Efficacy of a Training on Executive Functions in Potentiating Rehabilitation Effects in Stroke Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Procedure
2.2. Participants
2.3. Training Program
2.3.1. Stimuli
2.3.2. Working Memory (WM) Task
2.3.3. Interference Control and Inhibition (ICI) Task
2.3.4. Task-Switching (TS)
2.3.5. Monitoring Task (M)
2.4. Outcome Measures
2.5. Data Analyses
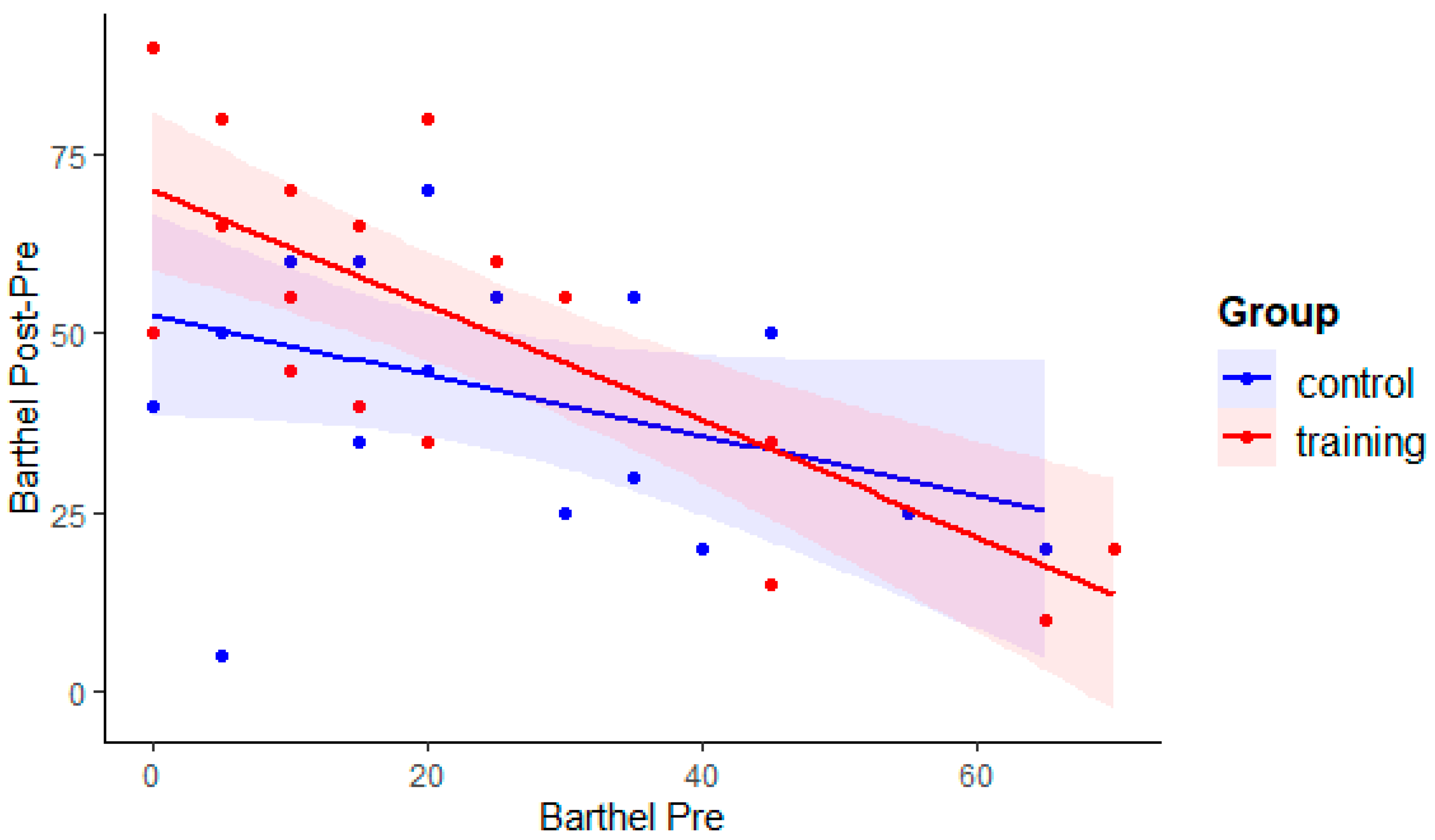
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, C.O.; Nguyen, M.; Roth, G.A.; Nichols, E.; Alam, T.; Abate, D.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; Abraha, H.N.; Abu-Rmeileh, N.M.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winstein, C.J.; Stein, J.; Arena, R.; Bates, B.; Cherney, L.R.; Cramer, S.C.; Deruyter, F.; Eng, J.J.; Fisher, B.; Harvey, R.L.; et al. Guidelines for adult stroke rehabilitation and recovery. Stroke 2016, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nys, G.M.S.; Van Zandvoort, M.J.E.; De Kort, P.L.M.; Van Der Worp, H.B.; Jansen, B.P.W.; Algra, A.; De Haan, E.H.F.; Kappelle, L.J. The prognostic value of domain-specific cognitive abilities in acute first-ever stroke. Neurology 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatemichi, T.K.; Desmond, D.W.; Stern, Y.; Paik, M.; Sano, M.; Bagiella, E. Cognitive impairment after stroke: Frequency, patterns, and relationship to functional abilities. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1994, 57, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poulin, V.; Korner-Bitensky, N.; Dawson, D.R.; Bherer, L. Efficacy of executive function interventions after stroke: A systematic review. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2012, 19, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, L.A.; Hayward, K.S.; Ward, N.S.; Stinear, C.M.; Rosso, C.; Fisher, R.J.; Carter, A.R.; Leff, A.P.; Copland, D.A.; Carey, L.M.; et al. Biomarkers of stroke recovery: Consensus-based core recommendations from the stroke recovery and rehabilitation roundtable*. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuss, D.T.; Alexander, M.P.; Shallice, T.; Picton, T.W.; Binns, M.A.; Macdonald, R.; Borowiec, A.; Katz, D.I. Multiple frontal systems controlling response speed. Neuropsychologia 2005, 43, 396–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, N.P.; Miyake, A. Unity and diversity of executive functions: Individual differences as a window on cognitive structure. Cortex 2017, 86, 186–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ambrosini, E.; Arbula, S.; Rossato, C.; Pacella, V.; Vallesi, A. Neuro-cognitive architecture of executive functions: A latent variable analysis. Cortex 2019, 119, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, B.; Schweizer, T.A.; O’Connor, C.; Turner, G.; Gillingham, S.; Stuss, D.T.; Manly, T.; Robertson, I.H. Rehabilitation of executive functioning in patients with frontal lobe brain damage with goal management training. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2011, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stablum, F.; Umiltà, C.; Mogentale, C.; Carlan, M.; Guerrini, C. Rehabilitation of executive deficits in closed head injury an anterior communicating artery aneurysm patients. Psychol. Res. 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, G.A.; Rentz, D.M.; Frey, M.T.; Locascio, J.J.; Johnson, K.A.; Sperling, R.A. Executive function and instrumental activities of daily living in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Royall, D.R.; Palmer, R.; Chiodo, L.K.; Polk, M.J. Declining executive control in normal aging predicts change in functional status: The Freedom House Study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowd, J.M.; Filion, D.L.; Pohl, P.S.; Richards, L.G.; Stiers, W. Attentional abilities and functional outcomes following stroke. J. Gerontol. Ser. B Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 2003, 58, P45–P53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, I.H.; Ridgeway, V.; Greenfield, E.; Parr, A. Motor recovery after stroke depends on intact sustained attention: A 2-year follow-up study. Neuropsychology 1997, 11, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanks, R.A.; Rapport, L.J.; Millis, S.R.; Deshpande, S.A. Measures of executive functioning as predictors of functional ability and social integration in a rehabilitation sample. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, P.A.; Gignac, G.E.; Weinborn, M.; Green, S.; Pestell, C. A meta-analysis of neuropsychological predictors of outcome following stroke and other non-traumatic acquired brain injuries in adults. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2020, 30, 194–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.S.Y.; Pollock, A.; Campbell, T.; Durward, B.R.; Hagen, S. Cognitive rehabilitation for executive dysfunction in adults with stroke or other adult non-progressive acquired brain damage. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 4, CD008391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Ven, R.M.; Murre, J.M.J.; Veltman, D.J.; Schmand, B.A. Computer-based cognitive training for executive functions after stroke: A systematic review. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cicerone, K.D.; Langenbahn, D.M.; Braden, C.; Malec, J.F.; Kalmar, K.; Fraas, M.; Felicetti, T.; Laatsch, L.; Harley, J.P.; Bergquist, T.; et al. Evidence-based cognitive rehabilitation: Updated review of the literature from 2003 through 2008. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2011, 92, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallesi, A. The quest for hemispheric asymmetries supporting and predicting executive functioning. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2020, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallesi, A. Organisation of executive functions: Hemispheric asymmetries. J. Cogn. Psychol. 2012, 24, 367–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuss, D.T.; Alexander, M.P. Is there a dysexecutive syndrome? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 2007, 362, 901–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Magni, E.; Binetti, G.; Bianchetti, A.; Rozzini, R.; Trabucchi, M. Mini-mental state examination: A normative study in Italian elderly population. Eur. J. Neurol. 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, G.; Colombo, L.; Vallar, G.; Rusconi, M.L.; Pinarello, A. TIB: Test di Intelligenza Breve per la valutazione del quoziente intellettivo attuale e premorboso. Prof. Psicol. 1997, 1, 2–24. [Google Scholar]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rorden, C.; Bonilha, L.; Fridriksson, J.; Bender, B.; Karnath, H.-O. Age-specific CT and MRI templates for spatial normalization. Neuroimage 2012, 61, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nachev, P.; Coulthard, E.; Jäger, H.R.; Kennard, C.; Husain, M. Enantiomorphic normalization of focally lesioned brains. Neuroimage 2008, 39, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garon, N.; Bryson, S.E.; Smith, I.M. Executive function in preschoolers: A review using an integrative framework. Psychol. Bull. 2008, 134, 31–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tottenham, N.; Tanaka, J.W.; Leon, A.C.; McCarry, T.; Nurse, M.; Hare, T.A.; Marcus, D.J.; Westerlund, A.; Casey, B.; Nelson, C. The NimStim set of facial expressions: Judgments from untrained research participants. Psychiatry Res. 2009, 168, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tarantino, V.; Mazzonetto, I.; Formica, S.; Causin, F.; Vallesi, A. The neural bases of event monitoring across domains: A simultaneous ERP-fMRI study. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, E.E.; Jonides, J. Working memory: A view from neuroimaging. Cogn. Psychol. 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vallesi, A.; Crescentini, C. Right fronto-parietal involvement in monitoring spatial trajectories. Neuroimage 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, M.; Costa, A.; Caltagirone, C.; Carlesimo, G.A. Forward and backward span for verbal and visuo-spatial data: Standardization and normative data from an Italian adult population. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 34, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Sala, S.; Laiacona, M.; Spinnler, H.; Ubezio, C. A cancellation test: Its reliability in assessing attentional deficits in Alzheimer’s disease. Psychol. Med. 1992, 22, 885–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giovagnoli, A.R.; Del Pesce, M.; Mascheroni, S.; Simoncelli, M.; Laiacona, M.; Capitani, E. Trail making test: Normative values from 287 normal adult controls. Ital. J. Neurol. Sci. 1996, 17, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartori, G.; Job, R. The oyster with four legs: A neuropsychological study on the interaction of visual and semantic information. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novelli, G.; Papagno, C.; Capitani, E.; Laiacona, M.; Vallar, G.; Cappa, S.F. Tre test clinici di ricerca e produzione lessicale. Taratura su soggetti normali. Arch. Psicol. Neurol. Psichiatr. 1986, 47, 477–506. [Google Scholar]
- Caffarra, P.; Vezzadini, G.; Dieci, F.; Zonato, F.; Venneri, A. Modified card sorting test: Normative data. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2004, 26, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopp, B.; Lange, F.; Steinke, A. The reliability of the Wisconsin card sorting test in clinical practice. Assessment 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattelani, R.; Dal Sasso, F.; Corsini, D.; Posteraro, L. The Modified Five-Point Test: Normative data for a sample of Italian healthy adults aged 16–60. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 32, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucha, L.; Aschenbrenner, S.; Koerts, J.; Lange, K.W. The Five-Point Test: Reliability, validity and normative data for children and adults. PLoS ONE 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caffarra, P.; Vezzadini, G.; Dieci, F.; Zonato, F.; Venneri, A. Una versione abbreviata del test di Stroop: Dati normativi nella popolazione Italiana. Nuova Riv. Neurol. 2002, 12, 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Galeoto, G.; Lauta, A.; Palumbo, A.; Castiglia, S.F.; Mollica, R.; Santilli, V.; Sacchetti, M.L. The Barthel Index: Italian translation, adaptation and validation. Int. J. Neurol. Neurother. 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesio, L.; Granger, C.V.; Perucca, L.; Franchignoni, F.P.; Battaglia, M.A.; Russell, C.F. The FIMTM instrument in the United States and Italy: A comparative study. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slade, A.; Penta, M.; Tripolski, M.; Biering-Sørensen, F.; Carter, J.; Marincek, C.; Phillips, S.; Simone, A.; Tennant, A.; Lundgren-Nilsson, Å.; et al. Cross-cultural validity of functional independence measure items in stroke: A study using Rasch analysis. J. Rehabil. Med. 2005, 37, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nunes, E.V.; Pavlicova, M.; Hu, M.C.; Campbell, A.N.; Miele, G.; Hien, D.; Klein, D.F. Baseline matters: The importance of covariation for baseline severity in the analysis of clinical trials. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abuse 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Paul, J.; Nantha-Aree, M.; Buckley, N.; Shahzad, U.; Cheng, J.; DeBeer, J.; Winemaker, M.; Wismer, D.; Punthakee, D.; et al. Empirical comparison of four baseline covariate adjustment methods in analysis of continuous outcomes in randomized controlled trials. Clin. Epidemiol. 2014, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lövdén, M.; Brehmer, Y.; Li, S.C.; Lindenberger, U. Training-induced compensation versus magnification of individual differences in memory performance. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clifton, L.; Clifton, D.A. The correlation between baseline score and post-intervention score, and its implications for statistical analysis. Trials 2019, 20, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vickers, A.J. Parametric versus non-parametric statistics in the analysis of randomized trials with non-normally distributed data. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feys, J. New nonparametric rank tests for interactions in factorial designs with repeated measures. J. Mod. Appl. Stat. Methods 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morris, S.B. Estimating effect sizes from pretest-posttest-control group designs. Organ. Res. Methods 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.M.; Wang, Y.-C.; Lee, C.-H.; Chen, M.-H.; Hsieh, C.-L. A comparison of test–retest reliability and random measurement error of the Barthel Index and modified Barthel Index in patients with chronic stroke. Disabil. Rehabil. 2020, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Putten, J.J.M.F.; Hobart, J.C.; Freeman, J.A.; Thompson, A.J. Measuring change in disability after inpatient rehabilitation: Comparison of the responsiveness of the Barthel Index and the Functional Independence Measure. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karbach, J.; Kray, J. How useful is executive control training? Age differences in near and far transfer of task-switching training. Dev. Sci. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgio, F.; Delazer, M.; Meneghello, F.; Pertl, M.-T.; Semenza, C.; Zamarian, L. Cognitive training improves ratio processing and decision making in patients with mild cognitive impairment. J. Alzheimer’s. Dis. 2018, 64, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weicker, J.; Villringer, A.; Thöne-Otto, A. Can impaired working memory functioning be improved by training? A meta-analysis with a special focus on brain injured patients. Neuropsychology 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikravesh, M.; Aghajanzadeh, M.; Maroufizadeh, S.; Saffarian, A.; Jafari, Z. Working memory training in post-stroke aphasia: Near and far transfer effects. J. Commun. Disord. 2021, 89, 106077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åkerlund, E.; Esbjörnsson, E.; Sunnerhagen, K.S.; Björkdahl, A. Can computerized working memory training improve impaired working memory, cognition and psychological health? Brain Inj. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamenova, V.; Levine, B. Effectiveness of goal management training® in improving executive functions: A meta-analysis. Neuropsychol. Rehabil. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tornås, S.; Løvstad, M.; Solbakk, A.-K.; Evans, J.; Endestad, T.; Hol, P.K.; Schanke, A.-K.; Stubberud, J. Rehabilitation of executive functions in patients with chronic acquired brain injury with goal management training, external cuing, and emotional regulation: A randomized controlled trial. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2016, 22, 436–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokopenko, S.V.; Mozheyko, E.Y.; Petrova, M.M.; Koryagina, T.D.; Kaskaeva, D.S.; Chernykh, T.V.; Shvetzova, I.N.; Bezdenezhnih, A.F. Correction of post-stroke cognitive impairments using computer programs. J. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 325, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, R.; Leonardi, S.; Spadaro, L.; Russo, M.; Aragona, B.; Torrisi, M.; Maggio, M.G.; Bramanti, A.; Naro, A.; De Cola, M.C.; et al. Improving cognitive function in patients with stroke: Can computerized training be the future? J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 27, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Tao, J.; Gao, Y.; Yin, D.; Chen, A.; Chen, L. Analysis of central mechanism of cognitive training on cognitive impairment after stroke: Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging study. J. Int. Med. Res. 2014, 42, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.A.; Schmitt, F.A.; Smith, C.D.; Gold, B.T. Distinct patterns of default mode and executive control network circuitry contribute to present and future executive function in older adults. Neuroimage 2019, 195, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Cao, X.; Hou, C.; Li, T.; Cheng, Y.; Jiang, L.; Luo, C.; Li, C.; Yao, D. Effects of cognitive training on resting-state functional connectivity of default mode, salience, and central executive networks. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McDonald, M.W.; Black, S.E.; Copland, D.A.; Corbett, D.; Dijkhuizen, R.M.; Farr, T.D.; Jeffers, M.S.; Kalaria, R.N.; Karayanidis, F.; Leff, A.P.; et al. Cognition in stroke rehabilitation and recovery research: Consensus-based core recommendations from the second stroke recovery and rehabilitation roundtable. Int. J. Stroke 2019, 14, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Training Group (n = 18) | Control Group (n = 19) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 64.6 (12.7) | 64.9 (12.7) | 0.946 |
| M/F | 12/6 | 14/5 | 0.728 |
| Education (years) | 9.4 (4) | 9.3 (4.2) | 0.925 |
| MMSE | 25.1 (2.5) | 24.6 (3.3) | 0.557 |
| TIB | 106.1 (9.4) | 101.1 (11.7) | 0.189 |
| Time since event (months) | 3.1 (2.4) | 4.2 (3.4) | 0.259 |
| Etiology | |||
| Ischemia | 13 | 12 | 0.999 |
| Hemorrhage | 6 | 6 | |
| Lesion side | |||
| Left hemisphere | 7 | 7 | 0.956 |
| Right hemisphere | 9 | 11 | |
| Bilateral | 1 | 1 | |
| Symptomatology | |||
| Aphasia, dysartria | 6 | 10 | 0.671 |
| Neglect | 7 | 8 | |
| Sensory-motor impairments (e.g., hemiplegia/ hemiparesis) | 18 | 19 | |
| Cortical visual impairments (e.g., hemianopsia) | 4 | 2 | |
| Rehabilitation program | |||
| Speech therapy | 5 | 9 | 0.803 |
| Motor therapy | 18 | 18 | |
| Occupational therapy | 8 | 8 | |
| Neuropsychological rehab | 12 | 17 | |
| Training Group | Control Group | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | T1 | n | p | T0 | T1 | n | p | d | |
| Memory | |||||||||
| Digit span forward | 4.6 (1) | 5.2 (0.9) | 16 | 0.050 | 4.7 (1) | 4.9 (0.9) | 16 | 0.331 | 0.56 |
| Digit span backward | 3.5 (0.8) | 3.2 (1.1) | 16 | 0.462 | 3.1 (1.3) | 2.7 (1) | 16 | 0.353 | 0.12 |
| Corsi block-tapping | 3.9 (0.9) | 4.2 (1) | 18 | 0.19 | 3.8 (1.1) | 4 (0.8) | 18 | 0.589 | 0.13 |
| Attention and processing speed | |||||||||
| Attentional matrices | 36.7 (13.5) | 42.6 (12.7) | 18 | 0.001 | 34.3 (10.6) | 37.1 (10.2) | 19 | 0.115 | 0.32 |
| TMT-A (s) | 87.1 (46.3) | 82.3 (55.3) | 17 | 0.543 | 77.9 (37.9) | 68.9 (28.2) | 16 | 0.077 | 0.16 |
| Language | |||||||||
| Naming | 14 (1.4) | 14.1 (1.6) | 17 | 0.276 | 13.8 (1.5) | 14.3 (1) | 17 | 0.069 | −0.37 |
| Phonemic fluency | 24.1 (11.8) | 29.1 (11.2) | 14 | 0.020 | 21.6 (11.3) | 22.6 (11.7) | 16 | 0.569 | 0.41 |
| Semantic fluency | 33.8 (13.3) | 34.2 (10.7) | 9 | 0.872 | 25.7 (11.3) | 26.6 (8) | 15 | 0.554 | −0.05 |
| Executive functions | |||||||||
| WCST cat | 4 (2) | 4.2 (1.9) | 16 | 0.521 | 3.2 (2) | 3.2 (1.9) | 16 | 0.807 | 0.13 |
| WCST err | 6.6 (4.4) | 5.4 (6.3) | 16 | 0.504 | 7 (4.7) | 7.2 (5.1) | 16 | 0.574 | −0.41 |
| Five Point error index | 24.3 (22.1) | 22.5 (24.3) | 18 | 0.802 | 24.4 (20.3) | 18.6 (12.8) | 18 | 0.158 | 0.25 |
| Stroop IES | 45.2 (45.1) | 37.5 (15.6) | 15 | 0.532 | 47.7 (26.4) | 44.6 (28.2) | 13 | 0.158 | −0.49 |
| Functional scales | |||||||||
| Barthel index | 25.5 (23.6) | 75 (15) | 18 | <0.001 | 24.5 (18.5) | 66.8 (20) | 19 | <0.001 | 0.42 |
| FIM | 56.3 (16.7) | 92.8 (13.5) | 18 | <0.001 | 53.4 (16.4) | 87.4 (21.1) | 19 | <0.001 | 0.19 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tarantino, V.; Burgio, F.; Toffano, R.; Rigon, E.; Meneghello, F.; Weis, L.; Vallesi, A. Efficacy of a Training on Executive Functions in Potentiating Rehabilitation Effects in Stroke Patients. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11081002
Tarantino V, Burgio F, Toffano R, Rigon E, Meneghello F, Weis L, Vallesi A. Efficacy of a Training on Executive Functions in Potentiating Rehabilitation Effects in Stroke Patients. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(8):1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11081002
Chicago/Turabian StyleTarantino, Vincenza, Francesca Burgio, Roberta Toffano, Elena Rigon, Francesca Meneghello, Luca Weis, and Antonino Vallesi. 2021. "Efficacy of a Training on Executive Functions in Potentiating Rehabilitation Effects in Stroke Patients" Brain Sciences 11, no. 8: 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11081002
APA StyleTarantino, V., Burgio, F., Toffano, R., Rigon, E., Meneghello, F., Weis, L., & Vallesi, A. (2021). Efficacy of a Training on Executive Functions in Potentiating Rehabilitation Effects in Stroke Patients. Brain Sciences, 11(8), 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11081002








