Optimized Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery to Avoid Vascular Damage: A Single-Center Retrospective Analysis of Path Planning for Various Deep Targets by MRI Image Fusion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Demographics and Clinical Characteristics
2.2. Stereotactic Systems and Implanted Devices
2.3. Surgical Procedure and Trajectory Planning
2.4. Angle Recording
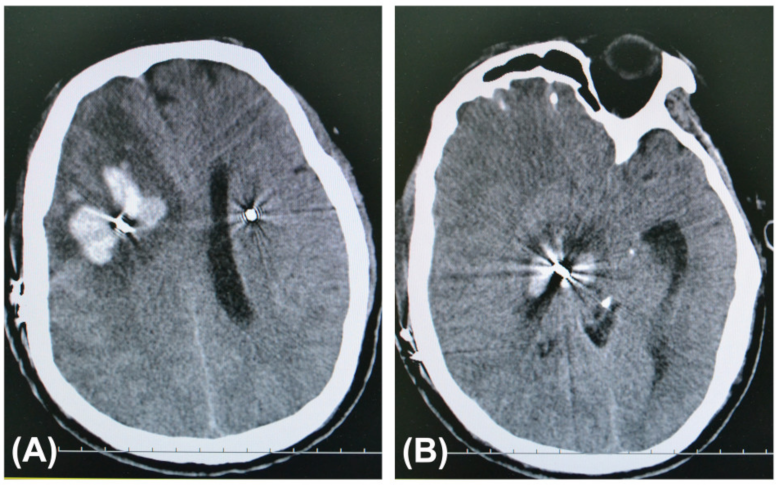
2.5. Diagnosis of ICH
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Clinical Characteristics between the Two Groups
3.2. Comparison of the Stereotactic Systems Used between the Two Groups
3.3. Comparison of ICH after DBS Surgery between the Two Groups
3.4. Image Fusion of Various MRI Sequences in the Trajectory Planning Group
3.5. Trajectory Angles Calculated by SurgiPlan for Four Targets
3.6. Images of Brain Regions in the Planned Paths of Electrodes for Four Targets
3.7. Avoiding Cerebral Vessels Using Various MRI Sequences
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Falowski, S.M.; Ooi, Y.C.; Bakay, R.A. Long-Term Evaluation of Changes in Operative Technique and Hardware-Related Complications With Deep Brain Stimulation. Neuromodulation 2015, 18, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.K.; Jung, N.Y.; Kim, M.; Chang, J.W. Analysis of Delayed Intracerebral Hemorrhage Associated with Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery. World Neurosurg. 2017, 104, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piacentino, M.; Zambon, G.; Pilleri, M.; Bartolomei, L. Comparison of the incidence of intracranial hemorrhage in two different planning techniques for stereotactic electrode placement in the deep brain stimulation. J. Neurosurg. Sci. 2013, 57, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sobstyl, M.; Brzuszkiewicz-Kuźmicka, G.; Aleksandrowicz, M.; Pasterski, T. Large Hemorrhagic Cerebral Venous Infarction due to Deep Brain Stimulation Leads Placement. Report of 2 Cases. Turk. Neurosurg. 2019, 29, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zekaj, E.; Saleh, C.; Ciuffi, A.; Franzini, A.; Servello, D. Venous Infarct after Sacrifice of Single Cortical Vein during Deep-Brain Stimulation Surgery. Asian J. Neurosurg. 2018, 13, 1276–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordeiro, J.G.; Diaz, A.; Davis, J.K.; Di Luca, D.G.; Farooq, G.; Luca, C.C.; Jagid, J.R. Safety of Noncontrast Imaging-Guided Deep Brain Stimulation Electrode Placement in Parkinson Disease. World Neurosurg. 2020, 134, e1008–e1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobstyl, M.; Aleksandrowicz, M.; Ząbek, M.; Pasterski, T. Hemorrhagic complications seen on immediate intraprocedural stereotactic computed tomography imaging during deep brain stimulation implantation. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 400, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, K.; Krel, M.; Bernstein, J.; Kashyap, S.; Ananda, A. Safety of the transventricular approach to deep brain stimulation: A retrospective review. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2019, 10, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isler, C.; Albi, A.; Schaper, F.L.; Temel, Y.; Duits, A. Neuropsychological Outcome in Subthalamic Nucleus Stimulation Surgeries with Electrodes Passing through the Caudate Nucleus. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2016, 94, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesio, V.; Rizzi, L.; Jiang, T.; Fronda, C.; Lanotte, M.; Castelli, L. Deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson’0027s disease: Relationship between the electrode trajectory and cognitive decline. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2019, 61, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costentin, G.; Derrey, S.; Gérardin, E.; Cruypeninck, Y.; Pressat-Laffouilhere, T.; Anouar, Y.; Wallon, D.; Le Goff, F.; Welter, M.-L.; Maltête, D. White matter tracts lesions and decline of verbal fluency after deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2019, 40, 2561–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H.; Li, N.; Ge, S.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Jing, J.; Su, M.; Zheng, Z.; et al. Clinical analysis and treatment of symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage after deep brain stimulation surgery. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 31, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binder, D.K.; Rau, G.M.; Starr, P.A. Risk factors for hemorrhage during microelectrode-guided deep brain stimulator implantation for movement disorders. Neurosurgery 2005, 56, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sansur, C.A.; Frysinger, R.C.; Pouratian, N.; Fu, K.-M.; Bittl, M.; Oskouian, R.J.; Laws, E.R.; Elias, W.J. Incidence of symptomatic hemorrhage after stereotactic electrode placement. J. Neurosurg. 2007, 107, 998–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zesiewicz, T.A.; Sullivan, K.L.; Hoffmann, M.; Benes, L.M.; Smith, D.A.; Ward, C.L.; Hauser, R.A. Delayed thalamic intracranial hemorrhage in an essential tremor patient following deep brain stimulation. Eur. Neurol. 2008, 59, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voges, J.; Hilker, R.; Botzel, K.; Kiening, K.L.; Kloss, M.; Kupsch, A.; Schnitzler, A.; Schneider, G.-H.; Steude, U.; Deuschl, G.; et al. Thirty days complication rate following surgery performed for deep-brain-stimulation. Mov. Disord. 2007, 22, 1486–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, F.; Ramirez-Zamora, A.; Gee, L.; Pilitsis, J. Unusual complications of deep brain stimulation. Neurosurg. Rev. 2015, 38, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, D.K.; Rau, G.; Starr, P.A. Hemorrhagic complications of microelectrode-guided deep brain stimulation. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2003, 80, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, I.L.; Roujeau, T.; Cif, L.; Gonzalez, V.; El-Fertit, H.; Vasques, X.; Bonafe, A.; Coubes, P. Magnetic resonance-based deep brain stimulation technique: A series of 478 consecutive implanted electrodes with no perioperative intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 2009, 65, 196–201. discussion 201–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.T.; Zhu, X.L.; Yeung, J.H.; Mok, V.C.; Wong, E.; Lau, C.; Wong, R.; Lau, C.; Poon, W.S. Complications of deep brain stimulation: A collective review. Asian J. Surg. 2009, 32, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonge, M.; Ackermans, L.; Kocabicak, E.; van Kranen-Mastenbroek, V.; Kuijf, M.; Oosterloo, M.; Kubben, P.; Temel, Y. A detailed analysis of intracerebral hemorrhages in DBS surgeries. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2015, 139, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahvash, M.; Pechlivanis, I.; Charalampaki, P.; Jansen, O.; Mehdorn, H.M. Visualization of small veins with susceptibility-weighted imaging for stereotactic trajectory planning in deep brain stimulation. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2014, 124, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, G.; Lang, M.J.; Mouchtouris, N.; Sharan, A.D.; Wu, C. Impact of Trajectory Planning With Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging for Intracranial Electrode Implantation. Oper. Neurosurg. 2018, 15, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bériault, S.; Sadikot, A.F.; Alsubaie, F.; Drouin, S.; Collins, D.L.; Pike, G.B. Neuronavigation using susceptibility-weighted venography: Application to deep brain stimulation and comparison with gadolinium contrast. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 121, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servello, D.; Sassi, M.; Bastianello, S.; Poloni, G.U.; Mancini, F.; Pacchetti, C. Electrode displacement after intracerebral hematoma as a complication of a deep brain stimulation procedure. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2009, 5, 183–187. [Google Scholar]
- Krüger, M.T.; Coenen, V.A.; Jenkner, C.; Urbach, H.; Egger, K.; Reinacher, P.C. Combination of CT angiography and MRI in surgical planning of deep brain stimulation. Neuroradiology 2018, 60, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, E.J.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, S.J. Delayed intracranial hemorrhage after deep brain stimulation in two Parkinson’0027s disease patients. J. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 342, 202–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Konrad, P.E.; Neimat, J.S.; Tatter, S.B.; Yu, H.; Datteri, R.D.; Landman, B.A.; Noble, J.H.; Pallavaram, S.; Dawant, B.M.; et al. Multisurgeon, multisite validation of a trajectory planning algorithm for deep brain stimulation procedures. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 2479–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neudorfer, C.; Hinzke, M.; Hunsche, S.; El, M.F.; Lozano, A.; Maarouf, M. Combined Deep Brain Stimulation of Subthalamic Nucleus and Ventral Intermediate Thalamic Nucleus in Tremor-Dominant Parkinson’s Disease Using a Parietal Approach. Neuromodulation 2019, 22, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bot, M.; van Rootselaar, F.; Contarino, M.F.; Odekerken, V.; Dijk, J.; de Bie, R.; Schuurman, R.; van den Munckhof, P. Deep Brain Stimulation for Essential Tremor: Aligning Thalamic and Posterior Subthalamic Targets in 1 Surgical Trajectory. Oper. Neurosurg. (Hagerstown) 2018, 15, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richieri, R.; Borius, P.Y.; Cermolacce, M.; Millet, B.; Lançon, C.; Régis, J. A Case of Recovery After Delayed Intracranial Hemorrhage After Deep Brain Stimulation for Treatment-Resistant Depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 83, e11–e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downes, A.E.; Pezeshkian, P.; Behnke, E.; Bordelon, Y.; Tagliati, M.; Mamelak, A.; Pouratian, N. Acute Ischemic Stroke During Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery of Globus Pallidus Internus: Report of 5 Cases. Oper. Neurosurg. 2016, 12, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| No Trajectory Planning | Trajectory Planning | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of male patients | 211 (53.3%) | 340 (54.6%) | 0.687 ※ |
| Diagnosed with hypertension | 42 (10.6%) | 109 (17.5%) | 0.003 ※ |
| Age at surgery * | 59 (49, 66) *** | 64 (54, 68) *** | 0.000 ※※ |
| Local anesthesia | 289 (73.0%) | 445 (71.4%) | 0.591 ※ |
| Number of enrolled patients | 396 | 623 | 0.647 ※※※ |
| Parkinson’s disease | 318 (80.3%) | 519 (83.3%) | |
| Essential tremor | 5 (1.3%) | 12 (1.9%) | |
| Dystonia | 47 (11.9%) | 53 (8.5%) | |
| Tourette’s syndrome | 4 (1.0%) | 6 (1.0%) | |
| Addiction | 13 (3.3%) | 17 (2.7%) | |
| Other psychiatric diseases | 7 (1.8%) | 11 (1.8%) | |
| Huntington’s disease | 2 (0.5%) | 4 (0.6%) | |
| Chronic pain | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (0.2%) | |
| Number of implanted leads ** | 691 | 1237 | 0.402 ※※※※ |
| STN | 557 (80.6%) | 1032 (83.4%) | |
| Vim | 22 (3.2%) | 31 (2.5%) | |
| GPi | 70 (10.1%) | 117 (9.5%) | |
| NAc/ALIC | 40 (5.8%) | 56 (4.5%) | |
| CM-Pf | 2 (0.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| VPL/VPM | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (0.1%) |
| Surgery Planning Systems/Headframe | No Trajectory Planning | Trajectory Planning | Total Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total number * | 396 | 623 | 1019 |
| Leksell SurgiPlan | 279 | 456 | 735 |
| CRW StereoCalc | 117 | 141 | 258 |
| Medtronic Framelink | 0 | 26 | 26 |
| p-Value | 0.000 ** | ||
| Leksell | 279 | 459 | 738 |
| CRW | 117 | 164 | 281 |
| p-Value | 0.262 ** |
| ICH | No Trajectory Planning | Trajectory Planning | Total Number | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Patients | No. of Leads | No. of Patients | No. of Leads | Patients | Leads | |
| Symptomatic ICH | 10 * | 10 ** | 3 * | 3 ** | 13 | 13 |
| Without symptomatic ICH | 386 * | 681 ** | 620 * | 1234 ** | 1006 | 1915 |
| Total number | 396 | 691 | 623 | 1237 | 1019 | 1928 |
| p-value | 0.005 * | 0.003 ** | ||||
| Fused MRI Images | Number (%) |
|---|---|
| A + B | 46 (7.4%) |
| A + B + C | 219 (35.2%) |
| A + B + D | 20 (3.2%) |
| A + B + E | 278 (44.6%) |
| A + B + C + E | 54 (8.7%) |
| A + B + C + D + E | 6 (1.0%) |
| Total number | 623 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Li, N.; Li, J.; Kou, H.; Wang, J.; Jing, J.; Su, M.; Li, Y.; Qu, L.; Wang, X. Optimized Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery to Avoid Vascular Damage: A Single-Center Retrospective Analysis of Path Planning for Various Deep Targets by MRI Image Fusion. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12080967
Wang X, Li N, Li J, Kou H, Wang J, Jing J, Su M, Li Y, Qu L, Wang X. Optimized Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery to Avoid Vascular Damage: A Single-Center Retrospective Analysis of Path Planning for Various Deep Targets by MRI Image Fusion. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(8):967. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12080967
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xin, Nan Li, Jiaming Li, Huijuan Kou, Jing Wang, Jiangpeng Jing, Mingming Su, Yang Li, Liang Qu, and Xuelian Wang. 2022. "Optimized Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery to Avoid Vascular Damage: A Single-Center Retrospective Analysis of Path Planning for Various Deep Targets by MRI Image Fusion" Brain Sciences 12, no. 8: 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12080967
APA StyleWang, X., Li, N., Li, J., Kou, H., Wang, J., Jing, J., Su, M., Li, Y., Qu, L., & Wang, X. (2022). Optimized Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery to Avoid Vascular Damage: A Single-Center Retrospective Analysis of Path Planning for Various Deep Targets by MRI Image Fusion. Brain Sciences, 12(8), 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12080967






