Consonantal Landmarks as Predictors of Dysarthria among English-Speaking Adults with Cerebral Palsy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Speech Samples
- (1) a.
- Except in the winter when the ooze or snow or ice prevents.
- b.
- He slowly takes a short walk in the open air each day.
- c.
- Usually minus several buttons.
- d.
- You wished to know all about my grandfather.
- e.
- But he always answers, banana oil.
- f.
- The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.
- g.
- She had your dark suit in greasy wash water all year.
- h.
- Giving those who observe him a pronounced feeling of the utmost respect.
- i.
- We have often urged him to walk more and smoke less.
- j.
- A long, flowing beard clings to his chin.
- k.
- Yet he still thinks as swiftly as ever.
- l.
- Well, he is nearly ninety-three years old.
- m.
- He dresses himself in an ancient black frock coat.
- n.
- Grandfather likes to be modern in his language.
- o.
- When he speaks, his voice is just a bit cracked and quivers a trifle.
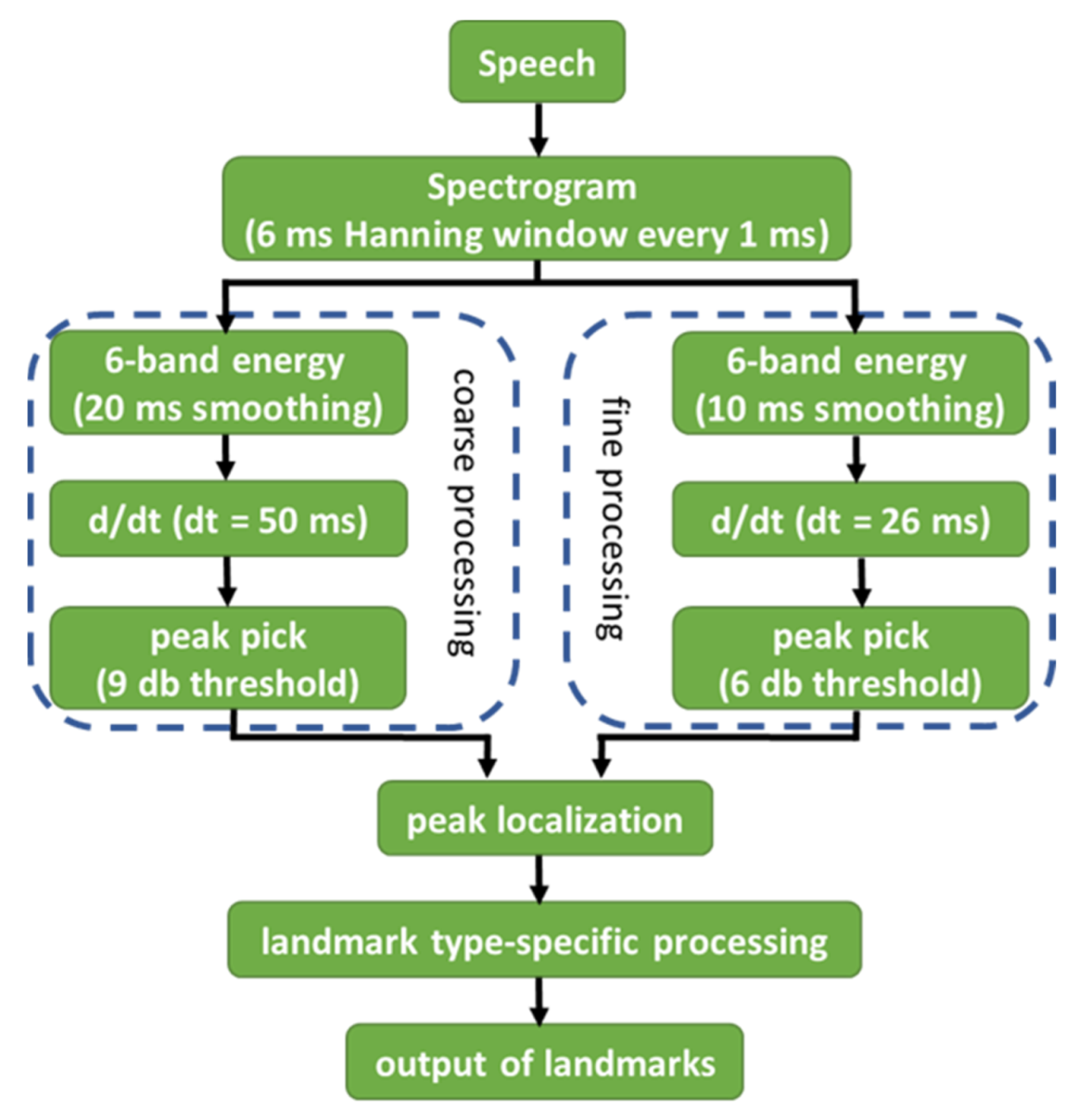
2.2. Landmark-based Acoustic Analysis and Perceptual Analysis
2.3. Descriptive and Inferential Statistics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boyle, C.A.; Boulet, S.; Schieve, L.A.; Cohen, R.A.; Blumberg, S.J.; Yeargin-Allsopp, M.; Visser, S.; Kogan, M.D. Trends in the prevalence of developmental disabilities in US children, 1997–2008. Pediatrics 2011, 127, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oskoui, M.; Coutinho, F.; Dykeman, J.; Jetté, N.; Pringsheim, T. An update on the prevalence of cerebral palsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2013, 55, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, D.; Van Naarden Braun, K.; Doernberg, N.S.; Maenner, M.J.; Arneson, C.L.; Durkin, M.S.; Benedict, R.E.; Kirby, R.S.; Wingate, M.S.; Fitzgerald, R.; et al. Prevalence of cerebral palsy, co-occurring autism spectrum disorders, and motor functioning–Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, USA, 2008. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2014, 56, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durkin, M.S.; Benedict, R.E.; Christensen, D.; Dubois, L.A.; Fitzgerald, R.T.; Kirby, R.S.; Maenner, M.J.; Van Naarden Braun, K.; Wingate, M.S.; Yeargin-Allsopp, M. Prevalence of cerebral palsy among 8-year-old children in 2010 and preliminary evidence of trends in its relationship to low birthweight. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2016, 30, 496–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maenner, M.J.; Blumberg, S.J.; Kogan, M.D.; Christensen, D.; Yeargin-Allsopp, M.; Schieve, L.A. Prevalence of cerebral palsy and intellectual disability among children identified in two US National Surveys, 2011–2013. Ann. Epidemiol. 2016, 26, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGuire, D.O.; Tian, L.H.; Yeargin-Allsopp, M.; Dowling, N.F.; Christensen, D.L. Prevalence of cerebral palsy, intellectual disability, hearing loss, and blindness, National Health Interview Survey, 2009–2016. Disabil. Health J. 2019, 12, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, K.; Livingstone, E.; Perra, O.; Kerr, C. Population-based study on the prevalence and clinical profile of adults with cerebral palsy in Northern Ireland. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e044614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Xia, J.; Gao, J.; Wang, L. Increasing prevalence of cerebral palsy among children and adolescents in China 1988-2020: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Rehabil. Med. 2021, 53, jrm00195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordberg, A.; Miniscalco, C.; Lohmander, A.; Himmelmann, K. Speech problems affect more than one in two children with cerebral palsy: S wedish population-based study. Acta Paediatr. 2013, 102, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, K.M.; Hustad, K.C. Data-driven classification of dysarthria profiles in children with cerebral palsy. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2018, 61, 2837–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mou, Z.; Teng, W.; Ouyang, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z. Quantitative analysis of vowel production in cerebral palsy children with dysarthria. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 66, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, M.; Verhoeven, L.; De Moor, J.; Van Balkom, H.; Van Leeuwe, J. Home literacy predictors of early reading development in children with cerebral palsy. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2009, 30, 445–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schölderle, T.; Staiger, A.; Lampe, R.; Ziegler, W. Dysarthria syndromes in adult cerebral palsy. J. Med. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2013, 20, 100–105. [Google Scholar]
- Schölderle, T.; Staiger, A.; Lampe, R.; Strecker, K.; Ziegler, W. Dysarthria in adults with cerebral palsy: Clinical presentation and impacts on communication. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2016, 59, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, W.; Staiger, A.; Schölderle, T.; Vogel, M. Gauging the auditory dimensions of dysarthric impairment: Reliability and construct validity of the Bogenhausen Dysarthria Scales (BoDyS). J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2017, 60, 1516–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, K.M.; Hustad, K.C. Acoustic predictors of pediatric dysarthria in cerebral palsy. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2018, 61, 462–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.M.; Hustad, K.C.; Kent, R.D.; Lin, Y.C. Dysarthria in Mandarin-speaking children with cerebral palsy: Speech subsystem profiles. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2018, 61, 525–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.T.; Chen, L.M.; Lin, Y.C.; Cheng, C.Y.; Lin, Y.C. Fricative productions of Mandarin-speaking children with cerebral palsy: The case of five-year-olds. Clin. Linguist. Phon. 2020, 34, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansel, B.M.; Kent, R.D. Acoustic-phonetic contrasts and intelligibility in the dysarthria associated with mixed cerebral palsy. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 1992, 35, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, J.Y. Intelligibility and Acoustic Characteristics of the Dysarthria in Mandarin Speakers with Cerebral Palsy. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Wisconsin at Madison, Madison, WI, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.M.; Tseng, C.H.; Tsao, F.M. Perceptual and acoustic analysis of speech intelligibility in Mandarin-speaking young adults with cerebral palsy. Clin. Linguist. Phon. 2000, 14, 447–464. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Stevens, K.N. An acoustical study of the fricative/s/in the speech of individuals with dysarthria. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2001, 44, 1300–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Martin, K.; Hasegawa-Johnson, M.; Perlman, A. Frequency of consonant articulation errors in dysarthric speech. Clin. Linguist. Phon. 2010, 24, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordberg, A.; Miniscalco, C.; Lohmander, A. Consonant production and overall speech characteristics in school-aged children with cerebral palsy and speech impairment. Int. J. Speech-Lang. Pathol. 2014, 16, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.T.J.; Chen, L.-M.; Lin, Y.-C.; Cheng, C.-F.A.; Chang, H.-C.J. Speech Intelligibility and the Production of Fricative and Affricate among Mandarin-Speaking Children with Cerebral Palsy. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Computational Linguistics and Speech Processing (ROCLING 2016), Tainan, Taiwan, 6–7 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez, A.; Lee, H.Y.; Chung, M. Acoustic analysis of fricatives in dysarthric speakers with cerebral palsy. Phon. Speech Sci. 2019, 11, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baum, S.R.; McNutt, J.C. An acoustic analysis of frontal misarticulation of/s/in children. J. Phon. 1990, 18, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Edwards, J.; Beckman, M.E. Contrast and covert contrast: The phonetic development of voiceless sibilant fricatives in English and Japanese toddlers. J. Phon. 2009, 37, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oller, D.K.; Niyogi, P.; Gray, S.; Richards, J.A.; Gilkerson, J.; Xu, D.; Yapanel, U.; Warren, S.F. Automated Vocal Analysis of Naturalistic Recordings from Children with Autism, Language Delay, and Typical Development. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13354–13359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.T. A First Step toward the Clinical Application of Landmark-Based Acoustic Analysis in Child Mandarin. Children 2021, 8, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, K.; Laurent, R. How we make good doctors into good teachers: A short course to support busy clinicians to improve their teaching skills. Med. Teach. 2013, 35, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damp, J.B.; Dewey, C.M.; Wells, Q.; Horn, L.; Kroop, S.F.; Mendes, L. Faculty development on clinical teaching skills: An effective model for the busy clinician. J. Med. Educ. Curric. Dev. 2016, 3, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boyce, S.; Fell, H.J.; McAuslan, J. SpeechMark: Landmark detection tool for speech analysis. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2012, Portland, OR, USA, 9–13 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, K.N. Evidence or the role of acoustic boundaries in the perception of speech sounds. In Phonetic Linguistics: Essays in Honor of Peter Ladefoged; Fromkin, V.A., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1985; pp. 243–255. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, K.N. On the quantal nature of speech. J. Phon. 1989, 17, 3–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, K.N. Diverse acoustic cues at consonantal landmarks. Phonetica 2000, 57, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, K.N. From Acoustic Cues to Segments, Features and Words. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Spoken Language Processing (ICSLP 2000), Beijing, China, 16–20 October 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, K.N. Toward a model for lexical access based on acoustic landmarks and distinctive features. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2002, 111, 1872–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.A. Landmark detection for distinctive feature-based speech recognition. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1996, 100, 3417–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howitt, A.W. Automatic Syllable Detection for Vowel Landmarks. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- MacAuslan, J. What Are Acoustic Landmarks, and What Do They Describe? Available online: https://speechmrk.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/Landmark-Descriptions.pdf (accessed on 21 September 2021).
- Ishikawa, K.; MacAuslan, J.; Boyce, S. Toward clinical application of landmark-based speech analysis: Landmark expression in normal adult speech. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2017, 142, EL441–EL447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishikawa, K.; MacAuslan, J. Landmark-Based Approach for Automatically Describing the Effect of Spasmodic Dysphonia on Speech Production: Preliminary Case Studies. Available online: https://speechmrk.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/FallVoice_2019_SD_LM_for_STAR.pdf (accessed on 21 September 2021).
- Huang, Z.; Epps, J.; Joachim, D. Investigation of Speech Landmark Patterns for Depression Detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP 2020), Virtual Conference, Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, K.; Rao, M.B.; MacAuslan, J.; Boyce, S. Application of a landmark-based method for acoustic analysis of dysphonic speech. J. Voice 2020, 34, e11–e645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladefoged, P.; Johnson, K. A Course in Phonetics, 7th ed.; Cengage Learning: Stamford, CT, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- DiCicco, T.M.; Patel, R. Automatic landmark analysis of dysarthric speech. J. Med. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2008, 4, 213–219. [Google Scholar]
- Boyce, S.; Fell, H.J.; Wilde, L.; MacAuslan, J. Automated tools for identifying syllabic landmark clusters that reflect changes in articulation. In Proceedings of the 7th International Workshop on Models and Analysis of Vocal Emissions for Biomedical Applications (MAVEBA 2011), Florence, Italy, 25–27 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chenausky, K.; MacAuslan, J.; Goldhor, R. Acoustic analysis of PD speech. Parkinson’s Dis. 2011, 2011, 435232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rudzicz, F. Using articulatory likelihoods in the recognition of dysarthric speech. Speech Commun. 2012, 54, 430–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudzicz, F.; Hirst, G.; Van Lieshouta, P. Vocal tract representation in the recognition of Cerebral Palsied speech. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2012, 55, 1190–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rudzicz, F.; Namasivayam, A.K.; Wolff, T. The TORGO database of acoustic and articulatory speech from speakers with dysarthria. Lang. Resour. Eval. 2012, 46, 523–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herndon, R.M. Handbook of Neurologic Rating Scales, 1st ed.; Demos Medical Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Yorkston, K.M.; Beukelman, D.R. Assessment of Intelligibility of Dysarthric Speech; C.C. Publications Inc: Tigard, OR, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Zue, V.; Seneff, S.; Glass, J. Speech database development: TIMIT and beyond. In Proceedings of the ESCA Tutorial and Research Workshop on Speech Input/Output Assessment and Speech Databases (SIOA-1989), Noordwijkerhout, The Netherlands, 20–23 September 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Menendez-Pidal, X.; Polikoff, J.B.; Peters, S.M.; Leonzjo, J.E.; Bunnell, H. The nemours database of dysarthric speech. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Spoken Language Processing, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 3–6 October 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wrench, A. The MOCHA-TIMIT Articulatory Database. Available online: http://www.cstr.ed.ac.uk/research/projects/artic/mocha.html (accessed on 21 September 2021).
- Shriberg, L.D.; Kwiatkowski, J. Phonological disorders III: A procedure for assessing severity of involvement. J. Speech Hear. Disord. 1982, 47, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagerberg, T.B.; Åsberg, J.; Hartelius, L.; Persson, C. Assessment of intelligibility using children’s spontaneous speech: Methodological aspects. Int. J. Lang. Comm. Disord. 2014, 49, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagerberg, T.B.; Hartelius, L.; Johnels, J.Å.; Ahlman, A.K.; Börjesson, A.; Persson, C. Swedish Test of Intelligibility for Children (STI-CH)–Validity and reliability of a computer-mediated single word intelligibility test for children. Clin. Linguist. Phon. 2015, 29, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosyns, M.; Mortier, G.; Janssens, S.; Bogaert, F.; D’Hondt, S.; Van Borsel, J. Articulation in schoolchildren and adults with neurofibromatosis type 1. J. Comm. Disord. 2012, 45, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, H. Automatic intelligibility assessment of dysarthric speech using phonologically-structured sparse linear model. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2015, 23, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Chung, M. Improving Dysarthric Speech Intelligibility using Cycle-consistent Adversarial Training. In Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies 2020, Valetta, Malta, 24–26 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kent, R. The biology of phonological development. In Phonological Development: Models, Research, Implications; Ferguson, C.A., Menn, L., Stoel-Gammon, C., Eds.; York Press: MD, Timonium, USA, 1992; pp. 65–90. [Google Scholar]
- Goberman, A.M.; Coelho, C. Acoustic analysis of Parkinsonian speech I: Speech characteristics and L-Dopa therapy. NeuroRehabilitation 2002, 17, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketn, R.D.; Kim, Y.J. Toward an acoustic typology of motor speech disorders. Clin. Linguist. Phon. 2003, 17, 427–445. [Google Scholar]
- Magee, M.; Copland, D.; Vogel, A.P. Motor speech and non-motor language endophenotypes of Parkinson’s disease. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2019, 19, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kent, R.D.; Read, W.C. The Acoustic Analysis of Speech, 2nd ed.; Singular Publishing: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Hustad, K.C.; Weismer, G. Predicting speech intelligibility with a multiple speech subsystems approach in children with cerebral palsy. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2014, 67, 1666–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, Z.; Chen, Z.; Yang, J.; Xu, L. Acoustic properties of vowel production in Mandarin-speaking patients with post-stroke dysarthria. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Wang, F.; Yang, L.; Xu, F.; Luo, M.; Chen, X.; Feng, X.; Zou, X. The physical significance of acoustic parameters and its clinical significance of dysarthria in Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2018, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuschmann, A.; Brenk, F.V. Acoustic Characterization of Dysarthria in Children with Cerebral Palsy: Exploring Age-related Effects. In Proceedings of the International Congress of Phonetics Sciences 2019, Melbourne, Australia, 5–9 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
| Symbol | Mnemonic | Acoustic Rule | Articulatory Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| ±g | Glottal | Beginning/end of sustained laryngeal vibration/motion | Onset/offset of vocal folds’ free vibration |
| ±p | Periodicity | Beginning/end of sustained periodicity (syllabicity) lasting for at least 32 milliseconds | The presence of ±p reflects the speaker’s ability to properly control the subglottal pressure and cricothyroid muscle. |
| ±b | Burst | At least 3 of 5 frequency bands show simultaneous power increases/decreases of at least 6 dB in both the finely smoothed and the coarsely smoothed contours, in an unvoiced segment (not between +g and the next −g) | Presence of a fricative, affricate or aspirated stop burst consonant (i.e. +b) or cessation of frication or aspiration noise (i.e. −b) |
| ±s | Syllabic | At least 3 of 5 frequency bands show simultaneous power increases/decreases of at least 6 dB in both the finely smoothed and the coarsely smoothed contours, in a voiced segment (between +g and the next −g) | Closure or release of a nasal or /l/ |
| ±f | Unvoiced frication | At least 3 of 5 frequency bands show simultaneous 6 dB power increases/decreases at high frequencies and decreases/increases at low frequencies (unvoiced segment) | Onset/offset of an unvoiced fricative |
| ±v | Voiced frication | At least 3 of 5 frequency bands show simultaneous 6 dB power increases/decreases at high frequencies and decreases/increases at low frequencies (voiced segment) | Onset/offset of a voiced fricative |
| Landmark Features | Dysarthric Speech | Normal Speech |
|---|---|---|
| +g | 0.964 (0.463) | 0.809 (0.241) |
| −g | 0.961 (0.462) | 0.827 (0.248) |
| +p | 2.008 (1.75) | 1.341 (0.462) |
| −p | 1.622 (1.252) | 1.195 (0.389) |
| +b | 0.394 (0.214) | 0.338 (0.206) |
| −b | 0.127 (0.114) | 0.169 (0.12) |
| +s | 0.7 (0.399) | 0.482 (0.27) |
| −s | 0.752 (0.439) | 0.43 (0.246) |
| +f | 0.003 (0.025) | 0.013 (0.04) |
| −f | 0.01 (0.028) | 0.029 (0.048) |
| +v | 0.023 (0.055) | 0.049 (0.085) |
| −v | 0.045 (0.078) | 0.038 (0.056) |
| Total Landmarks per Sentence | 7.61 (4.46) | 5.719 (1.493) |
| Landmark Features | CP 1 (Female) | CP 2 (Female) | CP 3 (Female) | CP 4 (Male) | CP 5 (Male) | CP 6 (Male) | CP 7 (Male) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| +g | 0.680 (0.246) | 0.789 (0.225) | 0.761 (0.222) | 0.807 (0.237) | 0.783 (0.242) | 1.631 (0.629) | 1.295 (0.320) |
| −g | 0.686 (0.243) | 0.796 (0.227) | 0.744 (0.226) | 0.801 (0.245) | 0.783 (0.242) | 1.624 (0.626) | 1.295 (0.320) |
| +p | 0.941 (0.431) | 1.154 (0.343) | 1.392 (0.473) | 1.530 (0.447) | 1.163 (0.391) | 5.568 (2.100) | 2.307 (0.597) |
| −p | 0.835 (0.354) | 0.969 (0.270) | 1.149 (0.359) | 1.344 (0.427) | 1.017 (0.335) | 4.141 (1.444) | 1.901 (0.461) |
| +b | 0.378 (0.152) | 0.410 (0.231) | 0.279 (0.173) | 0.358 (0.140) | 0.454 (0.163) | 0.284 (0.221) | 0.598 (0.244) |
| −b | 0.155 (0.146) | 0.113 (0.070) | 0.076 (0.076) | 0.064 (0.068) | 0.203 (0.154) | 0.096 (0.096) | 0.184 (0.091) |
| +s | 0.510 (0.259) | 0.395 (0.170) | 0.736 (0.210) | 0.809 (0.297) | 0.306 (0.136) | 1.394 (0.252) | 0.751 (0.182) |
| −s | 0.510 (0.160) | 0.417 (0.173) | 0.693 (0.240) | 0.967 (0.262) | 0.559 (0.236) | 1.484 (0.464) | 0.634 (0.338) |
| +f | 0.000 (0.000) | 0.000 (0.000) | 0.010 (0.040) | 0.000 (0.000) | 0.000 (0.000) | 0.000 (0.000) | 0.013 (0.052) |
| −f | 0.000 (0.000) | 0.007 (0.026) | 0.004 (0.016) | 0.004 (0.016) | 0.023 (0.041) | 0.005 (0.020) | 0.024 (0.042) |
| +v | 0.018 (0.038) | 0.041 (0.064) | 0.074 (0.093) | 0.000 (0.000) | 0.026 (0.058) | 0.000 (0.000) | 0.005 (0.020) |
| −v | 0.005 (0.020) | 0.055 (0.096) | 0.074 (0.067) | 0.019 (0.046) | 0.047 (0.059) | 0.061 (0.125) | 0.050 (0.075) |
| Total Landmarks per Sentence | 4.718 (1.736) | 5.145 (1.193) | 5.993 (1.437) | 6.703 (1.535) | 5.365 (1.437) | 16.288 (5.034) | 9.058 (2.011) |
| Average PCC Score | 44.32% (12.23) | 94.85% (4.12) | 100% (0) | 65.24% (15.41) | 76.14% (10.21) | 58.77% (11.87) | 81.12% (8.98) |
| Severity Level | Severe | Mild | Mild | Mild–Moderate | Mild–Moderate | Moderate–Severe | Mild |
| Landmark Features | TD 1 (Female) | TD 2 (Female) | TD 3 (Female) | TD 4 (Male) | TD 5 (Male) | TD 6 (Male) | TD 7 (Male) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| +g | 0.883 (0.217) | 0.715 (0.238) | 0.854 (0.219) | 0.884 (0.227) | 0.802 (0.216) | 0.938 (0.232) | 0.589 (0.187) |
| −g | 0.922 (0.233) | 0.738 (0.248) | 0.879 (0.231) | 0.888 (0.238) | 0.812 (0.222) | 0.942 (0.237) | 0.608 (0.190) |
| +p | 1.371 (0.467) | 1.392 (0.554) | 1.387 (0.386) | 1.299 (0.464) | 1.389 (0.449) | 1.513 (0.536) | 1.032 (0.267) |
| −p | 1.220 (0.397) | 1.171 (0.404) | 1.133 (0.303) | 1.213 (0.414) | 1.283 (0.406) | 1.408 (0.445) | 0.940 (0.211) |
| +b | 0.323 (0.173) | 0.264 (0.204) | 0.425 (0.204) | 0.352 (0.209) | 0.322 (0.212) | 0.365 (0.244) | 0.316 (0.195) |
| −b | 0.134 (0.125) | 0.085 (0.058) | 0.193 (0.102) | 0.205 (0.105) | 0.211 (0.143) | 0.167 (0.108) | 0.189 (0.143) |
| +s | 0.481 (0.266) | 0.705 (0.195) | 0.544 (0.201) | 0.568 (0.228) | 0.205 (0.144) | 0.201 (0.147) | 0.667 (0.166) |
| −s | 0.402 (0.160) | 0.610 (0.278) | 0.555 (0.184) | 0.407 (0.229) | 0.233 (0.173) | 0.196 (0.108) | 0.608 (0.179) |
| +f | 0.010 (0.026) | 0.000 (0.000) | 0.015 (0.040) | 0.013 (0.052) | 0.032 (0.071) | 0.015 (0.031) | 0.006 (0.022) |
| −f | 0.042 (0.054) | 0.009 (0.025) | 0.035 (0.057) | 0.025 (0.044) | 0.060 (0.056) | 0.010 (0.027) | 0.023 (0.053) |
| +v | 0.044 (0.068) | 0.047 (0.069) | 0.100 (0.092) | 0.021 (0.036) | 0.022 (0.039) | 0.004 (0.017) | 0.101 (0.151) |
| −v | 0.050 (0.07) | 0.046 (0.052) | 0.042 (0.070) | 0.021 (0.038) | 0.028 (0.041) | 0.030 (0.059) | 0.046 (0.058) |
| Total Landmarks per Sentence | 5.882 (1.576) | 5.784 (1.791) | 6.163 (1.349) | 5.896 (1.552) | 5.399 (1.458) | 5.787 (1.661) | 5.125 (0.987) |
| Landmarks | (1a) | (1b) | (1c) | (1d) | (1e) | (1f) | (1g) | (1h) | (1i) | (1j) | (1k) | (1l) | (1m) | (1n) | (1o) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CP | TD | CP | TD | CP | TD | CP | TD | CP | TD | CP | TD | CP | TD | CP | TD | CP | TD | CP | TD | CP | TD | CP | TD | CP | TD | CP | TD | CP | TD | |
| +g | 0.933 | 0.952 | 1.102 | 0.837 | 0.558 | 0.494 | 0.727 | 0.727 | 0.714 | 0.743 | 1.078 | 0.935 | 1.121 | 0.769 | 0.952 | 0.738 | 1.060 | 0.905 | 0.937 | 0.841 | 1.114 | 1.086 | 0.771 | 0.529 | 1.167 | 1.060 | 0.917 | 0.571 | 1.304 | 0.955 |
| (0.353) | (0.254) | (0.412) | (0.239) | (0.254) | (0.156) | (0.283) | (0.223) | (0.248) | (0.237) | (0.338) | (0.194) | (0.796) | (0.172) | (0.432) | (0.127) | (0.438) | (0.122) | (0.326) | (0.108) | (0.478) | (0.168) | (0.373) | (0.125) | (0.433) | (0.165) | (0.640) | (0.155) | (0.597) | (0.112) | |
| −g | 0.933 | 0.962 | 1.112 | 0.837 | 0.558 | 0.494 | 0.740 | 0.753 | 0.686 | 0.729 | 1.078 | 0.935 | 1.110 | 0.769 | 0.944 | 0.770 | 1.060 | 0.940 | 0.937 | 0.841 | 1.100 | 1.086 | 0.771 | 0.557 | 1.167 | 1.107 | 0.917 | 0.607 | 1.304 | 1.018 |
| (0.353) | (0.234) | (0.436) | (0.239) | (0.254) | (0.156) | (0.275) | (0.245) | (0.254) | (0.236) | (0.338) | (0.194) | (0.768) | (0.172) | (0.437) | (0.141) | (0.438) | (0.142) | (0.326) | (0.108) | (0.480) | (0.212) | (0.373) | (0.172) | (0.433) | (0.185) | (0.640) | (0.142) | (0.597) | (0.107) | |
| +p | 2.457 | 1.695 | 2.286 | 1.510 | 1.104 | 0.597 | 1.468 | 1.195 | 1.300 | 1.243 | 1.883 | 1.506 | 2.703 | 1.209 | 1.897 | 1.270 | 2.262 | 1.476 | 1.730 | 1.302 | 2.100 | 1.743 | 1.743 | 0.900 | 2.464 | 1.655 | 1.714 | 1.083 | 3.009 | 1.723 |
| (2.104) | (0.525) | (1.893) | (0.281) | (0.920) | (0.240) | (1.144) | (0.308) | (0.744) | (0.538) | (1.116) | (0.442) | (2.771) | (0.280) | (1.531) | (0.380) | (1.523) | (0.214) | (1.368) | (0.543) | (1.127) | (0.395) | (1.669) | (0.351) | (2.343) | (0.286) | (1.848) | (0.167) | (3.057) | (0.231) | |
| −p | 1.876 | 1.476 | 1.755 | 1.255 | 0.961 | 0.584 | 1.195 | 1.013 | 1.014 | 1.157 | 1.623 | 1.403 | 2.066 | 1.176 | 1.587 | 1.159 | 1.810 | 1.310 | 1.476 | 1.159 | 1.814 | 1.500 | 1.314 | 0.829 | 2.024 | 1.452 | 1.417 | 0.964 | 2.402 | 1.491 |
| (1.476) | (0.451) | (1.150) | (0.294) | (0.776) | (0.277) | (0.863) | (0.143) | (0.511) | (0.391) | (0.809) | (0.399) | (1.792) | (0.250) | (1.166) | (0.342) | (1.154) | (0.191) | (0.999) | (0.425) | (0.838) | (0.342) | (1.128) | (0.298) | (1.686) | (0.276) | (1.399) | (0.203) | (2.252) | (0.235) | |
| +b | 0.371 | 0.267 | 0.510 | 0.378 | 0.195 | 0.156 | 0.364 | 0.325 | 0.314 | 0.229 | 0.519 | 0.545 | 0.264 | 0.264 | 0.333 | 0.246 | 0.500 | 0.298 | 0.444 | 0.667 | 0.486 | 0.500 | 0.200 | 0.114 | 0.524 | 0.440 | 0.417 | 0.250 | 0.473 | 0.393 |
| (0.167) | (0.168) | (0.133) | (0.107) | (0.133) | (0.180) | (0.117) | (0.147) | (0.285) | (0.125) | (0.281) | (0.148) | (0.132) | (0.124) | (0.111) | (0.090) | (0.204) | (0.116) | (0.308) | (0.192) | (0.219) | (0.300) | (0.208) | (0.069) | (0.178) | (0.185) | (0.204) | (0.108) | (0.107) | (0.148) | |
| −b | 0.057 | 0.114 | 0.102 | 0.092 | 0.091 | 0.117 | 0.104 | 0.156 | 0.086 | 0.129 | 0.234 | 0.221 | 0.132 | 0.099 | 0.103 | 0.175 | 0.083 | 0.167 | 0.175 | 0.254 | 0.186 | 0.186 | 0.057 | 0.086 | 0.143 | 0.286 | 0.190 | 0.190 | 0.170 | 0.268 |
| (0.060) | (0.063) | (0.081) | (0.068) | (0.129) | (0.101) | (0.063) | (0.069) | (0.107) | (0.095) | (0.137) | (0.072) | (0.123) | (0.131) | (0.059) | (0.093) | (0.083) | (0.136) | (0.126) | (0.178) | (0.177) | (0.121) | (0.079) | (0.069) | (0.079) | (0.126) | (0.142) | (0.115) | (0.112) | (0.129) | |
| +s | 0.686 | 0.524 | 0.643 | 0.449 | 0.584 | 0.429 | 0.701 | 0.338 | 0.700 | 0.543 | 0.649 | 0.481 | 0.813 | 0.527 | 0.714 | 0.556 | 0.798 | 0.560 | 0.667 | 0.429 | 0.700 | 0.471 | 0.700 | 0.386 | 0.810 | 0.512 | 0.560 | 0.488 | 0.777 | 0.536 |
| (0.295) | (0.304) | (0.477) | (0.347) | (0.519) | (0.250) | (0.399) | (0.194) | (0.469) | (0.223) | (0.275) | (0.291) | (0.428) | (0.348) | (0.328) | (0.253) | (0.511) | (0.325) | (0.493) | (0.186) | (0.351) | (0.350) | (0.379) | (0.227) | (0.513) | (0.257) | (0.359) | (0.274) | (0.411) | (0.322) | |
| −s | 0.733 | 0.381 | 0.786 | 0.429 | 0.532 | 0.299 | 0.792 | 0.403 | 0.600 | 0.500 | 0.610 | 0.481 | 0.868 | 0.407 | 0.690 | 0.341 | 1.036 | 0.452 | 0.571 | 0.508 | 0.671 | 0.529 | 0.886 | 0.386 | 0.869 | 0.452 | 0.762 | 0.440 | 0.875 | 0.446 |
| (0.240) | (0.233) | (0.378) | (0.226) | (0.231) | (0.227) | (0.552) | (0.262) | (0.476) | (0.238) | (0.136) | (0.180) | (0.416) | (0.242) | (0.422) | (0.209) | (0.652) | (0.235) | (0.323) | (0.373) | (0.541) | (0.263) | (0.710) | (0.324) | (0.280) | (0.288) | (0.374) | (0.267) | (0.563) | (0.215) | |
| +f | 0.000 | 0.019 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.013 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.029 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.022 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.008 | 0.000 | 0.024 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.029 | 0.043 | 0.000 | 0.029 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.012 | 0.000 | 0.018 |
| (0.000) | (0.050) | (0.000) | (0.000) | (0.000) | (0.034) | (0.000) | (0.000) | (0.000) | (0.076) | (0.000) | (0.000) | (0.058) | (0.000) | (0.000) | (0.021) | (0.000) | (0.041) | (0.000) | (0.000) | (0.076) | (0.079) | (0.000) | (0.076) | (0.000) | (0.000) | (0.000) | (0.031) | (0.000) | (0.030) | |
| −f | 0.000 | 0.029 | 0.000 | 0.020 | 0.013 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.013 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.026 | 0.065 | 0.011 | 0.033 | 0.000 | 0.024 | 0.012 | 0.012 | 0.016 | 0.016 | 0.000 | 0.057 | 0.014 | 0.043 | 0.000 | 0.024 | 0.012 | 0.024 | 0.027 | 0.063 |
| (0.000) | (0.052) | (0.000) | (0.054) | (0.034) | (0.000) | (0.000) | (0.034) | (0.038) | (0.038) | (0.044) | (0.069) | (0.029) | (0.061) | (0.000) | (0.030) | (0.031) | (0.031) | (0.042) | (0.042) | (0.000) | (0.053) | (0.038) | (0.053) | (0.000) | (0.041) | (0.031) | (0.041) | (0.033) | (0.072) | |
| +v | 0.048 | 0.048 | 0.020 | 0.010 | 0.013 | 0.104 | 0.000 | 0.039 | 0.043 | 0.029 | 0.000 | 0.013 | 0.011 | 0.011 | 0.008 | 0.056 | 0.012 | 0.048 | 0.032 | 0.016 | 0.043 | 0.057 | 0.043 | 0.057 | 0.024 | 0.095 | 0.000 | 0.012 | 0.054 | 0.134 |
| (0.084) | (0.050) | (0.054) | (0.027) | (0.034) | (0.161) | (0.000) | (0.072) | (0.079) | (0.076) | (0.000) | (0.034) | (0.029) | (0.029) | (0.021) | (0.056) | (0.031) | (0.094) | (0.084) | (0.042) | (0.079) | (0.098) | (0.053) | (0.079) | (0.041) | (0.112) | (0.000) | (0.031) | (0.098) | (0.127) | |
| −v | 0.076 | 0.019 | 0.071 | 0.041 | 0.026 | 0.026 | 0.052 | 0.026 | 0.043 | 0.071 | 0.000 | 0.039 | 0.022 | 0.011 | 0.032 | 0.032 | 0.060 | 0.048 | 0.032 | 0.048 | 0.071 | 0.043 | 0.043 | 0.000 | 0.024 | 0.060 | 0.071 | 0.012 | 0.045 | 0.089 |
| (0.118) | (0.033) | (0.160) | (0.081) | (0.069) | (0.044) | (0.103) | (0.044) | (0.079) | (0.076) | (0.000) | (0.049) | (0.038) | (0.029) | (0.030) | (0.044) | (0.063) | (0.045) | (0.084) | (0.059) | (0.076) | (0.079) | (0.053) | (0.000) | (0.041) | (0.063) | (0.089) | (0.031) | (0.059) | (0.080) | |
| Total Landmarks | 8.171 | 6.486 | 8.388 | 5.857 | 4.636 | 3.312 | 6.143 | 4.987 | 5.514 | 5.414 | 7.701 | 6.623 | 9.143 | 5.275 | 7.262 | 5.373 | 8.690 | 6.238 | 7.016 | 6.079 | 8.314 | 7.300 | 6.543 | 3.914 | 9.214 | 7.143 | 6.976 | 4.655 | 10.438 | 7.134 |
| (4.505) | (0.964) | (4.706) | (1.159) | (2.824) | (1.036) | (3.347) | (0.709) | (2.091) | (1.589) | (2.538) | (1.029) | (6.814) | (0.605) | (4.069) | (0.878) | (4.365) | (0.794) | (3.453) | (1.205) | (3.504) | (1.266) | (4.210) | (1.049) | (5.376) | (1.182) | (5.144) | (0.657) | (7.397) | (0.835) | |
| PCC Scores | 73.91% | − | 75.00% | − | 74.73% | − | 76.79% | − | 69.23% | − | 84.13% | − | 81.63% | − | 67.28% | − | 76.87% | − | 76.47% | − | 69.05% | − | 75.04% | − | 72.02% | − | 72.11% | − | 70.95% | − |
| (20.85) | (22.36) | (25.01) | (17.94) | (25.90) | (19.88) | (19.13) | (24.10) | (16.13) | (20.66) | (21.00) | (22.57) | (28.23) | (21.19) | (21.66) | ||||||||||||||||
| Variables | B | S.E. | Wald | Sig. | Exp(B) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.219 | 0.405 | 0.292 | 0.589 | 1.244 |
| +g | −22.337 | 6.544 | 11.650 | 0.001 | <0.001 |
| −g | 20.236 | 6.272 | 10.411 | 0.001 | 614,041,778.992 |
| +p | −3.322 | 1.109 | 8.382 | 0.00379 | 0.040 |
| −p | 4.985 | 1.610 | 9.583 | 0.002 | 146.136 |
| +b | −1.604 | 1.142 | 1.973 | 0.160 | 0.201 |
| −b | 1.679 | 1.788 | 0.881 | 0.348 | 5.358 |
| +s | −0.592 | 0.812 | 0.424 | 0.515 | 0.589 |
| −s | −2.819 | 0.873 | 10.423 | 0.001 | 0.060 |
| +f | 9.685 | 6.373 | 2.309 | 0.129 | 16,075.299 |
| −f | 8.288 | 5.529 | 2.247 | 0.134 | 3974.111 |
| +v | 5.784 | 2.802 | 4.260 | 0.039 | 324.982 |
| −v | −0.032 | 2.940 | 0.000 | 0.991 | 1.032 |
| Constant | 1.750 | 0.666 | 6.899 | 0.009 | 5.757 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.-T.; Chen, Y.-s. Consonantal Landmarks as Predictors of Dysarthria among English-Speaking Adults with Cerebral Palsy. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11121550
Liu C-T, Chen Y-s. Consonantal Landmarks as Predictors of Dysarthria among English-Speaking Adults with Cerebral Palsy. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(12):1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11121550
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chin-Ting, and Yuan-shan Chen. 2021. "Consonantal Landmarks as Predictors of Dysarthria among English-Speaking Adults with Cerebral Palsy" Brain Sciences 11, no. 12: 1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11121550
APA StyleLiu, C.-T., & Chen, Y.-s. (2021). Consonantal Landmarks as Predictors of Dysarthria among English-Speaking Adults with Cerebral Palsy. Brain Sciences, 11(12), 1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11121550







