Predicting Relapse in Substance Use: Prospective Modeling Based on Intensive Longitudinal Data on Mental Health, Cognition, and Craving
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measures
2.3. Baseline Measures
2.4. Repeated Measures
2.5. Statistical Analyses
2.5.1. Group Level Analyses
2.5.2. Within-Subject Analyses
3. Results
Group-Level Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| ICD-Code. | Substance | Primary SUD-Diagnosis | Secondary SUD-Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|
| F10.2X | Alcohol | 6 | 3 |
| F12.2.X | Cannabinoids | 8 | 1 |
| F13.2X | Sedatives, hypnotics | 0 | 1 |
| F15.2X | Stimulants other than cocaine | 2 | 2 |
| F19.2X | Polysubstance use | 3 | 3 |

References
- Peisker, C.B.; Schüller, T.; Peters, J.; Wagner, B.J.; Schilbach, L.; Müller, U.J.; Vandewalle, V.V.; Kuhn, J. Nucleus accumbens deep brain stimulation in patients with substance use disorders and delay discounting. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brorson, H.H.; Arnevik, E.A.; Rand-Hendriksen, K.; Duckert, F. Drop-out from addiction treatment: A systematic review of risk factors. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2013, 33, 1010–1024. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0272735813001050?via%3Dihub (accessed on 13 June 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.; Taylor, S.; Bilek, E. Computational mechanisms of addiction: Recent evidence and its relevance to addiction medicine. Curr Addic Rep 2021, 8, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavicchioli, M.; Vassena, G.; Movalli, M.; Maffei, C. Is Craving a risk factor for substance use among treatment-seeking individuals with alcohol and other drugs use disorders? A meta-analytic review. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2020, 212, 108002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luciana, M. Risks Versus Consequences of Adolescent and Young Adult Substance Use: A Focus on Executive Control. Curr. Addict. Rep. 2020, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatseas, M.; Serre, F.; Swendsen, J.; Auriacombe, M. Effects of anxiety and mood disorders on craving and substance use among patients with substance use disorder: An ecological momentary assessment study. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2018, 187, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remmerswaal, D.; Jongerling, J.; Jansen, P.J.; Eielts, C.; Franken, I.H.A. Impaired subjective self-control in alcohol use: An ecological momentary assessment study. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019, 204, 107479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serre, F.; Fatseas, M.; Denis, C.; Swendsen, J.; Auriacombe, M. Predictors of craving and substance use among patients with alcohol, tobacco, cannabis or opiate addictions: Commonalities and specificities across substances. Addict. Behav. 2018, 83, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreno, E.M.; Domínguez-Salas, S.; Díaz-Batanero, C.; Lozano, Ó.M.; Marín, J.A.L.; Verdejo-García, A. Specific aspects of cognitive impulsivity are longitudinally associated with lower treatment retention and greater Relapse in therapeutic community treatment. J. Subst. Abus. Treat. 2019, 96, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, T.L.; Euler, M.J.; Butner, J.E. It’s about time: The role of temporal variability in improving assessment of executive functioning. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2020, 34, 619–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felton, J.W.; Shadur, J.M.; Havewala, M.; Gonçalves, S.; Lejuez, C.W. Impulsivity Moderates the Relation between Depressive Symptoms and Substance Use across Adolescence. J. Clin. Child Adolesc. Psychol. 2020, 49, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haywood, D.; Baughman, F.D.; Mullan, B.A.; Heslop, K.R. What Accounts for the Factors of Psychopathology? An Investigation of the Neurocognitive Correlates of Internalising, Externalising, and the p-Factor. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamates, A.L.; Lau-Barraco, C.; Braitman, A.L. Daily Impulsivity is Associated with Alcohol Use and Problems via Coping Motives, but Not Enhancement Motives. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2022, 232, 109333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassileva, J.; Conrod, P.J. Impulsivities and addictions: A multidimensional integrative framework informing assessment and interventions for substance use disorders. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2019, 374, 20180137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dvorak, R.D.; Pearson, M.R.; Sargent, E.M.; Stevenson, B.L.; Mfon, A.M. Daily associations between emotional functioning and alcohol involvement: Moderating effects of response inhibition and gender. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2016, 163, S46–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baurley, J.W.; McMahan, C.S.; Ervin, C.M.; Pardamean, B.; Bergen, A.W. Biosignature Discovery for Substance Use Disorders Using Statistical Learning. Trends Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, J.E.; Zellinger, M.M.; Kockler, T.; Wagner, M.; Miller, R.M. A Validated Seven-Subtest Short Form for the WAIS-IV. Appl. Neuropsychol. Adult 2013, 20, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, B.H.; Dalgard, O.S.; Tambs, K.; Rognerud, M. Measuring the mental health status of the Norwegian population: A comparison of the instruments SCL-25, SCL-10, SCL-5 and MHI-5 (SF-36). Nord. J. Psychiatry 2003, 57, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambs, K.; Moum, T. How well can a few questionnaire items indicate anxiety and depression? Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1993, 87, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, W.; Bieleke, M.; Englert, C.; Bertrams, A.; Schüler, J.; Martarelli, C. A single item measure of self-control–validation and location in a nomological network of self-control, boredom, and if-then planning. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 2021, 17, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, R.K.; Trinh, C.D.; Griffin, M.L.; Weiss, R.D. Validation of the craving scale in a large sample of adults with substance use disorders. Addict Behav. 2021, 113, 106651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayette, M.A.; Shiffman, S.; Tiffany, S.T.; Niaura, R.S.; Martin, C.S.; Schadel, W.G. The measurement of drug craving. Addiction 2000, 95, 189–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 13 June 2022).
- Revelle, W.; Revelle, M.W. Package ‘psych’. Compr. R Arch. Netw. 2015, 337, 338. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.A.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, W.H.; Bolin, J.E.; Kelley, K. Multilevel Modeling Using R; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bakdash, J.Z.; Marusich, L.R. Repeated Measures Correlation. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1–13. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00456 (accessed on 13 June 2022). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüdecke, D. Package ‘Parameters’. Cran R-Project. 2022. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/parameters/parameters.pdf (accessed on 13 June 2022).
- Lüdecke, D.; Ben-Shachar, M.S.; Patil, I.; Waggoner, P.; Makowski, D. performance: An R package for assessment, comparison and testing of statistical models. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanaugh, J.E.; Neath, A.A. The Akaike information criterion: Background, derivation, properties, application, interpretation, and refinements. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2019, 11, e1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, K.F.; Skjærvø, I.; Ravndal, E.; Clausen, T.; Bramness, J.G. Perceived Self-Control is Related to Mental Distress in Patients Entering Substance Use Disorder Treatment. Subst. Use Misuse 2018, 53, 1454–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herman, A.M.; Critchley, H.D.; Duka, T. The role of emotions and physiological arousal in modulating impulsive behaviour. Biol. Psychol. 2018, 133, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, K.; Russell, M.; Mennis, J.; Mason, M.; Neale, M. Emotion regulation dynamics predict substance use in high-risk adolescents. Addict. Behav. 2020, 106, 106374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garke, M.Å.; Isacsson, N.H.; Sörman, K.; Bjureberg, J.; Hellner, C.; Gratz, K.L.; Berghoff, C.R.; Sinha, R.; Tull, M.T.; Jayaram-Lindström, N. Emotion dysregulation across levels of substance use. Psychiatry Res. 2021, 296, 113662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanmaker, S.; Leijdesdorff, S.M.J.; Geraerts, E.; van de Wetering, B.J.M.; Renkema, P.J.; Franken, I.H.A. The efficacy of a working memory training in substance use patients: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2018, 40, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, V.W.S.; Costa, J.D.R.; Jung, M.F.; Choudhury, T. Using smartphone sensor data to assess inhibitory control in the wild: Longitudinal study. JMIR mHealth and uHealth 2020, 8, e21703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauvsnes, A.D.F.; Langaas, M.; Toussaint, P.; Gråwe, R.W. Mobile Sensing in Substance Use Research: A Scoping Review. Telemed. J. E Health 2020, 26, 1191–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Full Sample | Relapse | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YES | NO | ||||||||
| Median | IQR | Median | IQR | Median | IQR | r | p-Value | ||
| WAIS Baseline | |||||||||
| Working Memory Index | 85 | 9.5 | 82 | 10 | 86.5 | 14 | 0.235 | 0.327 | |
| Verbal Comprehension Index | 91 | 20.5 | 81 | 14 | 94 | 17 | 0.349 | 0.139 | |
| Perceptual reasoning: Block Design | 8 | 3.5 | 8 | 2 | 9 | 4.25 | 0.206 | 0.392 | |
| Processing Speed: Coding | 8 | 2 | 8 | 2 | 8.5 | 2.25 | 0.010 | 1.000 | |
| Visual Perception: Picture completion | 10.5 | 3 | 9 | 4 | 11 | 3 | 0.143 | 0.606 | |
| D-KEFS Baseline | |||||||||
| Cognitive Flexibility: Trail Making test (TMT) Scaled Score | 8 | 4 | 9 | 2.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 0.333 | 0.185 | |
| Color-Word Interference Test (Stroop) Scaled Score | 7 | 3.5 | 8 | 2.5 | 5.5 | 3 | 0.264 | 0.267 | |
| Cognitive flexibility: Verbal Fluency—Category switching | 9 | 3.5 | 8 | 2.5 | 9 | 3.5 | 0.236 | 0.324 | |
| CPT Baseline | |||||||||
| Inattentiveness: Commissions | 58.5 | 13.75 | 60 | 10.5 | 57 | 15.5 | 0.214 | 0.389 | |
| Inattentiveness: Omissions | 47 | 3.5 | 45 | 3.5 | 48 | 2.5 | 0.349 | 0.152 | |
| Impulsivity: Perseverations | 48 | 11.75 | 48 | 5.5 | 48 | 18 | 0.155 | 0.541 | |
| Vigilance HRT-ISI | 49 | 8 | 48 | 4 | 49 | 10.5 | 0.107 | 0.683 | |
| Hit reaction Time/Response Speed: HRT | 40.5 | 6 | 36 | 5.5 | 42 | 3 | 0.515 | 0.032 | * |
| Response Speed Consistency: HRT SD | 47.5 | 10.25 | 45 | 3 | 53 | 11.5 | 0.567 | 0.018 | * |
| Full Sample | Relapse | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YES | NO | |||||||
| Median | IQR | Median | IQR | Median | IQR | r | p-Value | |
| Craving | ||||||||
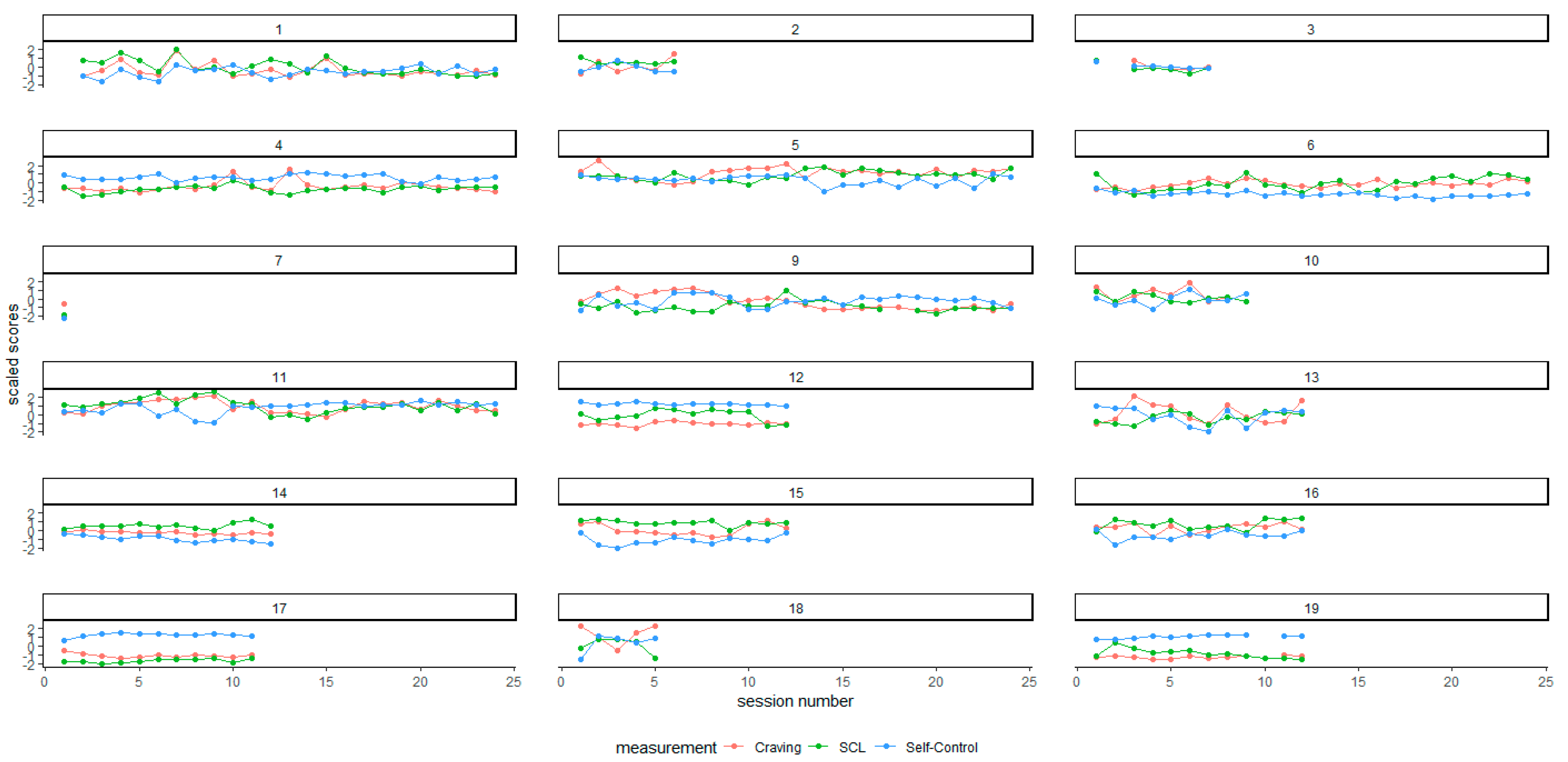
| Mean across occasions | 32.98 | 15.61 | 25.79 | 28.35 | 25.79 | 28.35 | 0.416 | 0.085 |
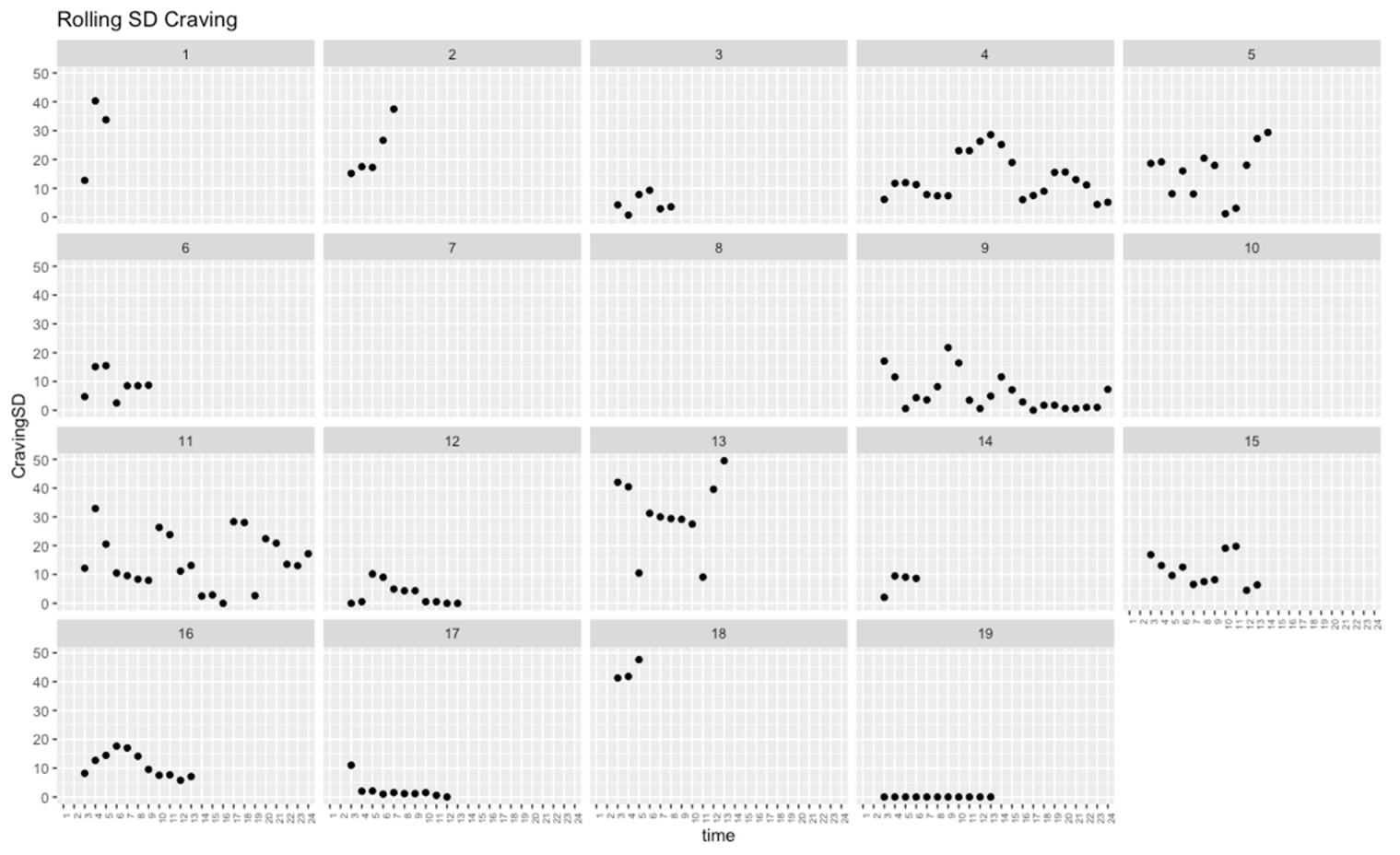
| SD across occasions | 15.29 | 14.68 | 12.93 | 11.51 | 12.93 | 11.51 | 0.402 | 0.107 |
| Self-Control | ||||||||
| Mean across occasions | 60.94 | 29.59 | 64.50 | 24.50 | 64.50 | 24.50 | 0.245 | 0.319 |
| SD across occasions | 13.45 | 8.17 | 10.57 | 4.18 | 10.57 | 4.18 | 0.308 | 0.223 |
| SCL | ||||||||
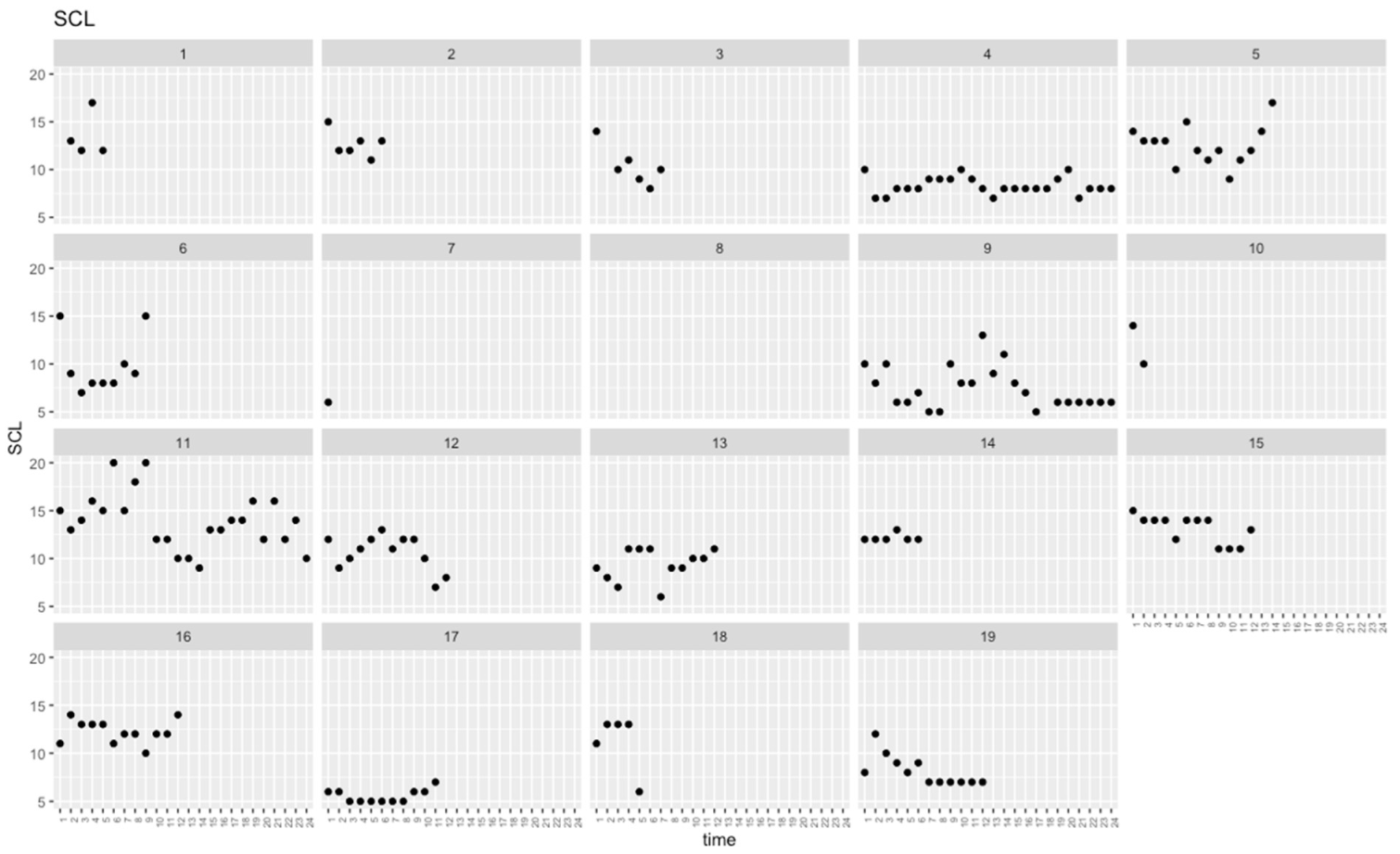
| Mean across occasions | 10.57 | 3.61 | 9.33 | 1.45 | 9.33 | 1.45 | 0.374 | 0.124 |
| SD across occasions | 1.83 | 0.88 | 1.63 | 1.21 | 1.63 | 1.21 | 0.308 | 0.223 |
| Beta | SE | R2 | AIC | Adj ICC | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1: Self-control t + 1 | 0.74 | 1251.8 | 0.71 | |||
| Intercept | 67.45 | 29.67 | 0.036 | |||
| SCL | −2.10 | 0.61 | 7.94 × 10−4 * | |||
| SCL 3-session rolling SD | −1.33 | 1.42 | 0.351 | |||
| CPT HRT SD (Baseline) | 0.38 | 0.55 | 0.493 | |||
| Model 2: Craving t + 1 | 0.56 | 1321.6 | 0.44 | |||
| Intercept | 79.83 | 27.60 | 0.086 | |||
| Self-control | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.787 | |||
| Self-control 3-session rolling SD | 0.55 | 0.24 | 0.023 * | |||
| SCL | 0.59 | 0.83 | 0.483 | |||
| SCL 3-session rolling SD | −2.42 | 2.00 | 0.229 | |||
| CPT HRT SDSD (Baseline) | −1.08 | 0.45 | 0.033 * | |||
| Model 3: Relapse t + 1 | 0.74 | 48.7 | 0.18 | |||
| Intercept | −6.69 | 3.45 | 0.053 | |||
| Self-control | −0.06 | 0.04 | 0.135 | |||
| Self-control 3-session rolling SD | −0.18 | 0.12 | 0.143 | |||
| SCL | 0.43 | 0.29 | 0.132 | |||
| SCL 3-session rolling SD | −0.43 | 0.59 | 0.470 | |||
| Craving | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.805 | |||
| Craving 3-session rolling SD | 0.18 | 0.10 | 0.061 | |||
| Model 4: Relapse t + 1 | 0.36 | 48.4 | 0.18 | |||
| Intercept | −5.10 | 1.27 | 5.79 × 10−5 * | |||
| Craving 3-session rolling SD | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.020 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lauvsnes, A.D.F.; Gråwe, R.W.; Langaas, M. Predicting Relapse in Substance Use: Prospective Modeling Based on Intensive Longitudinal Data on Mental Health, Cognition, and Craving. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 957. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12070957
Lauvsnes ADF, Gråwe RW, Langaas M. Predicting Relapse in Substance Use: Prospective Modeling Based on Intensive Longitudinal Data on Mental Health, Cognition, and Craving. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(7):957. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12070957
Chicago/Turabian StyleLauvsnes, Anders Dahlen Forsmo, Rolf W. Gråwe, and Mette Langaas. 2022. "Predicting Relapse in Substance Use: Prospective Modeling Based on Intensive Longitudinal Data on Mental Health, Cognition, and Craving" Brain Sciences 12, no. 7: 957. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12070957
APA StyleLauvsnes, A. D. F., Gråwe, R. W., & Langaas, M. (2022). Predicting Relapse in Substance Use: Prospective Modeling Based on Intensive Longitudinal Data on Mental Health, Cognition, and Craving. Brain Sciences, 12(7), 957. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12070957






