Brain Imaging of the GLP-1 Receptor in Obesity Using 68Ga-NODAGA-Exendin-4 PET
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Anthropometric Measurements
2.3. PET Imaging
2.4. Volume-of-Interest (VOI) Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Subjects
3.2. PET Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. 68Ga-NODAGA-Exendin-4 Uptake in Peripheral Organs
4.2. 68Ga-NODAGA-Exendin-4 Uptake in the Pituitary Area
4.3. No Significant Uptake of 68Ga-NODAGA-Exendin-4 in the Brain
4.4. Uptake of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in the Brain
4.5. Final Remarks and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mori, Y.; Matsui, T.; Hirano, T.; Yamagishi, S.-I. GIP as a Potential Therapeutic Target for Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease—A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drucker, D.J.; Nauck, M.A. The incretin system: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes. Lancet 2006, 368, 1696–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, M.; Llewellyn-Smith, I.J.; Reimann, F.; Gribble, F.; Trapp, S. Serotonergic modulation of the activity of GLP-1 producing neurons in the nucleus of the solitary tract in mouse. Mol. Metab. 2017, 6, 909–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heppner, K.M.; Kirigiti, M.; Secher, A.; Paulsen, S.J.; Buckingham, R.; Pyke, C.; Knudsen, L.B.; Vrang, N.; Grove, K.L. Expression and distribution of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor mRNA, protein and binding in the male nonhuman primate (Macaca mulatta) brain. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nauck, M.A.; Meier, J.J. The incretin effect in healthy individuals and those with type 2 diabetes: Physiology, pathophysiology, and response to therapeutic interventions. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016, 4, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.; Zaccardi, F.; Khunti, K.; Davies, M.J.; Patsko, E.; Dhalwani, N.; Kloecker, D.E.; Ioannidou, E.; Gray, L.J. Efficacy and tolerability of sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 1035–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cork, S.; Richards, J.E.; Holt, M.; Gribble, F.; Reimann, F.; Trapp, S. Distribution and characterisation of Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor expressing cells in the mouse brain. Mol. Metab. 2015, 4, 718–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yun, S.P.; Kam, T.-I.; Panicker, N.; Kim, S.; Oh, Y.; Park, J.-S.; Kwon, S.-H.; Park, Y.J.; Karuppagounder, S.S.; Park, H.; et al. Block of A1 astrocyte conversion by microglia is neuroprotective in models of Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabery, S.; Salinas, C.G.; Paulsen, S.J.; Ahnfelt-Rønne, J.; Alanentalo, T.; Baquero, A.F.; Buckley, S.T.; Farkas, E.; Fekete, C.; Frederiksen, K.S.; et al. Semaglutide lowers body weight in rodents via distributed neural pathways. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e133429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jensen, C.B.; Pyke, C.; Rasch, M.G.; Dahl, A.B.; Knudsen, L.B.; Secher, A. Characterization of the Glucagonlike Peptide-1 Receptor in Male Mouse Brain Using a Novel Antibody and In Situ Hybridization. Endocrinology 2017, 159, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mansur, R.B.; Fries, G.R.; Trevizol, A.P.; Subramaniapillai, M.; Lovshin, J.; Lin, K.; Vinberg, M.; Ho, R.; Brietzke, E.; McIntyre, R.S. The effect of body mass index on glucagon-like peptide receptor gene expression in the post mortem brain from individuals with mood and psychotic disorders. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019, 29, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athauda, D.; Foltynie, T. The glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP) receptor as a therapeutic target in Parkinson’s disease: Mechanisms of action. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 802–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Badawi, G.A.; El Fattah, M.A.A.; Zaki, H.F.; El Sayed, M.I. Sitagliptin and liraglutide reversed nigrostriatal degeneration of rodent brain in rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease. Inflammopharmacology 2017, 25, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, L.-L.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Shen, Y.; Fan, Y.; Yu, W.-B.; Jiang, D.-L.; Tang, Y.-L.; Yang, Y.-J.; Wu, P.; Zuo, C.-T.; et al. Neuroprotection of Exendin-4 by Enhanced Autophagy in a Parkinsonian Rat Model of α-Synucleinopathy. Neurotherapy 2021, 18, 962–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbassuoni, E.A.; Ahmed, R.F. Mechanism of the neuroprotective effect of GLP-1 in a rat model of Parkinson’s with pre-existing diabetes. Neurochem. Int. 2019, 131, 104583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, P.; Zhang, X.; Li, D.; Ji, C.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, R.; Xue, G.; Li, G.; Hölscher, C. Two novel dual GLP-1/GIP receptor agonists are neuroprotective in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuropharmacology 2018, 133, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hansen, H.H.; Fabricius, K.; Barkholt, P.; Mikkelsen, J.D.; Jelsing, J.; Pyke, C.; Knudsen, L.B.; Vrang, N. Characterization of liraglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, in rat partial and full nigral 6-hydroxydopamine lesion models of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res. 2016, 1646, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Tu, L.; Gu, R.; Yang, X.-L.; Liu, X.-J.; Zhang, G.-P.; Wang, Q.; Ren, Y.-P.; Wang, B.-J.; Tian, J.-Y. Neuroprotection of GLP-1/GIP receptor agonist via inhibition of mitochondrial stress by AKT/JNK pathway in a Parkinson’s disease model. Life Sci. 2020, 256, 117824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-S.; Kam, T.-I.; Lee, S.; Park, H.; Oh, Y.; Kwon, S.-H.; Song, J.-J.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.; Jhaldiyal, A.; et al. Blocking microglial activation of reactive astrocytes is neuroprotective in models of Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2021, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Li, D.; Feng, P.; Xue, G.; Ji, C.; Li, G.; Hölscher, C. A novel GLP-1/GIP dual agonist is more effective than liraglutide in reducing inflammation and enhancing GDNF release in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 812, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Hölscher, C. Neuroprotective effects of the novel GLP-1 long acting analogue semaglutide in the MPTP Parkinson’s disease mouse model. Neuropeptides 2018, 71, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Hölscher, C. Semaglutide is Neuroprotective and Reduces α-Synuclein Levels in the Chronic MPTP Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Park. Dis. 2019, 9, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Hölscher, C. GIP has neuroprotective effects in Alzheimer and Parkinson’s disease models. Peptides 2020, 125, 170184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, C.F.; Nauck, M.A.; Toft-Nielsen, M.; Pridal, L.; Willms, B.; Holst, J.J. Both Subcutaneously and Intravenously Administered Glucagon-Like Peptide I Are Rapidly Degraded From the NH2-Terminus in Type II Diabetic Patients and in Healthy Subjects. Diabetes 1995, 44, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information, PubChem Compound Summary for CID 53396299, Byetta. 2021. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Byetta (accessed on 19 October 2021).
- Mousa, S.A.; Ayoub, B.M. Repositioning of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and glucagon like peptide-1 agonists as potential neuroprotective agents. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 745–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athauda, D.; Maclagan, K.; Skene, S.; Bajwa-Joseph, M.; Letchford, D.; Chowdhury, K.; Hibbert, S.; Budnik, N.; Zampedri, L.; Dickson, J.; et al. Exenatide once weekly versus placebo in Parkinson’s disease: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 1664–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviles-Olmos, I.; Dickson, J.; Kefalopoulou, Z.; Djamshidian, A.; Ell, P.; Soderlund, T.; Whitton, P.; Wyse, R.; Isaacs, T.; Lees, A.; et al. Exenatide and the treatment of patients with Parkinson’s disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 2730–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egejl, M.; Gjedde, A.; Eegefjord, L.; Emøller, A.; Hansen, S.B.; Evang, K.; Rodell, A.B.; Ebraendgaard, H.; Egottrup, H.; Eschacht, A.; et al. In Alzheimer’s Disease, 6-Month Treatment with GLP-1 Analog Prevents Decline of Brain Glucose Metabolism: Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind Clinical Trial. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2016, 8, 108. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, T.; van Lith, S.; Boss, M.; Brom, M.; Joosten, L.; Béhé, M.; Buitinga, M.; Gotthardt, M. Exendin-4 analogs in insulinoma theranostics. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2019, 62, 656–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boss, M.; Rottenburger, C.; Brenner, W.; Blankenstein, O.; Prasad, V.; Prasad, S.; de Coppi, P.; Kühnen, P.; Buitinga, M.; Nuutila, P.; et al. 68Ga-NODAGA-exendin-4 PET improves the detection of focal congenital hyperinsulinism. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruze, R.; Xu, Q.; Liu, G.; Li, Y.; Chen, W.; Cheng, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, G.; Hu, S.; et al. Central GLP-1 contributes to improved cognitive function and brain glucose uptake after duodenum-jejunum bypass on obese and diabetic rats. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2021, 321, E392–E409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Cáceres, C.; Balland, E.; Prevot, V.; Luquet, S.; Woods, S.C.; Koch, M.; Horvath, T.L.; Yi, C.-X.; Chowen, J.A.; Verkhratsky, A.; et al. Role of astrocytes, microglia, and tanycytes in brain control of systemic metabolism. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buitinga, M.; Jansen, T.J.; van der Kroon, I.; van der Weg, W.W.-; Boss, M.; Janssen, M.; Aarntzen, E.; Behe, M.; Wild, D.; Visser, E.; et al. Succinylated Gelatin Improves the Theranostic Potential of Radiolabeled Exendin-4 in Insulinoma Patients. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 812–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Göke, R.; Larsen, P.J.; Mikkelsen, J.D.; Sheikh, S.P. Identification of specific binding sites for glucagon-like peptide-1 on the posterior lobe of the rat pituitary. Neuroendocrinology 1995, 62, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Körner, M.; Stöckli, M.; Waser, B.; Reubi, J.C. GLP-1 Receptor Expression in Human Tumors and Human Normal Tissues: Potential for In Vivo Targeting. J. Nucl. Med. 2007, 48, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, K.A.; Melhorn, S.J.; Sakai, R.R. Effects of Chronic Social Stress on Obesity. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2012, 1, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turton, M.D.; O’Shea, D.; Gunn, I.; Beak, S.A.; Edwards, C.M.B.; Meeran, K.; Choi, S.J.; Taylor, G.M.; Heath, M.M.; Lambert, P.D.; et al. A role for glucagon-like peptide-1 in the central regulation of feeding. Nature 1996, 379, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Valk, E.; Savas, M.; van Rossum, E.F.C. Stress and Obesity: Are There More Susceptible Individuals? Curr. Obes. Rep. 2018, 7, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kiss, A. Morphological aspects of the median eminence—Place of accumulation and secretion of regulatory neurohormones and neuropeptides. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 1997, 16, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clarke, I. Hypothalamus as an Endocrine Organ. Comprehensive Physiology 2014, 5, 217–253. [Google Scholar]
- Thoss, V.S.; Piwko, C.; Probst, A.; Hoyer, D. Autoradiographic analysis of somatostatin SRIF1 and SRIF2 receptors in the human brain and pituitary. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1997, 355, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Pan, D.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yan, J.; Wu, Q.; et al. PET evaluation of light-induced modulation of microglial activation and GLP-1R expression in depressive rats. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Sheng, J.; Pan, D.; Wang, X.; Yan, J.; Yang, R.; Yang, M. Age-related change of GLP-1R expression in rats can be detected by [18F]AlF-NOTA-MAL-Cys39-exendin-4. Brain Res. 2018, 1698, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, H.; Fujita, N.; Hamamatsu, K.; Murakami, T.; Nakamoto, Y.; Saga, T.; Ishimori, T.; Shimizu, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Sano, K.; et al. First-in-Human Evaluation of Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography With [18F]FB(ePEG12)12-Exendin-4: A Phase 1 Clinical Study Targeting GLP-1 Receptor Expression Cells in Pancreas. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 717101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, K.; Hölscher, C. Drugs developed to treat diabetes, liraglutide and lixisenatide, cross the blood brain barrier and enhance neurogenesis. BMC Neurosci. 2012, 13, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kastin, A.J.; Akerstrom, V. Entry of exendin-4 into brain is rapid but may be limited at high doses. Int. J. Obes. 2003, 27, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christensen, M.; Sparre-Ulrich, A.H.; Hartmann, B.; Grevstad, U.; Rosenkilde, M.M.; Holst, J.J.; Vilsbøll, T.; Knop, F.K. Transfer of liraglutide from blood to cerebrospinal fluid is minimal in patients with type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 1651–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luurtsema, G.; Delange, E.; Lammertsma, A.; Franssen, E. Transport across the blood-brain barrier: Stereoselectivity and PET-tracers. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2004, 6, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammerstad, J.P.; Pate, B.D.; Hewitt, K.A.; Chan, G.L.-Y.; Ruth, T.J.; Calne, D.B. The transport ofL-6-fluorodopa and its metabolites from blood to cerebrospinal fluid and brain. Ann. Neurol. 1993, 34, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luurtsema, G.; Elsinga, P.; Dierckx, R.; Boellaard, R.; Waarde, A. PET Tracers for Imaging of ABC Transporters at the Blood-Brain Barrier: Principles and Strategies. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 5779–5785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secher, A.; Jelsing, J.; Baquero, A.F.; Hecksher-Sørensen, J.; Cowley, M.; Dalbøge, L.S.; Hansen, G.; Grove, K.L.; Pyke, C.; Raun, K.; et al. The arcuate nucleus mediates GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide-dependent weight loss. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 4473–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
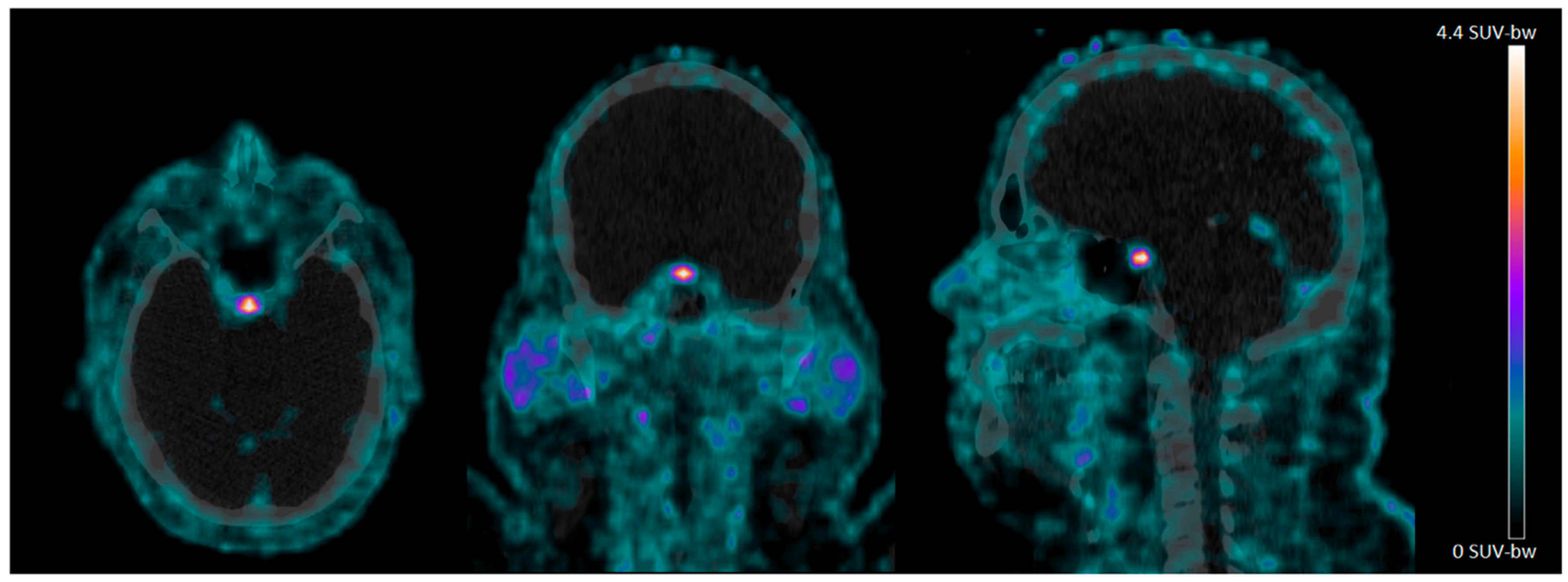
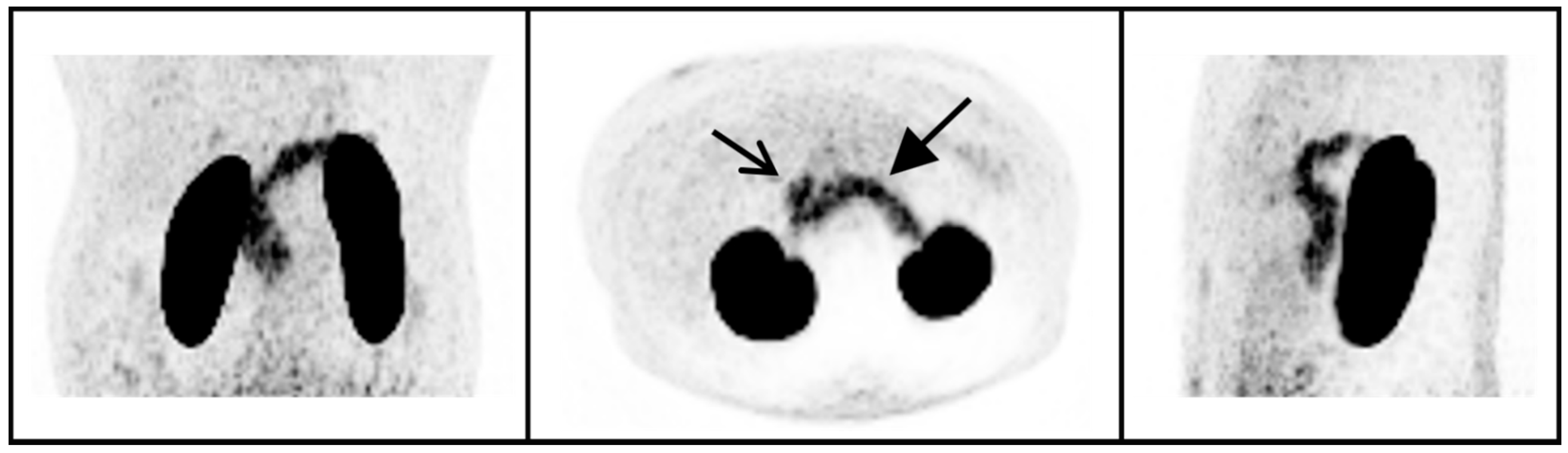
| Sex, Woman (%) | 7 (70%) |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 53 ± 5.5 |
| Weight (kg) | 113 ± 13 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 39 ± 4.4 |
| SUVmean | SUVmax | |
|---|---|---|
| Pituitary | 1.7 ± 0.6 (0.9–2.7) | 4.3 ± 2.3 (1.4–9.1) |
| Whole brain | 0.01 ± 0.01 (0.00–0.02) | 0.17 ± 0.10 (0.01–0.32) |
| Pancreas | 5.5 ± 1.8 (2.3–8.1) | 10.3 ± 3.0 (5.0–15.5) |
| Blood pool | 1.5 ± 0.2 (1.2–2.0) | 3.3 ± 0.6 (2.4–4.4) |
| Liver | 0.67 ± 0.17 (0.26–0.96) | 2.1 ± 0.6 (1.3–3.3) |
| SAT | 0.20 ± 0.05 (0.14–0.29) | 0.65 ± 0.16 (0.38–0.91) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deden, L.N.; Booij, J.; Grandjean, J.; Homberg, J.R.; Hazebroek, E.J.; Gotthardt, M.; Boss, M. Brain Imaging of the GLP-1 Receptor in Obesity Using 68Ga-NODAGA-Exendin-4 PET. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1647. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11121647
Deden LN, Booij J, Grandjean J, Homberg JR, Hazebroek EJ, Gotthardt M, Boss M. Brain Imaging of the GLP-1 Receptor in Obesity Using 68Ga-NODAGA-Exendin-4 PET. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(12):1647. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11121647
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeden, Laura N., Jan Booij, Joanes Grandjean, Judith R. Homberg, Eric J. Hazebroek, Martin Gotthardt, and Marti Boss. 2021. "Brain Imaging of the GLP-1 Receptor in Obesity Using 68Ga-NODAGA-Exendin-4 PET" Brain Sciences 11, no. 12: 1647. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11121647
APA StyleDeden, L. N., Booij, J., Grandjean, J., Homberg, J. R., Hazebroek, E. J., Gotthardt, M., & Boss, M. (2021). Brain Imaging of the GLP-1 Receptor in Obesity Using 68Ga-NODAGA-Exendin-4 PET. Brain Sciences, 11(12), 1647. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11121647








