Transcriptome Analysis of Alcohol Drinking in Non-Dependent and Dependent Mice Following Repeated Cycles of Forced Swim Stress Exposure
Abstract
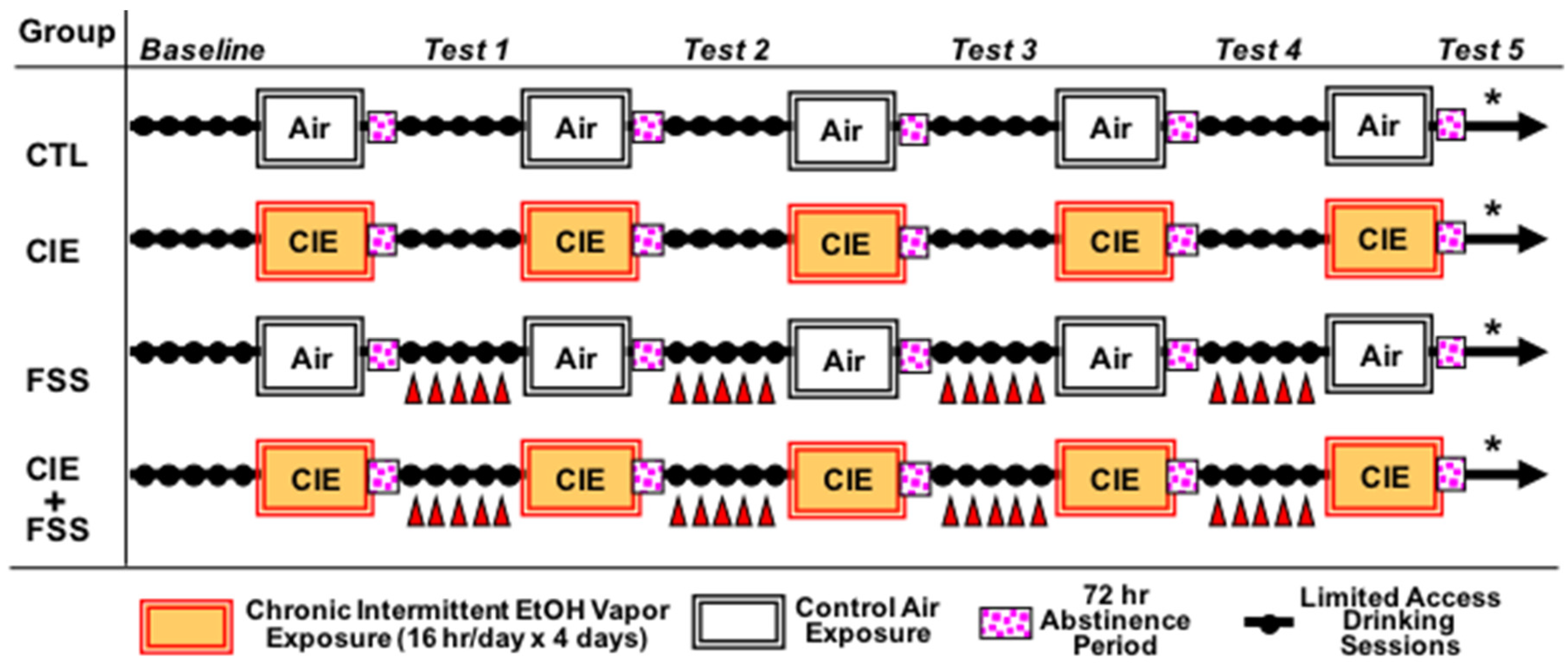
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Blood Ethanol Concentration during CIE Exposure Cycles
3.2. Voluntary Ethanol Intake
3.3. Overview of Differential Gene Expression
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- George, O.; Koob, G.F. Individual differences in the neuropsychopathology of addiction. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 19, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nestler, E.J.; Lüscher, C. The Molecular Basis of Drug Addiction: Linking Epigenetic to Synaptic and Circuit Mechanisms. Neuron 2019, 102, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farris, S.P.; Arasappan, D.; Hunicke-Smith, S.; Harris, R.A.; Mayfield, R.D. Transcriptome organization for chronic alcohol abuse in human brain. Mol. Psychiatry 2015, 20, 1438–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kapoor, M.; Wang, J.-C.; Farris, S.P.; Liu, Y.; McClintick, J.; Gupta, I.; Meyers, J.L.; Bertelsen, S.; Chao, M.; Nurnberger, J.; et al. Analysis of whole genome-transcriptomic organization in brain to identify genes associated with alcoholism. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, G.T.; Sheedy, D.; Kril, J.J. Using autopsy brain tissue to study alcohol-related brain damage in the genomic age. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2014, 38, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porsolt, R.D.; Bertin, A.; Jalfre, M. Behavioral despair in mice: A primary screening test for antidepressants. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 1977, 229, 327–336. [Google Scholar]
- Porsolt, R.D.; Le Pichon, M.; Jalfre, M. Depression: A new animal model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Nature 1977, 266, 730–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, W.C., 3rd; Lopez, M.F.; Becker, H.C. Intensity and duration of chronic ethanol exposure is critical for subsequent escalation of voluntary ethanol drinking in mice. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2009, 33, 1893–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, M.F.; Griffin, W.C., 3rd; Melendez, R.I.; Becker, H.C. Repeated cycles of chronic intermittent ethanol exposure leads to the development of tolerance to aversive effects of ethanol in C57BL/6J mice. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2012, 36, 1180–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez, M.F.; Anderson, R.I.; Becker, H.C. Effect of different stressors on voluntary ethanol intake in ethanol-dependent and nondependent C57BL/6J mice. Alcohol 2016, 51, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, R.I.; Lopez, M.F.; Becker, H.C. Forced swim stress increases ethanol consumption in C57BL/6J mice with a history of chronic intermittent ethanol exposure. Psychopharmacology 2016, 233, 2035–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koob, G.F. The dark side of emotion: The addiction perspective. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 753, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Osterndorff-Kahanek, E.A.; Becker, H.C.; Lopez, M.F.; Farris, S.P.; Tiwari, G.R.; Nunez, Y.O.; Harris, R.A.; Mayfield, R.D. Chronic ethanol exposure produces time- and brain region-dependent changes in gene coexpression networks. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.L.; Lopez, M.F.; Archer, K.J.; Wolen, A.R.; Becker, H.C.; Miles, M.F. Time-Course Analysis of Brain Regional Expression Network Responses to Chronic Intermittent Ethanol and Withdrawal: Implications for Mechanisms Underlying Excessive Ethanol Consumption. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyer, E.; Aglyamova, G.V.; Matz, M.V. Profiling gene expression responses of coral larvae (Acropora millepora) to elevated temperature and settlement inducers using a novel RNA-Seq procedure. Mol. Ecol. 2011, 20, 3599–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohman, B.K.; Weber, J.N.; Bolnick, D.I. Evaluation of TagSeq, a reliable low-cost alternative for RNAseq. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2016, 16, 1315–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Li, W. RSeQC: Quality control of RNA-seq experiments. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2184–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, E.Y.; Tan, C.M.; Kou, Y.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Meirelles, G.V.; Clark, N.R.; Ma’ayan, A. Enrichr: Interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuleshov, M.V.; Jones, M.R.; Rouillard, A.D.; Fernandez, N.F.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Koplev, S.; Jenkins, S.L.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Lachmann, A.; et al. Enrichr: A comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W90–W97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, K.; Sloan, S.A.; Bennett, M.L.; Scholze, A.R.; O’Keeffe, S.; Phatnani, H.P.; Guarnieri, P.; Caneda, C.; Ruderisch, N.; et al. An RNA-sequencing transcriptome and splicing database of glia, neurons, and vascular cells of the cerebral cortex. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 11929–11947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, R. Chronic stress, drug use, and vulnerability to addiction. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1141, 105–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodberg, E.M.; den Hartog, C.R.; Anderson, R.I.; Becker, H.C.; Moorman, D.E.; Vazey, E.M. Stress Facilitates the Development of Cognitive Dysfunction After Chronic Ethanol Exposure. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 41, 1574–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucki, I.; Dalvi, A.; Mayorga, A.J. Sensitivity to the effects of pharmacologically selective antidepressants in different strains of mice. Psychopharmacology 2001, 155, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEwen, B.S.; Eiland, L.; Hunter, R.G.; Miller, M.M. Stress and anxiety: Structural plasticity and epigenetic regulation as a consequence of stress. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diorio, D.; Viau, V.; Meaney, M.J. The role of the medial prefrontal cortex (cingulate gyrus) in the regulation of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal responses to stress. J. Neurosci. 1993, 13, 3839–3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herman, J.P.; Cullinan, W.E. Neurocircuitry of stress: Central control of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical axis. Trends Neurosci. 1997, 20, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKlveen, J.M.; Myers, B.; Herman, J.P. The medial prefrontal cortex: Coordinator of autonomic, neuroendocrine and behavioural responses to stress. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2015, 27, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niwa, M.; Jaaro-Peled, H.; Tankou, S.; Seshadri, S.; Hikida, T.; Matsumoto, Y.; Cascella, N.G.; Kano, S.-I.; Ozaki, N.; Nabeshima, T.; et al. Adolescent stress-induced epigenetic control of dopaminergic neurons via glucocorticoids. Science 2013, 339, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tye, K.M.; Mirzabekov, J.J.; Warden, M.R.; Ferenczi, E.A.; Tsai, H.-C.; Finkelstein, J.; Kim, S.-Y.; Adhikari, A.; Thompson, K.R.; Andalman, A.S.; et al. Dopamine neurons modulate neural encoding and expression of depression-related behaviour. Nature 2013, 493, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chelbi-Alix, M.K.; Brouard, A.; Boissard, C.; Pelaprat, D.; Rostene, W.; Thang, M.N. Induction by vasoactive intestinal peptide of interferon alpha/beta synthesis in glial cells but not in neurons. J. Cell. Physiol. 1994, 158, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blednov, Y.A.; Ponomarev, I.; Geil, C.; Bergeson, S.; Koob, G.F.; Harris, R.A. Neuroimmune regulation of alcohol consumption: Behavioral validation of genes obtained from genomic studies. Addict. Biol. 2012, 17, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, W.; Lu, T.; Chen, A.; Huang, Y.; Hansen, R.; Chandler, L.J.; Zhang, H.-T. Inhibition of phosphodiesterase-4 decreases ethanol intake in mice. Psychopharmacology 2011, 218, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blednov, Y.A.; Da Costa, A.J.; Tarbox, T.; Ponomareva, O.; Messing, R.O.; Harris, R.A. Apremilast Alters Behavioral Responses to Ethanol in Mice: I. Reduced Consumption and Preference. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 42, 926–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, R.L.; Lopez, M.F.; Cui, C.; Egli, M.; Johnson, K.W.; Franklin, K.M.; Becker, H.C. Ibudilast reduces alcohol drinking in multiple animal models of alcohol dependence. Addict. Biol. 2015, 20, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ray, L.A.; Bujarski, S.; Shoptaw, S.; Roche, D.J.; Heinzerling, K.; Miotto, K. Development of the Neuroimmune Modulator Ibudilast for the Treatment of Alcoholism: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Human Laboratory Trial. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 1776–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, C.P.; Kalinichenko, L.S.; Tiesel, J.; Witt, M.; Stöckl, T.; Sprenger, E.; Fuchser, J.; Beckmann, J.; Praetner, M.; Huber, S.E.; et al. Paradoxical antidepressant effects of alcohol are related to acid sphingomyelinase and its control of sphingolipid homeostasis. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 133, 463–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bell, R.L.; Hauser, S.R.; McClintick, J.; Rahman, S.; Edenberg, H.J.; Szumlinski, K.K.; McBride, W.J. Ethanol-Associated Changes in Glutamate Reward Neurocircuitry: A Minireview of Clinical and Preclinical Genetic Findings. In Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA , 2016; pp. 41–85. [Google Scholar]
- Palmisano, M.; Pandey, S.C. Epigenetic mechanisms of alcoholism and stress-related disorders. Alcohol 2017, 60, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, C.J.; Bagot, R.C.; Labonté, B.; Nestler, E.J. Epigenetic signaling in psychiatric disorders. J. Mol. Biol. 2014, 426, 3389–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Group | Name | 000-h | 072-h | 168-h | Number of Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (A) | |||||
| AIR | RNA polymerase II regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding (GO:0000977) | 5.09E−05 | 4.86E−02 | 1.39E−03 | 89 |
| AIR | kinase binding (GO:0019900) | 3.60E−04 | 1.99E−02 | 3.50E−03 | 84 |
| AIR | RNA polymerase II regulatory region DNA binding (GO:0001012) | 4.78E−04 | 2.16E−02 | 2.48E−03 | 45 |
| AIR | SUMO binding (GO:0032183) | 9.12E−04 | 2.34E−02 | 1.55E−02 | 6 |
| AIR | phosphoprotein phosphatase activity (GO:0004721) | 1.55E−03 | 6.64E−03 | 4.21E−03 | 33 |
| AIR | phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinase activity (GO:0016307) | 2.89E−03 | 1.13E−02 | 4.01E−03 | 7 |
| AIR | protein kinase binding (GO:0019901) | 4.57E−03 | 5.48E−03 | 1.33E−02 | 99 |
| AIR | purine ribonucleoside triphosphate binding (GO:0035639) | 1.51E−02 | 7.31E−03 | 2.75E−02 | 69 |
| AIR | ligand-dependent nuclear receptor transcription coactivator activity (GO:0030374) | 1.70E−02 | 2.42E−02 | 1.04E−02 | 17 |
| AIR | syntaxin-1 binding (GO:0017075) | 1.81E−02 | 1.94E−03 | 2.90E−02 | 6 |
| CIE | phosphatidylinositol binding (GO:0035091) | 4.66E−04 | 3.22E−02 | 9.13E−03 | 30 |
| FSS | histone methyltransferase activity (GO:0042054) | 7.13E−05 | 8.36E−05 | 1.98E−03 | 18 |
| FSS | steroid hormone receptor binding (GO:0035258) | 2.11E−04 | 4.14E−04 | 9.74E−04 | 22 |
| FSS | protein phosphorylated amino acid binding (GO:0045309) | 5.05E−04 | 4.83E−02 | 2.36E−02 | 12 |
| FSS | core promoter binding (GO:0001047) | 4.51E−03 | 1.41E−03 | 2.29E−03 | 24 |
| FSS | protein tyrosine kinase activity (GO:0004713) | 8.19E−03 | 5.03E−03 | 4.90E−02 | 36 |
| FSS | androgen receptor binding (GO:0050681) | 9.99E−03 | 1.28E−04 | 3.80E−03 | 11 |
| FSS | regulatory region DNA binding (GO:0000975) | 2.16E−02 | 1.99E−02 | 2.14E−02 | 44 |
| FSS | methylated histone binding (GO:0035064) | 2.46E−02 | 4.06E−02 | 4.66E−03 | 16 |
| FSS | histone deacetylase binding (GO:0042826) | 2.71E−02 | 3.67E−03 | 2.05E−02 | 19 |
| FSS | cadherin binding (GO:0045296) | 2.90E−02 | 2.44E−02 | 2.62E−02 | 60 |
| CIE + FSS | transmitter-gated ion channel activity (GO:0022824) | 3.11E−02 | 3.23E−02 | 2.54E−04 | 12 |
| (B) | |||||
| AIR | ubiquitin-specific protease binding (GO:1990381) | 4.96E−02 | 3.50E−02 | 2.81E−02 | 6 |
| CIE | GTP binding (GO:0005525) | 7.39E−06 | 9.18E−07 | 1.96E−03 | 43 |
| CIE | purine ribonucleoside binding (GO:0032550) | 1.61E−05 | 3.97E−06 | 9.53E−04 | 45 |
| CIE | guanyl ribonucleotide binding (GO:0032561) | 6.76E−05 | 1.31E−05 | 1.00E−03 | 46 |
| FSS | translation initiation factor activity (GO:0003743) | 2.51E−03 | 4.50E−05 | 4.00E−02 | 11 |
| FSS | translation factor activity, RNA binding (GO:0008135) | 3.24E−03 | 7.82E−05 | 3.21E−02 | 15 |
| CIE + FSS | syntaxin binding (GO:0019905) | 6.20E−03 | 1.99E−04 | 1.40E−02 | 22 |
| CIE + FSS | ubiquitin-protein transferase activity (GO:0004842) | 1.83E−02 | 6.60E−03 | 2.46E−02 | 73 |
| Group | Cell-Type | 000-h | 072-h | 168-h | Number of Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (A) | |||||
| Neurons | 1.22E−06 | 7.53E−23 | 6.91E−03 | 113 | |
| Oligodendrocytes | 5.49E−01 | 7.23E−01 | 6.99E−01 | 3 | |
| AIR | Astrocytes | 3.94E−01 | 2.00E−03 | 8.32E−01 | 34 |
| Microglia | 9.79E−01 | 9.97E−01 | 4.08E−01 | 48 | |
| Neurons | 7.06E−08 | 7.68E−03 | 5.53E−14 | 106 | |
| CIE | Oligodendrocytes | 3.52E−01 | 8.21E−01 | 6.39E−01 | 5 |
| Astrocytes | 9.33E−05 | 2.36E−02 | 5.06E−01 | 49 | |
| Microglia | 1.87E−20 | 8.67E−06 | 3.22E−01 | 140 | |
| Neurons | 1.25E−32 | 4.23E−06 | 1.13E−04 | 128 | |
| FSS | Oligodendrocytes | 2.68E−01 | 7.79E−01 | 1.88E−04 | 8 |
| Astrocytes | 1.02E−01 | 1.41E−03 | 4.36E−01 | 33 | |
| Microglia | 1.00E+00 | 7.12E−01 | 8.16E−01 | 41 | |
| Neurons | 2.58E−18 | 2.17E−08 | 1.02E−10 | 141 | |
| CIE + FSS | Oligodendrocytes | 2.81E−02 | 7.87E−10 | 8.68E−02 | 21 |
| Astrocytes | 2.57E−05 | 2.13E−05 | 8.76E−01 | 59 | |
| Microglia | 2.48E−17 | 2.11E−01 | 7.06E−01 | 124 | |
| (B) | |||||
| Neurons | 3.15E−02 | 5.73E−02 | 6.22E−02 | 55 | |
| Oligodendrocytes | 7.50E−01 | 9.08E−04 | 1.00E+00 | 9 | |
| AIR | Astrocytes | 3.36E−03 | 3.48E−01 | 1.38E−02 | 33 |
| Microglia | 9.49E−01 | 9.25E−01 | 8.35E−01 | 42 | |
| Neurons | 2.00E−05 | 7.31E−12 | 1.61E−03 | 90 | |
| CIE | Oligodendrocytes | 2.53E−01 | 5.76E−02 | 5.16E−01 | 7 |
| Astrocytes | 1.42E−11 | 2.95E−03 | 1.42E−03 | 58 | |
| Microglia | 9.71E−01 | 9.74E−01 | 9.93E−01 | 46 | |
| Neurons | 7.33E−03 | 1.90E−02 | 4.62E−02 | 55 | |
| FSS | Oligodendrocytes | 8.86E−01 | 3.48E−01 | 6.00E−01 | 4 |
| Astrocytes | 7.93E−02 | 9.34E−01 | 9.11E−02 | 26 | |
| Microglia | 7.75E−01 | 9.99E−01 | 5.56E−02 | 46 | |
| Neurons | 1.69E−07 | 2.81E−10 | 7.85E−03 | 80 | |
| CIE + FSS | Oligodendrocytes | 9.64E−02 | 1.00E+00 | 1.00E+00 | 4 |
| Astrocytes | 2.31E−13 | 5.40E−01 | 2.16E−06 | 59 | |
| Microglia | 7.69E−01 | 9.99E−01 | 1.96E−01 | 46 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farris, S.P.; Tiwari, G.R.; Ponomareva, O.; Lopez, M.F.; Mayfield, R.D.; Becker, H.C. Transcriptome Analysis of Alcohol Drinking in Non-Dependent and Dependent Mice Following Repeated Cycles of Forced Swim Stress Exposure. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10050275
Farris SP, Tiwari GR, Ponomareva O, Lopez MF, Mayfield RD, Becker HC. Transcriptome Analysis of Alcohol Drinking in Non-Dependent and Dependent Mice Following Repeated Cycles of Forced Swim Stress Exposure. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(5):275. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10050275
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarris, Sean P., Gayatri R. Tiwari, Olga Ponomareva, Marcelo F. Lopez, R. Dayne Mayfield, and Howard C. Becker. 2020. "Transcriptome Analysis of Alcohol Drinking in Non-Dependent and Dependent Mice Following Repeated Cycles of Forced Swim Stress Exposure" Brain Sciences 10, no. 5: 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10050275
APA StyleFarris, S. P., Tiwari, G. R., Ponomareva, O., Lopez, M. F., Mayfield, R. D., & Becker, H. C. (2020). Transcriptome Analysis of Alcohol Drinking in Non-Dependent and Dependent Mice Following Repeated Cycles of Forced Swim Stress Exposure. Brain Sciences, 10(5), 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10050275




