Behavioral and Oxidative Stress Changes in Mice Subjected to Combinations of Multiple Stressors Relevant to Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Housing and Habituation
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Behavioral Testing
2.3.1. Y Maze Test
2.3.2. Elevated Plus Maze
2.3.3. Forced Swim Test
2.4. Tissue Collection and Preparation
2.5. Biochemical Determinations
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Behavioral Parameters Evaluation
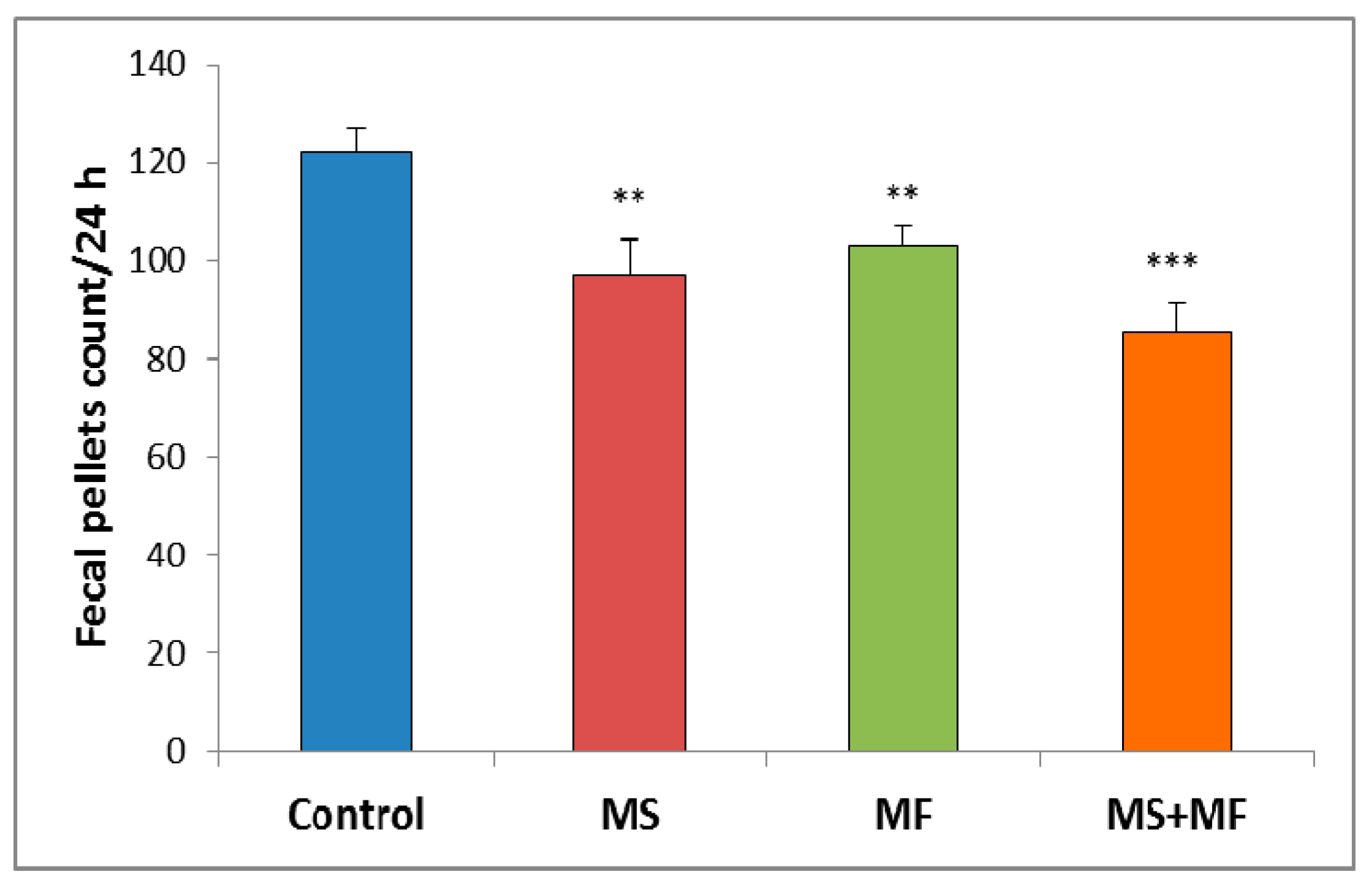
3.1.1. The Effect of Various Combinations of Stress Factors on Gastrointestinal Tract Habits
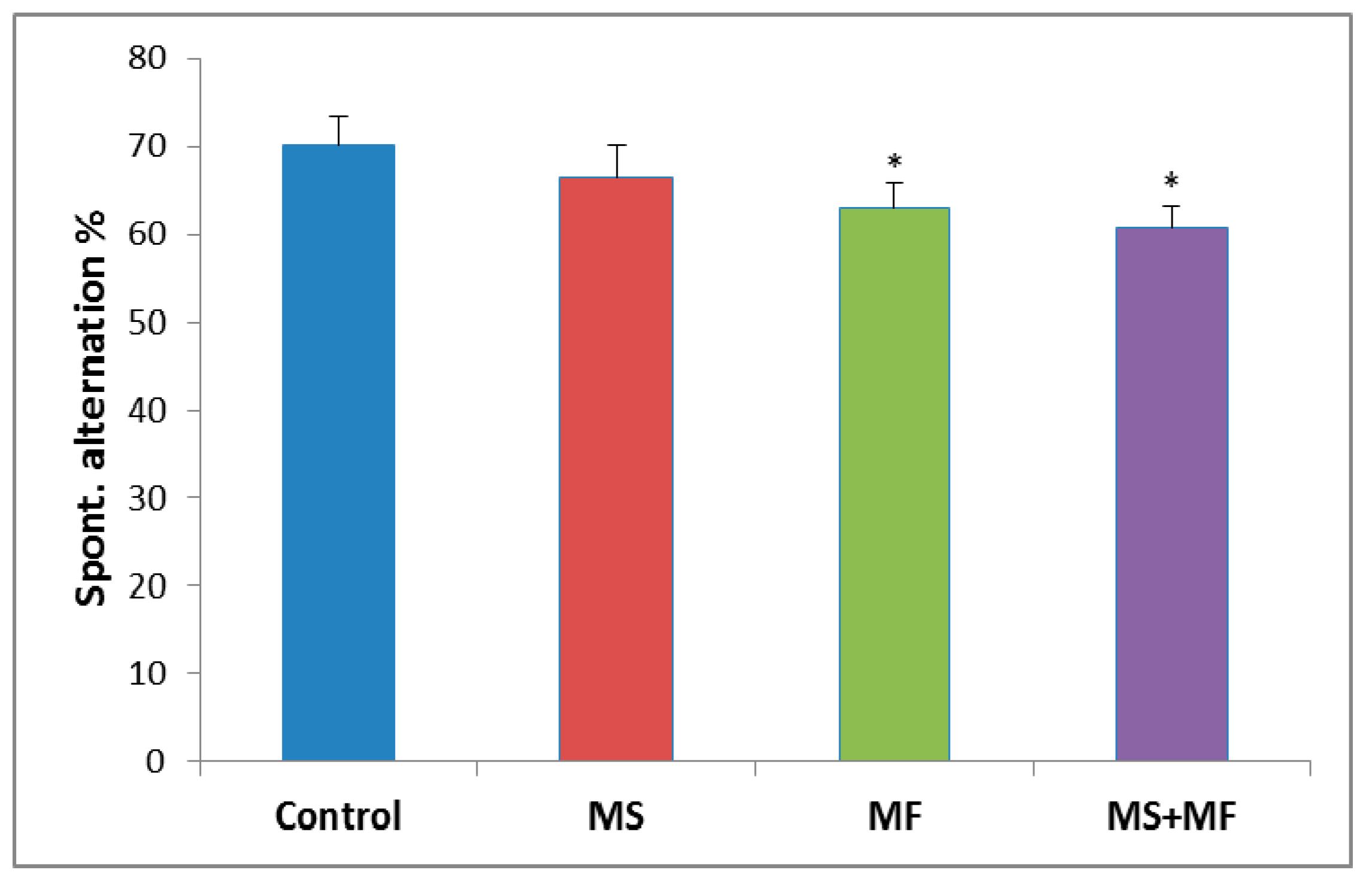
3.1.2. The Effects of Various Combinations of Stress Factors in the Y-Maze Test
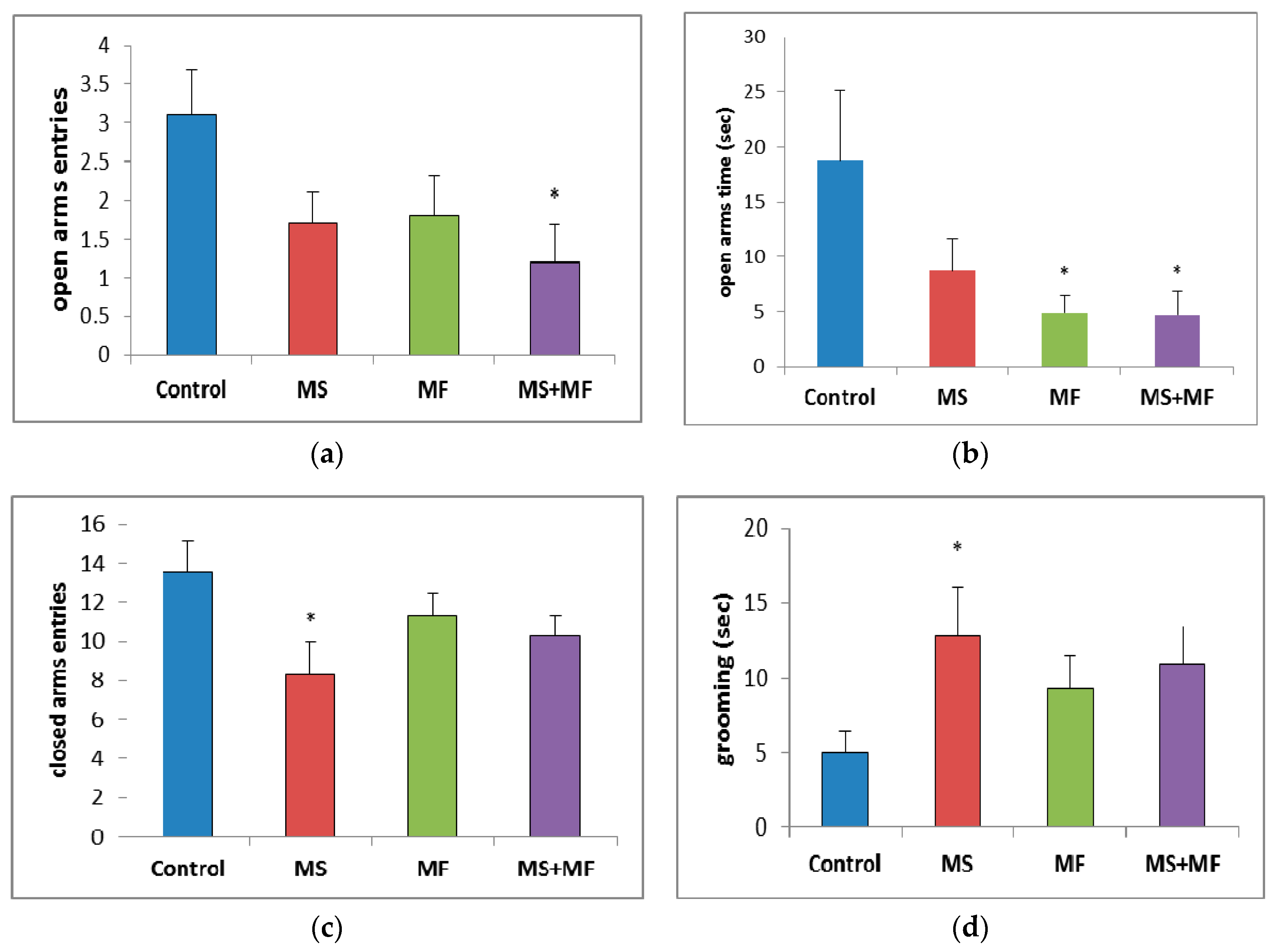
3.1.3. The Effects of Various Combinations of Stress Factors on the Parameters Evaluated in Elevated Plus Maze
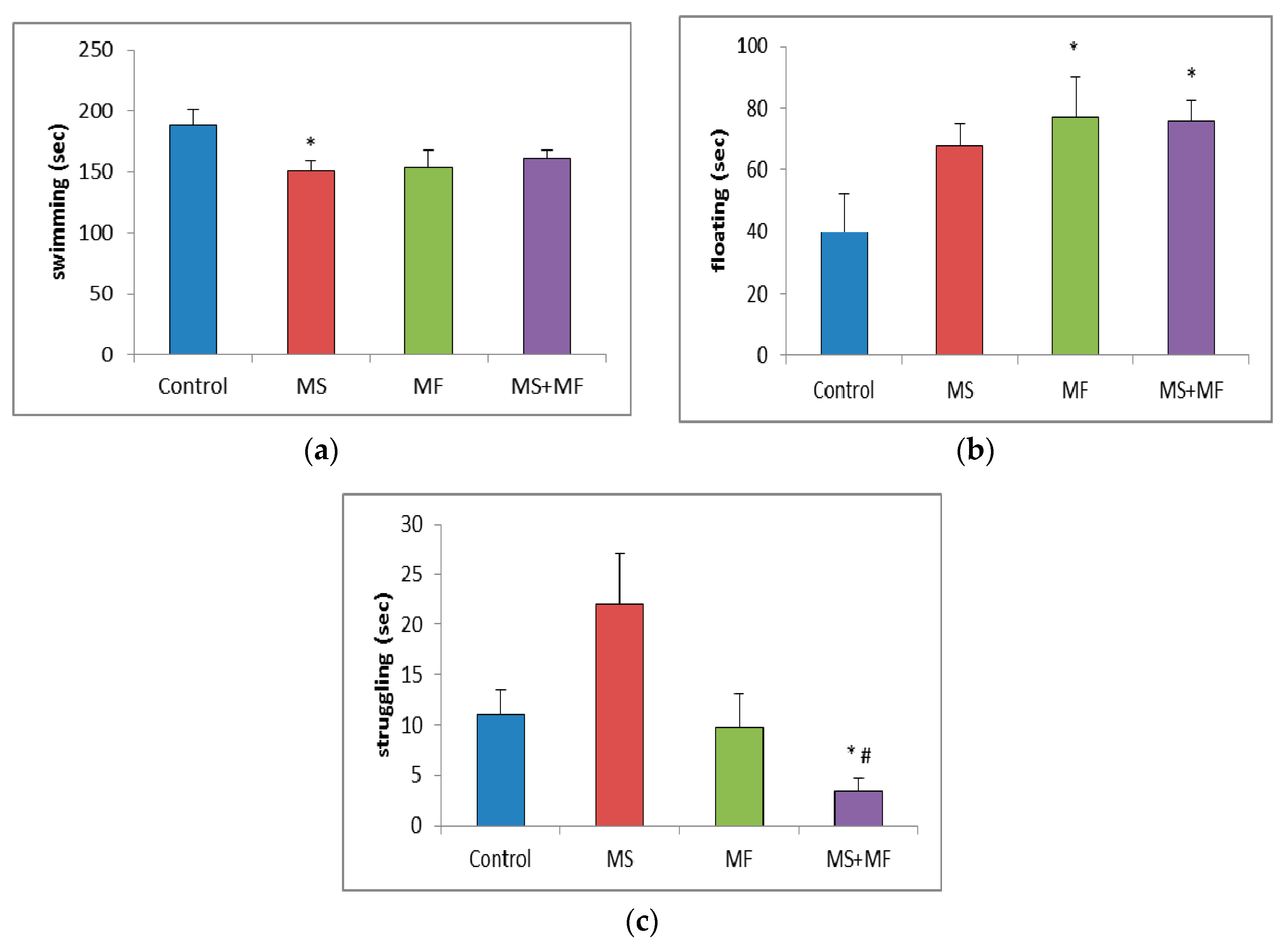
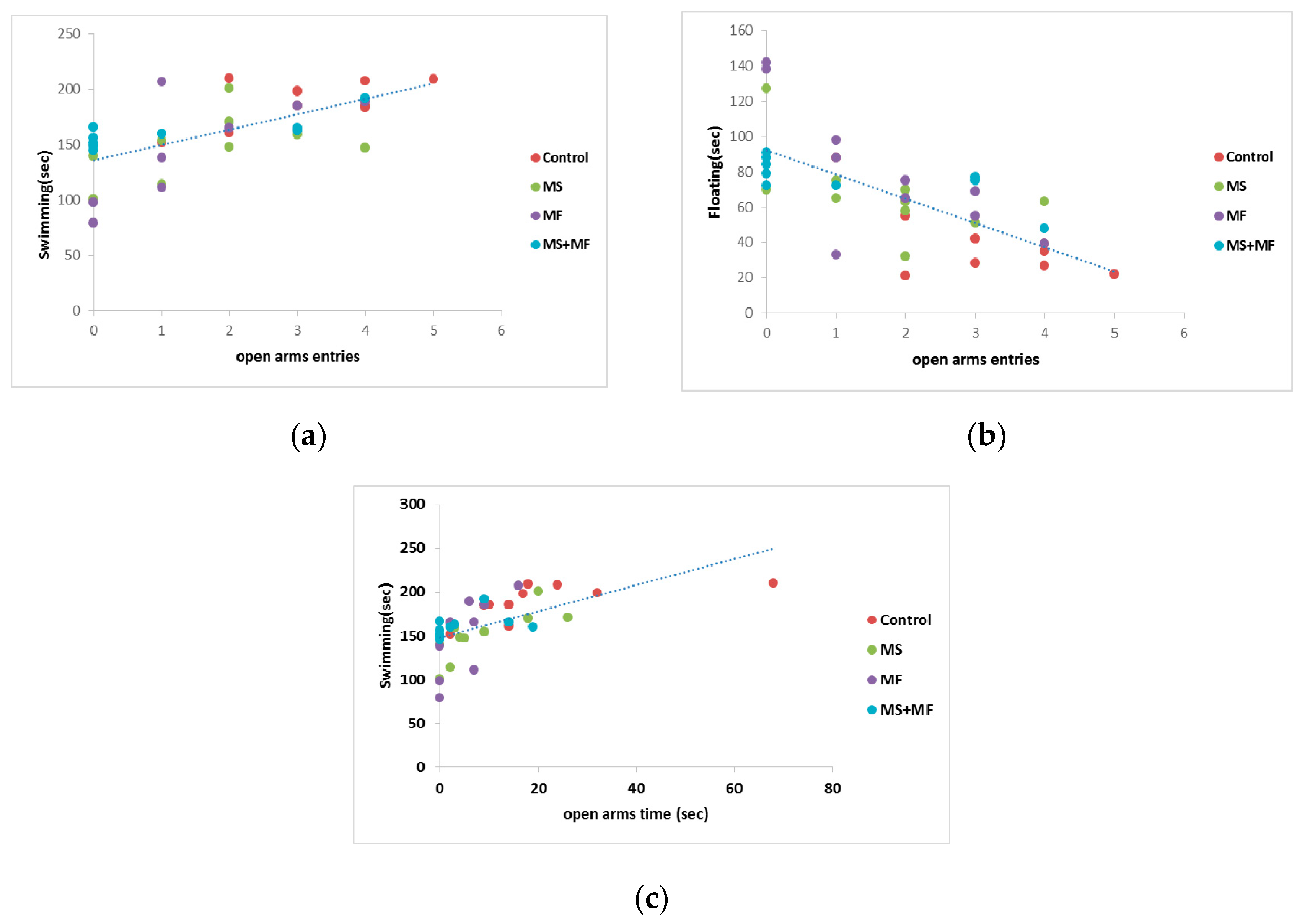
3.1.4. Effects of Various Combinations of Stress Factors on the Parameters Evaluated in Forced Swim Test
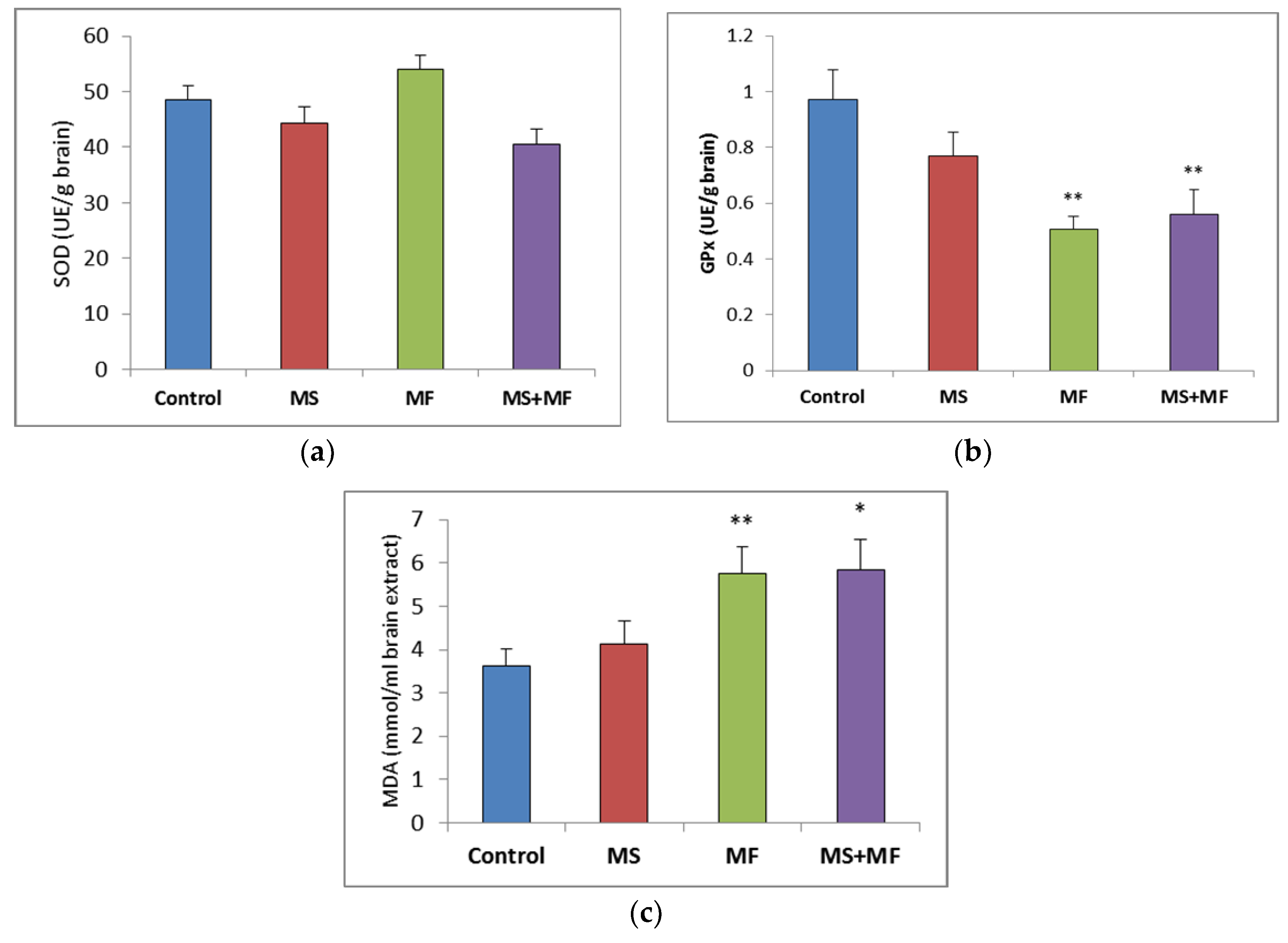
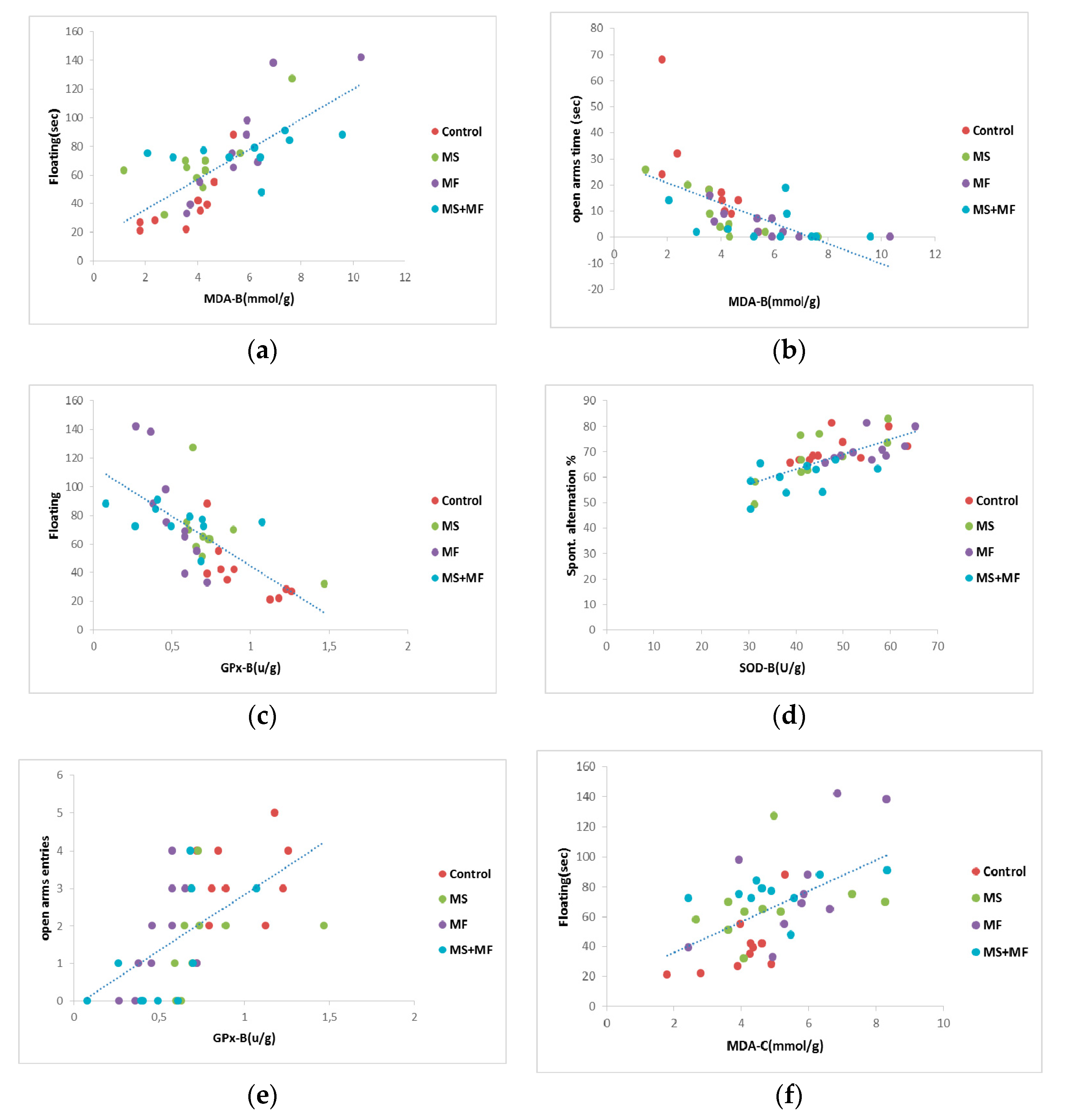
3.2. Brain Tissue Biochemical Parameters Evaluation
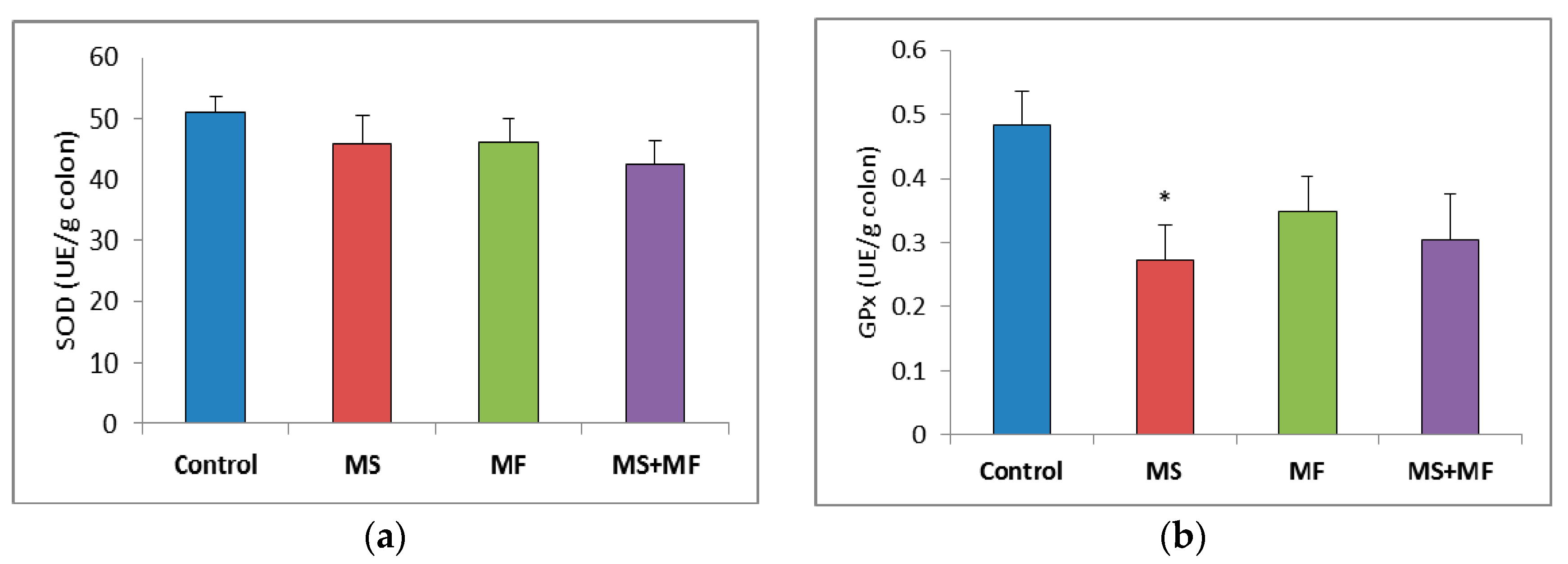
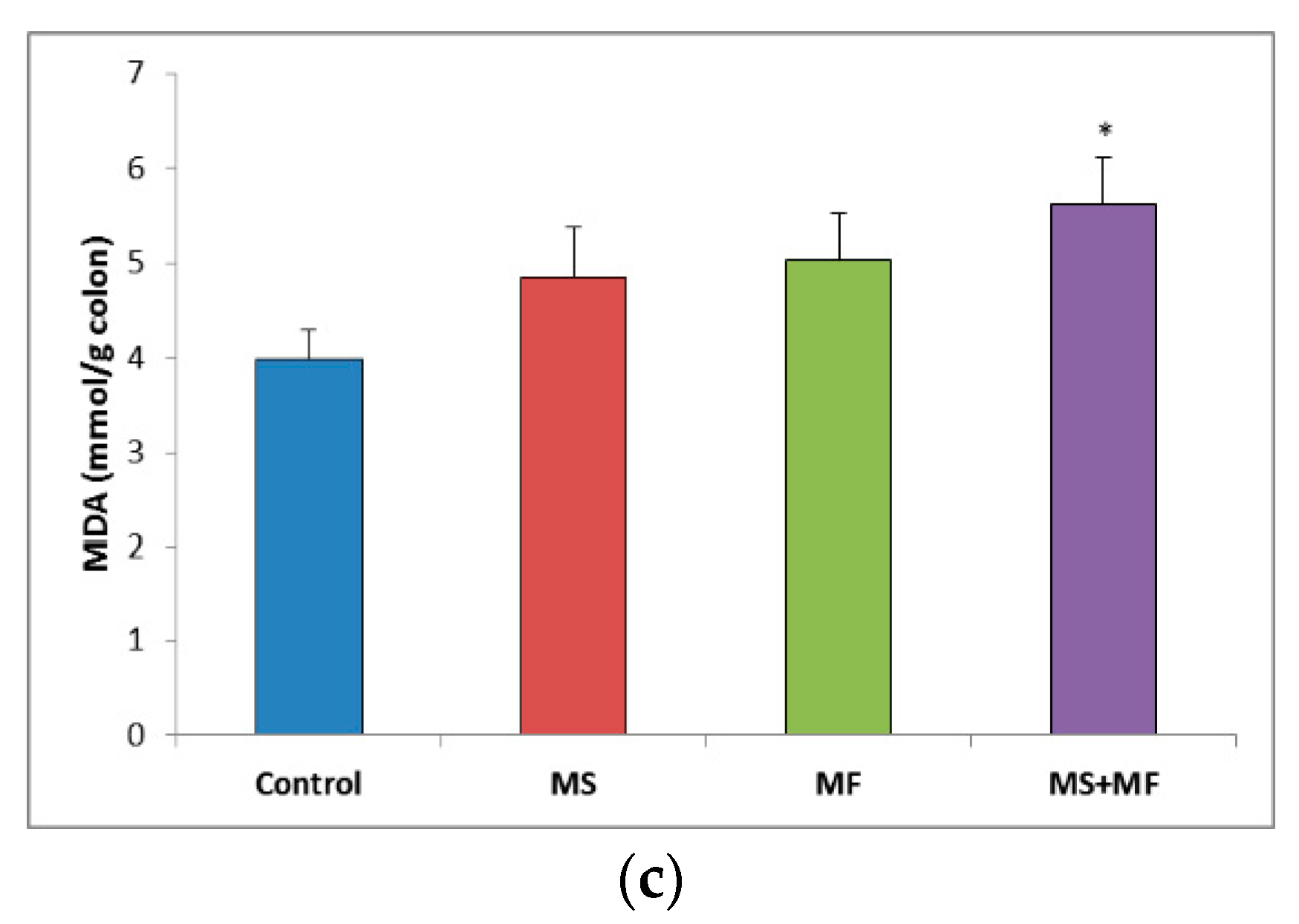
3.3. Bowel Tissue Biochemical Parameters Evaluation
3.4. Behavioral and Biochemical Parameters Correlations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Data Availability
References
- Enck, P.; Aziz, Q.; Barbara, G.; Farmer, A.D.; Fukudo, S.; Mayer, E.A.; Niesler, B.; Quigley, E.M.M.; Rajilić-Stojanović, M.; Schemann, M.; et al. Irritable bowel syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2016, 2, 16015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tack, J.; Drossman, D.A. What’s new in Rome IV? Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 20, e13053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.-Y.; Cheng, C.-W.; Tang, X.-D.; Bian, Z.-X. Impact of psychological stress on irritable bowel syndrome. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 14126–14131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, E.A. The neurobiology of stress and gastrointestinal disease. Gut 2000, 47, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bradesi, S.; Golovatscka, V.; Ennes, H.S.; McRoberts, J.A.; Karagiannidis, I.; Bakirtzi, K.; Pothoulakis, C.; Mayer, E.A. Role of astrocytes and altered regulation of spinal glutamatergic neurotransmission in stress-induced visceral hyperalgesia in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2011, 301, G580–G589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mayer, E.A.; Tillisch, K. The Brain-Gut Axis in Abdominal Pain Syndromes. Annu. Rev. Med. 2011, 62, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Zhu, G. Gut–Brain Axis and Mood Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Ling, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, H.; Ma, Z.; Haiyin, J.; Wang, W.; Tang, W.; Tan, Z.; Shi, J.; et al. Altered fecal microbiota composition in patients with major depressive disorder. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 48, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carabotti, M.; Scirocco, A.; Maselli, M.A.; Severi, C. The gut-brain axis: Interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 203–209. [Google Scholar]
- Tsang, S.W.; WAuyeung, K.K.; Bian, Z.X.; Ko, J.K.S. Pathogenesis, Experimental Models and Contemporary Pharmacotherapy of Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Story About the Brain-Gut Axis. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 842–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdollahi, M.; Esmaily, H.; Baeeri, M.; Asadi-Shahmirzadi, A.; Mozaffari, S.; Rahimi, R.; Sanei, Y.; Salehi-Surmaghi, M.-H. Effects of Hypericum perforatum extract on rat irritable bowel syndrome. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2011, 7, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Lee, M.Y.; Choi, C.S.; Sohn, Y.W.; Park, B.R.; Cho, Y.K.; Nah, Y.-H.; Choi, S.C. The effect of chronic variable stress on bowel habit and adrenal function in rats. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23, 1840–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadi-Shahmirzadi, A.; Mozaffari, S.; Sanei, Y.; Baeeri, M.; Hajiaghaee, R.; Monsef-Esfahani, H.R.; Abdollahi, M. Benefit of Aloe vera and Matricaria recutita mixture in rat irritable bowel syndrome: Combination of antioxidant and spasmolytic effects. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fish, E.W.; Shahrokh, D.; Bagot, R.; Caldji, C.; Bredy, T.; Szyf, M.; Meaney, M.J. Epigenetic Programming of Stress Responses through Variations in Maternal Care. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1036, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zou, N.; Lv, H.; Li, J.; Yang, N.; Xue, H.; Zhu, J.; Qian, J. Changes in brain G proteins and colonic sympathetic neural signaling in chronic-acute combined stress rat model of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Transl. Res. 2008, 152, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Bi, Z.; Wang, E.; Sun, B.; Zheng, Y.; Zhong, L.; Yuan, J. Rodent Model of Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Int. J. Gastroenterol. Disord. Ther. 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefter, R.; Ciobica, A.; Guenné, S.; Compaoré, M.; Kiendrebéogo, M.; Stanciu, C.; Trifan, A. Complex Neurobehavioral Testing of a Rat Model of the Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Neurophysiology 2018, 50, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomon, K.; Jin, A. Diathesis-Stress Model. In Encyclopedia of Behavioral Medicine; Gellman, M.D., Turner, J.R., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sequeira-Cordero, A.; Salas-Bastos, A.; Fornaguera, J.; Brenes, J.C. Behavioural characterisation of chronic unpredictable stress based on ethologically relevant paradigms in rats. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17403–17421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egrenham, S.; Clarke, G.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Brain?Gut?Microbe Communication in Health and Disease. Front. Physiol. 2011, 2, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayer, E.A.; Labus, J.S.; Tillisch, K.; Cole, S.W.; Baldi, P. Towards a systems view of IBS. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaudhary, N.A.; Truelove, S.C. The irritable colon syndrome. A study of the clinical features, predisposing causes, and prognosis in 130 cases. Q. J. Med. 1962, 31, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choghakhori, R.; Abbasnezhad, A.; Hasanvand, A.; Amani, R. Inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress biomarkers in irritable bowel syndrome: Association with digestive symptoms and quality of life. Cytokine 2017, 93, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mete, R.; Tulubas, F.; Oran, M.; Yilmaz, A.; Avci, B.A.; Yildiz, K.; Turan, C.B.; Gurel, A. The role of oxidants and reactive nitrogen species in irritable bowel syndrome: A potential etiological explanation. Med. Sci. Monit. 2013, 19, 762. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dolatabadi, F.; Abdolghaffari, A.H.; Farzaei, M.H.; Baeeri, M.; Ziarani, F.S.; Eslami, M.; Abdollahi, M.; Rahimi, R. The Protective Effect ofMelissa officinalis L. in Visceral Hypersensitivity in Rat Using 2 Models of Acid-induced Colitis and Stress-induced Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Possible Role of Nitric Oxide Pathway. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 24, 490–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Zhang, H.; Sun, H.; Zhou, L.; Chen, Y.; Xuan, L.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, S. Maternal Separation Induced Visceral Hypersensitivity from Childhood to Adulthood. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 23, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kokkinidis, L.; Anisman, H. Dissociation of the effects of scopolamine and d-amphetamine on a spontaneous alternation task. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1976, 5, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellow, S.; Chopin, P.; File, S.E.; Briley, M. Validation of open: Closed arm entries in an elevated plus-maze as a measure of anxiety in the rat. J. Neurosci. Methods 1985, 14, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porsolt, R.D.; Bertin, A.; Jalfre, M. Behavioral despair in mice: A primary screening test for antidepressants. Arch. Int. de Pharmacodyn. et de Ther. 1977, 229, 327–336. [Google Scholar]
- Ciobica, A.; Olteanu, Z.; Padurariu, M.; Hritcu, L. The effects of pergolide on memory and oxidative stress in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 68, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, W.E.; Palsson, O.; Jones, K.R. Systematic review of the comorbidity of irritable bowel syndrome with other disorders: What are the causes and implications? Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 1140–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanger, G.J.; Yoshida, M.; Yahyah, M.; Kitazumi, K. Increased defecation during stress or after 5-hydroxytryptophan: Selective inhibition by the 5-HT4 receptor antagonist, SB-207266. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 130, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Evangelista, S.; Evangelista, S. Experimental Models of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and the Role of the Enteric Neurotransmission. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saito, K.; Kasai, T.; Nagura, Y.; Ito, H.; Kanazawa, M.; Fukudo, S. Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone Receptor 1 Antagonist Blocks Brain–Gut Activation Induced by Colonic Distention in Rats. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 1533–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taché, Y.; Martínez, V.; Million, M.; Rivier, J. Corticotrophin-releasing hormone and the brain-gut motor response to stress. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 13, 18A–25A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- German, A.C.; Cunliffe, N.A.; Morgan, K.L. Faecal consistency and risk factors for diarrhoea and constipation in cats in UK rehoming shelters. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2016, 19, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Malley, D.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Neonatal maternal separation in the rat impacts on the stress responsivity of central corticotropin-releasing factor receptors in adulthood. Psychopharmacology 2010, 214, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savignac, H.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Resistance to Early-Life Stress in Mice: Effects of Genetic Background and Stress Duration. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2011, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savignac, H.; Finger, B.; Pizzo, R.; O’Leary, O.; Dinan, T.; Cryan, J.F. Increased sensitivity to the effects of chronic social defeat stress in an innately anxious mouse strain. Neuroscience 2011, 192, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tramullas, M.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Chronic psychosocial stress induces visceral hyperalgesia in mice. Stress 2011, 15, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.-Y.; Jiang, Y.-P.; Hu, H.-L.; Cao, Z.-J. Establishing rat models of slow transit constipation and chronic stress-induced depression: Correlation of constipation and depression. Chin. J. Tissue Eng. Res. 2015, 19, 4356–4360. [Google Scholar]
- Lieblich, I.; Guttman, R. Analysis of emotional defecation under severe and mild stress—Evidence for genotype-situation interaction. Life Sci. 1968, 7, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; Markou, A.; Lucki, I. Assessing antidepressant activity in rodents: Recent developments and future needs. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2002, 23, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; Page, M.E.; Lucki, I. Noradrenergic lesions differentially alter the antidepressant-like effects of reboxetine in a modified forced swim test. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 436, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyan, J.; Amir, S. Too Depressed to Swim or Too Afraid to Stop? A Reinterpretation of the Forced Swim Test as a Measure of Anxiety-Like Behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 931–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carola, V.; D’Olimpio, F.; Brunamonti, E.; Mangia, F.; Renzi, P. Evaluation of the elevated plus-maze and open-field tests for the assessment of anxiety-related behaviour in inbred mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2002, 134, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.-M.; Li, X.-J.; Meng, Z.-Z.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Zhao, H.-B.; Li, N.; Yan, Z.-Y.; Ma, Q.-Y.; Zhang, H.-T.; Chen, J.-X. Effects of Xiaoyaosan on Stress-Induced Anxiety-Like Behavior in Rats: Involvement of CRF1 Receptor. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walf, A.A.; Frye, C.A. The use of the elevated plus maze as an assay of anxiety-related behavior in rodents. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, S.H.; Kim, B.-H.; Ye, S.-K.; Kim, M.-H. Chronic Non-Social Stress Affects Depressive Behaviors But Not Anxiety in Mice. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2014, 18, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.-W.; Ko, M.J.; Gonzales, E.L.; Kang, R.J.; Kim, D.G.; Kim, Y.; Seung, H.; Oh, H.A.; Eun, P.H.; Shin, C.-Y. Social support rescues acute stress-induced cognitive impairments by modulating ERK1/2 phosphorylation in adolescent mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Pan, Z.; Hou, Z.; Huang, C.; Li, W.; Zhao, B. Learning, memory, and glial cell changes following recovery from chronic unpredictable stress. Brain Res. Bull. 2012, 88, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, M.S.; Bohlen, M.O.; Gunter, B.W.; Quentin, H.; Stockmeier, C.A.; Paul, I.A. Attenuation of social interaction-associated ultrasonic vocalizations and spatial working memory performance in rats exposed to chronic unpredictable stress. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 152, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lara, V.P.; Caramelli, P.; Teixeira, A.L.; Barbosa, M.T.; Carmona, K.C.; Carvalho, M.G.; Fernandes, A.P.; Gomes, K.B. High cortisol levels are associated with cognitive impairment no-dementia (CIND) and dementia. Clin. Chim. Acta 2013, 423, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sousa, V.C.; Vital, J.; Costenla, A.R.; Batalha, V.L.; Sebastião, A.M.; Ribeiro, J.A.; Lopes, L.V. Maternal separation impairs long term-potentiation in CA1-CA3 synapses and hippocampal-dependent memory in old rats. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 1680–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, M.A.; Hamel, A.F.; Kelly, B.J.; Dettmer, A.M.; Meyer, J.S. Stress, the HPA axis, and nonhuman primate well-being: A review. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2013, 143, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Sullivan, M.; Clayton, N.; Breslin, N.P.; Harman, I.; Bountra, C.; McLaren, A.; O’Morain, C.A. Increased mast cells in the irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2000, 12, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakas, E.Y. Evaluating unspecific oxidative stress parameters in the sera of patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Period. Biol. 2016, 118, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafir, A.; Banu, N. Induction of oxidative stress by restraint stress and corticosterone treatments in rats. Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 46, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Duda, W.; Curzytek, K.; Kubera, M.; Iciek, M.; Kowalczyk-Pachel, D.; Bilska-Wilkosz, A.; Lorenc-Koci, E.; Leskiewicz, M.; Basta-Kaim, A.; Budziszewska, B.; et al. The Effect of Chronic Mild Stress and Imipramine on the Markers of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant System in Rat Liver. Neurotox. Res. 2016, 30, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-López, A.L.; Jaime, H.B.; Villanueva, M.D.C.E.; Padilla, M.B.; Palacios, G.V.; Alarcón-Aguilar, F.J. Chronic unpredictable mild stress generates oxidative stress and systemic inflammation in rats. Physiol. Behav. 2016, 161, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribble, D.L.; Aw, T.Y.; Jones, D.P. The pathophysiological significance of lipid peroxidation in oxidative cell injury. Hepatology 1987, 7, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Rangel, A.; Torner-Aguilar, L.; Saavedra-Molina, A.; Manzo-Avalos, S. Effect of Maternal Separation on Oxidative and Nitrosative Stress in the Brain of Rat Offspring. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 779. [Google Scholar]
- Diehl, L.A.; Alvares, L.O.; Noschang, C.; Engelke, D.; Andreazza, A.C.; Gonçalves, C.A.S.; Quillfeldt, J.A.; Dalmaz, C. Long-Lasting Effects of Maternal Separation on an Animal Model of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: Effects on Memory and Hippocampal Oxidative Stress. Neurochem. Res. 2011, 37, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balmus, I.M.; Lefter, R.; Ciobica, A.; Antioch, I.; Ababei, D.; Dobrin, R. Preliminary data on some behavioral changes induced by short-term intraperitoneal oxytocin administration in aged rats. Psychiatr. Danub. 2018, 30, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanescu, C.; Ciobica, A. The relevance of oxidative stress status in first episode and recurrent depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2012, 143, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyette, P.; Labbé, C.; Trinh, T.T.; Xavier, R.J.; Rioux, J.D. Molecular pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease: Genotypes, phenotypes and personalized medicine. Ann. Med. 2007, 39, 177–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.A.; Rinaman, L.; Cryan, J.F. Stress & the gut-brain axis: Regulation by the microbiome. Neurobiol. Stress 2017, 7, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- George, E.D.; Bordner, K.A.; Elwafi, H.M.; Simen, A.A. Maternal separation with early weaning: A novel mouse model of early life neglect. BMC Neurosci. 2010, 11, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
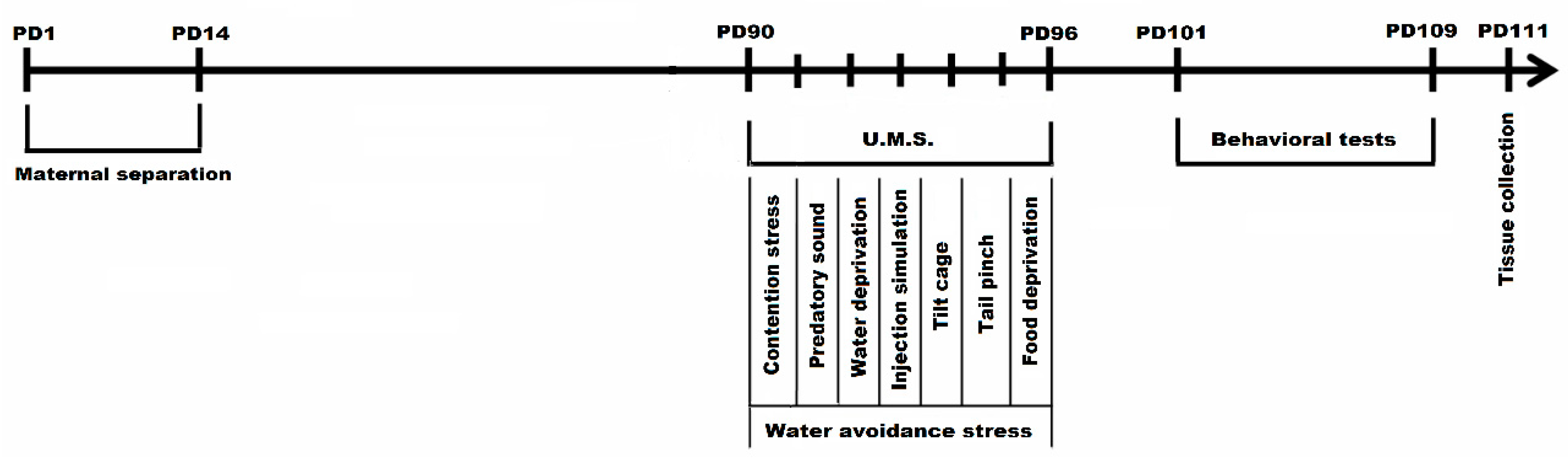

| Group 1 (MS) | Group 2 (MF) | Group 3 (MS+MF) | Group Control | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| maternal separation | maternal separation | ||||
| multifactorial stress | multifactorial stress | ||||
| a. unpredictable | b. repetitive | a. unpredictable | b. repetitive | ||
| (1) restraint stress | daily water avoidance stress | (1) restraint stress | daily water avoidance stress | ||
| (2) predator sound | (2) predator sound | ||||
| (3) water deprivation | (3) water deprivation | ||||
| (4) injection simulation | (4) injection simulation | ||||
| (5) tilt cage | (5) tilt cage | ||||
| (6) tail pinch | (6) tail pinch | ||||
| (7) food deprivation | (7) food deprivation | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cojocariu, R.O.; Balmus, I.M.; Lefter, R.; Ababei, D.C.; Ciobica, A.; Hritcu, L.; Kamal, F.; Doroftei, B. Behavioral and Oxidative Stress Changes in Mice Subjected to Combinations of Multiple Stressors Relevant to Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10110865
Cojocariu RO, Balmus IM, Lefter R, Ababei DC, Ciobica A, Hritcu L, Kamal F, Doroftei B. Behavioral and Oxidative Stress Changes in Mice Subjected to Combinations of Multiple Stressors Relevant to Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(11):865. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10110865
Chicago/Turabian StyleCojocariu, Roxana Oana, Ioana Miruna Balmus, Radu Lefter, Daniela Carmen Ababei, Alin Ciobica, Luminita Hritcu, Fatimazahra Kamal, and Bogdan Doroftei. 2020. "Behavioral and Oxidative Stress Changes in Mice Subjected to Combinations of Multiple Stressors Relevant to Irritable Bowel Syndrome" Brain Sciences 10, no. 11: 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10110865
APA StyleCojocariu, R. O., Balmus, I. M., Lefter, R., Ababei, D. C., Ciobica, A., Hritcu, L., Kamal, F., & Doroftei, B. (2020). Behavioral and Oxidative Stress Changes in Mice Subjected to Combinations of Multiple Stressors Relevant to Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Brain Sciences, 10(11), 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10110865







