Optimizing Motor Imagery Parameters for Robotic Arm Control by Brain-Computer Interface
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
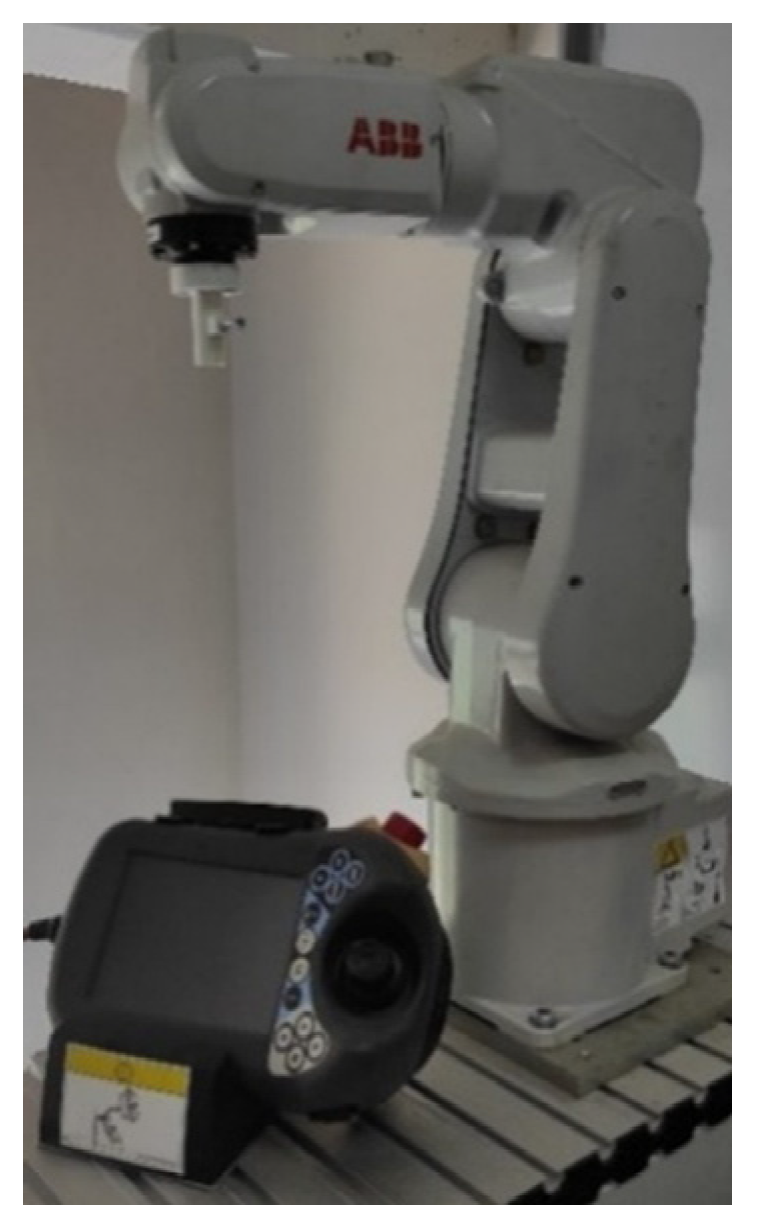
2.1. Data Recording
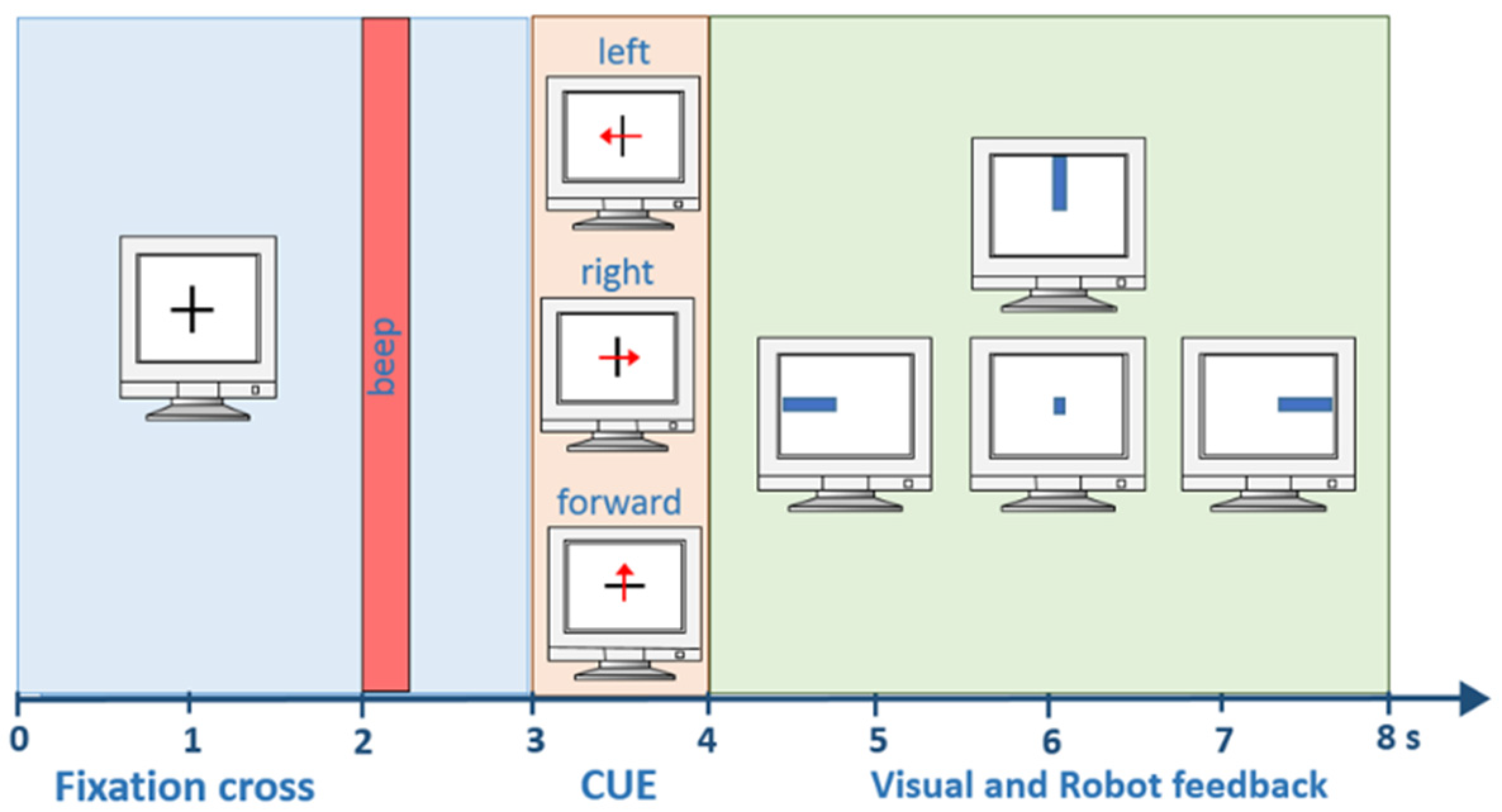
2.2. Experimental Paradigm
2.3. Feature Extraction and Classification
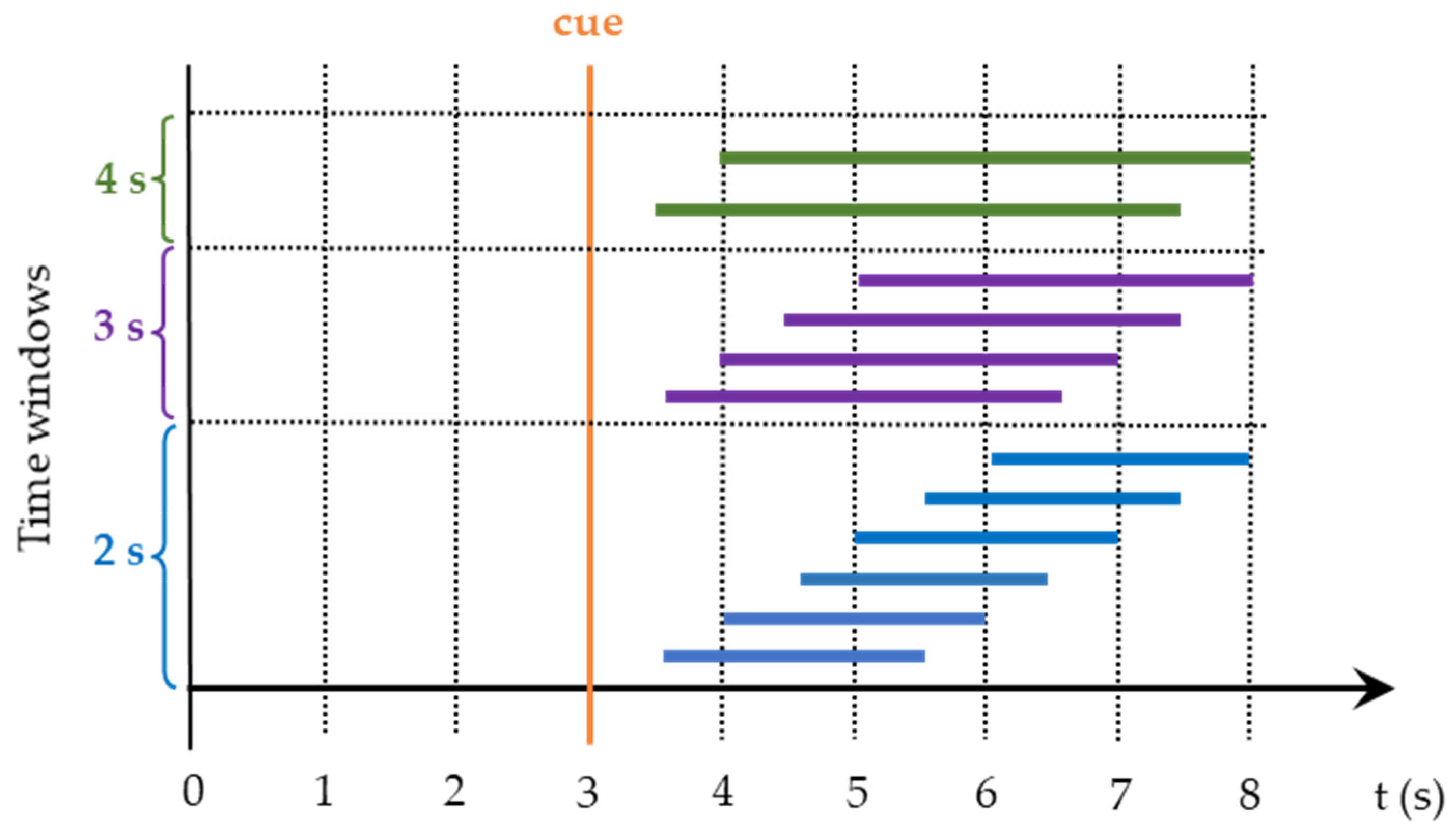
2.4. Off-Line Data Processing
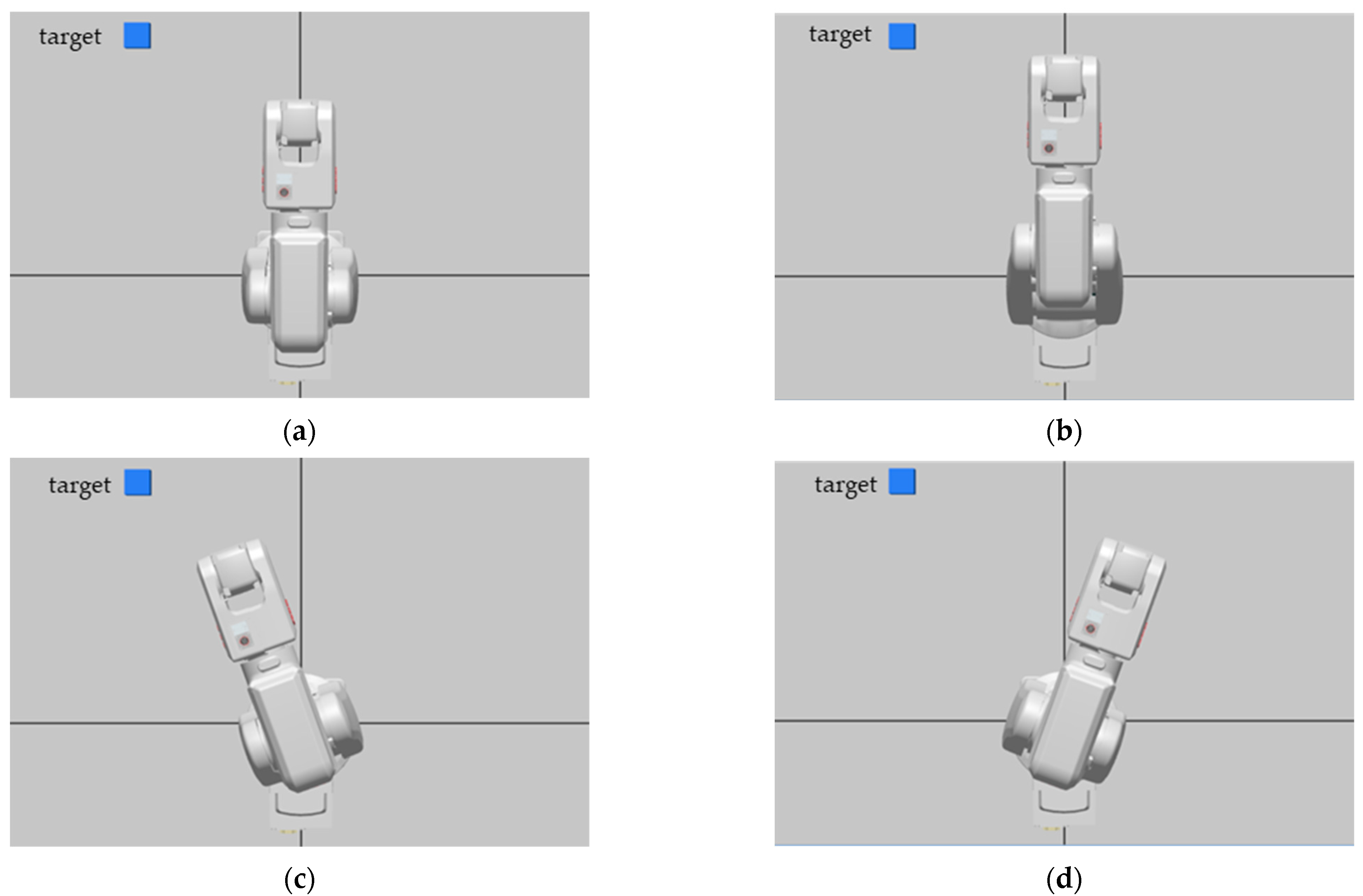
2.5. Robot Control Unit
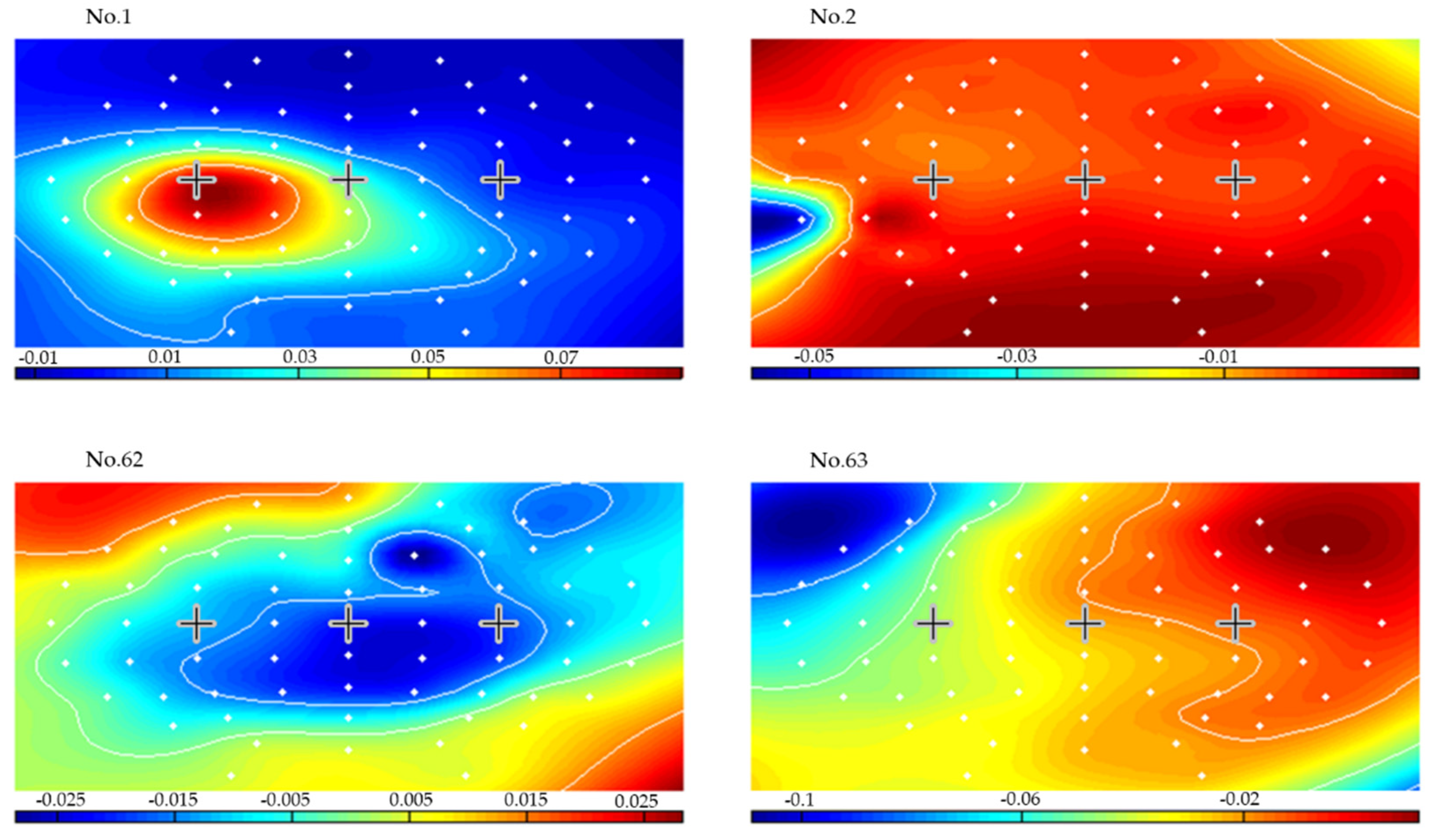
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Graimann, B.; Pfurtscheller, G.; Allison, B. Brain-Computer Interfaces; The Frontiers Collection; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; ISBN 978-3-642-02090-2. [Google Scholar]
- Wolpaw, J.R.; Birbaumer, N.; McFarland, D.J.; Pfurtscheller, G.; Vaughan, T.M. Brain–Computer Interfaces for Communication and Control. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2002, 113, 767–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B. Neural Engineering; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-4614-5226-3. [Google Scholar]
- Farwell, L.A.; Donchin, E. Talking off the Top of Your Head: Toward a Mental Prosthesis Utilizing Event-Related Brain Potentials. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1988, 70, 510–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugler, E.M.; Ruf, C.A.; Halder, S.; Bensch, M.; Kubler, A. Design and Implementation of a P300-Based Brain-Computer Interface for Controlling an Internet Browser. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2010, 18, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortner, R.; Guger, C.; Prueckl, R.; Grünbacher, E.; Edlinger, G. SSVEP Based Brain-Computer Interface for Robot Control. In Computers Helping People with Special Needs; Miesenberger, K., Klaus, J., Zagler, W., Karshmer, A., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 6180, pp. 85–90. ISBN 978-3-642-14099-0. [Google Scholar]
- Horki, P.; Solis-Escalante, T.; Neuper, C.; Müller-Putz, G. Combined Motor Imagery and SSVEP Based BCI Control of a 2 DoF Artificial Upper Limb. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2011, 49, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, R.; Müller, G.R.; Neuper, C.; Graimann, B.; Pfurtscheller, G. An Asynchronously Controlled EEG-Based Virtual Keyboard: Improvement of the Spelling Rate. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 51, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfurtscheller, G.; Neuper, C.; Flotzinger, D.; Pregenzer, M. EEG-Based Discrimination between Imagination of Right and Left Hand Movement. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1997, 103, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas-Alonso, L.F.; Gomez-Gil, J. Brain Computer Interfaces, a Review. Sensors 2012, 12, 1211–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfurtscheller, G.; Aranibar, A. Evaluation of Event-Related Desynchronization (ERD) Preceding and Following Voluntary Self-Paced Movement. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1979, 46, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfurtscheller, G.; Neuper, C. Motor Imagery and Direct Brain-Computer Communication. Proc. IEEE 2001, 89, 1123–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfurtscheller, G.; Guger, C.; Müller, G.; Krausz, G.; Neuper, C. Brain Oscillations Control Hand Orthosis in a Tetraplegic. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 292, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guger, C.; Edlinger, G.; Harkam, W.; Niedermayer, I.; Pfurtscheller, G. How Many People Are Able to Operate an Eeg-Based Brain-Computer Interface (Bci)? IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2003, 11, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, G.; Graimann, B.; Pfurtscheller, G. A Comparison of Common Spatial Patterns with Complex Band Power Features in a Four-Class BCI Experiment. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 53, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guger, C.; Ramoser, H.; Pfurtscheller, G. Real-Time EEG Analysis with Subject-Specific Spatial Patterns for a Brain-Computer Interface (BCI). IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 2000, 8, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blankertz, B.; Tomioka, R.; Lemm, S.; Kawanabe, M.; Muller, K. Optimizing Spatial Filters for Robust EEG Single-Trial Analysis. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2008, 25, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortner, R.; Irimia, D.-C.; Guger, C.; Edlinger, G. Human Computer Confluence in BCI for Stroke Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the Foundations of Augmented Cognition; Schmorrow, D.D., Fidopiastis, C.M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 304–312. [Google Scholar]
- Blankertz, B.; Kawanabe, M.; Tomioka, R.; Hohlefeld, F.U.; Nikulin, V.; Müller, K.-R. Invariant Common Spatial Patterns: Alleviating Nonstationarities in Brain-Computer Interfacing. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 3–6 December 2007; Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Xu, P.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Li, P.; Yao, D. Local Temporal Correlation Common Spatial Patterns for Single Trial EEG Classification during Motor Imagery. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2013, 2013, 591216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barachant, A.; Bonnet, S.; Congedo, M.; Jutten, C. Common Spatial Pattern Revisited by Riemannian Geometry. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing, Darmstadt, Germany, 15–17 October 2010; pp. 472–476. [Google Scholar]
- Aljalal, M.; Ibrahim, S.; Djemal, R.; Ko, W. Comprehensive Review on Brain-Controlled Mobile Robots and Robotic Arms Based on Electroencephalography Signals. Intell. Serv. Robot. 2020, 13, 539–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alturki, F.A.; AlSharabi, K.; Abdurraqeeb, A.M.; Aljalal, M. EEG Signal Analysis for Diagnosing Neurological Disorders Using Discrete Wavelet Transform and Intelligent Techniques. Sensors 2020, 20, 2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, R.; Hart, P.; Stork, D.G. Pattern Classification; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001; ISBN 978-0-471-05669-0. [Google Scholar]
- Wolpaw, J.R.; McFarland, D.J. Control of a Two-Dimensional Movement Signal by a Noninvasive Brain-Computer Interface in Humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 17849–17854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Royer, A.S.; Doud, A.J.; Rose, M.L.; He, B. EEG Control of a Virtual Helicopter in 3-Dimensional Space Using Intelligent Control Strategies. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2010, 18, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, B.; Maysam, O.; Veser, S.; Cao, L.; Li, J.; Jia, J.; Xie, H.; Birbaumer, N. A Combination Strategy Based Brain-Computer Interface for Two-Dimensional Movement Control. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12, 046021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, T.; del R. Millan, J. Brain-Controlled Wheelchairs: A Robotic Architecture. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2013, 20, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LaFleur, K.; Cassady, K.; Doud, A.; Shades, K.; Rogin, E.; He, B. Quadcopter Control in Three-Dimensional Space Using a Noninvasive Motor Imagery-Based Brain–Computer Interface. J. Neural Eng. 2013, 10, 046003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ang, K.K.; Guan, C.; Chua, K.S.G.; Ang, B.T.; Kuah, C.W.K.; Wang, C.; Phua, K.S.; Chin, Z.Y.; Zhang, H. A Large Clinical Study on the Ability of Stroke Patients to Use an EEG-Based Motor Imagery Brain-Computer Interface. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2011, 42, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Hong, B. Visual and Auditory Brain–Computer Interfaces. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 1436–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klem, G.H.; Lüders, H.O.; Jasper, H.H.; Elger, C. The Ten-Twenty Electrode System of the International Federation. The International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. Suppl. 1999, 52, 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- GTec Medical Engineering. GmbH|Brain-Computer Interface & Neurotechnology. Available online: https://www.gtec.at/ (accessed on 22 April 2021).
- Irimia, D.C.; Ortner, R.; Poboroniuc, M.S.; Ignat, B.E.; Guger, C. High Classification Accuracy of a Motor Imagery Based Brain-Computer Interface for Stroke Rehabilitation Training. Front. Robot. AI 2018, 5, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Afrakhteh, S.; Mosavi, M.R. An Efficient Method for Selecting the Optimal Features Using Evolutionary Algorithms for Epilepsy Diagnosis. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. 2020, 29, 2050195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MuÈller-Gerking, J.; Pfurtscheller, G.; Flyvbjerg, H. Designing Optimal Spatial Filters for Single-Trial EEG Classification in a Movement Task. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1999, 12, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortner, R.; Irimia, D.C.; Scharinger, J.; Guger, C. Brain-Computer Interfaces for Stroke Rehabilitation: Evaluation of Feedback and Classification Strategies in Healthy Users. In Proceedings of the 2012 4th IEEE RAS & EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), Rome, Italy, 24–27 June 2012; pp. 219–223. [Google Scholar]
- Lemm, S.; Blankertz, B.; Dickhaus, T.; Müller, K.-R. Introduction to Machine Learning for Brain Imaging. NeuroImage 2011, 56, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseer, N.; Hong, M.J.; Hong, K.-S. Online Binary Decision Decoding Using Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy for the Development of Brain-Computer Interface. Exp. Brain Res. 2014, 232, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irimia, D.C.; Ortner, R.; Krausz, G.; Guger, C.; Poboroniuc, M.S. BCI Application in Robotics Control. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2012, 45, 1869–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djemal, R.; Bazyed, A.G.; Belwafi, K.; Gannouni, S.; Kaaniche, W. Three-Class EEG-Based Motor Imagery Classification Using Phase-Space Reconstruction Technique. Brain Sci. 2016, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]







| Mean Errors Average | Min Errors Average | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subject | Variance Time Window | 2 s | 3 s | 4 s | 2 s | 3 s | 4 s |
| S1 | 1 s | 10.15 | 10.08 | 9.30 | 6.60 | 6.70 | 6.70 |
| 1.5 s | 7.12 | 4.98 | 6.20 | 2.76 | 2.48 | 2.20 | |
| 2 s | 7.28 | 7.33 | 5.80 | 1.65 | 2.48 | 0.55 | |
| S2 | 1 s | 35.04 | 33.83 | 34.20 | 29.27 | 28.08 | 27.80 |
| 1.5 s | 33.99 | 32.58 | 34.45 | 27.97 | 26.40 | 29.45 | |
| 2 s | 33.68 | 33.23 | 33.25 | 26.94 | 26.65 | 27.25 | |
| S3 | 1 s | 6.93 | 6.73 | 6.35 | 3.77 | 3.78 | 3.80 |
| 1.5 s | 6.62 | 6.10 | 6.05 | 1.68 | 1.58 | 2.50 | |
| 2 s | 7.80 | 7.63 | 8.70 | 2.10 | 1.90 | 1.30 | |
| S4 | 1 s | 37.30 | 40.78 | 46.40 | 33.55 | 37.53 | 43.75 |
| 1.5 s | 37.58 | 40.03 | 47.90 | 34.13 | 36.60 | 46.30 | |
| 2 s | 38.17 | 41.35 | 48.00 | 34.62 | 36.60 | 46.30 | |
| S5 | 1 s | 16.02 | 12.10 | 8.75 | 10.05 | 5.65 | 2.50 |
| 1.5 s | 12.32 | 8.40 | 8.75 | 5.87 | 2.83 | 2.50 | |
| 2 s | 10.85 | 6.65 | 5.85 | 5.45 | 2.23 | 1.90 | |
| S6 | 1 s | 40.95 | 41.95 | 41.00 | 31.67 | 33.45 | 36.25 |
| 1.5 s | 41.48 | 40.68 | 39.45 | 33.57 | 33.15 | 36.25 | |
| 2 s | 40.72 | 40.93 | 39.30 | 33.77 | 35.35 | 35.65 | |
| S7 | 1 s | 13.70 | 11.40 | 11.25 | 7.95 | 7.20 | 7.50 |
| 1.5 s | 10.93 | 10.38 | 9.90 | 6.25 | 7.55 | 6.90 | |
| 2 s | 10.78 | 10.05 | 10.45 | 5.85 | 5.65 | 8.15 | |
| Grand Average of Mean Errors | Grand Average of Minimal Errors | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variance Time Window | 2 s | 3 s | 4 s | 2 s | 3 s | 4 s |
| 1 s | 22.87 | 22.41 | 22.46 | 17.55 | 17.48 | 18.33 |
| 1.5 s | 21.43 | 20.45 | 21.81 | 16.03 | 15.80 | 18.01 |
| 2 s | 21.33 | 21.02 | 21.62 | 15.77 | 15.84 | 17.30 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hayta, Ü.; Irimia, D.C.; Guger, C.; Erkutlu, İ.; Güzelbey, İ.H. Optimizing Motor Imagery Parameters for Robotic Arm Control by Brain-Computer Interface. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12070833
Hayta Ü, Irimia DC, Guger C, Erkutlu İ, Güzelbey İH. Optimizing Motor Imagery Parameters for Robotic Arm Control by Brain-Computer Interface. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(7):833. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12070833
Chicago/Turabian StyleHayta, Ünal, Danut Constantin Irimia, Christoph Guger, İbrahim Erkutlu, and İbrahim Halil Güzelbey. 2022. "Optimizing Motor Imagery Parameters for Robotic Arm Control by Brain-Computer Interface" Brain Sciences 12, no. 7: 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12070833
APA StyleHayta, Ü., Irimia, D. C., Guger, C., Erkutlu, İ., & Güzelbey, İ. H. (2022). Optimizing Motor Imagery Parameters for Robotic Arm Control by Brain-Computer Interface. Brain Sciences, 12(7), 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12070833






