Abstract
To assess environmental risks related to the mobility and toxicity of AgNPs, the chemical availability of AgNPs and polyvinylpyrrolidone-coated AgNPs (PVP-AgNPs) in three agricultural soils was quantified in a pot experiment. Porewater collection and soil extractions with 0.01 M CaCl2, 0.4 M Glycine (pH 1.5) and 0.05 M NH4-EDTA were performed. The effect on soil exoenzyme activities was also assessed. Porewater concentration was low (<0.4% and <0.04% of dosed Ag, for AgNPs and PVP-AgNPs, respectively) and only detected in acidic soils (pH 4.4 and 4.9). The PVP-coating reduced the downward mobility of AgNPs in soil and possibly also their dissolution rate (and subsequent release of dissolved Ag+ ions into porewater). The effect of variation in organic matter on soil enzymatic activity was larger than that of AgNPs, as no significant additional inhibitory effect from Ag could be observed. Only at low pH and in the presence of complexing ligands that form very stable Ag complexes (0.4 M Glycine extraction at pH 1.5) up to 58% of the Ag added to soil was released (independently of PVP coating). An extraction with glycine is proposed as a useful indicator of potentially available Ag in soils.
1. Introduction
There is a growing development and use of nano-enabled products in agriculture due to their increased activity associated with the small size and to the potential for reduction of the amount of applied active ingredients [1,2,3]. Given its antimicrobial and chemical properties, silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) have been used in a large number of global market products, particularly for disinfection purposes [4,5,6,7]. Potential applications of AgNPs as fungicides in agriculture have also been investigated [8,9]. These were proven effective against pathogenic fungi which commonly affect crops such as corn, barley and rice or against mildew infestation on roses [10,11,12]. Suggested advantages on the use of AgNPs-enabled fungicides compared to AgNO3 or to conventional formulations relate to higher efficacy at lower application doses (15 g AgNPs ha−1, compared to commonly applied doses of 105 g ha−1 to 6 kg ha−1, for conventional fungicides), and reduction in human toxicity [8,10,11,12].
To develop environmentally safe management practices related to the use of AgNPs in agriculture, however, there is a need to understand geochemical processes regulating the fate of AgNPs in natural media like soil and to assess potential risks on terrestrial systems. Upon entry in the terrestrial ecosystem, a number of transformations occur depending on biogeochemical conditions that control fate, behaviour, and ecotoxicity of NPs in soil [13,14,15] including pH, organic matter, soil texture, clay content and type and amount of metal oxides, or presence of microbes [6,13,16,17]. Transformations of AgNPs in soil include oxidative dissolution, aggregation to the soil ligands or stabilization in suspension through natural coating by dissolved organic matter (DOM) [6,16,18,19,20,21,22]. The type of (artificial) surface coating of NPs also affects transformation processes like aggregation and dissolution processes in natural systems [23,24,25,26] which subsequently might affect their fate in soils. Several studies reported on the fate of AgNPs (and of Ag2S NPs) in agricultural soils following the application of sludge from wastewater treatment plants (WWTP) and biosolids [16,19,24,27,28]. These investigations showed that partitioning of Ag to pore water from AgNPs directly applied to soils is generally limited under natural soil conditions, and dependent on NPs oxidative dissolution; also, DOM stabilizes AgNPs in pore water and suppresses Ag oxidation, with short-chained compounds being preferentially adsorbed over long-chained, aromatic compounds; finally, organic ligands such as those present in root exudates or fertilizers may further facilitate the release of ionic Ag and increase bioavailability of Ag to organisms and plants [16,19,20,24,27,28]. So far, few studies addressed the impact of variable soil conditions and AgNPs properties on their geochemical fate in soil and subsequent potential effects on soil ecological functions and biodiversity. Such assessments are essential in order to promote and regulate the use of NPs in agriculture [29,30,31].
Traditionally, the chemical fate and ecological risks of metals including those in the form of NPs in soil in the terrestrial environment is assessed using several single extractions of increasing extraction strength. Dilute salt extractions (e.g., 0.01M CaCl2) or extractions using chelates (e.g., 0.4 M glycine or 0.05 M NH4-EDTA) [32,33] are able to represent the direct (or plant) availability or potential availability of metals (exchangeable and organically bound fraction of metals from soils) quite well [33,34,35]. Here we extend the use of such methods to evaluate the geochemical availability of Ag from both AgNPs and PVP-AgNPs in agricultural soils.
Aside from the geochemical aspects also the impact of NPs on ecosystem functioning is relevant since AgNPs and released silver cations can have a detrimental effect on soil (micro)organisms [15,36,37] and soil enzymes, indirectly affecting microbial-mediated processes including nutrients cycling [38]. Soil exoenzyme activities are considered relevant indicators of the overall biological functioning of soils. Even more so since activity levels, related to microbial-mediated processes [38,39], respond rapidly to changes in soil conditions like those brought forth by the introduction of AgNPs. So far, however, contrasting results were reported on the effect levels of AgNPs once added to soil on exoenzymes activities. Hänsch and Emmerling [36] tested the effects of AgNPs on the activities of leucine-amino-peptidase, β-cellobiohydrolase, acid phosphatase, β-glucosidase and xylosidase, and observed no effect of AgNPs for an Ag dose up to 0.32 µg g−1. Shin et al. [40] evaluated the inhibitory effect of AgNPs on the activities of specific soil exoenzymes related to nutrient cycles including urease, acid phosphatase, arylsulfatase and β-glucosidase, and found that AgNPs were capable of inhibiting exoenzyme activity but within a rather wide range from 1 to 1000 µg g−1. Shin et al. [40] attributed the observed adverse effects to that of the AgNPs themselves rather than that of toxicity of dissolved Ag+ ions. Similarly, Peyrot et al. [38] observed that soil enzyme activities were inhibited by particulate forms of AgNPs. Gaddam et al. [39] evaluated the effects of indigenous mycogenic AgNPs on soil exoenzymes, in mine-waste contaminated soils and observed an impact on activities of urease, phosphatase, dehydrogenase and β-glucosidase of AgNPs at Ag concentrations of 150 µg g−1.
The aim of the present study was twofold: (i) to evaluate the effect of soil properties and of a polymer coating on the geochemical distribution of AgNPs added to soil, and (ii) to assess the inhibitory effects on enzymatic activities of five soil exoenzymes related to nutrient cycles (β-glucosidase, cellulase, acid phosphatase, protease and urease.
In addition, the suitability of various soil extraction tests to characterize environmentally and agriculturally relevant pools of Ag in treated soil was evaluated. Polyvinylpyrrolidone was selected as a representative polymer coating because it has been widely used to improve long-term colloidal stability of AgNPs. A pot experiment was conducted to quantify the soil-pore water partitioning of AgNPs from soils, as well as the potential availability of Ag retained in the soil solid matrix upon addition of both coated and uncoated AgNPs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Characterization of Soil Samples
Soil samples from agricultural soils were collected from the 0 to 10 cm layer from non-contaminated grassland fields located in mining, rural and industrial areas across Portugal (located at Southwest, Centre, and Northwest Portugal, respectively) to ensure variability in soil type and soil properties, notably in pH, organic matter, and clay content. Samples were taken using a plastic spade, stored in plastic bags, air-dried at room temperature until constant weight and subsequently sieved at <2 mm (using a Nylon® sieve, Bioblock Tamis Nylon® DIN 4195, by Fisher Scientific SAS, Illkirch Cedex, France). This fraction was used for soil analyses and pot experiments.
The following parameters were determined in soil samples: pH-CaCl2, organic carbon content, clay content. Soil pH was measured using a glass electrode in a 1:5 (v/v) suspension of soils in CaCl2 according to the ISO 10390:1994 procedure. Organic carbon (OrgC) was determined after addition of hydrochloric acid to remove carbonates present (ISO 10694:1995). The clay content was analyzed using a Coulter LS230 laser diffraction particle size. Cation exchange capacity (CEC) was determined in barium chloride solution buffered at pH = 8.1 using triethanolamine as described by Bascomb [41].
Pseudo-total concentrations of Ag, Al, Ba, Cd, Cu, Cr, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn in soils were determined by aqua regia digestion; 3.0 g of dried soil were extracted with 21 mL HCl and 7 mL HNO3 (ISO 11466:1995)). Levels of chemical elements in the extract were measured by ICP-MS (Thermo X Series) according to ISO 17294-1:2005 and ISO 17294-2:2003.
2.2. Synthesis of AgNPs and Characterization of AgNPs Colloids
AgNPs were synthesized by reduction of silver nitrate (AgNO3) with an excess of sodium borohydride (NaBH4), needed to reduce the ionic silver and to stabilize the silver nanoparticles as described by Mulfinger et al. [42]. A 30 mL of NaBH4 solution (2.0 mM) (NaBH4, >96%; Sigma Aldrich, Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany) chilled in an ice-bath and under stirred vigorously with a magnetic stir, was slowly mixed (drop by drop) with 10 mL of AgNO3 (1.0 mM) (AgNO3, 99.9%; Sigma Aldrich, Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany). Stirring was ceased upon completion of the addition of 2 mL of silver nitrate. The resulting suspension which exhibited a light-yellow color was kept in the dark, at room temperature until analysis and used as stock suspension for soil amendment.
PVP-AgNPs were synthesized by the same procedure previously described through a chemical reduction method from the aqueous solution of silver nitrate using PVP as a stabilizing agent in the presence of sodium borohydride as a reducing agent [43]. The colloidal suspension was stored at room temperature, in the dark until analysis and use in amendment experiments.
The morphology of the AgNPs colloids was determined by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) using a Hitachi H-9000 TEM microscope operating at 300 kV and equipped with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) (Hitachi High-Tech Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). Samples for TEM analysis were prepared by putting one drop of AgNPs colloids onto a carbon-coated copper grid and then letting the solvent evaporate. The size of the AgNPs was evaluated by dynamic light scattering (DLS) using a Malvern Zeta-Sizer Nano-ZS (Model Zen3500, Malvern Panalytical Ltd., Malvern, UK), and derived from TEM images (mean NPs diameter was quantified based on measurements of at least 200 individual particles using ImageJ software). UV−Vis absorption spectra for the AgNPs were determined on a Jasco V-560 UV-VIS spectrophotometer (300–700 nm). Quartz cuvettes with 1cm-pathlength were used as sample holder for all UV-Vis analysis. The zeta potential was determine using phase analysis light scattering. Three replicate measurements of zeta potential were performed for each sample.
Bulk concentrations of Ag in AgNPs stock suspensions were determined by elemental analysis by ICP-OES (Jobin Yvon Activa M, Horiba, Palaiseau, France) following microwave-assisted aqua regia digestion using Teflon vessels (microwave oven: MARS model, CEM). A sub-sample of 2 mL of each suspension was digested with 2 mL aqua regia. The limit of quantification for Ag was 4 µg L−1. The bulk average Ag concentration in the two colloidal suspensions was 20 mg Ag L−1 (n = 3).
2.3. Pot Experiments
For each soil, pots were amended with AgNPs, PVP-AgNPs, or used as control (n = 3 for each treatment and the control). The control pots were prepared by adding 140 mL of ultrapure water to 500 g of air dried soil to obtain a water content of 70% of the soil water holding capacity. A volume of 140 mL of either AgNPs or PVP-AgNPs colloidal suspension was added to each AgNP treated pot. Nanoparticle suspensions for each pot were sonicated for 30 s, immediately applied after sonication, and thoroughly mixed with soil using a wooden stick. The dose applied was equivalent to an average concentration of 5.6 mg Ag kg−1 soil assuming a homogeneous distribution over the 500 g of soil in the pot. The actual distribution in soil is measured after completion of the pot experiment. An average concentration of 5.6 mg Ag kg−1 soil is comparable to those used in studies addressing partitioning and toxicity [6,44,45]. During the trial period (30 days) all pots were weighted every 2 to 3 days. Ultrapure water was added from the top of the pots to maintain a constant moisture content.
2.4. Sampling and Analysis of Pore Water
To extract in-situ pore water samples each pot was equipped with RhizonTM solution samplers [31]. Samplers were installed at 4 cm (“SF sampler”) and 7 cm below the soil surface (“SB sampler”). The pore water samplers had a microfiltration membrane with a nominal pore size of 0.12–0.17 µm with a low sorption capacity and no ion exchange capacity [31].
Pore-water samples were collected at t = 24, 48, and 72 h after the addition of AgNPs and PVP-AgNPs to the soil, and once a week after that, until day 30. Pore-water samples were kept at 4 °C and analyzed for Ag by ICP-OES within 1 to 4 days. The limit of quantification for Ag was 4 µg L−1.
2.5. Analysis of Ag Retained in the Soil Solid Matrix
After 30 days, the soil material was removed from all pots, divided into two equal parts (upper–SF-and bottom–SB-layers) and air-dried for 3–5 days (until constant weight). The pseudo-total content of Ag, Al, Fe and Mn in soils were determined by extraction using aqua regia and subsequent analyses of the elements by ICP using the same methods to characterize the soils mg Ag kg−1 soil.
In addition, the following extraction procedures were applied to air-dried soil samples from the SF layer:
Extraction with 0.01 M CaCl2 (1:10 weight to volume ratio). Thirty mL of 0.01 M CaCl2 solution were added to 3 g of soil in a polypropylene screw closure bottles [21,46]. The bottles were mechanically shaken with end-over-end rotation for 2 h at room temperature. The extracts were centrifuged during 10 min at 3000 rpm and subsequently filtered using a Millipore filter unit and a filter paper (0.45 µm). A portion of each filtrate was collected and preserved at 4 °C until analysis of Ag, Al, Fe and Mn by ICP-OES.
Extraction with 0.4 M glycine (adjusted to pH 1.5, with 37% HCl stock solution) at a 1:100 weight to volume ratio. Five hundred mg of air-dried soil sample was weighted into a polypropylene screw closure bottle and 50 mL of a 0.4 M solution were added [47]. The bottles were placed in an orbital incubator shaker at 37 °C for and shaken for 1 h. To ensure that all pH values were within 0.5 units of the starting pH (1.5), the pH was measured in part of the unfiltered extraction fluid. A portion of each filtrate was collected and preserved at 4 °C until analysis of Ag, Al, Fe and Mn by ICP-OES;
Extraction with 0.05 M NH4-EDTA solution adjusted to pH 7 with 37% HCl stock solution. Thirty mL of 0.05 M NH4-EDTA solution were added to 3 g of air-dried soil material in polypropylene bottles [48]. The bottles were placed in an orbital incubator shaker at room temperature and shaken for 1 h. The extracts were filtered using a Millipore filter unit and a filter paper (0.45 µm). A portion of each filtrate was collected and preserved at 4 °C until analysis of Ag, Al, Fe and Mn by ICP-OES.
All chemicals were of analytical grade or better and all solutions were prepared using ultrapure water. All extractions were performed in duplicate. Two extraction blanks were included in each batch of 20 extraction bottles.
2.6. Analysis of Soil Exoenzymes Activities
Soil sub-samples from the SF layer of pots at the end of the 30 days were also collected and stored at 4 °C. Samples were passed through a 2 mm sieve before analysis, and their dry matter content was determined to express the enzymatic activity on an oven-dried soil weight basis (105 °C, 48 h).
Acid phosphatase activity was measured by incubating 1 g of soil with p-nitrophenyl phosphate in modified universal buffer (pH 6.5, 4 mL) at 37 °C, as described by Alef et al. [49]. After 1 h, 0.5 M CaCl2 (1 mL) was added and the p-nitrophenol (PNP) released was extracted with 0.5 M NaOH (4 mL) and measured spectrophotometrically at 400 nm.
β-glucosidase activity was measured according to Eivazi and Tabatabai [50] and Alef and Nannipieri [51], in the same way as the acid phosphatase activity, except that the substrate was p-nitrophenyl-β-D-glucopyranoside and that the PNP released was extracted with 0.1 M tris(hidroxymetil)aminometane-NaOH at pH 12.0. β-glucosidase and acid phosphatase activities were both expressed in µmol PNP g (soil, d.w.)−1 h−1.
Cellulases activity was determined according to Hope and Burns [52] and refers to the combined action of endo-1,4-β-D-glucanase, exo-1,4-β-D-glucanase and β-D-glucosidase on Avicel, a purified depolymerised alpha cellulose. The reaction occurred by incubating 1 g of soil for 16 h at 40 °C, in a 0.1 M acetate buffer (pH 5.5, 0.2% NaN3). The reducing sugars produced were determined spectrophotometrically at 520 nm, after the addition of Cu(II) and molybdo-arsenate reagents. Cellulases activity was expressed in µmol glucose g (soil, d.w.)−1 h−1.
Urease activity was determined as described by Kandeler and Gerber [53], measuring the NH3 released after incubating by incubating 5 g of soil with a solution of urea for 2 h at 37 °C, in a borate buffer (pH 10). The ammonium content of the centrifuged extracts was determined spectrophotometrically, at 690 nm, after reaction with sodium dicloroisocyanide 0.1%. Urease activity was expressed in µmol NH4+-N g (soil, d.w.)−1 h−1.
Protease activity was measured after the incubation of 1 g of soil with sodium caseynate (2% w/v) in Tris-buffer pH 8.1, for 2 h at 50 °C [54,55]. Released tyrosine reacted with Folin-phenol reagent to form a blue complex, which was determined spectrophotometricaly at 700 nm. Protease activity was expressed in mmol tyrosine g (soil, d.w.)−1 h−1. All analytical measurements were carried out in triplicate.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Results for the soil enzymatic activities were analyzed using a Factorial Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) with soil type and AgNP treatment as factors which could explain their variance, and possible interactions of statistical significance. Moreover, results for each soil type were subjected to one-way ANOVA to discriminate if there was an effect of the AgNP treatments on soil enzymatic activities. Whenever significant differences were found (p < 0.05), a post hoc Tukey Honest Significant Difference (HSD) test was used to further elucidate differences among means (p < 0.05). Statistical analysis was carried out with the software Statistica 6.0.
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Soil Samples
Properties of the soils used in pot experiments are summarized in Table 1. Soil pH measured in 0.01 M CaCl2 ranged from pH 4.4 to 6.3 which is representative for agricultural soils from industrial, mining and rural areas in Portugal [34,56]. Soil organic carbon (Org C) ranged from 0.8% to 2.1%. The soil clay content varied from 2.6% in the soil from the industrial area to approx. 20% in soils from the mining and rural areas. The agricultural soil from the rural area had the highest concentration of Al and Fe compared to soils from the mining and industrial areas which is related largely to difference in the geochemical composition of the soil parent material. The analysis of other elements including Ba, Cd, Cu, Cr, Ni, Pb and Zn, measured levels in soils in this study are in line with values observed for Portuguese natural non-contaminated soils [56].

Table 1.
Soil properties, Al and Fe content for agricultural soils (mining, industrial and rural).
3.2. Characterization of AgNPs
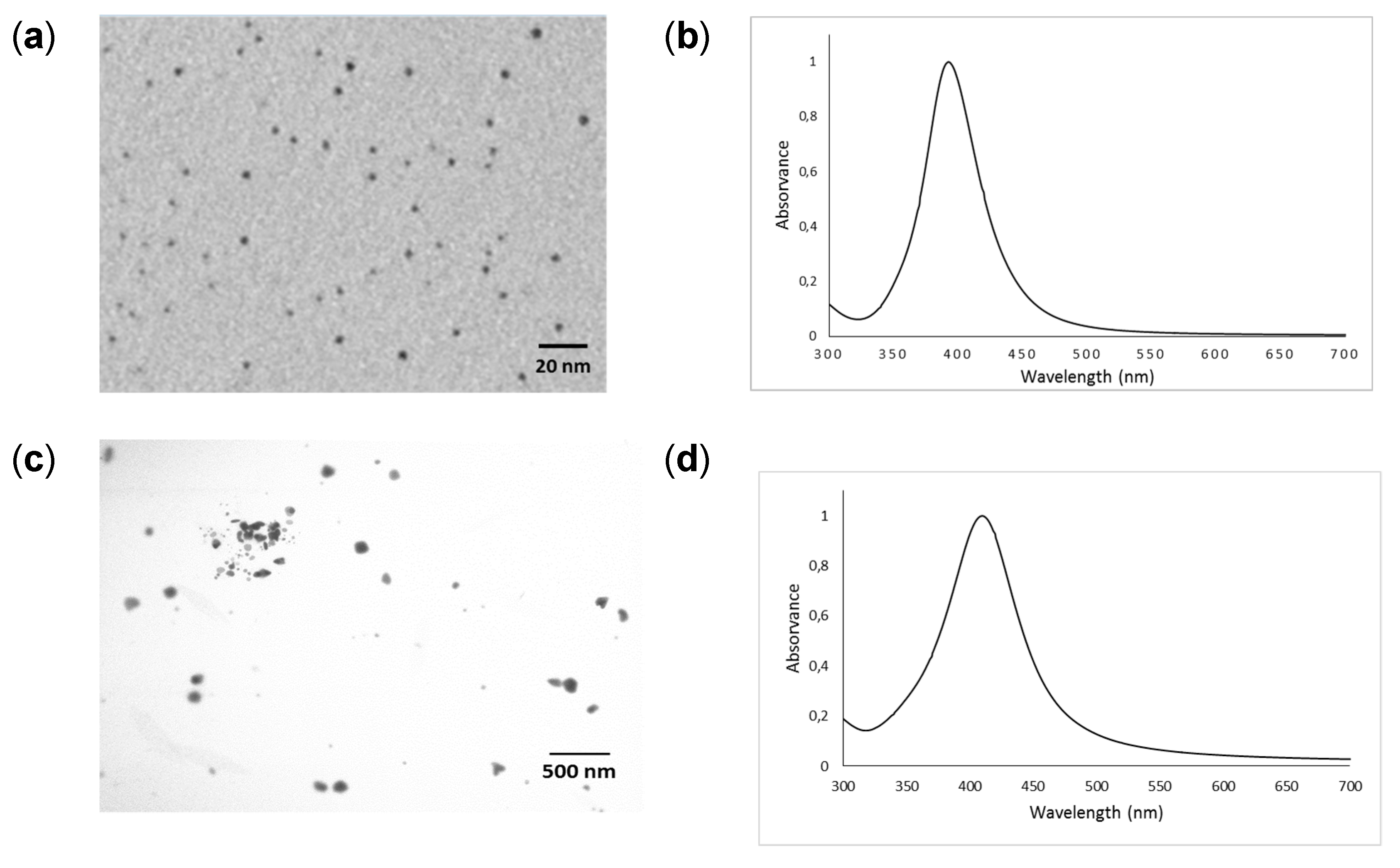
The TEM images and UV–VIS absorption spectra of the synthesized AgNPs and PVP-AgNPs are shown in Figure 1a,b and Figure 1c,d, respectively. The TEM images show that AgNPs and PVP-AgNPs prior to application to the soil are predominantly present as nanospheres. The estimated mean diameter of AgNPs determined by TEM was 2.9 ± 0.6 nm and ranged from 1.5 to 4.4 nm (n = 208). For PVP-AgNPs, the estimated mean diameter was 101 ± 14 nm and ranged from 57 to 141 nm (n = 105). The mean hydrodynamic diameter of AgNPs and PVP-AgNPs as determined by DLS was 24.2 and 110.6 nm, respectively. The presence of the capping agent (PVP) resulted in a markedly higher hydrodynamic diameter for the coated AgNPs compared to those from the colloidal Ag particles prepared by the borohydride method. As expected, the UV-VIS spectra (Figure 1b,d) of the AgNPs and PVP-AgNPs colloids show localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) bands at 393 nm and 412 nm, respectively [42,43].
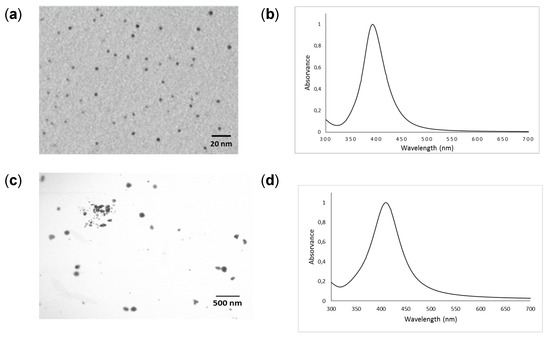
Figure 1.
Characterization of silver and silver coated with polyvinylpyrrolidone nanoparticles. (a) TEM image for the synthesized Ag colloid (b) UV-visible absorption spectra (c) TEM image for the synthesized PVP-Ag colloid (d) UV-visible absorption spectra.
The mean zeta potential of the synthesized AgNPs and PVP-AgNPs was −33.5 ± 2.7 mV and −11.8 ± 0.7 mV (n = 3), respectively. The pH values of the colloidal suspensions (AgNPs and PVP-AgNPs) were 9.23 and 5.21 (n = 3), respectively.
3.3. Pore Water Concentrations of AgNPs in Soils
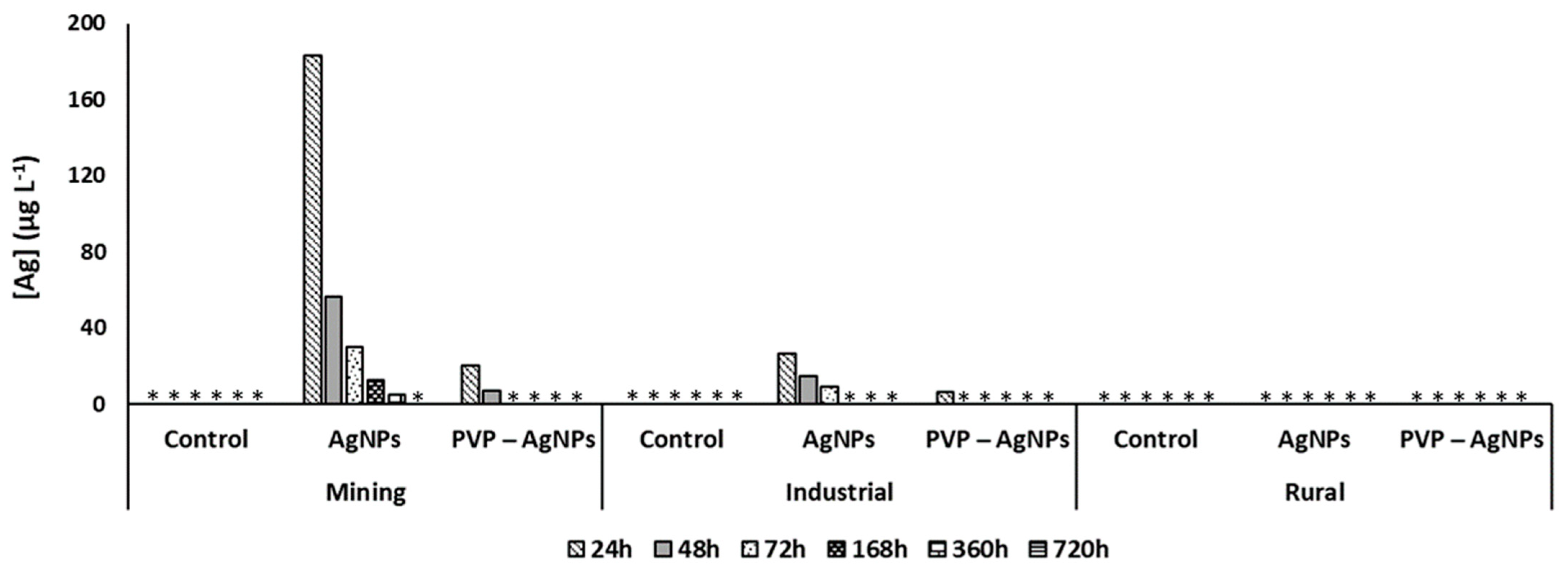
Figure 2 shows Ag pore water concentrations collected by SF samplers in all pots.

Figure 2.
Silver content in surface (SF) pore water samples during the 720 h of study for control, and AgNPs and PVP-AgNPs soil amendment in soils from mining, industrial and rural area. (*) below the limit of quantification.
In the SB samples, all Ag pore water concentrations remained below the quantification limit of 4 µg L−1. The Ag concentration in the SF pore water samples collected from the non-treated control pots and in treated pots containing rural soil was also below the quantification limit during the 30 days of the monitoring (Figure 2). In soils from both the mining and industrial areas, the pore water concentration of Ag was below 184 µg L−1 (for AgNPs) and below 21 µg L−1 (PVP-AgNPs) and decreased rapidly during a first period of 72 h upon dosing (Figure 2). Expressed as percentage of the dose of Ag added, the amount of Ag in pore water measured in SF soils decreased from 0.4% (24 h) to 0.01% (360 h) in the mining area and from 0.06% (24 h) to 0.02% (72 h) in industrial soil (Figure 2). In case of the PVP-AgNPs treated mining soils, the percentage of Ag in pore water decreased from 0.04% after 24 h to 0.01% after 48 h. For the industrial soil, 0.02% of the total added amount of Ag in the PVP-AgNPs treated soils was detected in pore water collected in the first day after amendment and remained below detection thereafter.
The observed low pore water concentrations of Ag in soil were only slightly higher than previous reports showing that 87% to 99% of the initial batch of AgNPs added to soil became retained in the solid matrix immediately after amendment [31,57].
Release of Ag into the pore water is known to be dependent on NPs dissolution and partly controlled by soil properties including soil pH and CEC [16,24,31]. The oxidative dissolution of Ag is favored at acidic pH [23]. In addition, higher Ag ions retention is expected in the soil with higher CEC. In this study, the variability in soil pH and CEC was in line with observed differences in the Ag pore water concentrations. The near neutral pH of 6.3 measured in the rural soil most likely limited dissolution of AgNPs, and the high CEC of 33 meq/100 g could have contributed to further immobilize Ag+ ions in the solid phase and reduce the release into the pore water from the rural soils compared to that of the other soil types. The more gradual decrease of Ag pore water concentrations from mining and industrial soils with time can be explained by the ongoing sorption of dissolved Ag+ ions to the soil solid reactive surfaces. Here, iron oxide surface groups, reduced S groups of organic matter, and microbial surfaces are relevant. In addition, precipitation of Ag in less soluble forms can occur [17,57,58]. Previous studies reported that changes in Ag speciation in soils and association of Ag with iron oxides and reduced S-groups are particularly important to retain Ag in soil over time [58].
The lower Ag pore water concentrations observed in PVP-AgNP treated soils compared to AgNPs treated soils (Figure 2) could result from a kinetically faster heteroaggregation of PVP-AgNPs compared to the non-coated NPs related to the interaction of the polymer coating (PVP) with humic substances present in soil organic matter. Moreover, higher pore straining is expected for PVP-AgNPs due to their larger size and hydrodynamic diameter compared to that of non-coated NPs [59]. Finally, the PVP coating also can reduce the dissolution rate of AgNPs in soil and thus leading to lower pore water concentrations of dissolved ionic Ag [24].
3.4. Concentration of Ag Retained in the Solid Matrix
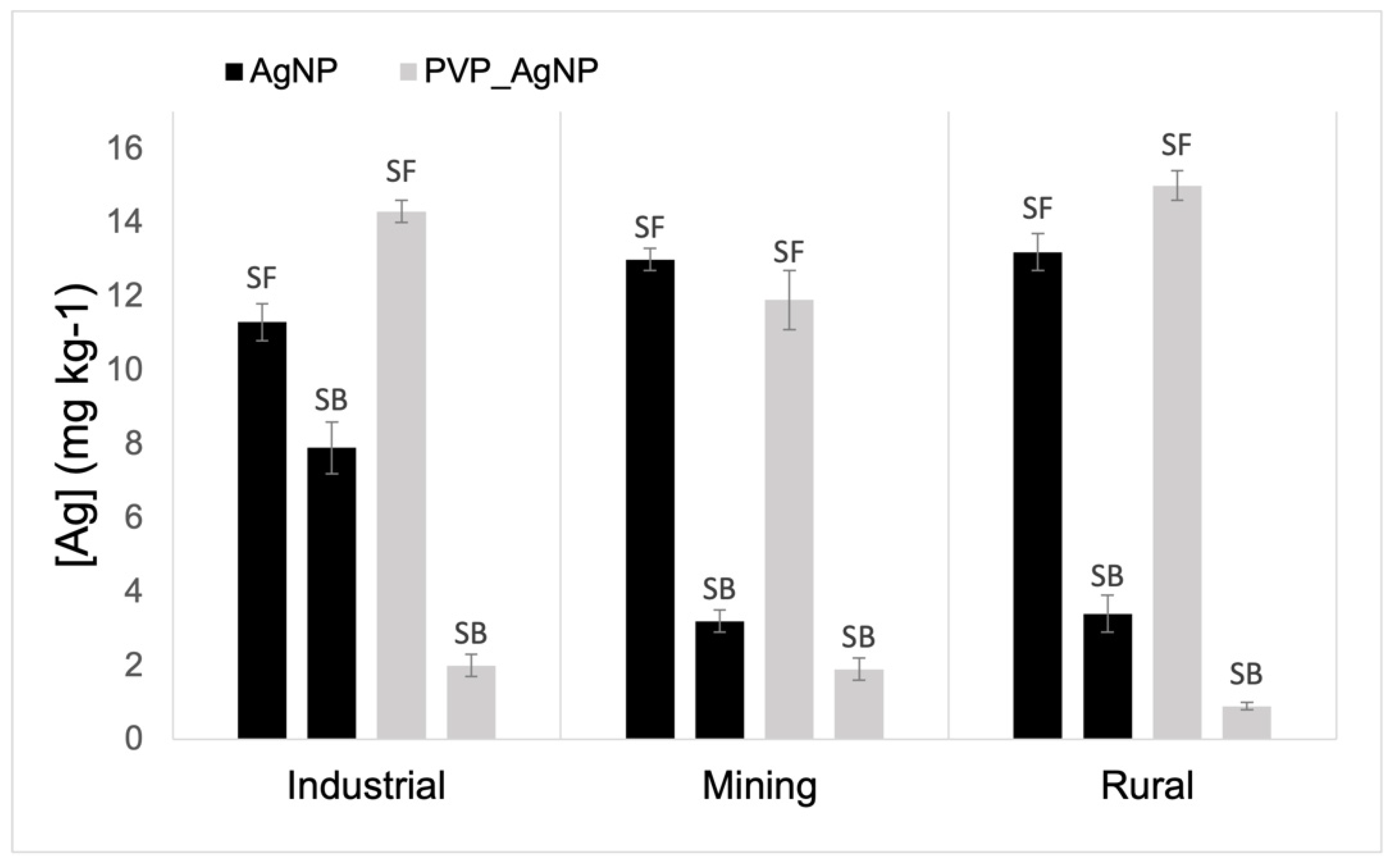
Figure 3 shows Ag concentration in soil as determined by the aqua regia (AR) digestion. The Ag content in SF soils was significantly higher (p < 0.01) than that in SB soils for pots of the three soils. This indicates that Ag is largely retained in the surface soil layers resulting in a highly heterogeneous distribution of dosed Ag between topsoil and subsoil layers in the pot. Moreover, the AR extractable Ag in the AgNPs treatment (11.3 to 13.2 mg kg−1) was significantly lower (p < 0.01) than that of the PVP-AgNPs treated soil (11.9 to 15.0 mg kg−1), suggesting that PVP-AgNPs are less mobile which then results in a higher concentration in the topsoil. This difference in mobility between PVP coated and non-coated NPs was further confirmed in the SB samples of all soils. In SB samples, AR extractable Ag ranged from 3.2–7.9 mg kg−1 in AgNP treated soils but was lower in PVP-AgNPs treated soils (0.9–2.0 mg kg−1). The low downward mobility of AgNPs in pots was particularly noticeable in samples from the mining and rural area with elevated clay content compared to the soil from the industrial area (Figure 3). This confirmed that the clay content was associated with the retention and reduced mobility of AgNPs in soils, particularly for uncoated particles.

Figure 3.
Total concentration of Ag (mg kg−1, d.w.), in upper (SF) and bottom layers (SB) of the three soils (mining, industrial and rural) collected from pots after 30 days of treatment with AgNP or PVP-AgNPs.
3.5. Potential Availability of Ag Retained in the Solid Matrix
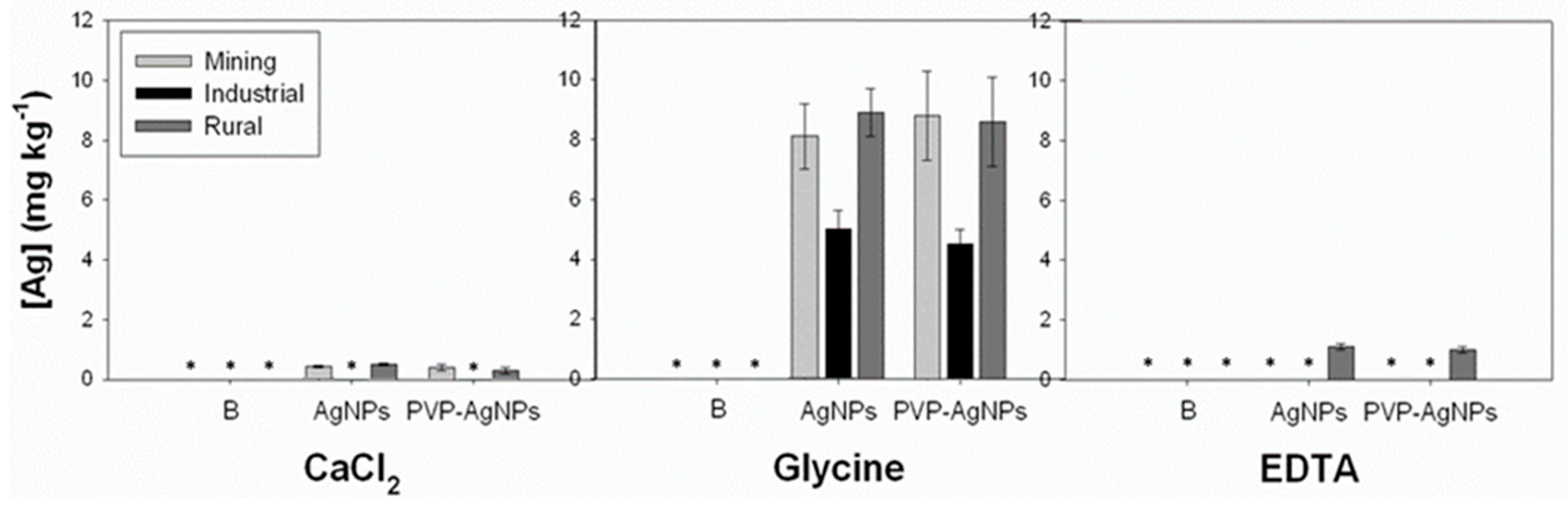
Figure 4 shows the concentrations of Ag extracted from SF soil using 0.01 M CaCl2, 0.4 M Glycine and 0.05 M NH4-EDTA. The amount of Ag extracted from soil decreased in the order Glycine > EDTA > CaCl2 (Figure 4). Both 0.01 M CaCl2 and EDTA extracted very low concentrations of Ag from soil: 0.3–0.5 mg kg−1 (CaCl2) and 1.0–1.1 mg kg−1 (EDTA) (corresponding to <3.2%, and <8.5% of total Ag added, respectively). In contrast to this, the glycine solution extracted between 21% and 58% (4.6–8.8 mg kg−1) of the total Ag added to the three soils.

Figure 4.
Concentration of Ag (in mg kg−1, d.w.) extracted from the SF layer of the three soils (mining, industrial and rural) after 30 days of soil treatment with AgNPs or PVP-AgNPs using three different single extraction methods (0.01 M CaCl2; 0.4 M glycine and 0.05 M NH4-EDTA). Control (B) pots contained non-amended soils. (*) below the limit of quantification.
Even though pH is a key factor that contributes to the extractability of Ag from soil, the large difference in pH between the three extracts alone is not sufficient to explain the differences in Ag extractability for the glycine or EDTA extraction tests. A study by Cruz et al. [60] revealed that the extraction efficiency using dilute (0.43 M) and concentrated (2M) HNO3 extractions was far lower compared to that of the glycine test performed at an equally acid level (pH 1.5). This confirmed that both low pH and the presence of complexing ligands that form very stable complexes with Ag are required to release appreciable amounts of Ag retained in soil [27,60]. In contrast to the documented suitability of the CaCl2 extraction to mimic the actual availability of metals from NPs like those from CuONPs [20], the 0.01 M CaCl2 extraction appeared to be a poor predictor of the available Ag fraction in soils treated with AgNPs which is most likely due to the precipitation of AgCl [61].
The 0.4 M glycine solution was capable of extracting similar Ag concentrations from both PVP-AgNPs and non-coated AgNPs treated soils (Figure 4) suggesting that the PVP coating did not limit NPs dissolution at pH 1.5. The concentration of Ag extracted by glycine were, however, affected by differences in soil properties (Figure 4). Here, the glycine extraction efficiency in soils from the industrial area (OrgC = 2.1%) was low compared to that in soils from the rural areas (OrgC = 0.8%) or mining area (OrgC = 1.2%). Apparently, differences in soil organic carbon levels in the range that occurs in soils in Portugal has a large impact on the release of AgNPs from soil during the glycine extraction but is in line with the documented geochemical behavior of Ag in soils. The strong association of Ag with organic matter due to binding to reduced S groups present in organic matter is well-documented [58]. Due to this specific binding of Ag to the solid soil matrix approximately 40 to 60% of the total Ag pool in soil cannot be released using the glycine extraction and hence is believed to remain immobile and not available for humans in case of soil ingestion, for plants or soil dwelling organisms exposed to such levels of Ag in soil. Even soil acidification down to pH levels of 3 which, under normal conditions, is already quite extreme, is unlikely to result in substantial remobilization of these retained pools of Ag in soil.
3.6. Analysis of Soil Exoenzymes Activities
Soil exoenzyme activities were analyzed in SF soils of each pot only because the downward mobility of Ag in the soil was relatively limited, as previously discussed.
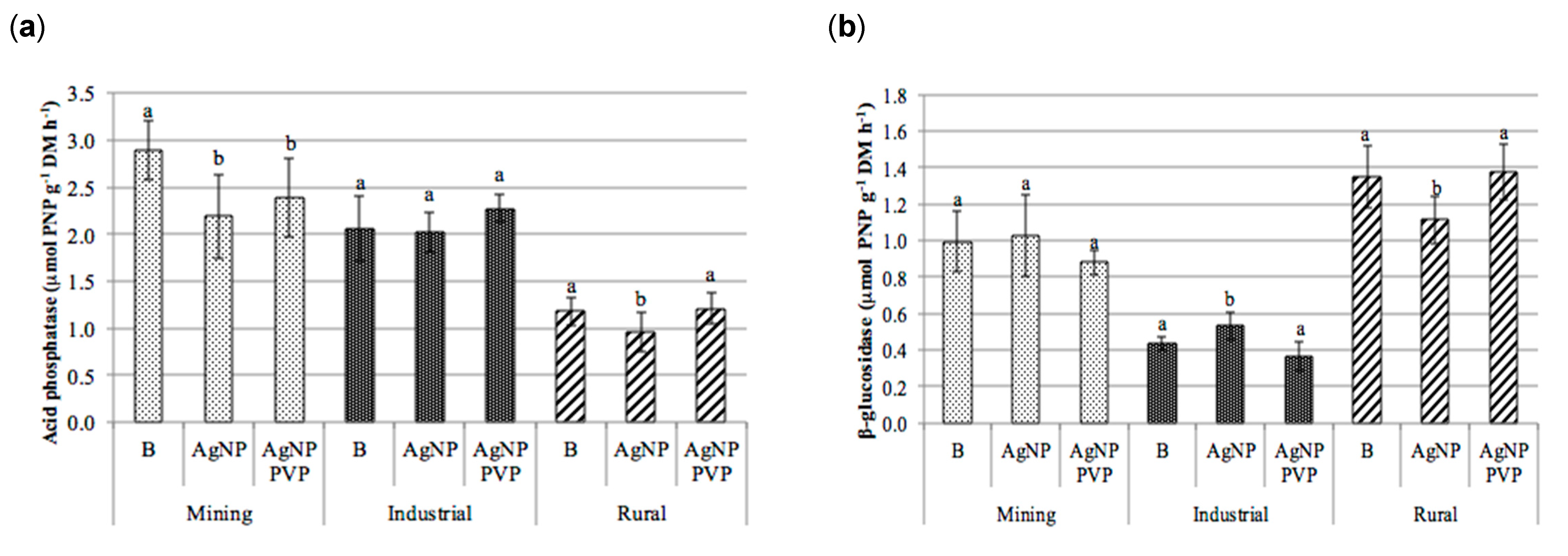
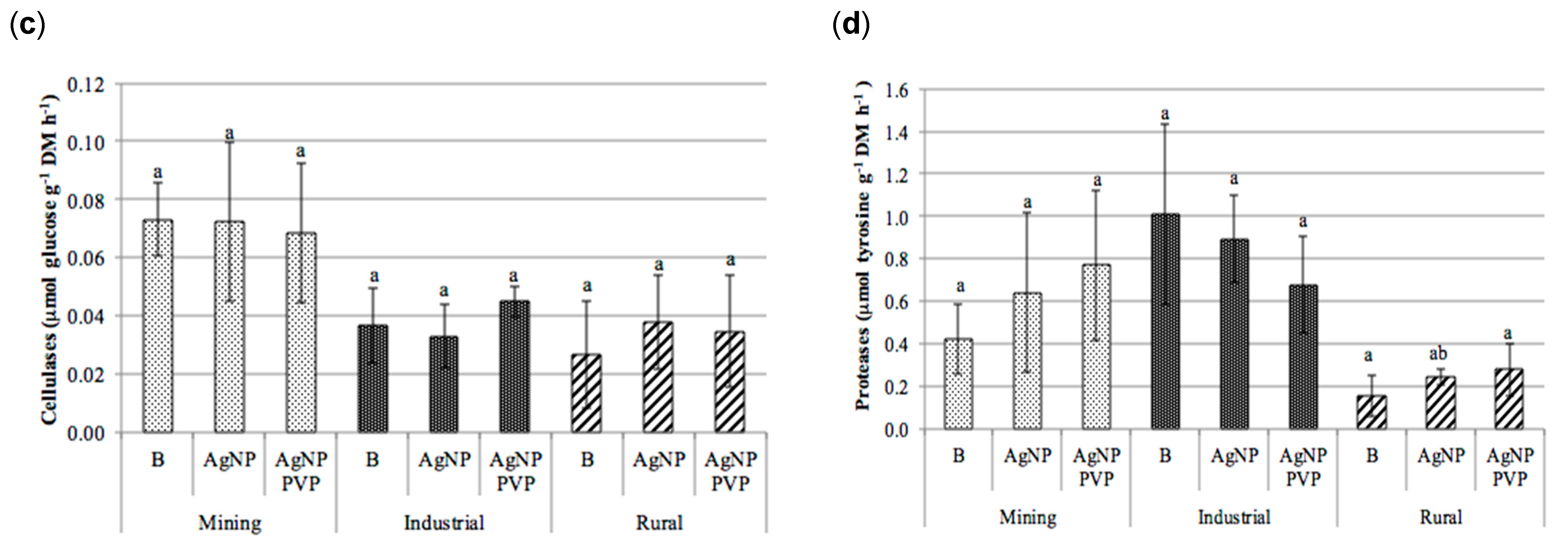
The test results revealed that there was no clear trend between treatment with either AgNPs or PVP-AgNPs and the enzymatic activities of β-glucosidase, cellulases, acid phosphatase or proteases (Figure 5).
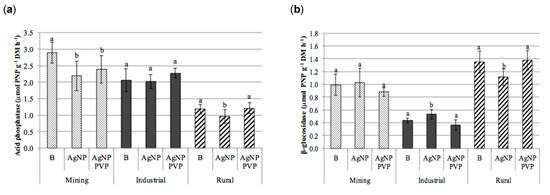
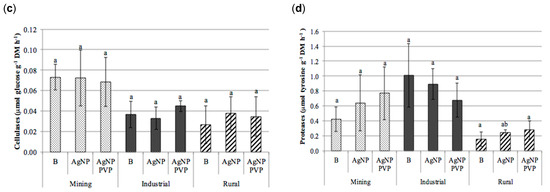
Figure 5.
Enzymatic activities obtained in the soils (mining, industrial and rural) subjected to the different treatments (B): blank; AgNPs: silver nanoparticles; and PVP-AgNPs: silver nanoparticles polyvinylpyrrolidone coated); (a) acid phosphatase (µmol PNP g−1 h−1), (b) β-glucosidase (µmol PNP g−1 h−1), (c) cellulases (µmol glucose g−1 h−1), and (d) protease (µmol tyrosine g−1 h−1) (mean ± standard deviation, n = 9). For each soil type, columns marked with the same letter are not significantly different (Tukey HSD test, p > 0.05). PNP: p-nitrophenol.
In the majority of soils and treatments no significant differences were observed between the control of each type of soil and its AgNPs or PVP-AgNPs treated counterparts. Exceptions to this were the mining soil were significant effects were observed for the acid phosphatase activity, which significantly decreased in the AgNPs and PVP-AgNPs treatments. This was also observed in case of the AgNPs application in the rural soil (Figure 5a), as well as for the β-glucosidase activity in the rural soil, which significantly decreased in the AgNPs treatment (Figure 5b). In general however, within the range of soil Ag concentrations applied in this study, the influence of soil origin and soil properties on the enzymatic activities was larger than that of the application of AgNPs (Figure 5 and Table 2).

Table 2.
Results from the Factorial ANOVA analysis (F values) for the soil exoenzymes activities.
In fact, results from the analysis of variance (Table 2) revealed that the soil type significantly affected soil exoenzyme activities (p ≤ 0.001) for all enzymes, whereas the effect of the type of AgNP treatment appeared to be significant only for the acid phosphatase activity. In addition, significant interactions between soil type and AgNP treatment were observed for β-glucosidase (p ≤ 0.001) and for acid phosphatase and proteases (p ≤ 0.01, Table 2), but not for cellulases. This again can be explained by differences in soil properties (Table 1). The low OrgC content of the rural soil (0.8%) was the most likely cause for the lower acid phosphatase, cellulase and protease activities, compared to the higher activity levels found in the mining and industrial soil.
The absence of a detectable impact of added Ag on soil enzymes activity at the Ag levels in soil applied in this study (11.3–15.0 mg kg−1) corroborates with the reported no-observed-effect concentrations (NOEC) for both the β-glucosidase and acid phosphatase activities [40]. In this study significant decreased activities for some soil enzymes (e.g., dehydrogenase, acid phosphatase and β-glucosidase), in soils treated with for AgNPs, only occurred at concentrations equal or higher than 100 mg kg−1 dry soil. This might explain that no consistent inhibitory effects were observed for those enzymes in the present study.
In the study by Shin et al. [40], the urease activity was especially sensitive to AgNPs, with significant decreased urease activities for AgNPs concentrations like those used in this study. However, the urease activities of the soils used in this study were below the quantification limit in all samples (<1.6 µmol N-NH4+ g−1 DM h−1), which did not allow to conclude on the effects of AgNPs or PVP-AgNPs to this enzyme activity.
4. Discussion
This study revealed that pore water Ag concentrations resulting from the application of non-coated and coated AgNPs to soils was very low (<184 µg L−1 (for AgNPs) and <21 µg L−1 (PVP-AgNPs), corresponding to <0.4% and <0.04% of dosed Ag, respectively). Measured Ag in soil pore water samples was mostly associated with the partition of dissolved Ag ions. Furthermore, dissolved Ag was detected only in topsoil samples from acidic soils and decreased further with an increase in soil organic carbon and clay content revealing the importance of soil properties in the retention of metallic NPs in soil along with their role in controlling NPs dissolution and bioavailability for plants and soil organisms. The type of NPs coating was an additional factor that controlled pore water concentrations and vertical displacement in soil. with the use of PVP-coated AgNPs that possess a larger hydrodynamic diameter resulted in lower pore water concentrations due to the combined effect of straining, reduced solubility and/or increased heteroaggregation with soil organic matter. This combined effect of reduced solubility, or increased retention in the topsoil, resulted in a 40–75% reduction of vertical displacement of PVP-AgNPs when comparing results with those from non-coated AgNPs. This effect was even stronger in soils with a higher clay content, higher pH and organic matter content. The impact of the PVP coating on the release of Ag seems to confirm that polymers can be used for a more controlled release of nanoforms of agrochemical products in soils and to reduce the potential risk of leaching of Ag to deep soil layers.
In view of its low direct availability in well-aerated soils the efficacy of the application of Ag-based NPs via soil for plant protection purposes may be questionable, unless it is intended to be used as a vector for controlled release of ionic Ag over time, e.g., at soil rhizospheres. In the rhizosphere of treated soils, the combined root exudation of protons and of low molecular weight organic ligands (e.g., citrate or malate) or aminoacids by plants under nutrient deficiency may potentially increase the dissolution and bioavailability of ionic Ag from AgNPs. This requires however further investigation. Moreover, targeting AgNPs application to plant rhizospheres must be accompanied by an integrated assessment of ecological risks since it may also cause higher potential localized exposure for sensitive receptors.
As for the soil exoenzymes activities studied, there was no clear effect of the AgNPs and of PVP-AgNPs on the enzymatic activities of β-glucosidase, cellulase, acid phosphatase and protease. In fact, for the Ag concentrations observed in the SF layer of in pots after 30 days of soil amendment (<16 µg g−1 dry soil), the influence of soil properties (particularly the low OrgC content) on the enzymatic activities surpassed that of the application of AgNPs, and no inhibitory effects in these soil enzymatic activities could be observed.
5. Conclusions
By far the highest extractability of Ag from soil was obtained in the presence of organic ligands (0.4 M glycine) in combination with acidic pH (pH 1.5) which was able to release between 33% and 74% of Ag retained in the upper soil after 30 days for the 3 soil types. This pool of extracted Ag seems not to be affected by polymer coating of AgNP, and likely reflects ionic Ag dissolved from AgNPs at pH 1.5 which formed stable complexes with glycine. These results suggest that the glycine extraction test could be used as a worst-case approximation for Ag release in risk assessment. This would correspond to the maximum amount of Ag ionic pool that potentially can be released from Ag-based NPs (e.g., in rhizospheres) and become available to plants and organisms in soils, regardless of polymer coatings.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.M.R.; methodology, E.P., P.A., P.F.A.M.R., S.M.R., and T.T.; investigation, N.C.C., M.F., C.M., and D.T.; resources, E.P., P.A., S.M.R., and T.T.; writing—original draft preparation, N.C.C.; writing—review and editing, P.A., P.F.A.M.R., and S.M.R.; supervision, A.C.D., E.P., and T.T.; funding acquisition, A.C.D., E.P., T.T., and S.M.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
S.M.R. acknowledges the financial support from the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT) (Project IF/01637/2013/CP1162/CT0020). Thanks are due to CESAM and to FCT/MCTES for the financial support to (UIDP/50017/2020+UIDB/50017/2020), through national funds. This work was supported by the project AgriTarget (POCI-01-0145-FEDER-029258 and PTDC/BAA-AGR/29258/2017) and project NanoFertil (POCI-01-0145-FEDER-016749-PTDC/AGR-PRO/6262/2014), funded by FEDER, through COMPETE2020—Programa Operacional Competitividade e Internacionalização (POCI), by LEAF (Linking Landscape, Environment, Agriculture and Food Research Unit), funded by FCT (UID/AGR/04129/2020) and by national funds (OE), through FCT/MCTES.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data utilized in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rodrigues, S.M.; Demokritou, P.; Dokoozlian, N.; Hendren, C.O.; Karn, B.; Mauter, M.S.; Sadik, O.A.; Safarpour, M.; Unrine, J.M.; Viers, J.; et al. Nanotechnology for sustainable food production: Promising opportunities and scientific challenges. Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 767–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raliya, R.; Saharan, V.; Dimkpa, C.; Biswas, P. Nanofertilizer for Precision and Sustainable Agriculture: Current State and Future Perspectives. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 66, 6487–6503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kah, M.; Kookana, R.S.; Gogos, A.; Bucheli, T.D. A critical evaluation of nanopesticides and nanofertilizers against their conventional analogues. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Badawy, A.M.; Luxton, T.P.; Silva, R.G.; Scheckel, K.G.; Suidan, M.T.; Tolaymat, T.M. Impact of Environmental Conditions (pH, Ionic Strength, and Electrolyte Type) on the Surface Charge and Aggregation of Silver Nanoparticles Suspensions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta-Videa, J.R.; Zhao, L.J.; Lopez-Moreno, M.L.; de la Rosa, G.; Hong, J.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L. Nanomaterials and the environment: A review for the biennium 2008–2010. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, R.; Wilkinson, K.J.; Sauvé, S. Partitioning of silver and chemical speciation of free Ag in soils amended with nanoparticles. Chem. Cent. J. 2013, 7, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Yin, Y.; Liu, J. Silver nanoparticles in the environment. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2013, 15, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogos, A.; Knauer, K.; Bucheli, T.D. Nanomaterials in Plant Protection and Fertilization: Current State, Foreseen Applications, and Research Priorities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 9781–9792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Upadhyaya, C.P.; Singh, A.; Abd-Elsalam, K.A.; Prasad, R. Applications of Silver Nanoparticles in Plant Protection. In Nanobiotechnology Applications in Plant Protection. Nanotechnology in the Life Sciences; Abd-Elsalam, K., Prasad, R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Sung, W.S.; Moon, S.; Choi, J.; Kim, J.G.; Lee, D.G. Antifungal Effect of Silver Nanoparticles on Dermatophytes. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 18, 1482–1484. [Google Scholar]
- Jo, Y.; Kim, B.H.; Jung, G. Antifungal Activity of Silver Ions and Nanoparticles on Phytopathogenic Fungi. Plant Dis. 2009, 93, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Park, C.S.; Murayama, M.; Hochella, M.F. Discovery and Characterization of Silver Sulfide Nanoparticles in Final Sewage Sludge Products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7509–7514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, S.M.; Trindade, T.; Duarte, A.C.; Pereira, E.; Koopmans, G.F.; Römkens, P.F.A.M. A framework to measure the availability of engineered nanoparticles in soils: Trends in soil tests and analytical tools. Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 75, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourinho, P.S.; van Gestel, C.A.M.; Lofts, S.; Svendsen, C.; Soares, A.; Loureiro, S. Metal-based nanoparticles in soil: Fate, behavior, and effects on soil invertebrates. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 1679–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelis, G.; Hund-Rinke, K.; Kuhlbusch, T.; van den Brink, N.; Nickel, C. Fate and Bioavailability of Engineered Nanoparticles in Soils: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 44, 2720–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutris, C.; Joner, E.J.; Oughton, D.H. Aging and soil organic matter content affect the fate of silver nanoparticles in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 420, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelis, G.; Pang, L.P.; Doolette, C.; Kirby, J.K.; McLaughlin, M.J. Transport of silver nanoparticles in saturated columns of natural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, G.V.; Espinasse, B.P.; Badireddy, A.R.; Richardson, C.J.; Reinsch, B.C.; Bryant, L.D.; Bone, A.J.; Deonarine, A.; Chae, S.; Therezien, M. Long-term transformation and fate of manufactured Ag nanoparticles in a simulated large scale freshwater emergent wetland. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7027–7036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batley, G.E.; Kirby, J.K.; McLaughlin, M.J. Fate and Risks of Nanomaterials in Aquatic and Terrestrial Environments. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klitzke, S.; Metreveli, G.; Peters, A.; Schaumann, G.E.; Lang, F. The fate of silver nanoparticles in soil solution—Sorption of solutes and aggregation. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 535, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.Y.; Spielman-Sun, E.; Rodrigues, S.M.; Casman, E.A.; Lowry, G.V. Time and Nanoparticle Concentration Affect the Extractability of Cu from CuO NP-Amended Soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2226–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Avellan, A.; Laughton, S.; Vaidya, R.; Rodrigues, S.M.; Casman, E.A.; Lowry, G.V. CuO Nanoparticle Dissolution and Toxicity to Wheat (Triticum aestivum) in Rhizosphere Soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2888–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levard, C.; Hotze, E.M.; Lowry, G.V.; Brown, G.E., Jr. Environmental Transformations of Silver Nanoparticles: Impact on Stability and Toxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6900–6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitley, A.; Levard, C.; Oostveen, E.; Bertsch, P.M.; Matocha, C.J.; von der Kammer, F.; Unrine, J.M. Behavior of Ag nanoparticles in soil: Effects of particle surface coating, aging and sewage sludge amendment. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 182, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedberg, J.; Oromieh, A.G.; Kleja, D.B.; Wallinder, I.O. Sorption and dissolution of bare and coated silver nanoparticles in soil suspensions—Influence of soil and particle characteristics. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2015, 50, 891–900. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, V.K.; Siskova, K.M.; Zboril, R.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L. Organic-coated silver nanoparticles in biological and environmental conditions: Fate, stability and toxicity. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 204, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, D.A.; Kirby, J.K.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Waddington, L.; Kookana, R.S. Remobilisation of silver and silver sulphide nanoparticles in soils. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 193, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doolette, C.L.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Kirby, J.K.; Navarro, D.A. Bioavailability of silver and silver sulfide nanoparticles to lettuce (Lactuca sativa): Effect of agricultural amendments on plant uptake. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 300, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, G.V.; Hotze, E.M.; Bernhardt, E.S.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Pedersen, J.A.; Wiesner, M.R.; Xing, B.S. Environmental Occurrences, Behavior, Fate, and Ecological Effects of Nanomaterials: An Introduction to the Special Series. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 1867–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagee, O.; Dror, I.; Berkowitz, B. Transport of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) in soil. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, D.S.; Rodrigues, S.M.; Cruz, N.; Carvalho, C.; Teixeira, T.; Carvalho, L.; Duarte, A.C.; Trindade, T.; Pereira, E.; Römkens, P.F.A.M. Soil-pore water distribution of silver and gold engineered nanoparticles in undisturbed soils under unsaturated conditions. Chemosphere 2015, 136, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Römkens, P.F.A.M.; Guo, H.Y.; Chu, C.L.; Liu, T.S.; Chiang, C.F.; Koopmans, G.F. Characterization of soil heavy metal pools in paddy fields in Taiwan: Chemical extraction and solid-solution partitioning. J. Soils Sediments 2009, 9, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, S.M.; Cruz, N.; Coelho, C.; Henriques, B.; Carvalho, L.; Duarte, A.C.; Pereira, M.E.; Römkens, P.F.A.M. Risk assessment for Cd Cu Pb and Zn in urban soils: Chemical availability as the central concept. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 183, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, S.M.; Henriques, B.; Ferreira da Silva, E.; Pereira, M.E.; Duarte, A.C.; Römkens, P.F.A.M. Evaluation of an approach for the characterization of reactive and available pools of twenty potentially toxic elements in soils: Part I—The role of key soil properties in the variation of contaminants reactivity. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedotov, P.S.; Kördel, W.; Miró, M.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Wennrich, R.; Huang, P. Extraction and Fractionation Methods for Exposure Assessment of Trace Metals, Metalloids, and Hazardous Organic Compounds in Terrestrial Environments. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 42, 1117–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänsch, M.; Emmerling, C. Effects of silver nanoparticles on the microbiota and enzyme activity in soil. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2010, 173, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velicogna, J.R.; Ritchie, E.E.; Scroggins, R.P.; Princz, J.I. A comparison of the effects of silver nanoparticles and silver nitrate on a suite of soil dwelling organisms in two field soils. Nanotoxicology 2016, 10, 1144–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyrot, C.; Wilkinson, K.J.; Desrosiers, M.; Sauvé, S. Effects of silver nanoparticles on soil enzyme activities with and without added organic matter. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaddam, D.P.; Devamma, N.; Prasad, T.N.V.K.V. Evaluation of the effect of indigenous mycogenic silver nanoparticles on soil exo-enzymes in barite mine contaminated soils. Appl. Nanosci. 2015, 5, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shin, Y.J.; Kwak, J.I.; An, Y.J. Evidence for the inhibitory effects of silver nanoparticles on the activities of soil exoenzymes. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bascomb, C.L. Method for the determination of cation exchange capacity of calcareous and non-calcareous soils. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1964, 15, 821–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulfinger, L.; Solomon, S.D.; Bahadory, M.; Jeyarajasingam, A.V.; Rutkowsky, S.A.; Boritz, C. Synthesis and Study of Silver Nanoparticles. J. Chem. Educ. 2007, 84, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malina, D.; Sobczak-Kupiec, A.; Wzorek, Z.; Kowalski, Z. Silver nanoparticles synthesis with different concentrations of polyvinylpyrrolidone. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2012, 7, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar]
- Unrine, J.M.; Hunyadi, S.E.; Tsyusko, O.V.; Rao, W.; Shoults-Wilson, W.A.; Bertsch, P.M. Evidence for Bioavailability of Au Nanoparticles from Soil and Biodistribution within Earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8308–8313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoutz-Wilson, W.A.; Reinsch, B.C.; Tsyusko, O.V.; Bertsch, P.M.; Lowry, G.L.; Unrine, J.M. Effect of silver nanoparticle surface coating on bioaccumulation and reproductive toxicity in earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Nanotoxicology 2011, 5, 432–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houba, V.J.G.; Temminghoff, E.J.M.; Gaikhorst, G.A.; Van Vark, W. Soil analysis procedures using 0.01 M calcium chloride as extraction reagent. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2000, 31, 1299–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Standard Operating Procedure for an In Vitro Bioaccessibility Assay for Lead in Soil EPA 9200; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 1–86.
- Houba, V.J.G.; van der Lee, J.J.; Novozamsky, I. Part 5b: Soil analysis procedures. In Soil and Plant Analysis a Series of Syllabi; Houba, V.J.G., Novozamsky, I., Eds.; Department of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition of Wageningen Agricultural University: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1995; 262p. [Google Scholar]
- Alef, K.; Nannipieri, P.; Trasar-Cepeda, C. Phosphatase activity. In Methods in Applied Soil Microbiology and Biochemistry; Alef, K., Nannipieri, P., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1995; pp. 335–344. [Google Scholar]
- Eivazi, F.; Tabatabai, M.A. Glucosidases and galactosidases in soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1988, 20, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alef, K.; Nannipieri, P. β-Glucosidase activity. In Methods in Applied Soil Microbiology and Biochemistry; Alef, K., Nannipieri, P., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1995; pp. 350–352. [Google Scholar]
- Hope, C.F.A.; Burns, R.G. Activity, origins and location of cellulase in a silt loam soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1987, 5, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandeler, E.; Gerber, H. Short-term assay of soil urease activity using colorimetric determination of ammonium. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1988, 6, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladd, J.N.; Butler, J.H.A. Short-term assays of soil proteolytic enzyme activities using proteins and dipeptide derivatives as substrates. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1972, 4, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alef, K.; Nannipieri, P. (Eds.) Protease activity. In Methods in Applied Soil Microbiology and Biochemistry; Academic Press: London, UK, 1995; pp. 313–315. [Google Scholar]
- Inácio, M.; Pereira, V.; Pinto, M. The Soil Geochemical Atlas of Portugal: Overview and applications. J. Geochem. Explor. 2008, 98, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelis, G.; Kirby, J.K.; Beak, D.; Chittleborough, D.; McLaughlin, M.J. A method for determination of retention of silver and cerium oxide manufactured nanoparticles in soils. Environ. Chem. 2010, 7, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settimio, L.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Kirby, J.K.; Langdon, K.A.; Lombi, E.; Donner, E.; Scheckel, K.G. Fate and lability of silver in soils: Effect of ageing. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 191, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanderVoot, A.R.; Tappero, R.; Arai, Y. Residence time effects on phase transformation of nanosilver in reduced soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 7828–7837. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, N.; Rodrigues, S.M.; Tavares, D.; Monteiro, R.J.R.; Carvalho, L.; Trindade, T.; Duarte, A.C.; Pereira, E.; Romkens, P.F.A.M. Testing single extraction methods and in vitro tests to assess the geochemical reactivity and human bioaccessibility of silver in urban soils amended with silver nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2015, 135, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamon, R.E.; Parker, D.R.; Lombi, E. Advances in isotopic dilution techniques in trace element research: A review of methodologies, benefits and limitations. Adv. Agron. 2008, 99, 289–343. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).