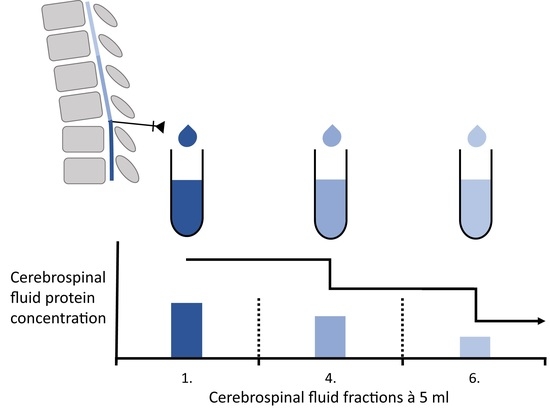
The Influence of the Ventricular-Lumbar Gradient on Cerebrospinal Fluid Analysis in Serial Samples
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. CSF and Serum Analytical Procedures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Differences between Serially Taken CSF Fractions in Patients with NIND
3.2. Differences in the First CSF Fraction between IIH and NPH
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teunissen, C.; Menge, T.; Altintas, A.; Álvarez-Cermeño, J.C.; Bertolotto, A.; Berven, F.S.; Brundin, L.; Comabella, M.; Degn, M.; Deisenhammer, F.; et al. Consensus definitions and application guidelines for control groups in cerebrospinal fluid biomarker studies in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2013, 19, 1802–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverberg, G.D.; Mayo, M.; Saul, T.; Rubenstein, E.; McGuire, D. Alzheimer’s disease, normal-pressure hydrocephalus, and senescent changes in CSF circulatory physiology: A hypothesis. Lancet Neurol. 2003, 2, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.D.; Fisher, C.M.; Hakim, S.; Ojemann, R.G.; Sweet, W.H. Symptomatic Occult Hydrocephalus with Normal Cerebrospinal-Fluid Pressure. N. Engl. J. Med. 1965, 273, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, A.K.; Clarke, C. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Lancet Neurol. 2006, 5, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedman, D.I.; Jacobson, D.M. Diagnostic criteria for idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurology 2002, 59, 1492–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walchenbach, R.; Geiger, E.; Thomeer, R.T.W.M.; Vanneste, J.A.L. The value of temporary external lumbar CSF drainage in predicting the outcome of shunting on normal pressure hydrocephalus. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2002, 72, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntyre, P.G. How many drops of CSF is enough? Postgrad. Med. J. 2007, 83, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carpenter, R.L.; Hogan, Q.H.; Liu, S.S.; Crane, B.; Moore, J. Lumbosacral Cerebrospinal Fluid Volume Is the Primary Determinant of Sensory Block Extent and Duration during Spinal Anesthesia. J. Am. Soc. Anesthesiol. 1998, 89, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumani, H.; Huss, A.; Bachhuber, F. The cerebrospinal fluid and barriers—Anatomic and physiologic considerations. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 146, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiber, H. Dynamics of brain-derived proteins in cerebrospinal fluid. Clin. Chim. Acta 2001, 310, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Djukic, M.; Spreer, A.; Lange, P.; Bunkowski, S.; Wiltfang, J.; Nau, R. Small cisterno-lumbar gradient of phosphorylated Tau protein in geriatric patients with suspected normal pressure hydrocephalus. Fluids Barriers CNS 2016, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seele, J.; Kirschfink, M.; Djukic, M.; Lange, P.; Gossner, J.; Bunkowski, S.; Wiltfang, J.; Nau, R. Cisterno-lumbar gradient of complement fractions in geriatric patients with suspected normal pressure hydrocephalus. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 486, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollenhauer, B.; Trautmann, E.; Otte, B.; Ng, J.; Spreer, A.; Lange, P.; Sixel-Döring, F.; Hakimi, M.; VonSattel, J.-P.; Nussbaum, R.; et al. α-Synuclein in human cerebrospinal fluid is principally derived from neurons of the central nervous system. J. Neural Transm. 2012, 119, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reiber, H. Cerebrospinal fluid—Physiology, analysis and interpretation of protein patterns for diagnosis of neurological diseases. Mult. Scler. J. 1998, 4, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegen, H.; Auer, M.; Zeileis, A.; Deisenhammer, F. Upper reference limits for cerebrospinal fluid total protein and albumin quotient based on a large cohort of control patients: Implications for increased clinical specificity. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2016, 54, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, M.; Alvarez-Cermeno, J.; Bernardi, G.; Cogato, I.; Fredman, P.; Frederiksen, J.; Fredrikson, S.; Gallo, P.; Grimaldi, L.M.; Gronning, M.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: A consensus report. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1994, 57, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reiber, H.; Lange, P. Quantification of virus-specific antibodies in cerebrospinal fluid and serum: Sensitive and specific detection of antibody synthesis in brain. Clin. Chem. 1991, 37, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felgenhauer, K.; Reiber, H. The diagnostic significance of antibody specificity indices in multiple sclerosis and herpes virus induced diseases of the nervous system. Klin. Wochenschr. 1992, 70, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiber, H.; Peter, J.B. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis: Disease-related data patterns and evaluation programs. J. Neurol. Sci. 2001, 184, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiber, H. External quality assessment in clinical neurochemistry: Survey of analysis for cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) proteins based on CSF/serum quotients. Clin. Chem. 1995, 41, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davson, H.; Welch, K.; Segal, M.B. Physiology and Pathophysiology of the Cerebrospinal Fluid; Churchill Livingstone: London, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Pollay, M. The function and structure of the cerebrospinal fluid outflow system. Cereb. Fluid Res. 2010, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sakka, L.; Coll, G.; Chazal, J. Anatomy and physiology of cerebrospinal fluid. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2011, 128, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seyfert, S.; Faulstich, A. Is the blood-CSF barrier altered in disease? Acta Neurol. Scand. 2003, 108, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerber, J.; Tumani, H.; Kolenda, H.; Nau, R. Lumbar and ventricular CSF protein, leukocytes, and lactate in suspected bacterial CNS infections. Neurol. 1998, 51, 1710–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiber, H. Proteins in cerebrospinal fluid and blood: Barriers, CSF flow rate and source-related dynamics. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2003, 21, 79–96. [Google Scholar]
- Wildemann, B.; Oschmann, P.; Reiber, H. Neurologische Labordiagnostik; Thieme: Stuttgart, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Blennow, K.; Fredman, P.; Wallin, A.; Gottfries, C.-G.; Långström, G.; Svennerholm, L. Protein Analyses in Cerebrospinal Fluid. Eur. Neurol. 1993, 33, 126–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, G.P.A.; Armstrong, H.; Ebers, G.C. Variation in immunoglobulin G and albumin concentrations during lumbar CSF removal: A reappraisal. Neurology 1982, 32, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurster, U. Protein gradients in the cerebrospinal fluid and the calculation of intracerebral IgG synthesis. J. Neuroimmunol. 1988, 20, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Konen, F.F.; Lange, P.; Wurster, U.; Jendretzky, K.F.; Gingele, S.; Möhn, N.; Sühs, K.-W.; Stangel, M.; Skripuletz, T.; Schwenkenbecher, P. The Influence of the Ventricular-Lumbar Gradient on Cerebrospinal Fluid Analysis in Serial Samples. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12030410
Konen FF, Lange P, Wurster U, Jendretzky KF, Gingele S, Möhn N, Sühs K-W, Stangel M, Skripuletz T, Schwenkenbecher P. The Influence of the Ventricular-Lumbar Gradient on Cerebrospinal Fluid Analysis in Serial Samples. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(3):410. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12030410
Chicago/Turabian StyleKonen, Franz Felix, Peter Lange, Ulrich Wurster, Konstantin Fritz Jendretzky, Stefan Gingele, Nora Möhn, Kurt-Wolfram Sühs, Martin Stangel, Thomas Skripuletz, and Philipp Schwenkenbecher. 2022. "The Influence of the Ventricular-Lumbar Gradient on Cerebrospinal Fluid Analysis in Serial Samples" Brain Sciences 12, no. 3: 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12030410
APA StyleKonen, F. F., Lange, P., Wurster, U., Jendretzky, K. F., Gingele, S., Möhn, N., Sühs, K.-W., Stangel, M., Skripuletz, T., & Schwenkenbecher, P. (2022). The Influence of the Ventricular-Lumbar Gradient on Cerebrospinal Fluid Analysis in Serial Samples. Brain Sciences, 12(3), 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12030410