Field Comparison of Active and Passive Soil Gas Sampling Techniques for VOC Monitoring at Contaminated Sites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Campaigns
2.2. Passive Samplers Employed
2.2.1. WMS
2.2.2. Sorbent Pens
2.2.3. Low-Density Polyethylene Films
2.3. Active Sampling
2.3.1. Vacuum Bottles
2.3.2. Canisters
2.3.3. Sorbent Tubes
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Porto Marghera Campaigns
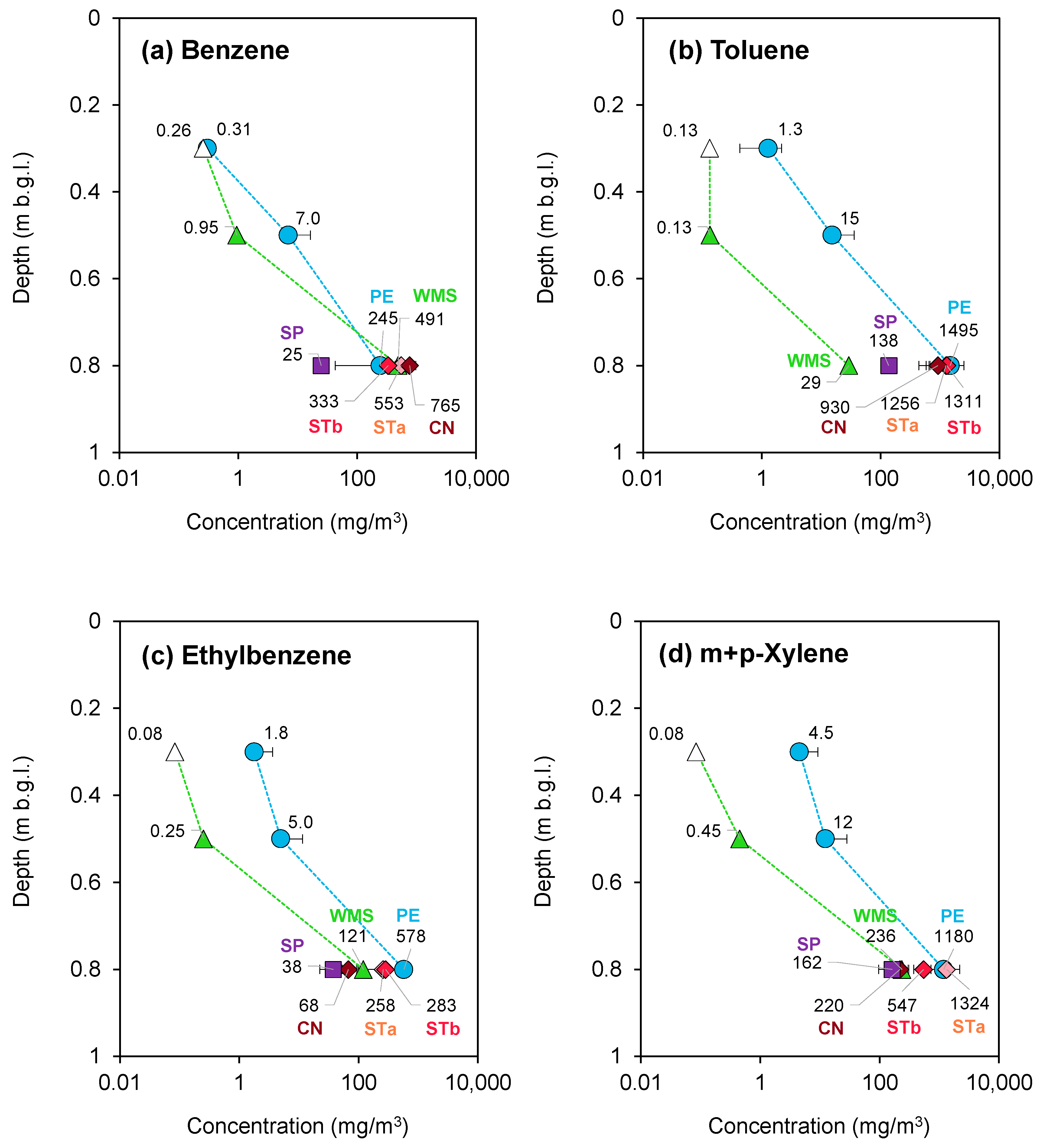
3.1.1. Porto Marghera—August 2020 Campaign
3.1.2. Porto Marghera—February 2022 Campaign
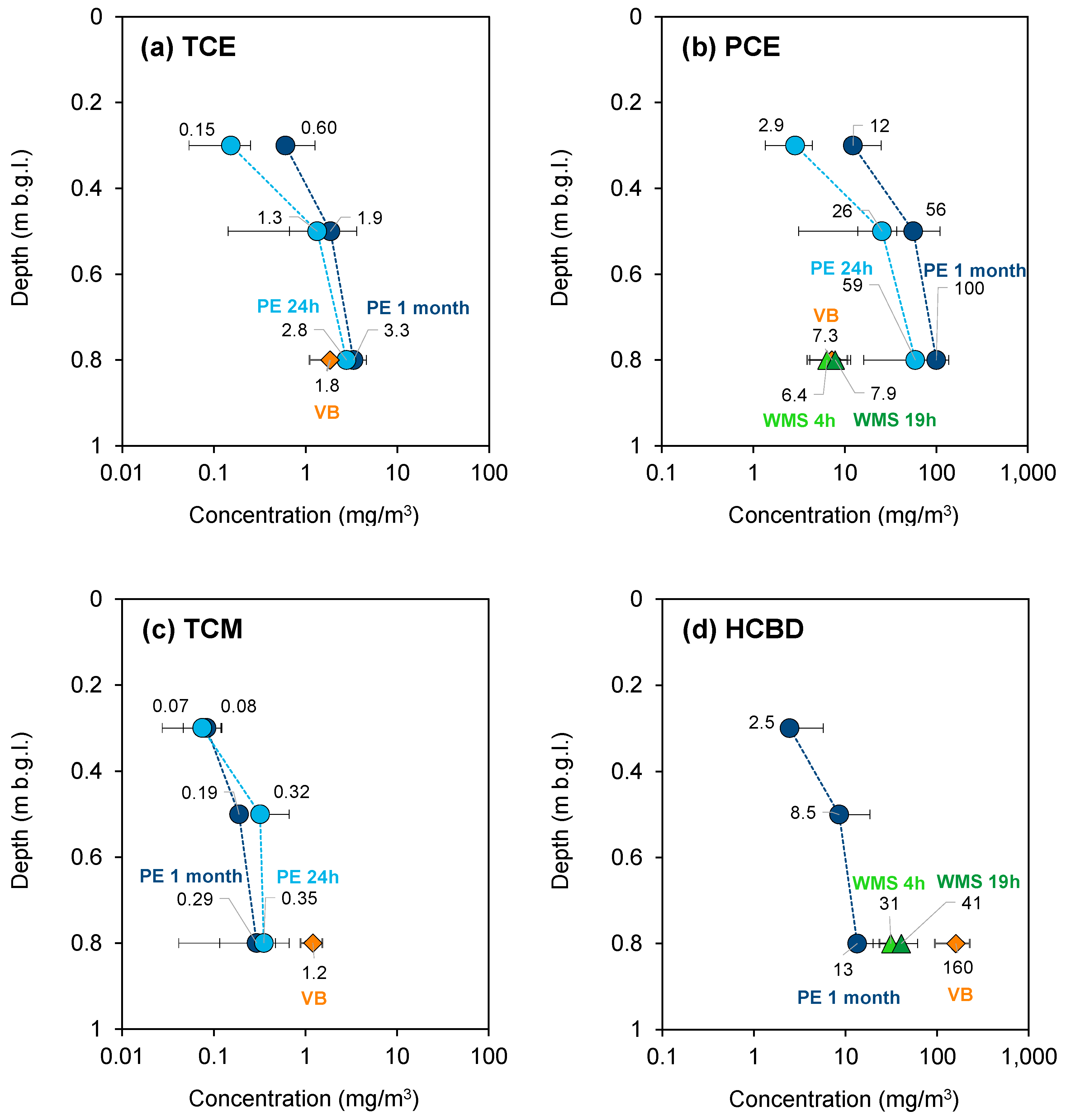
3.1.3. Porto Marghera—September 2022 Campaign
3.2. Ferrara Campaigns
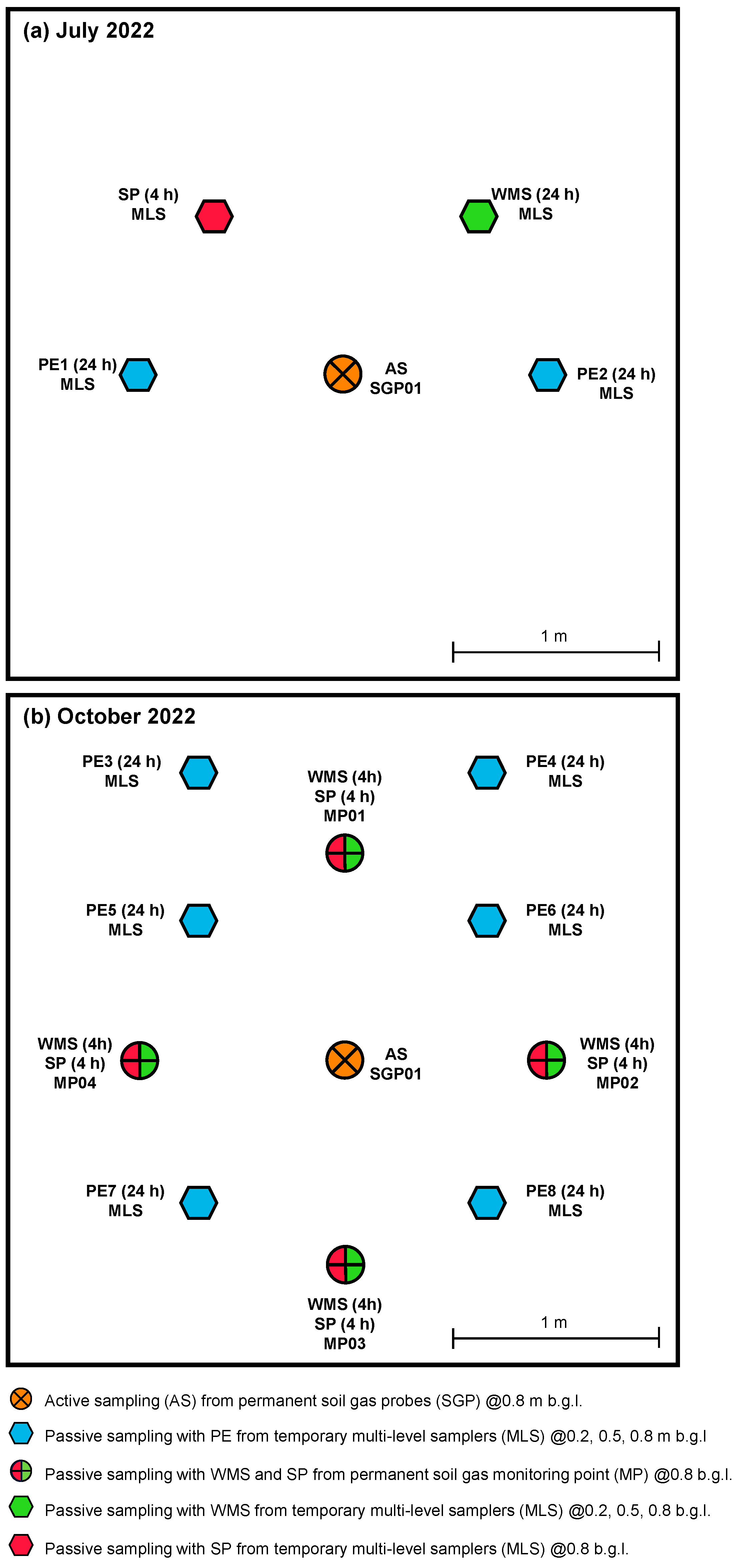
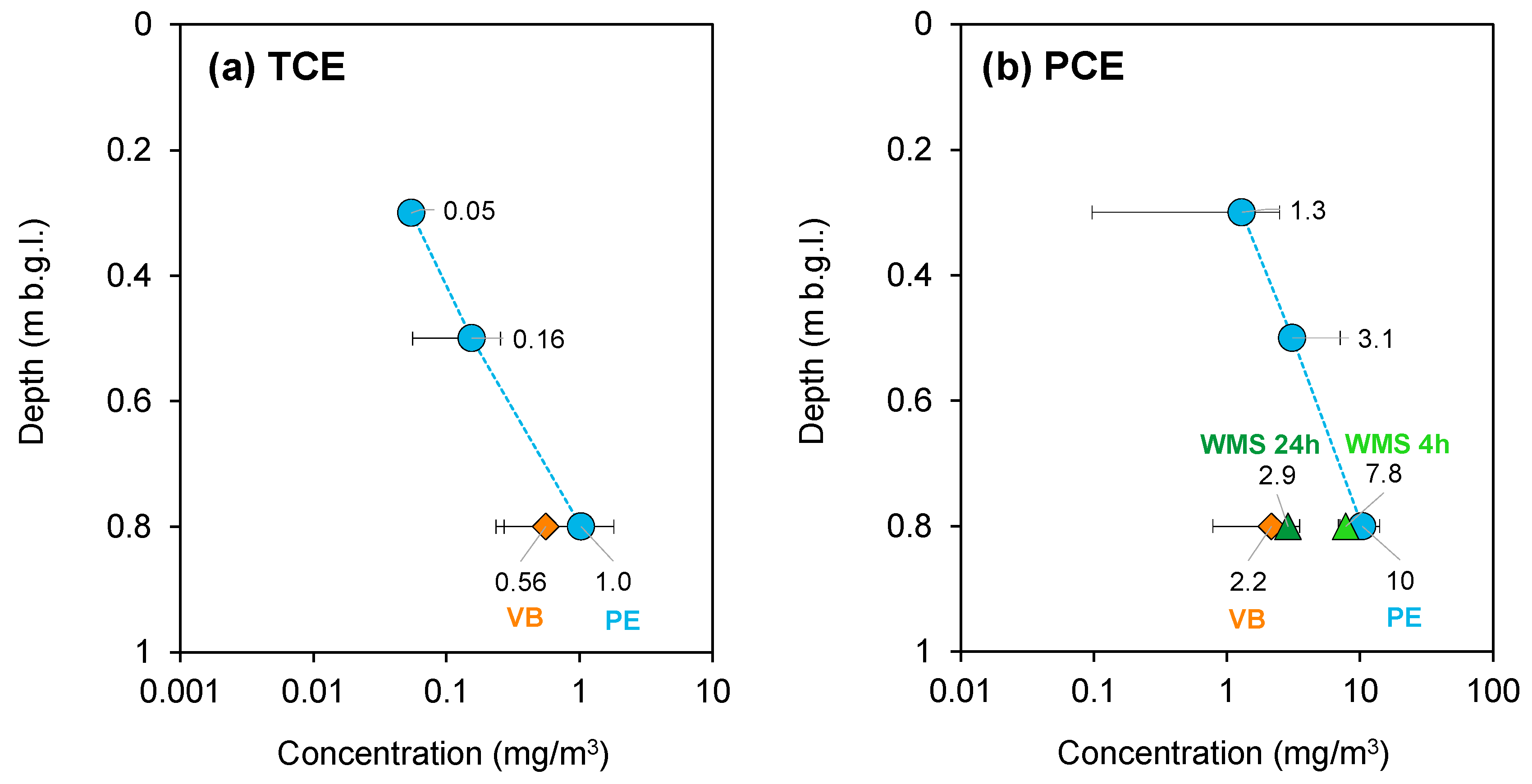
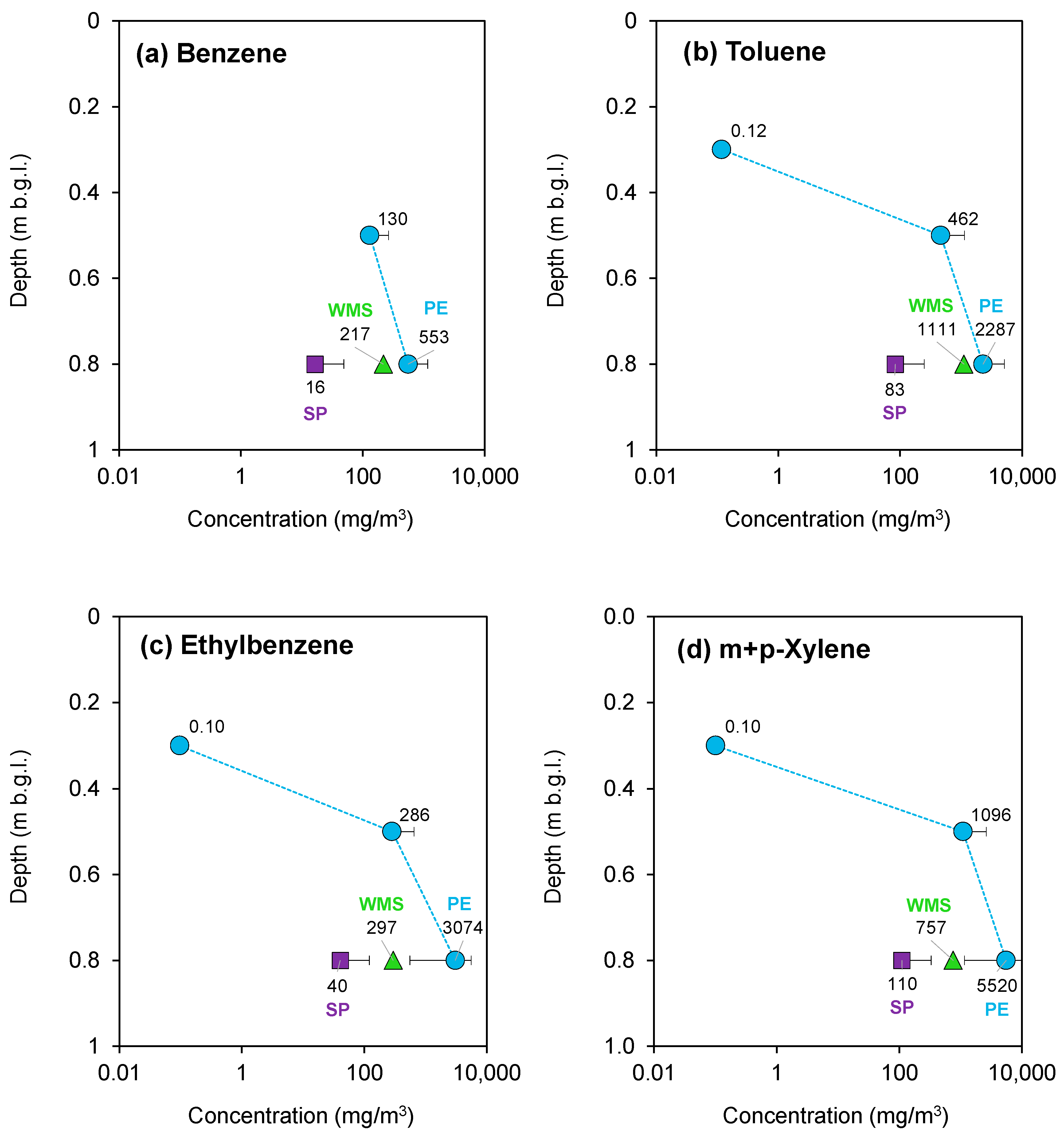
3.2.1. Ferrara—July 2022 Campaign
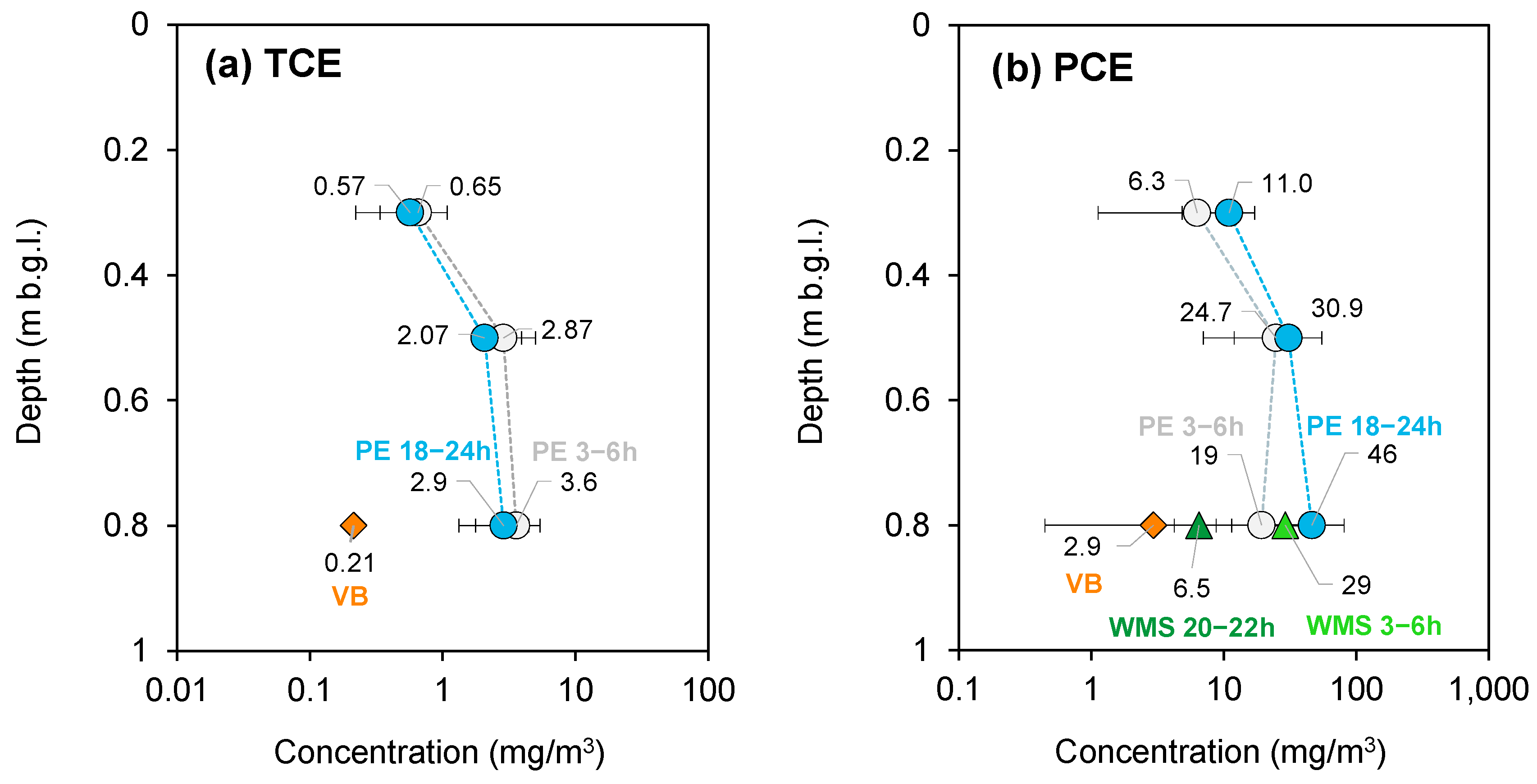
3.2.2. Ferrara—October 2022 Campaign
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AS | Active Sampling |
| b.g.l. | Below ground level |
| BTEX | Benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylenes |
| CN | Canister |
| DCE | Dichloroethene |
| GC-MS | Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry |
| HCBD | Hexachlorobutadiene |
| LOQ | Limit of quantification |
| MP | Monitoring point |
| PCE | Tetrachloroethene |
| PE | Polyethylene films |
| PID | Photoionization detector |
| PS | Passive sampling |
| SP | Sorbent pen |
| ST | Sorbent tube |
| TCE | Trichloroethene |
| TCM | Trichloromethane |
| UR | Uptake rate |
| VB | Vacuum bottle |
| VC | Vinyl chloride |
| VOC | Volatile Organic Compound |
| WMS | Waterloo Membrane Sampler |
References
- McHugh, T.E.; De Blanc, P.C.; Pokluda, R.J. Indoor Air as a Source of VOC Contamination in Shallow Soils Below Buildings. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2006, 15, 103–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Technical Guide for Assessing and Mitigating the Vapor Intrusion Pathway from Subsurface Vapor Sources to Indoor Air. OSWER Publication 9200.2–154. 2015. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/vaporintrusion/technical-guide-assessing-and-mitigating-vapor-intrusion-pathway-subsurface-vapor (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- Ma, J.; McHugh, T.; Beckley, L.; Lahvis, M.; DeVaull, G.; Jiang, L. Vapor Intrusion Investigations and Decision-Making: A Critical Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 7050–7069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM D5314-92e1; ASTM Standard Guide for Soil Gas Monitoring in the Vadose Zone. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2006.
- Verginelli, I.; Pecoraro, R.; Baciocchi, R. Using Dynamic Flux Chambers to Estimate the Natural Attenuation Rates in the Subsurface at Petroleum Contaminated Sites. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verginelli, I.; Baciocchi, R. Refinement of the Gradient Method for the Estimation of Natural Source Zone Depletion at Petroleum Contaminated Sites. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2021, 241, 103807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Verginelli, I.; Suuberg, E.M.; Eklund, B. Examining the Use of USEPA’s Generic Attenuation Factor in Determining Groundwater Screening Levels for Vapor Intrusion. Groundw. Monit. Remediat. 2018, 38, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verginelli, I.; Yao, Y. A Review of Recent Vapor Intrusion Modeling Work. Groundw. Monit. Remediat. 2021, 41, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorder, K.A.; Dettenmaier, E.M. Portable GC/MS Methods to Evaluate Sources of cVOC Contamination in Indoor Air. Groundw. Monit. Remediat. 2011, 31, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinemann, A. Volatile Emissions from Common Consumer Products. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2015, 8, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geosyntec Scoping Assessment of Soil Vapor Monitoring Protocols for Evaluating Subsurface Vapor Intrusion into Indoor Air 2009. Available online: https://www.geosyntec.com/vapor-intrusion-guidance (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- CalEPA, (California Environmental Protection Agency Department of Toxic Substances Control) Advisory: Active Soil Gas Investigations. 2015. Available online: https://www.waterboards.ca.gov/rwqcb4/water_issues/programs/ust/docs/VI_ActiveSoilGasAdvisory_FINAL.pdf (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- API. Collecting and Interpreting Soil Gas Samples from the Vadose Zone: A Practical Strategy for Assessing the Subsurface Vapor-to-Indoor Air Migration Pathway at Petroleum Hydrocarbon Sites; API Publication: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; Available online: https://www.api.org/~/media/files/ehs/clean_water/ground_water_quality/pub4741_vi_assessment_2005.pdf (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- ITRC. Vapor Intrusion Pathway: A Practical Guideline; VI-1; ITRC: Kansas City, MO, USA, 2007; Available online: https://itrcweb.org/petroleum-vapor-intrusion-2/ (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- SNPA. Progettazione del Monitoraggio dei Vapori Nei Siti Contaminati. Linee Guida SNPA 15/2018. 2018. Available online: https://www.snpambiente.it/snpa/progettazione-del-monitoraggio-di-vapori-nei-siti-contaminati/ (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- Cocheo, C.; Boaretto, C.; Pagani, D.; Quaglio, F.; Sacco, P.; Zaratin, L.; Cottica, D. Field Evaluation of Thermal and Chemical Desorption BTEX Radial Diffusive Sampler Radiello® Compared with Active (Pumped) Samplers for Ambient Air Measurements. J. Environ. Monit. 2009, 11, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAlary, T.; Wang, X.; Unger, A.; Groenevelt, H.; Górecki, T. Quantitative Passive Soil Vapor Sampling for VOCs- Part 1: Theory. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2014, 16, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAlary, T.; Groenevelt, H.; Seethapathy, S.; Sacco, P.; Crump, D.; Tuday, M.; Schumacher, B.; Hayes, H.; Johnson, P.; Górecki, T. Quantitative Passive Soil Vapor Sampling for VOCs—Part 2: Laboratory Experiments. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2014, 16, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAlary, T.; Groenevelt, H.; Nicholson, P.; Seethapathy, S.; Sacco, P.; Crump, D.; Tuday, M.; Hayes, H.; Schumacher, B.; Johnson, P.; et al. Quantitative Passive Soil Vapor Sampling for VOCs—Part 3: Field Experiments. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2014, 16, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAlary, T.; Groenevelt, H.; Seethapathy, S.; Sacco, P.; Crump, D.; Tuday, M.; Schumacher, B.; Hayes, H.; Johnson, P.; Parker, L.; et al. Quantitative Passive Soil Vapor Sampling for VOCs—Part 4: Flow-through Cell. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2014, 16, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAlary, T.; Groenevelt, H.; Disher, S.; Arnold, J.; Seethapathy, S.; Sacco, P.; Crump, D.; Schumacher, B.; Hayes, H.; Johnson, P.; et al. Passive Sampling for Volatile Organic Compounds in Indoor Air-Controlled Laboratory Comparison of Four Sampler Types. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamamin, D.F. Passive Soil Gas Technique for Investigating Soil and Groundwater Plume Emanating from Volatile Organic Hydrocarbon at Bazian Oil Refinery Site. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 1485–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Chang, J.-S.; Chen, T.-W.; Hou, Y. Passive Membrane Sampler for Assessing VOCs Contamination in Unsaturated and Saturated Media. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschwend, P.; MacFarlane, J.; Jensen, D.; Soo, J.; Saparbaiuly, G.; Borrelli, R.; Vago, F.; Oldani, A.; Zaninetta, L.; Verginelli, I.; et al. In Situ Equilibrium Polyethylene Passive Sampling of Soil Gas VOC Concentrations: Modeling, Parameter Determinations, and Laboratory Testing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 7810–7819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.-K.; Kim, P.-G.; Lee, K.Y.; Kwon, J.-H.; Hong, Y. Development of an in Situ Equilibrium Polydimethylsiloxane Passive Sampler for Measuring Volatile Organic Compounds in Soil Vapor. Chemosphere 2023, 325, 138419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.-G.; Tarafdar, A.; Lee, K.Y.; Kwon, J.-H.; Hong, Y. The Passive Sampler Assisted Human Exposure Risk Characterization for Tetrachloroethene Soil Vapor Intrusion Scenario. Environ. Res. 2023, 238, 117238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górecki, T.; Namieśnik, J. Passive Sampling. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2002, 21, 276–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Shan, W.; Xiao, H. Recent Advances in Passive Air Sampling of Volatile Organic Compounds. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 602–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.H.; Charlton, J.; Saunders, K.J. The Development of an Improved Diffusive Sampler. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1981, 42, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, W.K. Fundamentals of Passive Vapor Sampling. American Laboratory 1982, 14, 80–82. [Google Scholar]
- Seifert, B.; Abraham, H.-J. Use of Passive Samplers for the Determinaton of Gaseous Organic Substances in Indoor Air at Low Concentration Levels. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 1983, 13, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.G.; Mulik, J.D.; Coutant, R.W.; Wooten, G.W.; McMillin, C.R. Thermally Desorbable Passive Sampling Device for Volatile Organic Chemicals in Ambient Air. Anal. Chem. 1985, 57, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabiegała, B.; Kot-Wasik, A.; Urbanowicz, M.; Namieśnik, J. Passive Sampling as a Tool for Obtaining Reliable Analytical Information in Environmental Quality Monitoring. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 396, 273–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, R.; Tcaciuc, A.P.; Verginelli, I.; Baciocchi, R.; Guzzella, L.; Cesti, P.; Zaninetta, L.; Gschwend, P.M. Performance of Passive Sampling with Low-Density Polyethylene Membranes for the Estimation of Freely Dissolved DDx Concentrations in Lake Environments. Chemosphere 2018, 200, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodny, J.W.; Whetzel, J.E., Jr.; Anderson, H.S., II. Quantitative Passive Soil Gas and Air Sampling in Vapor Intrusion Investigations. In Proceedings of the AW&MA Vapor Intrusion 2009 Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 27–30 January 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, J.N.; Goodwin, D.F.; O’Neill, H.; Odencrantz, J.E. Application of Passive Soil Gas Technology to Determine the Source and Extent of a PCE Groundwater Plume in an Urban Environment. Remediat. J. 2008, 18, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seethapathy, S.; Górecki, T. Applications of Polydimethylsiloxane in Analytical Chemistry: A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 750, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosse, D.; McKernan, J. Passive Samplers for Investigations of Air Quality: Method Description, Implementation, and Comparison to Alternative Sampling Methods; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2014.
- Namiesnik, J.; Gorecki, T.; Kozlowski, E.; Torres, L.; Mathieu, J. Passive Dosimeters—An Approach to Atmospheric Pollutants Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 1984, 38, 225–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigley, C.E.; Lee, B.M. Determination of Sampling Rates of Passive Samplers for Organic Vapors Based on Estimated Diffusion Coefficients. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1987, 48, 873–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namieśnik, J.; Zabiegała, B.; Kot-Wasik, A.; Partyka, M.; Wasik, A. Passive Sampling and/or Extraction Techniques in Environmental Analysis: A Review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 381, 279–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seethapathy, S.; Górecki, T. Polydimethylsiloxane-Based Permeation Passive Air Sampler. Part II: Effect of Temperature and Humidity on the Calibration Constants. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 7907–7913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seethapathy, S.; Górecki, T. Polydimethylsiloxane-Based Permeation Passive Air Sampler. Part I: Calibration Constants and Their Relation to Retention Indices of the Analytes. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SIREM Instructions for Soil Gas Sampling with WMS-LUTM Samplers. 2016. Available online: https://www.siremlab.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/WMS-SOP-passive-soil-gas-sampling.pdf (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Compendium of Methods for the Determination of Toxic Organic Compounds in Ambient Air—Method TO-15: Determination of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) in Air Collected in Specially-Prepared Canisters and Analyzed by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (GC/MS); EPA/625/R-96/010b; Center for Environmental Research Information, Office of Research and Development, U.S. EPA: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1999.
- Ente Nazionale Italiano di Unificazione (UNI). UNI CEN/TS 13649: Stationary Source Emissions—Determination of the Mass Concentration of Individual Gaseous Organic Compounds—Adsorption on Solid Sorbent and Thermal Desorption/Gas Chromatographic Analysis; UNI: Milan, Italy, 2002. [Google Scholar]

| Campaign | AS Canister | AS Vacuum Bottles | AS Sorbent Tubes | PS PE | PS Sorbent Pen | PS WMS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Porto Marghera (August 2020) | 2 MP, 8 S | 4 MP, 12 S | 2 MP, 6 S | |||
| Porto Marghera (February 2022) | 2 MP, 8 S | 12 MP, 36 S | 2 MP, 3 S | |||
| Porto Marghera (September 2022) | 2 MP, 8 S | 8 MP, 24 S | 2 MP, 4S | |||
| Ferrara (July 2022) | 1 MP, 2 S | 1 MP, 6 S | 2 MP, 6 S | 1 MP, 2 S | 1 MP, 3 S | |
| Ferrara (October 2022) | 1 MP, 3 S | 1 MP, 6 S | 6 MP, 18 S | 4 MP, 4 S | 4 MP, 4 S |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borrelli, R.; Cecconi, A.; Oldani, A.; Fuin, F.; Emiliani, R.; Cacciari, F.; Vecchio, A.; Lanari, C.; Villani, F.; Bonfedi, G.; et al. Field Comparison of Active and Passive Soil Gas Sampling Techniques for VOC Monitoring at Contaminated Sites. Environments 2025, 12, 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12050141
Borrelli R, Cecconi A, Oldani A, Fuin F, Emiliani R, Cacciari F, Vecchio A, Lanari C, Villani F, Bonfedi G, et al. Field Comparison of Active and Passive Soil Gas Sampling Techniques for VOC Monitoring at Contaminated Sites. Environments. 2025; 12(5):141. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12050141
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorrelli, Raffaella, Alessandra Cecconi, Alessandro Oldani, Federico Fuin, Renata Emiliani, Fabrizio Cacciari, Antonella Vecchio, Camilla Lanari, Federico Villani, Guido Bonfedi, and et al. 2025. "Field Comparison of Active and Passive Soil Gas Sampling Techniques for VOC Monitoring at Contaminated Sites" Environments 12, no. 5: 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12050141
APA StyleBorrelli, R., Cecconi, A., Oldani, A., Fuin, F., Emiliani, R., Cacciari, F., Vecchio, A., Lanari, C., Villani, F., Bonfedi, G., Giacopetti, D., Baciocchi, R., & Verginelli, I. (2025). Field Comparison of Active and Passive Soil Gas Sampling Techniques for VOC Monitoring at Contaminated Sites. Environments, 12(5), 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12050141









