Age-Related Structural and Functional Changes of the Hippocampus and the Relationship with Inhibitory Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
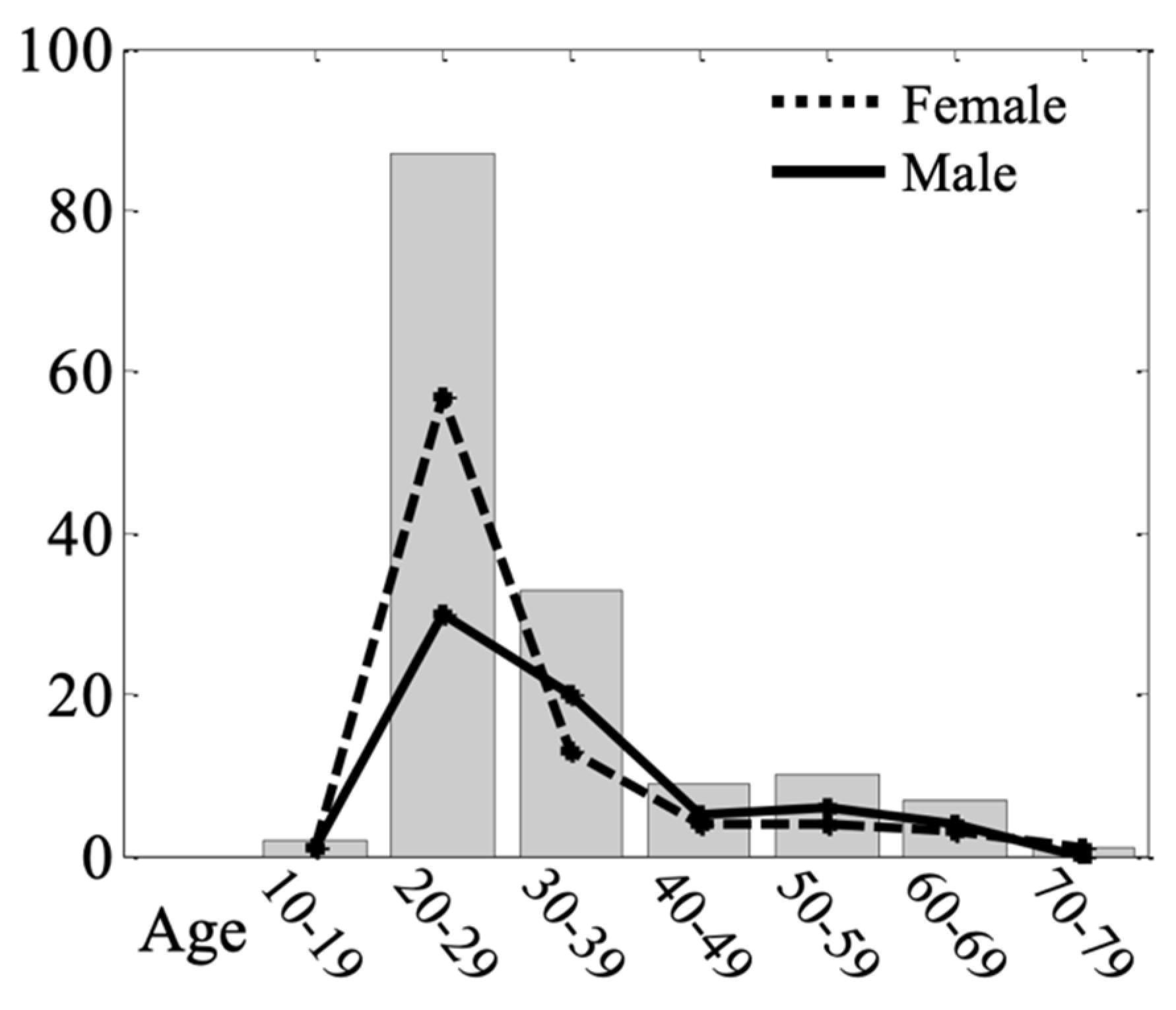
2.1. Participants
2.2. Stop Signal Task and Stop Signal Reaction Time
2.3. A Bayesian Model of Proactive Control
2.4. MRI Protocol
2.5. Gray Matter Volumes Derived with Voxel-Based Morphometry (VBM)
2.6. Preprocessing and Modeling of BOLD Data of the SST
2.7. Mediation Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Behavioral Performance
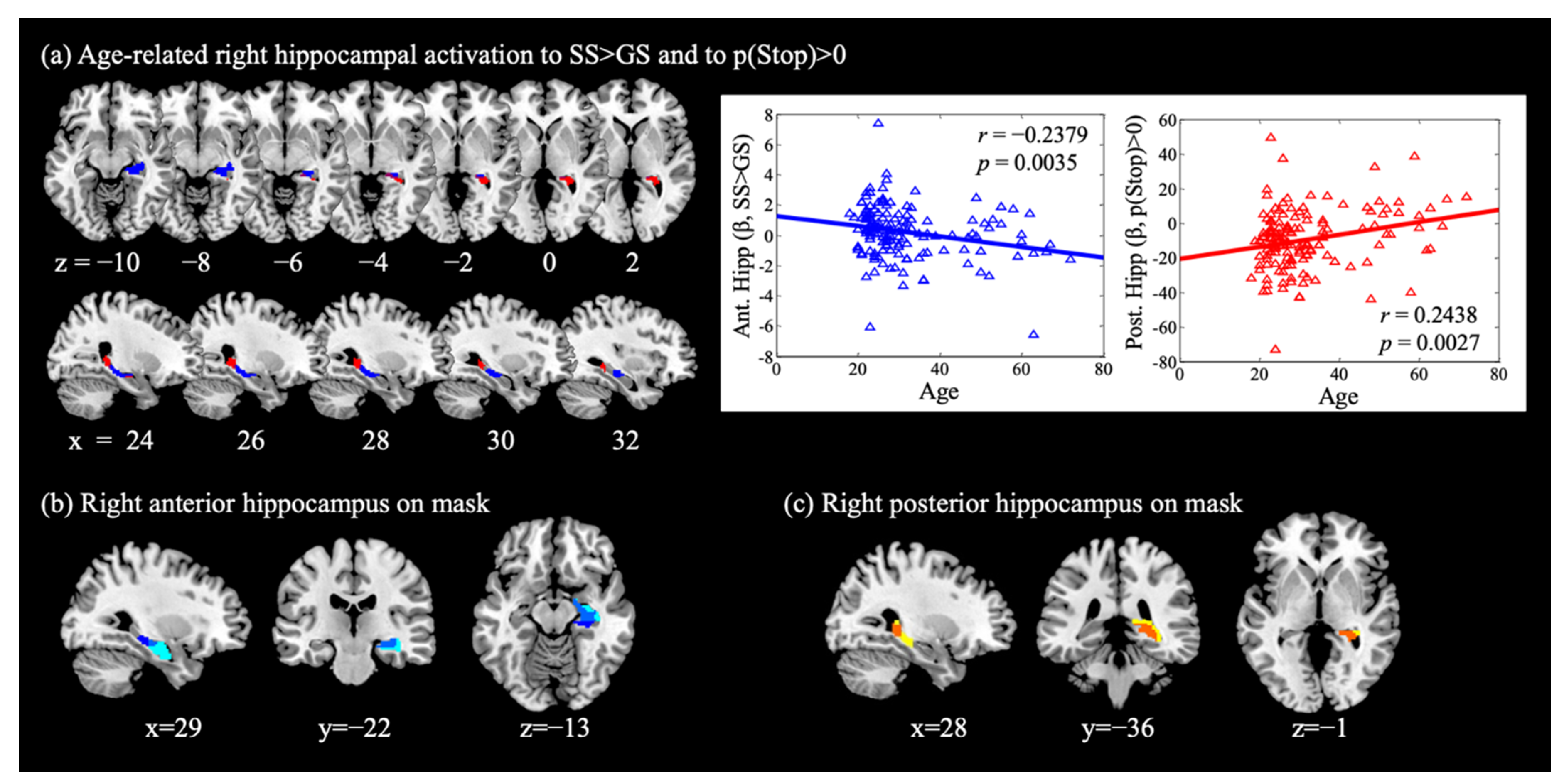
3.2. Age-Related Decreases in Hippocampal Gray Matter Volume (GMV)
3.3. Age and Hippocampal Activation in Reactive and Proactive Inhibitory Control
3.4. Age-Related Structural and Functional Changes in the Hippocampus
4. Discussion
4.1. The Hippocampus and Inhibitory Control
4.2. A Broader Role of Hippocampal Structure and Function in Age-Related Cognitive Decline
4.3. Structural and Functional Asymmetry of the Hippocampus
5. Limitations, Other Considerations, and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAL | Automatic Anatomic Labelling |
| AC-PC | Anterior Commissure-Posterior Commissure |
| AD | Alzheimer’s Disease |
| AR | Autoregressive |
| BOLD | Blood oxygenation level dependent |
| GS | Go success trials |
| GE | Go error trials |
| EPI | Echo-planar imaging |
| FWE | Familywise error |
| FWHM | Full Width at Half Maximum |
| GLM | Generalized linear model |
| GM | Gray matter |
| GMV | Gray matter volume |
| goRT | Go trial reaction time |
| HRF | Hemodynamic response function |
| MCI | Mild cognitive impairment |
| MNI | Montreal Neurological Institute |
| p(Stop) | Bayesian estimated probability of stop signal |
| RT | Reaction time |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SE | Stop error trials |
| SPM | Statistical Parametric Mapping |
| SS | Stop success trials |
| SSRT | Stop signal reaction time |
| SSD | Stop signal delay |
| SST | Stop signal task |
| SVC | Small volume correction |
| TE | Echo time |
| TR | Repetition time |
Appendix A
| Region | k | Z Value | MNI Coordinate (mm) | Correlation | r | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y | Z | with | |||||
| L ant. Hipp. | 632 | 6.36 | −15 | −2 | −14 | Age | −0.2344 | 0.0040 |
| SSRT | −0.1366 | 0.0966 | ||||||
| Seq. Effect | 0.0526 | 0.5241 | ||||||
| L post. Hipp. | 50 | 4.04 | −12 | −36 | 0 | Age | −0.2261 | 0.0056 |
| SSRT | −0.1279 | 0.1200 | ||||||
| Seq. Effect | 0.1676 | 0.0410 | ||||||
| R ant. Hipp. | 84 | 4.35 | 14 | −2 | −15 | Age | −0.2623 | 0.0012 |
| SSRT | −0.1499 | 0.0680 | ||||||
| Seq. Effect | 0.0827 | 0.3162 | ||||||
| R post. Hipp. | 298 | 4.62 | 21 | −21 | −17 | Age | −0.2290 | 0.0050 |
| SSRT | −0.1582 | 0.0540 | ||||||
| Seq. Effect | 0.1364 | 0.0972 | ||||||
| t | p | β | F | df | p | adj. R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ant. Hippocampus | |||||||
| Overall model | 3.2110 | 0.0016 | 1.2914 | 4.38 | 146 | 0.0142 | 0.0437 |
| Age | −2.9337 | 0.0039 | −0.0346 | ||||
| Sex | −0.0004 | 0.9996 | −0.0001 | ||||
| Ant. Hippocampus | |||||||
| Overall model | 3.4794 | 0.0007 | 2.7778 | 4.53 | 145 | 0.0046 | 0.0667 |
| SSRT | −2.1465 | 0.0335 | −0.0084 | ||||
| Age | −2.3231 | 0.0216 | −0.0280 | ||||
| Sex | 0.1879 | 0.8512 | 0.0527 | ||||
| Post. Hippocampus | |||||||
| Overall model | −5.089 | 0.0000 | −20.105 | 4.77 | 146 | 0.0099 | 0.0485 |
| Age | 3.0856 | 0.0024 | 0.3573 | ||||
| Sex | −0.5399 | 0.5901 | −1.4986 | ||||
| Post. Hippocampus | |||||||
| Overall model | −3.6526 | 0.0004 | −16.594 | 4 | 145 | 0.0090 | 0.0574 |
| SEQ | −1.5427 | 0.1251 | −16.534 | ||||
| Age | 3.0107 | 0.0031 | 0.3475 | ||||
| Sex | −0.4914 | 0.6239 | −1.3584 |

References
- Yonelinas, A.P.; Ranganath, C.; Ekstrom, A.D.; Wiltgen, B.J. A Contextual Binding Theory of Episodic Memory: Systems Consolidation Reconsidered. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 20, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, J.; Siegelbaum, S.A. The Corticohippocampal Circuit, Synaptic Plasticity, and Memory. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a021733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, S.; Keeser, D.; Reiser, M.F.; Teipel, S.; Meindl, T. Functional and Structural Mr Imaging in Neuropsychiatric Disorders, Part 1: Imaging Techniques and Their Application in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer Disease. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 33, 1845–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Kate, M.; Barkhof, F.; Boccardi, M.; Visser, P.J.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Lovblad, K.O.; Frisoni, G.B.; Scheltens, P.; Geneva Task Force for the Roadmap of Alzheimer’s Biomarkers. Clinical Validity of Medial Temporal Atrophy as a Biomarker for Alzheimer’s Disease in the Context of a Structured 5-Phase Development Framework. Neurobiol. Aging 2017, 52, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negash, S.; Kliot, D.; Howard, D.V.; Howard, J.H., Jr.; Das, S.R.; Yushkevich, P.A.; Pluta, J.B.; Arnold, S.E.; Wolk, D.A. Relationship of Contextual Cueing and Hippocampal Volume in Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment Patients and Cognitively Normal Older Adults. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2015, 21, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bonner-Jackson, A.; Mahmoud, S.; Miller, J.; Banks, S.J. Verbal and Non-Verbal Memory and Hippocampal Volumes in a Memory Clinic Population. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2015, 7, 61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Farras-Permanyer, L.; Guardia-Olmos, J.; Pero-Cebollero, M. Mild Cognitive Impairment and Fmri Studies of Brain Functional Connectivity: The State of the Art. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharath, S.; Joshi, H.; John, J.P.; Balachandar, R.; Sadanand, S.; Saini, J.; Kumar, K.J.; Varghese, M. A Multimodal Structural and Functional Neuroimaging Study of Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2017, 25, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahmasian, M.; Pasquini, L.; Scherr, M.; Meng, C.; Forster, S.; Mulej Bratec, S.; Shi, K.; Yakushev, I.; Schwaiger, M.; Grimmer, T.; et al. The Lower Hippocampus Global Connectivity, the Higher Its Local Metabolism in Alzheimer Disease. Neurology 2015, 84, 1956–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liang, P.; Jia, X.; Qi, Z.; Yu, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Lu, J.; Li, K. Baseline and Longitudinal Patterns of Hippocampal Connectivity in Mild Cognitive Impairment: Evidence from Resting State Fmri. J. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 309, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Xing, G.; Han, Y. Advances in Resting State Neuroimaging of Mild Cognitive Impairment. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabi, R.; Vasquez, B.P.; Alain, C.; Hasher, L.; Belleville, S.; Anderson, N.D. Inhibitory Control Deficits in Individuals with Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Meta-Analysis. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2020, 30, 97–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarino, A.; Favieri, F.; Boncompagni, I.; Agostini, F.; Cantone, M.; Casagrande, M. Executive Functions in Alzheimer Disease: A Systematic Review. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johns, E.K.; Phillips, N.A.; Belleville, S.; Goupil, D.; Babins, L.; Kelner, N.; Ska, B.; Gilbert, B.; Massoud, F.; de Boysson, C.; et al. The Profile of Executive Functioning in Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment: Disproportionate Deficits in Inhibitory Control. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2012, 18, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, D.; Dong, X.; Sun, H.; Xu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, X. The Overall Impairment of Core Executive Function Components in Patients with Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Neurol. 2012, 12, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wylie, S.A.; Ridderinkhof, K.R.; Eckerle, M.K.; Manning, C.A. Inefficient Response Inhibition in Individuals with Mild Cognitive Impairment. Neuropsychologia 2007, 45, 1408–1419. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alichniewicz, K.K.; Brunner, F.; Klunemann, H.H.; Greenlee, M.W. Neural Correlates of Saccadic Inhibition in Healthy Elderly and Patients with Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment. Front. Psychol. 2013, 4, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belanger, S.; Belleville, S.; Gauthier, S. Inhibition Impairments in Alzheimer’s Disease, Mild Cognitive Impairment and Healthy Aging: Effect of Congruency Proportion in a Stroop Task. Neuropsychologia 2010, 48, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cespon, J.; Galdo-Alvarez, S.; Diaz, F. Inhibition Deficit in the Spatial Tendency of the Response in Multiple-Domain Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment. An Event-Related Potential Study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2015, 7, 68. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Mudar, R.A.; Chiang, H.S.; Schneider, J.M.; Maguire, M.J.; Kraut, M.A.; Hart, J., Jr. Theta and Alpha Alterations in Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment in Semantic Go/Nogo Tasks. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, M.B.; Moser, E.I. Functional Differentiation in the Hippocampus. Hippocampus 1998, 8, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, S.A. The Longitudinal Axis of the Hippocampal Formation: Its Anatomy, Circuitry, and Role in Cognitive Function. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 13, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanselow, M.S.; Dong, H.W. Are the Dorsal and Ventral Hippocampus Functionally Distinct Structures? Neuron 2010, 65, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poppenk, J.; Evensmoen, H.R.; Moscovitch, M.; Nadel, L. Long-Axis Specialization of the Human Hippocampus. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2013, 17, 230–240. [Google Scholar]
- Manns, J.R.; Eichenbaum, H. Evolution of Declarative Memory. Hippocampus 2006, 16, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.L.; Barron, D.S.; Kirby, L.A.; Bottenhorn, K.L.; Hill, A.C.; Murphy, J.E.; Katz, J.S.; Salibi, N.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Fox, P.T. Neurofunctional Topography of the Human Hippocampus. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2015, 36, 5018–5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppenk, J.; Moscovitch, M. A Hippocampal Marker of Recollection Memory Ability among Healthy Young Adults: Contributions of Posterior and Anterior Segments. Neuron 2011, 72, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anacker, C.; Hen, R. Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Cognitive Flexibility—Linking Memory and Mood. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 335–346. [Google Scholar]
- Nadel, L.; Hoscheidt, S.; Ryan, L.R. Spatial Cognition and the Hippocampus: The Anterior-Posterior Axis. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2013, 25, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeidman, P.; Maguire, E.A. Anterior Hippocampus: The Anatomy of Perception, Imagination and Episodic Memory. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, I.C.; Ferreira, C.; Marques, J.; Castelo-Branco, M. Anterior/Posterior Competitive Deactivation/Activation Dichotomy in the Human Hippocampus as Revealed by a 3d Navigation Task. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Evensmoen, H.R.; Lehn, H.; Pintzka, C.W.; Haberg, A.K. Persistent Posterior and Transient Anterior Medial Temporal Lobe Activity During Navigation. Neuroimage 2010, 52, 1654–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Shea, A.; Cohen, R.A.; Porges, E.C.; Nissim, N.R.; Woods, A.J. Cognitive Aging and the Hippocampus in Older Adults. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2016, 8, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettio, L.E.B.; Rajendran, L.; Gil-Mohapel, J. The Effects of Aging in the Hippocampus and Cognitive Decline. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 79, 66–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuben, A.; Brickman, A.M.; Muraskin, J.; Steffener, J.; Stern, Y. Hippocampal Atrophy Relates to Fluid Intelligence Decline in the Elderly. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2011, 17, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papp, K.V.; Kaplan, R.F.; Springate, B.; Moscufo, N.; Wakefield, D.B.; Guttmann, C.R.; Wolfson, L. Processing Speed in Normal Aging: Effects of White Matter Hyperintensities and Hippocampal Volume Loss. Neuropsychol. Dev. Cogn. B Aging Neuropsychol. Cogn. 2014, 21, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, R.D.; Watson, P.D.; Duff, M.C.; Cohen, N.J. The Role of the Hippocampus in Flexible Cognition and Social Behavior. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyberg, L.; Andersson, M.; Lundquist, A.; Salami, A.; Wahlin, A. Frontal Contribution to Hippocampal Hyperactivity During Memory Encoding in Aging. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 229. [Google Scholar]
- Abela, A.R.; Dougherty, S.D.; Fagen, E.D.; Hill, C.J.; Chudasama, Y. Inhibitory Control Deficits in Rats with Ventral Hippocampal Lesions. Cereb. Cortex 2013, 23, 1396–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudasama, Y.; Doobay, V.M.; Liu, Y. Hippocampal-Prefrontal Cortical Circuit Mediates Inhibitory Response Control in the Rat. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 10915–10924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messanvi, F.; Perkins, A.; du Hoffmann, J.; Chudasama, Y. Fronto-Temporal Galanin Modulates Impulse Control. Psychopharmacology 2020, 237, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.; Byeon, J.S. Learning-Dependent Changes in the Neuronal Correlates of Response Inhibition in the Prefrontal Cortex and Hippocampus. Exp. Neurobiol. 2014, 23, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, R.J.; Ko, C.H.; Hong, N.S. Attenuation of Context-Specific Inhibition on Reversal Learning of a Stimulus-Response Task in Rats with Neurotoxic Hippocampal Damage. Behav. Brain Res. 2002, 136, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, R.J.; Balog, R.J.; Lee, J.Q.; Stuart, E.E.; Carrels, B.B.; Hong, N.S. Rats with Ventral Hippocampal Damage Are Impaired at Various Forms of Learning Including Conditioned Inhibition, Spatial Navigation, and Discriminative Fear Conditioning to Similar Contexts. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 351, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Job, M.; Jenks, S.K.; Chao, H.H.; Li, C.R. Imaging the Effects of Age on Proactive Control in Healthy Adults. Brain Imaging Behav. 2019, 13, 1526–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Ide, J.S.; Chao, H.H.; Castagna, B.; Fischer, K.A.; Zhang, S.; Li, C.R. Structural and Functional Cerebral Bases of Diminished Inhibitory Control During Healthy Aging. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2018, 39, 5085–5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Chao, H.H.; Winkler, A.D.; Li, C.S. The Effects of Age on Cerebral Activations: Internally Versus Externally Driven Processes. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2012, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Tseng, Y.C.; Winkler, A.D.; Li, C.S. Neural Bases of Individual Variation in Decision Time. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2014, 35, 2531–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hu, S.; Ide, J.S.; Zhang, S.; Li, C.R. The Right Superior Frontal Gyrus and Individual Variation in Proactive Control of Impulsive Response. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 12688–12696. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Li, C.S.R. Neural Processes of Preparatory Control for Stop Signal Inhibition. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2012, 33, 2785–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbruggen, F.; Aron, A.R.; Band, G.P.; Beste, C.; Bissett, P.G.; Brockett, A.T.; Brown, J.W.; Chamberlain, S.R.; Chambers, C.D.; Colonius, H.; et al. A Consensus Guide to Capturing the Ability to Inhibit Actions and Impulsive Behaviors in the Stop-Signal Task. Elife 2019, 8, e46323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ide, J.S.; Shenoy, P.; Yu, A.J.; Li, C.S. Bayesian Prediction and Evaluation in the Anterior Cingulate Cortex. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 2039–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Ide, J.S.; Zhang, S.; Li, C.S. Anticipating Conflict: Neural Correlates of a Bayesian Belief and Its Motor Consequence. Neuroimage 2015, 119, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, A.J.; Dayan, P.; Cohen, J.D. Dynamics of Attentional Selection under Conflict: Toward a Rational Bayesian Account. J. Exp. Psychol.-Hum. Percept. Perform. 2009, 35, 700–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, A.J.; Cohen, J.D. Sequential Effects: Superstition or Rational Behavior? In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Nips, 2008; Koller, D., Schuurmans, D., Bengio, Y., Bottou, L., Eds.; MIT: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2009; pp. 1873–1880. [Google Scholar]
- O’Doherty, J.; Dayan, P.; Schultz, J.; Deichmann, R.; Friston, K.; Dolan, R.J. Dissociable Roles of Ventral and Dorsal Striatum in Instrumental Conditioning. Science 2004, 304, 452–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daw, N.D.; O’Doherty, J.P.; Dayan, P.; Seymour, B.; Dolan, R.J. Cortical Substrates for Exploratory Decisions in Humans. Nature 2006, 441, 876–879. [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner, J.; Friston, K.J. Nonlinear Spatial Normalization Using Basis Functions. Hum. Brain Mapp. 1999, 7, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K.; Holmes, A.P.; Worsley, K.J.; Poline, J.B.; Frith, C.D.; Frackowiak, R. Statistical Parametric Maps in Functional Imaging: A General Linear Approach. Hum. Brain Mapp. 1995, 2, 189–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K.J.; Josephs, O.; Zarahn, E.; Holmes, A.P.; Rouquette, S.; Poline, J.B. To Smooth or Not to Smooth? Bias and Efficiency in Fmri Time-Series Analysis. Neuroimage 2000, 12, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della-Maggiore, V.; Chau, W.; Peres-Neto, P.R.; McIntosh, A.R. An Empirical Comparison of Spm Preprocessing Parameters to the Analysis of Fmri Data. Neuroimage 2002, 17, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, J.S.; Li, C.S. Error-Related Functional Connectivity of the Habenula in Humans. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2011, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKinnon, D.P.; Fairchild, A.J.; Fritz, M.S. Mediation Analysis. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2007, 58, 593–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis, 4th ed.; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Mathiasen, M.L.; O’Mara, S.M.; Aggleton, J.P. The Anterior Thalamic Nuclei and Nucleus Reuniens: So Similar but So Different. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 119, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, S.F.; Guo, W.; Fernandez, C.; Wagner, A.D. Prefrontal Reinstatement of Contextual Task Demand Is Predicted by Separable Hippocampal Patterns. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burman, D.D. Hippocampal Connectivity with Sensorimotor Cortex During Volitional Finger Movements: Laterality and Relationship to Motor Learning. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222064. [Google Scholar]
- De Loof, E.; Vassena, E.; Janssens, C.; De Taeye, L.; Meurs, A.; Van Roost, D.; Boon, P.; Raedt, R.; Verguts, T. Preparing for Hard Times: Scalp and Intracranial Physiological Signatures of Proactive Cognitive Control. Psychophysiology 2019, 56, e13417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parro, C.; Dixon, M.L.; Christoff, K. The Neural Basis of Motivational Influences on Cognitive Control. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2018, 39, 5097–5111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Zhang, X.; Fei, N.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, J.; Liu, P.; Yang, X.; Qin, W. Decreased Cortical and Subcortical Response to Inhibition Control after Sleep Deprivation. Brain Imaging Behav. 2019, 13, 638–650. [Google Scholar]
- Van Rooij, S.J.H.; Stevens, J.S.; Ely, T.D.; Hinrichs, R.; Michopoulos, V.; Winters, S.J.; Ogbonmwan, Y.E.; Shin, J.; Nugent, N.R.; Hudak, L.A.; et al. The Role of the Hippocampus in Predicting Future Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Symptoms in Recently Traumatized Civilians. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 84, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, H.C.; Odriozola, P.; Cohodes, E.M.; Mandell, J.D.; Li, A.; Yang, R.; Hall, B.S.; Haberman, J.T.; Zacharek, S.J.; Liston, C.; et al. Ventral Hippocampus Interacts with Prelimbic Cortex During Inhibition of Threat Response Via Learned Safety in Both Mice and Humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 26970–26979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Q.; D’Onofrio, G.; Sancarlo, D.; Bao, Z.; Greco, A.; Yu, Z. Potential Neuroimaging Biomarkers of Pathologic Brain Changes in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review. BMC Geriatr. 2016, 16, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanchi, D.; Giannakopoulos, P.; Borgwardt, S.; Rodriguez, C.; Haller, S. Hippocampal and Amygdala Gray Matter Loss in Elderly Controls with Subtle Cognitive Decline. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickerson, B.C.; Salat, D.H.; Greve, D.N.; Chua, E.F.; Rand-Giovannetti, E.; Rentz, D.M.; Bertram, L.; Mullin, K.; Tanzi, R.E.; Blacker, D.; et al. Increased Hippocampal Activation in Mild Cognitive Impairment Compared to Normal Aging and Ad. Neurology 2005, 65, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leal, S.L.; Landau, S.M.; Bell, R.K.; Jagust, W.J. Hippocampal Activation Is Associated with Longitudinal Amyloid Accumulation and Cognitive Decline. Elife 2017, 6, e22978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.L.; O’Keefe, K.M.; LaViolette, P.S.; DeLuca, A.N.; Blacker, D.; Dickerson, B.C.; Sperling, R.A. Longitudinal Fmri in Elderly Reveals Loss of Hippocampal Activation with Clinical Decline. Neurology 2010, 74, 1969–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celone, K.A.; Calhoun, V.D.; Dickerson, B.C.; Atri, A.; Chua, E.F.; Miller, S.L.; DePeau, K.; Rentz, D.M.; Selkoe, D.J.; Blacker, D.; et al. Alterations in Memory Networks in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease: An Independent Component Analysis. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 10222–10231. [Google Scholar]
- Trelle, A.N.; Henson, R.N.; Simons, J.S. Neural Evidence for Age-Related Differences in Representational Quality and Strategic Retrieval Processes. Neurobiol. Aging 2019, 84, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasse, L.K.; Peters, J.; Brassen, S. Cognitive Control Modulates Effects of Episodic Simulation on Delay Discounting in Aging. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oedekoven, C.S.; Jansen, A.; Keidel, J.L.; Kircher, T.; Leube, D. The Influence of Age and Mild Cognitive Impairment on Associative Memory Performance and Underlying Brain Networks. Brain Imaging Behav. 2015, 9, 776–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, C.; Jiang, T. Hippocampal Volume and Asymmetry in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease: Meta-Analyses of Mri Studies. Hippocampus 2009, 19, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar]
- Fraser, M.A.; Shaw, M.E.; Anstey, K.J.; Cherbuin, N. Longitudinal Assessment of Hippocampal Atrophy in Midlife and Early Old Age: Contrasting Manual Tracing and Semi-Automated Segmentation (Freesurfer). Brain Topogr. 2018, 31, 949–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, L.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Li, G.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Hu, M.; Xiao, S. Asymmetry of Hippocampus and Amygdala Defect in Subjective Cognitive Decline among the Community Dwelling Chinese. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardekani, B.A.; Hadid, S.A.; Blessing, E.; Bachman, A.H. Sexual Dimorphism and Hemispheric Asymmetry of Hippocampal Volumetric Integrity in Normal Aging and Alzheimer Disease. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mormino, E.C.; Brandel, M.G.; Madison, C.M.; Marks, S.; Baker, S.L.; Jagust, W.J. Abeta Deposition in Aging Is Associated with Increases in Brain Activation During Successful Memory Encoding. Cereb. Cortex 2012, 22, 1813–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltanifar, M.; Knight, K.; Dupuis, A.; Schachar, R.; Escobar, M. A Time Series-Based Point Estimation of Stop Signal Reaction Times: More Evidence on the Role of Reactive Inhibition-Proactive Inhibition Interplay on the Ssrt Estimations. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, J.S.; Hu, S.; Zhang, S.; Yu, A.J.; Li, C.S. Impaired Bayesian Learning for Cognitive Control in Cocaine Dependence. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2015, 151, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, S.; Li, C.-s.R. Age-Related Structural and Functional Changes of the Hippocampus and the Relationship with Inhibitory Control. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10121013
Hu S, Li C-sR. Age-Related Structural and Functional Changes of the Hippocampus and the Relationship with Inhibitory Control. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(12):1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10121013
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Sien, and Chiang-shan R. Li. 2020. "Age-Related Structural and Functional Changes of the Hippocampus and the Relationship with Inhibitory Control" Brain Sciences 10, no. 12: 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10121013
APA StyleHu, S., & Li, C.-s. R. (2020). Age-Related Structural and Functional Changes of the Hippocampus and the Relationship with Inhibitory Control. Brain Sciences, 10(12), 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10121013






