Multiple Subtypes of Alzheimer’s Disease Base on Brain Atrophy Pattern
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and MRI Processing
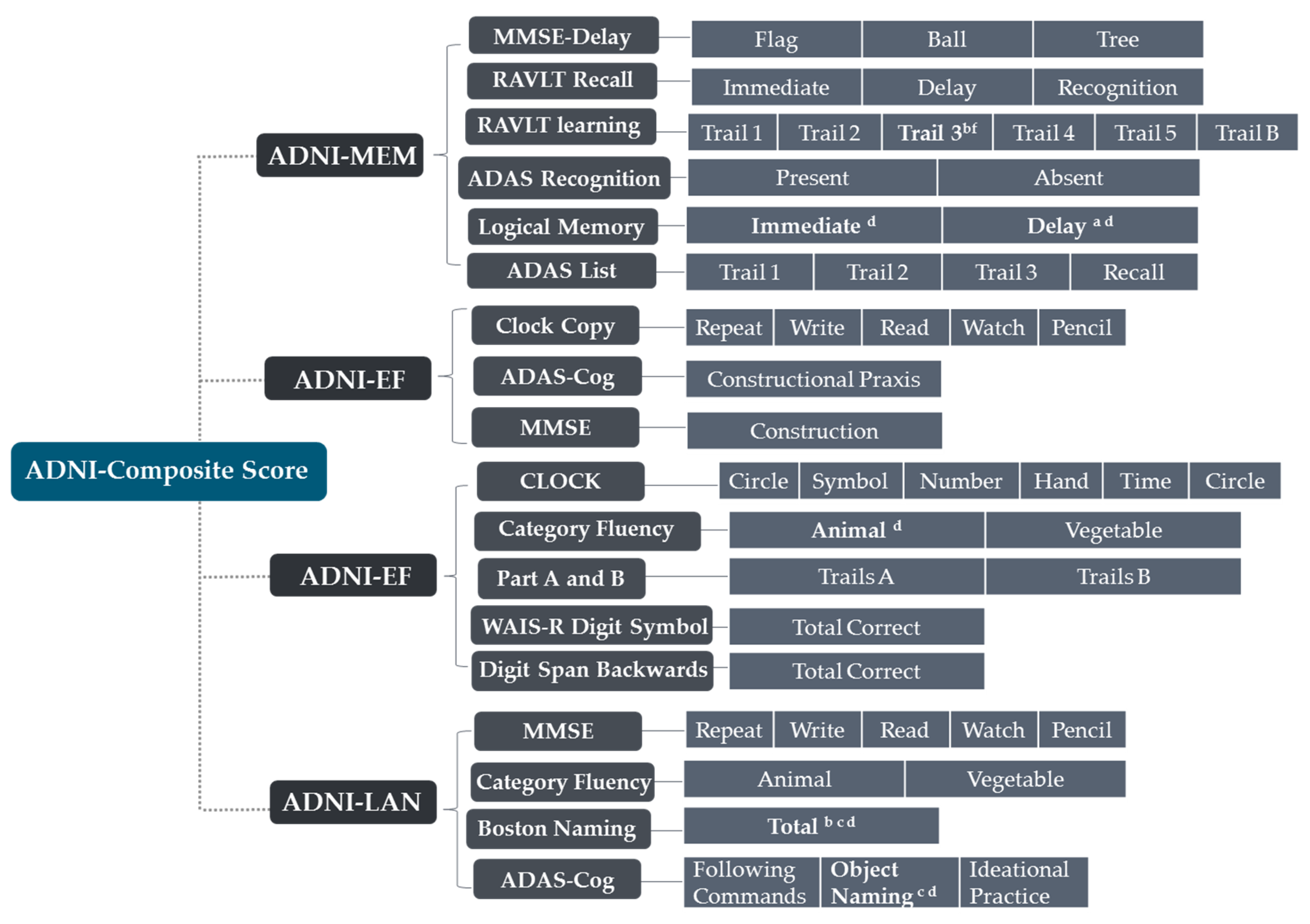
2.2. Neuropsychological Assessment and Neuropathological Data Collection
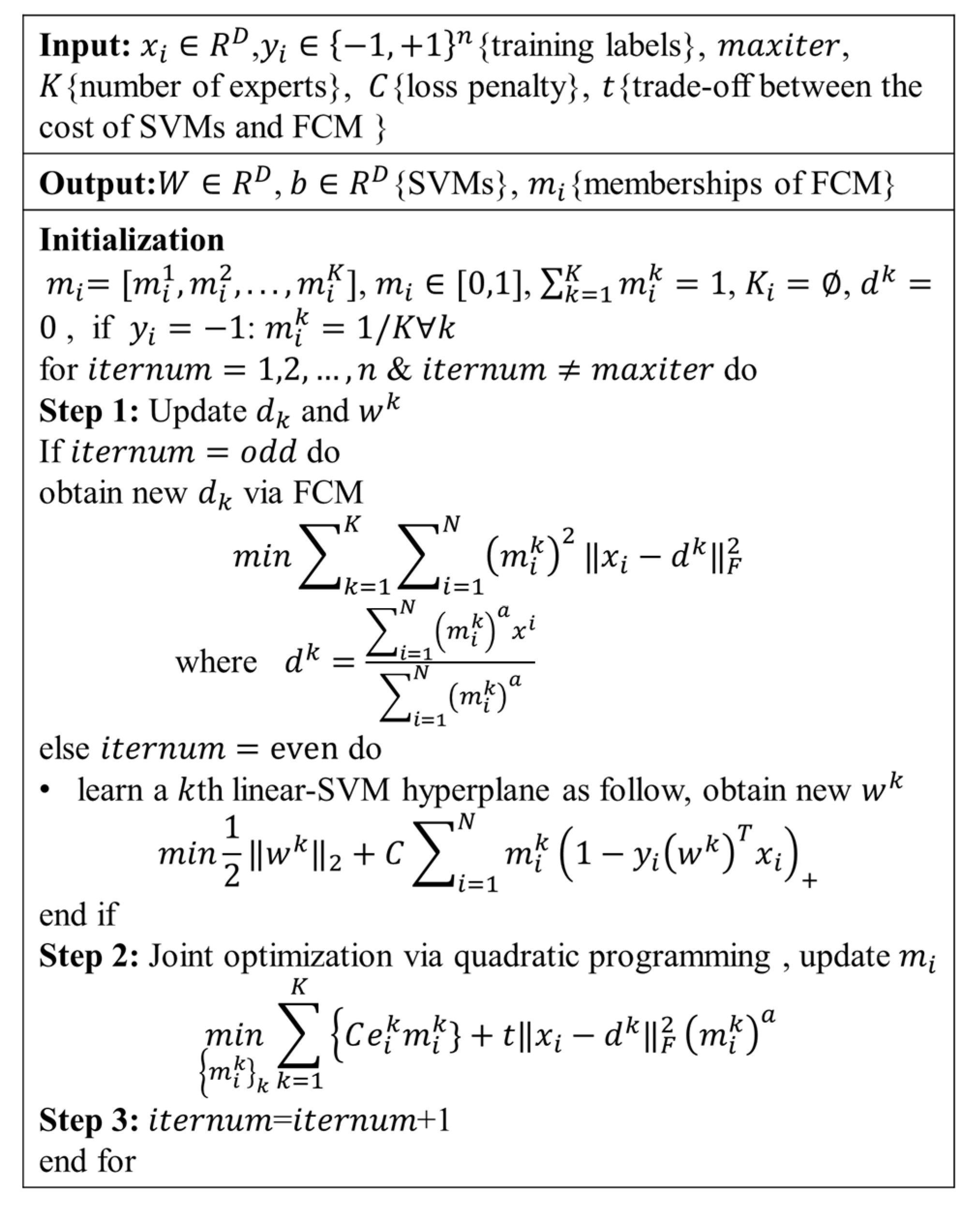
2.3. Definition of AD Subtype Using MOE
2.4. Evaluation of Multiple Piece-Wise Linear SVM
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
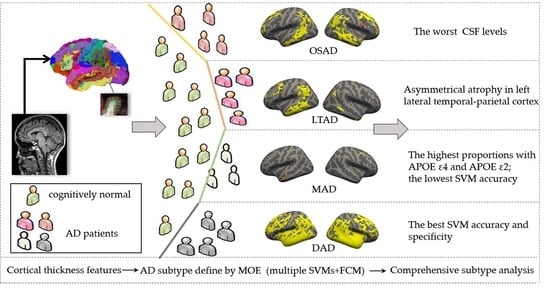
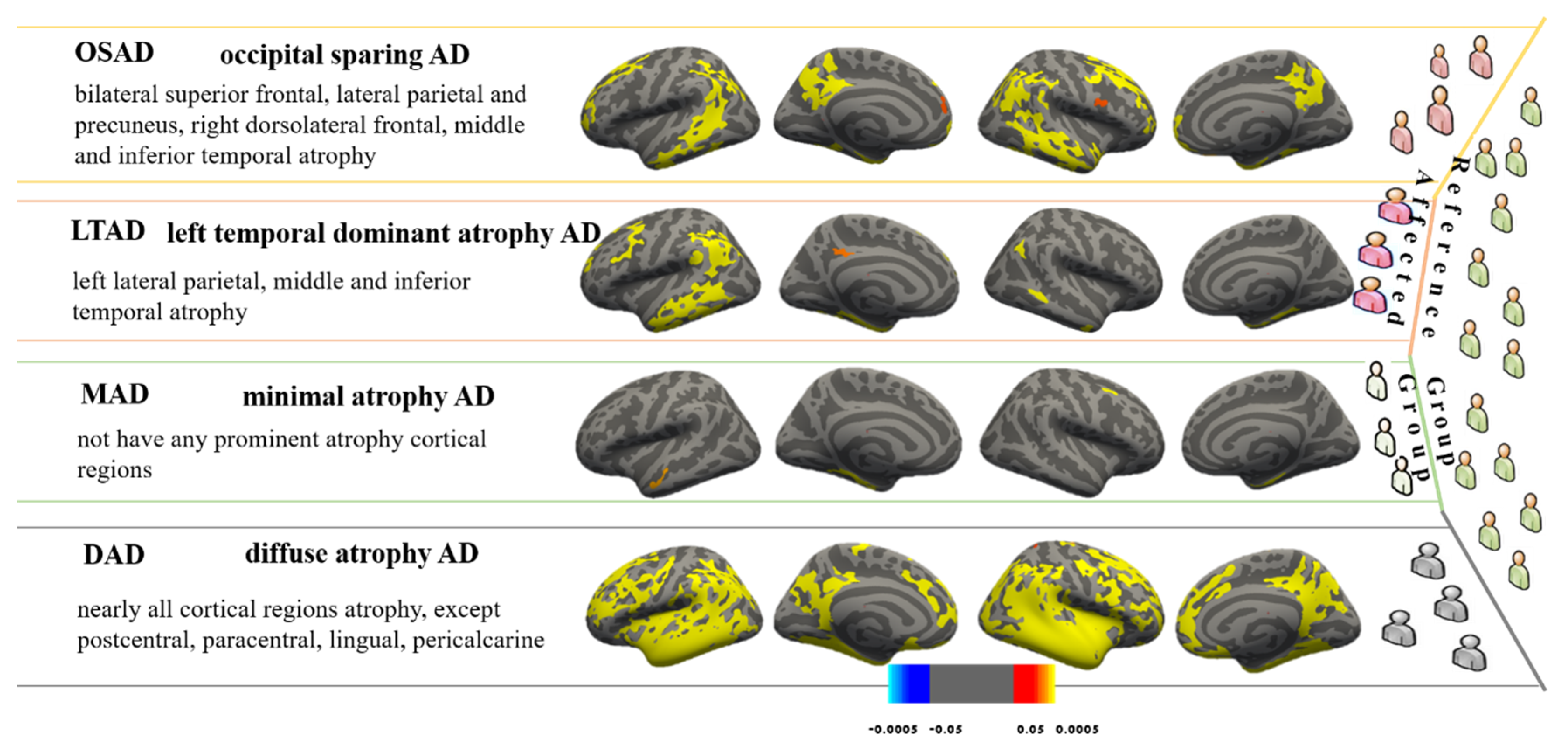
3.1. AD Subtypes Identified by MOE
3.2. Demographic and Cognitive Characteristics among Four AD Subtypes
3.3. Longitudinal Changes among Four Subtypes of AD
3.4. Neuropathological Characteristics among Four AD Subtypes
3.5. The Classification Performance of Multiple Piece-Wise Linear SVMs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiu, Y.; Jacobs, D.M.; Messer, K.; Salmon, D.P.; Feldman, H.H. Cognitive heterogeneity in probable Alzheimer disease: Clinical and neuropathologic features. Neurology 2019, 93, e778–e790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, M.E.; Graff-Radford, N.R.; Ross, O.A.; Petersen, R.C.; Duara, R.; Dickson, D.W. Neuropathologically defined subtypes of Alzheimer’s disease with distinct clinical characteristics: A retrospective study. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whitwell, J.L.; Dickson, D.W.; Murray, M.E.; Weigand, S.D.; Tosakulwong, N.; Senjem, M.L.; Knopman, D.S.; Boeve, B.F.; Parisi, J.E.; Petersen, R.C.; et al. Neuroimaging correlates of pathologically defined subtypes of Alzheimer’s disease: A case-control study. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, D.; Nordberg, A.; Westman, E. Biological subtypes of Alzheimer disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurology 2020, 94, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Risacher, S.L.; Anderson, W.H.; Charil, A.; Castelluccio, P.F.; Shcherbinin, S.; Saykin, A.J.; Schwarz, A.J. Alzheimer disease brain atrophy subtypes are associated with cognition and rate of decline. Neurology 2017, 89, 2176–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Byun, M.S.; Kim, S.E.; Park, J.; Yi, D.; Choe, Y.M.; Sohn, B.K.; Choi, H.J.; Baek, H.; Han, J.Y.; Woo, J.I.; et al. Heterogeneity of Regional Brain Atrophy Patterns Associated with Distinct Progression Rates in Alzheimer’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shima, K.; Matsunari, I.; Samuraki, M.; Chen, W.P.; Yamada, M. Posterior cingulate atrophy and metabolic decline in early stage Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 2006–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, D.; Verhagen, C.; Hernandez-Cabrera, J.A.; Cavallin, L.; Guo, C.J.; Ekman, U.; Muehlboeck, J.S.; Simmons, A.; Barroso, J.; Wahlund, L.O.; et al. Distinct subtypes of Alzheimer’s disease based on patterns of brain atrophy: Longitudinal trajectories and clinical applications. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, K.; Eldholm, R.S.; Barca, M.L.; Cavallin, L.; Ferreira, D.; Knapskog, A.B.; Selbaek, G.; Braekhus, A.; Saltvedt, I.; Westman, E.; et al. MRI-assessed atrophy subtypes in Alzheimer’s disease and the cognitive reserve hypothesis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ten Kate, M.; Dicks, E.; Visser, P.J.; van der Flier, W.M.; Teunissen, C.E.; Barkhof, F.; Scheltens, P.; Tijms, B.M.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging, I. Atrophy subtypes in prodromal Alzheimer’s disease are associated with cognitive decline. Brain 2018, 141, 3443–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.; Kim, C.M.; Jeon, S.; Lee, J.M.; Hong, Y.J.; Roh, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Koh, J.Y.; Na, D.L. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Prediction of Alzheimer’s disease pathophysiology based on cortical thickness patterns. Alzheimers Dement (Amst.) 2016, 2, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Noh, Y.; Jeon, S.; Lee, J.M.; Seo, S.W.; Kim, G.H.; Cho, H.; Ye, B.S.; Yoon, C.W.; Kim, H.J.; Chin, J. Anatomical heterogeneity of Alzheimer disease: Based on cortical thickness on MRIs. Neurology 2014, 83, 1936–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davatzikos, C.; Sotiras, A.; Fan, Y.; Habes, M.; Erus, G.; Rathore, S.; Bakas, S.; Chitalia, R.; Gastounioti, A.; Kontos, D. Precision diagnostics based on machine learning-derived imaging signatures. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 64, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, A.; Honnorat, N.; Gaonkar, B.; Davatzikos, C. CHIMERA: Clustering of Heterogeneous Disease Effects via Distribution Matching of Imaging Patterns. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Varol, E.; Sotiras, A.; Davatzikos, C.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging, I. HYDRA: Revealing heterogeneity of imaging and genetic patterns through a multiple max-margin discriminative analysis framework. Neuroimage 2017, 145, 346–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eavani, H.; Hsieh, M.K.; An, Y.; Erus, G.; Beason-Held, L.; Resnick, S.; Davatzikos, C. Capturing heterogeneous group differences using mixture-of-experts: Application to a study of aging. Neuroimage 2016, 125, 498–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eavani, H.; Habes, M.; Satterthwaite, T.D.; An, Y.; Hsieh, M.K.; Honnorat, N.; Erus, G.; Doshi, J.; Ferrucci, L.; Beason-Held, L.L.; et al. Heterogeneity of structural and functional imaging patterns of advanced brain aging revealed via machine learning methods. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 71, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, S.G.; Weiner, M.W.; Thal, L.J.; Petersen, R.C.; Jack, C.; Jagust, W.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Toga, A.W.; Beckett, L. The Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2005, 15, 869–877, xi–xii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petersen, R.C.; Aisen, P.S.; Beckett, L.A.; Donohue, M.C.; Gamst, A.C.; Harvey, D.J.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Jagust, W.J.; Shaw, L.M.; Toga, A.W.; et al. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI): Clinical characterization. Neurology 2010, 74, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Bernstein, M.A.; Fox, N.C.; Thompson, P.; Alexander, G.; Harvey, D.; Borowski, B.; Britson, P.J.; Whitwell, J.L.; Ward, C.; et al. The Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI): MRI methods. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2008, 27, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischl, B. FreeSurfer. Neuroimage 2012, 62, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, S.E.; Mukherjee, S.; Gibbons, L.E.; Sanders, R.E.; Jones, R.N.; Tommet, D.; Mez, J.; Trittschuh, E.H.; Saykin, A.; Lamar, M.; et al. Development and validation of language and visuospatial composite scores in ADNI. Alzheimers Dement. 2020, 6, e12072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, P.K.; Carle, A.; Gibbons, L.E.; Insel, P.; Mackin, R.S.; Gross, A.; Jones, R.N.; Mukherjee, S.; Curtis, S.M.; Harvey, D.; et al. Development and assessment of a composite score for memory in the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI). Brain Imaging Behav. 2012, 6, 502–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibbons, L.E.; Carle, A.C.; Mackin, R.S.; Harvey, D.; Mukherjee, S.; Insel, P.; Curtis, S.M.; Mungas, D.; Crane, P.K.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging, I. A composite score for executive functioning, validated in Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) participants with baseline mild cognitive impairment. Brain Imaging Behav. 2012, 6, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaw, L.M.; Vanderstichele, H.; Knapik-Czajka, M.; Figurski, M.; Coart, E.; Blennow, K.; Soares, H.; Simon, A.J.; Lewczuk, P.; Dean, R.A.; et al. Qualification of the analytical and clinical performance of CSF biomarker analyses in ADNI. Acta Neuropathol. 2011, 121, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shaw, L.M.; Vanderstichele, H.; Knapik-Czajka, M.; Clark, C.M.; Aisen, P.S.; Petersen, R.C.; Blennow, K.; Soares, H.; Simon, A.; Lewczuk, P.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarker signature in Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative subjects. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 65, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dave, R.N. Validating fuzzy partitions obtained through c-shells clustering. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 1996, 17, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulakis, K.; Pereira, J.B.; Mecocci, P.; Vellas, B.; Tsolaki, M.; Kloszewska, I.; Soininen, H.; Lovestone, S.; Simmons, A.; Wahlund, L.O.; et al. Heterogeneous patterns of brain atrophy in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 65, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, N.; Mormino, E.C.; Chen, J.; Sabuncu, M.R.; Yeo, B.T.T.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging, I. Multi-modal latent factor exploration of atrophy, cognitive and tau heterogeneity in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage 2019, 201, 116043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bejanin, A.; Schonhaut, D.R.; La Joie, R.; Kramer, J.H.; Baker, S.L.; Sosa, N.; Ayakta, N.; Cantwell, A.; Janabi, M.; Lauriola, M.; et al. Tau pathology and neurodegeneration contribute to cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2017, 140, 3286–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sorg, C.; Myers, N.; Redel, P.; Bublak, P.; Riedl, V.; Manoliu, A.; Perneczky, R.; Grimmer, T.; Kurz, A.; Forstl, H.; et al. Asymmetric loss of parietal activity causes spatial bias in prodromal and mild Alzheimer’s disease. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 71, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossenkoppele, R.; Schonhaut, D.R.; Scholl, M.; Lockhart, S.N.; Ayakta, N.; Baker, S.L.; O’Neil, J.P.; Janabi, M.; Lazaris, A.; Cantwell, A.; et al. Tau PET patterns mirror clinical and neuroanatomical variability in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2016, 139, 1551–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krištofiková, Z.; Kozmiková, I.; Hovorková, P.; Říčný, J.; Zach, P.; Majer, E.; Klaschka, J.; Řípová, D. Lateralization of hippocampal nitric oxide mediator system in people with Alzheimer disease, multi-infarct dementia and schizophrenia. Neurochem. Int. 2008, 53, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derflinger, S.; Sorg, C.; Gaser, C.; Myers, N.; Arsic, M.; Kurz, A.; Zimmer, C.; Wohlschläger, A.; Mühlau, M. Grey-matter atrophy in Alzheimer’s disease is asymmetric but not lateralized. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2011, 25, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldberg, T.E.; Huey, E.D.; Devanand, D.P. Association of APOE e2 genotype with Alzheimer’s and non-Alzheimer’s neurodegenerative pathologies. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, S. Progression of Alzheimer’s disease, tau propagation, and its modifiable risk factors. Neurosci. Res. 2019, 141, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorga, P.; Young, C.F. Mini-Mental State Examination for the Detection of Alzheimer Disease and Other Dementias in People with Mild Cognitive Impairment. Clin. Nurse Spec. 2015, 29, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanskanen, M.; Mäkelä, M.; Notkola, I.L.; Myllykangas, L.; Rastas, S.; Oinas, M.; Lindsberg, P.J.; Polvikoski, T.; Tienari, P.J.; Paetau, A. Population-based analysis of pathological correlates of dementia in the oldest old. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2017, 4, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.L.; Corrada, M.M.; Kovacs, G.G.; Dominique, M.; Caswell, C.; Xie, S.X.; Lee, V.M.-Y.; Kawas, C.H.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Non-Alzheimer’s contributions to dementia and cognitive resilience in The 90+ Study. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 136, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, P.T.; Dickson, D.W.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jack, C.R.; Boyle, P.A.; Arfanakis, K.; Rademakers, R.; Alafuzoff, I.; Attems, J.; Brayne, C. Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy (LATE): Consensus working group report. Brain 2019, 142, 1503–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
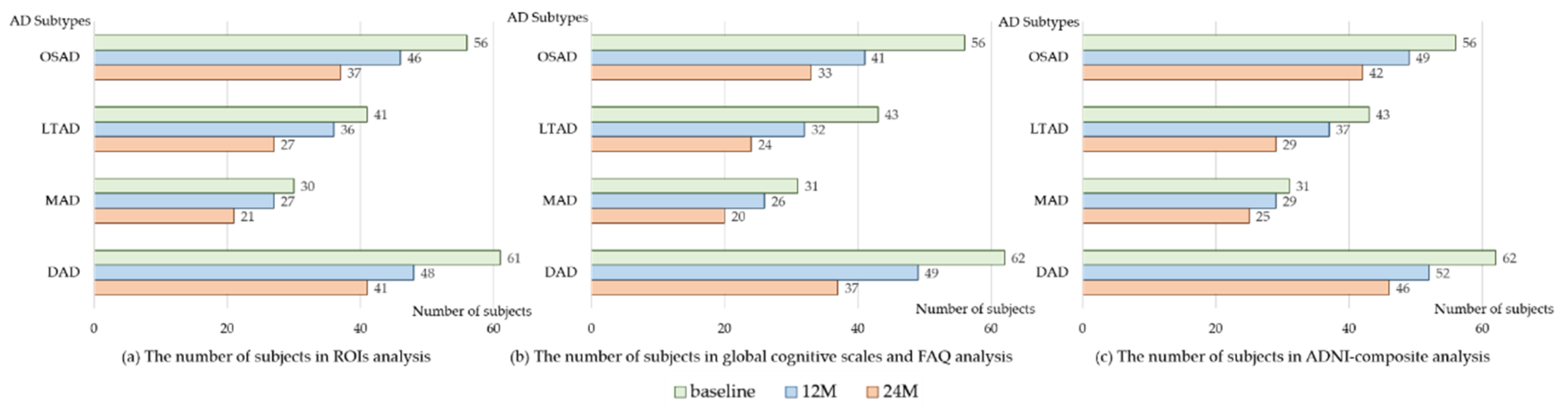
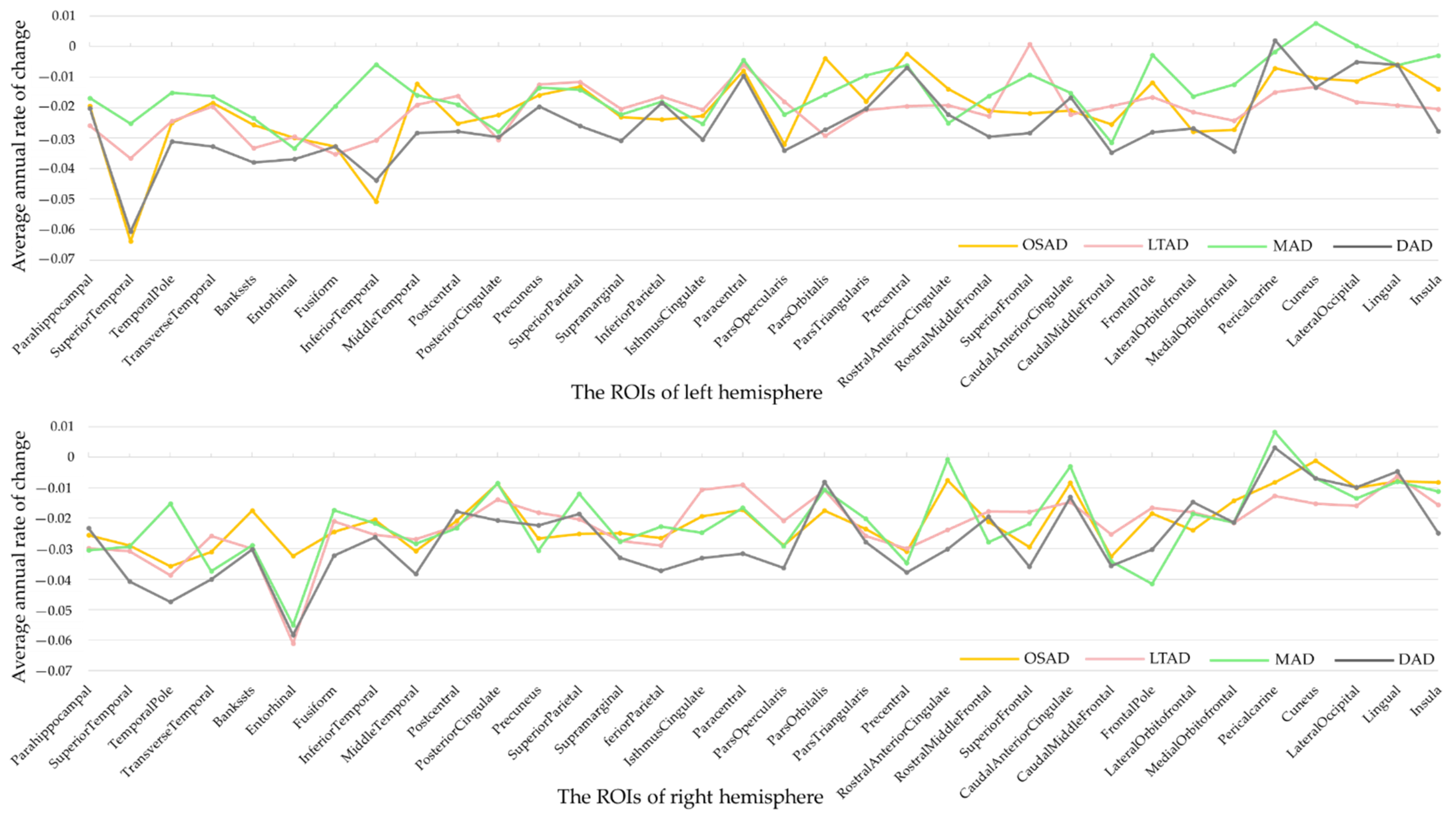
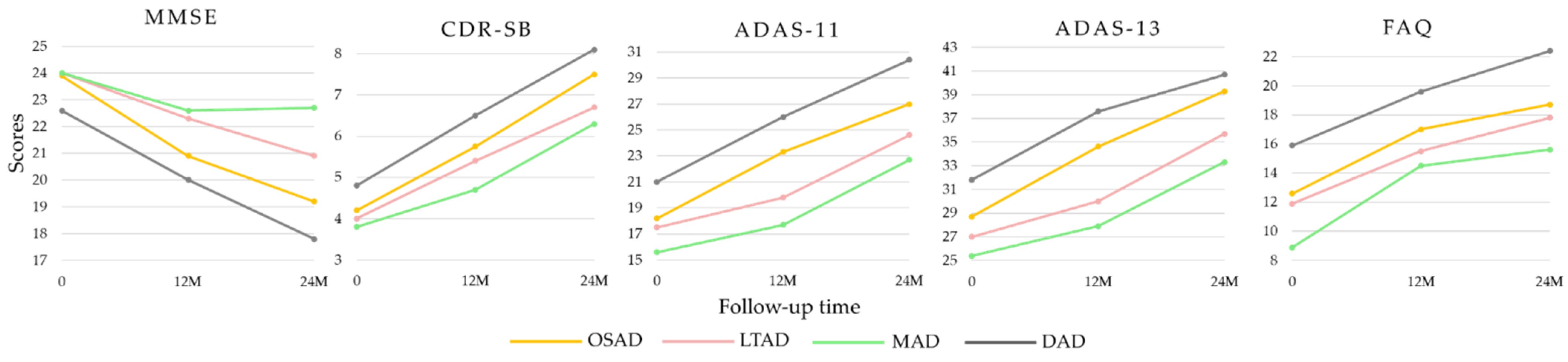


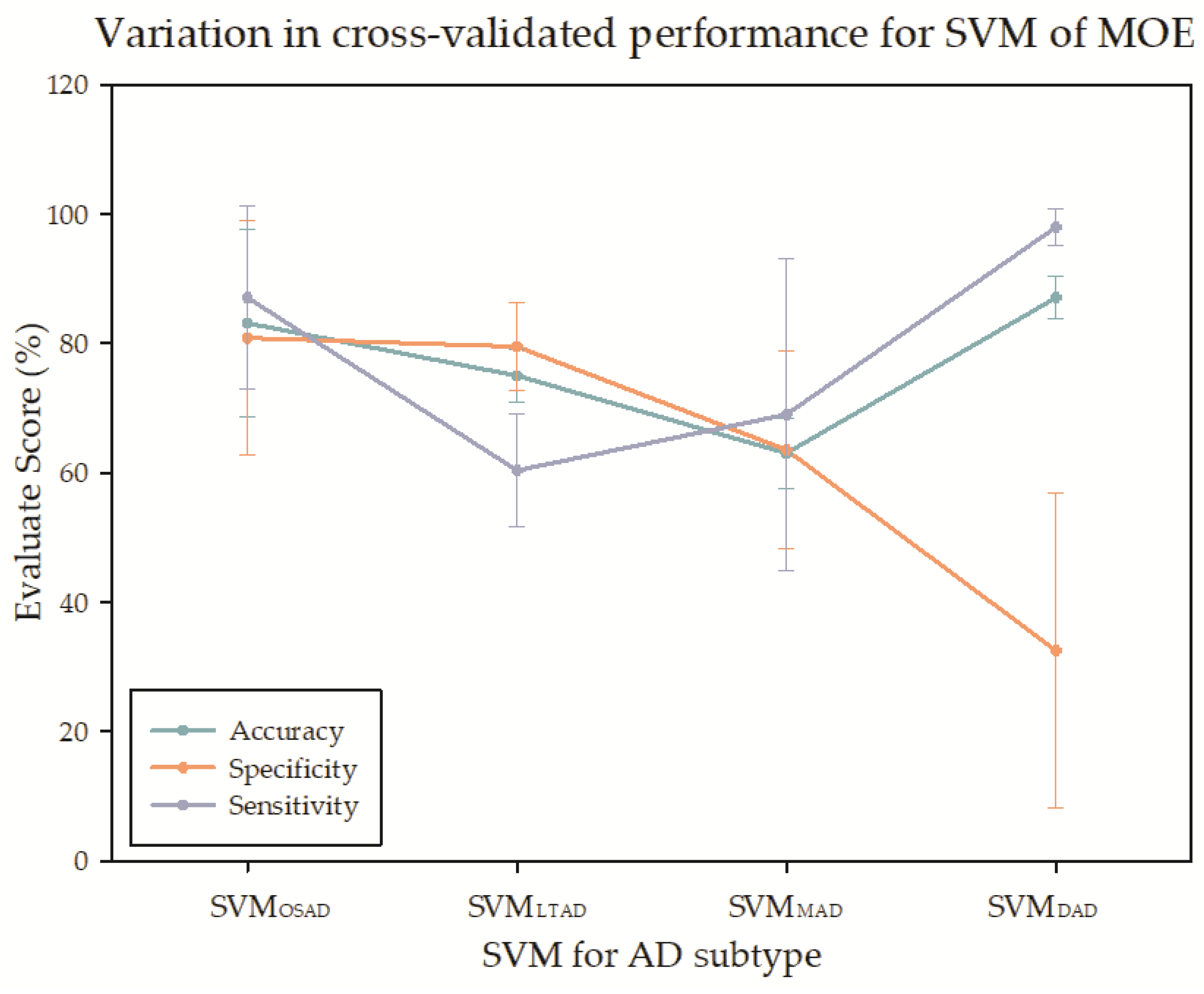
| Characteristics | CN | AD | OSAD | LTAD | MAD | DAD | p-Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | 228 | 192 | 56 (29.2%) | 43 (22.4%) | 31 (16.1%) | 62 (32.3%) | |
| Age (years) | 75.9 ± 5.0 | 75.4 ± 7.4 | 75.0 ± 7.8 | 76.3 ± 7.1 | 74.4 ± 7.7 | 75.6 ± 7.3 | 0.720 |
| Women, n (%) | 109 (47.8%) | 91 (47.4%) | 28 (50.0%) | 13 (30.2%) | 15 (48.4%) | 35 (56.5%) | 0.029 a,e,g |
| Education (years) | 16.1 ± 2.9 | 14.7 ± 3.1 | 14.7 ± 3.5 | 15.1 ± 2.6 | 14.3 ± 7.7 | 14.6 ± 3.0 | 0.680 |
| Age of onset (years) | 70.0 ± 14.5 | 68.5 ± 16.3 | 70.0 ± 18.0 | 71.7 ± 7.9 | 70.6 ± 12.5 | 0.524 | |
| Disease duration (years) | 3.1 ± 2.7 | 3.5 ± 2.9 | 2.3 ± 2.2 | 2.7 ± 2.2 | 3.6 ± 2.8 | 0.032 a,e | |
| Left-handedness | 17 (7.5%) | 11 (5.7%) | 5 (8.9%) | 3 (7.0%) | 0 | 3 (4.8) | 0.342 g |
| BMI | 26.7 ± 4.3 | 25.5 ± 3.9 | 26.1 ± 4.4 | 25.3 ± 3.8 | 25.1 ± 3.3 | 25.3 ± 3.7 | 0.561 |
| Systolic (mmHg) | 134.5 ± 16.9 | 137.6 ± 17.1 | 137.7 ± 16.2 | 140.3 ± 18.6 | 139.7 ± 19.0 | 137.7 ± 16.2 | 0.294 |
| Diastolic (mmHg) | 74.6 ± 10.3 | 73.8 ± 9.9 | 72.9 ± 8.7 | 73.3 ± 11.5 | 74.1 ± 9.7 | 74.7 ± 9.9 | 0.774 |
| Pulse rate (per minute) | 67.0 ± 10.8 | 63.7 ± 9.0 | 65.0 ± 7.9 | 62.3 ± 8.1 | 61.4 ± 10.8 | 64.5 ± 9.3 | 0.461 |
| Respirations (per minute) | 16.8 ± 3.2 | 17.0 ± 3.1 | 17.2 ± 2.0 | 17.1 ± 3.5 | 17.4 ± 2.9 | 16.5 ± 3.0 | 0.181 |
| MMSE | 29.1 ± 1.0 | 23.3 ± 2.0 | 23.9 ± 1.9 | 24.0 ± 2.0 | 24.0 ± 1.8 | 22.6 ± 2.1 | <0.001 e,f |
| CDR-SB | 0.03 ± 0.12 | 4.3 ± 1.6 | 4.2 ± 1.5 | 4.0 ± 1.4 | 3.8 ± 1.5 | 4.8 ± 1.8 | 0.011 e,f |
| FAQ | 0.14 ± 0.6 | 12.9 ± 6.9 | 12.6 ± 6.3 | 11.9 ± 6.4 | 8.9 ± 5.6 | 15.9 ± 7.1 | <0.001 b,c,d,e,f |
| ADAS-Cog 11 | 6.2 ± 2.9 | 18.5 ± 6.3 | 18.2 ± 6.7 | 17.5 ± 6.0 | 15.6 ± 4.0 | 21.0 ± 6.3 | <0.001 c,e,f |
| ADAS-Cog 13 | 9.5 ± 4.2 | 28.8 ± 7.6 | 28.7 ± 7.9 | 27.0 ± 7.1 | 25.4 ± 5.7 | 31.8 ± 7.6 | <0.001 c,e,f |
| ADNI-MEM | 0.97 ± 0.53 | −0.84 ± 0.55 | −0.89 ± 0.54 | −0.69 ± 0.45 | −0.60 ± 0.57 | −1.03 ± 0.56 | <0.001 e,c,b,f |
| ADNI-EF | 0.64 ± 0.75 | −0.96 ± 0.89 | −0.91 ± 0.78 | −0.85 ± 0.98 | −0.80 ± 0.94 | −1.13 ± 0.91 | 0.293 |
| ADNI-LAN | 0.78 ± 0.75 | −0.78 ± 0.89 | −0.67 ± 0.90 | −0.65 ± 0.88 | −0.51 ± 0.71 | −1.10 ± 0.90 | 0.05 c,e,f |
| ADNI-VS | 0.23 ± 0.60 | −0.60 ± 0.91 | −0.55 ± 0.80 | −0.52 ± 0.79 | −0.57 ± 0.96 | −0.72 ± 1.04 | 0.645 |
| Characteristics | CN | AD | OSAD | LTAD | MAD | DAD | p-Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APOE 4 (n(carry%)) | 60 (26.3%) | 127 (66.1%) | 38 (67.9%) | 27 (62.8%) | 22 (71.0%) | 40 (64.5%) | 0.962 f |
| 1 | 55 (24.1%) | 91 (47.4%) | 29 (51.8%) | 19 (44.2%) | 16 (51.6%) | 27 (43.5%) | |
| 2 | 5 (2.1%) | 36 (18.8%) | 9 (16.1%) | 8 (18.6%) | 6 (19.4%) | 13 (21.0%) | |
| APOE 2 (n(carry%)) | 21 (9.2%) | 14 (7.3%) | 3 (5.4%) | 1 (2.3%) | 7 (22.6%) | 3 (4.8%) | <0.018 b,c,e,f |
| Aβ1–42 (ng/L) | 205.8 ± 54.7 | 143.6 ± 40.6 | 132.0 ± 25.5 | 150.6 ± 41.7 | 168.5 ± 55.6 | 139.7 ± 41.4 | 0.033 b,e |
| Aβ1–42 (abnormal%) | 44 (37.6%) | 89 (91.3%) | 31 (97.0%) | 21 (84.0%) | 10 (76.9%) | 26 (93.9%) | 0.151 f |
| n missing | 111 (48.7%) | 94 (49.0%) | 24 (42.9%) | 18 (41.9%) | 18 (58.0%) | 34 (54.8%) | |
| t-tau (ng/L) | 69.7 ± 29.8 | 121.4 ± 57.6 | 131.9 ± 54.8 | 129.4 ± 69.5 | 88.1 ± 51 | 118.4 ± 49.3 | 0.112 |
| t-tau (abnormal%) | 21 (17.6%) | 64 (63.3%) | 25 (78.1%) | 17 (68.0%) | 4 (30.8%) | 18 (54.5%) | 0.014 b,f |
| n missing | 109 (47.8%) | 96 (50.0%) | 24 (42.9%) | 19 (44.2%) | 18 (58.0%) | 35 (56.5%) | |
| p-tau (ng/L) | 25.1 ± 14.6 | 41.5 ± 19.9 | 41.53 ± 17.8 | 41.88 ± 19.4 | 31.8 ± 19.2 | 44.8 ± 21.6 | 0.254 |
| p-tau (abnormal%) | 42 (35.3%) | 90 (87.4%) | 30 (93.8%) | 23 (92.0%) | 8 (61.5%) | 30 (90.9%) | 0.015 b,f |
| n missing | 94 (41.2%) | 89 (46.4%) | 24 (42.9%) | 18 (41.9%) | 18 (58.0%) | 29 (46.8%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Lin, L.; Wu, S.; Al-Masqari, Z.H.M.A. Multiple Subtypes of Alzheimer’s Disease Base on Brain Atrophy Pattern. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020278
Zhang B, Lin L, Wu S, Al-Masqari ZHMA. Multiple Subtypes of Alzheimer’s Disease Base on Brain Atrophy Pattern. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(2):278. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020278
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Baiwen, Lan Lin, Shuicai Wu, and Zakarea H. M. A. Al-Masqari. 2021. "Multiple Subtypes of Alzheimer’s Disease Base on Brain Atrophy Pattern" Brain Sciences 11, no. 2: 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020278
APA StyleZhang, B., Lin, L., Wu, S., & Al-Masqari, Z. H. M. A. (2021). Multiple Subtypes of Alzheimer’s Disease Base on Brain Atrophy Pattern. Brain Sciences, 11(2), 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020278