Brain Structural Covariance Networks in Behavioral Variant of Frontotemporal Dementia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. MRI Acquisition and Processing
2.3. Network Construction
2.4. Graph Theory Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Global Network Characteristics
3.3. Regional Network Characteristics
3.4. Correlation between Connectivity Metrics and Clinical Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Snowden, J.S.; Thompson, J.C.; Stopford, C.L.; Richardson, A.M.T.; Gerhard, A.; Neary, D.; Mann, D.M.A. The clinical diagnosis of early-onset dementias: Diagnostic accuracy and clinicopathological relationships. Brain J. Neurol. 2011, 134, 2478–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rascovsky, K.; Hodges, J.R.; Knopman, D.; Mendez, M.F.; Kramer, J.H.; Neuhaus, J.; van Swieten, J.C.; Seelaar, H.; Dopper, E.G.P.; Onyike, C.U.; et al. Sensitivity of revised diagnostic criteria for the behavioural variant of frontotemporal dementia. Brain 2011, 134, 2456–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, H.J.; Gorno-Tempini, M.L.; Goldman, W.P.; Perry, R.J.; Schuff, N.; Weiner, M.; Feiwell, R.; Kramer, J.H.; Miller, B.L. Patterns of brain atrophy in frontotemporal dementia and semantic dementia. Neurology 2002, 58, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boccardi, M.; Sabattoli, F.; Laakso, M.P.; Testa, C.; Rossi, R.; Beltramello, A.; Soininen, H.; Frisoni, G.B. Frontotemporal dementia as a neural system disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2005, 26, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitwell, J.L.; Przybelski, S.A.; Weigand, S.D.; Ivnik, R.J.; Vemuri, P.; Gunter, J.L.; Senjem, M.L.; Shiung, M.M.; Boeve, B.F.; Knopman, D.S.; et al. Distinct anatomical subtypes of the behavioural variant of frontotemporal dementia: A cluster analysis study. Brain 2009, 132, 2932–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bang, J.; Spina, S.; Miller, B.L. Frontotemporal dementia. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2015, 386, 1672–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seeley, W.W.; Crawford, R.K.; Zhou, J.; Miller, B.L.; Greicius, M.D. Neurodegenerative diseases target large-scale human brain networks. Neuron 2009, 62, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seeley, W.W. Mapping Neurodegenerative Disease Onset and Progression. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9, a023622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashish, R.; Fon, P. Models of Network Spread and Network Degeneration in Brain Disorders. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2018, 3, 788–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporns, O.; Zwi, J.D. The small world of the cerebral cortex. Neuroinformatics 2004, 2, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccaletti, S.; Latora, V.; Moreno, Y.; Chavez, M.; Hwang, D.-U. Complex networks: Structure and dynamics. Phys. Rep. 2006, 424, 175–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stam, C.J.; Reijneveld, J.C. Graph theoretical analysis of complex networks in the brain. Nonlinear Biomed. Phys. 2007, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bullmore, E.; Sporns, O. Complex brain networks: Graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Chen, Z.; Evans, A. Structural Insights into Aberrant Topological Patterns of Large-Scale Cortical Networks in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 4756–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Greicius, M.D.; Gennatas, E.D.; Growdon, M.E.; Jang, J.Y.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Kramer, J.H.; Weiner, M.; Miller, B.L.; Seeley, W.W. Divergent network connectivity changes in behavioural variant frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Brain J. Neurol. 2010, 133, 1352–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Filippi, M.; Agosta, F.; Scola, E.; Canu, E.; Magnani, G.; Marcone, A.; Valsasina, P.; Caso, F.; Copetti, M.; Comi, G.; et al. Functional network connectivity in the behavioral variant of frontotemporal dementia. Cortex J. Devoted Study Nerv. Syst. Behav. 2013, 49, 2389–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippi, M.; Basaia, S.; Canu, E.; Imperiale, F.; Meani, A.; Caso, F.; Magnani, G.; Falautano, M.; Comi, G.; Falini, A.; et al. Brain network connectivity differs in early-onset neurodegenerative dementia. Neurology 2017, 89, 1764–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vecchio, F.; Miraglia, F.; Curcio, G.; Altavilla, R.; Scrascia, F.; Giambattistelli, F.; Quattrocchi, C.C.; Bramanti, P.; Vernieri, F.; Rossini, P.M. Cortical brain connectivity evaluated by graph theory in dementia: A correlation study between functional and structural data. J. Alzheimers Dis. JAD 2015, 45, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigro, S.; Riccelli, R.; Passamonti, L.; Arabia, G.; Morelli, M.; Nisticò, R.; Novellino, F.; Salsone, M.; Barbagallo, G.; Quattrone, A. Characterizing structural neural networks in de novo Parkinson disease patients using diffusion tensor imaging. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2016, 37, 4500–4510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedeño, L.; Couto, B.; García-Cordero, I.; Melloni, M.; Baez, S.; Morales Sepúlveda, J.P.; Fraiman, D.; Huepe, D.; Hurtado, E.; Matallana, D.; et al. Brain Network Organization and Social Executive Performance in Frontotemporal Dementia. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. JINS 2016, 22, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farahani, F.V.; Karwowski, W.; Lighthall, N.R. Application of Graph Theory for Identifying Connectivity Patterns in Human Brain Networks: A Systematic Review. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander-Bloch, A.; Giedd, J.N.; Bullmore, E. Imaging structural co-variance between human brain regions. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 322–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spreng, R.N.; Turner, G.R. Structural Covariance of the Default Network in Healthy and Pathological Aging. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 15226–15234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- DuPre, E.; Spreng, R.N. Structural covariance networks across the life span, from 6 to 94 years of age. Netw. Neurosci. 2017, 1, 302–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.H.; Mazaika, P.; Mauras, N.; Buckingham, B.; Weinzimer, S.A.; Tsalikian, E.; White, N.H.; Reiss, A.L. Altered Integration of Structural Covariance Networks in Young Children With Type 1 Diabetes. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2016, 37, 4034–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bruno, J.L.; Hosseini, S.M.H.; Saggar, M.; Quintin, E.-M.; Raman, M.M.; Reiss, A.L. Altered Brain Network Segregation in Fragile X Syndrome Revealed by Structural Connectomics. Cereb. Cortex 2017, 27, 2249–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernhardt, B.C.; Bernasconi, N.; Concha, L.; Bernasconi, A. Cortical thickness analysis in temporal lobe epilepsy: Reproducibility and relation to outcome. Neurology 2010, 74, 1776–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bethlehem, R.A.I.; Romero-Garcia, R.; Mak, E.; Bullmore, E.T.; Baron-Cohen, S. Structural Covariance Networks in Children with Autism or ADHD. Cereb. Cortex 2017, 27, 4267–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, L.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, C.; Jiang, T. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative Abnormal cortical networks in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2010, 6, e1001006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, J.B.; Aarsland, D.; Ginestet, C.E.; Lebedev, A.V.; Wahlund, L.-O.; Simmons, A.; Volpe, G.; Westman, E. Aberrant cerebral network topology and mild cognitive impairment in early Parkinson’s disease. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2015, 36, 2980–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Minkova, L.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Abdulkadir, A.; Kaller, C.P.; Peter, J.; Scheller, E.; Lahr, J.; Roos, R.A.; Durr, A.; Leavitt, B.R.; et al. Large-scale brain network abnormalities in Huntington’s disease revealed by structural covariance. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2016, 37, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, D.; Chen, Q.; Huang, W. Impaired Topological Properties of Gray Matter Structural Covariance Network in Epilepsy Children With Generalized Tonic–Clonic Seizures: A Graph Theoretical Analysis. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yun, J.-Y.; Boedhoe, P.S.W.; Vriend, C.; Jahanshad, N.; Abe, Y.; Ameis, S.H.; Anticevic, A.; Arnold, P.D.; Batistuzzo, M.C.; Benedetti, F.; et al. Brain structural covariance networks in obsessive-compulsive disorder: A graph analysis from the ENIGMA Consortium. Brain 2020, 143, 684–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vijverberg, E.G.B.; Tijms, B.M.; Dopp, J.; Hong, Y.J.; Teunissen, C.E.; Barkhof, F.; Scheltens, P.; Pijnenburg, Y. Gray matter network differences between behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2017, 50, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Measso, G.; Cavarzeran, F.; Zappalà, G.; Lebowitz, B.D.; Crook, T.H.; Pirozzolo, F.J.; Amaducci, L.A.; Massari, D.; Grigoletto, F. The mini-mental state examination: Normative study of an Italian random sample. Dev. Neuropsychol. 1993, 9, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appollonio, I.; Leone, M.; Isella, V.; Piamarta, F.; Consoli, T.; Villa, M.L.; Forapani, E.; Russo, A.; Nichelli, P. The Frontal Assessment Battery (FAB): Normative values in an Italian population sample. Neurol. Sci. Off. J. Ital. Neurol. Soc. Ital. Soc. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2005, 26, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, A.M.; Fischl, B.; Sereno, M.I. Cortical surface-based analysis. I. Segmentation and surface reconstruction. NeuroImage 1999, 9, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischl, B.; Sereno, M.I.; Dale, A.M. Cortical surface-based analysis. II: Inflation, flattening, and a surface-based coordinate system. NeuroImage 1999, 9, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischl, B.; Dale, A.M. Measuring the thickness of the human cerebral cortex from magnetic resonance images. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 11050–11055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischl, B.; van der Kouwe, A.; Destrieux, C.; Halgren, E.; Ségonne, F.; Salat, D.H.; Busa, E.; Seidman, L.J.; Goldstein, J.; Kennedy, D.; et al. Automatically parcellating the human cerebral cortex. Cereb. Cortex 2004, 14, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ségonne, F.; Dale, A.M.; Busa, E.; Glessner, M.; Salat, D.; Hahn, H.K.; Fischl, B. A hybrid approach to the skull stripping problem in MRI. NeuroImage 2004, 22, 1060–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, A.M.; Sabuncu, M.R.; Yeo, B.T.T.; Fischl, B.; Greve, D.N.; Kochunov, P.; Nichols, T.E.; Blangero, J.; Glahn, D.C. Measuring and comparing brain cortical surface area and other areal quantities. NeuroImage 2012, 61, 1428–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desikan, R.S.; Ségonne, F.; Fischl, B.; Quinn, B.T.; Dickerson, B.C.; Blacker, D.; Buckner, R.L.; Dale, A.M.; Maguire, R.P.; Hyman, B.T.; et al. An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. NeuroImage 2006, 31, 968–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischl, B.; Salat, D.H.; Busa, E.; Albert, M.; Dieterich, M.; Haselgrove, C.; van der Kouwe, A.; Killiany, R.; Kennedy, D.; Klaveness, S.; et al. Whole brain segmentation: Automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron 2002, 33, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yun, J.-Y.; Kim, S.N.; Lee, T.Y.; Chon, M.-W.; Kwon, J.S. Individualized covariance profile of cortical morphology for auditory hallucinations in first-episode psychosis. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2016, 37, 1051–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Xia, M.; Liao, X.; Evans, A.; He, Y. GRETNA: A graph theoretical network analysis toolbox for imaging connectomics. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Achard, S.; Salvador, R.; Whitcher, B.; Suckling, J.; Bullmore, E. A resilient, low-frequency, small-world human brain functional network with highly connected association cortical hubs. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphries, M.D.; Gurney, K.; Prescott, T.J. The brainstem reticular formation is a small-world, not scale-free, network. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 273, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watts, D.J.; Strogatz, S.H. Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature 1998, 393, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinov, M.; Sporns, O. Complex network measures of brain connectivity: Uses and interpretations. NeuroImage 2010, 52, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.-N.; Ehmke, R.; Mennes, M.; Imperati, D.; Castellanos, F.X.; Sporns, O.; Milham, M.P. Network centrality in the human functional connectome. Cereb. Cortex 2012, 22, 1862–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Wijk, B.C.M.; Stam, C.J.; Daffertshofer, A. Comparing Brain Networks of Different Size and Connectivity Density Using Graph Theory. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achard, S.; Bullmore, E. Efficiency and cost of economical brain functional networks. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2007, 3, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Chen, Z.J.; Evans, A.C. Small-world anatomical networks in the human brain revealed by cortical thickness from MRI. Cereb. Cortex 2007, 17, 2407–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Zang, Y.; Yang, H.; Tang, H.; Gong, Q.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, C.; He, Y. Parcellation-dependent small-world brain functional networks: A resting-state fMRI study. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2009, 30, 1511–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Wu, Q.; Kuang, W.; Huang, X.; He, Y.; Gong, Q. Disrupted brain connectivity networks in drug-naive, first-episode major depressive disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 70, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Wang, J.; He, Y. BrainNet Viewer: A Network Visualization Tool for Human Brain Connectomics. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B-Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassett, D.S.; Wymbs, N.F.; Porter, M.A.; Mucha, P.J.; Carlson, J.M.; Grafton, S.T. Dynamic reconfiguration of human brain networks during learning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7641–7646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, M.; Huang, H.; Peng, Y.; Dong, Q.; He, Y. Toward Developmental Connectomics of the Human Brain. Front. Neuroanat. 2016, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, X.; Zou, Q.; He, Y.; Yang, Y. Topologically Reorganized Connectivity Architecture of Default-Mode, Executive-Control, and Salience Networks across Working Memory Task Loads. Cereb. Cortex 2016, 26, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, M.; He, Y. Magnetic resonance imaging and graph theoretical analysis of complex brain networks in neuropsychiatric disorders. Brain Connect. 2011, 1, 349–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornito, A.; Bullmore, E.T. Connectomic intermediate phenotypes for psychiatric disorders. Front. Psychiatry 2012, 3, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fornito, A.; Bullmore, E.T. Connectomics: A new paradigm for understanding brain disease. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. J. Eur. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015, 25, 733–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olde Dubbelink, K.T.E.; Hillebrand, A.; Stoffers, D.; Deijen, J.B.; Twisk, J.W.R.; Stam, C.J.; Berendse, H.W. Disrupted brain network topology in Parkinson’s disease: A longitudinal magnetoencephalography study. Brain J. Neurol. 2014, 137, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hou, Y.; Wei, Q.; Ou, R.; Yang, J.; Gong, Q.; Shang, H. Impaired topographic organization in Parkinson’s disease with mild cognitive impairment. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 414, 116861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brier, M.R.; Thomas, J.B.; Fagan, A.M.; Hassenstab, J.; Holtzman, D.M.; Benzinger, T.L.; Morris, J.C.; Ances, B.M. Functional connectivity and graph theory in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Afshari, S.; Jalili, M. Directed Functional Networks in Alzheimer’s Disease: Disruption of Global and Local Connectivity Measures. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2017, 21, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daianu, M.; Mezher, A.; Mendez, M.F.; Jahanshad, N.; Jimenez, E.E.; Thompson, P.M. Disrupted rich club network in behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia and early-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2016, 37, 868–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, V.; Premi, E.; Cristillo, V.; Gazzina, S.; Palluzzi, F.; Zanetti, O.; Gasparotti, R.; Padovani, A.; Borroni, B.; Grassi, M. Brain Connectivity and Information-Flow Breakdown Revealed by a Minimum Spanning Tree-Based Analysis of MRI Data in Behavioral Variant Frontotemporal Dementia. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meeter, L.H.; Kaat, L.D.; Rohrer, J.D.; van Swieten, J.C. Imaging and fluid biomarkers in frontotemporal dementia. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harciarek, M.; Cosentino, S. Language, Executive Function and Social Cognition in the Diagnosis of Frontotemporal Dementia Syndromes. Int. Rev. Psychiatry Abingdon Engl. 2013, 25, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnen, A.; Bertoux, M. Psychological and Cognitive Markers of Behavioral Variant Frontotemporal Dementia–A Clinical Neuropsychologist’s View on Diagnostic Criteria and Beyond. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Virani, K.; Jesso, S.; Kertesz, A.; Mitchell, D.; Finger, E. Functional neural correlates of emotional expression processing deficits in behavioural variant frontotemporal dementia. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. JPN 2013, 38, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| HC (n = 20) | bvFTD (n = 25) | p-Value | T/z | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic and clinical data | ||||
| Age at exam (years) | 63.60 ± 5.90 | 66.92 ± 7.69 | 0.08 | −1.74 |
| Sex (males/females) | 7/13 | 14/11 | 0.16 | 1.97 |
| Education (years) | 10.50 ± 4.88 | 8.32 ± 5.18 | 0.08 | 1.72 |
| MMSE | 27.90 ± 1.68 | 20.80 ± 5.57 | <0.001 | 4.78 |
| FAB (z-score) | −0.55 ± 0.95 | −4.81 ± 3.60 | <0.001 | 4.71 |
| Duration (years) | - | 2.86 ± 1.78 | - | - |
| Neuroimaging data | ||||
| Intracanial Volume (ml) | 1406.2 ± 155.71 | 1431.8 ± 163.69 | 0.81 | −0.23 |
| HC (n = 20) | bvFTD (n = 25) | p-Value | T/z | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| σ | 0.59 ± 0.04 | 0.55 ± 0.06 | 0.022 | 2.29 |
| λ | 0.42 ± 0.02 | 0.44 ± 0.02 | 0.008 | −2.66 |
| γ | 0.86 ± 0.07 | 0.82 ± 0.09 | 0.09 | 1.70 |
| Eglob | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | <0.001 | 4.42 |
| Local Efficiency. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Node | HC (n = 20) | bvFTD (n = 25) | p-Value FDR-Corrected | T/z |
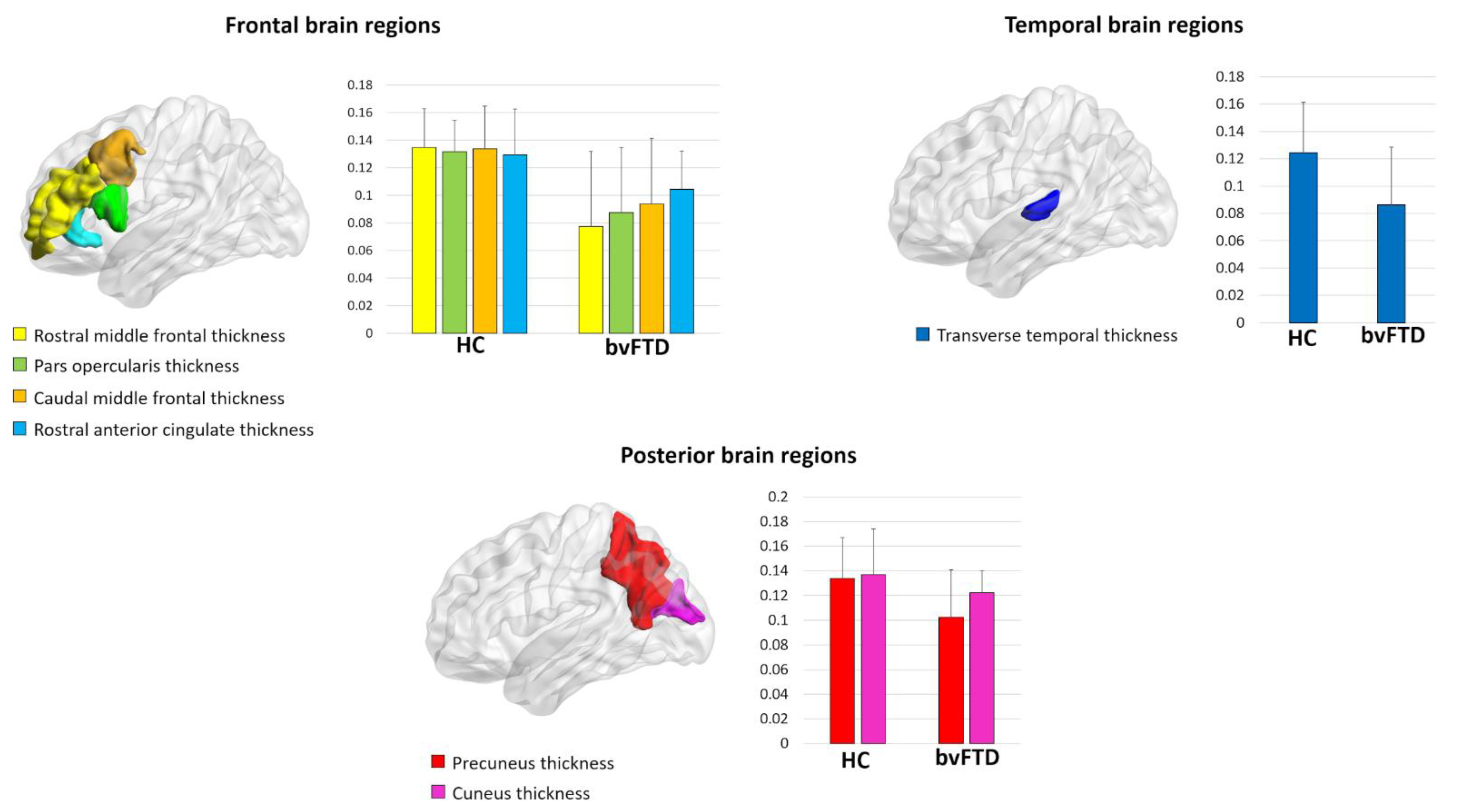
| Rostral middle frontal gyrus thickness | 0.14 ± 0.03 | 0.08 ± 0.05 | 0.02 | 3.69 |
| Pars opercularis thickness | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 0.09 ± 0.05 | 0.03 | 3.21 |
| Caudal middle frontal gyrus thickness | 0.13 ± 0.03 | 0.09 ± 0.05 | 0.03 | 3.16 |
| Precuneus thickness | 0.13 ± 0.03 | 0.10 ± 0.04 | 0.03 | 3.12 |
| Cuneus thickness | 0.14 ± 0.04 | 0.12 ± 0.02 | 0.04 | 3.00 |
| Transverse temporal thickness | 0.12 ± 0.04 | 0.09 ± 0.04 | 0.04 | 2.95 |
| Rostral anterior cingulate thickness | 0.13 ± 0.03 | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 0.05 | 2.84 |
| Clustering Coefficient | ||||
| Node | HC | bvFTD | p-Value | T/z |
| Inferior temporal gyrus thickness | 0.23 ± 0.01 | 0.20 ± 0.02 | <0.001 | 4.60 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nigro, S.; Tafuri, B.; Urso, D.; De Blasi, R.; Frisullo, M.E.; Barulli, M.R.; Capozzo, R.; Cedola, A.; Gigli, G.; Logroscino, G. Brain Structural Covariance Networks in Behavioral Variant of Frontotemporal Dementia. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020192
Nigro S, Tafuri B, Urso D, De Blasi R, Frisullo ME, Barulli MR, Capozzo R, Cedola A, Gigli G, Logroscino G. Brain Structural Covariance Networks in Behavioral Variant of Frontotemporal Dementia. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(2):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020192
Chicago/Turabian StyleNigro, Salvatore, Benedetta Tafuri, Daniele Urso, Roberto De Blasi, Maria Elisa Frisullo, Maria Rosaria Barulli, Rosa Capozzo, Alessia Cedola, Giuseppe Gigli, and Giancarlo Logroscino. 2021. "Brain Structural Covariance Networks in Behavioral Variant of Frontotemporal Dementia" Brain Sciences 11, no. 2: 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020192
APA StyleNigro, S., Tafuri, B., Urso, D., De Blasi, R., Frisullo, M. E., Barulli, M. R., Capozzo, R., Cedola, A., Gigli, G., & Logroscino, G. (2021). Brain Structural Covariance Networks in Behavioral Variant of Frontotemporal Dementia. Brain Sciences, 11(2), 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020192





