Short- and Long-Term Biochar Cadmium and Lead Immobilization Mechanisms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3.1. Donnan Membrane Technique Setup
2.3.2. The Rice Plant Collection
2.3.3. The Soil Samples Collection
2.3.4. The Soil Heavy Metals Fractions Detection
2.3.5. The Soil Enzymatic Activity Detection
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
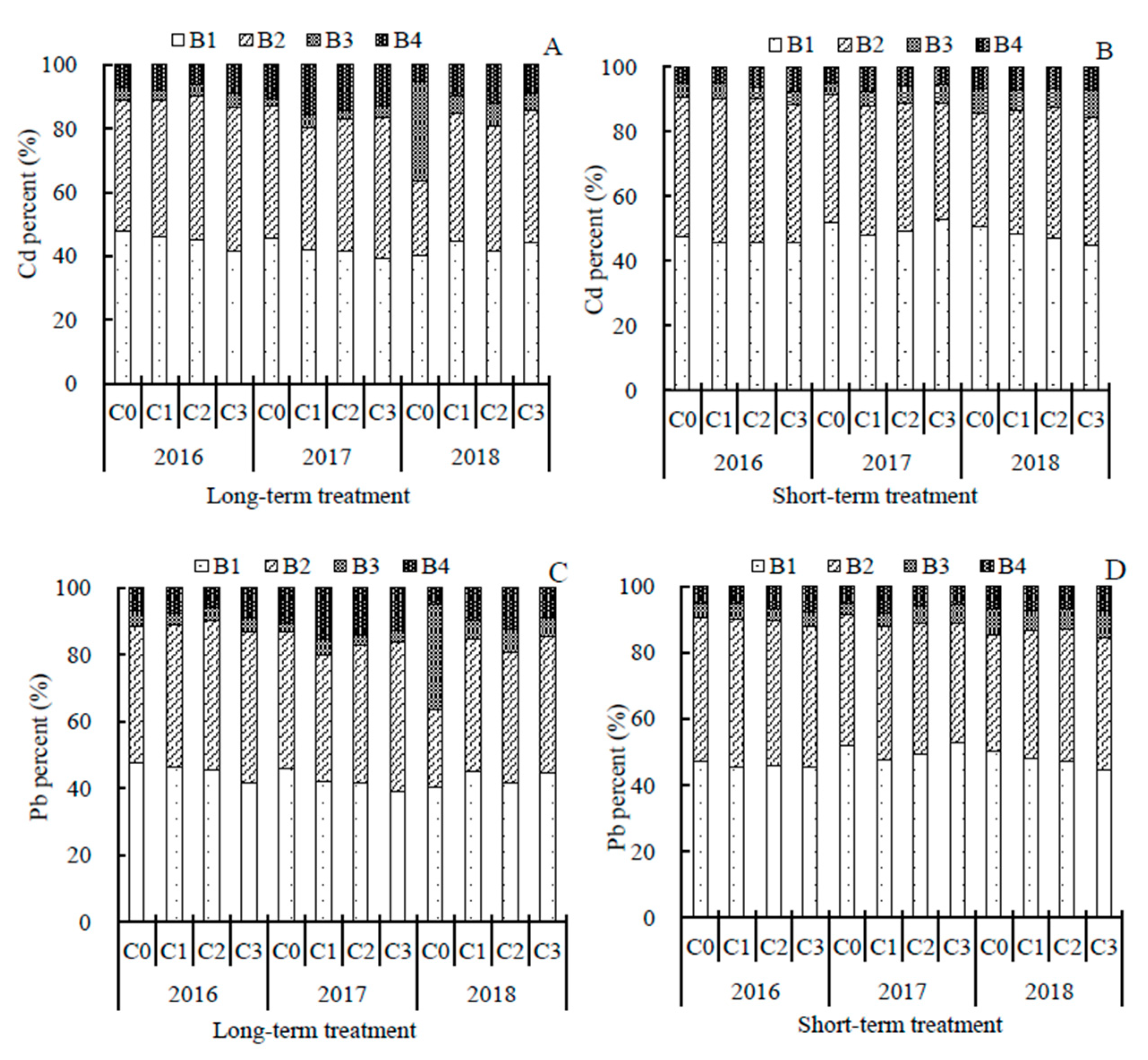
3.1. Biochar Effects on Cd and Pb in the Soil Water Soluble Phase and Various Pools
3.2. Biochar Effects on SOM, pH and Water Content
3.3. Biochar Effects on Cd and Pb Transfer in Rice
3.4. Biochar Effects on Soil Enzyme Activity and Microbial Diversity
3.5. The Influence of Biochar on Soil and Plant Characteristics in Relation to Cd and Pb Contamination
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, L.; Noerpel, M.; Scheckel, K.G.; Ippolito, J.A. Wheat straw biochar reduces environmental cadmium bioavailability. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, S.E.; Jensen, J.; Jakob, L.; Oleszczuk, P.; Hartnik, T.; Henriksen, T.; Okkenhaug, G.; Martinsen, V.; Cornelissen, G. Short-Term Effect of the Soil Amendments Activated Carbon, Biochar, and Ferric Oxyhydroxide on Bacteria and Invertebrates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8674–8683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MEP; MLR. The national soil contamination survey. Natl. Soil Pollut. Surv. Bull. 2014, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z.; Jin, F.; O’Connor, D.; Hou, D. Solidification/Stabilization for Soil Remediation: An Old Technology with New Vitality. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 11615–11617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yu, K.; Li, J.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Poon, C.S.; Yoo, J.; Baek, K.; Ding, S.; Hou, D.; Dai, J. Low-carbon and low-alkalinity stabilization/solidification of high-Pb contaminated soil. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 351, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senneca, O.; Cortese, L.; Di Martino, R.; Fabbricino, M.; Ferraro, A.; Race, M.; Scopino, A. Mechanisms affecting the delayed efficiency of cement based stabilization/solidification processes. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 121230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.Q.; Li, L.Q.; Zhang, A.F.; Pan, G.X.; Bao, D.D.; Chang, A. Biochar Amendment Greatly Reduces Rice Cd Uptake in a Contaminated Paddy Soil: A Two-Year Field Experiment. Bioresources 2011, 6, 2605–2618. [Google Scholar]
- Ippolito, J.A.; Laird, D.A.; Busscher, W.J. Environmental Benefits of Biochar. J. Environ. Qual. 2012, 41, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Rillig, M.C.; Thies, J.E.; Masiello, C.A.; Hockaday, W.C.; Crowley, D.E. Biochar effects on soil biota—A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1812–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, B.; Chen, G. Preparation and application of magnetic biochar in water treatment: A critical review. Sci. Biochem. Environ. 2020, 711, 134847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.H.; Gao, M.; Qiu, W.; Islam, M.S.; Song, Z. Mechanisms for cadmium adsorption by magnetic biochar composites in an aqueous solution. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemavathy, R.V.; Kumar, P.S.; Kanmani, K.; Jahnavi, N. Adsorptive separation of Cu(II) ions from aqueous medium using thermally/chemically treated Cassia fistula based biochar. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 249, 119390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Nan, H.; Kan, Y.; Xu, X.; Qiu, H.; Cao, X. Infiltration behavior of heavy metals in runoff through soil amended with biochar as bulking agent. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, P.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.; He, L.; Müller, K.; Shaheen, S.M.; Xu, S.; Rinklebe, J.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Ok, Y.S.; et al. Bamboo- and pig-derived biochars reduce leaching losses of dibutyl phthalate, cadmium, and lead from co-contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2018, 198, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ippolito, J.A.; Berry, C.M.; Strawn, D.G.; Novak, J.M.; Levine, J.; Harley, A. Biochars Reduce Mine Land Soil Bioavailable Metals. J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 46, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Feng, K.; Su, J.; Dong, J. The mechanism of cadmium sorption by sulphur-modified wheat straw biochar and its application cadmium-contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Wang, X.; Chen, C.; Peng, B.; Tan, C.; Li, H. Varying effect of biochar on Cd, Pb and As mobility in a multi-metal contaminated paddy soil. Chemosphere 2016, 152, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.; Wei, J.; Guan, F.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Luo, Y. Biochar and bacteria inoculated biochar enhanced Cd and Cu immobilization and enzymatic activity in a polluted soil. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, R.; Joseph, S.; Cui, L.; Pan, G.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, A.; Rutlidge, H.; Wong, S.; Chia, C. A three-year experiment confirms continuous immobilization of cadmium and lead in contaminated paddy field with biochar amendment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 272, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tang, S.; Jiang, C.; Jiang, X.; Guan, Y. Simultaneous and Efficient Capture of Inorganic Nitrogen and Heavy Metals by Polyporous Layered Double Hydroxide and Biochar Composite for Agricultural Nonpoint Pollution Control. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 43013–43030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujtaba Munir, M.A.; Liu, G.; Yousaf, B.; Ali, M.U.; Abbas, Q.; Ullah, H. Synergistic effects of biochar and processed fly ash on bioavailability, transformation and accumulation of heavy metals by maize (Zea mays L.) in coal-mining contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Pan, G.; Li, L.; Yan, J.; Zhang, A.; Bian, R.; Chang, A. The Reduction of Wheat Cd Uptake in Contaminated Soil Via Biochar Amendment: A Two-Year Field Experiment. Bioresources 2012, 7, 5666–5676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, L.; Pan, G.; Li, L.; Bian, R.; Liu, X.; Yan, J.; Quan, G.; Ding, C.; Chen, T.; Liu, Y.; et al. Continuous immobilization of cadmium and lead in biochar amended contaminated paddy soil: A five-year field experiment. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 93, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Lei, W.; Chen, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zeng, S.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, D.; Li, S. Chinese Soil Taxonomy. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2007, 21, 36–38. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R. Methods of inorganic pollutants analysis. In Soil and Agro-Chemical Analysis Methods; Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 205–266. [Google Scholar]
- Parat, C.; Pinheiro, J.P. ISIDORE, a probe for in situ trace metal speciation based on Donnan membrane technique with related electrochemical detection part 1: Equilibrium measurements. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 896, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ure, A.M.; Quevauviller, P.; Muntau, H.; Griepink, B. Speciation of Heavy Metals in Soils and Sediments. An Account of the Improvement and Harmonization of Extraction Techniques Undertaken Under the Auspices of the BCR of the Commission of the European Communities. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 1993, 51, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-P.; Shi, J.-Y.; Qi, L.; Chen, X.-C.; Chen, Y.-X. Heavy metal availability and impact on activity of soil microorganisms along a Cu/Zn contamination gradient. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 848–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Yan, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, L.; Quan, G.; Ding, C.; Chen, T.; Fu, Q.; Chang, A. Influence of biochar on microbial activities of heavy metals contaminated paddy fields. BioResources 2013, 8, 5536–5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Hu, F.; Liu, M.; Scheu, S. Earthworms differentially modify the microbiome of arable soils varying in residue management. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 121, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, H.P.; Town, R.M.; Buffle, J.; Cleven, R.F.M.J.; Davison, W.; Puy, J.; van Riemsdijk, W.H.; Sigg, L. Dynamic Speciation Analysis and Bioavailability of Metals in Aquatic Systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 8545–8556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Sun, J.; Quan, G.; Yan, J.; Gao, J.; Zou, X.; Cui, L. Insights into the effects of long-term biochar loading on water-soluble organic matter in soil: Implications for the vertical co-migration of heavy metals. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Seshadri, B.; Sarkar, B.; Wang, H.; Rumpel, C.; Sparks, D.; Farrell, M.; Hall, T.; Yang, X.; Bolan, N. Biochar modulates heavy metal toxicity and improves microbial carbon use efficiency in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhong, B.; Shafi, M.; Ma, J.; Guo, J.; Wu, J.; Ye, Z.; Liu, D.; Jin, H. Effects of biochar on growth, and heavy metals accumulation of moso bamboo (Phyllostachy pubescens), soil physical properties, and heavy metals solubility in soil. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xu, W.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Hao, S.; Chen, S. Pyrolysis of various phytoremediation residues for biochars: Chemical forms and environmental risk of Cd in biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 299, 122581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Dong, J.; Yi, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, Z. Proper Mode of Using Rice Straw Biochar To Treat Cd-Contaminated Irrigation Water in Mining Regions Based on a Multiyear in Situ Experiment. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 9928–9936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, D.; Tang, B.; Man, S.; Jia, Y.; Xu, H. Vermicompost and biochar as bio-conditioners to immobilize heavy metal and improve soil fertility on cadmium contaminated soil under acid rain stress. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, F.; Xie, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, A.; Li, L.; Xu, H. Effect of modified coconut shell biochar on availability of heavy metals and biochemical characteristics of soil in multiple heavy metals contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Li, L.; Li, G.; Xu, G. Feasibility of sludge-based biochar for soil remediation: Characteristics and safety performance of heavy metals influenced by pyrolysis temperatures. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beesley, L.; Inneh, O.S.; Norton, G.J.; Moreno-Jimenez, E.; Pardo, T.; Clemente, R.; Dawson, J.J.C. Assessing the influence of compost and biochar amendments on the mobility and toxicity of metals and arsenic in a naturally contaminated mine soil. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 186, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, J.M.; Busscher, W.J.; Watts, D.W.; Amonette, J.E.; Ippolito, J.A.; Lima, I.M.; Gaskin, J.W.; Das, K.C.; Steiner, C.; Ahmedna, M. Biochars impact on soil moisture storage in an Ultisol and two Aridisols. Soil Sci. 2012, 177, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ippolito, J.A.; Stromberger, M.E.; Lentz, R.D.; Dungan, R.S. Hardwood biochar influences calcareous soil physicochemical and microbiological status. J. Environ. Qual. 2014, 43, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ippolito, J.A.; Stromberger, M.E.; Lentz, R.D.; Dungan, R.S. Hardwood biochar and manure co-application to a calcareous soil. Chemosphere 2016, 142, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lentz, R.D.; Ippolito, J.A.; Lehrsch, G.A. Biochar, Manure, and Sawdust Alter Long-Term Water Retention Dynamics in Degraded Soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2019, 83, 1491–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Pu, S.; Deng, D.; Huang, H.; Yan, C.; Ma, H.; Razavi, B.S. Comparable effects of manure and its biochar on reducing soil Cr bioavailability and narrowing the rhizosphere extent of enzyme activities. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wang, H.; Al-Tabbaa, A. Leachability and heavy metal speciation of 17-year old stabilised/solidified contaminated site soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 278, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NHFPC; CFDA. National Standards for Food Safety Limits for Contaminants in Food; China Food and Drug Administration Press: Beijing, China, 2017; pp. 2–5.
- Turan, V.; Khan, S.A.; Mahmood ur, R.; Iqbal, M.; Ramzani, P.M.A.; Fatima, M. Promoting the productivity and quality of brinjal aligned with heavy metals immobilization in a wastewater irrigated heavy metal polluted soil with biochar and chitosan. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 161, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puga, A.P.; Abreu, C.A.; Melo, L.C.A.; Beesley, L. Biochar application to a contaminated soil reduces the availability and plant uptake of zinc, lead and cadmium. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 159, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, T.; Franks, A.E.; Xu, J.; Bolan, N.; Wang, H.; Tang, C. Chemical and biological immobilization mechanisms of potentially toxic elements in biochar-amended soils. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 50, 903–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabai, M.A. Soil enzymes. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2. Microbiological and Biochemical Properties; SSSA Book Series No. 5; Weaver, R.W., Angle, J.S., Bottomley, P.S., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1994; pp. 775–833. [Google Scholar]
- Moeskops, B.; Sukristiyonubowo; Buchan, D.; Sleutel, S.; Herawaty, L.; Husen, E.; Saraswati, R.; Setyorini, D.; De Neve, S. Soil microbial communities and activities under intensive organic and conventional vegetable farming in West Java, Indonesia. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2010, 45, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, A.B.; Sheaffe, M.J. Urease activity in soils. Plant Soil 1973, 39, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.G.; Zhang, W.; Yan-Bin, L.I.; Sun, Y.Y.; Bian, X.M. Effects of Long-Term Continuous Cropping System of Cotton on Soil Physical-Chemical Properties and Activities of Soil Enzyme in Oasis in Xinjiang. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2009, 42, 725–733. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Sarkar, B.; Shaheen, S.M.; Gielen, G.; Bolan, N.; Guo, J.; Che, L.; Sun, H.; et al. Animal carcass- and wood-derived biochars improved nutrient bioavailability, enzyme activity, and plant growth in metal-phthalic acid ester co-contaminated soils: A trial for reclamation and improvement of degraded soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 261, 110246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Dai, Q.; Jin, X.; Dong, X.; Peng, J.; Wu, M.; Liang, N.; Pan, B.; Xing, B. Negative Impacts of Biochars on Urease Activity: High pH, Heavy Metals, Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons, or Free Radicals? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12740–12747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Liu, L.; Zeng, G.; Xu, P.; Huang, C.; Deng, L.; Wang, R.; Wan, J. The effects of rice straw biochar on indigenous microbial community and enzymes activity in heavy metal-contaminated sediment. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, J.T.F.; Chen, X.; Deng, W.; Chai, Y.; Ng, C.W.W.; Wong, M.H. Effects of biochar on bacterial communities in a newly established landfill cover topsoil. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 236, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Bai, S.H.; Zhang, Y.; Teng, Y.; Xu, Z. Assisted phytoremediation of a co-contaminated soil with biochar amendment: Contaminant removals and bacterial community properties. Geoderma 2019, 348, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbeiss, S.; Gleixner, G.; Antonietti, M. Effect of biochar amendment on soil carbon balance and soil microbial activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Ren, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Luo, L.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, A. Physicochemical features, metal availability and enzyme activity in heavy metal-polluted soil remediated by biochar and compost. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, L.; Li, L.; Bian, R.; Yan, J.; Quan, G.; Liu, Y.; Ippolito, J.A.; Wang, H. Short- and Long-Term Biochar Cadmium and Lead Immobilization Mechanisms. Environments 2020, 7, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments7070053
Cui L, Li L, Bian R, Yan J, Quan G, Liu Y, Ippolito JA, Wang H. Short- and Long-Term Biochar Cadmium and Lead Immobilization Mechanisms. Environments. 2020; 7(7):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments7070053
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Liqiang, Lianqing Li, Rongjun Bian, Jinlong Yan, Guixiang Quan, Yuming Liu, James A. Ippolito, and Hui Wang. 2020. "Short- and Long-Term Biochar Cadmium and Lead Immobilization Mechanisms" Environments 7, no. 7: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments7070053
APA StyleCui, L., Li, L., Bian, R., Yan, J., Quan, G., Liu, Y., Ippolito, J. A., & Wang, H. (2020). Short- and Long-Term Biochar Cadmium and Lead Immobilization Mechanisms. Environments, 7(7), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments7070053