Daily Mortality in Different Age Groups Associated with Exposure to Particles, Nitrogen Dioxide and Ozone in Two Northern European Capitals: Stockholm and Tallinn
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Data
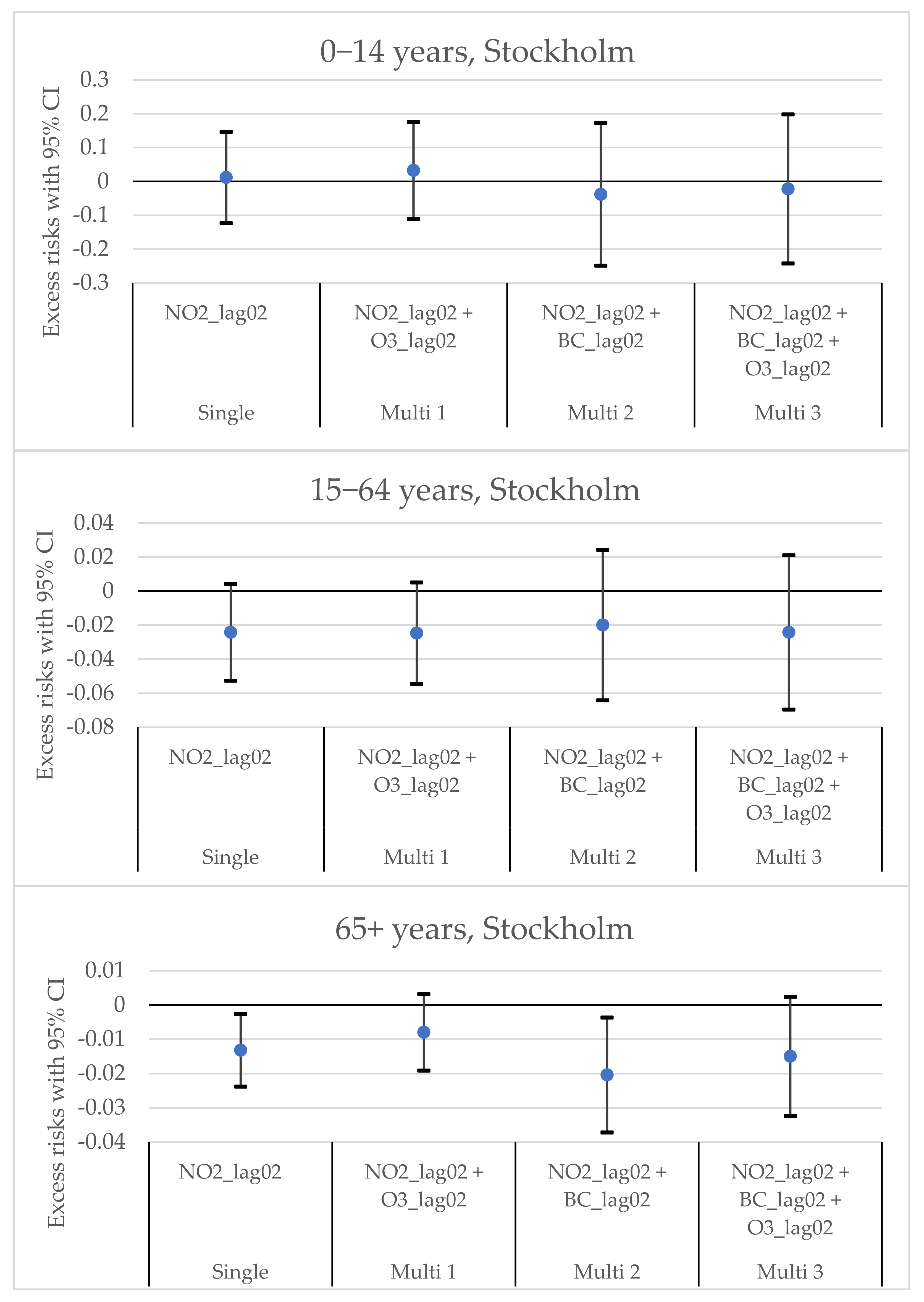
3.2. The Excess Risks in Different Age Groups in Stockholm and Tallinn
4. Discussion
4.1. Excess Risks in Different Age Groups
4.2. Effects of Different Air Pollutants at Low Concentrations
4.3. Other Than Mortality Effects
4.4. Strengths and Limitations of This Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A








References
- Makri, A.; Stilianakis, N.I. Vulnerability to air pollution health effects. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2008, 211, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mead, M.N. Who’s at risk? Gauging susceptibility to air pollutants. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, A176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacks, J.D.; Stanek, L.W.; Luben, T.J.; Johns, D.O.; Buckley, B.J.; Brown, J.S.; Ross, M. Particulate matter-induced health effects: Who is susceptible? Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geller, A.M.; Zenick, H. Aging and the environment: A research framework. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shumake, K.L.; Sacks, J.D.; Lee, J.S.; Johns, D.O. Susceptibility of older adults to health effects induced by ambient air pollutants regulated by the European Union and the United States. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2013, 25, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buka, I.; Koranteng, S.; Osornio-Vargas, A.R. The effects of air pollution on the health of children. Paediatr. Child Health 2006, 11, 513–516. [Google Scholar]
- Varotsos, C.; Efstathiou, M.; Tzanis, C.; Deligiorgi, D. On the limits of the air pollution predictability: The case of the surface ozone at Athens, Greece. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aga, E.; Samoli, E.; Touloumi, G.; Anderson, H.R.; Cadum, E.; Forsberg, B.; Goodman, P.; Goren, A.; Kotěšovec, F.; Kříž, B.; et al. Short-term effects of ambient particles on mortality in the elderly: Results from 28 cities in the APHEA2 project. Eur. Respir. J. Suppl. 2003, 40, 28s–33s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cakmak, S.; Dales, R.E.; Vidal, C.B. Air pollution and mortality in Chile: Susceptibility among the elderly. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Kan, H.; Chen, B.; Huang, W.; Bai, Z.; Song, G.; Pan, G. Association of particulate air pollution with daily mortality: The China Air Pollution and Health Effects Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 175, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; He, G.; Fan, M.; Chiu, K.Y.; Liu, C.; Xue, A.; Liu, T.; Pan, Y.; Mu, Q.; Zhou, M. Particulate air pollution and mortality in 38 of China’s largest cities: Time series analysis. BMJ 2017, 356, j667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanhueza, P.A.; Torreblanca, M.A.; Diaz-Robles, L.A.; Schiappacasse, L.N.; Silva, M.P.; Astete, T.D. Particulate air pollution and health effects for cardiovascular and respiratory causes in Temuco, Chile: A wood-smoke-polluted urban area. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2009, 59, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, J.; Ng, Y.; Yeo, K.K.; Sahlén, A.; Lam, C.S.P.; Lee, V.; Ma, S. Particulate air pollution on cardiovascular mortality in the tropics: Impact on the elderly. Environ. Health 2019, 18, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, P.; Hoek, G.; Brunekreef, B.; Verhoeff, A.; van Wijnen, J. Air pollution and mortality in The Netherlands: Are the elderly more at risk? Eur. Respir. J. Suppl. 2003, 40, 34s–38s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franklin, M.; Zeka, A.; Schwartz, J. Association between PM2.5 and all-cause and specific-cause mortality in 27 US communities. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2007, 17, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medina-Ramón, M.; Schwartz, J. Who is more vulnerable to die from ozone air pollution? Epidemiology 2008, 19, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, H.R.; Limb, E.S.; Bland, J.M.; de Leon, A.P.; Strachan, D.P.; Bower, J.S. Health effects of an air pollution episode in London, December 1991. Thorax 1995, 50, 1188–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filleul, L.; Le Tertre, A.; Baldi, I.; Tessier, J.F. Difference in the relation between daily mortality and air pollution among elderly and all-ages populations in southwestern France. Environ. Res. 2004, 94, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, G.J.; Cohen, G.; Elton, R.; Fowkes, F.; Agius, R. Urban air pollution and cardiopulmonary ill health: A 14.5 year time series study. Occup. Environ. Med. 1998, 55, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gouveia, N.; Fletcher, T. Time series analysis of air pollution and mortality: Effects by cause, age and socioeconomic status. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2000, 54, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ha, E.H.; Lee, J.T.; Kim, H.; Hong, Y.C.; Lee, B.E.; Park, H.S.; Christiani, D.C. Infant susceptibility of mortality to air pollution in Seoul, South Korea. Pediatrics 2003, 111, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberini, A.; Cropper, M.; Simon, N.B.; Sharma, P.K. The Health Effects of Air Pollution in Delhi, India; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Krishna, B.; Mandal, S.; Madhipatla, K.; Reddy, K.S.; Prabhakaran, D.; Schwartz, J.D. Daily nonaccidental mortality associated with short-term PM(2.5) exposures in Delhi, India. Environ. Epidemiol. 2021, 5, e167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jiao, Z.; Chen, P.; Fan, L.; Zhou, X.; Pu, Y.; Du, W.; Yin, L. Short-term effect of fine particulate matter and ozone on non-accidental mortality and respiratory mortality in Lishui district, China. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Zhu, X.; Chen, M.; Zhou, L.; Deng, R.; Zhang, Y.; Pu, X.; Pan, J. The burden of overall and cause-specific respiratory morbidity due to ambient air pollution in Sichuan Basin, China: A multi-city time-series analysis. Environ. Res. 2018, 167, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J. Low-Level Air Pollution Associated with Death: Policy and Clinical Implications. JAMA 2017, 318, 2431–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olstrup, H.; Johansson, C.; Forsberg, B.; Åström, C. Association between mortality and short-term exposure to particles, ozone and nitrogen dioxide in Stockholm, Sweden. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Auger, N.; Potter, B.J.; Smargiassi, A.; Bilodeau-Bertrand, M.; Paris, C.; Kosatsky, T. Association between quantity and duration of snowfall and risk of myocardial infarction. CMAJ 2017, 189, E235–E242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Statistics Estonia. Statistical Database. 2022. Available online: https://www.stat.ee/en (accessed on 4 June 2022).
- Socialstyrelsen. Statistical Databases. 2022. Available online: https://www.socialstyrelsen.se/statistik-och-data/statistik/statistikdatabasen/ (accessed on 4 June 2022).
- Wang, L.; Pinkerton, K.E. Air pollutant effects on fetal and early postnatal development. Birth Defects Res. Part C Embryo Today Rev. 2007, 81, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacasana, M.; Esplugues, A.; Ballester, F. Exposure to ambient air pollution and prenatal and early childhood health effects. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 20, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, W.-H.; Kim, Y.-Y.; Park, H.-Y. Air Pollution and Central Nervous System Disease: A Review of the Impact of Fine Particulate Matter on Neurological Disorders. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 575330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Andersen, Z.J.; Jensen, S.S.; Ketzel, M.; Sørensen, M.; Hansen, J.; Loft, S.; Tjønneland, A.; Overvad, K. Traffic air pollution and mortality from cardiovascular disease and all causes: A Danish cohort study. Environ. Health 2012, 11, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Münzel, T.; Hahad, O.; Daiber, A.; Lelieveld, J. Air pollution and cardiovascular diseases. Herz 2021, 46, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meister, K.; Johansson, C.; Forsberg, B. Estimated short-term effects of coarse particles on daily mortality in Stockholm, Sweden. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adar, S.D.; Filigrana, P.A.; Clements, N.; Peel, J.L. Ambient Coarse Particulate Matter and Human Health: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2014, 1, 258–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schins, R.P.; Lightbody, J.H.; Borm, P.J.; Shi, T.; Donaldson, K.; Stone, V. Inflammatory effects of coarse and fine particulate matter in relation to chemical and biological constituents. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 195, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Su, W.; Wang, H.; Li, N.; Song, Q.; Liang, Q.; Sun, C.; Liang, M.; Zhou, Z.; Song, E.J.; et al. Short-term exposure to ambient ozone and cardiovascular mortality in China: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2022, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auten, R.L.; Foster, W.M. Biochemical effects of ozone on asthma during postnatal development. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1810, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bräuner, E.V.; Zanobetti, A.; Schwartz, J. The Effect of Ozone on All Cause Mortality in the Elderly: Modification by Sex, Race, and Previous Heart, Lung, and Diabetes Related Hospital Admissions in a U. S. National Multicity Study. Epidemiology 2008, 19, S325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodi, S.; Vercelli, M.; Garrone, E.; Fontana, V.; Izzotti, A. Ozone air pollution and daily mortality in Genoa, Italy between 1993 and 1996. Public Health 2005, 119, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, N.; Ramsay, T.; Jerrett, M.; Krewski, D. Short-term effects of ozone and PM 2.5 on mortality in 12 Canadian cities. J. Environ. Prot. 2013, 4, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, C.F.; Ueda, K.; Nitta, H.; Takeuchi, A. Seasonal variation in the acute effects of ozone on premature mortality among elderly Japanese. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 8767–8776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, E.J.; Na, W.; Lee, K.E.; Jang, J.Y. Elderly Mortality and Exposure to Fine Particulate Matter and Ozone. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2019, 34, e311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wei, Y.; Fang, Z. Ozone Pollution: A Major Health Hazard Worldwide. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Day, D.B.; Xiang, J.; Mo, J.; Li, F.; Chung, M.; Gong, J.; Weschler, C.J.; Ohman-Strickland, P.A.; Sundell, J.; Weng, W.; et al. Association of Ozone Exposure with Cardiorespiratory Pathophysiologic Mechanisms in Healthy Adults. JAMA Intern. Med. 2017, 177, 1344–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olstrup, H.; Johansson, C.; Forsberg, B.; Åström, C.; Orru, H. Seasonal Variations in the Daily Mortality Associated with Exposure to Particles, Nitrogen Dioxide, and Ozone in Stockholm, Sweden, from 2000 to 2016. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varotsos, C.; Ondov, J.; Tzanis, C.; Öztürk, F.; Nelson, M.; Ke, H.; Christodoulakis, J. An observational study of the atmospheric ultra-fine particle dynamics. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 59, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines: Particulate Matter (PM2. 5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Di, Q.; Dai, L.; Wang, Y.; Zanobetti, A.; Choirat, C.; Schwartz, J.D.; Dominici, F. Association of short-term exposure to air pollution with mortality in older adults. JAMA 2017, 318, 2446–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Rosenberg, A.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P.; Yazdi, M.D.; Réquia, W.; Steenland, K.; Chang, H.; Sarnat, J.A.; Wang, W.; et al. Low-Concentration Air Pollution and Mortality in American Older Adults: A National Cohort Analysis (2001–2017). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 7194–7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicedo-Cabrera, A.M.; Sera, F.; Liu, C.; Armstrong, B.; Milojevic, A.; Guo, Y.; Tong, S.; Lavigne, E.; Kyselý, J.; Urban, A.; et al. Short term association between ozone and mortality: Global two stage time series study in 406 locations in 20 countries. BMJ 2020, 368, m108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yee, J.; Cho, Y.A.; Yoo, H.J.; Yun, H.; Gwak, H.S. Short-term exposure to air pollution and hospital admission for pneumonia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Health 2021, 20, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, Z.; Gorgi, H.A.; Shabaninejad, H.; Delavar, M.A.; Torani, S. Association between PM2.5 and risk of hospitalization for myocardial infarction: A systematic review and a meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, A.G.; Williams, G.M.; Schwartz, J.; Best, T.L.; Neller, A.H.; Petroeschevsky, A.L.; Simpson, R.W. The effects of air pollution on hospitalizations for cardiovascular disease in elderly people in Australian and New Zealand cities. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 1018–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larrieu, S.; Jusot, J.-F.; Blanchard, M.; Prouvost, H.; Declercq, C.; Fabre, P.; Pascal, L.; Le Tertre, A.; Wagner, V.; Rivière, S. Short term effects of air pollution on hospitalizations for cardiovascular diseases in eight French cities: The PSAS program. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 387, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Host, S.; Larrieu, S.; Pascal, L.; Blanchard, M.; Declercq, C.; Fabre, P.; Jusot, J.-F.; Chardon, B.; Le Tertre, A.; Wagner, V.; et al. Short-term associations between fine and coarse particles and hospital admissions for cardiorespiratory diseases in six French cities. Occup. Environ. Med. 2008, 65, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namdeo, A.; Tiwary, A.; Farrow, E. Estimation of age-related vulnerability to air pollution: Assessment of respiratory health at local scale. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spix, C.; Anderson, H.R.; Schwartz, J.; Vigotti, M.A.; Letertre, A.; Vonk, J.M.; Touloumi, G.; Balducci, F.; Piekarski, T.; Bacharova, L.; et al. Short-term effects of air pollution on hospital admissions of respiratory diseases in Europe: A quantitative summary of APHEA study results. Arch. Environ. Health Int. J. 1998, 53, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Luo, S.; Kwon, J.; Stock, T.H.; Delclos, G.; Kim, H.; Yun-Chul, H. Effects of air pollution on asthma hospitalization rates in different age groups in metropolitan cities of Korea. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2013, 6, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Pollutant | Stockholm (Södermalm) | Tallinn (Õismäe) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Instrument | Method | Instrument | |
| PM10 | Gravimetric | TEOM 1400A, Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA | Beta-attenuation | BAM 1020, Met One Instruments, USA |
| PM2.5–10 | Gravimetric (Subtracting PM2.5 from PM10) | TEOM 1400A, Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA | Beta-attenuation (Subtracting PM2.5 from PM10) | BAM 1020, Met One Instruments, USA |
| PM2.5 | Gravimetric | TEOM 1400A, Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA | Beta-attenuation monitoring | BAM 1020, Met One Instruments, USA |
| BC | Transmission of light through a filter | Aethalometers 8100, AE31, AE33, Magee Scientific Corporation, USA | NA | NA |
| PNC4 | Optical counting | Condensation particle counter, Model 3752/3022, TSI Inc., USA | NA | NA |
| NO2 | Chemiluminescence | AC32M, Environment S.A., France | Chemiluminescence | APNA-360, Horiba, Japan |
| O3 | UV absorption | O342M, Environment S.A., France | UV absorption | APOA-360, Horiba, Japan |
| Variable | Stockholm | Tallinn | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (IQR) | #Days (% Valid Data) | Mean (IQR) | #Days (% Valid Data) | |
| PM10 (µg m−3) | 14.5 (8.7) | 5999 (97%) | 14.9 (11.7) | 6207 (94%) |
| PM2.5–10 (µg m−3) | 8.0 (5.5) | 5352 (86%) | 6.6 (5.5) | 4258 (65%) |
| PM2.5 (µg m−3) | 6.5 (4.8) | 5358 (86%) | 8.1 (7.7) | 4423 (67%) |
| BC (µg m−3) | 0.6 (0.5) | 3316 (53%) | NA 2 | NA 2 |
| PNC4 nm (cm−3) | 6793 (3484) | 2727 (44%) | NA 2 | NA 2 |
| NO2 (µg m−3) | 14.4 (9.9) | 6101 (98%) | 11.0 (9.1) | 6386 (97%) |
| O3 (µg m−3) 1 | 51.2 (25.2) | 6133 (99%) | 51.3 (26.1) | 6395 (97%) |
| Mortality (N per day all ages) | 18.5 (7.0) | 6210 (100%) | 11.4 (5.0) | 6574 (100%) |
| Mortality (N per day 0–14 years of age) | 0.1 (0) | 6210 (100%) | 0.1 (0) | 6574 (100%) |
| Mortality (N per day 15–64 years of age) | 2.1 (2.0) | 6210 (100%) | 2.8 (2.0) | 6574 (100%) |
| Mortality (N per day ≥ 65 years of age) | 16.2 (6.0) | 6210 (100%) | 8.7 (4.0) | 6574 (100%) |
| Maximum temperature (°C) | 11.4 (15.0) | 6210 (100%) | 10.0 (15.8) | 6574 (100%) |
| Pollutant | PM10 | PM2.5–10 | PM2.5 | BC | PNC4 | NO2 | O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM10 | – | 0.82 | 0.76 | – | – | 0.50 | 0.00 |
| PM2.5–10 | 0.81 | – | 0.51 | – | – | 0.30 | 0.07 |
| PM2.5 | 0.72 | 0.17 | – | – | – | 0.40 | −0.09 |
| BC | 0.49 | 0.13 | 0.74 | – | – | – | – |
| PNC4 | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.10 | 0.24 | – | – | – |
| NO2 | 0.25 | 0.12 | 0.27 | 0.49 | 0.72 | – | −0.30 |
| O3 | 0.31 | 0.35 | 0.13 | −0.25 | −0.20 | −0.46 | – |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olstrup, H.; Åström, C.; Orru, H. Daily Mortality in Different Age Groups Associated with Exposure to Particles, Nitrogen Dioxide and Ozone in Two Northern European Capitals: Stockholm and Tallinn. Environments 2022, 9, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments9070083
Olstrup H, Åström C, Orru H. Daily Mortality in Different Age Groups Associated with Exposure to Particles, Nitrogen Dioxide and Ozone in Two Northern European Capitals: Stockholm and Tallinn. Environments. 2022; 9(7):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments9070083
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlstrup, Henrik, Christofer Åström, and Hans Orru. 2022. "Daily Mortality in Different Age Groups Associated with Exposure to Particles, Nitrogen Dioxide and Ozone in Two Northern European Capitals: Stockholm and Tallinn" Environments 9, no. 7: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments9070083
APA StyleOlstrup, H., Åström, C., & Orru, H. (2022). Daily Mortality in Different Age Groups Associated with Exposure to Particles, Nitrogen Dioxide and Ozone in Two Northern European Capitals: Stockholm and Tallinn. Environments, 9(7), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments9070083






