Intracranial Compliance Assessed by Intracranial Pressure Pulse Waveform †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Clinical and Intracranial Variables
2.4. Data Acquisition and Analysis
2.5. Sample Size
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
Sample Features
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zamir, M.; Moir, M.E.; Klassen, S.A.; Balestrini, C.S.; Shoemaker, J.K. Cerebrovascular Compliance Within the Rigid Confines of the Skull. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czosnyka, Z.H.; Lalou, A.D.; Nabbanja, E.; Garnett, M.; Keong, N.C.; Schmidt, E.A.; Kim, D.J.; Czosnyka, M. Lower Breakpoint of Intracranial Amplitude-Pressure Relationship in Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2021, 131, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierska, A.; Kasprowicz, M.; Czosnyka, M.; Placek, M.M.; Baledent, O.; Smielewski, P.; Czosnyka, Z. Compliance of the cerebrospinal space: Comparison of three methods. Acta Neurochir. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canac, N.; Jalaleddini, K.; Thorpe, S.G.; Thibeault, C.M.; Hamilton, R.B. Review: Pathophysiology of intracranial hypertension and noninvasive intracranial pressure monitoring. Fluids Barriers CNS 2020, 17, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Roux, P.; Menon, D.K.; Citerio, G.; Vespa, P.; Bader, M.K.; Brophy, G.; Diringer, M.N.; Stocchetti, N.; Videtta, W.; Armonda, R.; et al. The International Multidisciplinary Consensus Conference on Multimodality Monitoring in Neurocritical Care: Evidentiary tables: A statement for healthcare professionals from the Neurocritical Care Society and the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Neurocrit. Care 2014, 21 (Suppl. 2), S297–S361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robba, C.; Graziano, F.; Rebora, P.; Elli, F.; Giussani, C.; Oddo, M.; Meyfroidt, G.; Helbok, R.; Taccone, F.S.; Prisco, L.; et al. Intracranial pressure monitoring in patients with acute brain injury in the intensive care unit (SYNAPSE-ICU): An international, prospective observational cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nucci, C.G.; De Bonis, P.; Mangiola, A.; Santini, P.; Sciandrone, M.; Risi, A.; Anile, C. Intracranial pressure wave morphological classification: Automated analysis and clinical validation. Acta Neurochir. (Wien) 2016, 158, 581–588, discussion 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, E.R.; Rowan, J.O.; Galbraith, S. Analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid pulse wave in intracranial pressure. J. Neurosurg. 1983, 59, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai Ocamoto, G.; Spavieri Junior, D.L.; Matos Ribeiro, J.A.; Frigieri Vilela, G.H.; Catai, A.M.; Russo, T.L. Noninvasive Intracranial Pressure Monitoring in Chronic Stroke Patients with Sedentary Behavior: A Pilot Study. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2021, 131, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Jia, X.; Pahren, L.; Lee, J.; Foreman, B. Intracranial Pressure Monitoring Signals After Traumatic Brain Injury: A Narrative Overview and Conceptual Data Science Framework. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ince, J.; Mankoo, A.S.; Kadicheeni, M.; Swienton, D.; Panerai, R.B.; Robinson, T.G.; Minhas, J.S. Cerebrovascular tone and resistance measures differ between healthy control and patients with acute intracerebral haemorrhage: Exploratory analyses from the BREATHE-ICH study. Physiol. Meas. 2021, 42, 055001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czosnyka, M. Brain Venous Blood Outflow. Neurocrit. Care 2019, 31, 249–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, J.Y.; Kirkness, C.; Vicini, P.; Burr, R.; Mitchell, P. Intracranial pressure waveform morphology and intracranial adaptive capacity. Am. J. Crit. Care 2008, 17, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakmi, H.; Joseph, D.K.; Sohail, A.; Tessler, L.; Baltazar, G.; Stright, A. Sinking skin flap syndrome in the multi-trauma patient: A paradoxical management to TBI post craniectomy. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2020, 2020, rjaa172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahuquillo, J.; Dennis, J.A. Decompressive craniectomy for the treatment of high intracranial pressure in closed traumatic brain injury. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 12, Cd003983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czosnyka, M.; Smielewski, P.; Timofeev, I.; Lavinio, A.; Guazzo, E.; Hutchinson, P.; Pickard, J.D. Intracranial pressure: More than a number. Neurosurg. Focus 2007, 22, E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, I.; Shibaki, J.; Padua, B.; Silva, F.; Goncalves, T.; Spavieri-Junior, D.L.; Frigieri, G.; Mascarenhas, S.; Dias, C. Comparison of Waveforms Between Noninvasive and Invasive Monitoring of Intracranial Pressure. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2021, 131, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.Q.; Gao, W.Y.; Shi, Y.P.; Li, X.; Wang, H.Y. Comparison of starches from five plants of Sect. Stenophora Uline and Sect. Lasiophyton Uline of Dioscorea grown in China. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes Rabelo, N.; Goncalves de Sena Barbosa, M.; Pereira Silva Lemos, M.; Brasil, S.; Frigieri, G. Letter to the Editor. Intracranial pressure monitoring: Challenge beyond the threshold numerical value. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 134, 1682–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bor-Seng-Shu, E.; Figueiredo, E.G.; Amorim, R.L.; Teixeira, M.J.; Valbuza, J.S.; de Oliveira, M.M.; Panerai, R.B. Decompressive craniectomy: A meta-analysis of influences on intracranial pressure and cerebral perfusion pressure in the treatment of traumatic brain injury. J. Neurosurg. 2012, 117, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bor-Seng-Shu, E.; Figueiredo, E.G.; Fonoff, E.T.; Fujimoto, Y.; Panerai, R.B.; Teixeira, M.J. Decompressive craniectomy and head injury: Brain morphometry, ICP, cerebral hemodynamics, cerebral microvascular reactivity, and neurochemistry. Neurosurg. Rev. 2013, 36, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escamilla-Ocanas, C.E.; Albores-Ibarra, N. Current status and outlook for the management of intracranial hypertension after traumatic brain injury: Decompressive craniectomy, therapeutic hypothermia, and barbiturates. Neurologia 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Guan, J. Syndrome of trephined: An underreported complication following decompressive craniectomy. Neurosurg. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bor-Seng-Shu, E.; de-Lima-Oliveira, M.; Nogueira, R.C.; Almeida, K.J.; Paschoal, E.H.A.; Paschoal, F.M., Jr. Decompressive Craniectomy for Traumatic Brain Injury: Postoperative TCD Cerebral Hemodynamic Evaluation. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, A.; Paletta, N.; Verma, U.; Grabowska, M.E.; Batchala, P.P.; Abay, S.; Haughey, H.M.; Donahue, J.; Vender, J.; Sethuraman, S.; et al. Limiting Brain Shift in Malignant Hemispheric Infarction by Decompressive Craniectomy. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2021, 30, 105830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenova, Z.B.; Meshcheryakov, S.; Lukyanov, V.; Arsenyev, S. Decompressive Craniectomy for Traumatic Intracranial Hypertension in Children. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2021, 131, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawryluk, G.W.J.; Nielson, J.L.; Huie, J.R.; Zimmermann, L.; Saigal, R.; Ding, Q.; Hirschi, R.; Zeiler, F.A.; Ferguson, A.R.; Manley, G.T. Analysis of Normal High-Frequency Intracranial Pressure Values and Treatment Threshold in Neurocritical Care Patients: Insights into Normal Values and a Potential Treatment Threshold. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil, S.; Paiva, W.S.; de Carvalho Nogueira, R.; Macedo Salinet, A.; Teixeira, M.J. Letter to the Editor. Decompressive craniectomy in TBI: What is beyond static evaluations in terms of prognosis? J. Neurosurg. 2018, 129, 845–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.D.L.; Caldas, J.R.; Teixeira, M.J.; Bor-Seng-Shu, E. Letter to the Editor. PbtO₂ and prognosis after decompressive craniectomy. J. Neurosurg. JNS 2018, 129, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, T.; Lian, W.; Xu, K.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Lu, R.; Liu, M. Effect of combination invasive intracranial pressure (ICP) monitoring and transcranial Doppler in the treatment of severe craniocerebral injury patients with decompressive craniectomy. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2021, 10, 4472–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubillo, S.T.; Parrilla, D.M.; Blanco, J.; Morera, J.; Dominguez, J.; Belmonte, F.; López, P.; Molina, I.; Ruiz, C.; Clemente, F.J.; et al. Prognostic value of changes in brain tissue oxygen pressure before and after decompressive craniectomy following severe traumatic brain injury. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 128, 1538–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Timofeev, I.; Czosnyka, M.; Nortje, J.; Smielewski, P.; Kirkpatrick, P.; Gupta, A.; Hutchinson, P. Effect of decompressive craniectomy on intracranial pressure and cerebrospinal compensation following traumatic brain injury. J. Neurosurg. 2008, 108, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asgari, S.; Bergsneider, M.; Hamilton, R.; Vespa, P.; Hu, X. Consistent changes in intracranial pressure waveform morphology induced by acute hypercapnic cerebral vasodilatation. Neurocrit. Care 2011, 15, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ballestero, M.F.M.; Frigieri, G.; Cabella, B.C.T.; de Oliveira, S.M.; de Oliveira, R.S. Prediction of intracranial hypertension through noninvasive intracranial pressure waveform analysis in pediatric hydrocephalus. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2017, 33, 1517–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil, S.; Renck, A.C.; Taccone, F.S.; Fontoura Solla, D.J.; Tomazini, B.M.; Wayhs, S.Y.; Fonseca, S.; Bassi, E.; Lucena, B.; De Carvalho Nogueira, R.; et al. Obesity and its implications on cerebral circulation and intracranial compliance in severe COVID-19. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasil, S.; Taccone, F.S.; Wahys, S.Y.; Tomazini, B.M.; Annoni, F.; Fonseca, S.; Bassi, E.; Lucena, B.; Nogueira, R.C.; De-Lima-Oliveira, M.; et al. Cerebral Hemodynamics and Intracranial Compliance Impairment in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: A Pilot Study. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robba, C.; Messina, A.; Battaglini, D.; Ball, L.; Brunetti, I.; Bassetti, M.; Giacobbe, D.R.; Vena, A.; Patroniti, N.; Cecconi, M.; et al. Early Effects of Passive Leg-Raising Test, Fluid Challenge, and Norepinephrine on Cerebral Autoregulation and Oxygenation in COVID-19 Critically Ill Patients. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 674466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robba, C.; Ball, L.; Battaglini, D.; Cardim, D.; Moncalvo, E.; Brunetti, I.; Bassetti, M.; Giacobbe, D.R.; Vena, A.; Patroniti, N.; et al. Early effects of ventilatory rescue therapies on systemic and cerebral oxygenation in mechanically ventilated COVID-19 patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: A prospective observational study. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evensen, K.B.; Eide, P.K. Measuring intracranial pressure by invasive, less invasive or non-invasive means: Limitations and avenues for improvement. Fluids Barriers CNS 2020, 17, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkness, C.J.; Mitchell, P.H.; Burr, R.L.; March, K.S.; Newell, D.W. Intracranial pressure waveform analysis: Clinical and research implications. J. Neurosci. Nurs. 2000, 32, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrera, E.; Kim, D.J.; Castellani, G.; Zweifel, C.; Czosnyka, Z.; Kasparowicz, M.; Smielewski, P.; Pickard, J.D.; Czosnyka, M. What shapes pulse amplitude of intracranial pressure? J. Neurotrauma 2010, 27, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
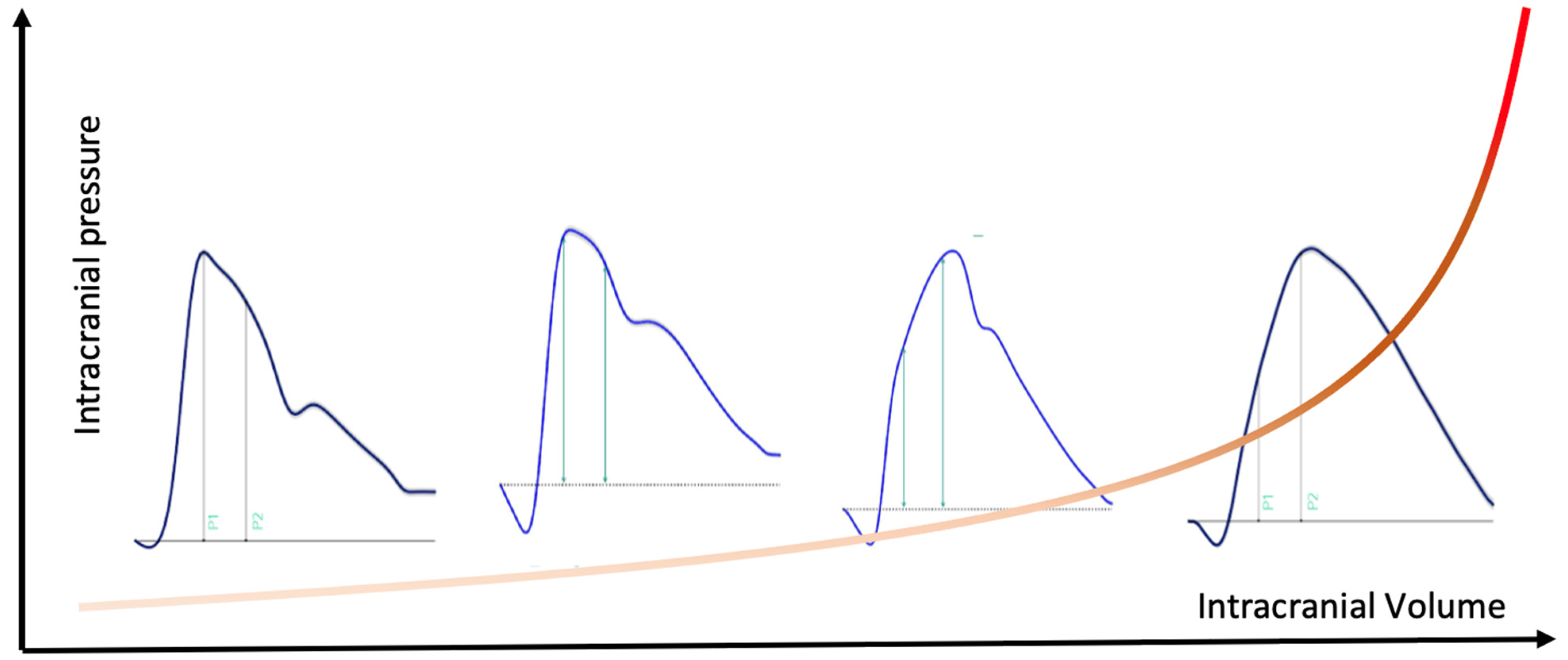

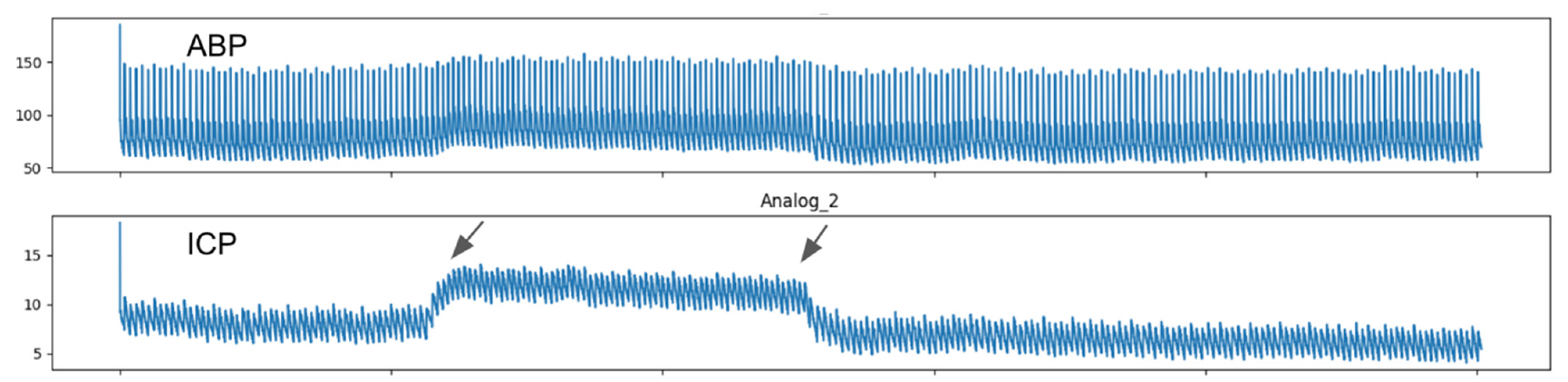

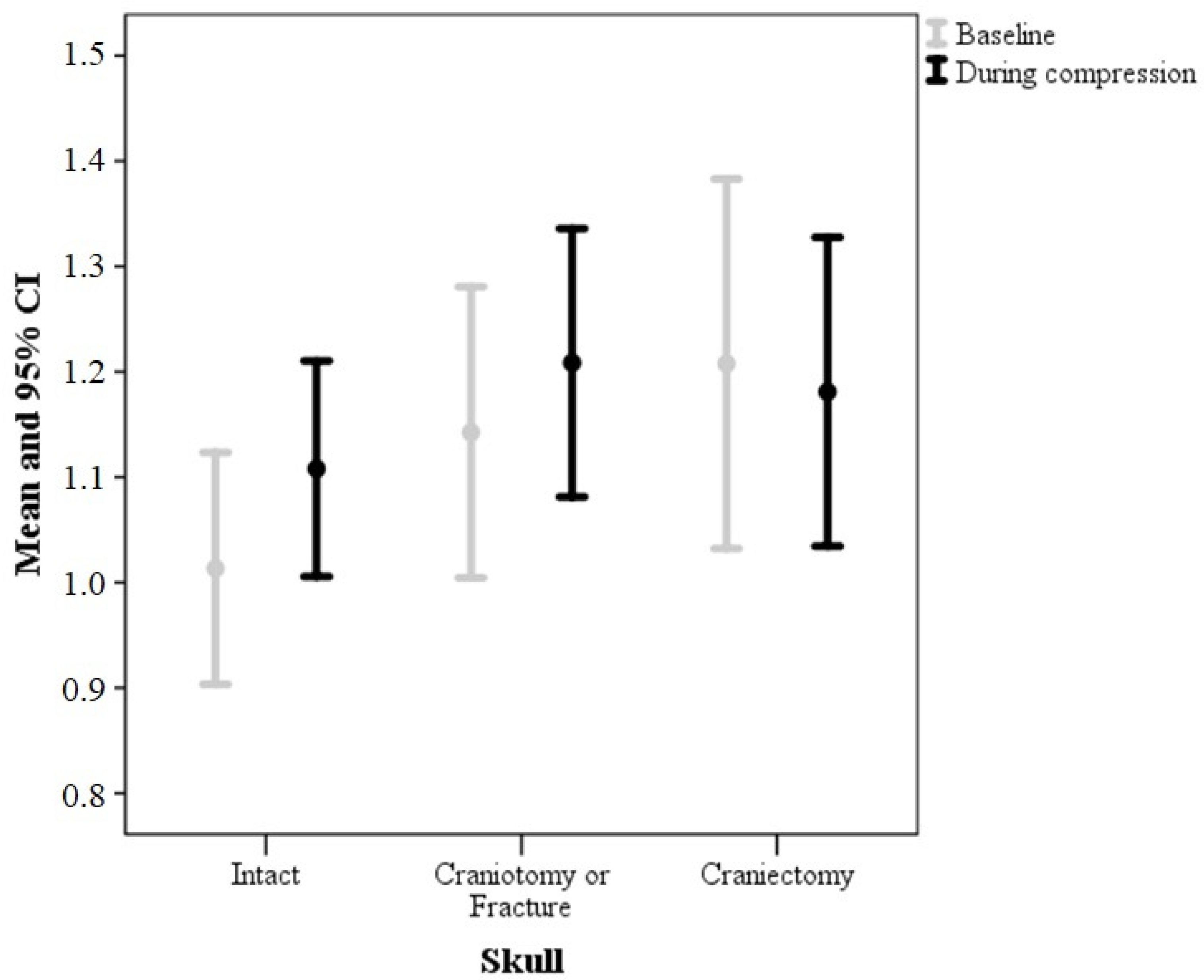

| Variable | Skull | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intact (21) | Craniotomy or Fracture (21) | Craniectomy (15) | ||
| Age | 38.3 ± 15.2 | 36.1 ± 11.1 | 36.5 ± 13.8 | 0.551 |
| Male sex | 15 (71.4) | 10 (47.6) | 12 (80.0) | 0.098 |
| Pathology | 0.028 | |||
| Traumatic brain injury | 17 (81.0) | 14 (66.7) | 9 (60.0) | |
| Subarachnoid hemorrhage | 4 (19.0) | 5 (23.8) | 1 (6.7) | |
| Stroke | 0 (0.0) | 1 (4.8) | 5 (33.3) | |
| Tumor | 0 (0.0) | 1 (4.8) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Hemoglobin | 10.3 ± 1.6 | 10.0 ± 1.5 | 10.3 ± 1.8 | 0.854 |
| <10 mg/dL | 8 (38.1) | 9 (42.9) | 6 (40.0) | 0.951 |
| <9 mg/dL | 5 (23.8) | 4 (19.0) | 4 (26.7) | 0.857 |
| <8 mg/dL | 2 (9.5) | 1 (4.8) | 0 (0.0) | 0.447 |
| SAPS3 | 53.5 ± 12.1 | 62.2 ± 12.6 | 63.2 ± 14.3 | 0.082 |
| Admission GCS | 8.4 ± 4.3 | 7 ± 3.3 | 6.7 ± 3.2 | 0.093 |
| BMI | 22.5 ± 4.2 | 22.9 ± 3.7 | 21.7 ± 2.5 | 0.143 |
| 30 days mortality | 5 (23) | 6 (28) | 5 (33) | 0.075 |
| Parameter | Skull | Baseline | Jugular Vein Compression | Difference (95% CI) | p-Value | Partial η2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intracranial pressure (mmHg) | Intact | 15.11 ± 8.10 | 19.45 ± 7.65 | 4.54 (3.22–5.87) | 0.565 | 0.021 |
| Craniotomy or Fracture | 15.33 ± 6.53 | 19.62 ± 7.44 | 3.90 (2.90–4.91) | |||
| Craniectomy | 20.81 ± 10.22 | 23.93 ± 9.46 | 2.44 (1.64–3.24) | |||
| P2/P1 ratio | Intact | 1.01 ± 0.24 | 1.11 ± 0.22 | 0.09 (0.04–0.15) | 0.010 | 0.161 |
| Craniotomy or Fracture | 1.14 ± 0.30 | 1.21 ± 0.28 | 0.07 (0.02–0.11) | |||
| Craniectomy | 1.21 ± 0.32 | 1.18 ± 0.26 | −0.03 (−0.8–0.03) | |||
| Time-to-peak (ms) | Intact | 0.20 ± 0.08 | 0.21 ± 0.08 | 0.01 (−0.01–0.03) | 0.693 | 0.014 |
| Craniotomy or Fracture | 0.23 ± 0.09 | 0.25 ± 0.08 | 0.02 (−0.01–0.05) | |||
| Craniectomy | 0.22 ± 0.10 | 0.23 ± 0.10 | 0.01 (−0.01–0.03) | |||
| Amplitude (mV) | Intact | 10.87 ± 7.80 | 11.35 ± 7.79 | 0.48 (−0.06–1.03) | 0.739 | 0.011 |
| Craniotomy or Fracture | 5.58 ± 3.32 | 6.06 ± 3.92 | 0.48 (0.07–0.90) | |||
| Craniectomy | 4.31 ± 3.09 | 4.56 ± 3.32 | 0.25 (−0.17–0.67) |
| Variable | Coefficient (95% CI) | SE | Standardized Coefficient | t Value | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Craniectomy (compared to intact or craniotomy/fracture) | −0.09 (−0.15–−0.02) | 0.03 | −0.33 | −2.72 | 0.009 |
| Altered baseline P2/P1 ratio | −0.07 (−0.13–−0.01) | 0.03 | −0.30 | −2.49 | 0.016 |
| Age | −0.001 (−0.002–0.001) | 0.001 | −0.20 | −1.74 | 0.088 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brasil, S.; Solla, D.J.F.; Nogueira, R.d.C.; Jacobsen Teixeira, M.; Malbouisson, L.M.S.; Paiva, W.S. Intracranial Compliance Assessed by Intracranial Pressure Pulse Waveform. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11080971
Brasil S, Solla DJF, Nogueira RdC, Jacobsen Teixeira M, Malbouisson LMS, Paiva WS. Intracranial Compliance Assessed by Intracranial Pressure Pulse Waveform. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(8):971. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11080971
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrasil, Sérgio, Davi Jorge Fontoura Solla, Ricardo de Carvalho Nogueira, Manoel Jacobsen Teixeira, Luiz Marcelo Sá Malbouisson, and Wellingson Silva Paiva. 2021. "Intracranial Compliance Assessed by Intracranial Pressure Pulse Waveform" Brain Sciences 11, no. 8: 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11080971
APA StyleBrasil, S., Solla, D. J. F., Nogueira, R. d. C., Jacobsen Teixeira, M., Malbouisson, L. M. S., & Paiva, W. S. (2021). Intracranial Compliance Assessed by Intracranial Pressure Pulse Waveform. Brain Sciences, 11(8), 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11080971







