Dissection of Mouse Hippocampus with Its Dorsal, Intermediate and Ventral Subdivisions Combined with Molecular Validation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
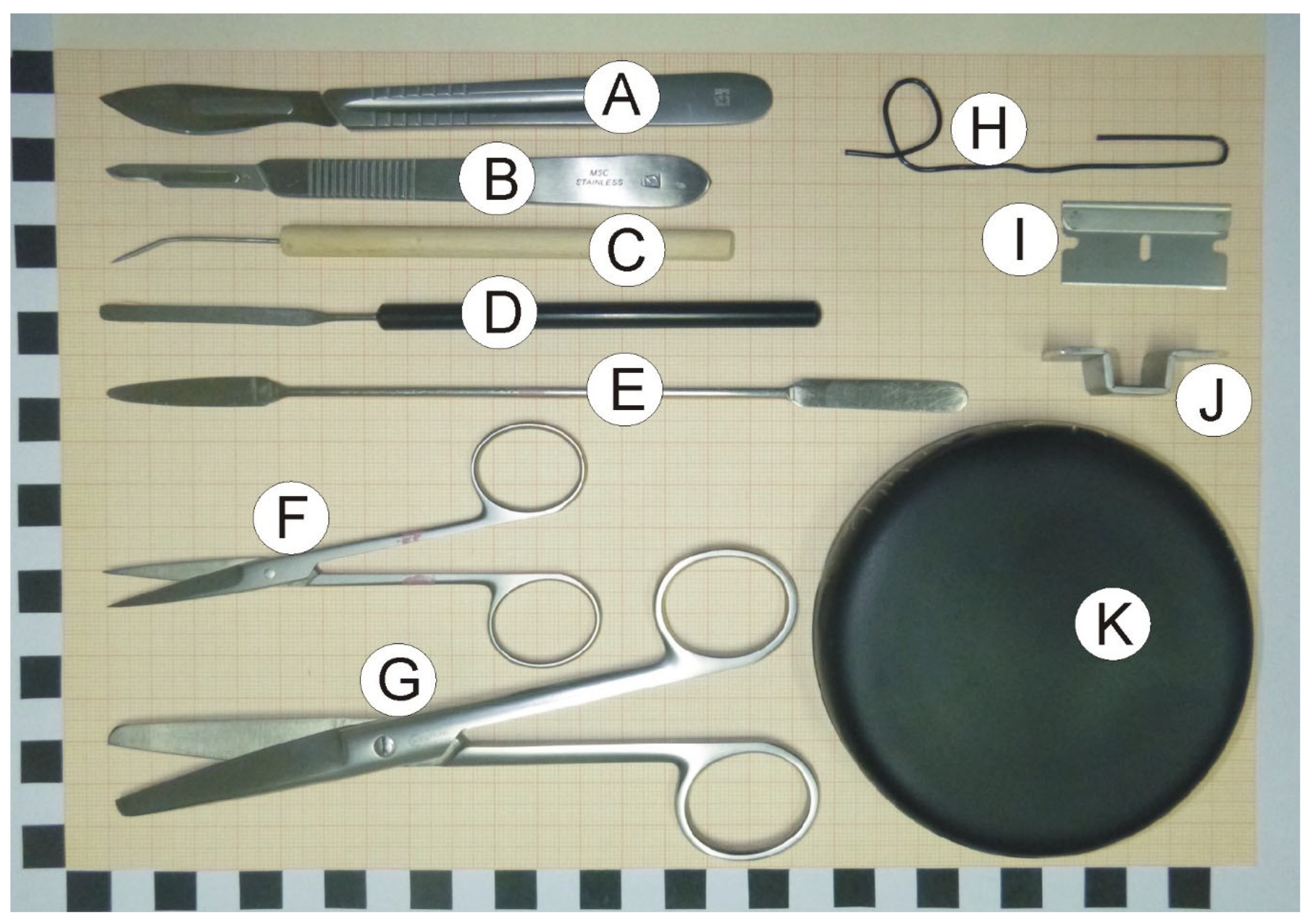
2.2. Dissection Tools and Materials
- -
- Scalpels with small (nb. 15) and large (nb. 24) blades (Figure 1A,B).
- -
- Bent dissecting needle (Figure 1C).
- -
- Stainless steel spatula with narrow blade (Figure 1D).
- -
- Stainless steel spatula with flat round and tapered arrow ends (Figure 1E).
- -
- Small surgical scissors (straight) with sharp tips (Figure 1F).
- -
- Large surgical scissors (Figure 1G).
- -
- A large paper clip that is used to prepare a loop restricting movement of dissected hippocampus at the time of rinsing with water (optional; Figure 1H).
- -
- Single edge razor blade (optional; Figure 1I).
- -
- Cutting form made from metal strip. The form helps to make precise vertical cuts (optional; Figure 1J).
- -
- Convex cover of the Petri dish that serves as a dissection table. Convex surface is important because it enables water to flow out of the dissection surface. The cover can be painted black with mat waterproof paint to increase contrast between the background and the dissected tissue (Figure 1K).
- -
- Wash bottle.
- -
- Styrofoam box.
- -
- Tabletop Illuminated Magnifier (3×).
- -
- Filter paper.
- -
- Millimeter paper.
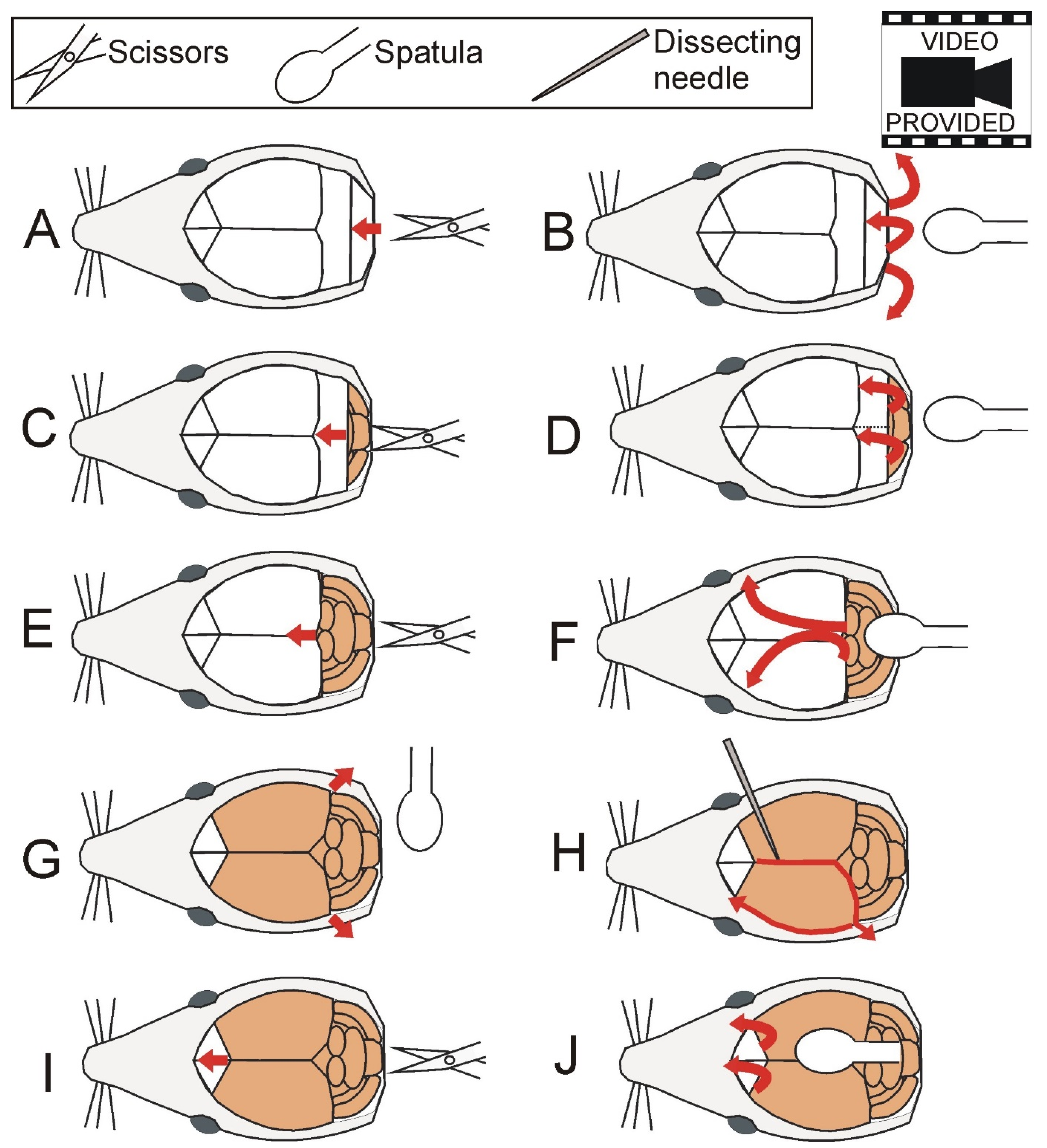
2.3. Brain Dissection
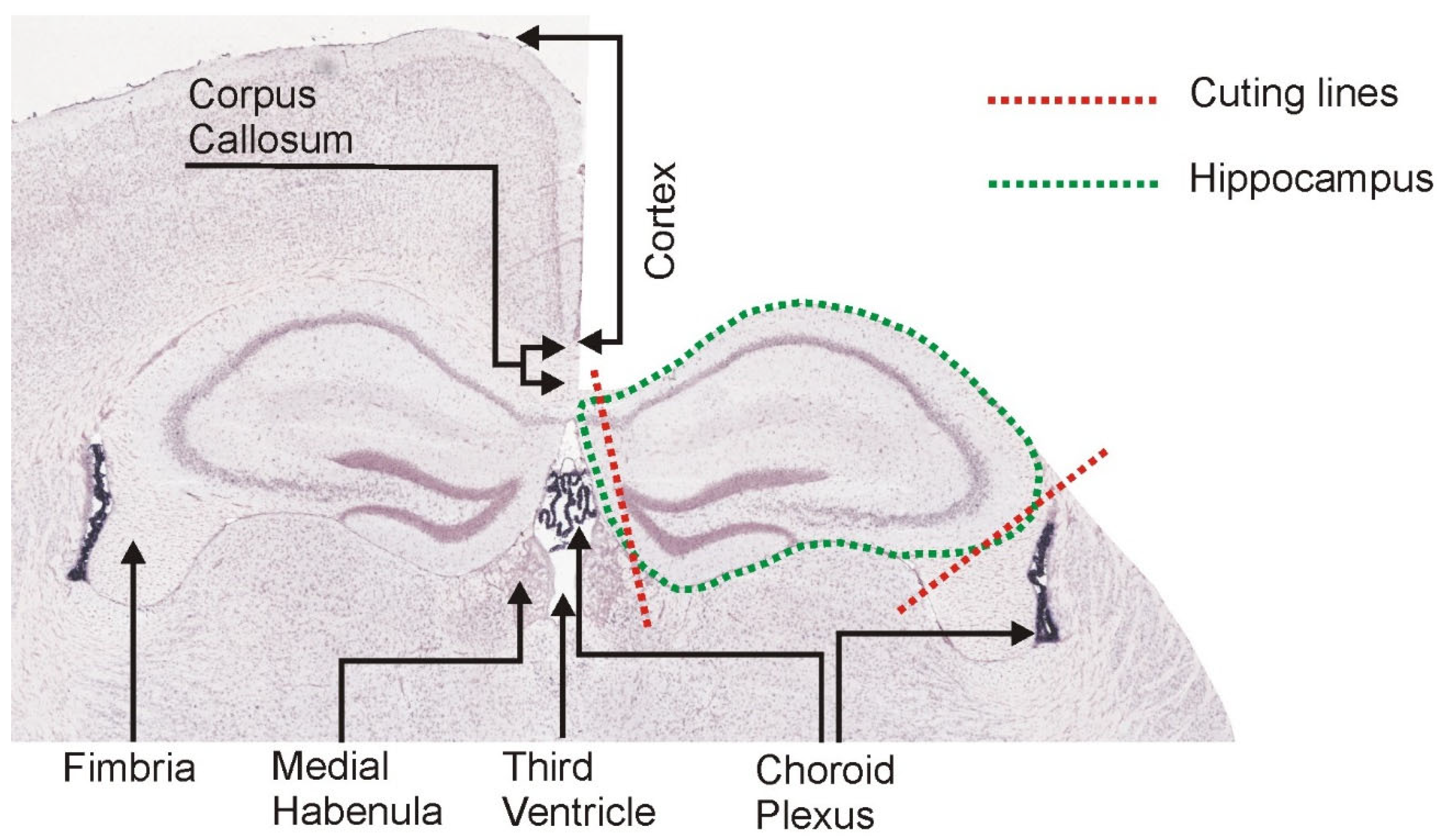
2.4. Hippocampal Dissection
2.5. Real-Time PCR (PCR)
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
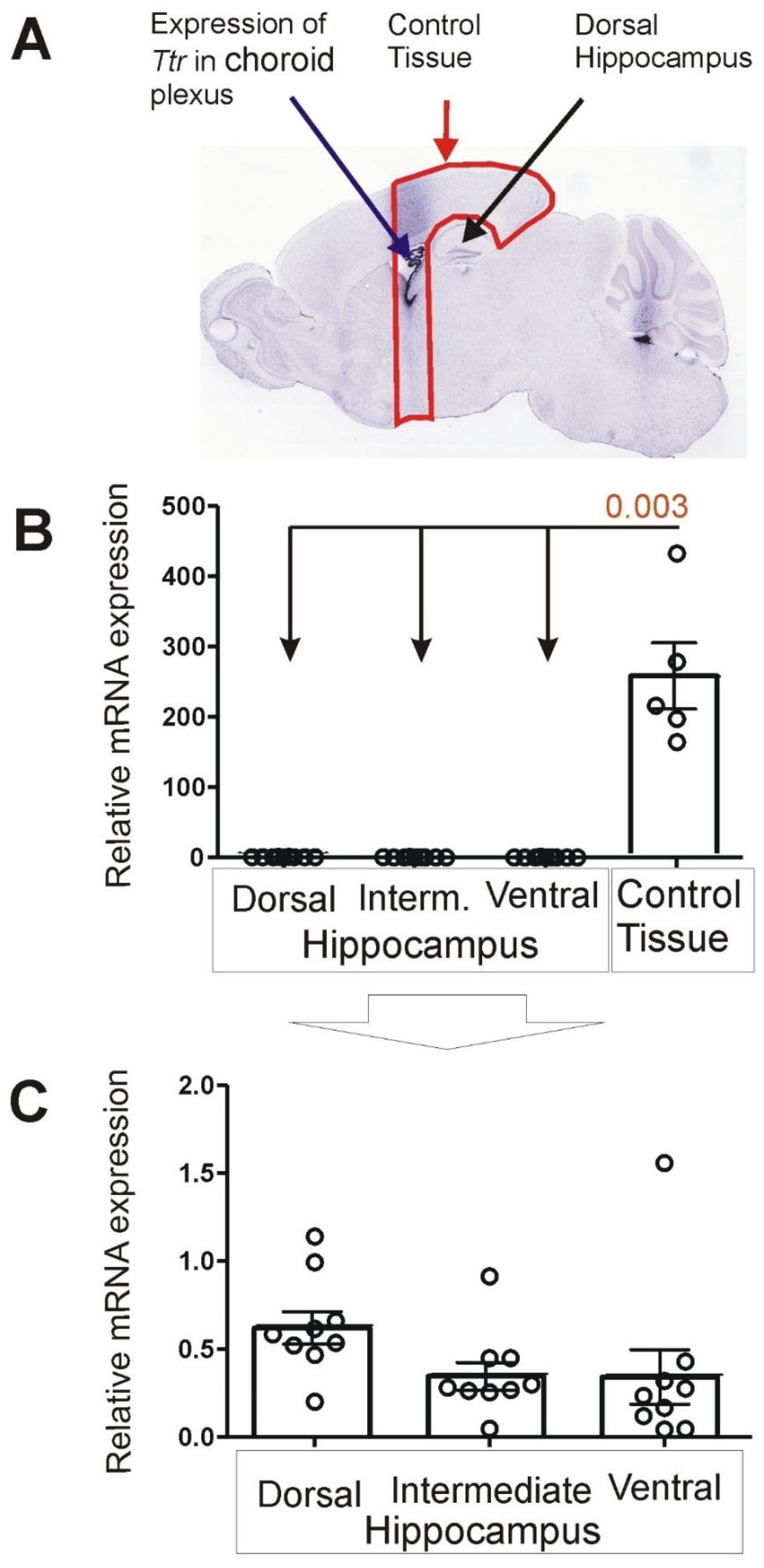
3.1. Expression of Choroid Marker Gene Ttr
3.2. Expression of Marker Genes Differentiating between Dorsal and Ventral Hippocampus
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fanselow, M.S.; Dong, H.W. Are the dorsal and ventral hippocampus functionally distinct structures? Neuron 2010, 65, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jaszczyk, A.; Juszczak, G.R. Glucocorticoids, metabolism and brain activity. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 126, 113–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roddy, D.W.; Farrell, C.; Doolin, K.; Roman, E.; Tozzi, L.; Frodl, T.; O’Keane, V.; O’Hanlon, E. The Hippocampus in Depression: More Than the Sum of Its Parts? Advanced Hippocampal Substructure Segmentation in Depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 85, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, J.M.; DiGangi, J.A.; Phan, K.L. Functional Neuroanatomy of Emotion and Its Regulation in PTSD. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 2018, 26, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieberman, J.A.; Girgis, R.R.; Brucato, G.; Moore, H.; Provenzano, F.; Kegeles, L.; Javitt, D.; Kantrowitz, J.; Wall, M.M.; Corcoran, C.M.; et al. Hippocampal dysfunction in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia: A selective review and hypothesis for early detection and intervention. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 23, 1764–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzikonstantinou, A. Epilepsy and the hippocampus. Front. Neurol. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 121–142. [Google Scholar]
- Moodley, K.; Chan, D. The Hippocampus in Neurodegenerative Disease. Hippocampus Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.C.; Cardoso, I.; Marques, F.; Saraiva, M.J.; Palha, J.A. Transthyretin and Alzheimer’s disease: Where in the brain? Neurobiol. Aging 2007, 28, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankiewicz, A.M.; Goscik, J.; Majewska, A.; Swiergiel, A.H.; Juszczak, G.R. The Effect of Acute and Chronic Social Stress on the Hippocampal Transcriptome in Mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, R.S.; Mullan, H.; Blusztajn, J.K.; Lehtinen, M.K. Comment on Multiple repressive mechanisms in the hippocampus during memory formation. Science 2016, 353, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stankiewicz, A.M.; Jaszczyk, A.; Goscik, J.; Juszczak, G.R. Stress and the brain transcriptome: Identifying com-monalities and clusters in standardized data from published experiments. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 110558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cembrowski, M.S.; Wang, L.; Sugino, K.; Shields, B.C.; Spruston, N. Hipposeq: A comprehensive RNA-seq data-base of gene expression in hippocampal principal neurons. Elife 2016, 5, e14997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lein, E.S.; Hawrylycz, M.J.; Ao, N.; Ayres, M.; Bensinger, A.; Bernard, A.; Boe, A.F.; Boguski, M.S.; Brockway, K.S.; Byrnes, E.J.; et al. Genome-wide atlas of gene expression in the adult mouse brain. Nature 2007, 445, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, A.A.; Bush, E.N.; Stanisic, D.; Kyncl, J.J.; Lin, C.T. Data normalization before statistical analysis: Keeping the horse before the cart. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1988, 9, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, K.; Lau, W.M.; Lau, H.T.; So, K.-F.; Chang, R.C.-C. Micro-dissection of Rat Brain for RNA or Protein Extraction from Specific Brain Region. J. Vis. Exp. 2007, e269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hagihara, H.; Toyama, K.; Yamasaki, N.; Miyakawa, T. Dissection of Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus from Adult Mouse. J. Vis. Exp. 2009, 33, e1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mathis, D.M.; Furman, J.L.; Norris, C.M. Preparation of Acute Hippocampal Slices from Rats and Transgenic Mice for the Study of Synaptic Alterations during Aging and Amyloid Pathology. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 49, e2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, F. Dissection of Different Areas from Mouse Hippocampus. Bio.-Protocol. 2013, 3, e955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villers, A.; Ris, L. Improved Preparation and Preservation of Hippocampal Mouse Slices for a Very Stable and Reproducible Recording of Long-term Potentiation. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 76, e50483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyerhoff, J.; Muhie, S.; Chakraborty, N.; Naidu, L.; Sowe, B.; Hammamieh, R.; Jett, M.; Gautam, A. Microdissection of Mouse Brain into Functionally and Anatomically Different Regions. J. Vis. Exp. 2021, 168, e61941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spijker, S. Dissection of Rodent Brain Regions. Neuromethods 2011, 57, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffner, T.G.; Hartman, J.A.; Seiden, L.S. A rapid method for the regional dissection of the rat brain. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1980, 13, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wager-Miller, J.; Green, M.M.; Shafique, H.; Mackie, K. Collection of Frozen Rodent Brain Regions for Downstream Analyses. J. Vis. Exp. 2020, 158, e60474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hoeymissen, E.; Philippaert, K.; Vennekens, R.; Vriens, J.; Held, K. Horizontal Hippocampal Slices of the Mouse Brain. J. Vis. Exp. 2020, 163, e61753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, T.W.; Gold, M.G. Preparation of Rat Organotypic Hippocampal Slice Cultures Using the Mem-brane-Interface Method. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2188, 243–257. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, A.-R.; Kim, J.-H.; Cho, E.; Kim, M.; Park, M. Dorsal and Ventral Hippocampus Differentiate in Functional Pathways and Differentially Associate with Neurological Disease-Related Genes during Postnatal Development. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Floriou-Servou, A.; von Ziegler, L.; Stalder, L.; Sturman, O.; Privitera, M.; Rassi, A.; Cremonesi, A.; Thöny, B.; Bohacek, J. Distinct Proteomic, Transcriptomic, and Epigenetic Stress Responses in Dorsal and Ventral Hippocampus. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 84, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atkins, N.; Miller, C.M.; Owens, J.R.; Turek, F.W. Non-laser capture microscopy approach for the microdissec-tion of discrete mouse brain regions for total RNA isolation and downstream next-generation sequencing and gene expres-sion profiling. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 57, e3125. [Google Scholar]



| Gene Name | Forward or Reverse Primer | Primer Sequence | Annealing Temperature | Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trhr | F | GAGCCTCTGCTAAGTGATCTTCC | 58° | 97% |
| R | ACGGGGACTCTAAAACATCTTTCC | |||
| Lct | F | CGTCAGCCAAGGTCTACGC | 60° | 93.7% |
| R | GTCTGTGCTTCTGCCGTGC | |||
| Ttr | F | TCGCGGATGTGGTTTTCACAG | 60° | 106.2% |
| R | CTCTCAATTCTGGGGGTTGCT | |||
| Hmbs | F | TCCTGGCTTTACTATTGGAG | 60° | 95.2% |
| R | TGAATTCCAGGTGGGGGAAC |
| Author | Entire Hippoc. | Subparts | Species | General Dissection Strategy | Video | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [16] | Yes | No | Rats | Separation of hemispheres and removal of the brainstem/diencephalon to expose lateral ventricle and medial side of the hippocampus | Yes | General |
| [18] | Yes | No | Rats | Separation of hemispheres and displacement of the brainstem/diencephalon preceding the exposition of lateral ventricle and medial side of the hippocampus | Yes | Electro- physiol |
| [17] | No | Dentate gyrus | Mice | Separation of hemispheres and removal of the brainstem/diencephalon to expose the lateral ventricle and medial side of the hippocampus | Yes | General |
| [20] | Yes | No | Mice | Separation of hemispheres and removal of the brainstem/diencephalon to expose the lateral ventricle and medial side of the hippocampus | Yes | Electro- physiol |
| [21] | Yes | No | Mice | Separation of hemispheres and eversion of the lateral ventricle | Yes | General |
| [19] | Yes | CA1, CA3 and Dentate gyrus | Mice | Separation of hemispheres and removal of occipital cortex starting from lateral side of the brain | No | Genera |
| [22] | Yes | No | Mice/ Rats | Removal of occipital cortex starting from the dorsal part of the brain | No | General |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaszczyk, A.; Stankiewicz, A.M.; Juszczak, G.R. Dissection of Mouse Hippocampus with Its Dorsal, Intermediate and Ventral Subdivisions Combined with Molecular Validation. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12060799
Jaszczyk A, Stankiewicz AM, Juszczak GR. Dissection of Mouse Hippocampus with Its Dorsal, Intermediate and Ventral Subdivisions Combined with Molecular Validation. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(6):799. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12060799
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaszczyk, Aneta, Adrian M. Stankiewicz, and Grzegorz R. Juszczak. 2022. "Dissection of Mouse Hippocampus with Its Dorsal, Intermediate and Ventral Subdivisions Combined with Molecular Validation" Brain Sciences 12, no. 6: 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12060799
APA StyleJaszczyk, A., Stankiewicz, A. M., & Juszczak, G. R. (2022). Dissection of Mouse Hippocampus with Its Dorsal, Intermediate and Ventral Subdivisions Combined with Molecular Validation. Brain Sciences, 12(6), 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12060799






