The Possibilities of Using Artificial Intelligence as a Key Technology in the Current Employee Recruitment Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Defining the Key Technology of Today in the Context of Management-Oriented Scientific Publications
2.2. Analysis of the Possibilities of Using AI in e-Recruitment
- 1.
- Recruitment planning
- 2.
- Preparation and publication of job offers
- 3.
- Candidate search and management
- 4.
- Managing CVs
- 5.
- Screening and testing of applicants
- 6.
- Management of interviews and assessments
- 7.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of the process
- Candidate quality—the skills and qualifications of the candidates recruited, cultural fit of candidates within the organization, feedback from hiring managers and new hires, and performance of new hires over time;
- Time to fill positions—the total time required to fill open positions, identifying any delays or inefficiencies in the process;
- Retention rate—the length of time new employees remain with the organization, comparison with industry standards, and assessment of any need to improve the recruitment process to increase retention rates;
- Cost—the total cost of the recruitment and selection process, including advertising costs, agency fees, and staff time, evaluating the return on investment in talent acquisition;
- Diversity—demographics of new hires, comparison to overall organization demographics, and identifying the need to improve appeal to diverse candidates;
- Candidate Experience—candidate feedback on their experience during the process, possible negative comments or reviews on job review websites, and assessing the impact of the candidate experience on their perception of the organization;
- Hiring Manager Satisfaction—the hiring manager’s satisfaction with the quality and suitability of candidates, assessment of whether the recruitment and selection process is meeting hiring managers’ needs, and analysis of hiring managers’ feedback on the recruitment and selection process.
3. Discussion
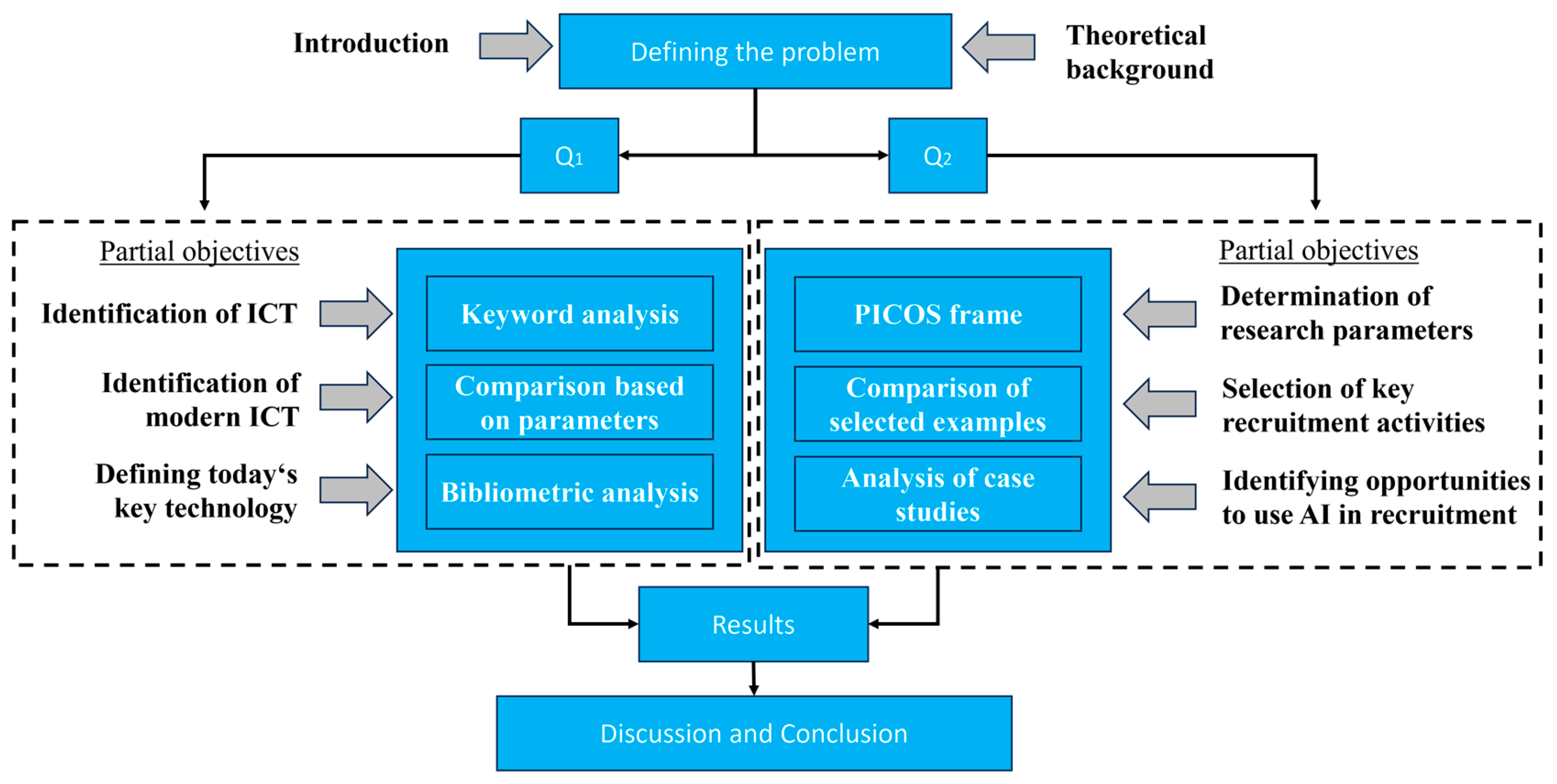
4. Materials and Methods
Q1: What is the current position of AI in contemporary academic research with a focus on management?
- Relevance—current technologies are based on the latest research, development, and innovation in the industry. Thus, modern ICTs can be said to be up to date if they are current trends in businesses and other ecosystems;
- Several publications—modern technologies are often reflected in a high number of publications and technical articles detailing their development, benefits, and application possibilities. This indicator suggests that the technology is a hot topic in the academic and professional community;
- Sufficient development—modern technologies have mature and proven concepts, methods, and solutions, signaling their robust base and ability to be applied in practice. If the technology is only at the level of abstraction, it cannot be considered modern but future-proof;
- Usability in the present—current technologies are up-to-date and applicable, with their benefits and ability to improve existing processes or contribute to innovation visible and recognized in practice.
Q2: What are the current trends in the use of AI in recruitment processes?
- Participants: specific AI tools and systems that are primarily intended for use in the recruitment process;
- Intervention: the activities for which AI tools and systems are used;
- Comparator: Examples of activities for which specific AI is used;
- Outcomes: Improved time efficiency in recruitment;
- Study design: Analysis of case studies.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adamovic, Mladen. 2022. When Ethnic Discrimination in Recruitment Is Likely to Occur and How to Reduce It: Applying a Contingency Perspective to Review Resume Studies. Human Resource Management Review 32: 100832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Shamima, and Allison Adams. 2010. Web Recruiting in Government Organizations. Public Performance & Management Review 33: 653–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamro, Saleh, Huseyin Dogan, Deniz Cetinkaya, Nan Jiang, and Keith Phalp. 2018. Conceptualising and Modelling E-Recruitment Process for Enterprises through a Problem Oriented Approach. Information 9: 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, Edward. 2019. AI in Talent Acquisition: A Review of AI-Applications Used in Recruitment and Selection. Strategic HR Review 18: 215–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allal-Chérif, Oihab, Alba Yela Aránega, and Rafael Castaño Sánchez. 2021. Intelligent Recruitment: How to Identify, Select, and Retain Talents from around the World Using Artificial Intelligence. Technological Forecasting and Social Change 169: 120822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, Fernando. 2022. Foresights for Big Data across Industries. Foresight 25: 334–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzhrani, Atyeh Mohammed. 2020. The Effectiveness of E-Recruitment Software Over Other Online-Based Recruitment Methods. Global Journal of Economics and Business 8: 330–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoni, Ľubomír, Ján Guniš, Peter Gurský, Štefan Horvát, Stanislav Krajči, Ondrej Krídlo, Miroslav Opiela, Alexander Szabari, Ľubomír Šnajder, Gabirela Andrejková, and et al. 2020. Data Science and Its Position in University Education within National Project IT Academy-Education for 21st Century. Paper presented at the 2020 18th International Conference on Emerging eLearning Technologies and Applications (ICETA), Virtual. November 12–13; pp. 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazán, Víctor, Ramón Hermoso, and Inés Escario. 2018. E-recruitment en España: Evolución y uso de las TIC para atraer candidatos. Acciones e Investigaciones Sociales 39: 201–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, Angela D., Scott D. Johnson, and K. Peter Kuchinke. 2002. The Use of Technology in the Digital Workplace: A Framework for Human Resource Development. Advances in Developing Human Resources 4: 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettoni, Andrea, Davide Matteri, Elias Montini, Bartłomiej Gładysz, and Emanuele Carpanzano. 2021. An AI Adoption Model for SMEs: A Conceptual Framework. IFAC-PapersOnLine 54: 702–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalerao, Kuldeep, Arya Kumar, and Purvi Pujari. 2022. A Study Of Barriers And Benefits Of Artificial Intelligence Adoption In Small And Medium Enterprise. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal 26: 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Black, J. Stewart, and Patrick van Esch. 2020. AI-Enabled Recruiting: What Is It and How Should a Manager Use It? Business Horizons 63: 215–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucher, Tobias, Anke Gericke, and Stefan Sigg. 2009. Process-Centric Business Intelligence. Business Process Management Journal 15: 408–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, Tiago Vieira de, and Renato José Sassi. 2014. An Alternative to Face Worldwide Financial Crisis of 2008: Best Practices Usage of a Business Intelligence Architecture in a Chemical Industry. International Journal of Business Innovation and Research 8: 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlwood, Andy, and Nigel Guenole. 2022. Can HR Adapt to the Paradoxes of Artificial Intelligence? Human Resource Management Journal 32: 729–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Chien-Chun, Chiu-Chi Wei, Su-Hui Chen, Lun-Meng Sun, and Hsien-Hong Lin. 2022. AI Predicted Competency Model to Maximize Job Performance. Cybernetics and Systems 53: 298–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Zhisheng. 2023. Ethics and Discrimination in Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Recruitment Practices. Humanities and Social Sciences Communications 10: 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiwara, Juliet R., Themba Q. Mjoli, and Willie T. Chinyamurindi. 2017. Factors That Influence the Use of the Internet for Job-Seeking Purposes amongst a Sample of Final-Year Students in the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa. SA Journal of Human Resource Management 15: 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, Soumyadeb, Sian Joel-Edgar, Prasanta Kumar Dey, Sudeshna Bhattacharya, and Alexander Kharlamov. 2023. Embedding Transparency in Artificial Intelligence Machine Learning Models: Managerial Implications on Predicting and Explaining Employee Turnover. The International Journal of Human Resource Management 34: 2732–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuah, Min-Hooi, and William Yeoh. 2009. Building a Capability Maturity Model for Enterprise Business Intelligence Initiative: A Preliminary Model. In Creating Global Economies Through Innovation And Knowledge Management: Theory & Practice, Vols 1–3. Edited by K. S. Soliman. Norristown: Building a Capability Maturity Model for Enterprise Business Intelligence Initiative, pp. 882–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daktela. 2023. Umelá Inteligencia Pomáha v Oblasti Ľudských Zdrojov. Daktela. Available online: https://www.daktela.com/sk/umela-inteligencia-pomaha-v-oblasti-ludskych-zdrojov/ (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Daroshka, Vitali, Igor Aleksandrov, Grigory Kulkaev, Sofya Skryabina, Irina Chekhovskikh, Anastasiya Vasilenkova, Victoria Ilina, and Ekaterina Ol. 2024. The Impact of Small Business on Sustainable Development in the Vuca- and Bani-Worlds. E3S Web of Conferences 531: 05035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decenzo, David A., and Stephen P. Robbins. 2011. Human Resource Management, 10th ed. New York: Wiley. [Google Scholar]
- Dixit, Sweta, Neha Sharma, Mohit Maurya, and Mridul Dharwal. 2022. AI Power: Making Recruitment Smarter. In Evolution of Digitized Societies Through Advanced Technologies. Edited by Amitava Choudhury, T. P. Singh, Arindam Biswas and Mrinal Anand. Singapore: Springer Nature, pp. 165–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulebohn, James H., and Dianna L. Stone. 2018. The Brave New World of eHRM 2.0 (Research in Human Resource Management). Charlotte: Information Age Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Eck, Nees Jan van, Ludo Waltman, Rommert Dekker, and Jan van den Berg. 2010. A Comparison of Two Techniques for Bibliometric Mapping: Multidimensional Scaling and VOS. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology 61: 2405–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelhauser, Eduard, Andreea Ionica, and Lucian Lupudima. 2010. A Business Intelligence Software Made in Romania, a Solution for Romanian Companies during the Economic Crisis. In Computational Intelligence in Business and Economics. World Scientific Proceedings Series on Computer Engineering and Information Science; Singapore: World Scientific, vol. 3, pp. 247–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enholm, Ida Merete, Emmanouil Papagiannidis, Patrick Mikalef, and John Krogstie. 2022. Artificial Intelligence and Business Value: A Literature Review. Information Systems Frontiers 24: 1709–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, Taeung, Chungwon Woo, and Dongphil Chun. 2022. Redicting an ICT Business Process Innovation as a Digital Transformation with Machine Learning Techniques. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management 2022: 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fachrizal, M. R., N. R. Radliya, and A. Manik. 2019. Development of E-Recruitment as a Decision Support System for Employee Recruitment. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering 662: 022018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faliagka, Evanthia, Athanasios Tsakalidis, and Giannis Tzimas. 2012. An Integrated E-recruitment System for Automated Personality Mining and Applicant Ranking. Internet Research 22: 551–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Xue, Gregory Richards, and Bijan Raheemi. 2009. The Road to Decision-Centric Business Intelligence. In 2009 International Conference On Business Intelligence And Financial Engineering, Proceedings. Edited by S. Y. Wang, L. Yu, F. H. Wen, S. Y. He, Y. Fang and K. K. Lai. Los Alamitos: IEEE Computer Society, pp. 514–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, Ana Beatriz Alves, and Carolina Feliciana Machado. 2022. E-Recruitment and the Impact of Digital Age on Recruitment: A Critical Literature Review. In Organizational Innovation in the Digital Age. Edited by Carolina Machado and J. Paulo Davim. Cham: Springer International Publishing, pp. 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Martínez, Carmen, and Alberto Fernández. 2020. AI and Recruiting Software: Ethical and Legal Implications. Paladyn, Journal of Behavioral Robotics 11: 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, Tiago Jacob Fernandes, Henrique São Mamede, João Manuel Pereira Barroso, and Vítor Manuel Pereira Duarte dos Santos. 2023. Artificial Intelligence Applied to Potential Assessment and Talent Identification in an Organisational Context. Heliyon 9: e14694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, Mauricio Noris, and Leandro Nunes de Castro. 2021. E-Recruitment Recommender Systems: A Systematic Review. Knowledge and Information Systems 63: 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritts, Megan, and Frank Cabrera. 2021. AI Recruitment Algorithms and the Dehumanization Problem. Ethics and Information Technology 23: 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, Vikas, and Richa Goel. 2021. Handbook of Research on Innovative Management Using AI in Industry 5.0 (Advances in Logistics, Operations, and Management Science). Hershey: Business Science Reference. Available online: https://www.amazon.com/Handbook-Innovative-Management-Logistics-Operations/dp/179988497X (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Geetha, R., and D. Bhanu Sree Reddy. 2018. Recruitment through Artificial Intelligence: A Conceptual Study. International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology 9: 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Gerken, Tom. 2023. Bill Gates: AI Is Most Important Tech Advance in Decades. BBC News. March 21. Available online: https://www.bbc.com/news/technology-65032848 (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Gilch, Phyllis Messalina, and Jost Sieweke. 2021. Recruiting Digital Talent: The Strategic Role of Recruitment in Organisations’ Digital Transformation. German Journal of Human Resource Management-Zeitschrift Fur Personalforschung 35: 53–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusain, Akshita, Tilottama Singh, Shweta Pandey, Vikrant Pachourui, Rajesh Singh, and Anil Kumar. 2023. E-Recruitment Using Artificial Intelligence as Preventive Measures. Paper presented at the 2023 International Conference on Sustainable Computing and Data Communication Systems (ICSCDS), Erode, India, March 23–25; pp. 516–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HireVue. 2023. HireVue Hiring Platform: Video Interviews, Assessment, Scheduling, AI, Chatbot|HireVue. Hirevue.Com. 2023. Available online: https://www.hirevue.com/ (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Holubčík, Martin, and Jakub Soviar. 2021. Main Problems of Cooperation Management: Insights from Slovak Companies. Sustainability 13: 6736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holubčík, Martin, Jakub Soviar, and Viliam Lendel. 2023. Through Synergy in Cooperation towards Sustainable Business Strategy Management. Sustainability 15: 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horodyski, Piotr. 2023. Applicants’ Perception of Artificial Intelligence in the Recruitment Process. Computers in Human Behavior Reports 11: 100303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosain, Md. Sajjad, Abu Hena Mohammad Manzurul Arefin, and Md. Altab Hossin. 2020. E-Recruitment: A Social Media Perspective. Asian Journal of Economics, Business and Accounting 16: 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM. 2023. IBM Watson Assistant—Virtual Agent. Available online: https://www.ibm.com/products/watson-assistant (accessed on 2 August 2023).
- Intelion Systems. 2023. (26) AI Recruitment Statistics|LinkedIn. 2023. Available online: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/ai-recruitment-statistics-intelion-systems/ (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Kanade, Vijay. 2022. What Is Artificial Intelligence (AI)? Definition, Types, Goals, Challenges, and Trends in 2022. Spiceworks (blog). Available online: https://www.spiceworks.com/tech/artificial-intelligence/articles/what-is-ai/ (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Keiff, Maximilian, Frederic Voigt, Anna Fuchs, Michael Kuhn, Jannek Squar, and Thomas Ludwig. 2022. Automated Performance Analysis Tools Framework for HPC Programs. Procedia Computer Science 207: 1067–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindly. 2023. Recruitment Chatbot Case Study l Kindly. 2023. Available online: https://www.kindly.ai/case-studies/recruitment-chatbot-adecco (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Kirby, Andrew. 2023. Exploratory Bibliometrics: Using VOSviewer as a Preliminary Research Tool. Publications 11: 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirya, Monica Twesiime. 2020. Promoting Anti-Corruption, Transparency and Accountability in the Recruitment and Promotion of Health Workers to Safeguard Health Outcomes. Global Health Action 13: 1701326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koivunen, Sami, Saara Ala-Luopa, Thomas Olsson, and Arja Haapakorpi. 2022. The March of Chatbots into Recruitment: Recruiters’ Experiences, Expectations, and Design Opportunities. Computer Supported Cooperative Work-the Journal of Collaborative Computing and Work Practices 31: 487–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köchling, Alina, and Marius Claus Wehner. 2020. Discriminated by an Algorithm: A Systematic Review of Discrimination and Fairness by Algorithmic Decision-Making in the Context of HR Recruitment and HR Development. Business Research 13: 795–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharčíková, Alžbeta, Martin Mičiak, Emese Tokarčíková, and Nikola Štaffenová. 2023. The Investments in Human Capital within the Human Capital Management and the Impact on the Enterprise’s Performance. Sustainability 15: 5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lada, Suddin, Brahim Chekima, Mohd. Rahimie Abdul Karim, Noor Fzlinda Fabeil, Mat Salleh Ayub, Sharifah Milda Amirul, Rudy Ansar, Mohamed Bouteraa, Lim Ming Fook, and Hafizah Omar Zaki. 2023. Determining Factors Related to Artificial Intelligence (AI) Adoption among Malaysia’s Small and Medium-Sized Businesses. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity 9: 100144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, Nell, and Jenny Marc. 2019. Want to Work for L’Oreal? Get Ready to Chat with an AI Bot. CNN. April 29. Available online: https://www.cnn.com/2019/04/29/tech/ai-recruitment-loreal/index.html (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Lohr, Steve. 2023. The A.I. Revolution Is Coming. But Not as Fast as Some People Think. The New York Times. August 29. Available online: https://www.nytimes.com/2023/08/29/technology/ai-revolution-time.html (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Lu, Yusheng, and Jiantong Zhang. 2021. Bibliometric Analysis and Critical Review of the Research on Big Data in the Construction Industry. Engineering, Construction and Architectural Management 29: 3574–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maree, Mohammed, Aseel B. Kmail, and Mohammed Belkhatir. 2019. Analysis and Shortcomings of E-Recruitment Systems: Towards a Semantics-Based Approach Addressing Knowledge Incompleteness and Limited Domain Coverage. Journal of Information Science 45: 713–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marler, Janet H., and Sandra L. Fisher. 2013. An Evidence-Based Review of e-HRM and Strategic Human Resource Management. Human Resource Management Review 23: 18–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, Dr Abdul Quddus. 2019. HR Analytics: A Modern Tool in HR for Predictive Decision Making. Rochester: SSRN Scholarly Paper. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/abstract=3525328 (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Moral-Munoz, Jose A., Antonio G. López-Herrera, Enrique Herrera-Viedma, and Manuel J. Cobo. 2019. Science Mapping Analysis Software Tools: A Review. In Springer Handbook of Science and Technology Indicators. Edited by Wolfgang Glänzel, Henk F. Moed, Ulrich Schmoch and Mike Thelwall. Springer Handbooks. Cham: Springer International Publishing, pp. 159–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalgoo. 2023. Nalgoo® ATS|Applicant Tracking System for Human Resources. 2023. Available online: https://nalgoo.com/ats-for-hr (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Nawaz, Nishad. 2019. How Far Have We Come with The Study of Artificial Intelligence for Recruitment Process. International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research 8: 488–98. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/335960597_How_Far_Have_We_Come_With_The_Study_Of_Artificial_Intelligence_For_Recruitment_Process#fullTextFileContent (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Nexttech. 2021. Umelá inteligencia môže rozhodnúť, či vás prijmú do zamestnania. IT News. July 26. Available online: https://www.nextech.sk/a/Umela-inteligencia-moze-rozhodnut--ci-vas-prijmu-do-zamestnania (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Ochmann, Jessica, and Sven Laumer. 2021. AI Recruitment: Explaining Job Seekers’ Acceptance of Automation in Human Resource Management. Available online: https://library.gito.de/2021/07/wi2020-zentrale-tracks-115/ (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Olan, Femi, Emmanuel Ogiemwonyi Arakpogun, Jana Suklan, Franklin Nakpodia, Nadja Damij, and Uchitha Jayawickrama. 2022. Artificial Intelligence and Knowledge Sharing: Contributing Factors to Organizational Performance. Journal of Business Research 145: 605–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panerai, Fiamma. 2018. Artificial Intelligence Needs Human Ingenuity and Moral. Medium (blog). June 27. Available online: https://medium.com/@fiammapanerai/artificial-intelligence-needs-human-ingenuity-and-moral-a6f0bcad8ca0 (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- PwC. 2023. Discover Your New Career with PwC. 2023. Available online: https://www.pwc.lu/en/careers/campus-job-search/description.html (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Recruiters LineUp. 2023. How Do You Evaluate the Effectiveness of Recruitment and Selection? Recruiters LineUp. January 10. Available online: https://www.recruiterslineup.com/how-do-you-evaluate-the-effectiveness-of-recruitment-and-selection/ (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Rodríguez-Sánchez, José-Luis, Antonio Montero-Navarro, and Rocío Gallego-Losada. 2019. The Opportunity Presented by Technological Innovation to Attract Valuable Human Resources. Sustainability 11: 5785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, Anita. 2016. We Live in a VUCA World: The Importance of Responsible Leadership. Development and Learning in Organizations: An International Journal 30: 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutzer, Daniel. 1990. Business Expert Systems: The Competitive Edge. Expert Systems with Applications 1: 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, Manan. 2022. Council Post: Artificial Intelligence: A Key Technology That’s Shaping Our Tomorrow. Forbes. Available online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestechcouncil/2022/01/21/artificial-intelligence-a-key-technology-thats-shaping-our-tomorrow/ (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Soviar, Jakub, Michal Varmus, and Milan Kubina. 2015. Modern Approach to Teaching as University—Students Love the Real Problem. Procedia—Social and Behavioral Sciences 205: 401–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statista.com. 2022. Global Recruiting Trends: Key Benefits of Artificial Intelligence 2017. Statista. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/831693/recruitment-trends-benefits-of-artificial-intelligence/ (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Strang, Kenneth David, and Zhaohao Sun. 2022. ERP Staff versus AI Recruitment with Employment Real-Time Big Data. Discover Artificial Intelligence 2: 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štaffenová, Nikola, and Alžbeta Kucharčíková. 2024. Human Capital Management—Values, Competencies, and Motivation—Concerning Industry 4.0. Economic Research-Ekonomska Istraživanja 37: 2324160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šuštaršič, Ana, Mateja Videmšek, Damir Karpljuk, Ivan Miloloža, and Maja Meško. 2022. Big Data in Sports: A Bibliometric and Topic Study. Business Systems Research: International Journal of the Society for Advancing Innovation and Research in Economy 13: 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talíř, Milan, and Jarmila Straková. 2023. Innovation of the Production Process of Engineering Companies in Relation to Business Portfolio. Entrepreneurship and Sustainability Issues 10: 118–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tërstena, Arben, Arta Jashari Goga, and Bujar Jashari. 2020. Improving the Efficiency of Human Resources with the Use of New Technologies and Reorganization Process. International Journal of Research in Business and Social Science (2147-4478) 9: 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thite, Mohan. 2019. E-HRM: Digital Approaches, Directions & Applications, 1st ed. London: Routledge. New York: Taylor & Francis Group. [Google Scholar]
- Timana, Gonzalo Reyes. 2023. Los Entornos VUCA y BANI en la inteligencia: Implicaciones. Revista Escpogra PNP 3: 105–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tummers, Lars, Peter M. Kruyen, Dominique M. Vijverberg, and Tessa J. Voesenek. 2015. Connecting HRM and Change Management: The Importance of Proactivity and Vitality. Journal of Organizational Change Management 28: 627–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedapradha, R., Ravi Hariharan, and Rajan Shivakami. 2019. Artificial Intelligence: A Technological Prototype in Recruitment. Journal of Service Science and Management 12: 382–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetráková, Milota, Miloš Hitka, Marek Potkány, Silvia Lorincová, and Lukáš Smerek. 2018. Corporate Sustainability in the Process of Employee Recruitment through Social Networks in Conditions of Slovak Small and Medium Enterprises. Sustainability 10: 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, Abdul, Miao Xiaoming, Salma Waheed, and Naveed Ahmad. 2019. The Role Of Social Networking Sites In Effective E-Recruitmen; A Study Of Telecom Sector In Context Of Pakistan. KSII Transactions on Internet and Information Systems 13: 3842–61. [Google Scholar]
- Waheed, Abdul, Miao Xiaoming, Salma Waheed, Naveed Ahmad, and Shang Tian-tian. 2020. E-HRM Implementation, Adoption and Its Predictors: A Case of Small and Medium Enterprises of Pakistan. International Journal of Information Technology and Management 19: 162–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Li-Qun, and Chung-Ming Lau. 2005. Market Orientation, HRM Importance and Competency: Determinants of Strategic HRM in Chinese Firms. The International Journal of Human Resource Management 16: 1901–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabanci, Orhan. 2019. From Human Resource Management to Intelligent Human Resource Management: A Conceptual Perspective. Human-Intelligent Systems Integration 1: 101–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakubu, Ruth. 2021. Using AI and Data Science to Eliminate Bias in Hiring. Creating Startups. March 15. Available online: https://devblogs.microsoft.com/startups/using-ai-and-data-science-to-eliminate-bias-in-hiring/ (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Yau, Kok-Lim Alvin, Norizan Mat Saad, and Yung-Wey Chong. 2021. Artificial Intelligence Marketing (AIM) for Enhancing Customer Relationships. Applied Sciences 11: 8562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Fang, Sanying Peng, Ahmad Zamri Khairani, and Jinghong Liang. 2024. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Efficacy of Physical Activity Interventions among University Students. Sustainability 16: 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, He, Qin Heng Zhao, and Beata Ślusarczyk. 2019. Sustainability and Digitalization of Corporate Management Based on Augmented/Virtual Reality Tools Usage: China and Other World IT Companies’ Experience. Sustainability 11: 4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žuľová, Jana. 2021. Používanie umelej inteligencie pri výbere zamestnancov z perspektívy GDPR. Justičné revue 73: 30–39. [Google Scholar]
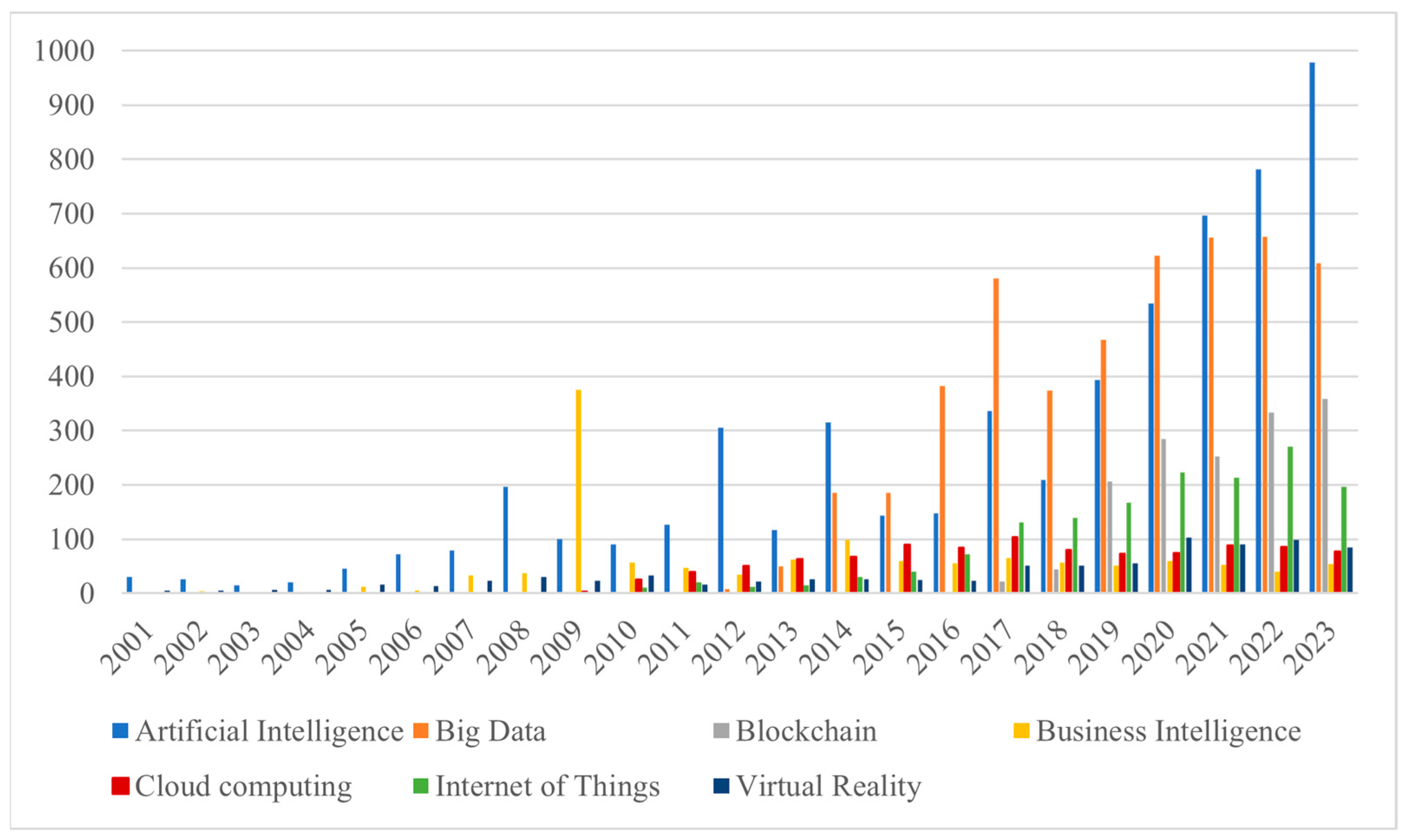


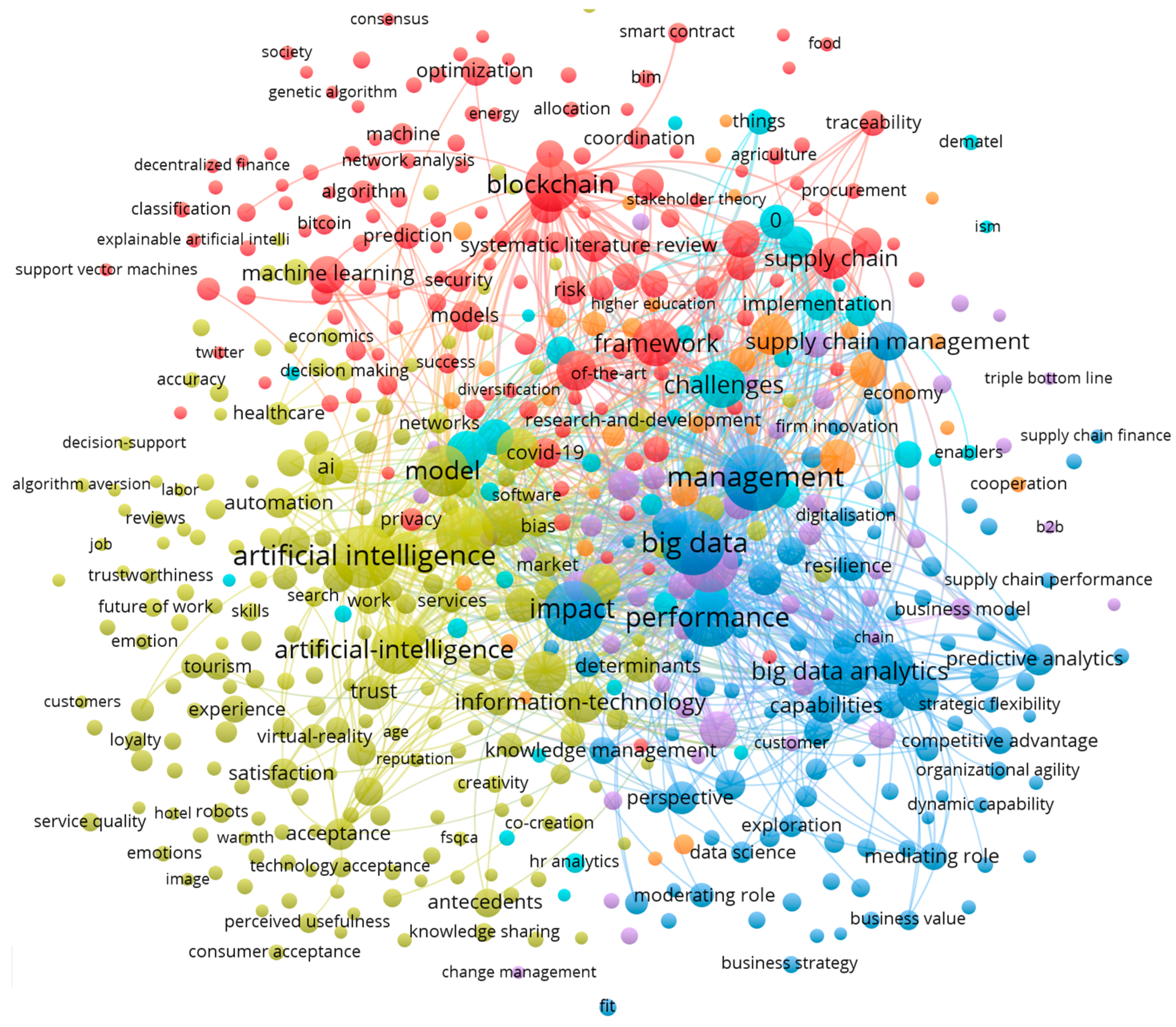
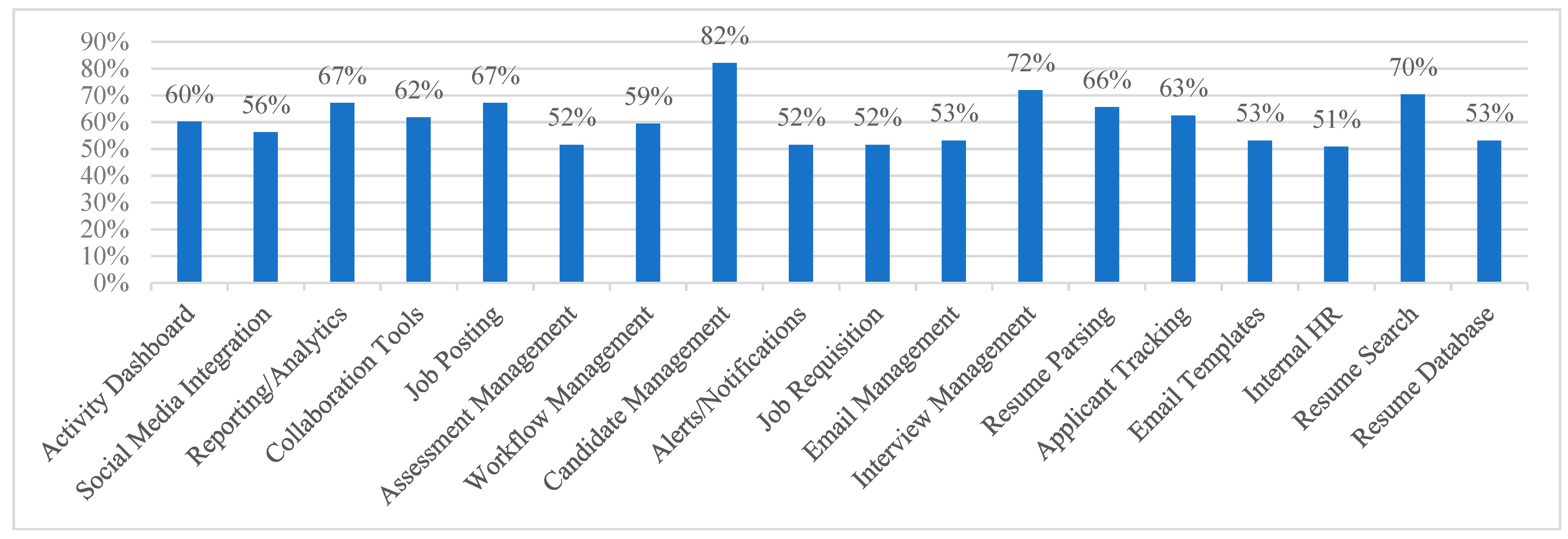
| Year | Number of Publications | Technology |
|---|---|---|
| 2001 | 20 | email, internet, world wide web |
| 2002 | 29 | internet, world wide web |
| 2003 | 12 | computer, world wide web |
| 2004 | 41 | business intelligence, email, internet, world wide web |
| 2005 | 72 | data warehousing, internet |
| 2006 | 150 | email, internet |
| 2007 | 180 | intelligent agents, world wide web |
| 2008 | 255 | artificial intelligence, business intelligence, data warehousing, social networks and media |
| 2009 | 259 | artificial intelligence, data mining, intelligent agents, RFID |
| 2010 | 229 | cloud computing, intelligent agents, smart grid, social networks and media, web 2.0 |
| 2011 | 333 | artificial intelligence, autonomous robots, data mining, data warehousing, intelligent agents, RFID, smart grid, virtual reality, web 2.0 |
| 2012 | 229 | artificial intelligence, cloud computing, data mining, data warehousing, RFID, social networks and media, virtual reality, web 2.0 |
| 2013 | 249 | artificial intelligence, business intelligence, cloud computing, data mining, data warehousing, intelligent agents, smart technologies, virtual reality |
| 2014 | 232 | artificial intelligence, cloud computing, data mining, data warehousing, intelligent agents, smart technologies, social networks and media, web 2.0, wireless sensor networks |
| 2015 | 254 | artificial intelligence, big data, business intelligence, cloud computing, intelligent agents, smart grid, smart technologies, social networks and media, web 2.0 |
| 2016 | 384 | artificial intelligence, big data, business intelligence, cloud computing, data mining, data warehousing, internet of everything, internet of things, smart technologies, social networks and media |
| 2017 | 278 | artificial intelligence, big data, business intelligence, cloud computing, intelligent agents, internet of everything, internet of things, smart grid, smart technologies, wireless sensor networks |
| 2018 | 256 | artificial intelligence, autonomous robots, big data, business intelligence, cloud computing, data mining, expert systems, industrial internet of things, internet of everything, internet of things, smart technologies, social networks and media, virtual reality |
| 2019 | 286 | artificial intelligence, augmented reality, autonomous robots, big data, business intelligence, cloud computing, edge computing, expert systems, industrial internet of things, intelligent agents, internet of everything, internet of things, RFID, smart technologies, social networks and media, virtual reality, wireless sensor networks |
| 2020 | 307 | artificial intelligence, augmented reality, autonomous robots, big data, blockchain, cloud computing, edge computing, expert systems, industrial internet of things, intelligent agents, internet of everything, internet of things, smart grid, smart technologies, virtual reality, wireless sensor networks |
| 2021 | 266 | artificial intelligence, augmented reality, autonomous robots, autonomous vehicles, big data, blockchain, business intelligence, cloud computing, data warehousing, digital twin, edge computing, expert systems, industrial internet of things, intelligent agents, internet of everything, internet of things, smart grid, smart technologies, swarm intelligence, virtual reality, wireless sensor networks |
| 2022 | 247 | artificial intelligence, augmented reality, autonomous robots, autonomous vehicles, big data, blockchain, business intelligence, cloud computing, digital twin, edge computing, expert systems, industrial internet of things, intelligent agents, internet of everything, internet of things, smart grid, smart technologies, swarm intelligence, virtual reality, wireless sensor networks |
| 2023 | 252 | artificial intelligence, augmented reality, big data, cloud computing, internet of things, internet, smart technologies, social networks and media, unmanned aerial vehicles, virtual reality |
| Technology | Keyword Modification | Occurrence | Cumulative Occurrence | Share |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Artificial intelligence | “ai” | 55 | 508 | 28.78% |
| “ai adoption” | 5 | |||
| “artificial intelligence” | 264 | |||
| “artificial intelligence (ai)” | 31 | |||
| “artificial- intelligence” | 153 | |||
| Big Data | “big-data” | 8 | 449 | 25.44% |
| “big data” | 291 | |||
| “big data analytics” | 138 | |||
| “big data analytics capability” | 12 | |||
| Blockchain | “blockchain” | 188 | 262 | 14.84% |
| “blockchain adoption” | 7 | |||
| “blockchain technology” | 67 | |||
| Internet of things | “internet of things” | 43 | 91 | 5.16% |
| “IoT” | 32 | |||
| “internet of things (IoT)” | 16 | |||
| Virtual reality | “virtual-reality” | 24 | 48 | 2.72% |
| “virtual reality” | 24 | |||
| Cloud computing | “cloud computing” | 26 | 39 | 2.21% |
| “cloud computing adoption” | 13 | |||
| Business intelligence | “business intelligence” | 25 | 25 | 1.42% |
| Activity | Feature | Feature Description |
|---|---|---|
| Recruitment planning | Job Requisition | scheduling a new employee |
| Preparation and publication of job offers | Job Posting | posting, monitoring, and managing job offers on various channels (e.g., social media, company career site) |
| Email Templates | pre-prepared examples and templates for emails | |
| Candidate search and management | Social Media Integration | integration with social networks, e.g., Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn |
| Candidate Management | building, monitoring, and maintaining relationships with candidates | |
| Email Management | integration with email, e.g., Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo | |
| Applicant Tracking | searching for and managing potential candidates, their applications, and CVs | |
| Managing CVs | Resume Parsing | converting your CV into a structured format for storage purposes |
| Resume Search | search for saved CVs | |
| Resume Database | a searchable repository of candidate profiles | |
| Screening and testing of applicants | Assessment Management | creating tests or questionnaires for candidates |
| Management of interviews and assessments | Interview Management | creating and tracking interviews |
| Evaluating the effectiveness of the process | Activity Dashboard | dashboard to view activity statistics |
| Reporting/Analytics | analysis and reporting on the effectiveness of the recruitment process | |
| Managing the recruitment process | Collaboration Tools | communication and cooperation |
| Alerts/Notifications | alerts/notifications within the system | |
| Internal HR | recruitment software for internal recruiters or HR managers | |
| Workflow Management | creating, designing, and visually representing the recruitment process |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koman, G.; Boršoš, P.; Kubina, M. The Possibilities of Using Artificial Intelligence as a Key Technology in the Current Employee Recruitment Process. Adm. Sci. 2024, 14, 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci14070157
Koman G, Boršoš P, Kubina M. The Possibilities of Using Artificial Intelligence as a Key Technology in the Current Employee Recruitment Process. Administrative Sciences. 2024; 14(7):157. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci14070157
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoman, Gabriel, Patrik Boršoš, and Milan Kubina. 2024. "The Possibilities of Using Artificial Intelligence as a Key Technology in the Current Employee Recruitment Process" Administrative Sciences 14, no. 7: 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci14070157
APA StyleKoman, G., Boršoš, P., & Kubina, M. (2024). The Possibilities of Using Artificial Intelligence as a Key Technology in the Current Employee Recruitment Process. Administrative Sciences, 14(7), 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci14070157






