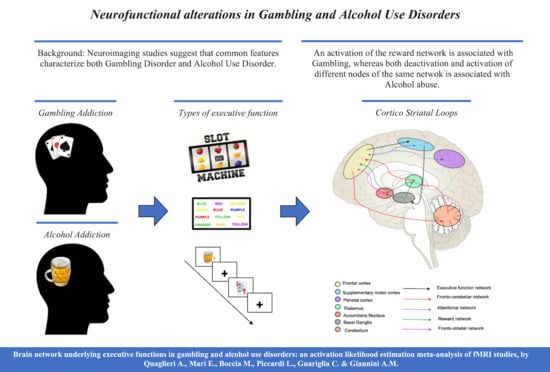
Brain Network Underlying Executive Functions in Gambling and Alcohol Use Disorders: An Activation Likelihood Estimation Meta-Analysis of fMRI Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Neuropsychological Features of GD and AUD
3. Neurobiological and Neurofunctional Alterations in GD and AUD
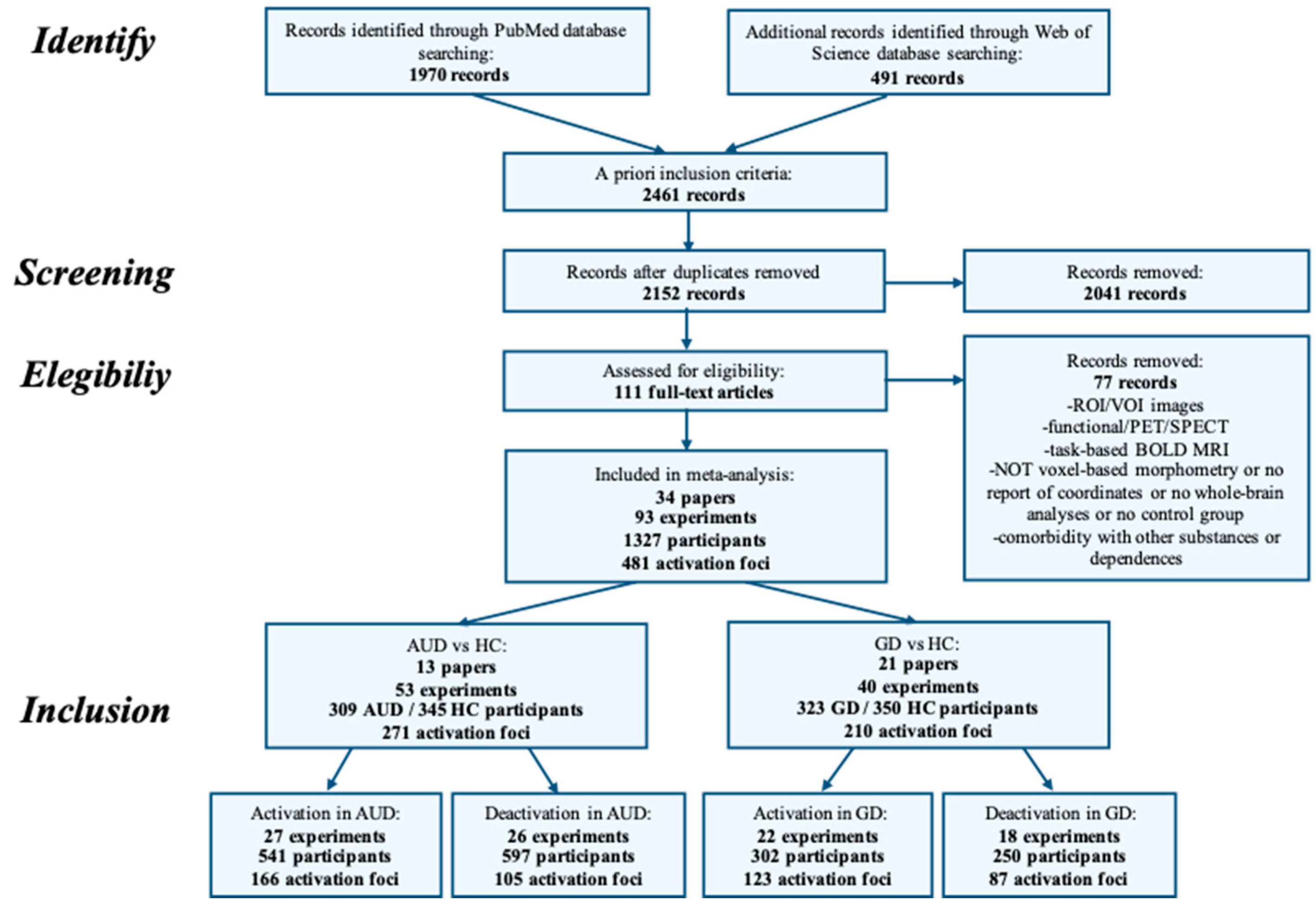
4. Methods
4.1. Inclusion Criteria for Papers
4.2. Activation Likelihood Estimation
5. Results
5.1. Neural Alterations in Gambling Disorder
5.2. Neural Alterations in Alcohol Use Disorder
6. Discussion
6.1. Neurofunctional Alterations in the Executive Function Brain Network in GD
6.2. Neurofunctional Alterations in the Executive Function Brain Network in AUD
6.3. Evidence for the Neurobiological Hypothesis of AUD and GD
6.4. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders; American Psychiatric Association Publishing: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders; American Psychiatric Association Publishing: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5®); American Psychiatric Publishing: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Petry, N.M.; Kiluk, B.D. Suicidal ideation and suicide attempts in treatment-seeking pathological gamblers. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 2002, 190, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potenza, M.N.; Fiellin, D.; Heninger, G.R.; Rounsaville, B.J.; Mazure, C.M. Gambling. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2002, 17, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudriaan, A.E.; Oosterlaan, J.; de Beurs, E.; Brink, W.V.D. Pathological gambling: A comprehensive review of biobehavioral findings. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2004, 28, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tackett, J.L.; Krieger, H.; Neighbors, C.; Rinker, D.; Rodriguez, L.; Edward, G. Comorbidity of Alcohol and Gambling Problems in Emerging Adults: A Bifactor Model Conceptualization. J. Gambl. Stud. 2017, 33, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alavi, S.S.; Ferdosi, M.; Jannatifard, F.; Eslami, M.; Alaghemandan, H.; Setare, M. Behavioral Addiction versus Substance Addiction: Correspondence of Psychiatric and Psychological Views. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2012, 3, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mayo Clinic. Compulsive Gambling. 2016. Available online: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/compulsive-gambling/symptoms-causes/syc-20355178 (accessed on 6 May 2019).
- Young-Wolff, K.C.; Enoch, M.-A.; Prescott, C.A. The influence of gene–environment interactions on alcohol consumption and alcohol use disorders: A comprehensive review. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2011, 31, 800–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welte, J.; Barnes, G.; Wieczorek, W.; Tidwell, M.C.; Parker, J. Alcohol, and gambling pathology among U.S. adults: Prevalence, demographic patterns and comorbidity. J. Stud. Alcohol 2001, 62, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahnejad, R.; Delfabbro, P.; Denson, L. Psychiatric co-morbidity in problem and pathological gamblers: Investigating the confounding influence of alcohol use disorder. Addict. Behav. 2014, 39, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rash, C.J.; Weinstock, J.; van Patten, R. A review of gambling disorder and substance use disorders. Subst. Abus. Rehab. 2016, 7, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejoyeux, M.; Boulenguiez, S.; Fichelle, A.; McLoughlin, M.; Claudon, M.; Adès, J. Alcohol dependence among patients admitted to psychiatric emergency services. Gen. Hosp. Psychiat. 2000, 22, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petry, N.M.; Stinson, F.S.; Grant, B.F. Comorbidity of DSM-IV pathological gambling and other psychiatric disorders: Results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. J. Clin. Psychiat. 2005, 66, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, J.E.; Brewer, J.A.; Potenza, M.N. The neurobiology of substance and behavioral addictions. CNS Spectrums 2006, 11, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potenza, M.N. The neurobiology of pathological gambling and drug addiction: An overview and new findings. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2008, 363, 3181–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Ruiter, M.B.; Veltman, D.J.; E Goudriaan, A.; Oosterlaan, J.; Sjoerds, Z.; Brink, W.V.D. Response Perseveration and Ventral Prefrontal Sensitivity to Reward and Punishment in Male Problem Gamblers and Smokers. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 34, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrase, J.; Schlagenhauf, F.; Kienast, T.; Wüstenberg, T.; Bermpohl, F.; Kahnt, T.; Beck, A.; Ströhle, A.; Juckel, G.; Knutson, B.; et al. Dysfunction of reward processing correlates with alcohol craving in detoxified alcoholics. Neurolmage 2007, 35, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudriaan, A.E.; de Ruiter, M.B.; Brink, W.V.D.; Oosterlaan, J.; Veltman, D.J. Brain activation patterns associated with cue reactivity and craving in abstinent problem gamblers, heavy smokers, and healthy controls: An fMRI study. Addict. Boil. 2010, 15, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noel, X.; van der Linden, M.; D’Acremont, M.; Bechara, A.; Dan, B.; Hanak, C.; Verbanck, P. Alcohol cues increase cognitive impulsivity in individuals with alcoholism. Psychopharmacology 2007, 192, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, J.; Thompson, L.; Claus, E.; Dalwani, M.; Hutchison, K.; Banich, M.T. Prefrontal cortex activity is reduced in gambling and nongambling substance users during decision-making. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2007, 28, 1276–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewig, J.; Kretschmer, N.; Trippe, R.H.; Hecht, H.; Coles, M.G.; Holroyd, C.B.; Miltner, W.H. Hypersensitivity to Reward in Problem Gamblers. Boil. Psychiat. 2010, 67, 781–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, L.; Stokes, P.R.; Wu, K.; Michalczuk, R.; Benecke, A.; Watson, B.J.; Lingford-Hughes, A.R. Striatal dopamine D2/D3 receptor binding in pathological gambling is correlated with mood-related impulsivity. Neurolmage 2012, 63, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, T.W. The Vulnerable Faces of Pathological Gambling. Psychiat. Edgemont 2005, 2, 34–42. [Google Scholar]
- Kerns, J.G.; Nuechterlein, K.H.; Braver, T.S.; Barch, D.M. Executive Functioning Component Mechanisms and Schizophrenia. Boil. Psychiat. 2008, 64, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Holst, R.J.; Brink, W.V.D.; Veltman, D.J.; Goudriaan, A.E. Brain Imaging Studies in Pathological Gambling. Curr. Psychiat. Rep. 2010, 12, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petry, N.M.; Blanco, C.; Auriacombe, M.; Borges, G.; Bucholz, K.; Crowley, T.J.; Grant, B.F.; Hasin, D.S.; O’Brien, C. An overview of and rationale for changes proposed for pathological gambling in DSM-5. J. Gambl. Stud. 2014, 30, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conversano, C.; Marazziti, D.; Carmassi, C.; Baldini, S.; Barnabei, G.; Dell’Osso, L. Pathological Gambling: A Systematic Review of Biochemical, Neuroimaging, and Neuropsychological Findings. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 2012, 20, 130–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ruiter, M.B.; Oosterlaan, J.; Veltman, D.J.; Brink, W.V.D.; Goudriaan, A.E. Similar hyporesponsiveness of the dorsomedial prefrontal cortex in problem gamblers and heavy smokers during an inhibitory control task. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2012, 121, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, J.; Raedler, T.; Rose, M.; Hand, I.; Gläscher, J.; Büchel, C. Pathological gambling is linked to reduced activation of the mesolimbic reward system. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 147–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaszczynski, A.; Steel, Z.; McConaghy, N. Impulsivity in pathological gambling: The antisocial impulsivist. Addiction 1997, 92, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potenza, M.N.; Leung, H.-C.; Blumberg, H.P.; Peterson, B.S.; Fulbright, R.K.; Lacadie, C.M.; Skudlarski, P.; Gore, J.C. An fMRI Stroop Task Study of Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortical Function in Pathological Gamblers. Am. J. Psychiat. 2003, 160, 1990–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, J.E.; Chamberlain, S.R. Gambling disorder. In Integrating Psychological and Pharmacological Treatments for Addictive Disorders: An Evidence-Based Guide; Taylor and Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 205–220. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, L.; Lawrence, A.; Astley-Jones, F.; Gray, N. Gambling Near-Misses Enhance Motivation to Gamble and Recruit Win-Related Brain Circuitry. Neuron 2009, 61, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapp, P.; Bhave, S.V.; Hoffman, P.L. How Adaptation of the Brain to Alcohol Leads to Dependence. Alcohol Res. Heal. J. Natl. Inst. Alcohol Abus. Alcohol. 2008, 31, 310–339. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, V.R.; Finkbeiner, S. NMDA and AMPA receptors: Old channels, new tricks. Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulder, R.T. Alcoholism and Personality. Aust. New Zealand J. Psychiat. 2002, 36, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trull, T.J.; Waudby, C.J.; Sher, K.J. Alcohol, Tobacco, and Drug Use Disorders and Personality Disorder Symptoms. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2004, 12, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, M.E.; Buckman, J.F.; Nguyen, T.T. A role for cognitive rehabilitation in increasing the effectiveness of treatment for alcohol use disorders. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2013, 23, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.; Halsey, A.; MacPherson, H.; Billington, J.; Hill, S.; Johnson, G.; Raju, K.; Abbott, P. The Psycho-Social Rehabilitation of Patients with Alcohol-Related Brain Damage in the Community. Alcohol Alcohol. 2012, 47, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beylergil, S.B.; Beck, A.; Deserno, L.; Lorenz, R.; Rapp, M.A.; Schlagenhauf, F.; Heinz, A.; Obermayer, K. Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex contributes to the impaired behavioral adaptation in alcohol dependence. Neurolmage Clin. 2017, 15, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobova, L.; Finn, P.R.; Rickert, M.E.; Lucas, J. Disinhibitory psychopathology and delay discounting in alcohol dependence: Personality and cognitive correlates. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2009, 17, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, R.M.; Meyer, J.R.; Huettel, S.A. Functional neuroimaging of intertemporal choice models: A review. J. Neurosci. Psychol. Econ. 2010, 3, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boettiger, C.A.; Mitchell, J.M.; Tavares, V.C.; Robertson, M.; Joslyn, G.; D’Esposito, M.; Fields, H.L. Immediate Reward Bias in Humans: Fronto-Parietal Networks and a Role for the Catechol-O-Methyltransferase 158Val/Val Genotype. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 14383–14391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, A.C.; Cservenka, A.; Ray, L. Effects of Alcohol Dependence Severity on Neural Correlates of Delay Discounting. Alcohol Alcohol. 2017, 52, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- le Berre, A.-P.; Rauchs, G.; la Joie, R.; Mézenge, F.; Boudehent, C.; Vabret, F.; Segobin, S.; Viader, F.; Allain, P.; Eustache, F.; et al. Impaired decision-making and brain shrinkage in alcoholism. Eur. Psychiat. 2014, 29, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, Y.; Goodyear, B.; Crockford, D.N. Neural Correlates of Pathological Gamblers Preference for Immediate Rewards During the Iowa Gambling Task: An fMRI Study. J. Gambl. Stud. 2011, 28, 623–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brevers, D.; Noël, X.; He, Q.; Melrose, J.A.; Bechara, A.; Melrose, A. Increased ventral-striatal activity during monetary decision making is a marker of problem poker gambling severity. Addict. Boil. 2015, 21, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miedl, S.F.; Fehr, T.; Meyer, G.; Herrmann, M. Neurobiological correlates of problem gambling in a quasi-realistic blackjack scenario as revealed by fMRI. Psychiat. Res. Neurolmag. 2010, 181, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brevers, D.; Bechara, A.; Hermoye, L.; Divano, L.; Kornreich, C.; Verbanck, P.; Noel, X. Comfort for uncertainty in pathological gamblers: A fMRI study. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 278, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelskov, S.V.; Madsen, K.H.; Ramsøy, T.Z.; Siebner, H.R. Aberrant neural signatures of decision-making: Pathological gamblers display cortico-striatal hypersensitivity to extreme gambles. Neurolmage 2016, 128, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potenza, M.N.; Steinberg, M.A.; Skudlarski, P.; Fulbright, R.K.; Lacadie, C.M.; Wilber, M.K.; Rounsaville, B.J.; Gore, J.C.; Wexler, B.E. Gambling Urges in Pathological Gambling. Arch. Gen. Psychiat. 2003, 60, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Miedl, S.F.; Peters, J.; Büchel, C. Altered Neural Reward Representations in Pathological Gamblers Revealed by Delay and Probability Discounting. Arch. Gen. Psychiat. 2012, 69, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moccia, L.; Pettorruso, M.; de Crescenzo, F.; de Risio, L.; di Nuzzo, L.; Martinotti, G.; Bifone, A.; Janiri, L.; di Nicola, M. Neural correlates of cognitive control in gambling disorder: A systematic review of fMRI studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 78, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Q.; Kahnt, T.; Beck, A.; Cohen, M.X.; Dolan, R.; Wrase, J.; Heinz, A. Prefrontal cortex fails to learn from reward prediction errors in alcohol dependence. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 7749–7753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjoerds, Z.; de Wit, S.; van den Brink, W.; Robbins, T.W.; Beekman, A.T.; Penninx, B.W.; Veltman, D.J. Behavioural and neuroimaging evidence for overreliance on habit learning in alcohol-dependent patients. Transl. Psychiatry 2013, 3, e337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galandra, C.; Basso, G.; Cappa, S.; Canessa, N. The alcoholic brain: Neural bases of impaired reward-based decision-making in alcohol use disorders. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 39, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balleine, B.W.; Dickinson, A. Goal-directed instrumental action: Contingency and incentive learning and their cortical substrates. Neuropharmacology 1998, 37, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbit, L.H.; Balleine, B.W. The role of prelimbic cortex in instrumental conditioning. Behav. Brain Res. 2003, 146, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbit, L.H.; Janak, P.H. Habitual Alcohol Seeking: Neural Bases and Possible Relations to Alcohol Use Disorders. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2016, 40, 1380–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.; Schlagenhauf, F.; Wüstenberg, T.; Hein, J.; Kienast, T.; Kahnt, T.; Wrase, J. Ventral striatal activation during reward anticipation correlates with impulsivity in alcoholics. Biol. Psychiat. 2009, 66, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grodin, E.; Steckler, L.E.; Momenan, R. Altered Striatal Response During Effort-Based Valuation and Motivation in Alcohol-Dependent Individuals. Alcohol Alcohol. 2016, 51, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Holst, R.J.; Clark, L.; Veltman, D.J.; Brink, W.V.D.; Goudriaan, A.E. Enhanced striatal responses during expectancy coding in alcohol dependence. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014, 142, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjork, J.; Momenan, R.; Smith, A.R.; Hommer, D.W. Reduced posterior mesofrontal cortex activation by risky rewards in substance-dependent patients. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2008, 95, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Sundby, K.; Bjork, J.; Momenan, R. Alcohol Dependence and Altered Engagement of Brain Networks in Risky Decisions. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amlung, M.; MacKillop, J. Understanding the effects of stress and alcohol cues on motivation for alcohol via behavioral economics. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2014, 38, 1780–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claus, E.D.; Kiehl, K.A.; Hutchison, K.E. Neural and behavioral mechanisms of impulsive choice in alcohol use disorder. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2011, 35, 1209–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seghier, M.L. The angular gyrus: Multiple functions and multiple subdivisions. Neuroscientist 2013, 19, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClure, S.M.; Laibson, D.; Loewenstein, G.; Cohen, J.D. Separate Neural Systems Value Immediate and Delayed Monetary Rewards. Science 2004, 306, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClure, S.M.; Ericson, K.M.; Laibson, D.I.; Loewenstein, G.; Cohen, J.D. Time Discounting for Primary Rewards. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 5796–5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talairach, J.; Tournoux, P. Co-planar stereotaxic atlas of the human brain. Theime 1988, 270, 90128–90135. [Google Scholar]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA Statement for Reporting Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses of Studies That Evaluate Health Care Interventions: Explanation and Elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.A.D.; Altman, D.G. PRISMA 2009 flow diagram. PRISMA Statement 2009, 6, 1000097. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, V.I.; Cieslik, E.C.; Laird, A.R.; Fox, P.T.; Radua, J.; Mataix-Cols, D.; Tench, C.R.; Yarkoni, T.; Nichols, T.E.; Turkeltaub, P.E.; et al. Ten simple rules for neuroimaging meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 84, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, M.R.; Wilson, A.; Habib, R. Neurological correlates of slot machine win size in pathological gamblers. Behav. Process. 2014, 104, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiehler, A.; Petzschner, F.H.; Stephan, K.E.; Peters, J. Episodic Tags Enhance Striatal Valuation Signals during Temporal Discounting in pathological Gamblers. Eneuro 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sescousse, G.; Barbalat, G.; Domenech, P.; Dreher, J.-C. Imbalance in the sensitivity to different types of rewards in pathological gambling. Brain 2013, 136, 2527–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miedl, S.F.; Wiswede, D.; Marco-Pallarés, J.; Ye, Z.; Fehr, T.; Herrmann, M.; Münte, T.F. The neural basis of impulsive discounting in pathological gamblers. Brain Imag. Behav. 2015, 9, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Holst, R.J.; Veltman, D.J.; Büchel, C.; Brink, W.V.D.; Goudriaan, A.E. Distorted Expectancy Coding in Problem Gambling: Is the Addictive in the Anticipation? Boil. Psychiat. 2012, 71, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balodis, I.M.; Kober, H.; Worhunsky, P.D.; Stevens, M.C.; Pearlson, G.D.; Potenza, M.N. Diminished Frontostriatal Activity During Processing of Monetary Rewards and Losses in Pathological Gambling. Boil. Psychiat. 2012, 71, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurumi, K.; Kawada, R.; Yokoyama, N.; Sugihara, G.; Sawamoto, N.; Aso, T.; Takahashi, H. Insular activation during reward anticipation reflects duration of illness in abstinent pathological gamblers. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Crockford, D.; Goodyear, B.; Edwards, J.; Quickfall, J.; El-Guebaly, N. Cue-Induced Brain Activity in Pathological Gamblers. Boil. Psychiat. 2005, 58, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, R.; Dixon, M.R. Neurobehavioral evidence for the “near-miss” effect in pathological gamblers. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 2010, 93, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limbrick-Oldfield, E.H.; Mick, I.; E Cocks, R.; Mcgonigle, J.; Sharman, S.; Goldstone, A.P.; A Stokes, P.R.; Waldman, A.D.; Erritzoe, D.; Bowden-Jones, H.; et al. Neural substrates of cue reactivity and craving in gambling disorder. Transl. Psychiat. 2017, 7, e992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujino, J.; Kawada, R.; Tsurumi, K.; Takeuchi, H.; Murao, T.; Takemura, A.; Tei, S.; Murai, T.; Takahashi, H. An fMRI study of decision-making under sunk costs in gambling disorder. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018, 28, 1371–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, A.; Tsurumi, K.; Kawada, R.; Murao, T.; Takeuchi, H.; Murai, T.; Takahashi, H. Deficit of state-dependent risk attitude modulation in gambling disorder. Transl. Psychiat. 2017, 7, e1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilman, J.M.; Smith, A.R.; Bjork, J.; Ramchandani, V.A.; Momenan, R.; Hommer, D.W. Cumulative gains enhance striatal response to reward opportunities in alcohol-dependent patients. Addict. Boil. 2014, 20, 580–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.-C.; Schulte, T.; Müller-Oehring, E.M.; Namkoong, K.; Pfefferbaum, A.; Sullivan, E.V. Compromised frontocerebellar circuitry contributes to nonplanning impulsivity in recovering alcoholics. Psychopharmacology 2014, 231, 4443–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Czapla, M.; Baeuchl, C.; Simon, J.J.; Richter, B.; Kluge, M.; Friederich, H.-C.; Mann, K.; Herpertz, S.C.; Loeber, S. Do alcohol-dependent patients show different neural activation during response inhibition than healthy controls in an alcohol-related fMRI go/no-go-task? Psychopharmacology 2017, 234, 1001–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte, T.; Jung, Y.-C.; Sullivan, E.V.; Pfefferbaum, A.; Serventi, M.; Müller-Oehring, E.M. The neural correlates of priming emotion and reward systems for conflict processing in alcoholics. Brain Imag. Behav. 2016, 11, 1751–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Ide, J.; Zhang, S.; Sinha, R.; Li, C.-S.R. Conflict anticipation in alcohol dependence—A model-based fMRI study of stop signal task. Neurolmage Clin. 2015, 8, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-S.R.; Luo, X.; Yan, P.; Bergquist, K.; Sinha, R. Altered impulse control in alcohol dependence: Neural measures of stop signal performance. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2009, 33, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilman, J.M.; Davis, M.B.; Hommer, D.W. Greater Activation in Left Hemisphere Language-Related Regions During Simple Judgment Tasks Among Substance-Dependent Patients in Treatment for Alcoholism. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2010, 34, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, L.E.; Kohno, M.; McCready, H.D.; Schwartz, D.L.; Schwartz, B.; Lahna, D.; Nagel, B.J.; Mitchell, S.H.; Hoffman, W.F. Correction to: Neural correlates of reward magnitude and delay during a probabilistic delay discounting task in alcohol use disorder. Psychopharmacology 2020, 237, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkeltaub, P.E.; Eden, G.F.; Jones, K.M.; Zeffiro, T.A. Meta-analysis of the functional neuroanatomy of single word reading: method and validation. Neurolmage 2002, 16, 765–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkeltaub, P.E.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Laird, A.R.; Fox, M.; Wiener, M.; Fox, P.T. Minimizing within-experiment and within-group effects in Activation Likelihood Estimation meta-analyses. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2011, 33, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eickhoff, S.B.; Laird, A.R.; Grefkes, C.; Wang, L.E.; Zilles, K.; Fox, P.T. Coordinate-based activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis of neuroimaging data: A random-effects approach based on empirical estimates of spatial uncertainty. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2009, 30, 2907–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eickhoff, S.; Amunts, K.; Mohlberg, H.; Zilles, K. The Human Parietal Operculum. II. Stereotaxic Maps and Correlation with Functional Imaging Results. Cereb. Cortex 2005, 16, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sörös, P.; Inamoto, Y.; Martin, R.E. Functional brain imaging of swallowing: An activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis. Human Brain Mapp. 2009, 30, 2426–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spreng, R.N.; Mar, R.A.; Kim, A.S.N. The Common Neural Basis of Autobiographical Memory, Prospection, Navigation, Theory of Mind, and the Default Mode: A Quantitative Meta-analysis. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2009, 21, 489–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, P.B.; Laird, A.R.; Maller, J.; Daskalakis, Z.J. A meta-analytic study of changes in brain activation in depression. Human Brain Mapp. 2008, 29, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, L.; Chamberlain, S.R.; Laird, A.R.; Thelen, S.M.; Sahakian, B.J.; Bullmore, E.T. Integrating evidence from neuroimaging and neuropsychological studies of obsessive-compulsive disorder: The orbitofronto-striatal model revisited. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2007, 32, 525–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eickhoff, S.B.; Laird, A.R.; Fox, P.M.; Lancaster, J.L.; Fox, P.T. Implementation errors in the GingerALE Software: Description and recommendations. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2016, 38, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, P.T.; Lancaster, J.L.; Laird, A.R.; Eickhoff, S.B. Meta-analysis in human neuroimaging: Computational modeling of large-scale databases. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 37, 409–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eickhoff, S.B.; Nichols, T.E.; Laird, A.R.; Hoffstaedter, F.; Amunts, K.; Fox, P.T.; Bzdok, D.; Eickhoff, C.R. Behavior, sensitivity, and power of activation likelihood estimation characterized by massive empirical simulation. Neurolmage 2016, 137, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Holst, R.J.; van der Meer, J.N.; McLaren, D.; Brink, W.V.D.; Veltman, D.J.; Goudriaan, A.E. Interactions between Affective and Cognitive Processing Systems in Problematic Gamblers: A Functional Connectivity Study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Holst, R.J.; van Holstein, M.; Brink, W.V.D.; Veltman, D.J.; Goudriaan, A.E. Response Inhibition during Cue Reactivity in Problem Gamblers: An fMRI Study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comings, D.E.; Blum, K. Reward deficiency syndrome: Genetic aspects of behavioral disorders. In Progress in Brain Research; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 325–341. [Google Scholar]
- Robbins, T.W. Shifting and stopping: Fronto-striatal substrates, neurochemical modulation, and clinical implications. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2007, 362, 917–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalley, J.W.; Mar, A.C.; Economidou, D.; Robbins, T.W. Neurobehavioral mechanisms of impulsivity: Fronto-striatal systems and functional neurochemistry. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2008, 90, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.-J.; Deng, W.; Wang, H.-Y.; Guo, W.-J.; Li, T.; Lam, C.; Lin, X. Reward pathway dysfunction in gambling disorder: A meta-analysis of functional magnetic resonance imaging studies. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 275, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutson, B.; Cooper, J.C. Functional magnetic resonance imaging of reward prediction. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2005, 18, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luijten, M.; Schellekens, A.F.; Machielse, M.W.J.; Sescousse, G.; Kühn, S. Disruption of Reward Processing in Addiction. JAMA Psychiat. 2017, 74, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balodis, I.M.; Potenza, M.N. Anticipatory reward processing in addicted populations: A focus on the monetary incentive delay task. Boil. Psychiat. 2014, 77, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hommer, D.W.; Bjork, J.; Gilman, J.M. Imaging brain response to reward in addictive disorders. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2011, 1216, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, T.E.; Berridge, K. The incentive sensitization theory of addiction: Some current issues. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2008, 363, 3137–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, K.; Braverman, E.R.; Holder, J.M.; Lubar, J.F.; Monastra, V.J.; Miller, D.; Lubar, J.O.; Chen, T.J.; Comings, D.E. Reward deficiency syndrome: A biogenetic model for the diagnosis and treatment of impulsive, addictive, and compulsive behaviors. J. Psychoact. Drugs 2000, 32, 1–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diekhof, E.K.; Falkai, P.; Gruber, O. Functional neuroimaging of reward processing and decision-making: A review of aberrant motivational and affective processing in addiction and mood disorders. Brain Res. Rev. 2008, 59, 164–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gambling Disorder | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paper | Subjects GD | Age M (SD) | Subjects HC | Age M (SD) | Experiments | Foci | Task | Enhanced Activation in GD (Relative to HC) | Reduced Activation in GD (Relative to HC) |
| Gelskov et al. 2016 [52] | 14 (All male) | 29.43 (6.05) | 15 (All male) | 29.87 (6.06) | 3 | 27 | Gambling | 2 | 1 |
| Brevers et al. 2015 [51] | 10 (8 Male) | 34.00 (8.53) | 10 (8 Male) | 36.20 (12.95) | 2 | 2 | Card-Deck Paradigm Task | - | 2 |
| Dixon et al. 2014 [76] | 12 (All male) | - | 10 (All Male) | - | 2 | 16 | Slot-Machine Task | 2 | - |
| Miedl et al. 2012 [54] | 16 (15 male) | 35.00 (2.00) | 16 (15 male) | 38.00 (2.00) | 1 | 6 | Delay discounting Task | 1 | - |
| Power et al. 2012 [48] | 13 (All male) | 42.40 (10.80) | 13 (All male) | 41.00 (11.00) | 2 | 8 | Iowa Gambling Task | 1 | 1 |
| Wiehler et al. 2017 [77] | 24 (All Male) | 29.68 (10.88) | 24 (All male) | 28.47 (7.13) | 1 | 1 | Delayed Monetary Reward Task | 1 | - |
| Sescousse et al. 2013 [78] | 18 (All male) | 34.10 (11.60) | 20 (All male) | 31.00 (7.30) | 1 | 14 | Monetary Incentive delay Task | 1 | - |
| Miedl et al. 2015 [79] | 15 (All male) | 36.70 (5.80) | 15 (All male) | 36.80 (5.60) | 1 | 5 | Monetary-choice Task | 1 | - |
| Miedl et al. 2010 [50] | 12 (All male) | 39.50 (9.30) | 12 (All male) | 33.40 (8.00) | 3 | 11 | Quasi-realistic Blackjack Task | 2 | 1 |
| Goudriaan et al. 2010 [20] | 17 (All male) | 35.30 (9.40) | 17 (All male) | 34.70 (9.70) | 1 | 6 | Cue Reactivity Task | 1 | - |
| Van Holst et al. 2012 [80] | 15 (All male) | 38.00 (13.42) | 16 (All male) | 34.92 (11.98) | 3 | 7 | Card guessing Task | 3 | - |
| Balodis et al. 2012 [81] | 14 (10 male) | 35.08 (11.70) | 14 (10 male) | 37.10 (11.30) | 5 | 17 | Monetary Incentive delay Task | - | 5 |
| Tsurumi et al. 2014 [82] | 23 (All male) | 32.6 (6.90) | 27 (All male) | 33.40 (8.00) | 1 | 2 | Monetary Incentive delay Task | - | 1 |
| Reuter et al. 2005 [31] | 12 (All male) | 37.30 (7.40) | 12 (All male) | 32.30 (5.60) | 2 | 7 | Card guessing Task | 2 | - |
| Crockford et al. 2005 [83] | 10 (All male) | 39.30 (7.60) | 10 (All male) | 39.20 (8.30) | 1 | 3 | Cue Reactivity Task | 1 | - |
| Habib et al. 2010 [84] | 11 (10 male) | - | 11 (4 male) | - | 5 | 32 | Computerize Slot-machine Task | 2 | 3 |
| Potenza et al. 2003 [33] | 13 (All male) | 31.15 (7.97) | 11 (All male) | 29.00 (7.81) | 2 | 20 | Stroop Task | 1 | 1 |
| Potenza et al. 2003 [53] | 10 (All male) | 36.20 (11.95) | 11 (All male) | 30.09 (7.71) | 1 | 18 | Video scenario gambling | - | 1 |
| Limbrick-Oldfield et al. 2017 [85] | 20 (All male) | 31.00 (range27-51) | 22 (All male) | 28.00 (range 25–52) | 1 | 4 | Cue reactivity Task | 1 | - |
| Fujino et al. 2018 [86] | 23 (All male) | 32.70 (7.80) | 35 (All male) | 29.30 (9.30) | 1 | 3 | Monetary Reward Task | - | 1 |
| Fujimoto et al. 2017 [87] | 21 (All male) | 34.70 (8.82) | 29 (All male) | 30.90 (10.40) | 1 | 1 | Goal-Instructed Gambling Task | - | 1 |
| Total | 323 | 350 | 40 | 210 | |||||
| Alcohol Use Disorder | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paper | Subjects AUD | Age M (SD) | Subjects HC | Age M (SD) | Experiments | Foci | Task | Enhanced Activation in AUD (Relative to HC) | Reduced Activation in AUD (Relative to HC) |
| Von Holst et al. 2014 [64] | 18 (All male) | 42.50 (10.40) | 19 (All male) | 40.40 (10.70) | 3 | 6 | Card guessing task | 3 | - |
| Gilman et al. 2015 [88] | 18 (12 male) | 31.20 (7.10) | 18 (12 male) | 30.50 (5.10) | 5 | 13 | Risk-taking Task | 2 | 3 |
| Jung et al. 2014 [89] | 26 (All male) | 50.20 (9.50) | 26 (All male) | 49.50 (11.40) | 2 | 3 | Decision-making Task | 1 | 1 |
| Beylergil et al. 2017 [42] | 34 (All male) | 44.73 (8.27) | 26 (All male) | 41.92 (9.59) | 4 | 16 | Reward-guided decision Task | - | 4 |
| Czapla et al. 2017 [90] | 19 (17 male) | 51.21 (7.36) | 21 (17 male) | 41.95 (9.99) | 4 | 46 | Go/No Go Task | 3 | 1 |
| Schulte et al. 2017 [91] | 26 (18 male) | 49.90 (9.50) | 26 (17 male) | 49.10 (11.00) | 11 | 40 | Alcohol Priming Stroop Task | 5 | 6 |
| Hu et al. 2015 [92] | 24 (18 male) | 38.70 (8.00) | 70 (43 male) | 35.10 (10.00) | 2 | 9 | Stop signal Task | 1 | 1 |
| Wrase et al. 2007 [19] | 16 (All male) | 42.38 (7.52) | 16 (All male) | 39.94 (8.59) | 4 | 9 | Monetary Incentive Delay Task | 2 | 2 |
| Li et al. 2009 [93] | 24 (18 male) | 38.70 (8.30) | 24 (18 male) | 35.50 (5.90) | 3 | 17 | Stop signal Task | 1 | 2 |
| Beck et al. 2009 [62] | 19 (All male) | 41.84 (6.79) | 19 (All male) | 41.68 (8.97) | 3 | 13 | Monetary Incentive Delay Task | - | 3 |
| Gilman et al. 2010 [94] | 15 (8 male) | 35.29 (7.34) | 15 (8 male) | 33.30 (8.60) | 6 | 52 | Judgment decision task | 6 | - |
| Sjoerds et al. 2013 [57] | 31 (18 male) | 48.50 (8.50) | 19 (12 male) | 47.70 (10.60) | 4 | 6 | Instrumental learning Task | 2 | 2 |
| Dennis et al. 2020 [95] | 39 (29 male) | 40.51 (9.09) | 46 (28 male) | 35.00 (11.80) | 2 | 41 | Probabilistic Discounting Task | 1 | 1 |
| Total | 309 | 345 | 53 | 271 | |||||
| Cluster | Region | Hemisphere | ALE | p | Z | x | y | z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Caudate Head | RH | 0.013 | 0.000 | 4.282 | 16 | 14 | −2 |
| Caudate Head | RH | 0.012 | 0.000 | 3.920 | 18 | 22 | −2 | |
| 2 | Caudate Body | LH | 0.014 | 0.000 | 4.428 | −10 | 12 | 8 |
| Caudate Head | LH | 0.011 | 0.000 | 3.806 | −8 | 14 | −12 | |
| Caudate Head | LH | 0.010 | 0.000 | 3.551 | −14 | 14 | −2 | |
| 3 | Putamen | RH | 0.016 | 0.000 | 4.825 | 32 | 10 | −6 |
| 4 | Middle Frontal Gyrus | RH | 0.013 | 0.000 | 4.241 | 34 | 24 | 52 |
| 5 | Hypothalamus | RH | 0.015 | 0.000 | 4.509 | 10 | −2 | −10 |
| Cluster | Region | Hemisphere | ALE | p | Z | x | y | z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Putamen | LH | 0.021 | 0.000 | 5.149 | −20 | 0 | 16 |
| 2 | Middle Frontal gyrus | RH | 0.020 | 0.000 | 5.008 | 38 | 12 | 58 |
| 3 | Precuneus | LH | 0.020 | 0.000 | 4.994 | −20 | −74 | 28 |
| Cluster | Region | Hemisphere | ALE | p | Z | x | y | z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Middle Frontal gyrus | LH | 0.018 | 0.000 | 4.747 | −34 | 10 | 52 |
| Middle Frontal gyrus | LH | 0.017 | 0.000 | 4.721 | −38 | 10 | 52 | |
| 2 | Middle Frontal gyrus | RH | 0.019 | 0.000 | 5.028 | 40 | 34 | 40 |
| 3 | Cingulate gyrus | LH | 0.025 | 0.000 | 5.847 | −8 | 14 | 30 |
| Cingulate gyrus | LH | 0.010 | 0.000 | 3.383 | −8 | 22 | 38 | |
| 4 | Putamen | LH | 0.017 | 0.000 | 4.693 | −16 | 14 | −10 |
| 5 | Middle Frontal gyrus | RH | 0.018 | 0.000 | 4.867 | 24 | 8 | 64 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quaglieri, A.; Mari, E.; Boccia, M.; Piccardi, L.; Guariglia, C.; Giannini, A.M. Brain Network Underlying Executive Functions in Gambling and Alcohol Use Disorders: An Activation Likelihood Estimation Meta-Analysis of fMRI Studies. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060353
Quaglieri A, Mari E, Boccia M, Piccardi L, Guariglia C, Giannini AM. Brain Network Underlying Executive Functions in Gambling and Alcohol Use Disorders: An Activation Likelihood Estimation Meta-Analysis of fMRI Studies. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(6):353. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060353
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuaglieri, Alessandro, Emanuela Mari, Maddalena Boccia, Laura Piccardi, Cecilia Guariglia, and Anna Maria Giannini. 2020. "Brain Network Underlying Executive Functions in Gambling and Alcohol Use Disorders: An Activation Likelihood Estimation Meta-Analysis of fMRI Studies" Brain Sciences 10, no. 6: 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060353
APA StyleQuaglieri, A., Mari, E., Boccia, M., Piccardi, L., Guariglia, C., & Giannini, A. M. (2020). Brain Network Underlying Executive Functions in Gambling and Alcohol Use Disorders: An Activation Likelihood Estimation Meta-Analysis of fMRI Studies. Brain Sciences, 10(6), 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060353