Neurosurgical Management and Outcome Parameters in 237 Patients with Spondylodiscitis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of the Patients
3.2. Symptoms and Neurological Status
3.3. Laboratory Findings and Microbiology
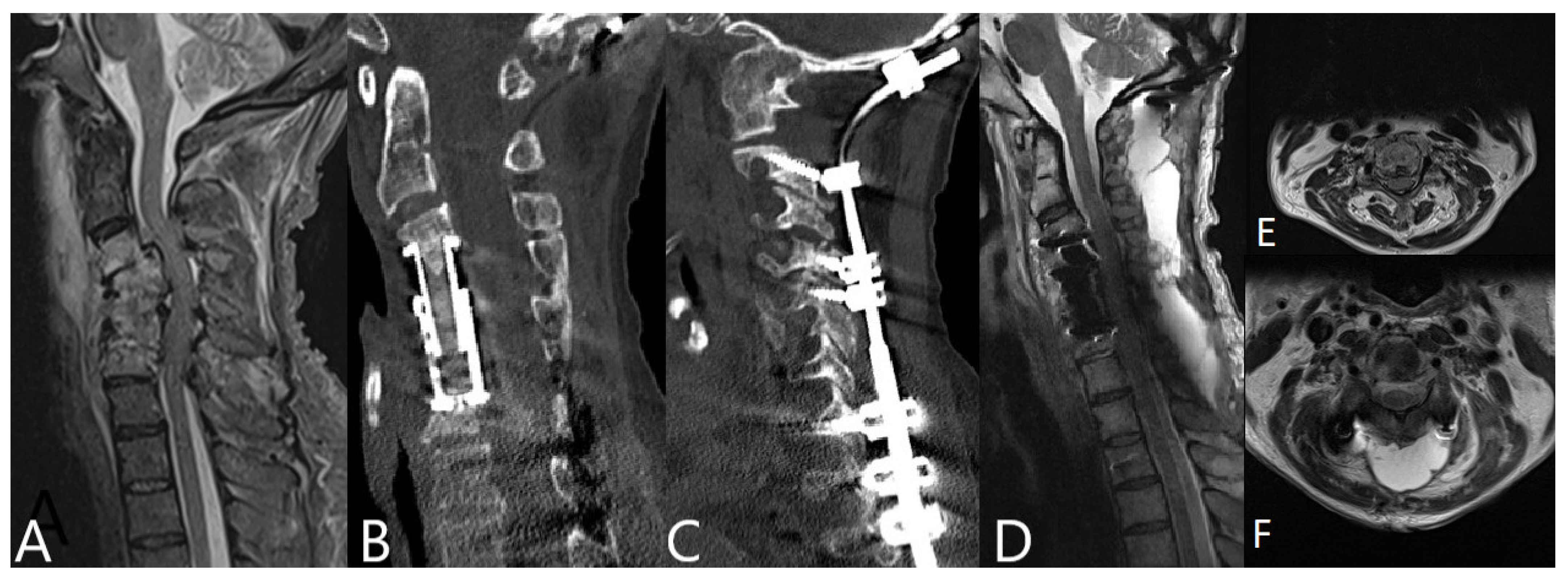
3.4. Operative Therapy
3.5. Etiology and Concomitant Infections
3.6. Antibiotic Therapy
3.7. Outcome
3.7.1. Healing of Infection and Recovery of Infection Parameters
3.7.2. Pain Reduction and Neurological Status
3.7.3. Outcome Measurement
4. Discussion
4.1. Conservative vs. Operative Treatment of Spondylodiscitis
4.2. General Characteristics, Neurological Deficits and Mortality
4.3. Value of Measurement of Laboratory Infection Parameters
4.4. Surgical Therapy
4.5. Influence of Concomitant Infections
4.6. Outcome Parameters
4.7. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pola, E.; Taccari, F.; Autore, G.; Giovannenze, F.; Pambianco, V.; Cauda, R.; Maccauro, G.; Fantoni, M. Multidisciplinary management of pyogenic spondylodiscitis: Epidemiological and clinical features, prognostic factors and long-term outcomes in 207 patients. Eur. Spine J. 2018, 27, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouliouris, T.; Aliyu, S.H.; Brown, N.M. Spondylodiscitis: Update on diagnosis and management. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nickerson, E.K.; Sinha, R. Vertebral osteomyelitis in adults: An update. Br. Med. Bull. 2016, 117, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kehrer, M.; Pedersen, C.; Jensen, T.G.; Lassen, A.T. Increasing incidence of pyogenic spondylodiscitis: A 14-year population-based study. J. Infect. 2014, 68, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kehrer, M.; Pedersen, C.; Jensen, T.G.; Hallas, J.; Lassen, A.T. Increased short- and long-term mortality among patients with infectious spondylodiscitis compared with a reference population. Spine J. 2015, 15, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren Gök, S.; Kaptanoğlu, E.; Celikbaş, A.; Ergönül, O.; Baykam, N.; Eroğlu, M.; Dokuzoğuz, B. Vertebral osteomyelitis: Clinical features and diagnosis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar]
- Ramanathan, D.; Sahasrabudhe, N.; Kim, E. Disseminated Coccidioidomycosis to the Spine-Case Series and Review of Literature. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, K.H.; Lee, M.S.; Hong, I.K.; Sung, J.Y.; Choi, S.H.; Park, S.O.; Shin, M.J.; Chung, H.W.; Lee, S.H. Bone involvement in secondary syphilis: A case report and systematic review of the literature. Sex. Transm. Dis. 2014, 41, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herren, C.; Jung, N.; Pishnamaz, M.; Breuninger, M.; Siewe, J.; Sobottke, R. Spondylodiscitis: Diagnosis and Treatment Options. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2017, 114, 875–882. [Google Scholar]
- Sobottke, R.; Röllinghoff, M.; Zarghooni, K.; Schlüter-Brust, K.; Delank, K.S.; Seifert, H.; Zweig, T.; Eysel, P. Spondylodiscitis in the elderly patient: Clinical mid-term results and quality of life. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2010, 130, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackermair, S.; Egermann, H.; Müller, A. Distribution of Underlying Causative Organisms, Patient Age, and Survival in Spontaneous spondylodiscitis with Special Focus on Elderly Patients. J. Neurol. Surg. Part A Cent. Eur. Neurosurg. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustemi, O.; Raneri, F.; Alvaro, L.; Gazzola, L.; Beggio, G.; Rossetto, L.; Cervelli, P. Single-approach vertebral osteosynthesis in the treatment of spinal osteolysis by spondylodiscitis. Neurosurg. Focus 2019, 46, E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quack, V.; Hermann, I.; Rath, B.; Dietrich, K.; Spreckelsen, C.; Lüring, C.; Arbab, D.; Mueller, C.-A.; Shousha, M.; Clusmann, H. Current treatment strategies for spondylodiscitis in surgical clinics in Germany. Z Orthop. Unf. 2014, 152, 577–583. [Google Scholar]
- Berbari, E.F.; Kanj, S.S.; Kowalski, T.J.; Darouiche, R.O.; Widmer, A.F.; Schmitt, S.K.; Hendershot, E.F.; Holtom, P.D.; Huddleston, P.M., III; Petermann, G.W.; et al. Executive Summary: 2015 Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Native Vertebral Osteomyelitis in Adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, F.S.; Kline, M.J. Diagnostic yield of CT-guided percutaneous aspiration procedures in suspected spontaneous infectious diskitis. Radiology 2001, 218, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pola, E.; Autore, G.; Formica, V.M.; Pambianco, V.; Colangelo, D.; Cauda, R.; Fantoni, M. New classification for the treatment of pyogenic spondylodiscitis: Validation study on a population of 250 patients with a follow-up of 2 years. Eur. Spine J. 2017, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lener, S.; Hartmann, S.; Barbagallo, G.M.V.; Certo, F.; Thomé, C.; Tschugg, A. Management of spinal infection: A review of the literature. Acta Neurochir. 2018, 160, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behmanesh, B.; Gessler, F.; Schnoes, K.; Dubinski, D.; Won, S.Y.; Konczalla, J.; Seifert, V.; Weise, L.; Setzer, M. Infective endocarditis in patients with pyogenic spondylodiscitis: Implications for diagnosis and therapy. Neurosurg. Focus 2019, 46, E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shiban, E.; Janssen, I.; Wostrack, M.; Krieg, S.M.; Ringel, F.; Meyer, B.; Stoffel, M. A retrospective study of 113 consecutive cases of surgically treated spondylodiscitis patients. A single-center experience. Acta Neurochir. 2014, 156, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farah, K.; Peyriere, H.; Graillon, T.; Prost, S.; Dufour, H.; Blondel, B.; Fuentes, S. Minimally invasive posterior fixation and anterior debridement-fusion for thoracolumbar spondylodiscitis: A 40-case series and review of the literature. Neurochirurgie 2020, 66, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.T.; Yang, S.C.; Niu, C.C.; Lai, P.L.; Lee, M.H.; Chen, L.H.; Chen, W.-J. Early surgery with antibiotics treatment had better clinical outcomes than antibiotics treatment alone in patients with pyogenic spondylodiscitis: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valancius, K.; Hansen, E.S.; Høy, K.; Helmig, P.; Niedermann, B.; Bünger, C. Failure modes in conservative and surgical management of infectious spondylodiscitis. Eur. Spine J. 2013, 22, 1837–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Nammari, S.S.; Lucas, J.D.; Lam, K.S. Hematogenous methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus spondylodiscitis. Spine 2007, 32, 2480–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiban, E.; Janssen, I.; Wostrack, M.; Krieg, S.M.; Horanin, M.; Stoffel, M.; Meyer, B.; Ringel, F. Spondylodiscitis by drug-multiresistant bacteria: A single-center experience of 25 cases. Spine J. 2014, 14, 2826–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appalanaidu, N.; Shafafy, R.; Gee, C.; Brogan, K.; Karmani, S.; Morassi, G.; Elsayed, S. Predicting the need for surgical intervention in patients with spondylodiscitis: The Brighton Spondylodiscitis Score (BSDS). Eur. Spine J. 2019, 28, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, S.; Fernando, H.; Baker, J.F. The Brighton Spondylodiscitis Score Does Not Accurately Predict the Need for Surgery: A Retrospective Cohort Study in New Zealand. Glob. Spine J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezai, A.R.; Woo, H.H.; Errico, T.J.; Cooper, P.R. Contemporary management of spinal osteomyelitis. Neurosurgery 1999, 44, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Jiang, L.S.; Dai, L.Y. Surgical treatment of pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis with spinal instrumentation. Eur. Spine J. 2007, 16, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hee, H.T.; Majd, M.E.; Holt, R.T.; Pienkowski, D. Better treatment of vertebral osteomyelitis using posterior stabilization and titanium mesh cages. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2002, 15, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czigléczki, G.; Benkő, Z.; Misik, F.; Banczerowski, P. Incidence, Morbidity, and Surgical Outcomes of Complex Spinal Inflammatory Syndromes in Adults. World Neurosurg. 2017, 107, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackshota, N.; Nash, A.; Bussey, I.; Shasti, M.; Brown, L.; Vishwanath, V.; Malik, Z.; Banagan, K.E.; Koh, E.Y.; Ludwing, S.C.; et al. Outcomes of multilevel vertebrectomy for spondylodiscitis. Spine J. 2019, 19, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhardt, B.W.; Müller, S.J.; Wagner, A.C.; Oertel, J.M. Anterior cervical spine surgery for the treatment of subaxial cervical spondylodiscitis: A report of 30 consecutive patients. Neurosurg. Focus 2019, 46, E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karadimas, E.J.; Bunger, C.; Lindblad, B.E.; Hansen, E.S.; Høy, K.; Helmig, P.; Kennerup, A.S.; Niedermann, B. Spondylodiscitis. A retrospective study of 163 patients. Acta Orthop. 2008, 79, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Homagk, L.; Homagk, N.; Klauss, J.R.; Roehl, K.; Hofmann, G.O.; Marmelstein, D. Spondylodiscitis severity code: Scoring system for the classification and treatment of non-specific spondylodiscitis. Eur. Spine J. 2016, 25, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michiels, I.; Jäger, M. Spondylodiscitis: Current strategies for diagnosis and treatment. Orthopäde 2017, 46, 785–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragsted, C.; Aagaard, T.; Ohrt-Nissen, S.; Gehrchen, M.; Dahl, B. Mortality and health-related quality of life in patients surgically treated for spondylodiscitis. J. Orthop. Surg. 2017, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemaignen, A.; Ghout, I.; Dinh, A.; Gras, G.; Fantin, B.; Zarrouk, V.; Carlier, R.; Loret, J.E.; Denes, E.; Greder, A.; et al. Characteristics of and risk factors for severe neurological deficit in patients with pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis: A case-control study. Medicine 2017, 96, e6387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhavan, K.; Chieng, L.O.; Armstrong, V.L.; Wang, M.Y. Spondylodiscitis in end-stage renal disease: A systematic review. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2019, 30, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantoni, M.; Trecarichi, E.M.; Rossi, B.; Mazzotta, V.; Di Giacomo, G.; Nasto, L.A.; Di Meco, E.; Pola, E. Epidemiological and clinical features of pyogenic spondylodiscitis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 16, 2–7. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, S.; Schütze, M.; Sola, S.; Piek, J. Nonspecific pyogenic spondylodiscitis: Clinical manifestations, surgical treatment, and outcome in 24 patients. Neurosurg. Focus 2004, 17, E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pee, Y.H.; Park, J.D.; Choi, Y.G.; Lee, S.H. Anterior debridement and fusion followed by posterior pedicle screw fixation in pyogenic spondylodiscitis: Autologous iliac bone strut versus cage. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2008, 8, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobran, M.; Iacoangeli, M.; Nasi, D.; Nocchi, N.; Di Rienzo, A.; di Somma, L.; Colasanti, R.; Vaira, C.; Benigni, R.; Liverotti, V.; et al. Posterior Titanium Screw Fixation without Debridement of Infected Tissue for the Treatment of Thoracolumbar Spontaneous Pyogenic Spondylodiscitis. Asian Spine J. 2016, 10, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foreman, S.C.; Schwaiger, B.J.; Meyer, B.; Gersing, A.S.; Zimmer, C.; Gempt, J.; Kirschke, J.S. Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Parameters Associated with Poor Clinical Outcome in Spondylodiscitis. World Neurosurg. 2017, 104, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maus, U.; Andereya, S.; Gravius, S.; Ohnsorge, J.A.; Miltner, O.; Niedhart, C. Procalcitonin (PCT) as diagnostic tool for the monitoring of spondylodiscitis. Z Orthop. Unf. 2009, 147, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutges, J.P.; Kempen, D.H.; van Dijk, M.; Oner, F.C. Outcome of conservative and surgical treatment of pyogenic spondylodiscitis: A systematic literature review. Eur. Spine J. 2016, 25, 983–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Kim, Y.S.; Peck, K.R.; Kim, E.S.; Cho, S.Y.; Ha, Y.E.; Kang, C.-I.; Chung, D.R.; Song, J.-H. Outcome of culture-negative pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis: Comparison with microbiologically confirmed pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2014, 44, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Wang, M.; Chen, G.; Chen, K.H.; Wan, Y.; Chen, B.; Zou, X.; Peng, X. Early surgery with antibiotic medication was effective and efficient in treating pyogenic spondylodiscitis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobrial, G.M.; Beygi, S.; Viereck, M.J.; Maulucci, C.M.; Sharan, A.; Heller, J.; Jallo, J.; Prasad, S.; Harrop, J.S. Timing in the surgical evacuation of spinal epidural abscesses. Neurosurg. Focus 2014, 37, E1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, B.S.; Kim, K.H.; Kuh, S.U.; Park, J.Y.; Chin, D.K.; Kim, K.S.; Cho, Y.-E. Surgical Treatment in Patients with Cervical Osteomyelitis: Single Institute’s Experiences. Korean J. Spine 2014, 11, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschugg, A.; Hartmann, S.; Lener, S.; Rietzler, A.; Sabrina, N.; Thomé, C. Minimally invasive spine surgery in lumbar spondylodiscitis: A retrospective single-center analysis of 67 cases. Eur. Spine J. 2017, 26, 3141–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, A.P.; Aiyer, S.N.; Kanna, R.M.; Maheswaran, A.; Rajasekaran, S. Pyogenic lumbar spondylodiscitis treated with transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: Safety and outcomes. Int. Orthop. 2016, 40, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaldz, C.; Özdemir, N.; Yaman, O.; Feran, H.G.; Tansug, T.; Minoglu, M. A Retrospective Study of 39 Patients Treated with Anterior Approach of Thoracic and Lumbar Spondylodiscitis: Clinical Manifestations, Anterior Surgical Treatment, and Outcome. Medicine 2015, 94, e2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhsheshian, J.; Dahdaleh, N.S.; Lam, S.K.; Savage, J.W.; Smith, Z.A. The use of vancomycin powder in modern spine surgery: Systematic review and meta-analysis of the clinical evidence. World Neurosurg. 2015, 83, 816–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagna, A.; Troeltzsch, M.; Birkenmaier, C.; Schwartz, C.; Suchorska, B.; Zausinger, S. Oral Cavity Infection: An Underestimated Source of Pyogenic Spondylodiscitis? J. Neurol. Surg. Part A Cent. Eur. Neurosurg. 2018, 79, 218–223. [Google Scholar]
- van Gerven, C.; Eid, K.; Krüger, T.; Fell, M.; Kendoff, D.; Friedrich, M.; Kraft, C.N. Serum C-reactive protein and WBC count in conservatively and operatively managed bacterial spondylodiscitis. J. Orthop. Surg. 2021, 29, 2309499020968296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntalos, D.; Schoof, B.; Thiesen, D.M.; Viezens, L.; Kleinertz, H.; Rohde, H.; Both, A.; Luebke, A.; Strahl, A.; Dreimann, M.; et al. Implementation of a multidisciplinary infections conference improves the treatment of spondylodiscitis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschugg, A.; Lener, S.; Hartmann, S.; Rietzler, A.; Neururer, S.; Thomé, C. Primary acquired spondylodiscitis shows a more severe course than spondylodiscitis following spine surgery: A single-center retrospective study of 159 cases. Neurosurg. Rev. 2018, 41, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, D.; Kim, S.W.; Jeon, I. Antimicrobial therapy and assessing therapeutic response in culture-negative pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis: A retrospective comparative study with culture-positive pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Patient Characteristics | Number |
|---|---|
| Overall number of patients (n) | n = 237 (100%) |
| Gender | |
| Male | 150 (63.3%) |
| Mean age (years) | 71.4 (Standard deviation SD ± 12.9) |
| Mean follow-up (months) | 31.62 (SD ± 19.5) |
| MRI of the spine at follow-up | 125 patients (52.7%) |
| Average duration of hospital stay (days) | 14.1 (SD ± 8.2) |
| Mortality | |
| Death during the initial hospital stay | 21 patients (8.9%) |
| Death up to two years following discharge | 5 (2.1%) |
| Spine level (n) | |
| Cervical | 45 patients (19%) |
| Thoracic | 73 (30.8%) |
| Lumbosacral | 119 (50.2%) |
| Psoas muscle abscess | 35 (14.8%) |
| Spinal levels (n) | |
| One level | 174 patients (73.4%) |
| Two levels | 44 (18.7%) |
| Three levels | 7 (3%) |
| Four or more levels | 12 (5%) |
| Mean number of infected levels (n) | 1.33 (SD: 1.204) |
| Epidural empyema (n) | |
| Present | 146 (61.6%) |
| Absent | 91 (38.4%) |
| Mean number of segments of empyema spread (n) | 1.43 (SD 2.165) |
| Concomitant diseases | 185 patients (78%) |
| Two or more diseases | 155 (65.4%) |
| Arterial hypertension | 145 (61.2%) |
| Renal insufficiency | 70 (29.5%) |
| Lung diseases | 81 (34.2%) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 74 (31.2%) |
| Malignant primary tumors | 46 (19.4%) |
| Obesity | 40 (16.9%) |
| History of alcohol abuse | 18 (7.6%) |
| Smokers | 26 (11%) |
| History of drug abuse | 9 (3.8%) |
| Patient Characteristics | Number |
|---|---|
| Pain preoperative | 225 patients (94.9%) |
| Mean preoperative VAS | 8.17 (SD: 2.5). |
| Mean postoperative VAS | 2.03 (SD: 0.19), p < 0.001 |
| Neurological deficits preoperative | 172 patients (72.6%) |
| Motor deficits with paresis of one or more muscles | 63 patients (26.6%) |
| Motor deficits with paraparesis | 22 patients (9.3%) |
| Motor deficits with tetraparesis | 4 patients (1.7%) |
| Sensory deficits | 75 patients (31.6%) |
| Ataxia | 30 patients (12.7%) |
| Time from onset of symptoms to diagnosis | 17.9 days (range 1–67 days, SD: 14.8). |
| Neurological status at follow-up | |
| Improved | 101 patients (42.6%), p = 0.002 |
| Unchanged | 95 patients (40%) |
| Worsened | 15 patients (6.3%) |
| Laboratory Findings | Value |
|---|---|
| Mean leukocyte (WBC) count preoperative (G/L) | 11.66 (SD: 5.28) |
| Mean leukocyte (WBC) count postoperative (G/L) | 8. 03 (SD: 4.05), p < 0.001 |
| Mean C-reactive protein (CRP) preoperative (mg/L) | 160.8 (SD: 159.52) |
| Mean C-reactive protein (CRP) postoperative (mg/L) | 45.44 (SD: 68.85), p < 0.001 |
| Microbiological findings | |
| Isolation of pathogen in intraoperative specimen (n = 237) No | 57 patients (24%) |
| Yes | 180 patients (76%) |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 77 |
| MRSA | 13 |
| Streptococcus spp. | 8 |
| Enterococcus spp. | 8 |
| Other | 74 |
| Isolation of pathogen in blood culture (n = 237) | |
| No | 182 patients (76.8%) |
| Yes | 55 patients (23.2%) |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 26 (11%) |
| Pathogens in patients who died during the initial hospital stay | 21 patients |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 5 |
| MRSA | 2 |
| Streptococcus spp. | 1 |
| No pathogen isolation | 13 |
| Operative Therapy | Number of Patients |
|---|---|
| Overall number of patients | 237 (100%) |
| Cervical spine | 45 |
| Ventral discectomy with PEEK (Polyetheretherketon) cage | 31 |
| Corpectomy with Titanium expandable cage | 14 |
| Additional dorsal stabilization | 23 |
| Thoracic and lumbar spine | |
| Decompression and empyema evacuation without stabilization | 54 |
| Dorsal stabilization | 138 |
| Without cage | 36 |
| With cage | 102 |
| TLIF (Transforaminal interbody fusion) PEEK Cage | 45 |
| TLIF Titan Cage | 35 |
| XLIF (Extreme lateral interbody fusion) PEEK Cage | 22 |
| Dorsal stabilization overall | 161 |
| One segment | 25 |
| Two segments | 47 |
| Three and more segments | 89 |
| Single surgery | 122 (51.5%) |
| Multiple surgeries | 115 (48.5%) |
| Early surgery (within 24 h) | 222 (93.7%) |
| Psoas muscle abscess | 35 |
| CT-guided punction | 19 |
| Conservative therapy | 16 |
| Surgical complications | 51 (21.5%) |
| Hardware failure | 28 |
| Wound healing deficits | 44 |
| Concomitant Infections | Patients |
|---|---|
| Overall number of patients | 237 (100%) |
| Present | 89 (37.6%) |
| Pneumonia | 48 (20.25%) |
| Urinary tract infections | 40 (16.9%) |
| Endocarditis | 10 (4.2%) |
| Stap aureus | 7 |
| MRSA | 1 |
| Haemophilus influenzae | 1 |
| Pseudomonos aeruginosa | 1 |
| Sepsis | 46 (19.4%) |
| Antibiotic Therapy | Number (Days) |
|---|---|
| Mean time of application of empiric IV antibiotic therapy | 9.6 ± 3.4 (SD:11) |
| Mean total time of application of IV antibiotic therapy (empiric and tailored) | 20.5 (SD: 22, range 2–297 days) |
| Oral antibiotic therapy in cases where pathogens could have been isolated from the intraoperative specimen | 47.4 ± 0.9 (SD:45.2). |
| Cummulative oral antibiotic therapy in all cases | 58.9 (SD: 46.3, range 2–462 days) |
| Mean time of cummulative application of antibiotic therapy | 73.9 (SD: 54) |
| Outcome Parameters | Outcome (n = 237 Patients) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Significant decline of C-reactive protein, significant decline of VAS score, improved or unchanged neurological status | Favorable (n = 156) | p = 0.005 |
| Absence of concomitant infections | Favorable (n = 148) | p = 0.005 |
| Completely normalized CRP_value (CRP less than 5 mg/L) | Favorable (n = 96) | p = 0.02 |
| Antibiotic therapy longer than 6 weeks | Favorable (n = 91) | p = 0.017 |
| Higher preoperative CRP value | Unfavorable (n = 85) | p = 0.009 |
| Postoperative spondylodiscitis | Unfavorable (n = 62) | p < 0.02 |
| Recurrent spondylodiscitis | Unfavorable (n = 18) | p < 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pojskić, M.; Carl, B.; Schmöckel, V.; Völlger, B.; Nimsky, C.; Saβ, B. Neurosurgical Management and Outcome Parameters in 237 Patients with Spondylodiscitis. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11081019
Pojskić M, Carl B, Schmöckel V, Völlger B, Nimsky C, Saβ B. Neurosurgical Management and Outcome Parameters in 237 Patients with Spondylodiscitis. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(8):1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11081019
Chicago/Turabian StylePojskić, Mirza, Barbara Carl, Vincent Schmöckel, Benjamin Völlger, Christopher Nimsky, and Benjamin Saβ. 2021. "Neurosurgical Management and Outcome Parameters in 237 Patients with Spondylodiscitis" Brain Sciences 11, no. 8: 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11081019
APA StylePojskić, M., Carl, B., Schmöckel, V., Völlger, B., Nimsky, C., & Saβ, B. (2021). Neurosurgical Management and Outcome Parameters in 237 Patients with Spondylodiscitis. Brain Sciences, 11(8), 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11081019








