- Article
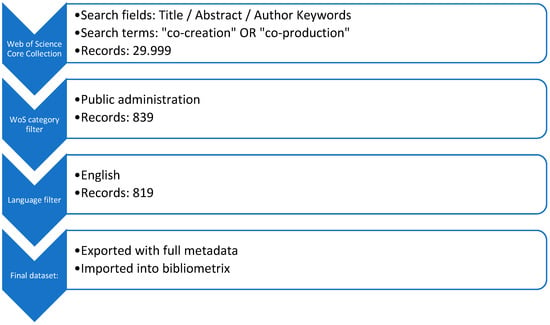
This study presents a comprehensive bibliometric and science mapping analysis of research on co-creation and co-production in public administration, based on 819 publications indexed in the Web of Science (WoS). The analysis of scientific production in this field shows sparse early contributions before 2005, followed by steady growth after 2010 and accelerated expansion from 2016 onward, driven primarily by European and United States research communities. In terms of scholarly influence, the results identify a stable core of highly productive and influential authors, institutions, and countries, with strong concentration in Northern and Western Europe and Anglo-Saxon contexts. To address the intellectual structure of the field, science mapping identifies four dominant thematic clusters: (1) co-production and value creation, (2) participation and public engagement, (3) governance and policy, and (4) knowledge development, lessons learned, and evaluative insights. Examining thematic and keyword evolution over time, the findings indicate a shift from early conceptual and normative discussions toward more applied and implementation-oriented research, with increasing attention to barriers, challenges, and enabling conditions in recent years. Overall, the findings show that research on co-creation and co-production has evolved from conceptual fragmentation toward greater thematic consolidation and analytical maturity, while persistent implementation challenges remain. By systematically mapping these developments, the study provides a structured overview that supports future conceptual integration and informs both research agendas and practice-oriented discussions on co-creation and co-production in public administration.
21 January 2026