Clinical Characterization and Founder Effect Analysis in Chinese Patients with Phospholipase A2-Associated Neurodegeneration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Molecular Genetics
2.3. Haplotype Analysis
2.4. Literature Review
3. Results
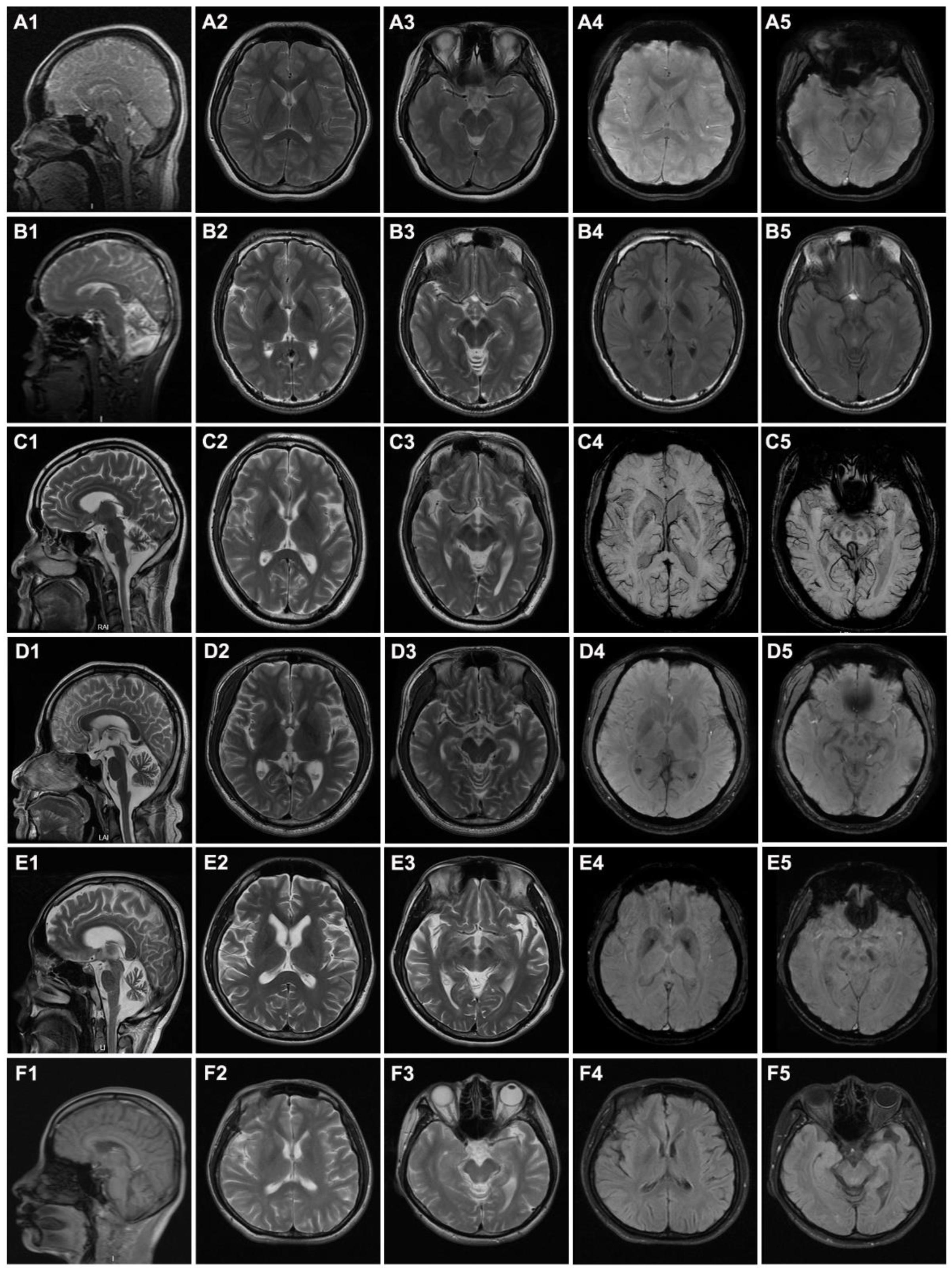
3.1. Clinical Features of the Patients
3.2. Identification of Variants by WES
3.3. Founder Effect of the c.991G>T Mutation among Chinese Patients
3.4. Genotypes and Phenotypes of Chinese PLAN Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, Y.P.; Tang, B.S.; Guo, J.F. PLA2G6-Associated Neurodegeneration (PLAN): Review of Clinical Phenotypes and Genotypes. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morgan, N.V.; Westaway, S.K.; Morton, J.E.; Gregory, A.; Gissen, P.; Sonek, S.; Cangul, H.; Coryell, J.; Canham, N.; Nardocci, N.; et al. PLA2G6, encoding a phospholipase A2, is mutated in neurodegenerative disorders with high brain iron. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 752–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, S.; Yang, L.; Liu, H.; Chen, W.; Li, J.; Yu, P.; Sun, Z.S.; Chen, X.; Du, J.; Cai, T. Identification of Novel Compound Mutations in PLA2G6-Associated Neurodegeneration Patient with Characteristic MRI Imaging. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 4636–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurian, M.A.; Morgan, N.V.; Macpherson, L.; Foster, K.; Peake, D.; Gupta, R.; Philip, S.G.; Hendriksz, C.; Morton, J.E.; Kingston, H.M.; et al. Phenotypic spectrum of neurodegeneration associated with mutations in the PLA2G6 gene (PLAN). Neurology 2008, 70, 1623–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paisan-Ruiz, C.; Bhatia, K.P.; Li, A.; Hernandez, D.; Davis, M.; Wood, N.W.; Hardy, J.; Houlden, H.; Singleton, A.; Schneider, S.A. Characterization of PLA2G6 as a locus for dystonia-parkinsonism. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 65, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Chen, Y.C.; Dong, H.L.; Li, L.X.; Ni, W.; Li, H.F.; Wu, Z.Y. Novel PLA2G6 mutations and clinical heterogeneity in Chinese cases with phospholipase A2-associated neurodegeneration. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2018, 49, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Li, Y.; Shi, C.; Gao, Y.; Yang, J.; Liang, D.; Yang, Z.; Xu, Y. Identification of a novel mutation in PLA2G6 gene and phenotypic heterogeneity analysis of PLA2G6-related neurodegeneration. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2019, 65, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magrinelli, F.; Mehta, S.; Di Lazzaro, G.; Latorre, A.; Edwards, M.J.; Balint, B.; Basu, P.; Kobylecki, C.; Groppa, S.; Hegde, A.; et al. Dissecting the Phenotype and Genotype of PLA2G6-Related Parkinsonism. Mov. Disord. 2021, 37, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altuame, F.D.; Foskett, G.; Atwal, P.S.; Endemann, S.; Midei, M.; Milner, P.; Salih, M.A.; Hamad, M.; Al-Muhaizea, M.; Hashem, M.; et al. The natural history of infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khateeb, S.; Flusser, H.; Ofir, R.; Shelef, I.; Narkis, G.; Vardi, G.; Shorer, Z.; Levy, R.; Galil, A.; Elbedour, K.; et al. PLA2G6 Mutation Underlies Infantile Neuroaxonal Dystrophy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 79, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romani, M.; Kraoua, I.; Micalizzi, A.; Klaa, H.; Benrhouma, H.; Drissi, C.; Turki, I.; Castellana, S.; Mazza, T.; Valente, E.M.; et al. Infantile and childhood onset PLA2G6-associated neurodegeneration in a large North African cohort. Eur. J. Neurol. 2015, 22, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.T.; Lin, H.Y.; Chen, P.L.; Lin, C.H. Genotype-phenotype correlations of adult-onset PLA2G6-associated Neurodegeneration: Case series and literature review. BMC Neurol. 2020, 20, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, H.L.; Wei, Q.; Li, J.Q.; Li, H.F.; Bai, G.; Ma, H.; Wu, Z.Y. Genetic spectrum of MCM3AP and its relationship with phenotype of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2020, 25, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Wang, K. InterVar: Clinical interpretation of genetic variants by the 2015 ACMG-AMP guidelines. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 100, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kopanos, C.; Tsiolkas, V.; Kouris, A.; Chapple, C.E.; Albarca Aguilera, M.; Meyer, R.; Massouras, A. VarSome: The human genomic variant search engine. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 1978–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, J.C.; Fry, B.; Maller, J.; Daly, M.J. Haploview: Analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Retterer, K.; Juusola, J.; Cho, M.T.; Vitazka, P.; Millan, F.; Gibellini, F.; Vertino-Bell, A.; Smaoui, N.; Neidich, J.; Monaghan, K.G.; et al. Clinical application of whole-exome sequencing across clinical indications. Genet. Med. 2016, 18, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elsayed, L.E.O.; Mohammed, I.N.; Hamed, A.A.A.; Elseed, M.A.; Salih, M.A.M.; Yahia, A.; Siddig, R.A.; Amin, M.; Koko, M.; Elbashir, M.I.; et al. Case report of a novel homozygous splice site mutation in PLA2G6 gene causing infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy in a Sudanese family. BMC Med. Genet. 2018, 19, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.J.; Lyoo, C.H.; Hong, S.; Kim, N.Y.; Lee, M.S. Neuroimaging studies and whole exome sequencing of PLA2G6-associated neurodegeneration in a family with intrafamilial phenotypic heterogeneity. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2015, 21, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, H.; Taha, A.Y.; Cheon, Y.; Kim, H.; Turk, J.; Rapoport, S.I. iPLA2β Knockout Mouse, a Genetic Model for Progressive Human Motor Disorders, Develops Age-Related Neuropathology. Neurochem. Res. 2014, 39, 1522–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhao, C.; Bi, W.; Yue, Z.; Ma, Z.A. Genetic ablation of PLA2G6 in mice leads to cerebellar atrophy characterized by Purkinje cell loss and glial cell activation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, J.K.; Youn, J.; Cho, J.W. Intrafamilial variability and clinical heterogeneity in a family with PLA2G6-associated neurodegeneration. Precis. Future Med. 2019, 3, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, J.; White, T.D.; Nelson, A.J.; Lei, X.; Ramanadham, S. iPLA2β and its role in male fertility, neurological disorders, metabolic disorders, and inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2019, 1864, 846–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, L.A.; Jing, Z.; O’Brien, D.E.; Sun, M.; Kotzbauer, P.T. Catalytic function of PLA2G6 is impaired by mutations associated with infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy but not dystonia-parkinsonism. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozes, B.; Karagoz, N.; Schüle, R.; Rebelo, A.; Sobrido, M.J.; Harmuth, F.; Synofzik, M.; Pascual, S.; Colak, M.; Ciftci-Kavaklioglu, B.; et al. PLA2G6 mutations associated with a continuous clinical spectrum from neuroaxonal dystrophy to hereditary spastic paraplegia. Clin. Genet. 2017, 92, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Patient | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | Case 5 | Case 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | F | M | M | M | M | F |
| Age at onset (year) | 6 | 15 | 20 | 29 | 31 | 35 |
| Disease duration (years) | 7 | 10 | 22 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| Family History | No | No | Yes | No | No | No |
| Province of origin | Jiangxi | Anhui | Zhejiang | Zhejiang | Anhui | Zhejiang |
| Variants | p.D331Y, c.1427+2T>A | p.M358IfsX, p.S557L | p.D331Y, p.G373R | p.D331Y, p.A639Qfs*27 | p.V323M, p.D484Y | p.D331Y, p.M544T |
| Initial symptoms | Gait disturbance | Gait disturbance | Slowly walking | Gait disturbance | Slurred speech | Slowly walking |
| Abnormal posture and gait | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Difficulty walking | + | + | + | + | − | + |
| Parkinsonism | − | + | + | + | + | + |
| Bradykinesia | − | + | + | + | − | + |
| Rest tremor | − | − | − | + | + | + |
| Rigidity | − | + | + | + | + | + |
| Dysarthria | − | + | + | + | + | + |
| Cognitive decline | + | + | + | − | + | + |
| Psychiatric symptoms | − | − | − | + | − | + |
| Autonomic dysfunction | − | + | − | + | + | + |
| Sensory dysfunction | − | + | + | + | − | − |
| Nystagmus | − | + | − | − | − | − |
| Eye movement abnormality | − | + | + | − | + | − |
| Dysphagia | − | − | + | − | − | + |
| Dystonia | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Myoclonus | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| Muscle strength decline | − | + | + | − | − | + |
| UL/LL Tendon reflexes | ++/++ | −/− | ++/+++ | +++/++ | +++/+ | +++/+++ |
| Babinski’s sign | + | − | + | + | − | + |
| Ataxia signs | − | + | + | − | + | − |
| Cerebellar atrophy | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Cerebral atrophy | − | − | + | − | + | + |
| Iron deposition in globus pallidus | + | + | − | − | + | − |
| Benefit from Levodopa | NA | NA | + | + | + | NA |
| TSNP | MAF | Family 1 | Family 3 | Family 4 | Family 6 | Previous Report Family | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | Mother | Case 3 | Mother | Father | Case 4 | Mother | Father | Case 6 | Mother | Father | Case | Mother | Father | ||||||||||||||||
| 22-37462926-G-A | 0.429 | G | G | G | G | G | A | G | A | G | A | G | A | G | A | G | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | G | G | G | G | G | G |
| 22-37528576-A-G | 0.467 | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | G | A | G | A | G | G | G | A | A | G | A | G | A | G | A | A | A | A | G | A | G |
| 22-37603390-C-T | 0.324 | C | T | T | T | C | T | C | T | T | T | C | T | C | T | C | C | C | T | C | T | C | T | T | T | T | T | C | T |
| 22-37707962-C-T | 0.424 | C | T | C | T | T | C | C | C | T | T | C | T | C | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | C | T | C | T | C | T |
| 22-37825220-G-C | 0.4 | G | C | G | C | G | C | G | C | G | C | G | G | G | G | G | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | G | C | C | C | G | C |
| 22-37905632-G-A | 0.495 | G | G | A | A | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | A | G | G | G | A | A |
| 22-38032709-A-G | 0.49 | G | A | G | A | A | A | A | G | A | A | G | A | G | A | G | G | G | A | G | A | G | A | G | A | A | A | G | G |
| 22-38122448-C-T | 0.381 | C | T | T | T | T | T | C | T | C | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | C | T | C | T | C | T | T | T | T | T | T | T |
| 22-38237562-C-A | 0.486 | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | C | A | A | A | A | A | A |
| 22-38303155-C-T | 0.486 | C | T | C | T | T | T | C | T | C | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | C | T | C | T | C | T | C | T | T | T | C | C |
| 22-38463968-A-G | 0.305 | G | G | A | G | G | G | A | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | A | G | A | G | A | G | G | G | G | G | G | G |
| 22-38528924-G-T | G | T | G | T | G | T | G | G | G | T | G | T | G | T | G | G | G | T | G | T | G | G | G | T | G | T | G | G | |
| 22-38543453-T-C | 0.357 | C | T | T | T | C | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | C | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | C | T | C |
| 22-38622598-C-A | 0.357 | A | C | C | C | C | C | C | A | A | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | A | C | C | C | C | C | C | A | C | A |
| 22-38723050-C-T | 0.376 | C | T | T | T | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | T | T | C | T | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C |
| 22-38829774-G-C | 0.367 | G | G | G | C | G | C | G | C | G | C | C | C | G | C | G | C | G | C | G | C | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G |
| 22-38918894-T-G | 0.39 | T | T | T | T | G | T | T | G | G | G | G | G | T | G | T | G | G | T | T | T | T | G | T | G | T | G | T | T |
| 22-39029695-T-C | 0.486 | T | T | C | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | C | C | T | T | C | T | C | C | C | T | C | T | C |
| 22-39157384-G-A | 0.467 | A | G | G | G | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | G | G | G | A | A | A | G | G | G | G | A | G | G | G | A | G | A |
| 22-39258795-G-A | 0.457 | C | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | C | G | G | G | G | C | C | G | G | C | C | C |
| 22-39355415-A-G | 0.500 | G | A | G | A | G | G | G | G | G | G | A | G | G | G | G | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | G | A | G | A |
| 22-39449014-C-T | 0.429 | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C |
| 22-39551989-G-A | 0.467 | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | A | G | A | A | A | G | G | G | G | A | G | G | G | G | G | A |
| 22-39663185-A-G | 0.386 | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | A | G | A | G | G | G | A | G | A | G | G | G | G | G | G | G |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, H.-L.; Chen, Y.-J.; Xue, Y.-Y.; Wu, Z.-Y.; Li, H.-F.; Wang, N. Clinical Characterization and Founder Effect Analysis in Chinese Patients with Phospholipase A2-Associated Neurodegeneration. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12050517
Cheng H-L, Chen Y-J, Xue Y-Y, Wu Z-Y, Li H-F, Wang N. Clinical Characterization and Founder Effect Analysis in Chinese Patients with Phospholipase A2-Associated Neurodegeneration. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(5):517. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12050517
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Hao-Ling, Yi-Jun Chen, Yan-Yan Xue, Zhi-Ying Wu, Hong-Fu Li, and Ning Wang. 2022. "Clinical Characterization and Founder Effect Analysis in Chinese Patients with Phospholipase A2-Associated Neurodegeneration" Brain Sciences 12, no. 5: 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12050517
APA StyleCheng, H.-L., Chen, Y.-J., Xue, Y.-Y., Wu, Z.-Y., Li, H.-F., & Wang, N. (2022). Clinical Characterization and Founder Effect Analysis in Chinese Patients with Phospholipase A2-Associated Neurodegeneration. Brain Sciences, 12(5), 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12050517








