Cortical Resonance to Visible and Invisible Visual Rhythms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Stimuli and Tasks
2.3. EEG Recordings
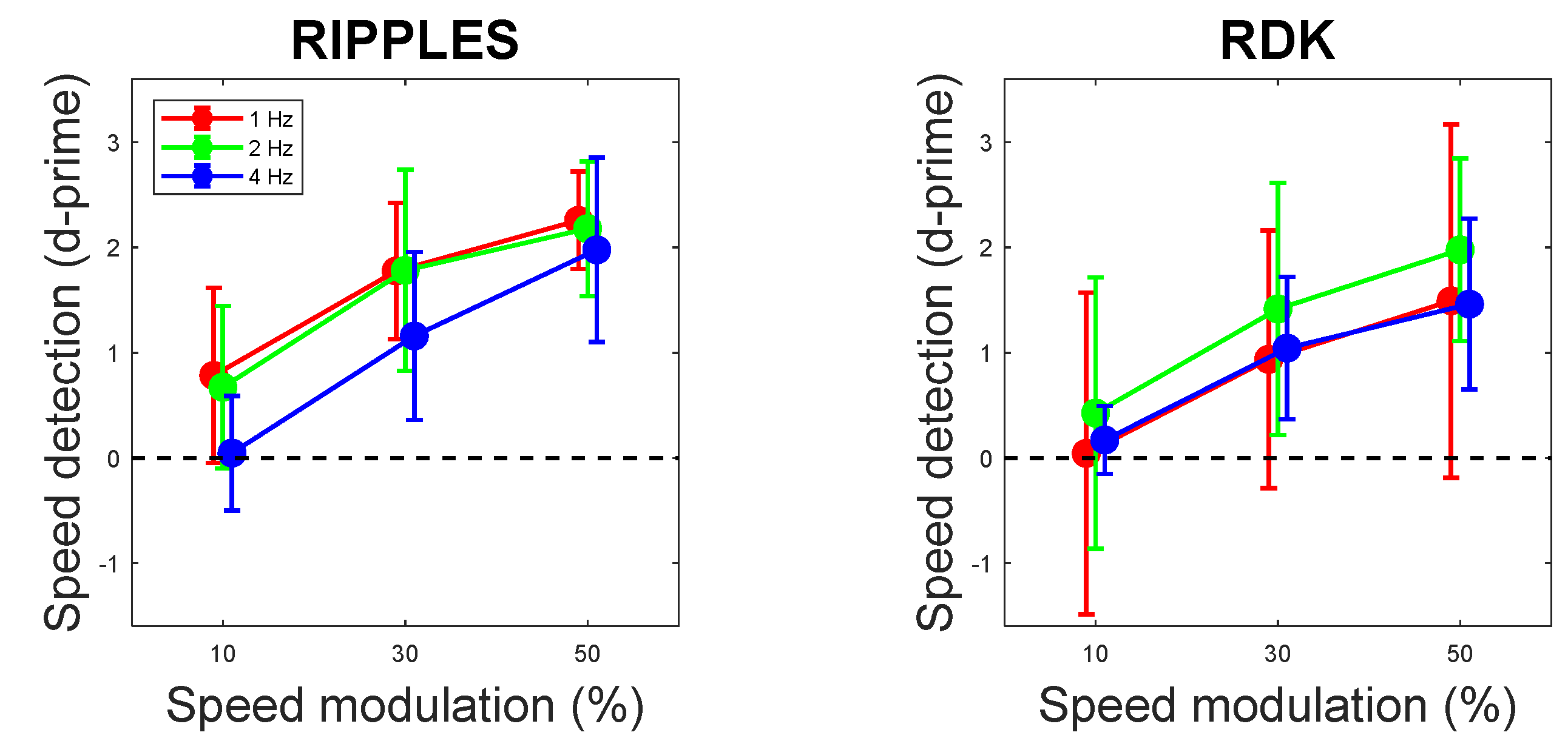
2.4. Data Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Shape and Distribution of Cortical Responses
4.2. Attentive Subliminal Resonance
4.3. Limitations
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De’Sperati, C.; Baud Bovy, G. Low perceptual sensitivity to altered video speed in viewing a soccer match. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossi, F.; Montanaro, E.; de’Sperati, C. Speed Biases With Real-Life Video Clips. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuliani, E.; Caputi, M.; Scaini, S.; de’Sperati, C. Videos look faster as children grow up: Sense of speed and impulsivity throughout primary school. J. Exp. Child. Psychol. 2019, 179, 190–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burr, D.; Thompson, P. Motion psychophysics: 1985–2010. Vis. Res. 2011, 51, 1431–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nishimoto, S.; Vu, A.T.; Naselaris, T.; Benjamini, Y.; Yu, B.; Gallant, J.L. Reconstructing visual experiences from brain activity evoked by natural movies. Curr. Biol. CB 2011, 21, 1641–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Macmillan, N.A.; Creelman, C.D. Detection Theory: A User’s Guide, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gregori Grgic, R.; Crespi, S.A.; de’Sperati, C. Assessing Self-Awareness through Gaze Agency. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, G.S.; White, K.G. The optimal correction for estimating extreme discriminability. Behav. Res. Methods 2005, 37, 436–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bates, D.; Kliegl, R.; Vasishth, S.; Baayen, R. Parsimonious mixed models. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1506.04967. [Google Scholar]
- Payne, B.R.; Lee, C.L.; Federmeier, K.D. Revisiting the incremental effects of context on word processing: Evidence from single-word event-related brain potentials. Psychophysiology 2015, 52, 1456–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vialatte, F.B.; Maurice, M.; Dauwels, J.; Cichocki, A. Steady-state visually evoked potentials: Focus on essential paradigms and future perspectives. Prog. Neurobiol. 2010, 90, 418–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snowden, R.J.; Ullrich, D.; Bach, M. Isolation and characteristics of a steady-state visually-evoked potential in humans related to the motion of a stimulus. Vis. Res. 1995, 35, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niedeggen, M.; Wist, E.R. Characteristics of visual evoked potentials generated by motion coherence onset. Brain Res. Cogn. Brain Res. 1999, 8, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patzwahl, D.R.; Zanker, J.M. Mechanisms of human motion perception: Combining evidence from evoked potentials, behavioural performance and computational modelling. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braddick, O.J.; O’Brien, J.M.; Wattam-Bell, J.; Atkinson, J.; Hartley, T.; Turner, R. Brain areas sensitive to coherent visual motion. Perception 2001, 30, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuba, M.; Kubova, Z.; Kremlacek, J.; Langrova, J. Motion-onset VEPs: Characteristics, methods, and diagnostic use. Vis. Res. 2007, 47, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nozaradan, S.; Peretz, I.; Missal, M.; Mouraux, A. Tagging the neuronal entrainment to beat and meter. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 10234–10240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehaene, S.; Changeux, J.P.; Naccache, L.; Sackur, J.; Sergent, C. Conscious, preconscious, and subliminal processing: A testable taxonomy. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2006, 10, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Merikle, P.M.; Smilek, D.; Eastwood, J.D. Perception without awareness: Perspectives from cognitive psychology. Cognition 2001, 79, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overgaard, M.; Rote, J.; Mouridsen, K.; Ramsoy, T. Is conscious perception gradual or dychotomous? A comparison of report methodologies during a visual task. Conscious. Cogn. 2006, 15, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| e | t | d | p | l | u | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amplitude | 0.036 | 4.437 | 86 | <0.001 | 0.020 | 0.051 |
| Frequency | −0.0136 | −1.312 | 86 | 0.193 | −0.341 | 0.070 |
| Amplitude:Frequency | 0.001 | 0.402 | 86 | 0.689 | −0.005 | 0.007 |
| e | t | d | p | l | u | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amplitude | 16.439 | 3.030 | 716 | 0.003 | 5.789 | 27.090 |
| Frequency | −144.841 | −2.068 | 716 | 0.039 | −282.341 | −7.341 |
| Amplitude:Frequency | −2.542 | −1.240 | 716 | 0.215 | −6.568 | 1.484 |
| Channel | e | t | d | p | l | u |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1 | 153.240 | 1.218 | 716 | 0.224 | 400.210 | 93.734 |
| O2 | 85.014 | 0.676 | 716 | 0.499 | 331.990 | 161.960 |
| P3 | 30.566 | 0.243 | 716 | 0.808 | 277.540 | 216.410 |
| P4 | 185.070 | 1.471 | 716 | 0.142 | 61.900 | 432.040 |
| C1 | 141.630 | 1.126 | 716 | 0.261 | 388.610 | 105.340 |
| C2 | 231.030 | 1.834 | 716 | 0.067 | 478.000 | 15.944 |
| F3 | 78.625 | 0.625 | 716 | 0.532 | 168.350 | 325.600 |
| F4 | 377.780 | 3.003 | 716 | 0.003 | 130.810 | 624.750 |
| Perceptual Responses | Cortical Responses | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ripples | RDK | Ripples | RDK | |
| Amplitude | 0.598 | 0.649 | 0.249 | 0.170 |
| Frequency | 0.164 | 0.172 | 0.440 | 0.381 |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de’Sperati, C. Cortical Resonance to Visible and Invisible Visual Rhythms. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10010037
de’Sperati C. Cortical Resonance to Visible and Invisible Visual Rhythms. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(1):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10010037
Chicago/Turabian Stylede’Sperati, Claudio. 2020. "Cortical Resonance to Visible and Invisible Visual Rhythms" Brain Sciences 10, no. 1: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10010037
APA Stylede’Sperati, C. (2020). Cortical Resonance to Visible and Invisible Visual Rhythms. Brain Sciences, 10(1), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10010037




