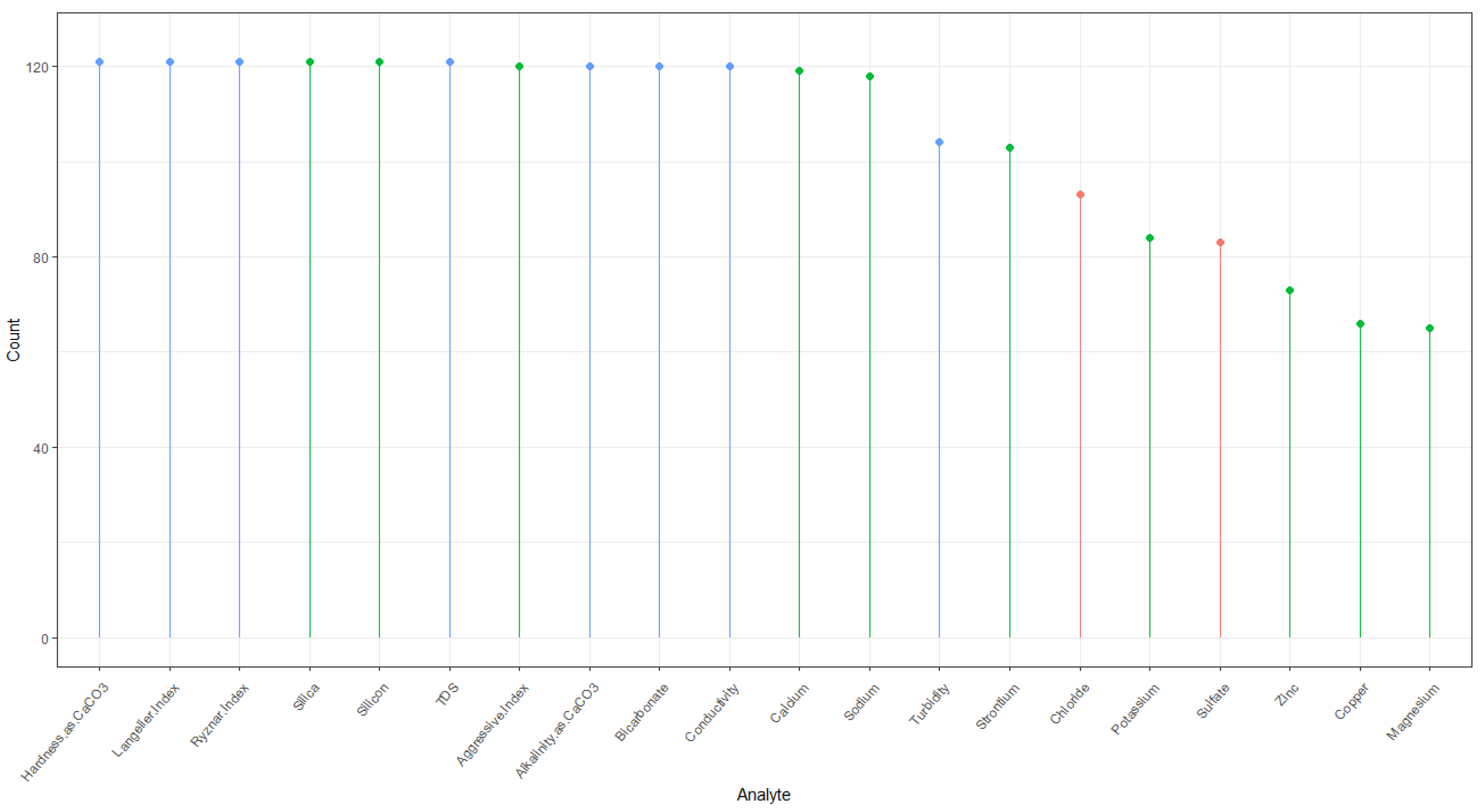
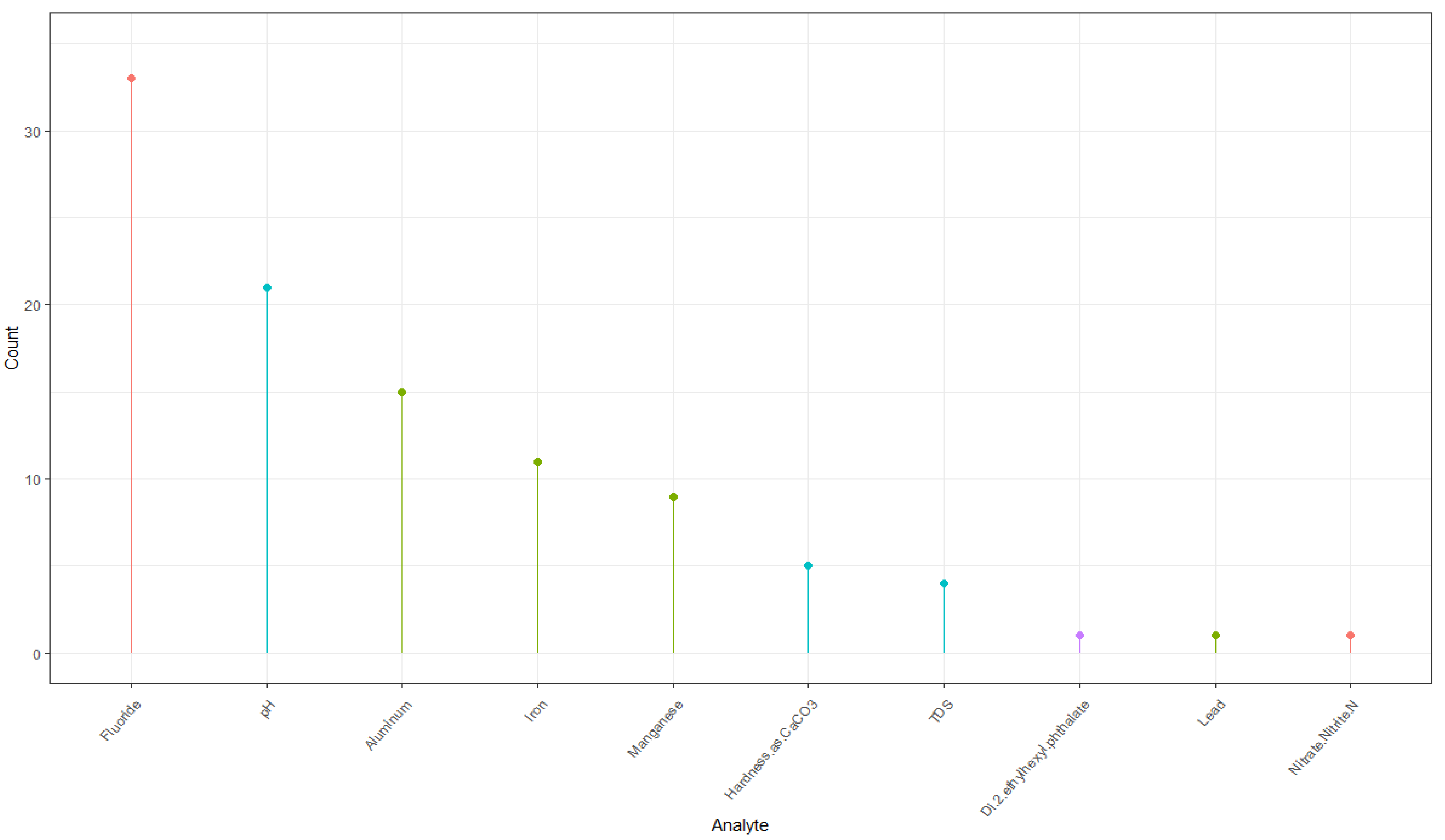
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Laboratory Rating
2.5. Exposure Assignment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kulthanan, K.; Nuchkull, P.; Varothai, S. The pH of water from various sources: An overview for recommendation for patients with atopic dermatitis. Asia Pac. Allergy 2013, 3, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinka, M.O. Safe drinking water: Concepts, benefits, principles and standards. Water Chall. Urban. World 2018, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, S.; Rehman, F. Hardness in drinking-water, its sources, its effects on humans and its household treatment. J. Chem. Appl. 2018, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Barloková, D.; Ilavskỳ, J.; Kapusta, O.; Šimko, V. Importance of calcium and magnesium in water-water hardening. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2017; Volume 92, p. 012002. [Google Scholar]
- Brandt, M.; Johnson, K.; Elphinston, A.; Ratnayaka, D. Chapter 7—Chemistry, Microbiology, and Biology of Water. In Twort’s Water Supply, 7th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 235–321. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, A.; Sharma, V. Water Quality Monitoring and Management: Importance, Applications, and Analysis. In Applied Water Science Volume 1: Fundamentals and Applications; Published online; Scrivener Publishing LLC: Beverly, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 421–440. [Google Scholar]
- Järup, L. Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br. Med. Bull. 2003, 68, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjad, M.; Hussain, S.; Javed, K.; Khan, A.R.; Shahjahan, M. The sources, toxicity, determination of heavy metals and their removal techniques from drinking water. World 2020, 5, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, S.; Salam, A.; Chhajro, M.A.; Fu, Q.; Khan, M.J.; Zhu, J.; Shaaban, M.; Kubar, K.A.; Ali, U.; Hu, H. Comparative efficiency of rice husk-derived biochar (RHB) and steel slag (SS) on cadmium (Cd) mobility and its uptake by Chinese cabbage in highly contaminated soil. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2018, 20, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, I.A.; Upula, S.A. Physicochemical, bacteriological, and correlational evaluation of water obtained from boreholes and springs in a sub-urban community. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2021, 11, 134–145. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, A.P. Caffeine as an environmental indicator for assessing urban aquatic ecosystems. Cad. De Saúde Pública 2005, 21, 1884–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, D.; Miller, G. The role of public health improvements in health advances: The twentieth-century United States. Demography 2005, 42, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiemann, M. Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA): A Summary of the Act and Its Major Requirements; Congressional Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2014.
- Woolf, A.D.; Stierman, B.D.; Barnett, E.D.; Byron, L.G.; Bole, A.; Balk, S.J.; Huerta-Montañez, G.M.; Landrigan, P.J.; Marcus, S.M.; Nerlinger, A.L.; et al. Drinking water from private wells and risks to children. Pediatrics 2023, 151, e2022060645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankhla, M.S.; Kumari, M.; Nandan, M.; Kumar, R.; Agrawal, P. Heavy metals contamination in water and their hazardous effect on human health-a review. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2016, 5, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, A.; Zulfiqar, M.; Samiah, S.; Rashid, E.U.; Nawaz, S.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Jesionowski, T.; Bilal, M.; Zdarta, J. Removal of toxic metals from water by nanocomposites through advanced remediation processes and photocatalytic oxidation. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2023, 9, 338–358. [Google Scholar]
- Strosnider, W.; Schultz, S.; Strosnider, K.J.; Nairn, R. Effects on the underlying water column by extensive floating treatment wetlands. J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 46, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Song, K.; He, X.; Peng, Y.; Liu, D.; Liu, J. Identification of groundwater pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of a landfill in a low permeability area. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Chen, G.; Meng, J.; Wu, X.; Alsaedi, A.; Ahmad, B. Virtual water accounting for a building construction engineering project with nine sub-projects: A case in E-town, Beijing. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 4691–4700. [Google Scholar]
- Cannon, C. Examining rural environmental injustice: An analysis of ruralness, class, race, and gender on the presence of landfills across the United States. J. Rural Community Dev. 2020, 15, 89–114. [Google Scholar]
- James, S.C. Metals in municipal landfill leachate and their health effects. Am. J. Public Health 1977, 67, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sule, I.A.; Saleh, M.; Lawan, M.; Bunawa, A.A.; Jibril, F.M. Assessment of groundwater quality condition at Tarauni dumpsite area, Kano Northwestern Nigeria. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2020, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldsen, T.H.; Hansen, E.W.; Christensen, J.D.; Moesby, L. Baclofen influences lipopolysaccharide-mediated interleukin-6 release from murine pituicytes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 451, 209–215. [Google Scholar]
- Mor, S.; Ravindra, K.; Dahiya, R.; Chandra, A. Leachate characterization and assessment of groundwater pollution near municipal solid waste landfill site. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 118, 435–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrijheid, M. Health effects of residence near hazardous waste landfill sites: A review of epidemiologic literature. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108 (Suppl. S1), 101–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Siddiqua, A.; Hahladakis, J.N.; Al-Attiya, W.A.K. An overview of the environmental pollution and health effects associated with waste landfilling and open dumping. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 58514–58536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brender, J.D.; Maantay, J.A.; Chakraborty, J. Residential proximity to environmental hazards and adverse health outcomes. Am. J. Public Health 2011, 101 (Suppl. S1), S37–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Aziz, O.I. Wetland Processes, Modeling, and Use in Watershed Management. In Environmental Water Resources Institute Congress; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Census Bureau. QuickFacts: Charles City County, Virginia. U.S. Census Bureeau QuickFacts. Available online: https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/charlescitycountyvirginia/PST045222 (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Charles City County Planning Commission. Charles City County Comprehensive Land Use Plan; Charles City County: Charles City, VA, USA, 2006; Volume 188, Available online: https://www.charlescityva.us/DocumentCenter/View/536/2014-Final-Comp-Plan-002 (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- PlanRVA. Land & Water Use. PlanRVA Environment-Lower Chickahominy. Available online: https://planrva.org/environment/lc_landwater-use/ (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Benham, B.L.; Ling, E.; Ziegler, P.; Krometis, L.A.H. What’s in your water? In Development and Evaluation of the Virginia Household Water Quality Program and Virginia Master Well Owner Network; The School of Human Sciences at Mississippi State University: Starkville, MS, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tossas, K.Y.; Owens, B.D.; Reitzel, S.; Wilt, J.K.; Mejía, P.T.R.; Hunley, R.; Groesbeck, H.; Boucher, H.; Schifano, K.; Brown, S.L.; et al. The Chickahominy TRUTH (Trust, Research, Understand, Teach, and Heal) Project—A Tribal Community–Academic Partnership for Understanding the Impact of Structural Factors on Perceived Cancer Risk in Rural Virginia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2024, 21, 262. [Google Scholar]
- Vaverková, M.D. Landfill impacts on the environment. Geosciences 2019, 9, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaverková, M.D.; Maxianová, A.; Winkler, J.; Adamcová, D.; Podlasek, A. Environmental consequences and the role of illegal waste dumps and their impact on land degradation. Land Use Policy 2019, 89, 104234. [Google Scholar]
- Yeşiller, N.; Hanson, J.L.; Kopp, K.B.; Yee, E.H. Heat management strategies for MSW landfills. Waste Manag. 2016, 56, 246–254. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Census Bureau. TIGER/Line Shapefile. Available online: https://catalog.data.gov/dataset/tiger-line-shapefile-2017-state-north-carolina-current-block-group-state-based (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Geology and Mineral Resources. Virginia Department of Energy. Available online: https://energy.virginia.gov/webmaps/GeologyMineralResources/ (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- SafeHome Ultimate Drinking Water Test Kit. SafeHome Test Kits. Available online: https://safehometestkits.com/product/safe-home-ultimate-drinking-water-test-kit-lab (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- Cambon, J.; Hernangómez, D.; Belanger, C.; Possenriede, D. tidygeocoder: An R package for geocoding. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 3544. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, A.; Tabinda, A.B.; Yasar, A. Environmental risk assessment of a young landfill site and its vicinity for possible human exposure. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2021, 27, 258–273. [Google Scholar]
- Talalaj, I.A.; Biedka, P. Use of the landfill water pollution index (LWPI) for groundwater quality assessment near the landfill sites. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 24601–24613. [Google Scholar]
- Budnick, L.D.; Sokal, D.C.; Falk, H.; Logue, J.N.; Fox, J.M. Cancer and birth defects near the Drake Superfund site, Pennsylvania. Arch. Environ. Health Int. J. 1984, 39, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, M.S.; Al-Homsi, N.; Goulet, L.; Riberdy, H. Incidence of cancer among persons living near a municipal solid waste landfill site in Montreal, Quebec. Arch. Environ. Health Int. J. 1995, 50, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abiriga, D.; Vestgarden, L.S.; Klempe, H. Groundwater contamination from a municipal landfill: Effect of age, landfill closure, and season on groundwater chemistry. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 140307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, P. Potential health impacts of hard water. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 4, 866. [Google Scholar]
- Dargahi, A.; Shokri, R.; Mohammadi, M.; Azizi, A.; Tabandeh, L.; Jamshidi, A.; Beidaghi, S. Investigating of the corrosion and deposition potentials of drinking water sources using corrosion index: A case study of Dehloran. J. Chem. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 974, 2115. [Google Scholar]
- Sherrard, J.H.; Moore, D.R.; Dillaha, T.A. Total dissolved solids: Determination, sources, effects, and removal. J. Environ. Educ. 1987, 18, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjovu, G.E.; Stephen, H.; James, D.; Ahmad, S. Measurement of total dissolved solids and total suspended solids in water systems: A review of the issues, conventional, and remote sensing techniques. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, A.M.; Devesa, R. Characterization and removal of minerals that cause taste. In Taste and Odour in Source and Drinking Water: Causes, Controls, and Consequences; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2019; pp. 113–142. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, H.; Burlingame, G.; Ikehata, K.; Furatian, L.; Suffet, I.H. The effect of pH on taste and odor production and control of drinking water. AQUA—Water Infrastruct. Ecosyst. Soc. 2022, 71, 1278–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozsvath, D.L. Fluoride and environmental health: A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2009, 8, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, H.; Gupta, A.K.; Tripathy, S. Fluoride and human health: Systematic appraisal of sources, exposures, metabolism, and toxicity. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 1116–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, R. A comparative study of acid water treatment by grasses. Sustain. Agri. Food Environ. Res. Discontin. 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondy, S.C. Prolonged exposure to low levels of aluminum leads to changes associated with brain aging and neurodegeneration. Toxicology 2014, 315, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bondy, S.C. Low levels of aluminum can lead to behavioral and morphological changes associated with Alzheimer’s disease and age-related neurodegeneration. Neurotoxicology 2016, 52, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirlohi, S. Characterization of metallic off-flavors in drinking water: Health, consumption, and sensory perception. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, M.; Birajdar, F. Ensuring Purity and Health: A Comprehensive Study of Water Quality Testing Labs in Solapur District for Community Well-being. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Res. Technol. 2024, 9, 271–281. [Google Scholar]
- Legg, R.; Prior, J.; Adams, J.; McIntyre, E. The relations between mental health and psychological wellbeing and living with environmental contamination: A systematic review and conceptual framework. J. Environ. Psychol. 2023, 87, 101994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieter, C.A.; Maupin, M.A. Public Supply and Domestic Water Use in the United States, 2015; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2017.
- MacDonald Gibson, J.; Pieper, K.J. Strategies to improve private-well water quality: A North Carolina perspective. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 076001. [Google Scholar]
- Stillo, F.; MacDonald Gibson, J. Exposure to Contaminated Drinking Water and Health Disparities in North Carolina. Am. J. Public Health 2017, 107, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaur, M.; Lombard, M.A.; Ayotte, J.D.; Harvey, D.E.; Bostick, B.C.; Chillrud, S.N.; Navas-Acien, A.; Nigra, A.E. Associations between private well water and community water supply arsenic concentrations in the conterminous United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.M.; Fisher, M.; Clonch, A.; MacDonald, J.M.; Cook, P.J. Children drinking private well water have higher blood lead than those with city water. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 16898–16907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy-Bushrow, A.E.; Sitarik, A.R.; Havstad, S.; Park, S.K.; Bielak, L.F.; Austin, C.; Johnson, C.C.; Arora, M. Burden of higher lead exposure in African-Americans starts in utero and persists into childhood. Environ. Int. 2017, 108, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Public Health Association. Creating the Healthiest Nation: Water and Health Equity; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mohai, P.; Pellow, D.; Roberts, J.T. Environmental justice. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2009, 34, 405–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaney, C.D.; Wing, S.; Wilson, S.M.; Campbell, R.L.; Caldwell, D.; Hopkins, B.; O’Shea, S.; Yeatts, K. Public infrastructure disparities and the microbiological and chemical safety of drinking and surface water supplies in a community bordering a landfill. J. Environ. Health 2013, 75, 24–37. [Google Scholar]
- Levin, R.; Villanueva, C.M.; Beene, D.; Cradock, A.L.; Donat-Vargas, C.; Lewis, J.; Martinez-Morata, I.; Minovi, D.; Nigra, A.E.; Olson, E.D.; et al. US drinking water quality: Exposure risk profiles for seven legacy and emerging contaminants. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2024, 34, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Analyte | Outcome | Exposure | p-Value | Odds Ratio (95% Confidence Interval) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zinc (Metals) | Fair or worse | Stream, <1 mi | 0.015 | 2.63 (1.23, 5.86) |
| Turbidity (Physical properties) | Fair or worse | Stream, <1 mi | 0.028 | 4.31 (1.31, 19.53) |
| Hardness as CaCO3 (Physical properties) | Poor or worse | Stream, <0.5 mi | 0.013 | 10.71 (1.64, 86.96) |
| Water pH (Physical properties) | Bad | Landfill, <1 mi | 0.026 | 10.50 (1.16, 95.68) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Owens, B.D.; Boyle, J.; Adkins, D.; Adkins, S.; Boucher, H.; Burch, J.; Thomson, M.D.; Tossas, K.Y. Associations Between Landfill Proximity and Water Quality Analytes from Private Domestic Wells in Rural Virginia. Environments 2025, 12, 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12040103
Owens BD, Boyle J, Adkins D, Adkins S, Boucher H, Burch J, Thomson MD, Tossas KY. Associations Between Landfill Proximity and Water Quality Analytes from Private Domestic Wells in Rural Virginia. Environments. 2025; 12(4):103. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12040103
Chicago/Turabian StyleOwens, Bianca D., Joseph Boyle, Dana Adkins, Stephen Adkins, Hillary Boucher, James Burch, Maria D. Thomson, and Katherine Y. Tossas. 2025. "Associations Between Landfill Proximity and Water Quality Analytes from Private Domestic Wells in Rural Virginia" Environments 12, no. 4: 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12040103
APA StyleOwens, B. D., Boyle, J., Adkins, D., Adkins, S., Boucher, H., Burch, J., Thomson, M. D., & Tossas, K. Y. (2025). Associations Between Landfill Proximity and Water Quality Analytes from Private Domestic Wells in Rural Virginia. Environments, 12(4), 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12040103






