Social Isolation, Loneliness and Generalized Anxiety: Implications and Associations during the COVID-19 Quarantine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Social Isolation during COVID-19: Health Consequences
3.2. Loneliness during COVID-19: Health Concerns
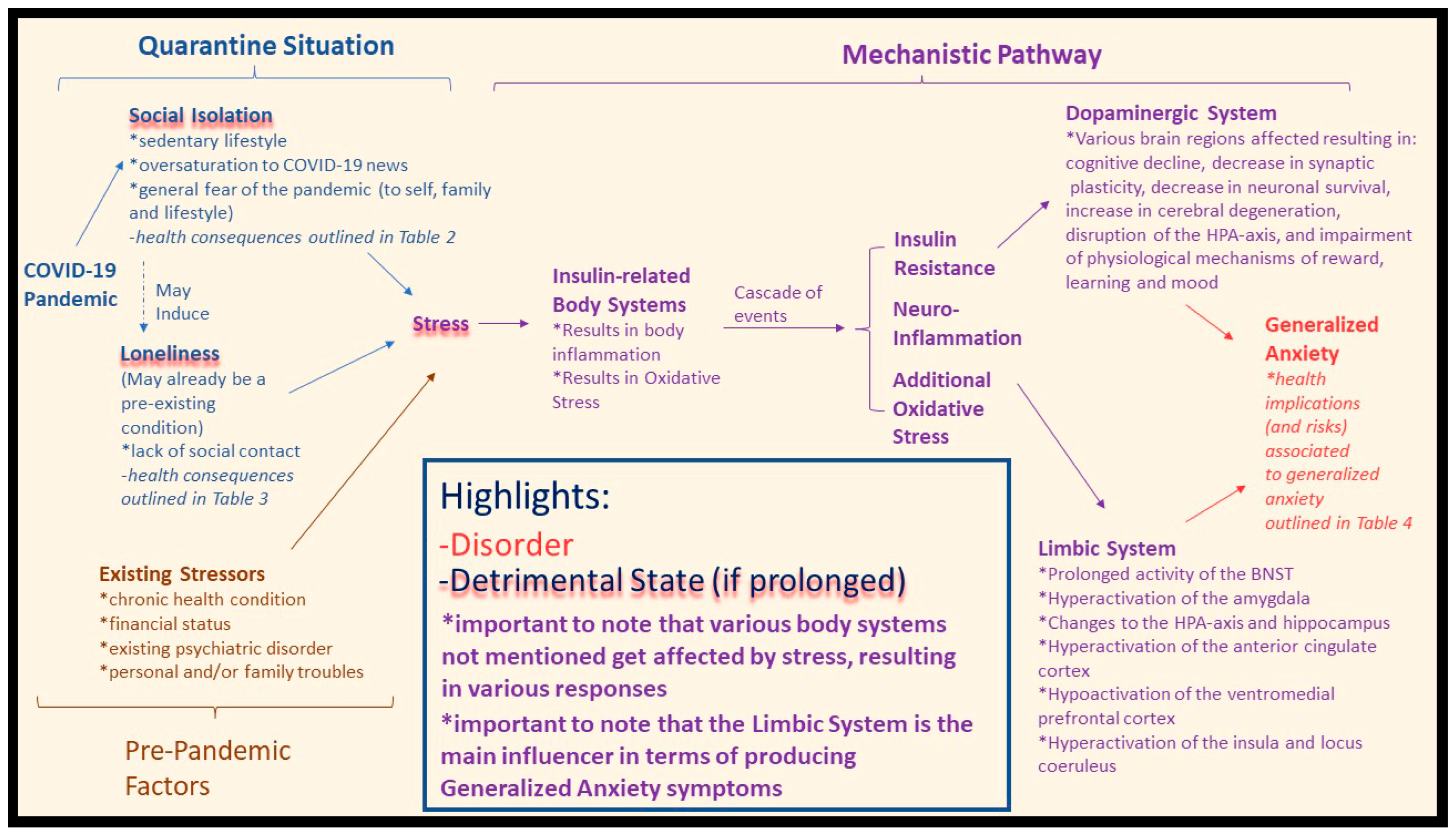
3.3. Social Isolation, Loneliness, and Generalized Anxiety during COVID-19
3.4. Quarantine and the Limbic System: A Mechanistic Perspective
4. Discussion
4.1. Future Directions: Solutions
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19). Events as They Happen. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/events-as-they-happen (accessed on 16 July 2020).
- Dunford, D.; Dale, B.; Stylianou, N.; Lowther, E.; Ahmed, M.; de la Torra Arenas, I. The world in lockdown in maps and charts. BBC News, 7 April 2020.
- Kraemer, M.U.G.; Yang, C.-H.; Gutierrez, B.; Wu, C.-H.; Klein, B.; Pigott, D.M.; Open COVID-19 Data Working Group; du Plessis, L.; Faria, N.R.; Li, R.; et al. The effect of human mobility and control measures on the COVID-19 epidemic in China. Science 2020, 368, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holt-Lunstad, J.; Smith, T.B.; Baker, M.; Harris, T.; Stephenson, D. Loneliness and Social Isolation as Risk Factors for Mortality: A Meta-Analytic Review. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2015, 10, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hämmig, O. Health risks associated with social isolation in general and in young, middle and old age. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, M.Z.; Ahmed, O.; Aibao, Z.; Hanbin, S.; Siyu, L.; Ahmad, A. Epidemic of COVID-19 in China and associated Psychological Problems. Asian J. Psychiatry 2020, 51, 102092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Losada-Baltar, A.; Jiménez-Gonzalo, L.; Gallego-Alberto, L.; Pedroso-Chaparro, M.D.S.; Fernandes-Pires, J.; Márquez-González, M. “We’re staying at home”. Association of self-perceptions of aging, personal and family resources and loneliness with psychological distress during the lock-down period of COVID-19. J. Gerontol. B Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 2021, 76, e10–e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lei, L.; Huang, X.; Zhang, S.; Yang, J.; Yang, L.; Xu, M. Comparison of Prevalence and Associated Factors of Anxiety and Depression Among People Affected by versus People Unaffected by Quarantine During the COVID-19 Epidemic in Southwestern China. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e924609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Xue, J.; Zhao, N.; Zhu, T. The Impact of COVID-19 Epidemic Declaration on Psychological Consequences: A Study on Active Weibo Users. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Özdin, S.; Bayrak Özdin, Ş. Levels and predictors of anxiety, depression and health anxiety during COVID-19 pandemic in Turkish society: The importance of gender. Int. J. Soc. Psychiatry 2020, 66, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacioppo, J.T.; Patrick, W. Loneliness: Human Nature and the Need for Social Connection; W.W. Norton & Co.: New York, NY, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-0-393-06170-3. [Google Scholar]
- Coan, J.A.; Sbarra, D.A. Social Baseline Theory: The Social Regulation of Risk and Effort. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2015, 1, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, C.; Majeed, A.; Gill, H.; Tamura, J.; Ho, R.C.; Mansur, R.B.; Nasri, F.; Lee, Y.; Rosenblat, J.D.; Wong, E.; et al. The Effect of Loneliness on Distinct Health Outcomes: A Comprehensive Review and Meta-Analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 294, 113514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.C.; Chang, O.D.; Lucas, A.G.; Li, M.; Beavan, C.B.; Eisner, R.S.; McManamon, B.M.; Rodriguez, N.S.; Katamanin, O.M.; Bourke, E.C.; et al. Depression, Loneliness, and Suicide Risk among Latino College Students: A Test of a Psychosocial Interaction Model. Soc. Work 2019, 64, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotney, A. The Risks of Social Isolation. Available online: https://www.apa.org/monitor/2019/05/ce-corner-isolation (accessed on 16 July 2020).
- Han, R.T.; Kim, Y.-B.; Park, E.-H.; Kim, J.Y.; Ryu, C.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, J.; Pahk, K.; Shanyu, C.; Kim, H.; et al. Long-Term Isolation Elicits Depression and Anxiety-Related Behaviors by Reducing Oxytocin-Induced GABAergic Transmission in Central Amygdala. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trout, D.L. The Role of Social Isolation in Suicide. Suicide Life-Threat. Behav. 1980, 10, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.S.; Aguilar-Gaxiola, S.; Alonso, J.; Angermeyer, M.C.; Borges, G.; Bromet, E.J.; Bruffaerts, R.; de Girlolamo, G.; de Graaf, R.; Gureje, O.; et al. Worldwide Use of Mental Health Services for Anxiety, Mood, and Substance Disorders: Results from 17 Countries in the WHO World Mental Health (WMH) Surveys. Lancet 2007, 370, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gale, C.; Davidson, O. Generalised anxiety disorder. BMJ 2007, 334, 579–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bystritsky, A.; Khalsa, S.S.; Cameron, M.E.; Schiffman, J. Current Diagnosis and Treatment of Anxiety Disorders. Pharm. Ther. 2013, 38, 30–57. [Google Scholar]
- Harvard Health Publishing Anxiety and Physical Illness. Available online: https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/anxiety_and_physical_illness (accessed on 13 May 2020).
- Qiu, J.; Shen, B.; Zhao, M.; Wang, Z.; Xie, B.; Xu, Y. A nationwide survey of psychological distress among Chinese people in the COVID-19 epidemic: Implications and policy recommendations. Gen. Psychiatry 2020, 33, e100213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bacon, A.M.; Corr, P.J. Coronavirus (COVID-19) in the United Kingdom: A personality-based perspective on concerns and intention to self-isolate. Br. J. Health Psychol. 2020, 25, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Fan, B.; Xie, B.; Liao, Y.; Han, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, L.; Iacobucci, M.; Lee, Y.; Lui, L.M.W.; et al. Mental health conditions among the general population, healthcare workers and quarantined population during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. Psychol. Health Med. 2020, 1–13, Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, D.; Li, S.; Yang, N. Social Capital and Sleep Quality in Individuals Who Self-Isolated for 14 Days During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in January 2020 in China. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e923921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg-Weger, M.; Morley, J.E. Loneliness and Social Isolation in Older Adults during the Covid-19 Pandemic: Implications for Gerontological Social Work. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2020, 24, 456–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stravynski, A.; Boyer, R. Loneliness in Relation to Suicide Ideation and Parasuicide: A Population-Wide Study. Suicide Life-Threat. Behav. 2001, 31, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Tilburg, T.G.; Steinmetz, S.; Stolte, E.; van der Roest, H.; de Vries, D.H. Loneliness and Mental Health During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Study Among Dutch Older Adults. J. Gerontol. Ser. B 2021, 76, e249–e255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araújo, P.A.; Asante, K.O.; dos Santos Puga Barbosa, R.M.; Nahas, M.V.; Dias, D.T.; Pelegrini, A. Association between loneliness, physical activity, and participation in physical education among adolescents in Amazonas, Brazil. J. Health Psychol. 2021, 26, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bu, F.; Steptoe, A.; Fancourt, D. Who is lonely in lockdown? Cross-cohort analyses of predictors of loneliness before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. medRxiv 2020, 186, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Pan, R.; Wan, X.; Tan, Y.; Xu, L.; McIntyre, R.S.; Choo, F.N.; Tran, B.; Ho, R.; Sharma, V.K.; et al. A longitudinal study on the mental health of general population during the COVID-19 epidemic in China. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 87, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, F.; Tan, W.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, X.; Zou, Y.; Hu, Y.; Luo, X.; Jiang, X.; McIntyre, R.S.; et al. Do psychiatric patients experience more psychiatric symptoms during COVID-19 pandemic and lockdown? A case-control study with service and research implications for immunopsychiatry. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 87, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, F.; Tam, W.; Hu, X.; Tan, W.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, X.; Zou, Y.; Hu, Y.; et al. A quantitative and qualitative study on the neuropsychiatric sequelae of acutely ill COVID-19 inpatients in isolation facilities. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.S.N.; Leung, L.; Lo, V.; Xiong, C.; Wu, T. Internet Communication Versus Face-to-face Interaction in Quality of Life. Soc. Indic. Res. 2011, 100, 375–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, R.S.; Lee, Y. Preventing suicide in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. World Psychiatry 2020, 19, 250–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, R.S.; Lee, Y. Projected increases in suicide in Canada as a consequence of COVID-19. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 290, 113104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matias, T.; Dominski, F.H.; Marks, D.F. Human needs in COVID-19 isolation. J. Health Psychol. 2020, 25, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazargan-Hejazi, S.; Bazargan, M.; Gaines, T.; Jemanez, M. Alcohol Misuse and Report of Recent Depression Symptoms among Emergency Department Patients. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2008, 26, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiang, Y.-T.; Yang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Cheung, T.; Ng, C.H. Timely mental health care for the 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak is urgently needed. Lancet Psychiatry 2020, 7, 228–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narici, M.; De Vito, G.; Franchi, M.; Paoli, A.; Moro, T.; Marcolin, G.; Grassi, B.; Baldassarre, G.; Zuccarelli, L.; Biolo, G.; et al. Impact of sedentarism due to the COVID-19 home confinement on neuromuscular, cardiovascular and metabolic health: Physiological and pathophysiological implications and recommendations for physical and nutritional countermeasures. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2020, 21, 614–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, S.K.; Webster, R.K.; Smith, L.E.; Woodland, L.; Wessely, S.; Greenberg, N.; Rubin, G.J. The psychological impact of quarantine and how to reduce it: Rapid review of the evidence. Lancet 2020, 395, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baker, E.; Clark, L.L. Biopsychopharmacosocial approach to assess impact of social distancing and isolation on mental health in older adults. Br. J. Community Nurs. 2020, 25, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, N.F.; Badr, M.S.; Belenky, G.; Bliwise, D.L.; Buxton, O.M.; Buysse, D.; Dinges, D.F.; Gangwisch, J.; Grandner, M.A.; Kushida, C.; et al. Joint Consensus Statement of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and Sleep Research Society on the Recommended Amount of Sleep for a Healthy Adult: Methodology and Discussion. Sleep 2015, 38, 1161–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, A.M. An increasing risk of family violence during the Covid-19 pandemic: Strengthening community collaborations to save lives. Forensic Sci. Int. Rep. 2020, 2, 100089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Lipsitz, O.; Nasri, F.; Lui, L.M.W.; Gill, H.; Phan, L.; Chen-Li, D.; Iacobucci, M.; Ho, R.; Majeed, A.; et al. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on mental health in the general population: A systematic review. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 277, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, T.-J.; Rabheru, K.; Peisah, C.; Reichman, W.; Ikeda, M. Loneliness and Social Isolation during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2020, 32, 1217–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gori, T.; Lelieveld, J.; Münzel, T. Perspective: Cardiovascular disease and the Covid-19 pandemic. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2020, 115, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacioppo, J.T.; Hawkley, L.C.; Berntson, G.G.; Ernst, J.M.; Gibbs, A.C.; Stickgold, R.; Hobson, J.A. Do Lonely Days Invade the Nights? Potential Social Modulation of Sleep Efficiency. Psychol. Sci. 2002, 13, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg-Weger, M.; Morley, J.E. Loneliness in Old Age: An Unaddressed Health Problem. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2020, 24, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valtorta, N.K.; Kanaan, M.; Gilbody, S.; Ronzi, S.; Hanratty, B. Loneliness and social isolation as risk factors for coronary heart disease and stroke: Systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal observational studies. Heart 2016, 102, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, E.E.; Depp, C.; Palmer, B.W.; Glorioso, D.; Daly, R.; Liu, J.; Tu, X.M.; Kim, H.-C.; Tarr, P.; Yamada, Y.; et al. High Prevalence and Adverse Health Effects of Loneliness in Community-dwelling Adults Across the Lifespan: Role of Wisdom as a Protective Factor. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2019, 31, 1447–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jakobsson, U.; Hallberg, I.R. Loneliness, fear, and quality of life among elderly in Sweden: A gender perspective. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2005, 17, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisschop, M.I.; Kriegsman, D.M.W.; van Tilburg, T.G.; Penninx, B.W.J.H.; van Eijk, J.T.M.; Deeg, D.J.H. The influence of differing social ties on decline in physical functioning among older people with and without chronic diseases: The Longitudinal Aging Study Amsterdam. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2003, 15, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ekwall, A.K.; Sivberg, B.V.; Hallberg, I.R. Loneliness as a predictor of quality of life among older caregivers. J. Adv. Nurs. 2005, 49, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fässberg, M.M.; van Orden, K.A.; Duberstein, P.; Erlangsen, A.; Lapierre, S.; Bodner, E.; Canetto, S.S.; Leo, D.D.; Szanto, K.; Waern, M. A Systematic Review of Social Factors and Suicidal Behavior in Older Adulthood. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 722–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herlitz, J.; Wiklund, I.; Caidahl, K.; Hartford, M.; Haglid, M.; Karlsson, B.W.; Sjöland, H.; Karlsson, T. The feeling of loneliness prior to coronary artery bypass grafting might be a predictor of short-and long-term postoperative mortality. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 1998, 16, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Penninx, B.W.J.H.; van Tilburg, T.; Kriegsman, D.M.W.; Deeg, D.J.H.; Boeke, A.J.P.; van Eijk, J.T.M. Effects of Social Support and Personal Coping Resources on Mortality in Older Age: The Longitudinal Aging Study Amsterdam. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1997, 146, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacioppo, J.T.; Cacioppo, S. The growing problem of loneliness. Lancet 2018, 391, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holt-Lunstad, J.; Smith, T.B.; Layton, J.B. Social Relationships and Mortality Risk: A Meta-analytic Review. PLoS Med. 2010, 7, e1000316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellaway, A.; Wood, S.; Macintyre, S. Someone to talk to? The role of loneliness as a factor in the frequency of GP consultations. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 1999, 49, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Geller, J.; Janson, P.; McGovern, E.; Valdini, A. Loneliness as a predictor of hospital emergency department use. J. Fam. Pract. 1999, 48, 801–804. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Russell, D.W.; Cutrona, C.E.; de la Mora, A.; Wallace, R.B. Loneliness and nursing home admission among rural older adults. Psychol. Aging 1997, 12, 574–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilvis, R.S.; Jolkkonen, K.P.J.; Strandberg, T.E. Social networks and dementia. Lancet 2000, 356, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkialis, L.; Rodrigues, N.; Majeed, A.; Lee, Y.; Lipsitz, O.; Gill, H.; Tamura, J.; Nasri, F.; Lui, L.M.W.; Siegel, A.; et al. Loneliness-based Impaired Reward System Pathway: Theoretical and Clinical Analysis and Application. Psychiatry Res. 2021, 298, 113800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC COVID-19 Response Team. Severe Outcomes Among Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)—United States, February 12–March 16, 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly Rep. 2020, 69, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, A.D.; Uchino, B.N.; Wethington, E. Loneliness and Health in Older Adults: A Mini-Review and Synthesis. Gerontology 2016, 62, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ornell, F.; Schuch, J.B.; Sordi, A.O.; Kessler, F.H.P. “Pandemic fear” and COVID-19: Mental health burden and strategies. Braz. J. Psychiatry 2020, 42, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shigemura, J.; Ursano, R.J.; Morganstein, J.C.; Kurosawa, M.; Benedek, D.M. Public responses to the novel 2019 coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in Japan: Mental health consequences and target populations. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 74, 281–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIMH. Domain: Negative Valence Systems. Available online: https://www.nimh.nih.gov/research/research-funded-by-nimh/rdoc/constructs/negative-valence-systems.shtml (accessed on 7 July 2020).
- NIMH. Negative Valence Systems: Workshop Proceedings. Available online: https://www.nimh.nih.gov/research/research-funded-by-nimh/rdoc/negative-valence-systems-workshop-proceedings.shtml (accessed on 9 July 2020).
- Davis, M.; Walker, D.L.; Miles, L.; Grillon, C. Phasic vs. Sustained Fear in Rats and Humans: Role of the Extended Amygdala in Fear vs. Anxiety. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 105–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lebow, M.A.; Chen, A. Overshadowed by the amygdala: The bed nucleus of the stria terminalis emerges as key to psychiatric disorders. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 450–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maciejczyk, M.; Żebrowska, E.; Chabowski, A. Insulin Resistance and Oxidative Stress in the Brain: What’s New? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamer, J.A.; Testani, D.; Mansur, R.B.; Lee, Y.; Subramaniapillai, M.; McIntyre, R.S. Brain insulin resistance: A treatment target for cognitive impairment and anhedonia in depression. Exp. Neurol. 2019, 315, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kullmann, S.; Heni, M.; Hallschmid, M.; Fritsche, A.; Preissl, H.; Häring, H.-U. Brain Insulin Resistance at the Crossroads of Metabolic and Cognitive Disorders in Humans. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 1169–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kleinridders, A.; Pothos, E.N. Impact of Brain Insulin Signaling on Dopamine Function, Food Intake, Reward, and Emotional Behavior. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2019, 8, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinridders, A.; Cai, W.; Cappellucci, L.; Ghazarian, A.; Collins, W.R.; Vienberg, S.G.; Pothos, E.N.; Kahn, C.R. Insulin resistance in brain alters dopamine turnover and causes behavioral disorders. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 3463–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, E.I.; Ressler, K.J.; Binder, E.; Nemeroff, C.B. The Neurobiology of Anxiety Disorders: Brain Imaging, Genetics, and Psychoneuroendocrinology. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 32, 549–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michopoulos, V.; Powers, A.; Gillespie, C.F.; Ressler, K.J.; Jovanovic, T. Inflammation in Fear- and Anxiety-Based Disorders: PTSD, GAD, and Beyond. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 254–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stein, M.B.; Simmons, A.N.; Feinstein, J.S.; Paulus, M.P. Increased Amygdala and Insula Activation During Emotion Processing in Anxiety-Prone Subjects. AJP 2007, 164, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapp, Z.M.; Godbout, J.P.; Kokiko-Cochran, O.N. A Tilted Axis: Maladaptive Inflammation and HPA Axis Dysfunction Contribute to Consequences of TBI. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, J.C.; Lissek, S.; Grillon, C.; Norcross, M.A.; Pine, D.S. Development of anxiety: The role of threat appraisal and fear learning. Depress. Anxiety 2011, 28, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cha, J.; Greenberg, T.; Song, I.; Simpson, H.B.; Posner, J.; Mujica-Parodi, L.R. Abnormal Hippocampal Structure and Function in Clinical Anxiety and Comorbid Depression. Hippocampus 2016, 26, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robinson, O.J.; Krimsky, M.; Lieberman, L.; Allen, P.; Vytal, K.; Grillon, C. The dorsal medial prefrontal (anterior cingulate) cortex–amygdala aversive amplification circuit in unmedicated generalised and social anxiety disorders: An observational study. Lancet Psychiatry 2014, 1, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Motzkin, J.C.; Philippi, C.L.; Wolf, R.C.; Baskaya, M.K.; Koenigs, M. Ventromedial prefrontal cortex is critical for the regulation of amygdala activity in humans. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 77, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borodovitsyna, O.; Joshi, N.; Chandler, D. Persistent Stress-Induced Neuroplastic Changes in the Locus Coeruleus/Norepinephrine System. Available online: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/np/2018/1892570/ (accessed on 8 July 2020).
- Lieberz, J.; Shamay-Tsoory, S.G.; Saporta, N.; Esser, T.; Kuskova, E.; Stoffel-Wagner, B.; Hurlemann, R.; Scheele, D. Loneliness and the Social Brain: How Perceived Social Isolation Impairs Human Interactions. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2102076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, J.A.; Murray, E.R.; Yu, K.E.; Ramsey, M.; Nguyen, T.T.; Mishra, J.; Martis, B.; Thomas, M.L.; Lee, E.E. Neurobiology of loneliness: A systematic review. Neuropsychopharmacology 2021, 46, 1873–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shutterstock.com. Brain-Locus-Coeruleus-Hi-Res.jpg (1165 × 1024). Available online: https://gero.usc.edu/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/brain-locus-coeruleus-hi-res.jpg (accessed on 14 November 2019).
- Pan, P.J.D.; Chang, S.-H.; Yu, Y.-Y. A Support Group for Home-Quarantined College Students Exposed to SARS: Learning from Practice. J. Spec. Group Work. 2005, 30, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Yang, B.X.; Liu, Q.; Luo, D.; Kang, L.; Yang, F.; Ma, S.; Lu, W.; Chen, L.D.; Rosenblat, J.D.; et al. Synergistic effect of social media use and psychological distress on depression in China during the COVID-19 epidemic. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 74, 552–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Chudzicka-Czupała, A.; Grabowski, D.; Pan, R.; Adamus, K.; Wan, X.; Hetnał, M.; Tan, Y.; Olszewska-Guizzo, A.; Xu, L.; et al. The Association between Physical and Mental Health and Face Mask Use during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Comparison of Two Countries with Different Views and Practices. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 569981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Yang, B.X.; Luo, D.; Liu, Q.; Ma, S.; Huang, R.; Lu, W.; Majeed, A.; Lee, Y.; Lui, L.M.W.; et al. The Mental Health Effects of COVID-19 on Health Care Providers in China. AJP 2020, 177, 635–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.; Hao, F.; McIntyre, R.S.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, X.; Zou, Y.; Hu, Y.; Luo, X.; et al. Is returning to work during the COVID-19 pandemic stressful? A study on immediate mental health status and psychoneuroimmunity prevention measures of Chinese workforce. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 87, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felger, J.C. Imaging the Role of Inflammation in Mood and Anxiety-related Disorders. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 533–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.-L.; Inserra, A.; Lewis, M.D.; Mastronardi, C.A.; Leong, L.; Choo, J.; Kentish, S.; Xie, P.; Morrison, M.; Wesselingh, S.L.; et al. Inflammasome signaling affects anxiety- and depressive-like behavior and gut microbiome composition. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, J. Flexible working will be a new normal after virus. BBC News, 22 May 2020. [Google Scholar]

| Outcome of Interest | Scale/Measurement |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Physiological Changes | Psychological Changes | |
|---|---|---|
| Body System | Symptom/Change | |
| Neuropsychology System |
|
|
|
| |
| Neuromuscular System |
|
|
|
| |
| Muscle Protein Metabolism |
|
|
|
| |
| Glucose Homeostasis |
|
|
|
| |
|
| |
| Cardiorespiratory System |
|
|
|
| |
|
| |
| Digestive System/Energy Balance |
|
|
|
| |
| Sympathetic Nervous System |
| |
| Physical Health Consequences/Risks | Mental Health Consequences/Risks |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
| Direct | Indirect |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wilkialis, L.; Rodrigues, N.B.; Cha, D.S.; Siegel, A.; Majeed, A.; Lui, L.M.W.; Tamura, J.K.; Gill, B.; Teopiz, K.; McIntyre, R.S. Social Isolation, Loneliness and Generalized Anxiety: Implications and Associations during the COVID-19 Quarantine. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11121620
Wilkialis L, Rodrigues NB, Cha DS, Siegel A, Majeed A, Lui LMW, Tamura JK, Gill B, Teopiz K, McIntyre RS. Social Isolation, Loneliness and Generalized Anxiety: Implications and Associations during the COVID-19 Quarantine. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(12):1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11121620
Chicago/Turabian StyleWilkialis, Linas, Nelson B. Rodrigues, Danielle S. Cha, Ashley Siegel, Amna Majeed, Leanna M. W. Lui, Jocelyn K. Tamura, Barjot Gill, Kayla Teopiz, and Roger S. McIntyre. 2021. "Social Isolation, Loneliness and Generalized Anxiety: Implications and Associations during the COVID-19 Quarantine" Brain Sciences 11, no. 12: 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11121620
APA StyleWilkialis, L., Rodrigues, N. B., Cha, D. S., Siegel, A., Majeed, A., Lui, L. M. W., Tamura, J. K., Gill, B., Teopiz, K., & McIntyre, R. S. (2021). Social Isolation, Loneliness and Generalized Anxiety: Implications and Associations during the COVID-19 Quarantine. Brain Sciences, 11(12), 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11121620






