Early Right Motor Cortex Response to Happy and Fearful Facial Expressions: A TMS Motor-Evoked Potential Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
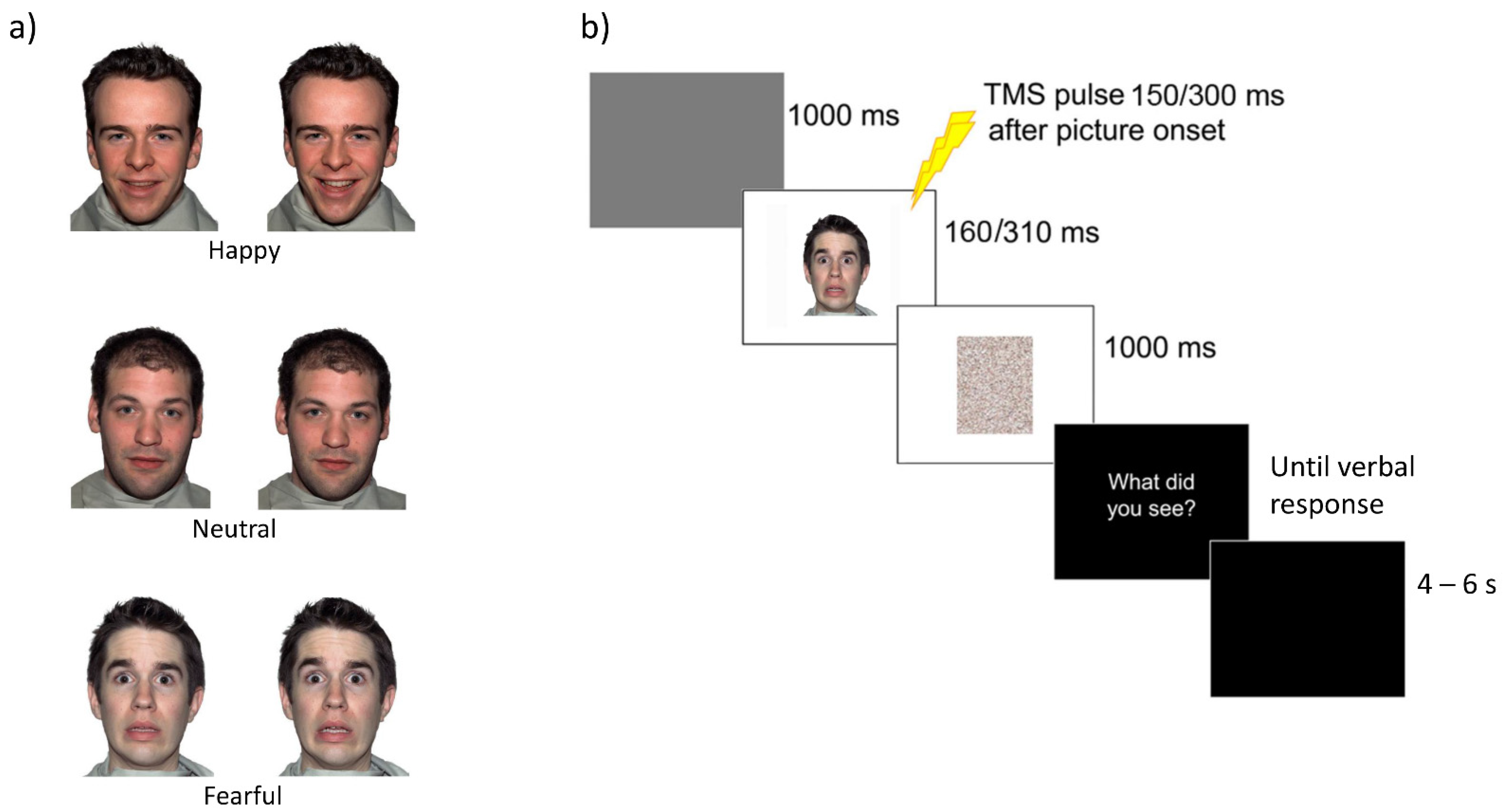
2.2. Visual Stimuli and Pilot Experiments
2.3. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation and Electromyography Recording
2.4. Procedure and Experimental Design
2.5. Subjective Measures
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Subjective Measures
3.2. Neurophysiological Data
3.3. Relations between Changes in Motor Excitability and Dispositional Empathy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olson, I.R.; Marshuetz, C. Facial attractiveness is appraised in a glance. Emotion 2005, 5, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoa, L.; Japee, S.; Ungerleider, L.G. Visual awareness and the detection of fearful faces. Emotion 2005, 5, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bar, M.; Neta, M.; Linz, H. Very first impressions. Emotion 2006, 6, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Willis, J.; Todorov, A. First impressions: Making up your mind after a 100-ms exposure to a face. Psychol. Sci. 2006, 17, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusar-Poli, P.; Placentino, A.; Carletti, F.; Landi, P.; Allen, P.; Surguladze, S.; Benedetti, F.; Abbamonte, M.; Gasparotti, R.; Barale, F.; et al. Functional atlas of emotional faces processing: A voxel-based meta-analysis of 105 functional magnetic resonance imaging studies. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2009, 34, 418–432. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fusar-Poli, P.; Placentino, A.; Carletti, F.; Allen, P.; Landi, P.; Abbamonte, M.; Barale, F.; Perez, J.; McGuire, P.; Politi, P.L. Laterality effect on emotional faces processing: ALE meta-analysis of evidence. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 452, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vytal, K.; Hamann, S. Neuroimaging support for discrete neural correlates of basic emotions: A voxel-based meta-analysis. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2010, 22, 2864–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vuilleumier, P.; Pourtois, G. Distributed and interactive brain mechanisms during emotion face perception: Evidence from functional neuroimaging. Neuropsychologia 2007, 45, 174–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, S.; Bublatzky, F. Attention and emotion: An integrative review of emotional face processing as a function of attention. Cortex 2020, 130, 362–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keysers, C.; Gazzola, V. Expanding the mirror: Vicarious activity for actions, emotions, and sensations. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2009, 19, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, A.; Rychlowska, M.; Korb, S.; Niedenthal, P. Fashioning the face: Sensorimotor simulation contributes to facial expression recognition. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2016, 20, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paracampo, R.; Tidoni, E.; Borgomaneri, S.; di Pellegrino, G.; Avenanti, A. Sensorimotor network crucial for inferring amusement from smiles. Cereb. Cortex 2017, 27, 5116–5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izard, C.E. Innate and universal facial expressions: Evidence from developmental and cross-cultural research. Psychol. Bull. 1994, 115, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekman, P.; Davidson, R.J. The Nature of Emotion: Fundamental Questions; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Frijda, N.H. Emotion experience and its varieties. Emot. Rev. 2009, 1, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, T.; Willi, M.; Jäncke, L. Modulation of corticospinal activity by strong emotions evoked by pictures and classical music: A transcranial magnetic stimulation study. Neuroreport 2007, 18, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajcak, G.; Molnar, C.; George, M.S.; Bolger, K.; Koola, J.; Nahas, Z. Emotion facilitates action: A transcranial magnetic stimulation study of motor cortex excitability during picture viewing. Psychophysiology 2007, 44, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coombes, S.A.; Tandonnet, C.; Fujiyama, H.; Janelle, C.M.; Cauraugh, J.H.; Summers, J.J. Emotion and motor preparation: A transcranial magnetic stimulation study of corticospinal motor tract excitability. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2009, 9, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, C.M.; Lipp, O.V.; Marinovic, W.; Wallis, G.; Riek, S. Increased corticospinal excitability induced by unpleasant visual stimuli. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 481, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Loon, A.M.; van den Wildenberg, W.P.M.; van Stegeren, A.H.; Hajcak, G.; Ridderinkhof, K.R. Emotional stimuli modulate readiness for action: A transcranial magnetic stimulation study. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2010, 10, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borgomaneri, S.; Gazzola, V.; Avenanti, A. Temporal dynamics of motor cortex excitability during perception of natural emotional scenes. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2014, 9, 1451–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borgomaneri, S.; Gazzola, V.; Avenanti, A. Motor mapping of implied actions during perception of emotional body language. Brain Stimul. 2012, 5, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgomaneri, S.; Gazzola, V.; Avenanti, A. Transcranial magnetic stimulation reveals two functionally distinct stages of motor cortex involvement during perception of emotional body language. Brain Struct. Funct. 2015, 220, 2765–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borgomaneri, S.; Vitale, F.; Gazzola, V. Seeing fearful body language rapidly freezes the observer ’ s motor cortex. Cortex 2015, 65, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgomaneri, S.; Vitale, F.; Avenanti, A. Early changes in corticospinal excitability when seeing fearful body expressions. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgomaneri, S.; Vitale, F.; Avenanti, A. Early motor reactivity to observed human body postures is affected by body expression, not gender. Neuropsychologia 2020, 146, 107541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hortensius, R.; de Gelder, B.; Schutter, D.J.L.G. When anger dominates the mind: Increased motor corticospinal excitability in the face of threat. Psychophysiology 2016, 53, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Engelen, T.; Zhan, M.; Sack, A.T.; de Gelder, B. The influence of conscious and unconscious body threat expressions on motor evoked potentials studied with continuous flash suppression. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borgomaneri, S.; Vitale, F.; Avenanti, A. Behavioral inhibition system sensitivity enhances motor cortex suppression when watching fearful body expressions. Brain Struct. Funct. 2017, 222, 3267–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuthbert, B.N.; Schupp, H.T.; Bradley, M.M.; Birbaumer, N.; Lang, P.J. Brain potentials in affective picture processing: Covariation with autonomic arousal and affective report. Biol. Psychol. 2000, 52, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keil, A.; Bradley, M.M.; Hauk, O.; Rockstroh, B.; Elbert, T.; Lang, P.J. Large-scale neural correlates of affective picture processing. Psychophysiology 2002, 39, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olofsson, J.K.; Nordin, S.; Sequeira, H.; Polich, J. Affective picture processing: An integrative review of ERP findings. Biol. Psychol. 2008, 77, 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schutter, D.J.L.G.; Hofman, D.; Van Honk, J. Fearful faces selectively increase corticospinal motor tract excitability: A transcranial magnetic stimulation study. Psychophysiology 2008, 45, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicario, C.M.; Rafal, R.D.; Borgomaneri, S.; Paracampo, R.; Kritikos, A.; Avenanti, A. Pictures of disgusting foods and disgusted facial expressions suppress the tongue motor cortex. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2017, 12, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tottenham, N.; Tanaka, J.W.; Leon, A.C.; McCarry, T.; Nurse, M.; Hare, T.A.; Marcus, D.J.; Westerlund, A.; Casey, B.J.; Nelson, C. The NimStim set of facial expressions: Judgments from untrained research participants. Psychiatry Res. 2009, 168, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fadiga, L.; Fogassi, L.; Pavesi, G.; Rizzolatti, G. Motor facilitation during action observation: A magnetic stimulation study. J. Neurophysiol. 1995, 73, 2608–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avenanti, A.; Candidi, M.; Urgesi, C. Vicarious motor activation during action perception: Beyond correlational evidence. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naish, K.R.; Houston-Price, C.; Bremner, A.J.; Holmes, N.P. Effects of action observation on corticospinal excitability: Muscle specificity, direction, and timing of the mirror response. Neuropsychologia 2014, 64, 331–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainotti, G. Emotional behavior and hemispheric side of the lesion. Cortex 1972, 8, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silberman, E.K.; Weingartner, H. Hemispheric lateralization of functions related to emotion. Brain Cogn. 1986, 5, 322–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bryson, S.E.; McLaren, J.; Wadden, N.P.; MacLean, M. Differential asymmetries for positive and negative emotion: Hemisphere or stimulus effects? Cortex 1991, 27, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borod, J.C. Interhemispheric and intrahemispheric control of emotion: A focus on unilateral brain damage. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 1992, 60, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, R.J.; Hugdahl, K. Brain Asymmetry; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995; ISBN 0262540797. [Google Scholar]
- Borod, J.C. The Neuropsychology of Emotion; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Harmon-Jones, E. Contributions from research on anger and cognitive dissonance to understanding the motivational functions of asymmetrical frontal brain activity. Biol. Psychol. 2004, 67, 51–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carver, C.S.; Harmon-Jones, E. Anger is an approach-related affect: Evidence and implications. Psychol. Bull. 2009, 135, 183–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamm, C.; Batson, C.D.; Decety, J. The neural substrate of human empathy: Effects of perspective-taking and cognitive appraisal. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2007, 19, 42–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamm, C.; Porges, E.C.; Cacioppo, J.T.; Decety, J. Perspective taking is associated with specific facial responses during empathy for pain. Brain Res. 2008, 1227, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morelli, S.A.; Rameson, L.T.; Lieberman, M.D. The neural components of empathy: Predicting daily prosocial behavior. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2012, 9, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gazzola, V.; Aziz-Zadeh, L.; Keysers, C. Empathy and the somatotopic auditory mirror system in humans. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, 1824–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferri, F.; Stoianov, I.P.; Gianelli, C.; D’Amico, L.; Borghi, A.M.; Gallese, V. When action meets emotions: How facial displays of emotion influence goal-related behavior. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepage, J.-F.; Tremblay, S.; Théoret, H. Early non-specific modulation of corticospinal excitability during action observation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2010, 31, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hortensius, R.; Schutter, D.J.L.G.; de Gelder, B. Personal distress and the influence of bystanders on responding to an emergency. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2016, 16, 672–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oldfield, R.C. The assessment and analysis of handedness: The Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 1971, 9, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Hallett, M.; Rossini, P.M.; Pascual-Leone, A.; Nasreldin, M.; Nakatsuka, M.; Koganemaru, S.; Fawi, G.; Group, T.S. of T.C. Safety, ethical considerations, and application guidelines for the use of transcranial magnetic stimulation in clinical practice and research. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2009, 120, 2008–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossini, P.M.; Burke, D.; Chen, R.; Cohen, L.G.; Daskalakis, Z.; Di Iorio, R.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Ferreri, F.; Fitzgerald, P.B.; George, M.S.; et al. Non-invasive electrical and magnetic stimulation of the brain, spinal cord, roots and peripheral nerves: Basic principles and procedures for routine clinical and research application. An updated report from an I.F.C.N. Committee. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 1071–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fourkas, A.D.; Ionta, S.; Aglioti, S.M. Influence of imagined posture and imagery modality on corticospinal excitability. Behav. Brain Res. 2006, 168, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tidoni, E.; Borgomaneri, S.; di Pellegrino, G.; Avenanti, A. Action simulation plays a critical role in deceptive action recognition. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bastani, A.; Jaberzadeh, S. A higher number of TMS-elicited MEP from a combined hotspot improves intra- and inter-session reliability of the upper limb muscles in healthy individuals. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tokimura, H.; Tokimura, Y.; Oliviero, A.; Asakura, T.; Rothwell, J.C. Speech-induced changes in corticospinal excitability. Ann. Neurol. 1996, 40, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meister, I.G.; Boroojerdi, B.; Foltys, H.; Sparing, R.; Huber, W.; Töpper, R. Motor cortex hand area and speech: Implications for the development of language. Neuropsychologia 2003, 41, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Classen, J.; Gerloff, C.; Celnik, P.; Wassermann, E.M.; Hallett, M.; Cohen, L.G. Depression of motor cortex excitability by low-frequency transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neurology 1997, 48, 1398–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.H. Empathy: A Social Psychological Approach; Westview Press: Boulder, CO, USA, 1996; ISBN 0813330017. [Google Scholar]
- Devanne, H.; Lavoie, B.A.; Capaday, C. Input-output properties and gain changes in the human corticospinal pathway. Exp. Brain Res. 1997, 114, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, R. Parametric measures of effect size. In The Handbook of Research Synthesis; Hedges, L.V., Cooper, H., Eds.; Russell Sage Foundation: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 231–244. [Google Scholar]
- Gainotti, G. Emotions and the right hemisphere: Can new data clarify old models? Neuroscientist 2019, 25, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomero-Gallagher, N.; Amunts, K. A short review on emotion processing: A lateralized network of neuronal networks. Brain Struct. Funct. 2021. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanković, M. A conceptual critique of brain lateralization models in emotional face perception: Toward a hemispheric functional-equivalence (HFE) model. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2021, 160, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thierry, G.; Pegna, A.J.; Dodds, C.; Roberts, M.; Basan, S.; Downing, P. An event-related potential component sensitive to images of the human body. Neuroimage 2006, 32, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borhani, K.; Borgomaneri, S.; Làdavas, E.; Bertini, C. The effect of alexithymia on early visual processing of emotional body postures. Biol. Psychol. 2016, 115, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avenanti, A.; Bolognini, N.; Maravita, A.; Aglioti, S.M. Somatic and motor components of action simulation. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 2129–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Urgesi, C.; Maieron, M.; Avenanti, A.; Tidoni, E.; Fabbro, F.; Aglioti, S.M. Simulating the future of actions in the human corticospinal system. Cereb. Cortex 2010, 20, 2511–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Batson, C.D.; Polycarpou, M.P.; Harmon-Jones, E.; Imhoff, H.J.; Mitchener, E.C.; Bednar, L.L.; Klein, T.R.; Highberger, L. Empathy and attitudes: Can feeling for a member of a stigmatized group improve feelings toward the group? J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1997, 72, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avenanti, A.; Minio-Paluello, I.; Bufalari, I.; Aglioti, S.M. The pain of a model in the personality of an onlooker: Influence of state-reactivity and personality traits on embodied empathy for pain. Neuroimage 2009, 44, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbi, M.; Swart, M.; Keysers, C. Empathy for positive and negative emotions in the gustatory cortex. Neuroimage 2007, 34, 1744–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarela, M.V.; Hlushchuk, Y.; Williams, A.C.; Schürmann, M.; Kalso, E.; Hari, R. The compassionate brain: Humans detect intensity of pain from another’s face. Cereb. Cortex 2007, 17, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolassa, I.-T.; Miltner, W.H.R. Psychophysiological correlates of face processing in social phobia. Brain Res. 2006, 1118, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossignol, M.; Campanella, S.; Maurage, P.; Heeren, A.; Falbo, L.; Philippot, P. Enhanced perceptual responses during visual processing of facial stimuli in young socially anxious individuals. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 526, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, C.; Mothes-Lasch, M.; Straube, T. Automatic neural processing of disorder-related stimuli in social anxiety disorder: Faces and more. Front. Psychol. 2013, 4, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wassermann, E.M.; Greenberg, B.D.; Nguyen, M.B.; Murphy, D.L. Motor cortex excitability correlates with an anxiety-related personality trait. Biol. Psychiatry 2001, 50, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, E.J.; Shaw, P.; Giampietro, V.P.; Surguladze, S.; Brammer, M.J.; David, A.S. The role of “shared representations” in social perception and empathy: An fMRI study. Neuroimage 2006, 29, 1173–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriguchi, Y.; Ohnishi, T.; Lane, R.D.; Maeda, M.; Mori, T.; Nemoto, K.; Matsuda, H.; Komaki, G. Impaired self-awareness and theory of mind: An fMRI study of mentalizing in alexithymia. Neuroimage 2006, 32, 1472–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, R.T.; Macaluso, E.; Avenanti, A.; Santangelo, V.; Cazzato, V.; Aglioti, S.M. Their pain is not our pain: Brain and autonomic correlates of empathic resonance with the pain of same and different race individuals. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2013, 34, 3168–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borgomaneri, S.; Bolloni, C.; Sessa, P.; Avenanti, A. Blocking facial mimicry affects recognition of facial and body expressions. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kret, M.E.; Denollet, J.; Grèzes, J.; de Gelder, B. The role of negative affectivity and social inhibition in perceiving social threat: An fMRI study. Neuropsychologia 2011, 49, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Happy Expression | Fearful Expression | Neutral Expression | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Valence | 7.02 ± 1.51 | 2.23 ± 1.34 | 4.76 ± 0.62 |
| Arousal | 5.35 ± 1.72 | 6.45 ± 1.93 | 1.50 ± 1.08 |
| Implied motion | 6.37 ± 1.53 | 6.72 ± 1.55 | 1.03 ± 0.71 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borgomaneri, S.; Vitale, F.; Battaglia, S.; Avenanti, A. Early Right Motor Cortex Response to Happy and Fearful Facial Expressions: A TMS Motor-Evoked Potential Study. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11091203
Borgomaneri S, Vitale F, Battaglia S, Avenanti A. Early Right Motor Cortex Response to Happy and Fearful Facial Expressions: A TMS Motor-Evoked Potential Study. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(9):1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11091203
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorgomaneri, Sara, Francesca Vitale, Simone Battaglia, and Alessio Avenanti. 2021. "Early Right Motor Cortex Response to Happy and Fearful Facial Expressions: A TMS Motor-Evoked Potential Study" Brain Sciences 11, no. 9: 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11091203
APA StyleBorgomaneri, S., Vitale, F., Battaglia, S., & Avenanti, A. (2021). Early Right Motor Cortex Response to Happy and Fearful Facial Expressions: A TMS Motor-Evoked Potential Study. Brain Sciences, 11(9), 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11091203








